Abstract
Accurate and updated finer resolution maps of rubber plantations and stand ages are needed to understand and assess the impacts of rubber plantations on regional ecosystem processes. This study presented a simple method for mapping rubber plantation areas and their stand ages by integration of PALSAR 50-m mosaic images and multi-temporal Landsat TM/ETM+ images. The L-band PALSAR 50-m mosaic images were used to map forests (including both natural forests and rubber trees) and non-forests. For those PALSAR-based forest pixels, we analyzed the multi-temporal Landsat TM/ETM+ images from 2000 to 2009. We first studied phenological signatures of deciduous rubber plantations (defoliation and foliation) and natural forests through analysis of surface reflectance, Normal Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI), and Land Surface Water Index (LSWI) and generated a map of rubber plantations in 2009. We then analyzed phenological signatures of rubber plantations with different stand ages and generated a map, in 2009, of rubber plantation stand ages (≤5, 6–10, >10 years-old) based on multi-temporal Landsat images. The resultant maps clearly illustrated how rubber plantations have expanded into the mountains in the study area over the years. The results in this study demonstrate the potential of integrating microwave (e.g., PALSAR) and optical remote sensing in the characterization of rubber plantations and their expansion over time.
1. Introduction
As economies and industries develop, the need for natural rubber products has been increasing over time, which has led to substantial and continuous expansions of rubber plantations around the world. The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) reported a twenty percent expansion of global rubber plantations in the past two decades, and 90% of the expansion is in Asia [1], mainly distributed in Indonesia, Thailand, Malaysia, and China. Rubber trees were first successfully planted in Southern China in the 1950s, and then expanded from their original planting places (10° N–10° S) to areas as far north as 22° N, including Hainan and Yunnan provinces, China [2]. The expansion mainly occurred at the expense of natural forests and shifting agriculture [3,4]. Now Southern China has been a hotspot for northward-expansion of rubber plantations. The dramatic expansion may negatively impact forest carbon stocks and biodiversity [3,4,5,6]. Accurate and updated maps of rubber plantation cover areas and their stand ages are needed to quantify Land Use Land Cover Changes (LULCC) and assess its impacts on biodiversity, carbon sinks, and water cycles in the tropical forest areas.
Satellite remote sensing technology has played a vital role to map rubber plantation cover at local and regional scales [7,8,9]. Previous studies can be generally divided into three groups based on sensor types: optical sensors, microwave or radar sensors, and integration of optical and radar sensors. A few studies used images from optical sensors (MODIS, Landsat and ASTER) and calculated image statistics and classified images to map rubber plantations in Southeast Asia [7,10,11]. As cloud cover occurs frequently in the moist tropical areas, high temporal resolution image data (e.g., MODIS) make it possible to obtain some cloud-free observations. Based on the temporal analysis of MODIS data, Senf et al. (2013) and Liu et al. (2013) mapped the rubber plantations in Xishuangbanna, Yunnan Province, China. Because of its coarse spatial resolutions (250–500 m), it is difficult to identify and map small patches of rubber plantations using MODIS images. Tropical regions lack high-resolution, satellite-based maps of their forests due to persistent cloud cover [12,13,14]. Clouds on optical images obscure the dense humid tropical forest over 70% of the time [15], hence optical images are constrained to use for monitoring forests [12,13,14,16].
Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) can penetrate clouds, haze and dust, and provide cloud-free images for mapping forests in moist tropical regions, where frequent cloud cover makes it difficult to acquire cloud-free optical images from those optical sensors with long revisit cycles (e.g., 16-day revisit cycle from Landsat). Radar images from long wavelength sensors (e.g., L-band SAR) are also capable of penetrating tree canopies [17] and are sensitive to forest structure and the moisture content of the forest canopy. The Phased Arrayed L-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (PALSAR) from Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) provided multi-year cloud-free images (2006–2010) for the global land surface, and several studies have used multiple polarization images (HH, HV, VH, VV) to map forests at local scale in tropical regions [14,15,18,19]. Based on the backscatter coefficient values (HH, HV) of PALSAR orthorectified mosaic data, forest cover maps at 50-m spatial resolution were developed at regional and global scales [18,20,21]. However, these PALSAR-based forest cover maps do not differentiate between evergreen forests and deciduous forests (e.g., rubber plantations). Rubber trees in Southern China often have a defoliation phase (leaf-off) and foliation phase (leaf-on, new leaf emergence) during the relatively cold and dry winters [22,23]. Combining these phenological features, rubber plantations can be identified from natural forest based on a PALSAR-based forest map [23].
In an effort to take full advantage of both optical and radar data, several recent studies combined radar and multi-temporal optical data to map tropical forests [24] and rubber plantations [25]. For example, the PALSAR images in 2009 were first used to generate a forest cover map, and the resultant forest cover map in 2009 was combined with the phenology information (defoliation and foliation phases) from multi-temporal MODIS images [25] and Landsat images [23] to map rubber plantations in Hainan Island, China, which has the largest area of rubber plantations in China. The multi-temporal MODIS and Landsat images from 2009 provide information on whether a forest pixel experienced a defoliation and/or foliation phase (timing and duration). The pilot study area in Hainan Island, China is located in areas with relatively simple and flat topography. But in our study area, rubber plantations are cultivated in mountains. The complex topography and climate in the mountainous regions pose challenges for the characterization and mapping of rubber plantations.
When trying to compare mapping methods of rubber plantations, few references were found that attempted to retrieve stand age by remote sensing technology [26]. It is well known that stand ages of forests are important in many research fields such as monitoring and management of forest ecosystems, carbon flux estimates, and biomass estimates [27,28,29,30,31,32,33]. At present, stand ages of plantation forests are mainly retrieved from field surveys and historical planting records of local forestry bureaus [34,35]. Field surveys are always limited by transportation conditions and complex montane topography, as well as human and financial resources [35]. Additionally, updated stand age map cannot be made available regularly because field surveys are time-consuming work. Fortunately, long-term free Landsat data provide an opportunity to trace rubber plantation planting stages and identify their stand ages. Until now, there have been no efficient ways to identify rubber plantation stand ages in Xishuangbanna at fine spatial resolutions. Therefore, there is a need to develop an algorithm that can establish stand ages of rubber plantations in a rapid and repeatable way for dynamically monitoring rubber plantations.
This study aimed to address the above-mentioned challenges in mapping rubber plantation areas and their stand ages in topographically complex settings. The specific objectives of this study are threefold: (1) generate a forest cover map using PALSAR images from 2009 at 50-m spatial resolution; (2) generate a map of rubber plantations in 2009 at 30-m spatial resolution, based on the PALSAR-forest map and phenological analysis of Landsat images in 2009; and (3) to generate a stand age map of rubber plantations with a 30-m spatial resolution (≤5, 6–10, and >10 years old). This pilot study will contribute to evaluate the integrated approach used in Hainan Island [23] and use both PALSAR images from 2009 and time series Landsat data (2000–2012). The study area is located in Jinghong City of Xishuangbanna Dai Nationality Autonomous Prefecture, China, where there are good-quality Landsat images and extensive rubber plantations.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Xishuangbanna Dai Nationality Autonomous Prefecture (Xishuangbanna) is located in southern Yunnan Province, China, with a latitude range of 21.08° N to 22.36° N and longitude of 99.56° E to 101.50° E. Montane area accounts for 95% of the total land area [36], and the elevation ranges from 368 m to 2401 m above sea level. The average annual temperature varies between 18 °C and 22 °C. May to October is the rainy season, whereas the dry season takes place November to April. Initial introduction of rubber trees in the region occurred in the 1950s. According to the Xishuangbanna Statistical Yearbook 2011, it has a rubber plantation area of 2873.73 km2.
In this study, we selected a subset of Xishuangbanna as a case study (Figure 1) that has a high rubber plantation density, multiple land cover types (rubber plantations, evergreen forests, built-up lands, villages, croplands, etc.), various elevations (from 489 m to 1428 m), and abundant field survey data.
2.2. Data Pre-Processing
2.2.1. PALSAR Data and Pre-Processing
Fifty-meter PALSAR Orthorectified Mosaic data are freely available from the ALOS Kyoto and Carbon Initiative [37]. These data have been geometrically rectified using 90-m digital elevation model (DEM) and geo-referenced to geographical latitude and longitude coordinates [38]. The details of PALSAR data processing methods and algorithms (such as calibration and validation) can be found in previous literatures [39,40]. HH and HV of PALSAR 50-m orthorectified mosaic products with Fine Beam Dual (FBD) observational mode were downloaded and used in this study. According to the Equation (1) [41], the two polarization (HH and HV) data were converted from amplitude into normalized radar cross-section backscatter (dB),
where σ0 is the backscattering coefficient, DN is the digital number value of pixels in HH or HV, and CF is the absolute calibration factor of –83. Besides HH and HV polarization images, two composited images (the ratio and difference of HH and HV) were also generated, since these indices have been shown to be valuable for land cover classification [21]. This study analyzed the PALSAR 50-m mosaics of Xishuangbanna with FBD (Fine Beam Dual) polarization modes from July to October 2009.
2.2.2. Landsat Data and Pre-Processing
In this study, multi-temporal Landsat data were used for phenological characteristic analysis of rubber plantations. Two hundred twenty-six standard level-one terrain-corrected products of Landsat 5/7 TM/ETM+ images (path/row 130/045) from 2000 to 2012 (Table 1) were downloaded from the USGS Earth Resources Observation and Science (EROS) Data Center [42]. The overall geometric fidelity has been fitted using ground control points and a digital elevation model in level-one Terrain-corrected Landsat products [43].
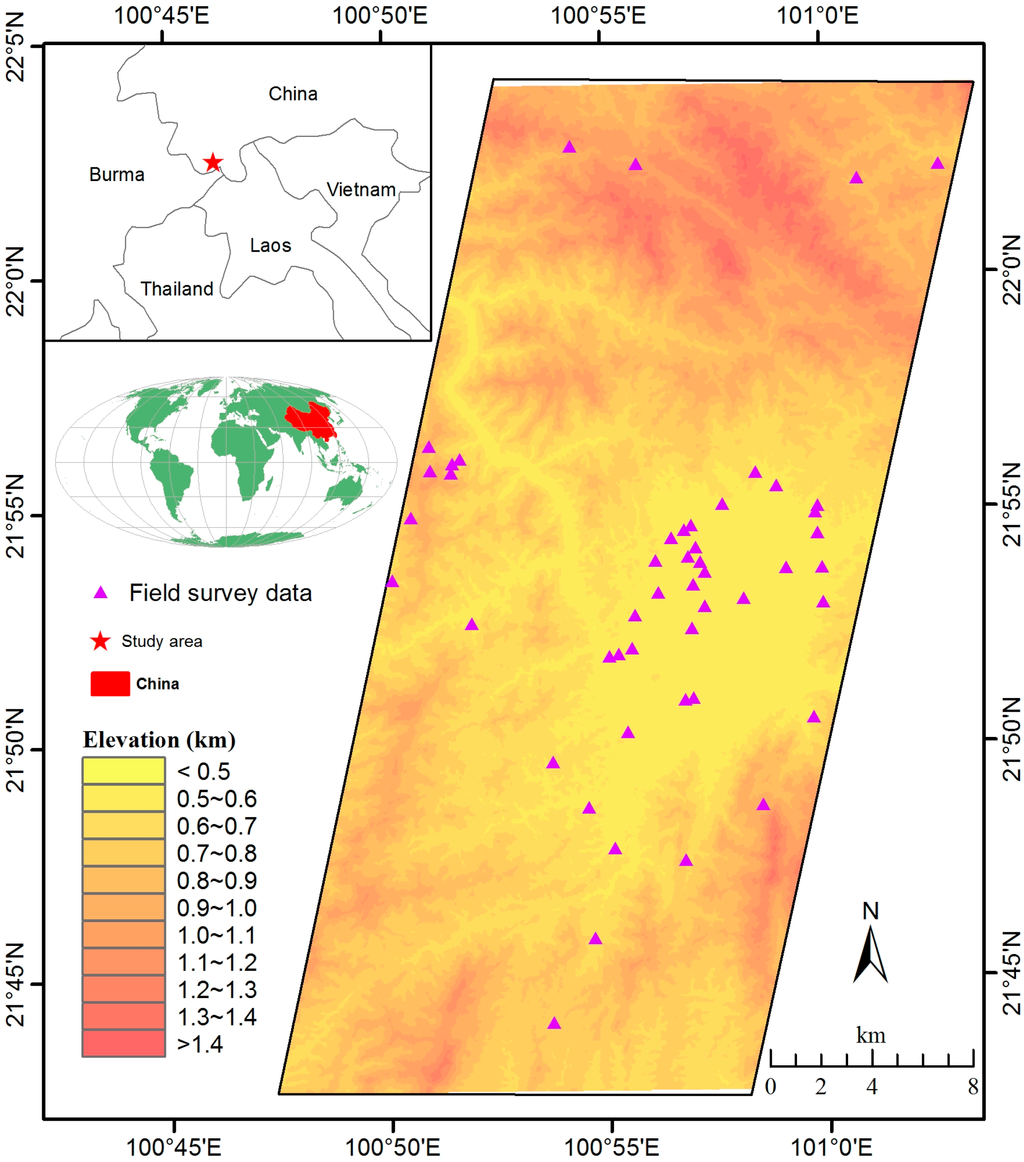
Figure 1.
The study area is located in Jinghong County Xishuangbanna Dai Nationality Autonomous Prefecture, Yunnan, China. This region has a typical humid tropical forest environment, a high rubber density, and more than thirty-year rubber planting history. The purple triangles mark the locations of field survey data of rubber plantations.

Table 1.
A summary of the number of Landsat images (Path/Row 130/045) used for each acquisition year during 2000–2012 in this study.
| Year | Landsat 5 | Landsat TM/ETM+ 7 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 12 | 8 | 20 |
| 2001 | 13 | 8 | 21 |
| 2002 | 11 | 6 | 17 |
| 2003 | 17 | 7 | 24 |
| 2004 | 15 | 8 | 23 |
| 2005 | 2 | 11 | 13 |
| 2006 | 1 | 14 | 15 |
| 2007 | 2 | 12 | 14 |
| 2008 | 0 | 14 | 14 |
| 2009 | 6 | 12 | 18 |
| 2010 | 2 | 14 | 16 |
| 2011 | 2 | 11 | 13 |
| 2012 | 0 | 18 | 18 |
| Total | 83 | 143 | 226 |
(1) Atmospheric correction
The Landsat Ecosystem Disturbance Adaptive Processing System (LEDAPS) uses the 6S radiative transfer approach to conduct atmospheric correction and retrieve surface reflectance of Landsat images [44,45]. Following previous studies [23,46], here, we also employed LEDAPS to conduct atmospheric correction and retrieve surface reflectance from 226 Landsat images.
(2) Clouds, cloud shadows, and SLC-Off gaps
In tropical and subtropical regions, clouds are major barriers for analysis of optical satellite data [16]. Fmask is a free software for automated processing of clouds, cloud shadows, and snow for Landsat 4, 5, 7 and 8 images [47]. We used Fmask to identify and map clouds and cloud shadows on Landsat TM/ETM+ imagery.
Landsat 7 images acquired after 31 May 2003 have strips of missing data, as the Scan Line Corrector (SLC), which compensates for the forward motion of Landsat 7, failed. There are no data for these SLC-off gaps and blank margins. The gaps and blank margins of images were marked with flags. This study used the minimum of all images in the defoliation phrase to generate a composite map, which almost have no gap in observations. So gap-fill was not further conducted.
(3) Vegetation indices
Normal Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) [48], Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI) [49] and Land Surface Water Index (LSWI) [50,51] were calculated based on the following Equations (2)–(4).
where ρNIR, ρred, ρMIR, and ρblue are the surface reflectance values of near infrared, red, shortwave-infrared, and blue bands in Landsat 4, 5 and 7 images.
2.3. Ground Reference Data for Algorithm Training and Product Validation
2.3.1. Geo-Referenced Field Photos (Points of Interest)
Geo-referenced field photos are very important for validation of rubber plantations and natural forests [23,25]. Geo-referenced field photos can be collected by GPS camera or the Field Photo Apps that are freely available for both iOS and Android [52]. In 2013, a field survey was conducted and about 800 geo-referenced field photos of rubber plantations and other land cover types were taken by a Casio Exolim EX-H20G GPS camera in study area. These geo-referenced field photos were uploaded into the Global Geo-Referenced Field Photo Library [52], which is a data portal for the public and science community to upload, download, store, manage, and share geo-referenced field photos. The KML files of these photos were generated and downloaded from the web portal to serve as the points of interest (POIs) in this study. We also obtained stand age information from 49 rubber plantation sites through interviews with workers in the plantation fields. Although this study used Landsat and PALSAR imagery from 2009 for mapping rubber plantations, ground truth data from 2013 are suitable as rubber trees grow for many years with consistent seasonal phenology.
2.3.2. Regions of Interest (ROIs) for Algorithm Training and Product Validation
Google Earth images with high-resolution have good geo-metric accuracy and finer spatial resolution (e.g., 0.61-m QUCKBIRD images) and were used to validate the results of land cover classifications [46,53,54,55,56,57] and maps of forests and rubber plantations [21,23,25]. In this study, ROIs (Table 2) for result validating and algorithm training (Figure 2) are from two sources: Google Earth high-resolution imagery and field survey data.
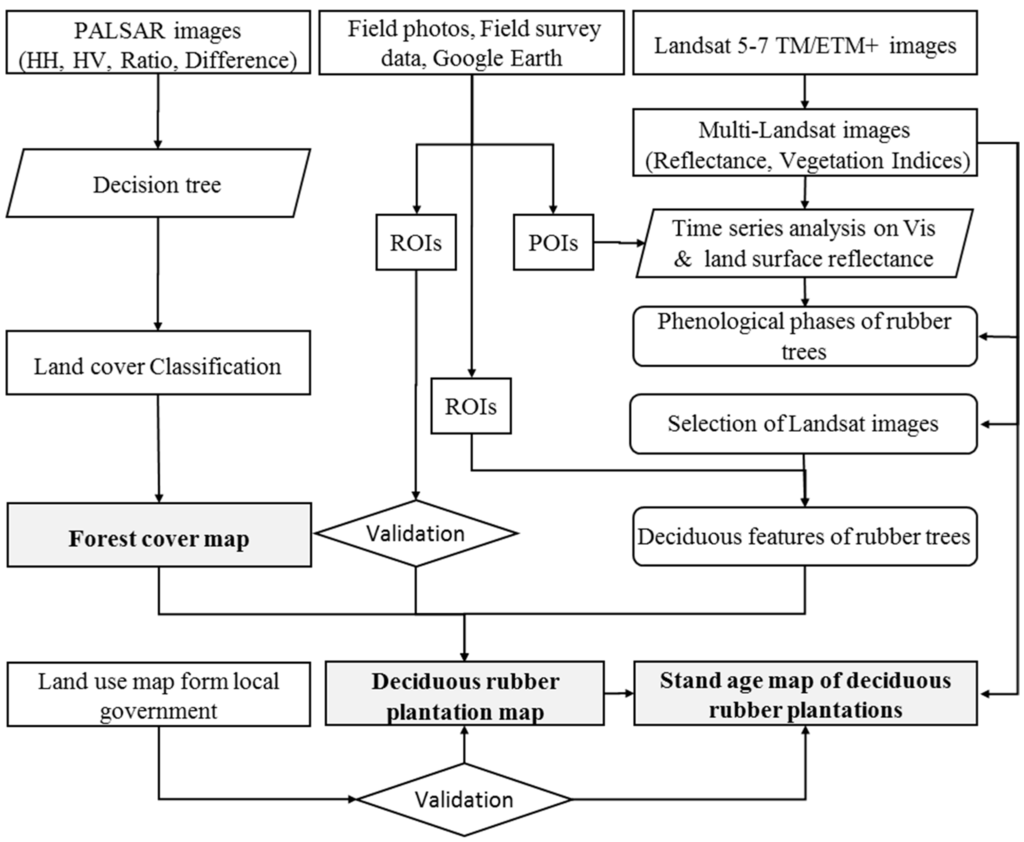
Figure 2.
The workflow for mapping deciduous rubber plantations and their stand ages based on 50-m Phased Arrayed L-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (PALSAR) orthorectified mosaic product and 30-m Landsat images in the study area. Firstly, a PALSAR-based forest/tree map and a Landsat-based phenology feature map of rubber plantations were mapped independently, then overlaid two maps to generate a deciduous rubber plantation map, and lastly based on the pixels of the deciduous rubber plantation map identified backward the stand ages of rubber plantations according to Land Surface Water Index (LSWI) < 0. Three groups of ground truth data are used: (1) the points of interest (POIs) were used for the phenology stage extraction (fifteen natural forest and ten rubber plantation samples) by using multi-temporal Landsat images, (2) the training regions of interest (ROIs) were used to acquire the phenology feature of rubber plantations based on the Landsat images in the foliation stage, and (3) the validation ROIs were used for accuracy assessments of land cover classification and the rubber plantation map.

Table 2.
Regions of Interest (ROIs) for algorithm training and result validations.
| ID | Land Cover Types | Pixels | Sources | Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Natural forest | 845 | Google Earth | Algorithm training |
| Rubber | 1016 | |||
| 2 | Natural forest | 8245 | Google Earth | Validation of PALSAR forest/non forest map |
| Non-forest | 1878 | |||
| 3 | Rubber | 7118 | Google Earth | Validation of resultant rubber plantation map |
| Natural forest | 2814 | |||
| Non-forest | 2974 | |||
| 4 | ≤5 year-old rubber | 4260 | Survey data | Validation of rubber stand age map |
| 6–10 year-old rubber | 4425 | |||
| >10 year-old rubber | 3647 |
2.4. Map of Forest Cover in 2009 from PALSAR Imagery
Considering tropical montane characteristic of our study area, we mapped a forest/non-forest map instead of the global forest/non-forest products based on PALSAR [20] and Landsat [58]. PALSAR 50-m mosaic images from 2009 were used to generate a forest/non-forest map in Southeast Asia [21,23]. Forests and other land cover types have different PALSAR backscatter signatures. For example, forests have higher backscatter values than water and cropland. First, the feed-forward Neural Network (NN) algorithm with one hidden layer and PALSAR 50 m data (HH, HV, Ratio, and Difference Images) were used to map four land cover types (forest, water urban and cropland) [21]. Then, we generated the forest/non-forest map of the study area in 2009. The PALSAR-based forest map was processed by a 3 by 3 majority filter to recode isolated pixels classified differently than the majority class of the window [59]. The resultant 50-m PALSAR forest/non-forest map was resampled to 30-m to match the Landsat spatial resolution.
2.5. Map of Deciduous Rubber Plantations for 2009 through Integrating PALSAR and Landsat Images
The forest map from the 50-m PALSAR does not differentiate between natural forests and deciduous rubber plantations. Analysis of a year-worth of time series optical images can indicate whether a forest pixel is deciduous or evergreen through a year. If a forest pixel from the PALSAR-based forest map has deciduous characteristics of rubber trees, we can identify it as rubber plantation and thus produce a map of rubber plantations [21,23].
In this study area, rubber trees defoliate about from middle January to early February every year in response to cold air temperatures [8,22,23]. Both defoliation and early foliation stages are suitable for identifying and mapping deciduous rubber plantations [23]. When comparing the images from various phases within plant growing season to those images from the defoliation phase, there are many distinguishable features for identifying deciduous rubber plantations from natural forests (Figure 3). In Figure 3 the rubber plantations and the natural forests are very different in defoliation (a) and foliation phase (b), but similar in growth phase (c). In the defoliation phase (a), the rubber plantation is readily visible as purple patches (a, B) but the natural forest is green (a, A). In the foliation phase (b), the rubber plantation has light green patches (b, B) but natural forest is dark green (b, A). In the growth phase, the rubber plantation is dark green (c, B) as well as natural forest (c, A).
Based on 845 natural forest POIs and 1016 rubber plantation POIs, we analyzed the spectral and phenological signatures of deciduous rubber plantations and natural forests using the images in the defoliation stage. Three Landsat 5–7 TM/ETM+ images (Path/Row 130/045) during the defoliation phase in 2009 were composited to quantify the differences in surface reflectance and vegetation indices (NDVI, EVI, and LSWI). The image compositing avoids the effects of clouds and other bad observations and ensures good-quality observation data of vegetation phenology. A set of threshold values was then obtained to separate rubber plantations from natural forests in the defoliation phase. The defoliation characteristic layer was overlaid with the forest baseline map mentioned in Section 2.4 to generate a rubber plantation map.
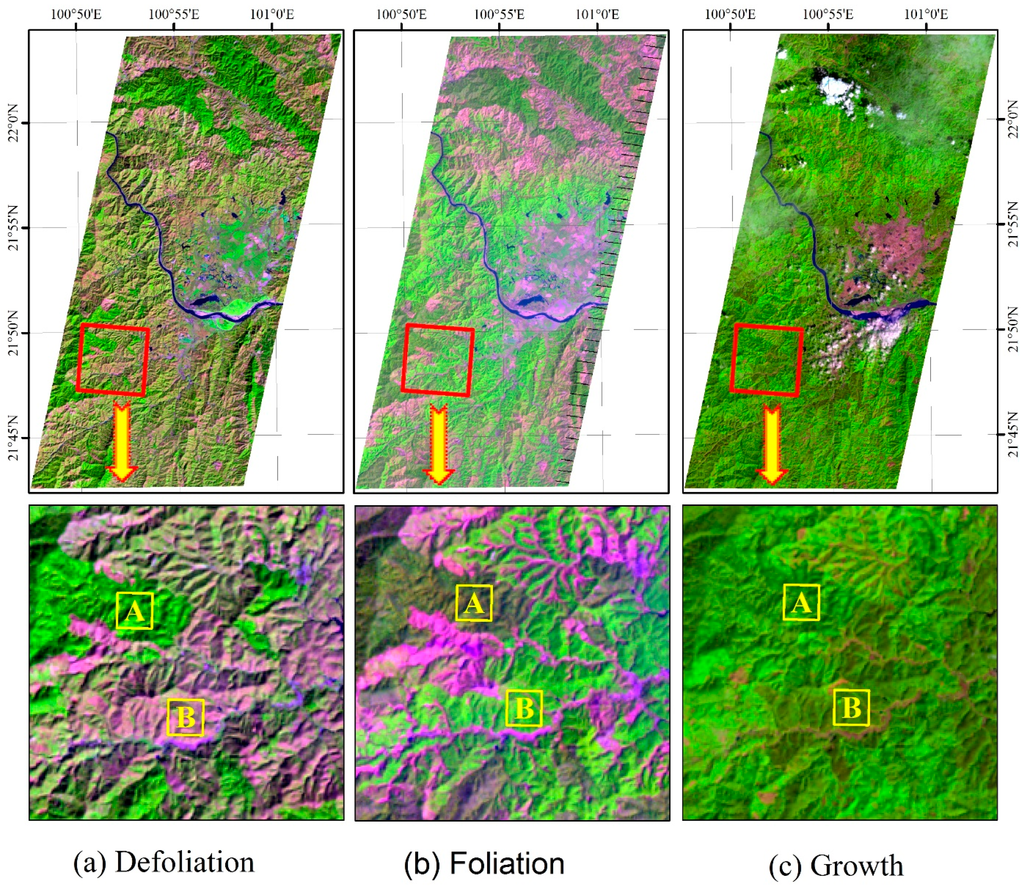
Figure 3.
Three false color composite map (R/G/B = Band 5/4/3) of Landsat ETM+ 7 images in (a) the defoliation phase (18 January 2009), (b) the foliation phase (7 March 2009), and (c) the growth phase (7 October 2002). The rubber plantation and the natural forest are very different in the defoliation (a) and the foliation phase (b), but similar in the growth phase (c). In the defoliation phase (a), the rubber plantation is readily visible as purple patches (a, B) but the natural forest is green (a, A). In the foliation phase (b), the rubber plantation has light green patches (b, B) but natural forest is dark green (b, A). In the growth phase (c), the rubber plantation is dark green (c, B) as well as natural forest (c, A).
2.6. Map of Stand Age of Deciduous Rubber Plantations
2.6.1. Landsat-Based Signature Analysis of Rubber Plantations with Different Stand Ages
Because the spectral characteristics in the defoliation stage can help distinguish rubber plantations from natural forests, the conversion from natural forest to rubber plantations can be detected by using the changes in vegetation indices. For example, Figure 4 showed the temporal changes of three vegetation indices at one Landsat pixel point (21.87877° N, 101.01783° E) where natural forest was converted into rubber plantation around 2004 based on 226 Landsat images in the defoliation phase. Three key stages of landscape images were captured from Google Earth high-resolution images: 9 January 2001 (Figure 4b), 22 June 2004 (Figure 4c) and 13 May 2012 (Figure 4d). Verified by referenced data and textures, the land cover types of three images at different periods can be identified as natural forest (Figure 4b), clear-cut field and newly planted rubber plantation (Figure 4c), and rubber plantation (Figure 4d). Observed from Landsat image time series (Figure 4a), a sudden decline in vegetation index time series (such as NDVI, EVI and LSWI) appeared in about 2004, which means the conversion from natural forests to rubber plantations can be detected by vegetation indices.
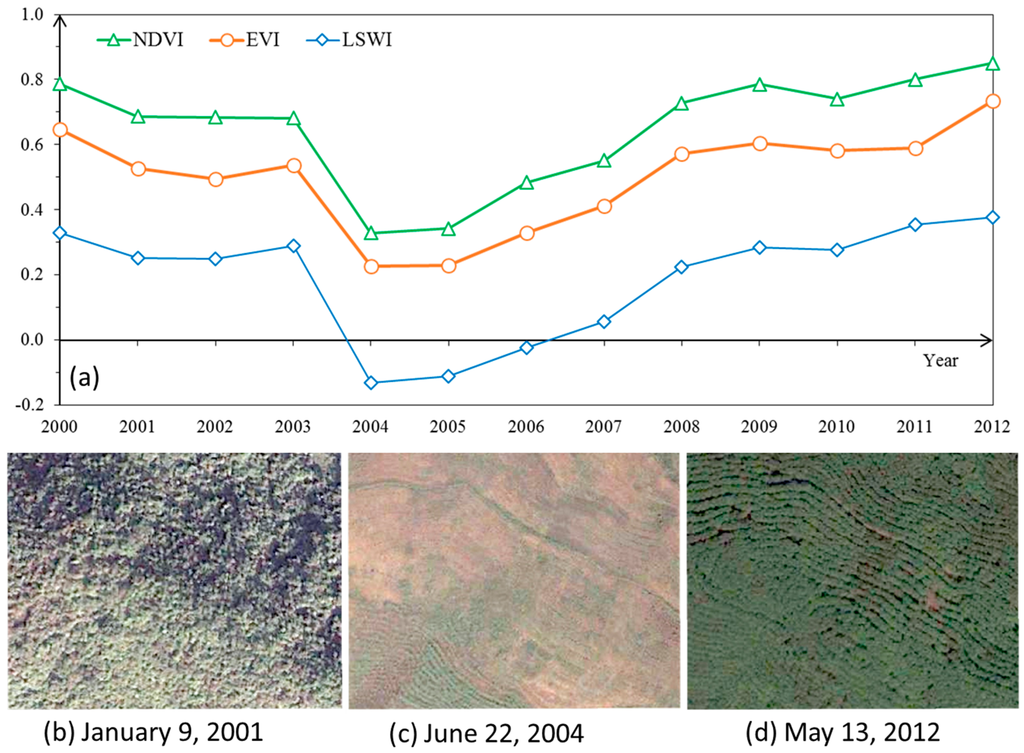
Figure 4.
Temporal profiles of Normal Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI) and Land Surface Water Index (LSWI) based on 30-m Landsat 5–7 TM/ETM+ images in the defoliation phase from 2000 to 2012. One point of interest (21.87877° N, 101.01783° E) was used to extract the NDVI, EVI and LSWI values of rubber plantations in the study area. Three images of the Points of interest (POI) were clipped from Google Earth high-resolution images in 9 January 2001 (a), 22 June 2004 (b) and 13 May 2012 (c). According to the referenced data and their textures, (a) is natural forest, (b) is a new planting field, and (c) is rubber plantation.
Furthermore, rubber plantations with different stand ages may have various features (e.g., defoliation intensity), which can help to identify their stand ages. To determine the signatures of different stand ages of rubber plantations in the defoliation phase, we used 49 rubber plantation field survey POIs (Figure 1) with stand ages and 10 natural forest POIs and then grouped the 49 POIs into five age groups (≤5, 6–10, 11–15, 16–20, and 21–25 years old), based on the field survey in 2011 (also assumed as the baseline year). Time series NDVI, EVI, and LSWI from Landsat 5/7 TM/ETM+ images in the defoliation phase during 2000–2011 were used for individual pixels and used to analyze the characteristics of deciduous rubber plantations with different stand age groups (≤5, 6–10, 11–15, 16–20, and 21–25 years old). The relationships between vegetation indices (NDVI, EVI and LSWI) and the stand ages from these 49 POIs were quantified.
2.6.2. Map of Deciduous Rubber Plantations with Different Stand Ages
As shown in Figure 4, LSWI value was negative in clear-cut fields and newly cultivated rubber plantations. We used LSWI to detect disturbance (negative LSWI value in a time series LSWI data over 2000–2009 for a rubber plantation pixel in 2009). The stand age of a rubber plantation pixel in 2009 was determined using the following steps: first, we tracked and recorded the year when LSWIdefoliation < 0 occurred for the first time between 2000 and 2009 (10 years), which was considered to be the starting year of rubber plantations; second, we grouped and reported the resultant stand ages into two age groups (≤5 years, 6–10 years); third, those rubber plantation pixels that did not have any observations with LSWIdefoliation < 0 during 2000–2009 were considered to be >10 years.
2.7. Validation and Comparison
Confusion matrices created from ROIs were used to validate the resampled 30-m PALSAR forest/non-forest map, the 30-m resultant map of deciduous rubber plantations and their stand ages. Eight thousand two hundred forty-five forest POIs and one thousand eight hundred seventy-eight non-forest POIs created from Google Earth high-resolution images were used to verify the resampled 30-m PALSAR forest map. Seven thousand one hundred eighteen rubber plantation POIs, two thousand eight hundred fourteen natural forest and two thousand nine hundred seventy-four non-forest POIs from Google Earth high-resolution images were used to verify the 30-m resultant rubber plantation map. For evaluating the stand age map of rubber plantations in 2009, 4260 five-year-old and younger, 4425 six-to-ten-year-old, and 3647 greater than ten-year-old rubber plantation POIs were created from a survey map from the Jinghong Forestry Bureau.
3. Results
3.1. Map of Forest Cover from PALSAR Imagery in 2009
The resultant PALSAR-based forest map (Figure 5a) has a high accuracy based on the validation ROIs. The overall accuracy was 95%, and the Kappa coefficient was 0.89. Both the user’s accuracy and producer's accuracy of the forest cover were higher than 96% (Table 3). Therefore, the forest map can serve as a reliable base map for rubber plantation delineation. The categories of cropland and other land cover had lower accuracies than those of forest and water; for example, the other land cover category had a low user’s accuracy (71%) and producer’s accuracy (64%) due to the complex backscatter from built-up land. However, this is not of any critical concern as the focus in this study is forest.
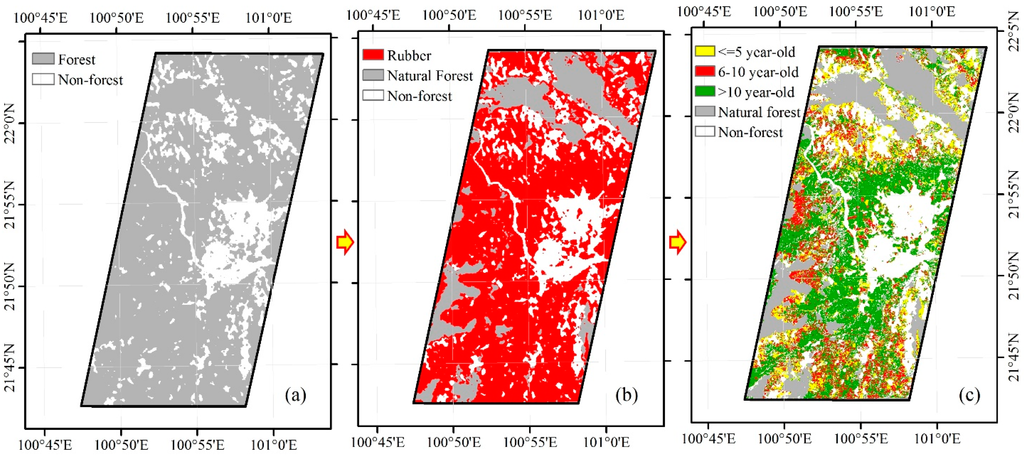
Figure 5.
Overlaying the resampled 30-m Phased Arrayed L-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (PALSAR) forest map with 30-m Landsat images during the defoliation phase in 2009: (a) is the resampled 30-m forest map in 2009, derived from PALSAR 50-m orthorectified mosaic images; and (b) is the 30-m resultant rubber plantation map in 2009 and has three land cover types (rubber, natural forest and Non-forest). It was generated by overlaying the resampled 30-m PALSAR forest map with 30-m Landsat-based phenology map in 2009; (c) is the 30-m rubber plantation map with three five-interval stand ages (five year-old and younger, six-to-ten-year-old, and eleven-years-old and older) in the study area in 2009. The stand ages were identified by recording the first occurrence of Land Surface Water Index (LSWI) < 0 from 2000 to 2009 based on pixels of the resultant 30-m rubber plantation map.

Table 3.
Accuracy assessment of the resampled 30-m forest/non-forest map based on 50-m Phased Arrayed L-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (PALSAR) data in the study area, Xishuangbanna, Yunnan, China. The overall accuracy is 95%, and the Kappa coefficient is 0.89. Non-forest includes built-up land, barren land, water body, cropland, and other land cover types.
| Class | Ground Truth (Pixels) | Total Classified Pixels | User’s Accuracy | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forest | Non-Forest | ||||
| Classified results | Forest | 7917 | 328 | 8245 | 96% |
| Non-forest | 174 | 1704 | 1878 | 91% | |
| Total ground truth pixels | 8091 | 2032 | 10,123 | - | |
| Producer’s accuracy | 98% | 84% | - | 95% | |
3.2. Map of Rubber Plantations in 2009
3.2.1. Seasonal Phenology of Deciduous Rubber Plantations in 2009 from Landsat
Figure 6 shows the seasonal dynamics of three vegetation indices (NDVI, EVI, and LSWI) in 2009 for rubber plantations and natural forests. In the peak period of the plant-growing season, both rubber plantations and natural forests had a relatively similar high level of vegetation indices (NDVI, EVI and LSWI). From the middle of January to early February, however, rubber trees defoliated substantially. During the defoliation phase, the canopy density of rubber trees decreased by ~20% [54]. From the middle of February to early March, rubber trees underwent quick foliation and canopy recovery [23]. In the defoliation phase, the minimum NDVI, EVI, and LSWI of rubber plantations are separately lower than natural forests. In the foliation phase, the minimum EVI is higher than the highest natural forests (Figure 6). This indicates that rubber plantations are distinguishable from natural forests in the defoliation phase or the foliation phase in the study area. The results from this study are consistent with the results reported in a previous study in Danzhou City, Hainan Province [23].
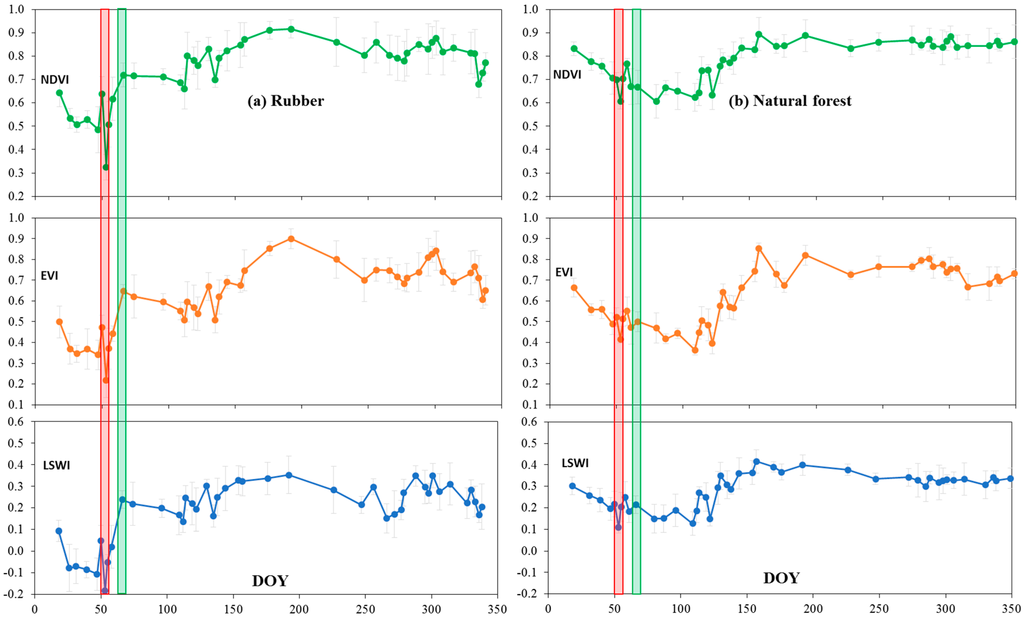
Figure 6.
The temporal profiles of Landsat time series vegetation indices of Normal Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI) and Land Surface Water Index (LSWI) for (a) rubber plantations and (b) natural forests. Fifteen points of interests (POIs) were extracted for rubber plantations and ten points of interests for natural forests. The points shown in the graphics are their average values. Rubber plantations and natural forest are evidently different in two typical phenology phases: defoliation (the long red and narrow boxes) and foliation (the long green and narrow boxes). In the figure, DOY is day of the year.
Spectral signature analyses of individual land cover types were conducted, using six land surface reflectance of spectral bands (Blue, Green, Red, NIR, SWIR1, and SWIR2) and three vegetation indices (NDVI, EVI, and LSWI). Rubber plantations and natural forests have similar values in the six bands of surface reflectance, but NDVI (0.4726 ± 0.0782), EVI (0.2657 ± 0.0604), and LSWI (−0.0189 ± 0.0961) of rubber plantations are much lower than in natural forests, 0.7168 ± 0.0358, 0.4324 ± 0.0756, and 0.3051 ± 0.0556, respectively, during the defoliation phase in the study area (Figure 7). Considering the minimum space features and the separability for the phenological metric, NDVI and LSWI were used to construct the phenology metric to separate natural forests and rubber plantations. The threshold NDVI ≤ 0.6159 and LSWI ≤ 0.1634 was used to discriminate rubber plantations from natural forests in the defoliation phase.
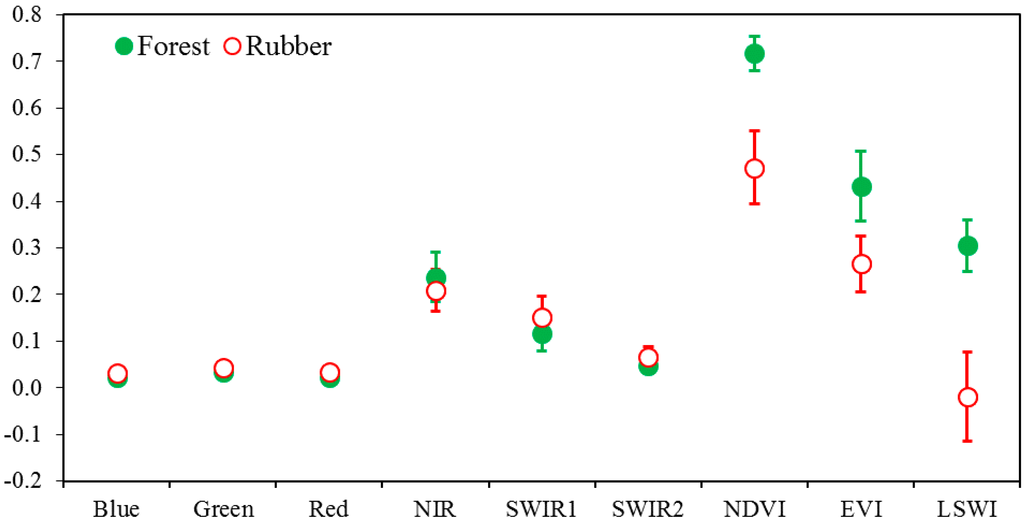
Figure 7.
Signature analysis of six land surface reflectance of spectral bands (blue, green, red NIR, SWIR1, SWIR2) and three vegetation indices (Normal Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI) and Land Surface Water Index (LSWI)) between rubber plantations and natural forests based on an image composited from the minimum value of six spectral bands and three vegetation indices from three TM/ETM+ images on Day of the Year (DOY) 018, 050, and 066 in 2009. NDVI, EVI, and LSWI have a good separability for separating rubber plantations from natural forests, but six spectral bands have not.
3.2.2. Map of Deciduous Rubber Plantations from PALSAR and Landsat in 2009
By overlaying the resampled 30-m PALSAR-based forest map for 2009 with the 30-m Landsat-based rubber phenology map, the map of deciduous rubber plantations in 2009 was generated (Figure 5b). We estimated a total area of 512 km2 rubber plantation in 2009, which was higher than the area estimates reported in the survey data from the local government (458 km2) in 2006, with an increasing rate of approximately 11.8%. The resultant rubber plantation map has a high accuracy according to the confusion matrix using the ground truth ROIs. The overall accuracy is 91%, and the Kappa coefficient is 0.85 (Table 4). The producer’s accuracy of the interpretation accuracy of rubber plantations is 95%, and the user accuracy is 91%.

Table 4.
Accuracy assessment of the land cover classification map based on 30-m Landsat 5/7 Themetic Mapper (TM)/Ehanced Thematic Mapper Plus (ETM+) images in the study area. The overall accuracy is 92%, and the Kappa coefficient is 0.87. Non-forest includes built-up land, barren land, water body, cropland, and other land cover types.
| Class | Ground Truth (Pixels) | Total Classified Pixels | User’s Accuracy | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rubber | Natural Forest | Non-Forest | ||||
| Classified results | Rubber | 6480 | 37 | 601 | 7118 | 91% |
| Natural Forest | 21 | 2780 | 13 | 2814 | 99% | |
| Non-forest | 359 | 6 | 2609 | 2974 | 88% | |
| Total ground truth pixels | 6860 | 2823 | 3223 | 12906 | ||
| Producer’s accuracy | 94% | 98% | 81% | - | - | |
3.3. Map of Stand Ages of Rubber Plantations in 2009
3.3.1. Changes in Seasonal Phenology of Deciduous Rubber Plantations at Different Stand Ages from Landsat iMages in 2000–2011
Defoliation features of deciduous rubber plantations during the defoliation stage may vary depending on their stand ages. In this study, 49 rubber plantation sites with various stand ages were used to analyze the different spectral and phenological characteristics of deciduous rubber plantations. These 49 sites were divided into five age groups: 5 year-old, 10 year-old, 15 year-old, 20 year-old, and 25 year-old rubber plantation groups. Vegetation index time series (NDVI, EVI, and LSWI) were extracted from 226 Landsat 5–7 TM/ETM+ images (path/row 130/045) from 2000 to 2011.
The natural forest clear-up and new rubber plantation planting period can be observed from vegetation time series extracted from multi-temporal Landsat data in the defoliation phase. As shown in Figure 8, from 2000 to 2011, rubber plantations during the defoliation phase in the 5 year-old group had a sudden drop in vegetation indices in 2005 and the 10 year-old ones in 2002. Such sudden drops were not found in vegetation indices at rubber plantation groups of 15 year-old, 20 year-old, and 25 year-old. That is, LSWI of 5 year-old rubber plantations dramatically changed from positive to negative in their cultivation year. After the change, the negative LSWI kept increasing continuously, and about five years later, it reached a positive level. This means that for about five year-old rubber plantations, the LSWI is more sensitive than their NDVI and EVI to detect the defoliation feature due to the cold air temperature.
We calculated the average values of NDVI, EVI, and LSWI of individual stand age groups of rubber plantations and natural forests. Figure 9 shows that the average values of NDVI, EVI, and LSWI of rubber plantations had an increasing trend from the 5 to the 25 year-old group. The LSWI of 5 year-old rubber plantations are negative and their NDVI and EVI are positive in the defoliation phase. In comparison, these three vegetation indices always keep a relatively stable and higher positive level in natural forests.
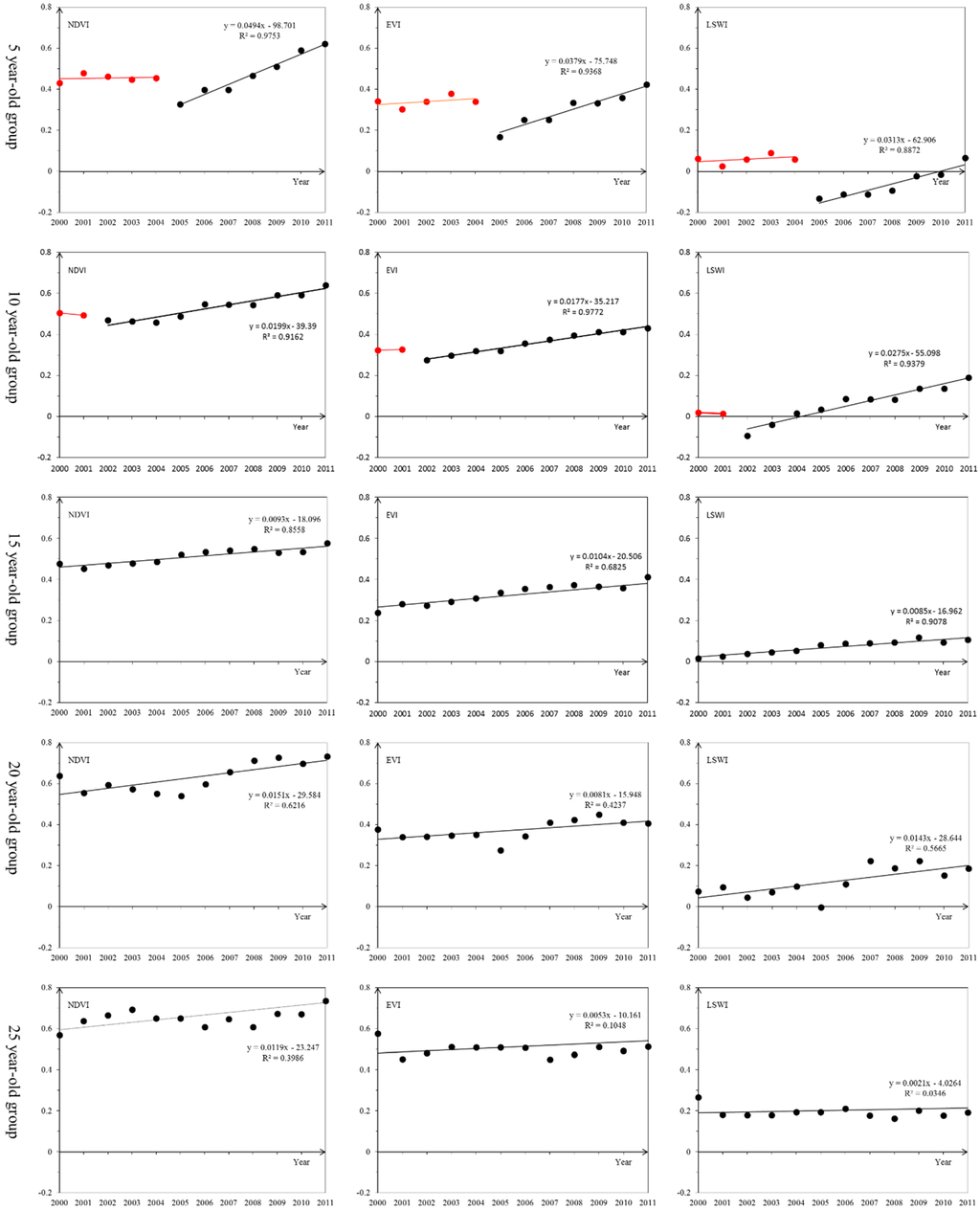
Figure 8.
Time series analysis of NDVI, EVI and LSWI were conducted for rubber plantations with different stand ages based on 30-m Landsat 5–7 TM/ETM+ images in the defoliation phase (from middle January to early February) between 2000 and 2011. The stand age data for analysis were from a field survey in 2011. LSWI suddenly changed from positive to negative in five and ten year-old rubber plantations. After the changes, negative LSWI kept continuously increasing for about five years.
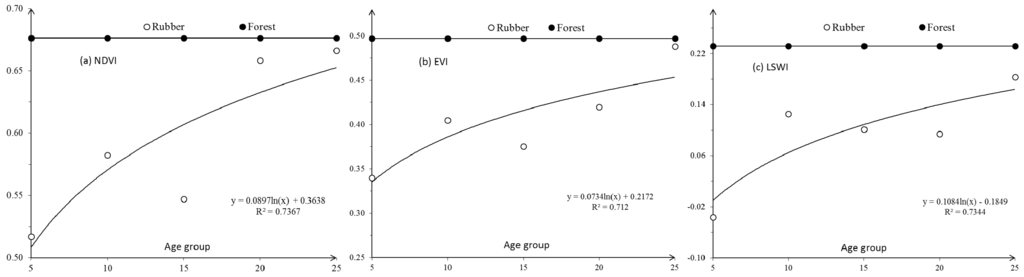
Figure 9.
Comparing vegetation index (NDVI, EVI and LSWI) variations between rubber plantations with different stand ages in the defoliation phase and natural forests. From the youngest group (5 year-old) to the oldest (25 year-old) rubber plantation group, the NDVI, EVI and LSWI were increasing toward to that of natural forests, but natural forests kept a relative stable level. 49 POIs of rubber plantations with stand ages in the defoliation phase in 2011 and 10 Points of interest (POIs) of natural forests were used in this analysis. The points shown in the figures are the average NDVI, EVI and LSWI of these POIs.
3.3.2. Map of Stand Age of Deciduous Rubber Plantations in 2009
A stand age map of deciduous rubber plantations was generated based on 30-m Landsat 5/7 TM/ETM+ images (Figure 5c). To validate the stand age map, this study extracted ROIs from a reference map with age information that was from local forestry bureau. Based on these ROIs, we built a confusion matrix (Table 5) to validate the stand age map. According to the confusion matrix, the overall accuracy is 85%, and the Kappa coefficient is 0.78. The individual user’s accuracies of ≤5, 6–10, and ≥11 year-old rubber plantations are 88%, 87%, and 80%, respectively, and the producer’s accuracies are 87%, 81%, and 90%, respectively.

Table 5.
Accuracy assessment of the stand age map based on 30-m Landsat images in the study area. Overall accuracy is 85%, and the Kappa coefficient is 0.78.
| Class (year-old) | Ground Truth (Pixels) | Total Classified Pixels | User’s Accuracy | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <6 | 6–10 | >10 | ||||
| Classified results | <6 | 3763 | 388 | 109 | 4260 | 88% |
| 6–10 | 373 | 3843 | 209 | 4425 | 87% | |
| >10 | 180 | 540 | 2927 | 3647 | 80% | |
| Total ground truth pixels | 4316 | 4771 | 3245 | 12332 | ||
| Producer’s accuracy | 87% | 81% | 90% | |||
The spatial distribution of rubber plantations with different stand ages is closely related to the elevation in the study area (Figure 10). The eleven-year-old and older rubber plantations in 2009 were mostly distributed in a low elevation area, the six-to-ten-year-old rubber plantations at intermediate level elevation, and the five-year-old and younger rubber plantations at high elevation level. This suggests a continuous expansion of rubber plantations from low elevation to high elevation during the period of 2000–2009.
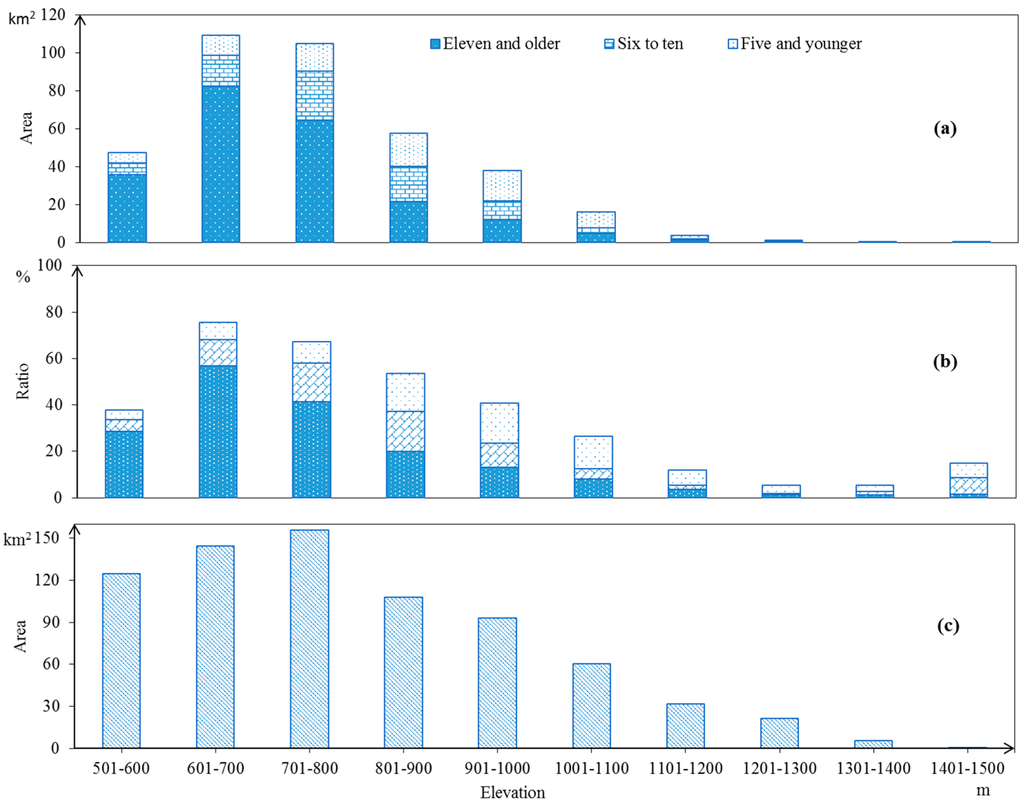
Figure 10.
The relationship between the distribution of rubber plantations and elevations. (a) Area distribution of rubber plantations with different stand ages in different elevations. (b) Area % of rubber plantations with different stand ages versus the surface of the corresponding elevation category. (c) Area distribution of different elevation categories in the study area.
4. Discussions
4.1. Major Findings and Potentials for Mapping Forest, Rubber Plantations, and Their Stand Ages
Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) data (e.g., PALSAR images) have a number of advantages in mapping forests over optical sensors, particularly in moist and cloudy tropical regions, and have been used recently to map (1) forest cover in Southeast Asia [8,21,22,23,25,60,61], the Amazon basin [24], and across the globe [20], and (2) industrial forest plantations such as rubber, oil palm, coconut, and wattle plantations [23,62]. In this study, we used L-band PALSAR 50-m orthorectified mosaic images to generate a forest and non-forest map for 2009 at 50-m spatial resolution in the study area, using the same algorithm reported in previous studies [21,23]. As L-band PALSAR images are sensitive to forest structure, biomass and water content of the canopy, this study has demonstrated the potential of PALSAR 50-m orthorectified mosaic images for mapping forests in the moist tropical areas. Several other studies have also evaluated the potential of combing PALSAR and Landsat images to improve forest mapping [63,64,65], future studies might be needed to evaluate the potential of combining Landsat 8 and PALSAR-2 images in 2015.
Rubber plantations in China are deciduous broadleaf forests. A number of studies have recognized the defoliation phase in the relatively cold and dry winter season as a key phenological stage for separating evergreen natural forests and deciduous rubber plantations in Xishuangbanna, China [9,35]. Satellite images including Landsat images [9,21,23,35] and HJ-1 images [8,22], within the defoliation phase in one year were often selected for image-based classification to identify and map rubber plantations. In addition to the defoliation phase, another study also recognized the foliation phase (new leaf emergence) as a key phenological stage for separating evergreen natural forests and deciduous rubber plantations in Hainan Island, which has the largest area of rubber plantations in China [23]. The results from our study in Xishuangbanna also show that both the defoliation and foliation periods are good for identifying and mapping rubber plantations, which is consistent with the findings in the previous study in Hainan, China [23]. The longer time window from either defoliation or foliation stages make it possible to have good quality satellite observations available for image analysis.
Several studies used NDVI time series data to characterize and map deciduous rubber plantations in Xishuangbanna and Southeast Asia [7,9,35,46,61]. Liu et al. determined that mature rubber plantations are different from other land cover types and that young rubber plantations (< 10 years old) were often confused with fallow croplands and tea gardens. One recent study used MODIS-based EVI and shortwave infrared band (SWIR) in 2010 to map rubber plantations in Xishuangbanna [46]. Similar to the previous study in Hainan Island [21,23,25], in this study we evaluated NDVI, EVI, and LSWI data to characterize phenological phases of deciduous rubber plantations and evergreen natural forests in the mountainous areas. Our results show that NDVI and LSWI provide additional insight into the characterization of vegetation phenology, and that it is beneficial to use all three vegetation indices in phenological studies.
The algorithms and procedures used to map deciduous rubber plantations in previous studies can be grouped into two approaches. The image-based approach first calculates image statistics in optical image(s) for various land cover types and then applies a clustering method (e.g., maximum likelihood, decision tree) to map rubber plantations [7,9,35,46,61]. The pixel-based approach first investigates time series data (vegetation indices and spectral reflectance) for a forest pixel over year(s) and then applies signal detection methods to determine whether a pixel is rubber plantation or not in that year(s) [21,23]. This study is a follow-on case study of the pixel-based approach for mapping rubber plantations in complex mountainous areas, and it also uses a PALSAR-based forest map as the baseline for analysis of deciduous and evergreen trees.
Stand ages of deciduous rubber plantations are critical information for management of rubber plantations. This study mapped and reported stand ages for rubber plantations at 5-year intervals (≤ 5 years old, 6–10 years old, and ≥11 years old), based on analysis of time series Landsat images from 2000 to 2009. It started with a signature analysis of rubber plantations at different stand ages, using time series NDVI, EVI, and LSWI data from 2000 to 2009. When the stand ages of deciduous rubber plantations are 5 years or less, their LSWI values are negative during the defoliation stage in the study area. We used this unique feature to develop a simple method to determine stand ages of deciduous rubber plantations at 5-year intervals, based on 30-m Landsat 5–7 TM/ETM+ imagery from 2000 to 2009 in the defoliation phase. Compared to the traditional field survey method, the new method can estimate stand ages of deciduous rubber plantations over a large region without limitations like transportation or weather conditions.
4.2. Sources of Errors and Uncertainties in Mapping of Forest, Rubber Plantations, and Stand Ages
In this study, we generated a map of forests in 2009 at 50-m spatial resolution from analysis of PALSAR images, a map of rubber plantations in 2009 at 30-m spatial resolution from analysis of multi-temporal Landsat images in 2009 for all PALSAR-based forest pixels, and a map of stand ages of rubber plantations in 2009. There are some uncertainties in each of resultant maps in the study due to data quality and availability as well as algorithm design. First, the forest/non-forest map from the L-band PALSAR data are likely to omit young (one- or two-year-old) rubber plantations due to their small and sparse canopies and low height in the fields. In addition, 50-m PALSAR data may be too coarse to identify sparse forests and woodlands in the classification (especially towards the lower cover threshold of 10%), which may result in underestimating the total area [20]. Second, topographic factors (such as slopes, aspects, and elevations) may affect backscatter coefficients of PALSAR images and spectral properties of deciduous rubber plantations. Third, stand age factor may also affect backscatter coefficients of PALSAR images and the spectral properties of rubber plantations, specifically during the defoliation and foliation processes (timing, duration, and magnitude). These factors together suggest that the time windows for selection of Landsat images and the threshold values in classification algorithms may vary in different areas, and therefore, additional studies across the subtropical areas in China and Southeast Asia are needed in the near future. In addition, the improvement in data quality, numbers, and continuity of available satellite images may present further opportunities in mapping stand ages of rubber plantations. An application of the approach used in this study clearly needs to carried out on the regional scale and evaluated in the future studies.
4.3. Field Survey Data and High Resolution Images
Validation or accuracy assessment of land cover maps developed from analysis of satellite images is important to all land cover mapping studies however, it is often restrained by insufficient data from the field. Due to high costs of getting reliable field survey data and super high resolution imagery (≤1 m) in land cover and use change research, insufficient accuracy assessment via field survey data may cause considerable error and misinterpretation [23,66]. Sharing scientific field survey data among scientists is a feasible way to mitigate the problem of insufficient ground data. The field survey data in this study are based on the Global Geo-Referenced Field Photo Library [67], which has a large amount of geo-referenced field photos (120,000+ as of July 2014) shared by scientists from all over the world and provides effective support for many research fields, such as land cover and land use changes and biogeography [18,23]. Although these geo-referenced field photos can provide abundant spatial information, they still cannot fully support needs for algorithm training and resultant map validation. We used the Google Earth high spatial resolution images to extend the POIs from abundant field photos into ROIs. Some previous studies also used these free high-resolution images on Google Earth for algorithm training or classification result validation [10,17,21,23,25,54,55,57]. This study also used the multi-temporal high-resolution images on Google Earth to validate the planting period of rubber plantations (Figure 4).
Additionally, disturbances from clouds, cloud shadows, and gaps affect the data quality of Landsat data. In this study, they were taken into account to improve Landsat data quality, but in some of previous studies [23,25,35,46] they were not; in previous studies, the cloud-free Landsat images were chosen and used, but in humid, tropical montane regions, cloud-free images are very limited. The clouds and their shadows can be well detected by Fmask [47].
4.4. Implications for the Expansion of Rubber Plantations in Xishuangbanna
The spatial distribution and areas of rubber plantations in the Xishuangbanna received broad attention from many researchers in China and the world and were reported in several studies [4,8,9,35,46,61,68]. These studies used either MODIS data (250-m spatial resolution) or Landsat images (30-m spatial resolution) to generate maps of rubber plantations in Xishuangbanna, which is covered by three Landsat path/row scenes. Our study did not cover the entire Xishuangbanna region, but did showcase a new methodology of combining SAR and optical data to map rubber plantations and their stand ages in complex mountainous areas. The defoliation stage of deciduous rubber plantations is a key phenological stage for discriminating rubber plantations and evergreen natural forests. In this stage, based on the PALSAR-derived forest cover map, a map of rubber plantations can be generated by using phenological signals in the time series NDVI and LSWI data. We found that LSWI is a strong variable for estimating stand ages of deciduous rubber plantations through analysis of LSWI data during the defoliation period. Based on 30-m multi temporal Landsat imagery in defoliation phase, we can generate a map of stand ages of deciduous rubber plantations by using the rule LSWI < 0.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we have developed a novel, simple and robust procedure that combines Phased Array type L-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (PALSAR) 50-m orthorectified images and multi-temporal Landsat images to map forest, deciduous rubber plantations, and stand ages of rubber plantations in tropical regions. We applied the procedure to a small area (Jinghong city area) in Xishuangbanna, the 2nd largest natural production base in China, using PALSAR 50-m orthorectified images in 2009 and Landsat images in 2000–2009. The resultant forest map in 2009 from 50-m PALSAR orthorectified mosaic data has high producer and user accuracies, which clearly demonstrates the potential of PALSAR images for forest mapping. The algorithm uses unique spectral properties during the defoliation stage of deciduous rubber plantations, and then discriminates deciduous rubber plantations from evergreen natural forests through analysis of time series Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) and Land Surface Water Index (LSWI) data derived from Landsat images. The resultant map of deciduous rubber plantations also has high producer’s (94%) and user’s accuracies (91%), which highlights the potential of combining PALSAR and Landsat images for mapping rubber plantations. We also found that LSWI (LSWI < 0) is a good variable (the overall accuracies is 85%) for estimating stand ages of deciduous rubber plantations through analysis of LSWI data during the defoliation period. The resultant stand age map of deciduous rubber plantations clearly shows spatial-temporal patterns that rubber plantations expanded from regions with low elevation level into mountains over years (2000–2009). To our limited knowledge, this study was the first effort that maps forest, deciduous rubber plantation, and stand age of rubber plantation through integration of PALSAR and Landsat images. The algorithms developed in this study need to be applied and further evaluated when both PALSAR-2 (launched on 24 May 2014) and Landsat 8 (launched on 11 February 2013) images are freely available to map forest cover, deciduous rubber plantation and stand age of rubber plantations. Additional studies are also needed to combine multi-year PALSAR (2006–2010), JERS-1 (1992–1993) and Landsat 5/7 (1985–2013) to track expansion and stand age of rubber plantations at local, regional and continental scales over decades. The resultant geospatial datasets from these proposed future studies are important inputs for us to better understand the consequences of rubber plantation expansion in the region on biodiversity, carbon, water and climate.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by US NASA Land Use and Land Cover Change program (NNX09AC39G, NNX11AJ35G), the US National Science Foundation (NSF) EPSCoR program (NSF-IIA-1301789), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31400493,41201340,31300403). Landsat imagery is available from the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) EROS Data Center. The original PALSAR data are provided by JAXA as the ALOS products. We thank Sarah Xiao for her English editing and comments.
Author Contributions
Weili Kou, Xiangming Xiao, and Jinwei Dong designed the study and conducted the data processing and manuscript writing. Shu Gan, Deli Zhai, Geli Zhang, Yuanwei Qin, and Li Li contributed to the PALSAR and other related data processing and manuscript editing. All the authors worked on the interpretation of results and manuscript revisions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- FAO. Global Forest Resources Assessment 2010. Available online: http://www.fao.org/docrep/013/i1757e/i1757e.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2014).
- Fox, J.; Castella, J.-C. Expansion of rubber (Hevea brasiliensis) in mainland Southeast Asia: What are the prospects for smallholders? J. Peasant Stud. 2013, 40, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, A.D.; Fox, J.M.; Xu, J.C. The rubber juggernaut. Science 2009, 324, 1024–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Aide, T.M.; Ma, Y.; Liu, W.; Cao, M. Demand for rubber is causing the loss of high diversity rain forest in SW China. Biodivers. Conserv. 2007, 16, 1731–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J. Where the rubber meets the garden. Nature 2009, 457, 246–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Z.-F.; Cannon, C.H.; Chen, J.; Ye, C.-X.; Swetnam, R.D. Developing indicators of economic value and biodiversity loss for rubber plantations in Xishuangbanna, Southwest China: A case study from Menglun township. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 36, 788–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Fox, J.M. Mapping rubber tree growth in mainland southeast Asia using time-series MODIS 250 m NDVI and statistical data. Appl. Geogr. 2012, 32, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, G.; Huang, C. Analysis of distribution characteristics of Hevea brasiliensis in the Xishuangbanna area based on HJ-1 satellite data. Sci. China Inform. Sci. 2011, 41, 166–176. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Feng, Z.; Jiang, L.; Jiang, Y. Rubber plantations in Xishuangbanna: Remote sensing identification and digital mapping. Resour. Sci. 2012, 34, 1769–1780. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Fox, J.M. Integrating Mahalanobis typicalities with a neural network for rubber distribution mapping. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 2, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z. Rubber tree distribution mapping in Northeast Thailand. Int. J. Geosci. 2011, 2, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, M.; Fransson, J.E.S.; Eriksson, L.E.B.; Magnusson, M.; Ulander, L.M.H.; Olsson, H. Signatures of ALOS PALSAR l-band backscatter in Swedish forest. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 4001–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFries, R.; Achard, F.; Brown, S.; Herold, M.; Murdiyarso, D.; Schlamadinger, B.; de Souza, C., Jr. Earth observations for estimating greenhouse gas emissions from deforestation in developing countries. Environ. Sci. Policy 2007, 10, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.C.; Roy, D.P.; Lindquist, E.; Adusei, B.; Justice, C.O.; Altstatt, A. A method for integrating MODIS and Landsat data for systematic monitoring of forest cover and change in the Congo basin. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 2495–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, W.S.; Stickler, C.M.; Kellndorfer, J.M.; Kirsch, K.M.; Nepstad, D.C. Large-area classification and mapping of forest and land cover in the Brazilian Amazon: A comparative analysis of ALOS/PALSAR and Landsat data sources. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2010, 3, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asner, G.P. Cloud cover in Landsat observations of the Brazilian Amazon. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 3855–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghdadi, N.; Boyer, N.; Todoroff, P.; Hajj, E.M.; Begue, A. Potential of SAR sensors TerraSAR-X, ASAR/ENVISAT and PALSAR/ALOS for monitoring sugarcane crops on Reunion Island. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1724–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Sheldon, S.; Biradar, C.; Zhang, G.; Duong, N.D.; Hazarika, M.; Wikantika, K.; Takeuhci, W.; Moore, B., III. A 50-m forest cover map in Southeast Asia from ALOS/PALSAR and its application on forest fragmentation assessment. PLoS One 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, R.M.; Clewley, D.; Accad, A.; Butler, D.; Armston, J.; Bowen, M.; Bunting, P.; Carreiras, J.; Dwyer, J.; Eyre, T.; et al. Mapping forest growth and degradation stage in the Brigalow Belt Bioregion of Australia through integration of ALOS PALSAR and Landsat-derived foliage projective cover data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 155, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, M.; Itoh, T.; Motooka, T.; Watanabe, M.; Shiraishi, T.; Thapa, R.; Lucas, R. New global forest/non-forest maps from ALOS PALSAR data (2007–2010). Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 155, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Sheldon, S.; Biradar, C.; Duong, N.D.; Hazarika, M. A comparison of forest cover maps in mainland Southeast Asia from multiple sources: PALSAR, MERIS, MODIS and FRA. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 127, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, W.; Li, X.; Zhao, Z.; Li, C. Rubber planting area extraction in Xishuangbanna region based on HJ-1 CCD remote sensing image. Chin. J. Agrometeorol. 2013, 34, 493–497. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Chen, B.; Torbick, N.; Jin, C.; Zhang, G.; Biradar, C. Mapping deciduous rubber plantations through integration of PALSAR and multi-temporal Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 134, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, S.; Xiao, X.; Biradar, C. Mapping evergreen forests in the Brazilian Amazon using MODIS and PALSAR 500-m mosaic imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 74, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Sheldon, S.; Biradar, C.; Xie, G. Mapping tropical forests and rubber plantations in complex landscapes by integrating PALSAR and MODIS imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 74, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suratman, M.N.; Bull, G.Q.; Leckie, D.G.; Lemay, V.M.; Marshall, P.L.; Mispan, M.R. Prediction models for estimating the area, volume, and age of rubber (Hevea brasiliensis) plantations in Malaysia using Landsat TM data. Int. Forestry Rev. 2004, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Chen, J.M.; Pan, Y.; Peters, W.; Birdsey, R.; McCullough, K.; Xiao, J. The use of forest stand age information in an atmospheric CO2 inversion applied to North America. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 5335–5348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Chen, J.M.; Pan, Y.; Peters, W.; Birdsey, R.; McCullough, K.; Xiao, J. Forest stand age information improves an inverse North American carbon flux estimate. Biogeosci. Discuss. 2013, 10, 4781–4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, G.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y. How temperature, precipitation and stand age control the biomass carbon density of global mature forests. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2014, 23, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretzsch, H.; Biber, P.; Schütze, G.; Bielak, K. Changes of forest stand dynamics in Europe: Facts from long-term observational plots and their relevance for forest ecology and management. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2014, 316, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Chen, Z.; Piao, S.; Peng, C.; Ciais, P.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.; Zhu, X. High carbon dioxide uptake by subtropical forest ecosystems in the East Asian monsoon region. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4910–4915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivanpillai, R.; Smith, C.T.; Srinivasan, R.; Messina, M.G.; Wu, X.B. Estimation of managed loblolly pine stand age and density with Landsat ETM+ data. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2006, 223, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Cao, J.; Wang, J.; Wu, Z.; Tao, Z.; Chen, J.; Yang, C.; Xie, G. Estimation of rubber stand age in typhoon and chilling injury afflicted area with Landsat TM data: A case study in Hainan Island, China. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2012, 274, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Xie, G.; Tao, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, X. Characteristics of soil carbon and total nitrogen contents of rubber plantations at different age stages in Danzhou, Hainan Island. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2009, 18, 1484–1491. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Feng, Z.; Jiang, L.; Li, P.; Liao, C.; Yang, Y.; You, Z. Rubber plantation and its relationship with topographical factors in the border region of China, Laos and Myanmar. J. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 23, 1019–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Liu, W.; Luo, Q. Ecohydrological effects of litter layer in a mountainous rubber plantation in Xishuangbanna, Southwest China. Chin. J. Ecol. 2011, 30, 2129–2136. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), K&C Mosaic Homepage—PALSAR 50 m Orthorectified Mosaic Product. Available online: http://www.eorc.jaxa.jp/ALOS/en/kc_mosaic/kc_map_50.htm (accessed on 10 September 2014).
- Longepe, N.; Rakwatin, P.; Isoguchi, O.; Shimada, M.; Uryu, Y.; Yulianto, K. Assessment of ALOS PALSAR 50 m orthorectied FBD data for regional land cover classification by support vector machines. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 2135–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, M.; Isoguchi, O.; Rosenqvist, A. PALSAR calval and generation of the continent scale mosaic products for Kyoto and Carbon projects. In Proceedings of Geoscience and remote sensing Symposium, IEEE International, Boston, MA, USA, 7–11 July 2008.
- Shimada, M.; Ohtaki, T. Generating large-scale high-quality SAR mosaic datasets: Application to PALSAR data for global monitoring. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2010, 3, 637–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenqvist, A.; Shimada, M.; Ito, N.; Watanabe, M. ALOS PALSAR: A pathfinder mission for global-scale monitoring of the environment. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 3307–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The National Center for Earth Resource Observations and Science. Available online: http://earthexplorer.usgs.gov (accessed on 10 September 2014).
- The National Center for Earth Resource Observations and Science (EROS). Landsat 7 Science Data Users Handbook. Available online: http://landsathandbook.Gsfc.Nasa.Gov/pdfs/landsat7_handbook.Pdf. (accessed on 10 September 2014).
- Masek, J.G.; Vermote, E.F.; Saleous, N.E.; Wolfe, R.; Hall, F.G.; Huemmrich, K.F.; Gao, F.; Kutler, J.; Lim, T.K. A Landsat surface reflectance dataset for North America, 1990–2000. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 3, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, E.F.; ElSaleous, N.; Justice, C.O.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Privette, J.L.; Remer, L.; Roger, J.C.; Tanre, D. Atmospheric correction of visible to middle-infrared EOS-MODIS data over land surfaces: Background, operational algorithm and validation. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos 1997, 102, 17131–17141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senf, C.; Pflugmacher, D.; van der Linden, S.; Hostert, P. Mapping rubber plantations and natural forests in Xishuangbanna (Southwest China) using multi-spectral phenological metrics from MODIS time series. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 2795–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Woodcock, C.E. Object-based cloud and cloud shadow detection in Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 118, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.J. Red and photographic infrared linear combinations for monitoring vegetation. Remote Sens. Environ. 1979, 8, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T.; Rodriguez, E.P.; Gao, X.; Ferreira, L.G. Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Hollinger, D.; Aber, J.; Goltz, M.; Davidson, E.A.; Zhang, Q.; Moore, M., III. Satellite-based modeling of gross primary production in an evergreen needleleaf forest. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 89, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.M.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Hollinger, D.; Aber, J.; Moore, B. Modeling gross primary production of an evergreen needleleaf forest using MODIS and climate data. Ecol. Appl. 2004, 15, 954–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X. Earth Observation and Modeling Facility (EOMF). Available online: http://www.eomf.ou.edu (accessed on 10 September 2014).
- Benedek, C.; Sziranyi, T. Change detection in optical aerial images by a multilayer conditional mixed markov model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 3416–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, W.B.; Yang, Z.G.; Kennedy, R. Detecting trends in forest disturbance and recovery using yearly Landsat time series: 2. Timesync–Tools for calibration and validation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2911–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.Q.; Coward, S.N.; Masek, J.G.; Thomas, N.; Zhu, Z.L.; Vogelmann, J.E. An automated approach for reconstructing recent forest disturbance history using dense Landsat time series stacks. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesano, P.M.; Nelson, R.; Sun, G.; Margolis, H.; Kerber, A.; Ranson, K.J. MODIS tree cover validation for the circumpolar taiga-tundra transition zone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2130–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potere, D. Horizontal positional accuracy of google earth’s high-resolution imagery archive. Sensors 2008, 8, 7973–7981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.C.; Potapov, P.V.; Moore, R.; Hancher, M.; Turubanova, S.A.; Tyukavina, A.; Thau, D.; Stehman, S.V.; Goetz, S.J.; Loveland, T.R.; et al. High-resolution global maps of 21st-century forest cover change. Science 2013, 342, 850–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, F.; Sawaya, K.E.; Loeffelholz, B.C.; Bauer, M.E. Land cover classification and change analysis of the Twin Cities (Minnesota) metropolitan area by multitemporal Landsat remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 98, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Feng, Z.; Jiang, L. Application of decision tree classification to rubber plantations extraction with remote sensing. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agr. Eng. 2013, 29, 163–172. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.; Liu, X.; Jiang, L.; Li, P. Spatial-temporal analysis of rubber plantation and its relationship with topographical factors in the border region of China, Laos and Myanmar. J. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 68, 1442–1446. [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen, J.; Liew, S.C. Separability of insular Southeast Asian woody plantation species in the 50 m resolution ALOS PALSAR mosaic product. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 2, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, W.S.; Stickler, C.M.; Kellndorfer, J.M.; Kirsch, K.M.; Nepstad, D.C. Large-area classification and mapping of forest and land cover in the Brazilian Amazon: A comparative analysis of ALOS/PALSAR and Landsat data sources. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2010, 3, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, E.A.; Caccetta, P.A.; Zheng-Shu, Z.; McNeill, S.J.; Xiaoliang, W.; Mitchell, A.L. Joint processing of Landsat and ALOS-PALSAR data for forest mapping and monitoring. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijaya, A.; Gloaguen, R. In fusion of ALOS PALSAR and Landsat ETM data for land cover classification and biomass modeling using non-linear methods. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 3, III-581–III-584. [Google Scholar]
- Foody, G.M. Assessing the accuracy of land cover change with imperfect ground reference data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2271–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Dorovskoy, P.; Biradar, C.; Bridge, E. A library of georeferenced photos from the field. EOS Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2011, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Schaefer, D.A.; Chan, O.C.; Zou, X. Decomposition differences of labile carbon from litter to soil in a tropical rain forest and rubber plantation of Xishuangbanna, Southwest China. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2013, 55, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).