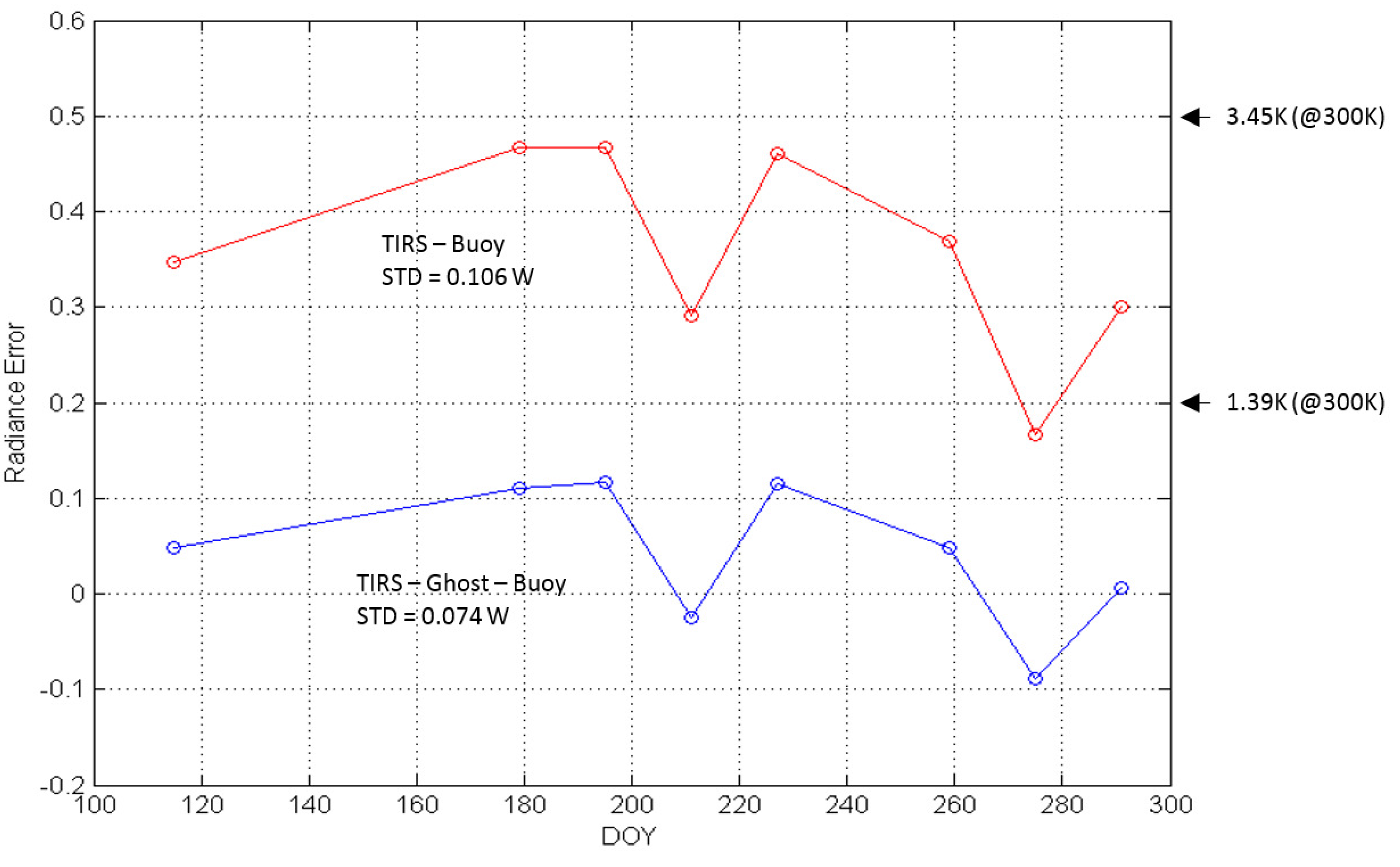
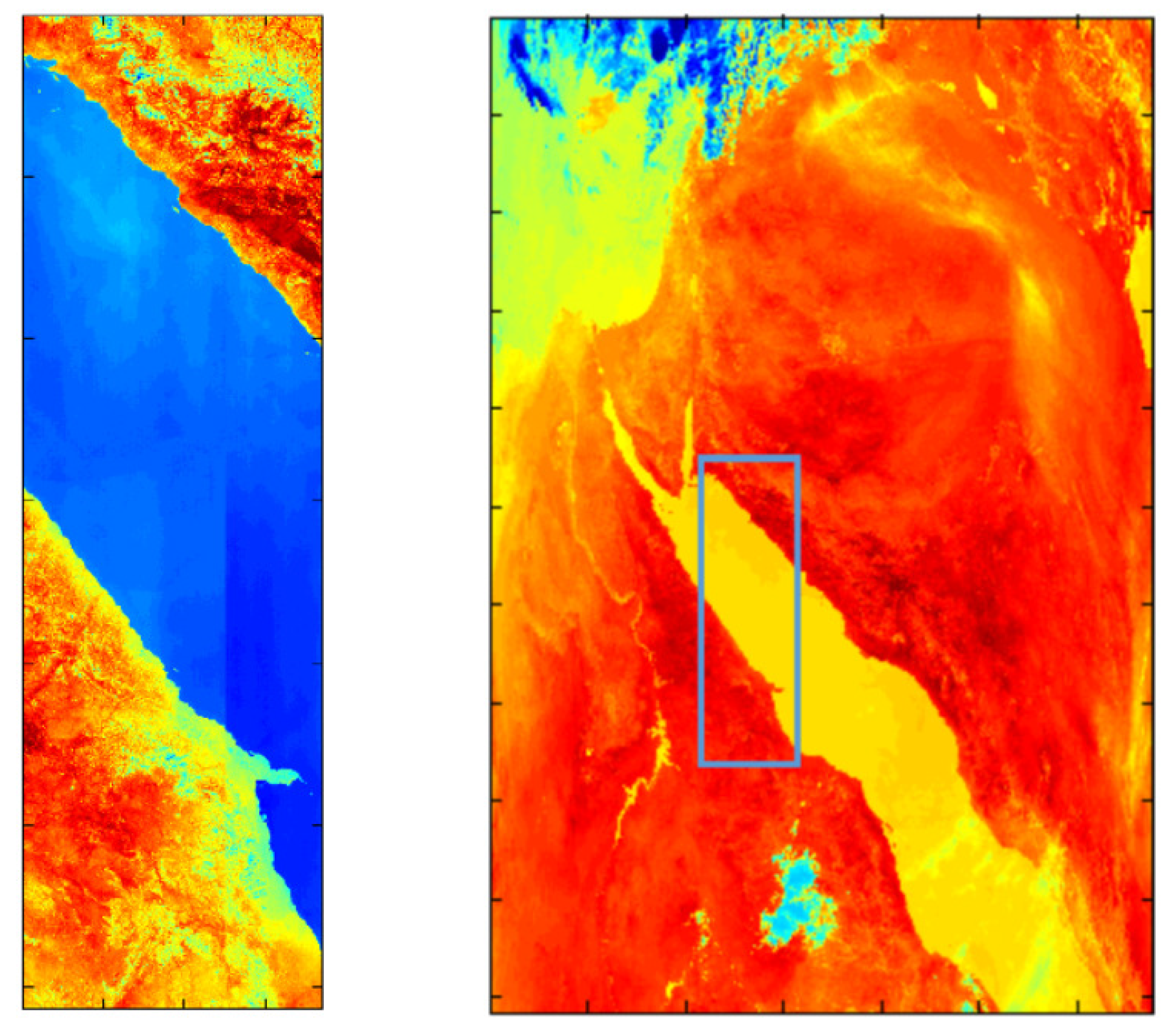
The cause of the artifacts seen in Earth imagery was theorized to be radiance from outside the scene scattering into the field-of-view. The effect of the scattering is not uniform across the field-of-view (i.e., the scattering, or ghosting effect, will be different for each detector across the focal plane). This implies that a unique correction will be required for each detector to correct for the ghosting effect in the TIRS image data.
Special Lunar Collect
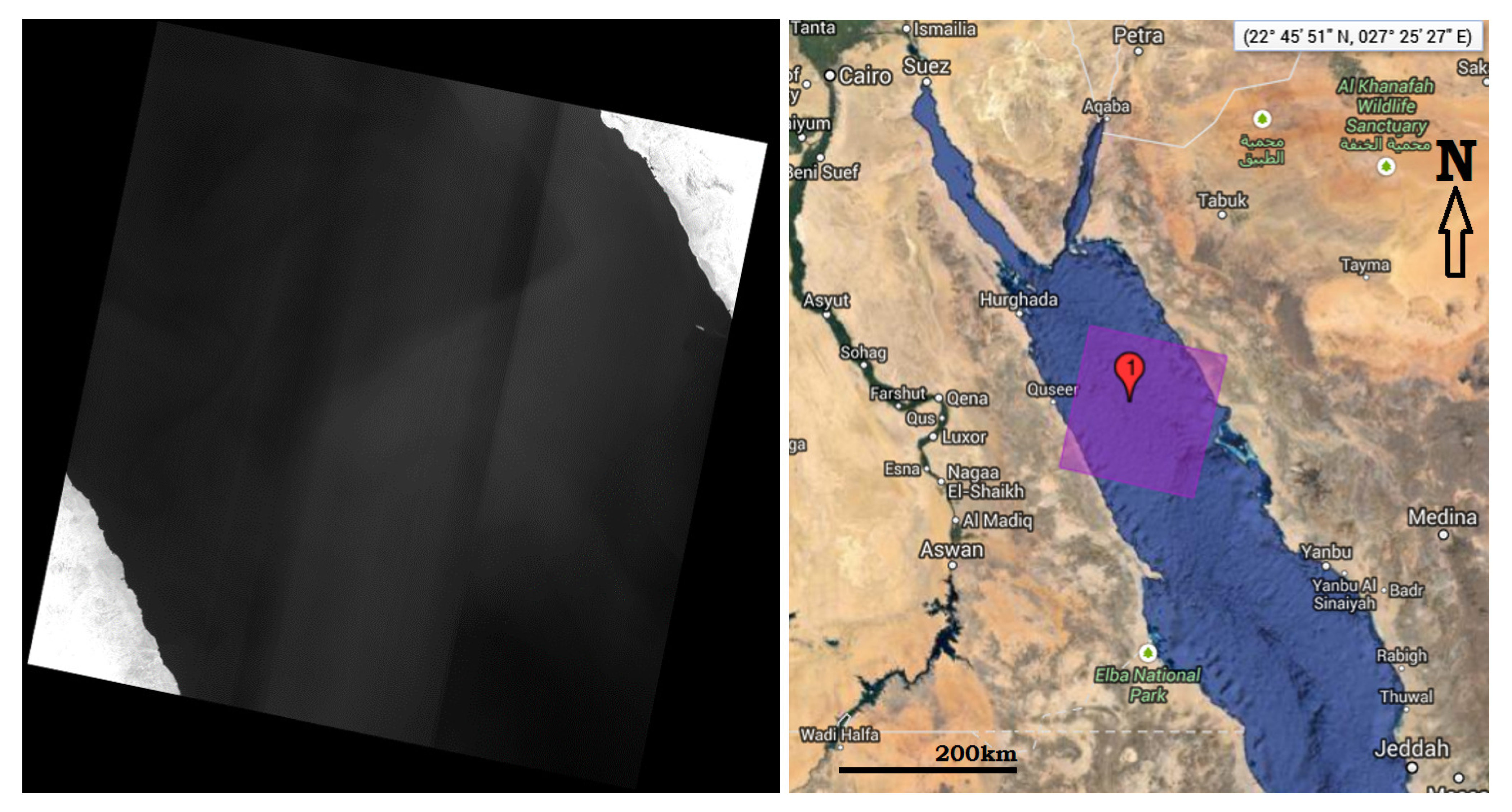
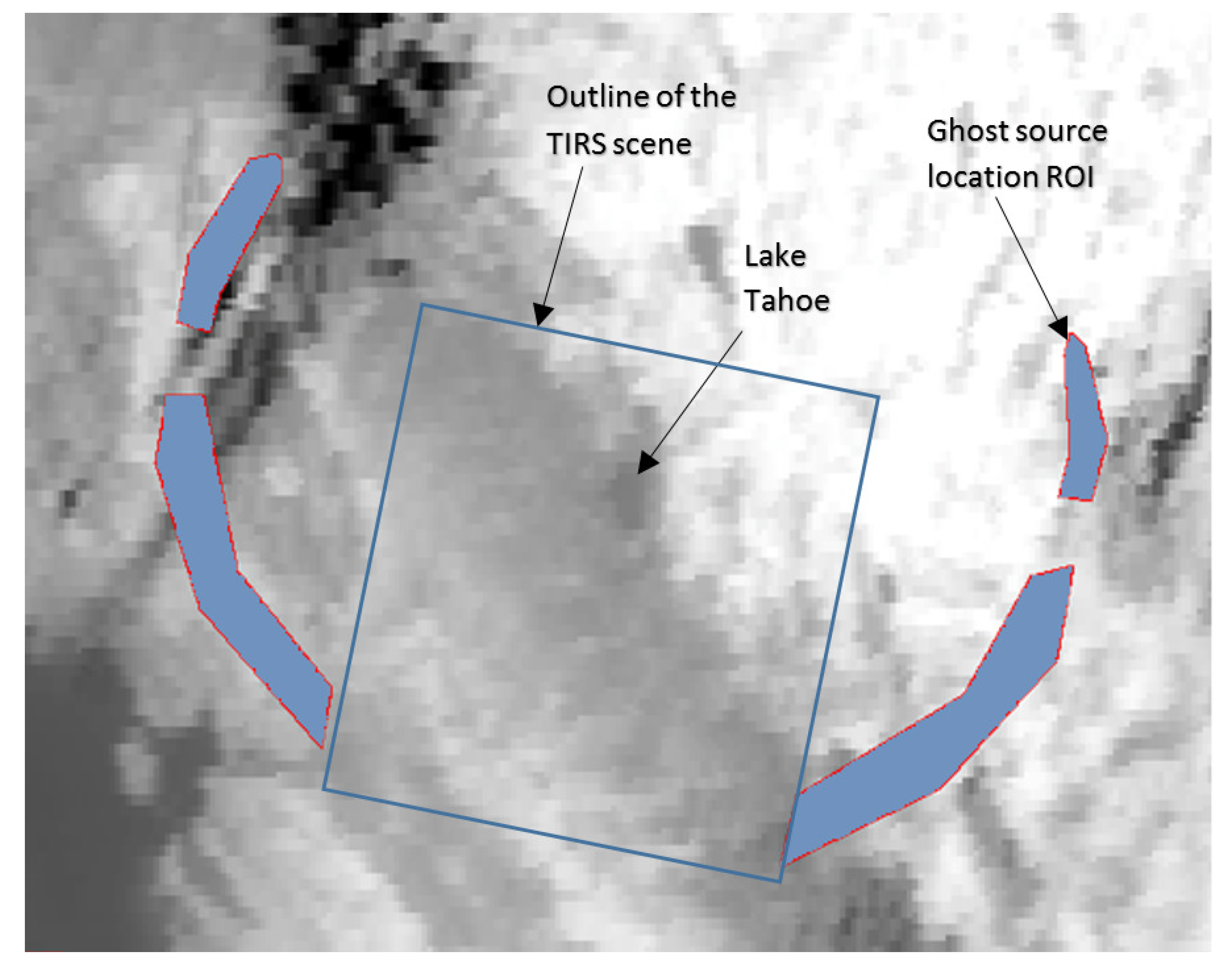
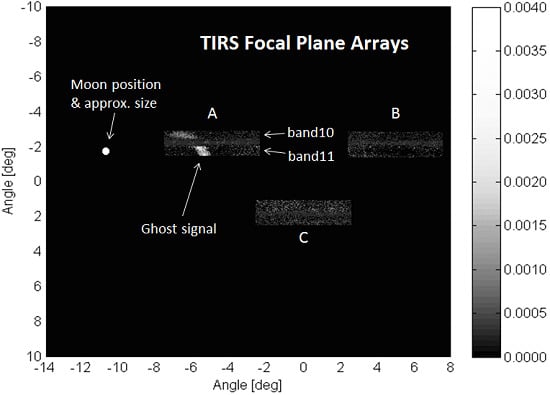
One way to test this theory is to place a concentrated source outside the field-of-view and observe the signal on the focal plane. Ideally, no signal from this source should be detected as the source is not directly viewed by TIRS. Any signal that is detected would be a ghost signal from the out-of-field source from the particular location of the source. If the source is raster scanned throughout the out-of-field area of TIRS, then a map of the ghost source locations for each detector may be constructed. The moon provides such a concentrated source.
Referring to
Figure 4, the Landsat 8 observatory was commanded through a series of slews in which the moon was scanned over the TIRS in-field and out-of-field-of-view. A total of five scans were obtained, with each scan consisting of three vertical segments, for a total of 15 vertical segments covering at least ±18° from the instrument boresight in both the across-track and along-track directions. The spacing of the vertical scans in the across-track direction was at most 2.56°. Coverage in the along-track direction reached as far as ±40° due to the operation of the observatory’s attitude control system in executing these maneuvers.
In addition to the special lunar scans, the observatory performs a lunar scan once a month to collect in-field data for the companion Landsat 8 sensor, the Operational Land Imager (OLI). TIRS takes advantage of these routine OLI-driven maneuvers by imaging throughout the Earth-to-Moon slew. Towards the end of the slew, the moon is usually observed crossing one or more of the focal plane arrays. This opportunity allows for additional ghosting data to be collected (to assist in populating the source maps) as the moon approaches from outside the field-of-view before being directly imaged by the arrays.
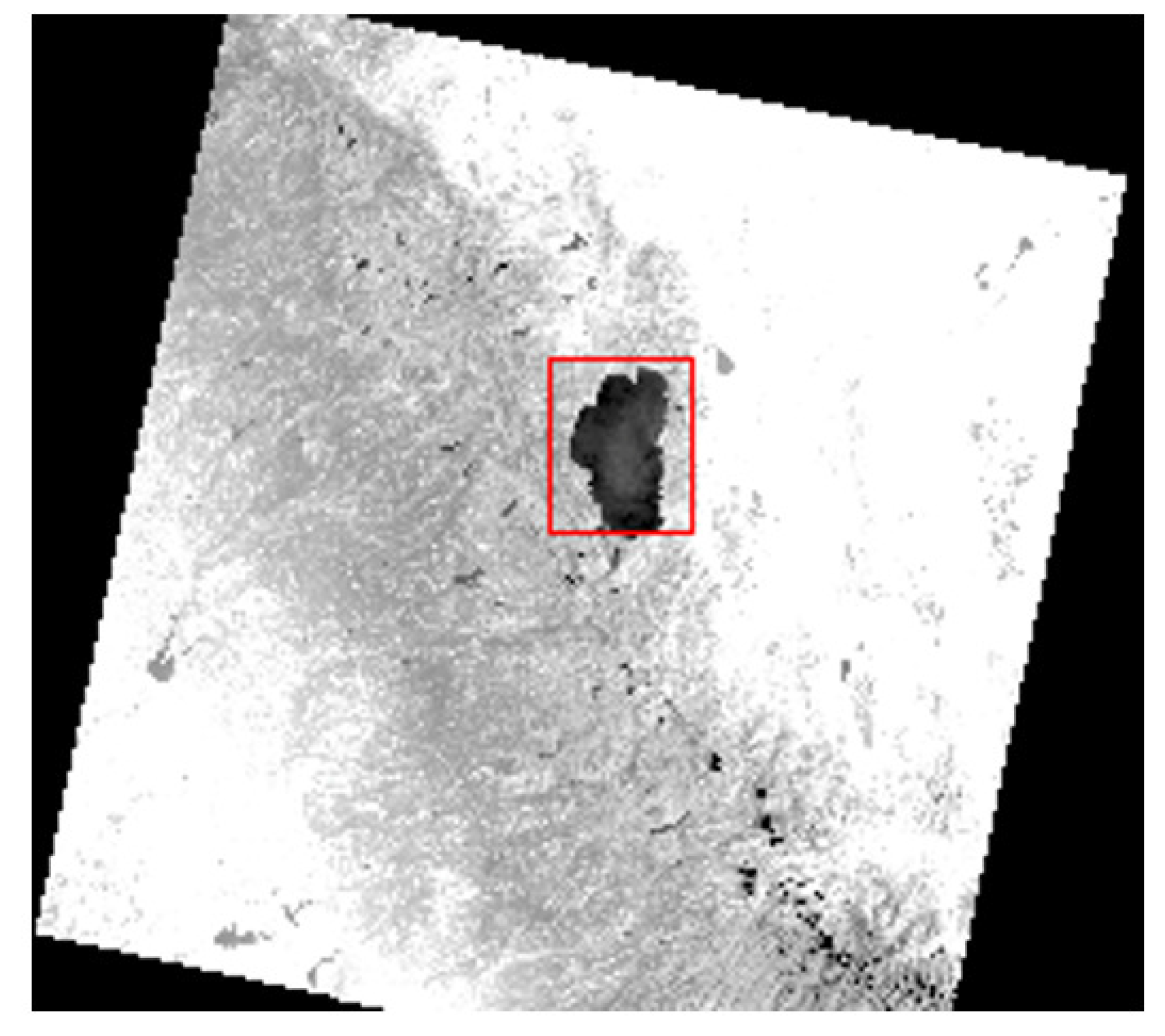
Figure 4 illustrates the track of the moon for all the special lunar scans along with the additional Earth-to-Moon slews.
Figure 4.
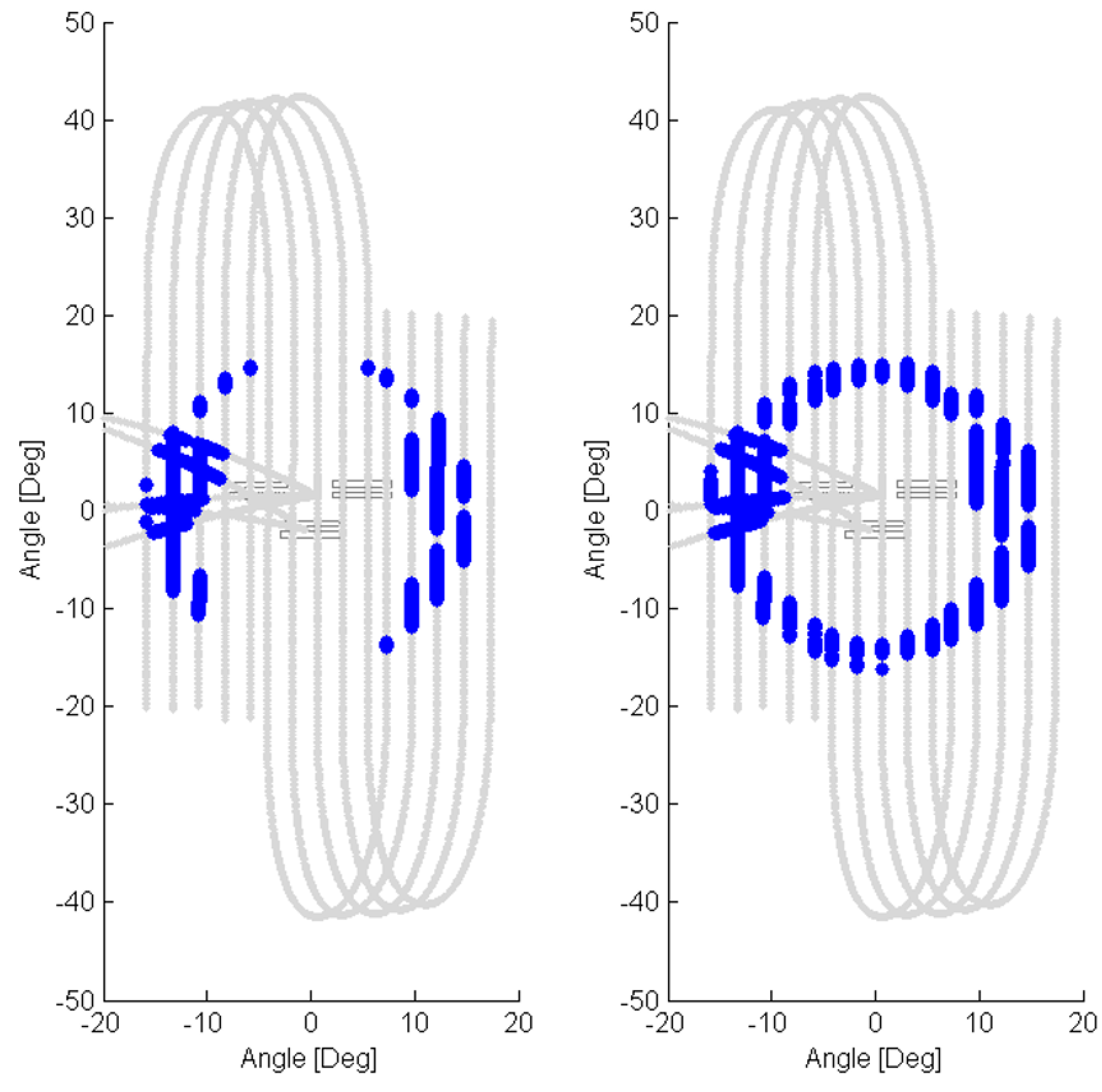
Illustration of the path of the moon (gray lines) relative to the focal plane array spectral filters during the special lunar scans and the Earth-to-Moon slews. Lunar locations in which a ghost signal was detected anywhere on the band 10 detectors (left) or the band 11 detectors (right) are highlighted in blue. Angles are relative to the optical boresight.
Figure 4.
Illustration of the path of the moon (gray lines) relative to the focal plane array spectral filters during the special lunar scans and the Earth-to-Moon slews. Lunar locations in which a ghost signal was detected anywhere on the band 10 detectors (left) or the band 11 detectors (right) are highlighted in blue. Angles are relative to the optical boresight.
The TIRS focal plane was switched to its diagnostic mode readout for all the lunar collects. The particular diagnostic mode reads out all rows under the spectral filters from each focal plane array at a slower frame rate instead of the usual six rows in the push-broom mode. The frame rate of approximately 2 Hz along with the slew rate of the spacecraft resulted in oversampling of the moon in the along-track direction. Whereas raw Earth imagery are processed to units of radiance in the standard ground processing system [
8], the lunar imagery was manually processed for this work. All of the raw data was first linearized. Then, an image frame that contained no direct moon signal or ghost signal was used as a background frame to subtract from the rest of the dataset. Finally, all background-subtracted data was scaled to the direct lunar signal. That is, all data is divided by the signal from the moon when it is directly imaged on the focal plane detectors. The resulting magnitude of the image data is expressed as a fraction of the direct lunar signal.
By design, the moon is usually outside of the direct field-of-view of the detectors during these scans. The location of the moon relative to the TIRS detector arrays can be calculated from the spacecraft pointing telemetry. The spacecraft position relative to the Earth and the pointing quaternions are available in the downlinked telemetry throughout the lunar scans. This information is used with the SPICE system to calculate a direction vector of the moon relative to the TIRS optical boresight [
11]. A diagram is constructed for one moment in time (
i.e., for one image frame) in which the processed array image data are drawn spatially as they are arranged on the focal plane. A cartoon of the moon is drawn at the appropriate location relative to the array images. This diagram allows for a visual inspection of any ghosting signal on the arrays and also provides a sense of where the moon was located for this particular frame. A diagram is created for all image frames to inspect for ghosting artifacts for all the scanned lunar positions.
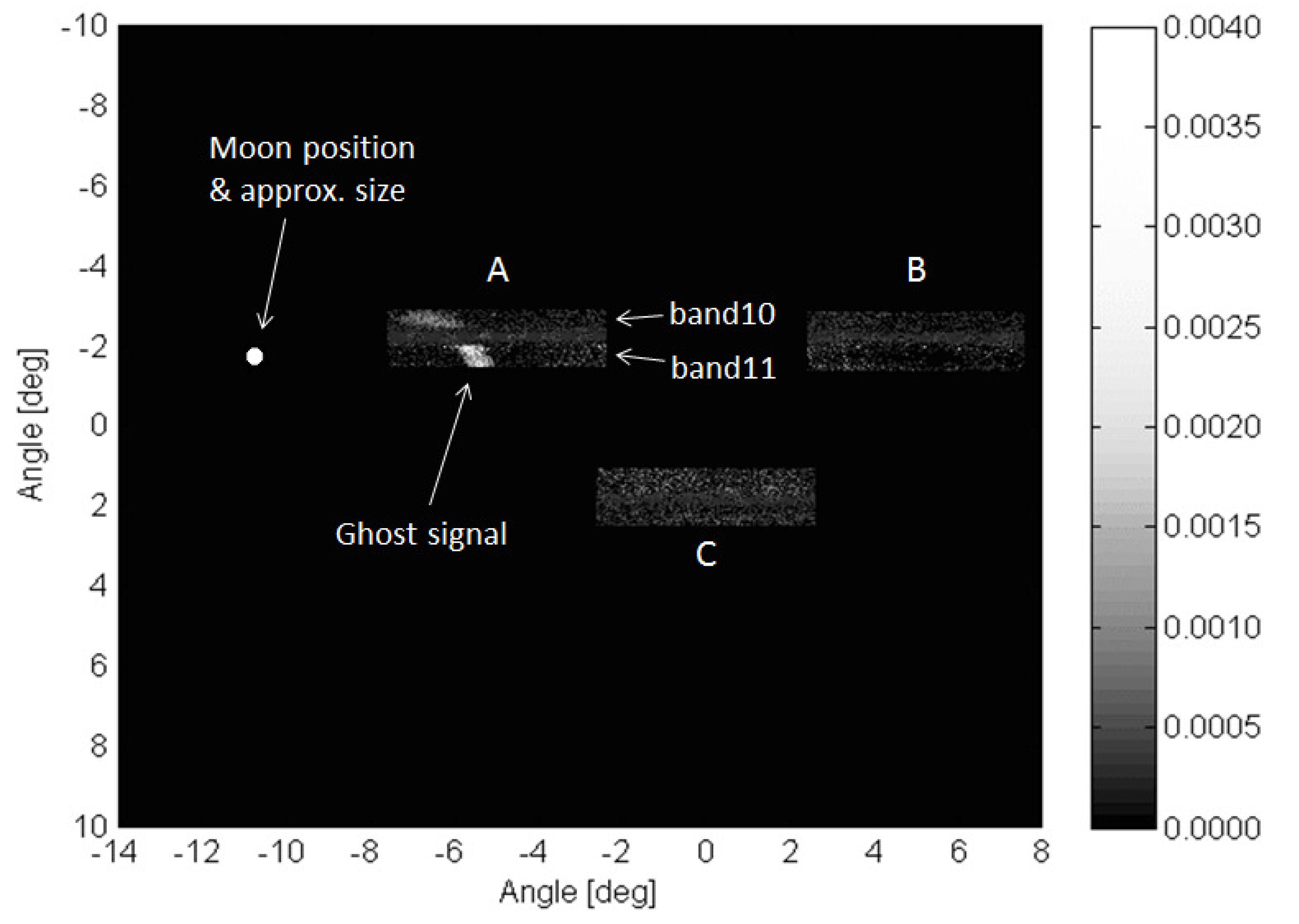
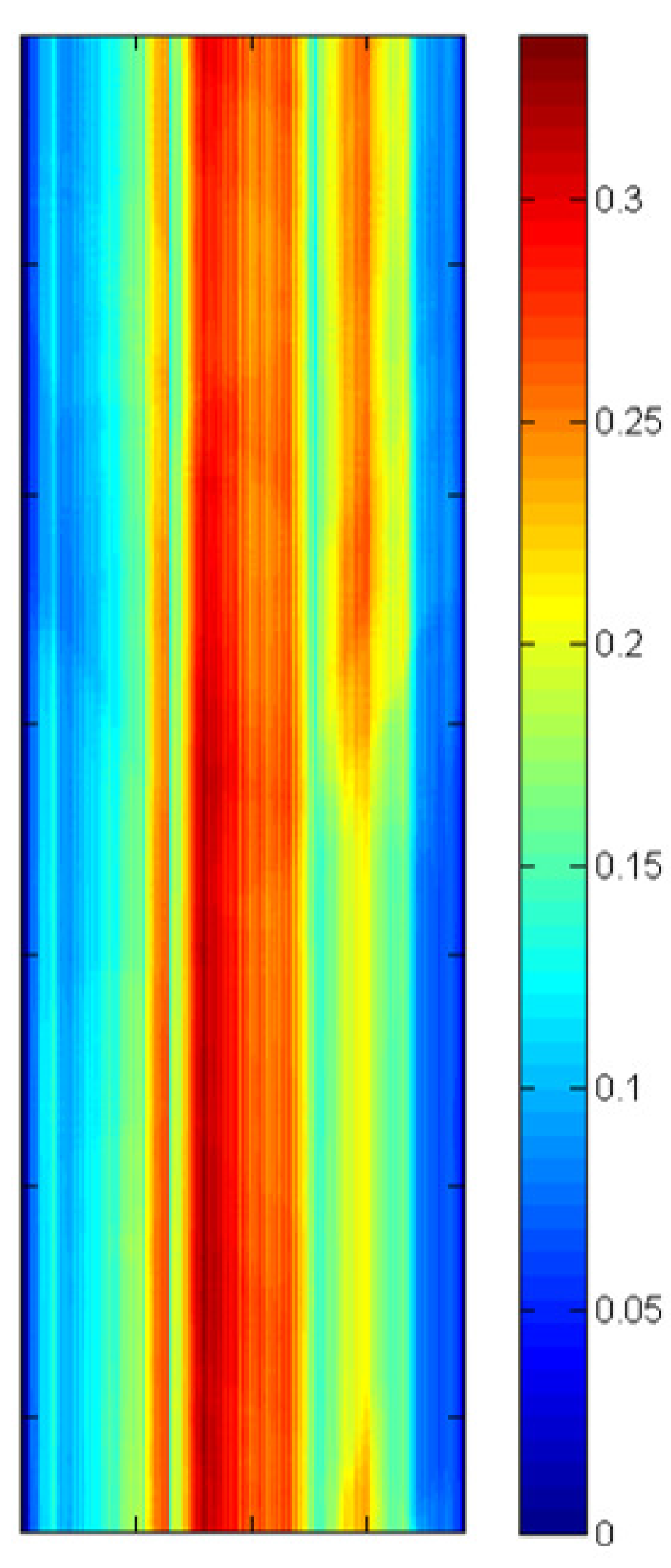
Figure 5.
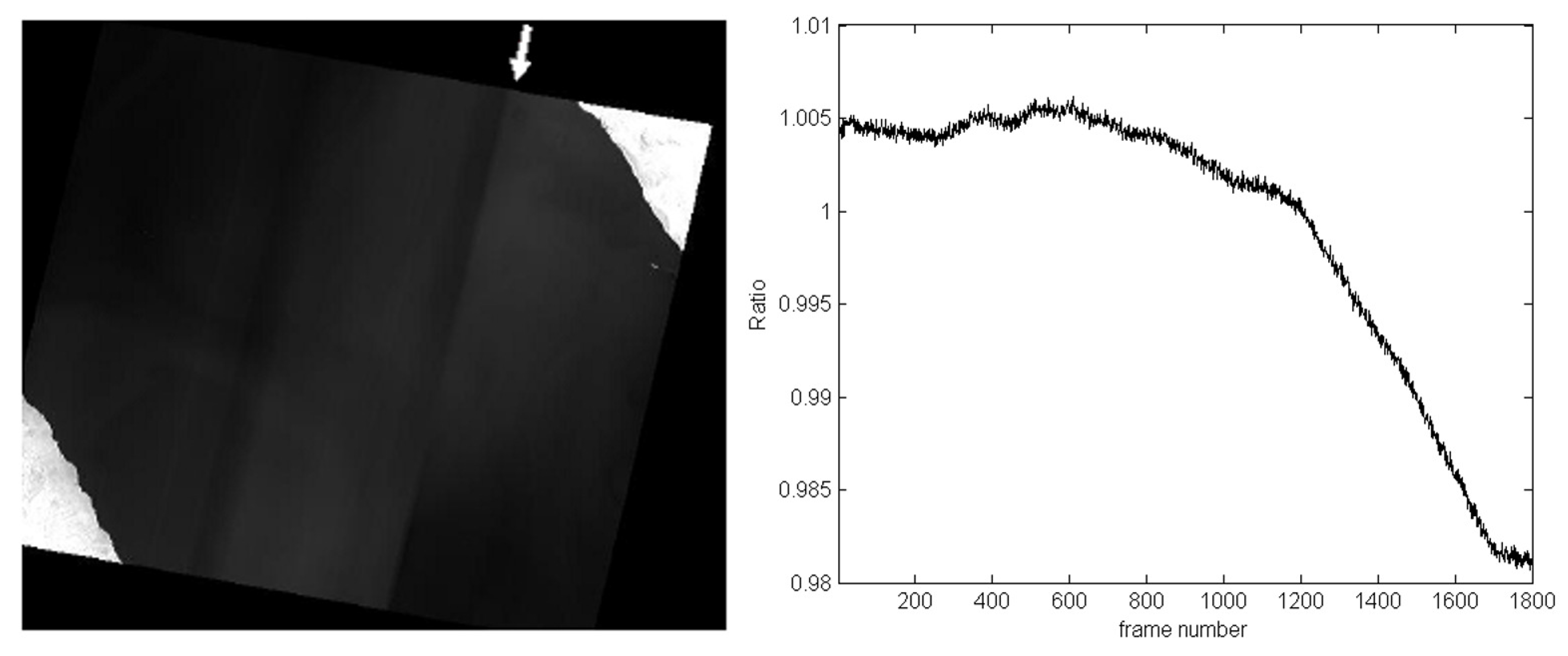
Diagram demonstrating the processed lunar scan data as the focal plane arrays are spatially oriented. The position of the moon relative to the arrays is indicated (angles are relative to the optical boresight). For this particular lunar position, a ghost signal appears on both bands in array -A as indicated. The contrast scale indicates the fraction of the directly-imaged lunar signal.
Figure 5.
Diagram demonstrating the processed lunar scan data as the focal plane arrays are spatially oriented. The position of the moon relative to the arrays is indicated (angles are relative to the optical boresight). For this particular lunar position, a ghost signal appears on both bands in array -A as indicated. The contrast scale indicates the fraction of the directly-imaged lunar signal.
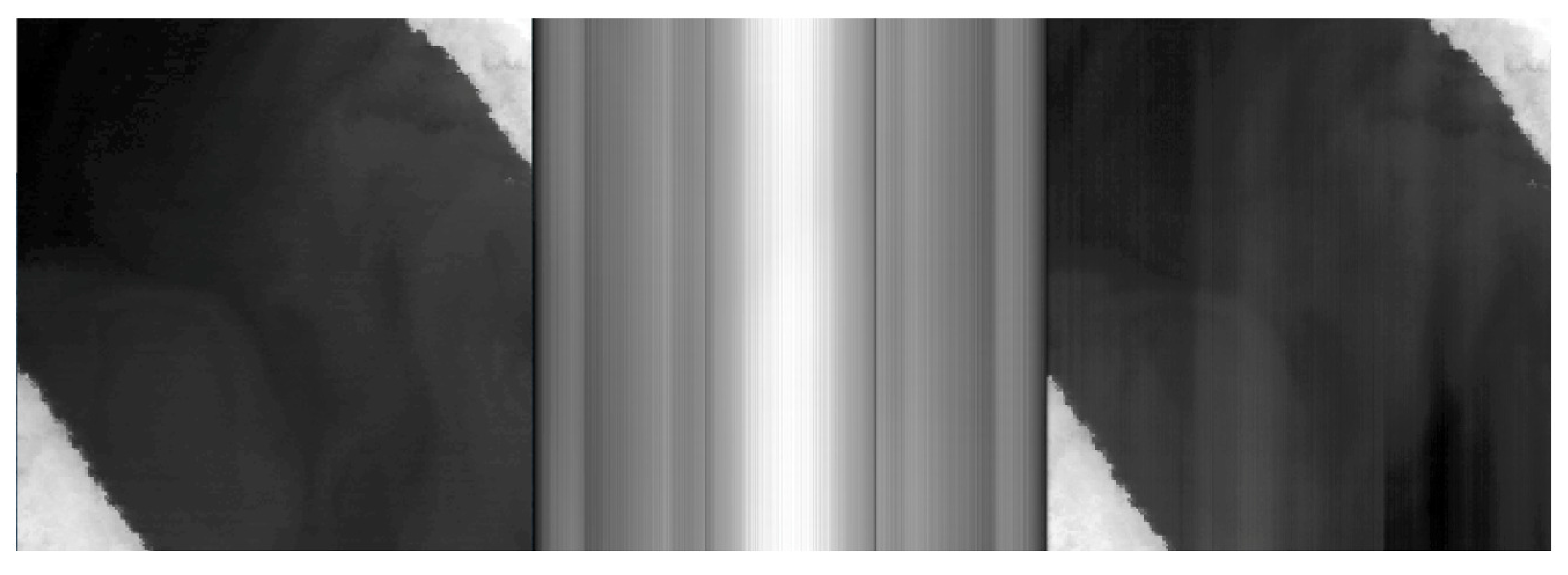
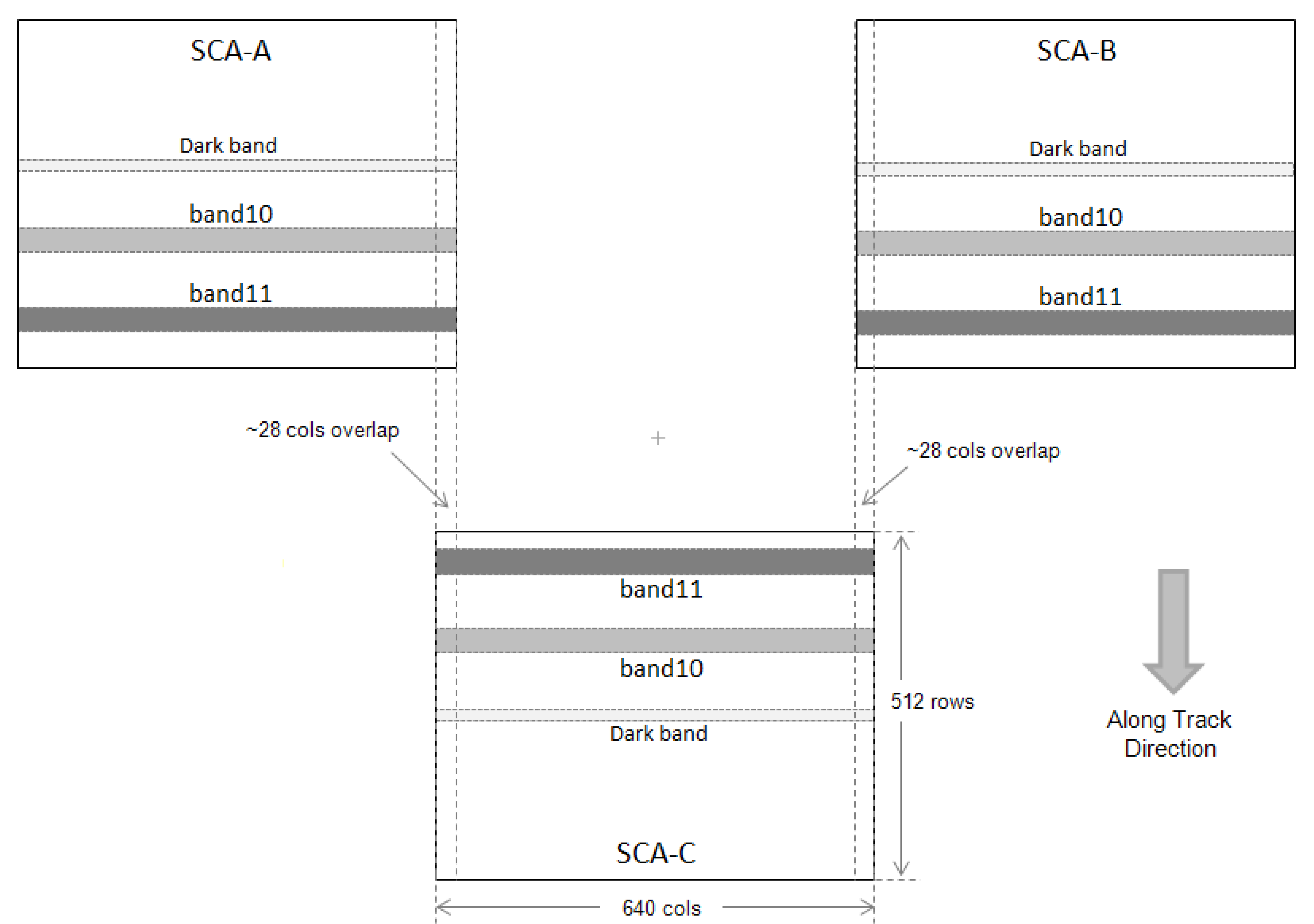
A diagram of one frame from the lunar scans is shown in
Figure 5. The image data for the three focal plane arrays are labeled -A, -B, and -C. The particular diagnostic mode used for these collects reads out 180 rows of the 512 total rows from each array. Therefore each array image frame is 180 rows by 640 columns of image data and includes all the rows under and between the spectral filters for band 10 and band 11. The calculated moon position is indicated on the diagram and the size of the moon cartoon is approximately the size of the moon as it would appear to TIRS. The ghost signal has approximate magnitudes of 0.002 and 0.004 of the direct lunar signal for band 10 and band 11, respectively, for the particular lunar location shown in the diagram. The location of the ghost signal changes with the position of the moon (illustrated in
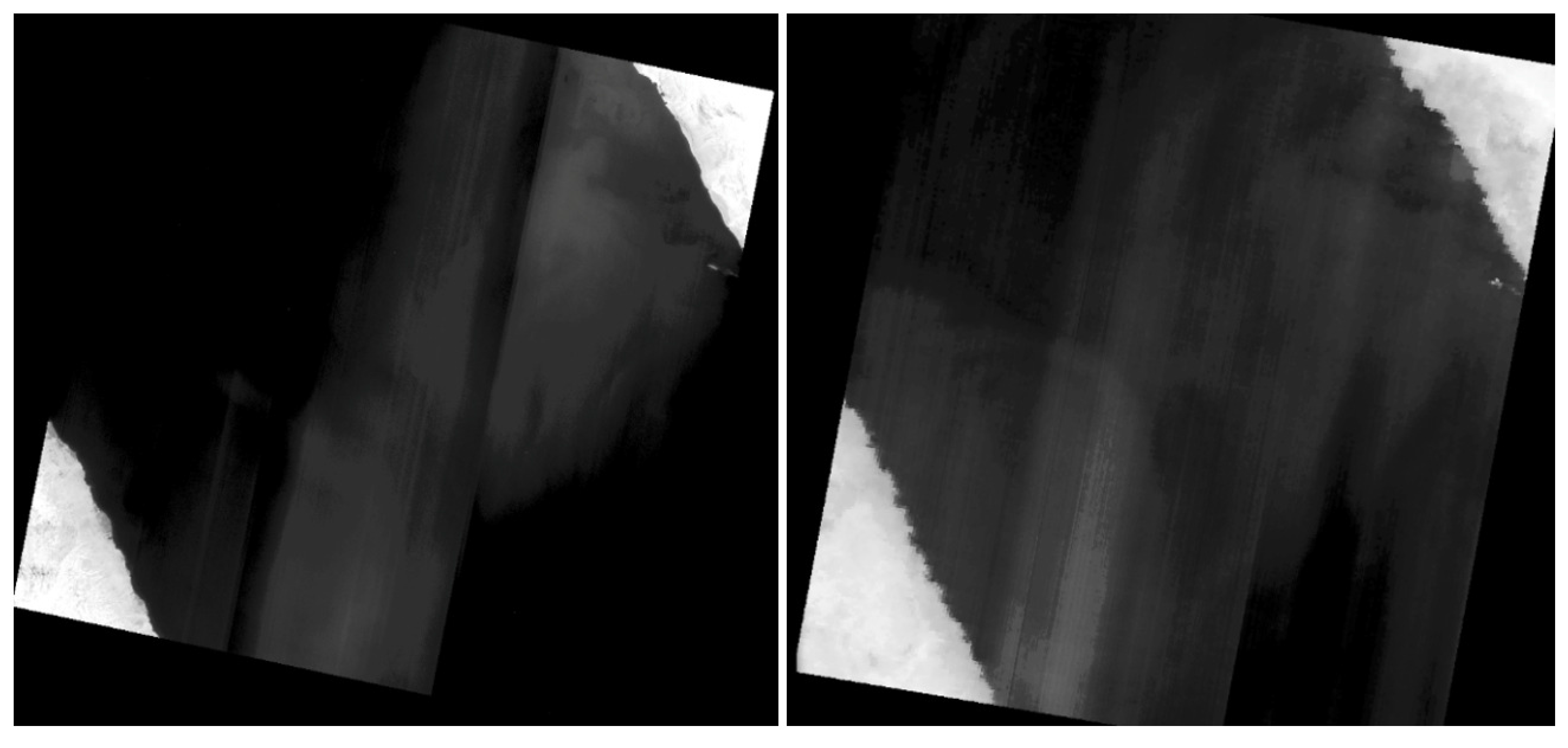
Figure 6) indicating that the ghost signal on a particular detector may originate from multiple out-of-field sources. It also indicates that each detector will have a different ghost signal from different sources.
Figure 6.
Demonstration that the ghost signal on the arrays is a function of lunar position. The lunar position is different in each of the three figures. The resulting shape of the ghost signal on the arrays is unique for each lunar position.
Figure 6.
Demonstration that the ghost signal on the arrays is a function of lunar position. The lunar position is different in each of the three figures. The resulting shape of the ghost signal on the arrays is unique for each lunar position.
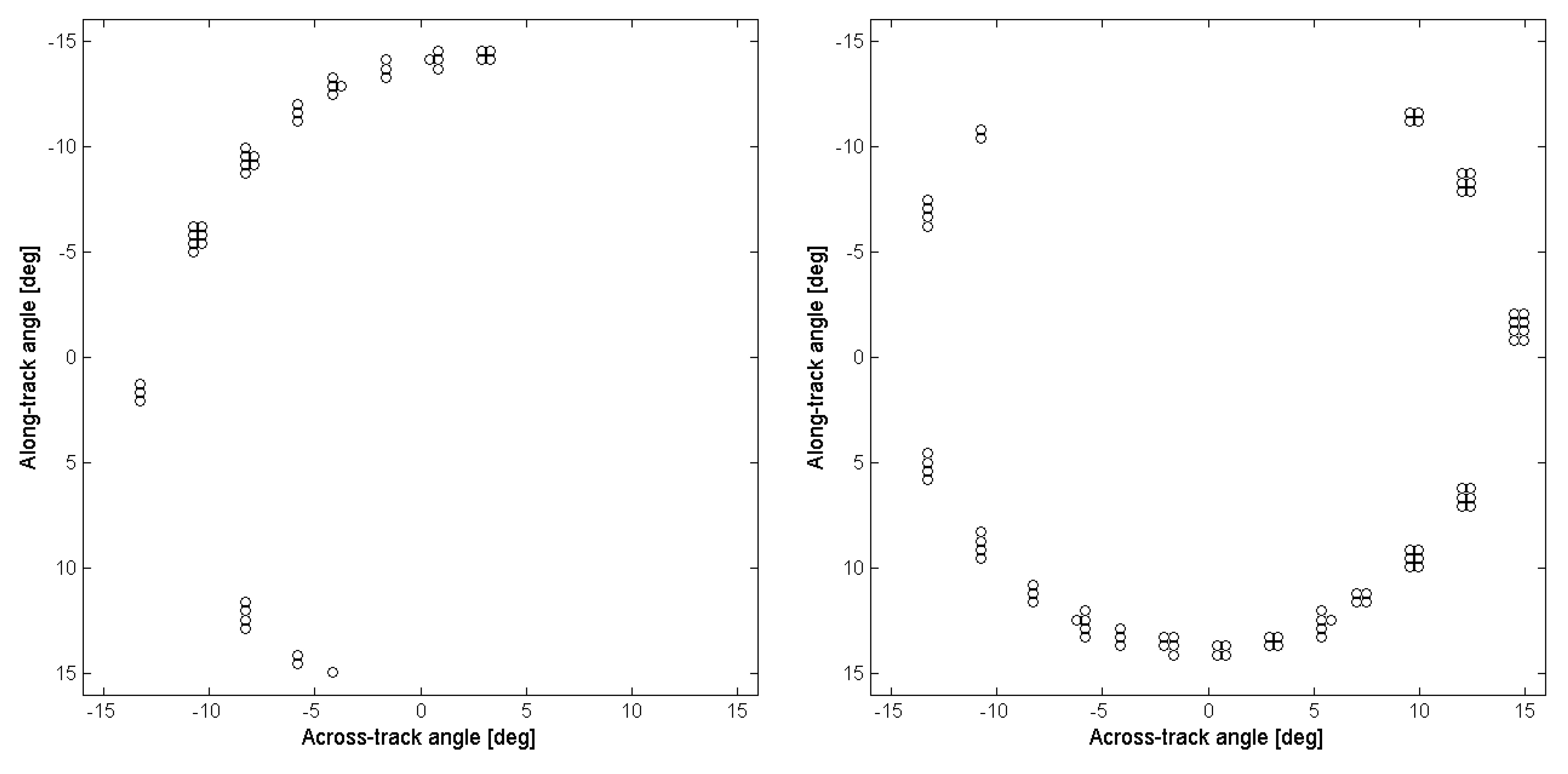
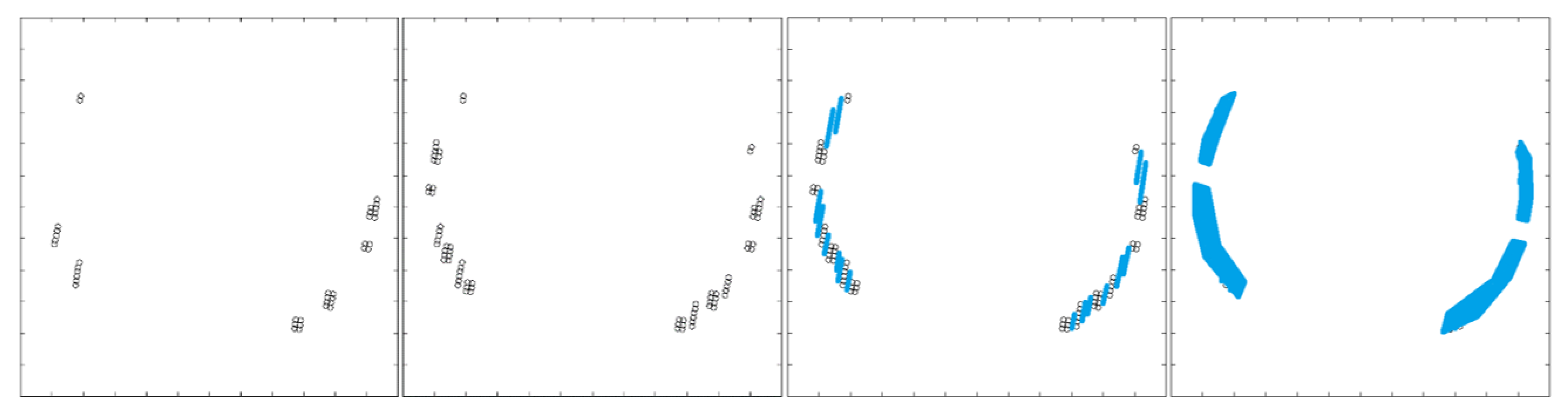
Figure 7.
Graphs of the ghosting source locations of two different detectors from array -A (left) and array -C (right) in band 11 based on the lunar scans. Each data point represents a lunar location (an angle in the across-track and along-track direction from the optical boresight) from which a ghost signal was observed for the particular detector. As implied in these diagrams, the ghost sources are different for each detector across the focal plane.
Figure 7.
Graphs of the ghosting source locations of two different detectors from array -A (left) and array -C (right) in band 11 based on the lunar scans. Each data point represents a lunar location (an angle in the across-track and along-track direction from the optical boresight) from which a ghost signal was observed for the particular detector. As implied in these diagrams, the ghost sources are different for each detector across the focal plane.
It is clear from the lunar scan diagrams that out-of-field radiance is scattering onto the TIRS detectors. The scans also demonstrate that the scattering sources originate from an area roughly 15° from the optical boresight (
Figure 4). To reduce the lunar image data to a manageable form, the image data was pulled for only the detectors used in the final data product (
i.e., the rows used in the normal push-broom imaging mode). After smoothing the image data slightly to reduce noise, the data was separated such that any signals above a certain threshold (approximately 0.0005 of the peak lunar signal - roughly the noise level) were flagged as ghosts while any signals below the threshold were considered background noise. Additionally, signals that could be attributed to direct lunar positions (when the moon was directly on or very close to the detectors) were removed since the purpose of these scans was to isolate out-of-field ghost sources only. The resulting dataset contains a list of every detector and all of the associated lunar position vectors in which a ghost occurred for that detector. For example, detector #1 on band 11 of array -A might have 20 position vectors associated with moon locations that produced a ghost signal on that detector. Detector #2 might have 25 lunar position vectors associated with ghosts for that particular detector, and so on. Two examples from this dataset are illustrated in
Figure 7.