Combining Spatial Models for Shallow Landslides and Debris-Flows Prediction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area
3. Methodology
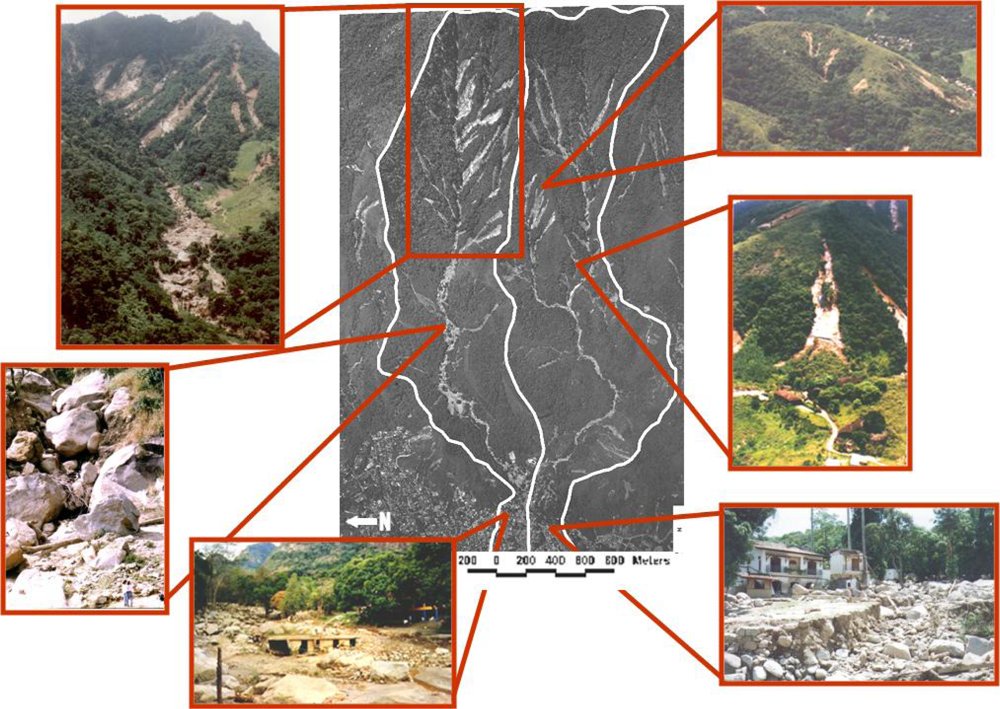
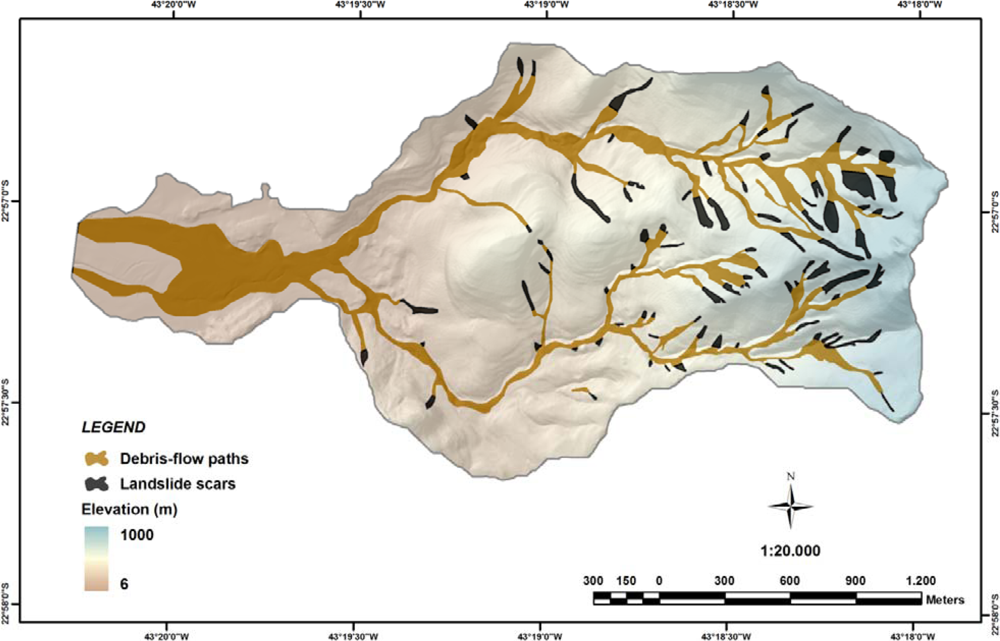
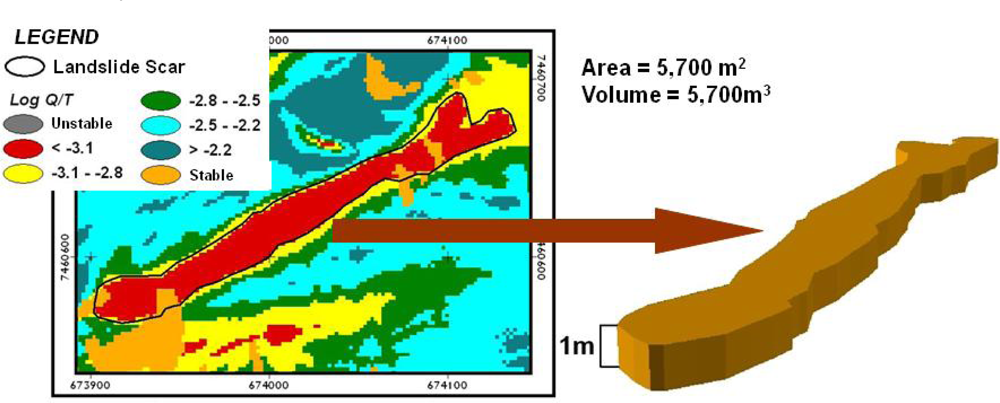
3.1. Elaboration of DEM and Photo-Interpretation of Landslide Scars and Debris-Flow Deposits
3.2. SHALSTAB Model
3.2.1. SHALSTAB Model Formulation
3.2.2. Application and Validation of SHALSTAB Model
3.3. Debris-Flows Simulations
3.3.1. FLO-2D Model Formulation
3.3.2. Determination of Rheological Parameters of Debris-Flow
3.4. Combining the SHALSTAB and FLO-2D Models
4. Results
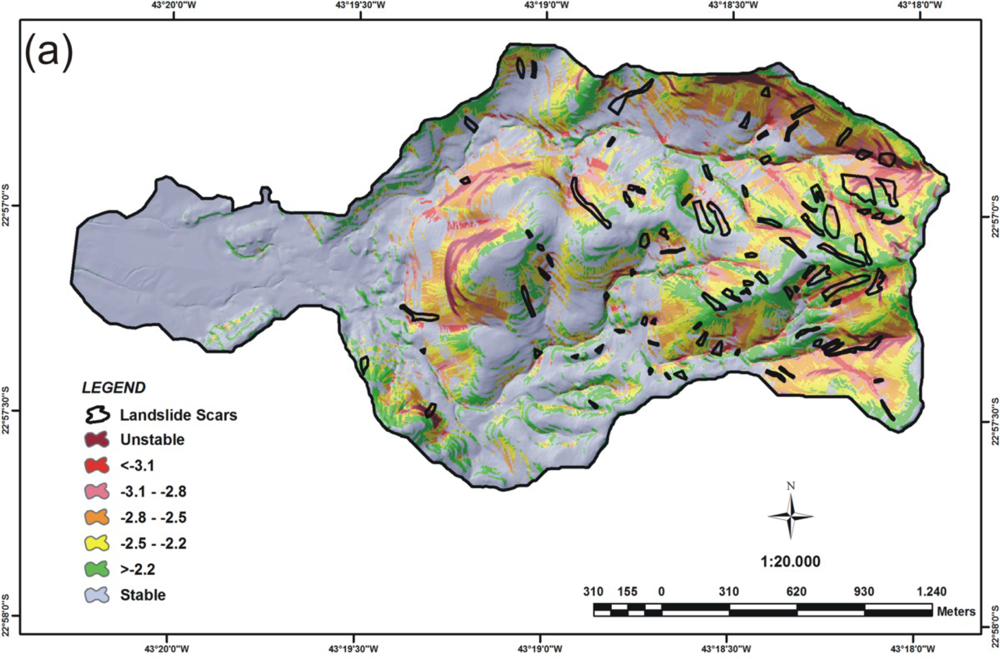
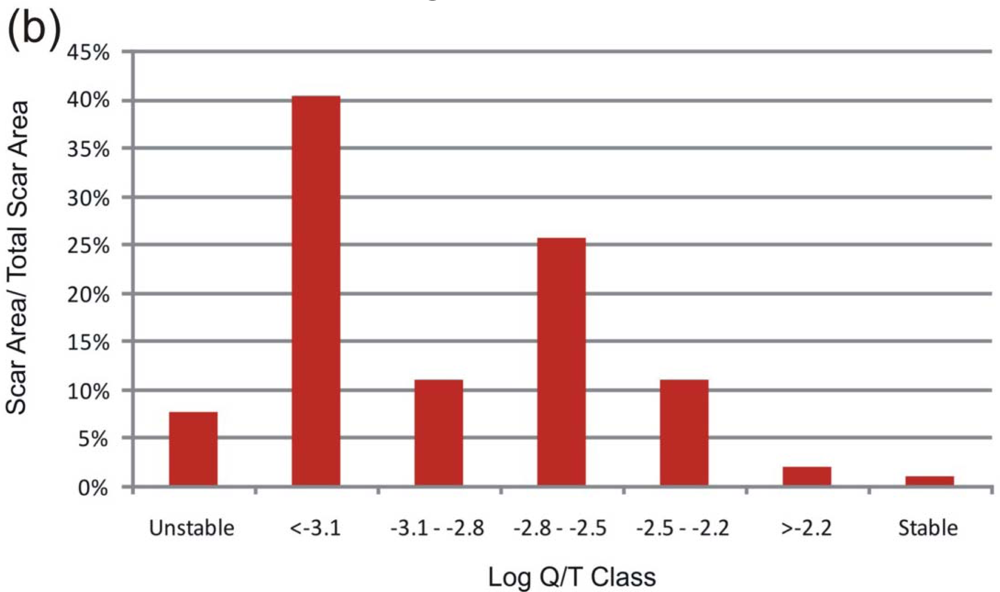
4.1. Results of the SHALSTAB Model
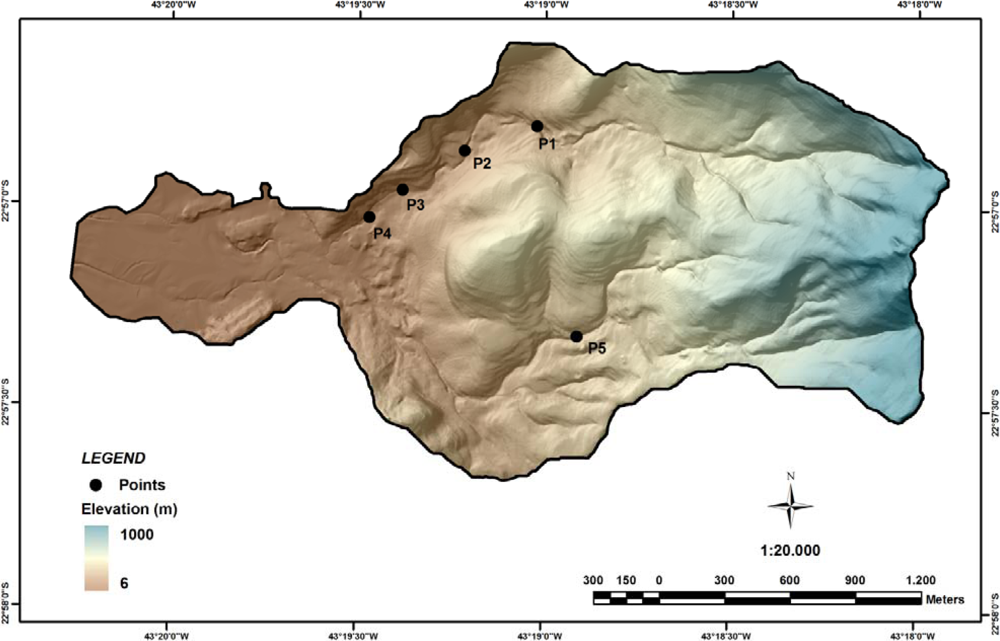
4.2. Results of the Back-Analysis for Rheological Properties
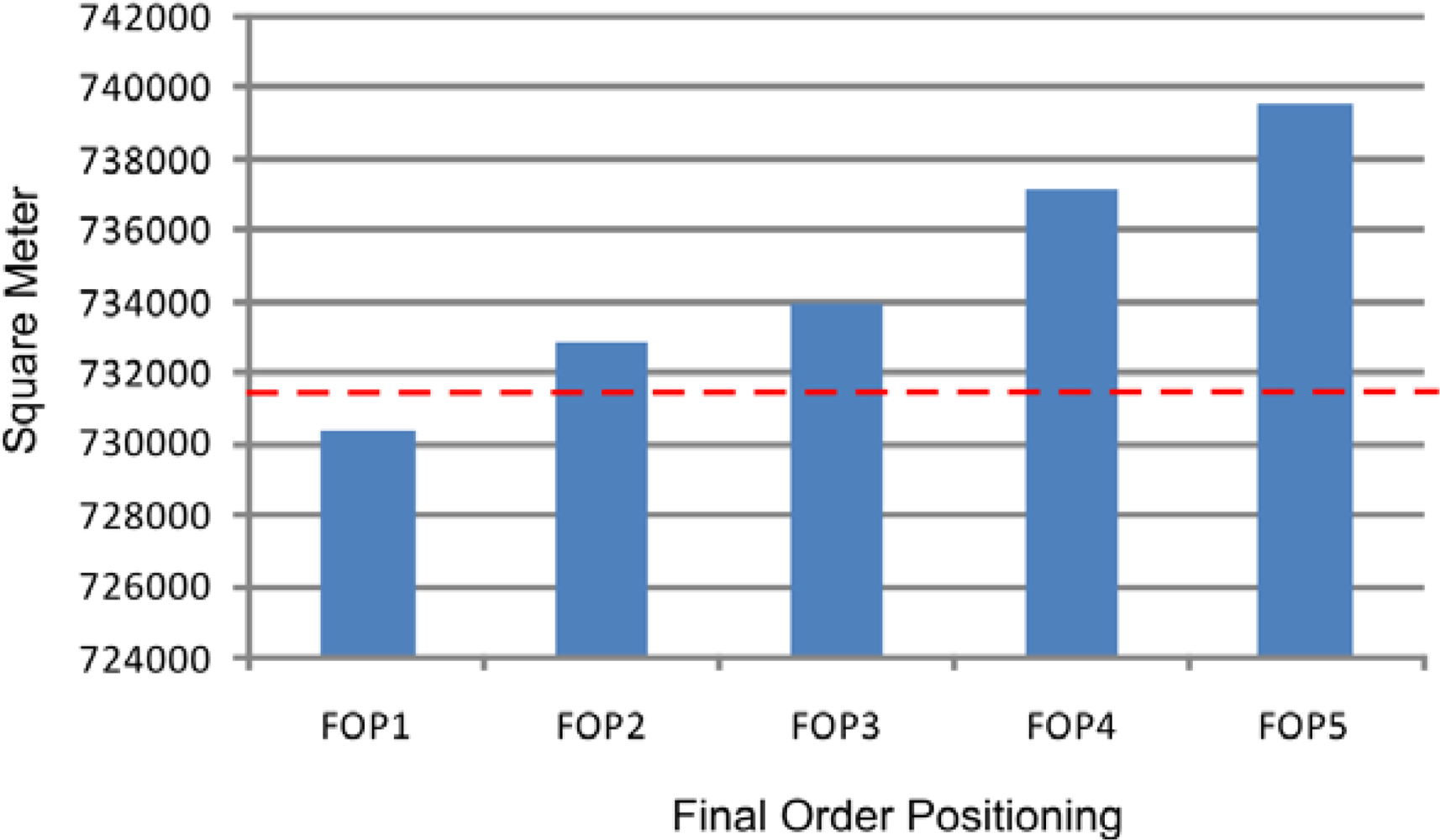
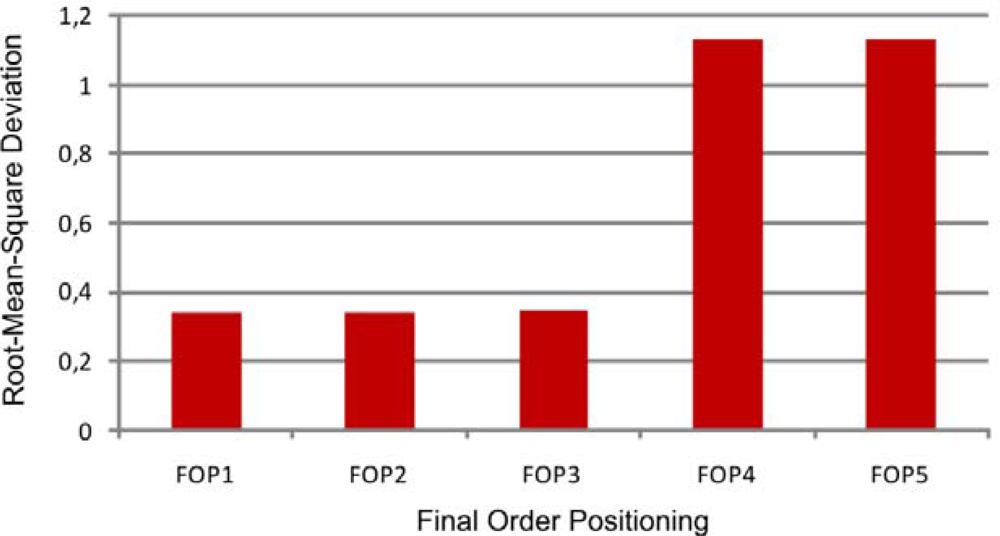
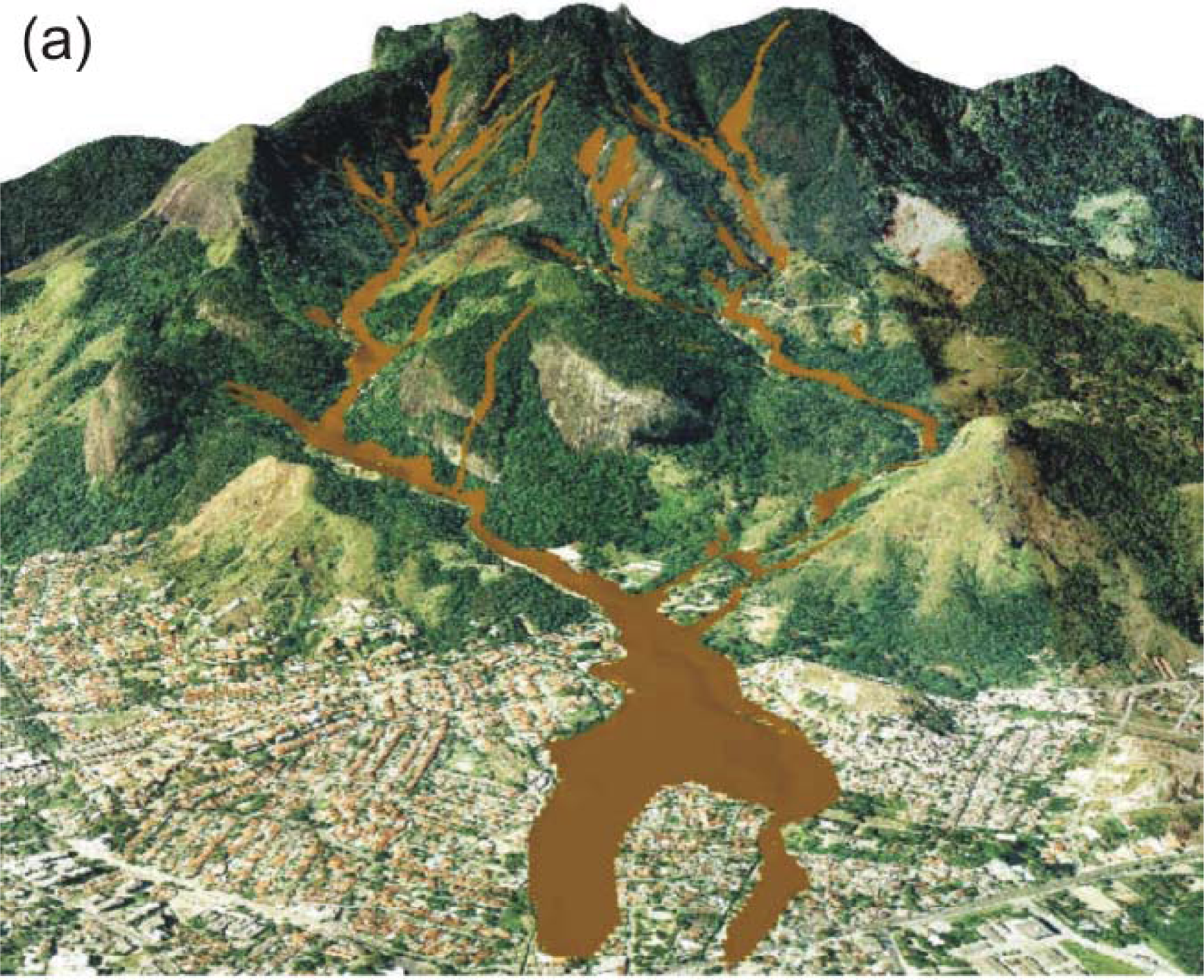
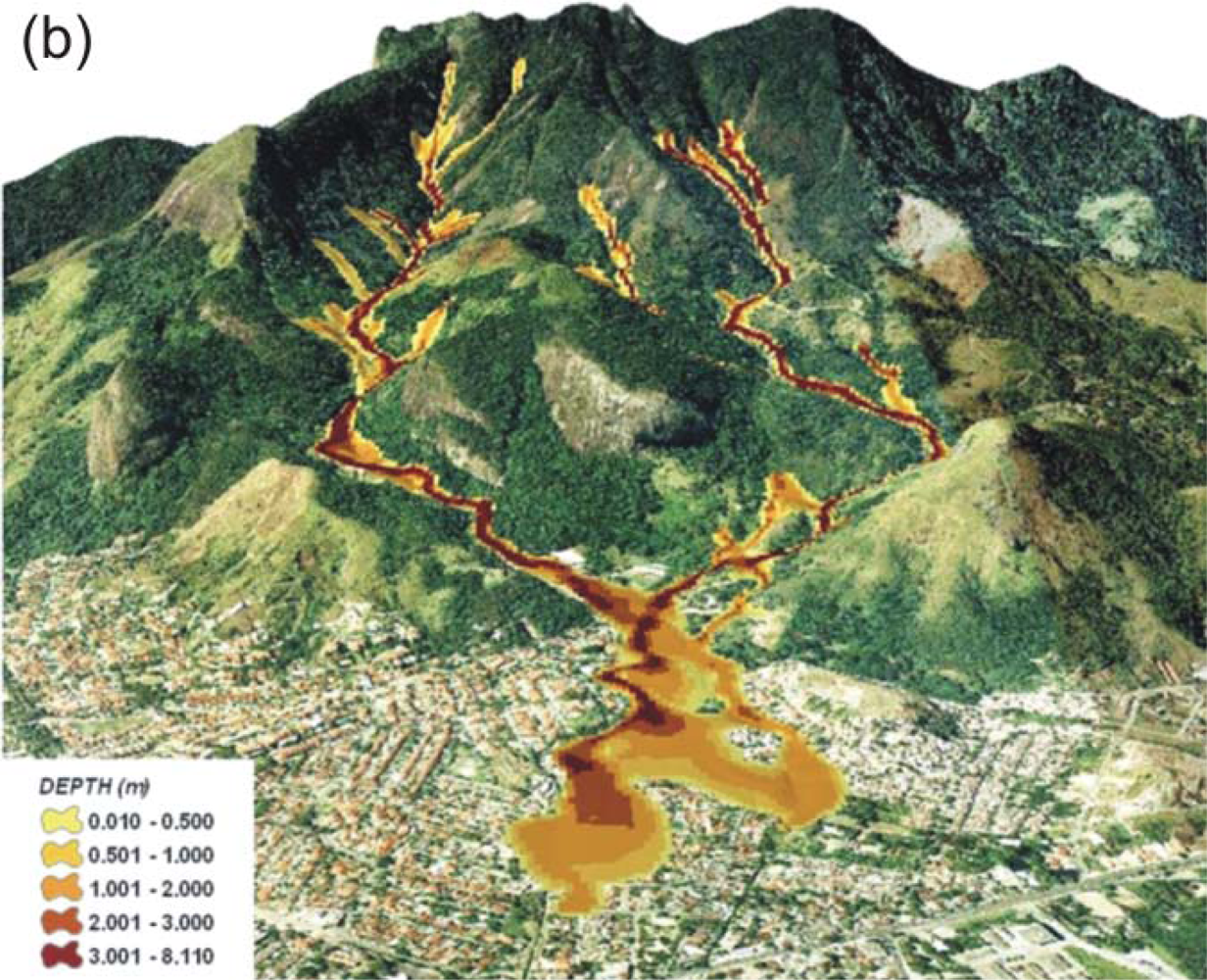
4.3. Results of the Integration of Models SHALSTAB and FLO-2D
5. Conclusion
Acknowledgments
- Conflict of InterestThe authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- United Nations. Working party on world landslide inventory. Bull. IAEG 1993, 41, 5–12.
- Montgomery, D.R. Road surface drainage, channel initiation, and slope stability. Water Resour. Res. 1994, 30, 1925–1932. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, M.C.; Torres-Sanchez, A.J. The frequency and distribution of recent landslides in three montane tropical regions of Puerto Rico. Geomorphology 1998, 24, 309–331. [Google Scholar]
- Haneberg, W.C. Deterministic and probabilistic approaches to geologic hazard assessment. Environ. Eng. Geosci. 2000, 6, 209–226. [Google Scholar]
- Irigaray, C.; Fernàndez, T.; El Hamdouni, R.; Cachòn, J. Verification of landslide susceptibility mapping: A case study. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1999, 24, 537–544. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, F.C.; Lee, C.F. Terrain-based mapping of landslide susceptibility using a geographical information system: A case study. Can. Geotech. J. 2001, 38, 911–923. [Google Scholar]
- Baeza, C.; Corominas, J. Assessment of shallow landslide susceptibility by means of multivariate statistical techniques. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2001, 26, 1251–1263. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Chwae, U.; Min, K. Landslide susceptibility mapping by correlation between topography and geological structure: The Janghun area, Korea. Geomorphology 2002, 46, 149–162. [Google Scholar]
- Haneberg, W.C. Deterministic and probabilistic approaches to geologic hazard assessment. Environ. Eng. Geosci. 2000, 6, 209–226. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, D.R.; Dietrich, W.E. A physically based model for the topographic control on shallow landsliding. Water Resour. Res. 1994, 30, 1153–1171. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Sidle, R.C. A distributed slope stability model for steep forested basins. Water Resour. Res. 1995, 31, 2097–2110. [Google Scholar]
- Van Westen, C.J.; Terlien, M.T.J. Deterministic landslide hazard analysis in GIS: A case study from Manizales (Columbia). Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1996, 21, 853–868. [Google Scholar]
- Mankelow, J.M.; Murphy, W. Using GIS in the probabilistic assessment of earthquake triggered landslide hazards. J. Earthq. Eng. 1998, 20, 593–623. [Google Scholar]
- Pack, R.T.; Tarboton, D.G.; Goodwin, C.N. The Sinmap Approach to Terrain Stability Mapping. Proceedings of the 8th Congress of the International Association of Engineering Geology, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 21–25 September 1998; pp. 21–25.
- Baum, R.L.; Savage, W.Z.; Godt, J.W. TRIGRS—A Fortran Program for Transient Rainfall Infiltration and Grid-Based Regional Slope-Stability Analysis. US Geological Survey Open-File Report 02-0424. Available online: http://pubs.usns.∼ov/of/2002/ofr-02-424 (accessed on 12 February 2013).
- Savage, W.Z.; Godt, J.W.; Baum, R.L. Modeling Time-Dependent Aerial Slope Stability. Proceedings of 9th International Symposium on Landslides, Landslides-Evaluation and Stabilization, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil, 28 June–2 July 2004; 1, pp. 23–36.
- GeoStudio, GeoStudio Tutorials Includes Student Edition Lessons, 1st ed; Geo-Slope International Ltd: Calgary, AB, Canada, 2005; p. 485.
- Rossi, G.; Catani, F.; Leoni, L.; Segoni, S.; Tofani, V. HIRESSS: A physically based slope stability simulator for HPC applications. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 151–166. [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich, W.E.; Bellugi, D.; Real de Asua, R. Validation of the Shallow Landslide Model, SHALSTAB, for forest management. Water Sci. Appl. 2001, 2, 195–227. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, D.R.; Sullivan, K.; Greenberg, M.H. Regional test of a model for shallow landsliding. Hydrol. Process. 1998, 12, 943–955. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, D.R.; Schmidt, K.M.; Greenberg, H.M.; Dietrich, W.E. Forest clearing and regional landsliding. Geology 2000, 28, 311–314. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, D.R.; Greenberg, H.M.; Laprade, B.; Nasham, B. Sliding in Seattle: Test of a Model of Shallow Landsliding Potential in an Urban Environment. In Land Use and Watersheds: Human Influence on Hydrology and Geomorphology in Urban and Forest Areas-Water Science and Application Monograph; Wigmosta, M.S., Burges, S.J., Eds.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2001; Volume 2, pp. 59–73. [Google Scholar]
- Guimarães, R.F.; Montgomery, D.R.; Greenberg, H.M.; Fernandes, N.F.; Gomes, R.A.T.; Carvalho Júnior, O.A. Parameterization of soil properties for a model of topographic controls on shallow landsliding: Application to Rio de Janeiro. Eng. Geol. 2003, 69, 99–108. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, R.A.T.; Guimarães, R.F.; Carvalho, O.A., Júnior; Fernandes, N.F. Análise de um modelo de previsão de deslizamentos (SHALSTAB) em diferentes escalas cartográficas. Rev. Solos e Rocha 2005, 28, 85–97. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, N.F.; Guimarães, R.F.; Gomes, R.A.T; Vieira, B.C.; Montgomery, D.R.; Greenberg, H. Topographic controls of landslide in Rio de Janeiro: Field evidences and modeling. Catena 2004, 55, 163–181. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, R.A.T.; Guimarães, R.F.; Carvalho, O.A., Júnior; Fernandes, N.F.; Vargas, E., Júnior. Identification of the affected areas by mass movement through a physically based model of landslide hazard combined with an empirical model of debris flow. Nat. Hazards 2008, 45, 197–209. [Google Scholar]
- Guimarães, R.F.; Gomes, R.A.T.; Carvalho, O.A., Júnior; Martins, E.S.; Fernandes, N.F. Análise temporal das áreas susceptíveis a escorregamentos rasos no Parque Nacional da Serra dos Órgãos (RJ) a partir de dados pluviométricos. Rev. Brasil. de Geociênc. 2009, 39, 192–200. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, V.M.; Guimarães, R.F.; Carvalho, O.A., Júnior; Redivo, A.L.; Gomes, R.A.T.; Cardoso, F.B.F; Fernandes, N.F. Algorithm development for incorporating soil physical properties of each different soil class in a landslide prediction model (SHALSTAB). Soils and Rocks 2007, 30, 139–148. [Google Scholar]
- Selby, M.J. Hillslope Materials & Processes; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993; p. 450. [Google Scholar]
- Carrara, A.; Crosta, G.; Frattini, P. Comparing models of debris-flow susceptibility in the alpine environment. Geomorphology 2008, 94, 257–260. [Google Scholar]
- Imran, J.; Harff, P.; Parker, G. A numerical model of submarine debris-flow with graphical user interface. Comput. Geosci. 2001, 27, 717–729. [Google Scholar]
- Hungr, O. A model for the runout analysis of rapid flow slide, debris flow, and avalanches. Can. Geotech. J. 1995, 32, 610–623. [Google Scholar]
- O’Brien, J.S.; Julien, P.Y. Physical Processes of Hyperconcentrated Sediment Flows. Proceedings of the ASCE Specialty Conference on the Delineation of Landslides, Floods, and Debris Flow Hazards, Logan, UT, USA, 14–15 June 1985; pp. 260–279.
- Bertolo, P.; Wieczorek, G.F. Calibration of numerical models for small debris flows in Yosemite Valley, California, USA. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2005, 5, 993–1001. [Google Scholar]
- Boniello, M.A.; Calligaris, C.; Lapasin, R.; Zini, L. Rheological investigation and simulation of a debris-flow event in the Fella watershed. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 10, 989–997. [Google Scholar]
- Cascini, L.; Cuomo, S.; de Santis, A. Numerical modelling of the December 1999 Cervinara flow-like mass movements (Southern Italy). Ital. J. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2011, 635–644. [Google Scholar]
- Stolz, A.; Huggel, C. Debris flows in the Swiss National Park: The influence of different flow models and varying DEM grid size on modeling results. Landslides 2008, 5, 311–319. [Google Scholar]
- Gentile, F.; Bisantino, T.; Liuzzi, G.T. Debris-flow risk analysis in south Gargano watersheds (Southern-Italy). Nat. Hazards 2008, 44, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Bisantino, T.; Fischer, P.; Gentile, F. Rheological characteristics of debris-flow material in South-Gargano watersheds. Nat. Hazards 2009, 54, 209–223. [Google Scholar]
- GEORIO, Estudos Geológicos-Geotécnicos a Montante dos Condomínios Capim Melado e Vilarejo; GEORIO: Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil, 1996; p. 96.
- Pirulli, M.; Sorbino, G. Assessing potential debris flow runout: A comparison of two simulation models. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2008, 8, 961–971. [Google Scholar]
- Guzzetti, F.; Mondini, A.C.; Cardinali, M.; Fiorucci, F.; Santangelo, M.; Chang, K.-T. Landslide inventory maps: New tools for an old problem. Earth Sci. Rev. 2012, 112, 42–66. [Google Scholar]
- Metternicht, G.; Hurni, L.; Gogu, R. Remote sensing of landslides: An analysis of the potential contribution to geo-spatial systems for hazard assessment in mountainous environments. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 98, 284–303. [Google Scholar]
- Carrara, A.; Cardinali, M.; Detti, R.; Guzzetti, F.; Pasqui, V.; Reichenbach, P. GIS techniques and statistical models in evaluating landslide hazard. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1991, 16, 427–445. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, K.; Wei, C.; Chang, S. Locating landslides using multitemporal satellite images. Adv. Space Res. 2004, 33, 296–301. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, P.S.; Lin, J.Y.; Hung, H.C.; Yang, M.D. Assessing debris flow hazard in a watershed in Taiwan. Eng. Geol. 2002, 66, 295–313. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.; Lee, C.; Li, J.; Xu, Z. On the spatial relationship between landslides and causative factors on Lantau Island, Hong Kong. Geomorphology 2002, 43, 197–207. [Google Scholar]
- Tofani, V.; Segoni, S.; Agostini, A.; Catani, F.; Casagli, N. Use of remote sensing for landslide studies in Europe. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 299–309. [Google Scholar]
- Mantovani, F.; Soeters, R.; van Westen, C. Remote sensing techniques for landslide studies and hazard zonation in Europe. Geomorphology 1996, 15, 213–225. [Google Scholar]
- O’Loughlin, E.M. Prediction of surface saturation zones in natural catchments by topographic analysis. Water Resour. Res. 1986, 22, 794–804. [Google Scholar]
- Borga, M.; Dalla Fontana, G.; da Ros, D.; Marchi, L. Shallow landslide hazard assessment using a physically based model and digital elevation data. Environ. Geol. 1998, 35, 81–88. [Google Scholar]
- O’Brien, J.S.; Julien, P.Y. Flo-2D User’s Manual, Version 2000.01; Flo-Engineering: Nutrioso, AZ, USA, 2000; p. 170. [Google Scholar]
- O’Brien, J.S.; Julien, P.Y. Laboratory analysis of mudflows properties. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1988, 114, 877–887. [Google Scholar]
- Hübl, J.; Steinwendtner, H. Two-dimensional simulation of two viscous debris-flows in Austria. Phys. Chem. Earth P. C. Solar T. P. 2001, 26, 639–644. [Google Scholar]
- Armento, M.C.; Genevois, R.; Tecca, P.R. Comparison of numerical models of two debris flows in the Cortina d’ Ampezzo area, Dolomites, Italy. Landslides 2008, 5, 143–150. [Google Scholar]
- Bertolo, P.; Bottino, G. Debris-flow event in the Frangerello Stream-Susa Valley (Italy)—Calibration of numerical models for the back analysis of the 16 October, 2000 rainstorm. Landslides 2008, 5, 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, S.M.; Chiou, L.B.; Lin, G.F.; Chao, C.H.; Wen, H.Y.; Ku, C.Y. Applications of simulation technique on debris-flow hazard zone delineation: A case study in Hualien County, Taiwan. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 10, 535–545. [Google Scholar]
- Sosio, R.; Crosta, G.B.; Frattini, P. Field observations, rheological testing and numerical modelling of a debris-flow event. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2007, 32, 290–306. [Google Scholar]
- Tecca, P.R.; Armento, C.; Genevois, R. Debris flow hazard and mitigation works in Fiames slope (Dolomites, Italy). Trans. Ecol. Environ. 2006, 90, 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.-L.; Huang, J.-J. Debris flow run off simulation and verification—Case study of Chen-You-LanWatershed, Taiwan. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2005, 5, 439–445. [Google Scholar]
- Macias, J.; Amaral, C.; Vargas Júnior, E. Retroanálise do Comportamento Mecânico das Corridas de Massa de 1996 no Rio de Janeiro: Determinação da Velocidade de Deslocamento e da Viscosidade dos Materiais Envolvidos. Proceedings of the 2nd Pan-American Symposium on Landslides (II PSL)/2a Conferência Brasileira Sobre Estabilidade de Encostas (2a COBRAE), Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil, 10–14 November 1997; pp. 243–251.
- Arattano, M.; Franzi, L.; Marchi, L. Influence of rheology on debris-flow simulation. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2006, 6, 519–528. [Google Scholar]
- Remaitre, A.; Malet, J.; Maquaire, O.; Ancey, C.; Locat, J. Flow behaviour and runout modelling of complex debris flow in a clay-shale basin. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2005, 30, 479–488. [Google Scholar]
- Prochaska, A.B.; Santi, P.M.; Higgins, J.D.; Cannon, S.H. A study of methods to estimate debris flow velocity. Landslides 2008, 5, 431–444. [Google Scholar]
- Hungr, O.; Morgan, G.C.; Kellerhals, R. Quantitative analysis of debris torrent hazards for design of remedial measures. Can. Geotech. J. 1984, 21, 663–677. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, A.M. Debris Flow. In Slope Instability; Brunsden, D., Prior, D.B., Eds.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1984; pp. 257–361. [Google Scholar]
- Jordan, R.P. Debris Flows in the Southern Coast Mountains, British Columbia: Dynamic Behaviour and Physical Properties. 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Marina, P.; Giuseppe, S. The Runout of Debris Flows: Application of Two Numerical Models and Comparison of Results. Proceedings of the First North American Landslide Conference, Vail, CO, USA, 3–8 June 2007.
- Rickenmann, D.; Koch, T. Comparison of Debris Flow Modelling Approaches. In Debris-Flow Hazards Mitigation: Mechanics, Prediction, and Assessment; Chen, C.-L., Ed.; ASCE: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 576–585. [Google Scholar]
- Soule, N.C. The Influence of Coarse Material on the Yield Strength and Viscosity of Debris Flows. 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, D.; Zhang, S. Velocity Profile Assessment for Debris Flow Hazards. In Debris-Flow Hazards Mitigation: Mechanics, Prediction, and Assessment; Chen, C.-L., Ed.; ASCE: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 474–483. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, A.M.; Martosudarmo, S.Y. Discrimination between Inertial and Macroviscous Flows of Fine-Grained Debris with a Rolling-Sleeve Viscometer. In Debris-Flow Hazards Mitigation: Mechanics, Prediction, and Assessment; Chen, C.-L., Ed.; ASCE: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 229–238. [Google Scholar]
- Locat, J. Normalized Rheological Behaviour of Fine Muds and Their Flow Properties in a Pseudoplastic Regime. In Debris-Flow Hazards Mitigation: Mechanics, Prediction, and Assessment; Chen, C.-L., Ed.; ASCE: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 260–269. [Google Scholar]


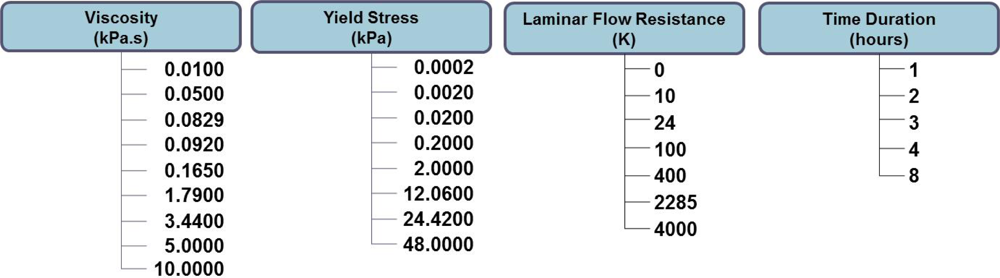
| FOP | Viscosity (kPa·s) | Yield Stress (kPa) | Laminar Flow Resistance (K) | Time Duration (h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.092 | 0.02 | 0 | 2 |
| 2 | 0.092 | 0.002 | 0 | 2 |
| 3 | 1.79 | 0.02 | 100 | 2 |
| 4 | 1.79 | 0.002 | 100 | 2 |
| 5 | 0.0829 | 0.02 | 0 | 2 |
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Gomes, R.A.T.; Guimarães, R.F.; De Carvalho, Júnior, O.A.; Fernandes, N.F.; Do Amaral Júnior, E.V. Combining Spatial Models for Shallow Landslides and Debris-Flows Prediction. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 2219-2237. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs5052219
Gomes RAT, Guimarães RF, De Carvalho, Júnior OA, Fernandes NF, Do Amaral Júnior EV. Combining Spatial Models for Shallow Landslides and Debris-Flows Prediction. Remote Sensing. 2013; 5(5):2219-2237. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs5052219
Chicago/Turabian StyleGomes, Roberto Arnaldo Trancoso, Renato Fontes Guimarães, Osmar Abílio De Carvalho, Júnior, Nelson Ferreira Fernandes, and Eurípedes Vargas Do Amaral Júnior. 2013. "Combining Spatial Models for Shallow Landslides and Debris-Flows Prediction" Remote Sensing 5, no. 5: 2219-2237. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs5052219
APA StyleGomes, R. A. T., Guimarães, R. F., De Carvalho, Júnior, O. A., Fernandes, N. F., & Do Amaral Júnior, E. V. (2013). Combining Spatial Models for Shallow Landslides and Debris-Flows Prediction. Remote Sensing, 5(5), 2219-2237. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs5052219






