Time-Series Modeling of Ozone Concentrations Constrained by Residual Variance in China from 2005 to 2020
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data
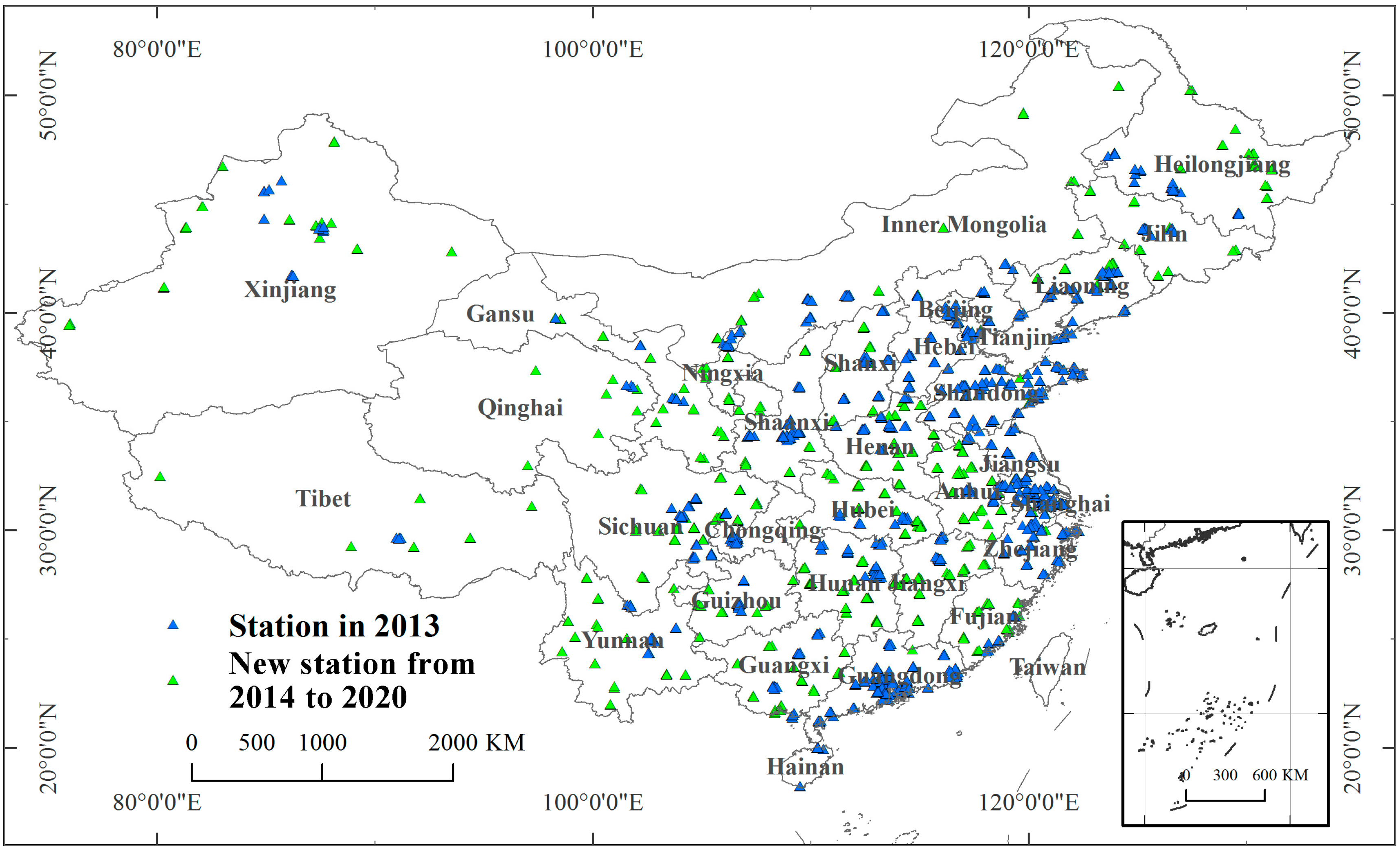
2.1.1. Ground Monitoring Data
2.1.2. NO2 Tropospheric Vertical Column Density Data
2.1.3. HCHO Column Concentration Data
2.1.4. Meteorological Data
2.1.5. WorldPop Data
2.1.6. Other Auxiliary Data
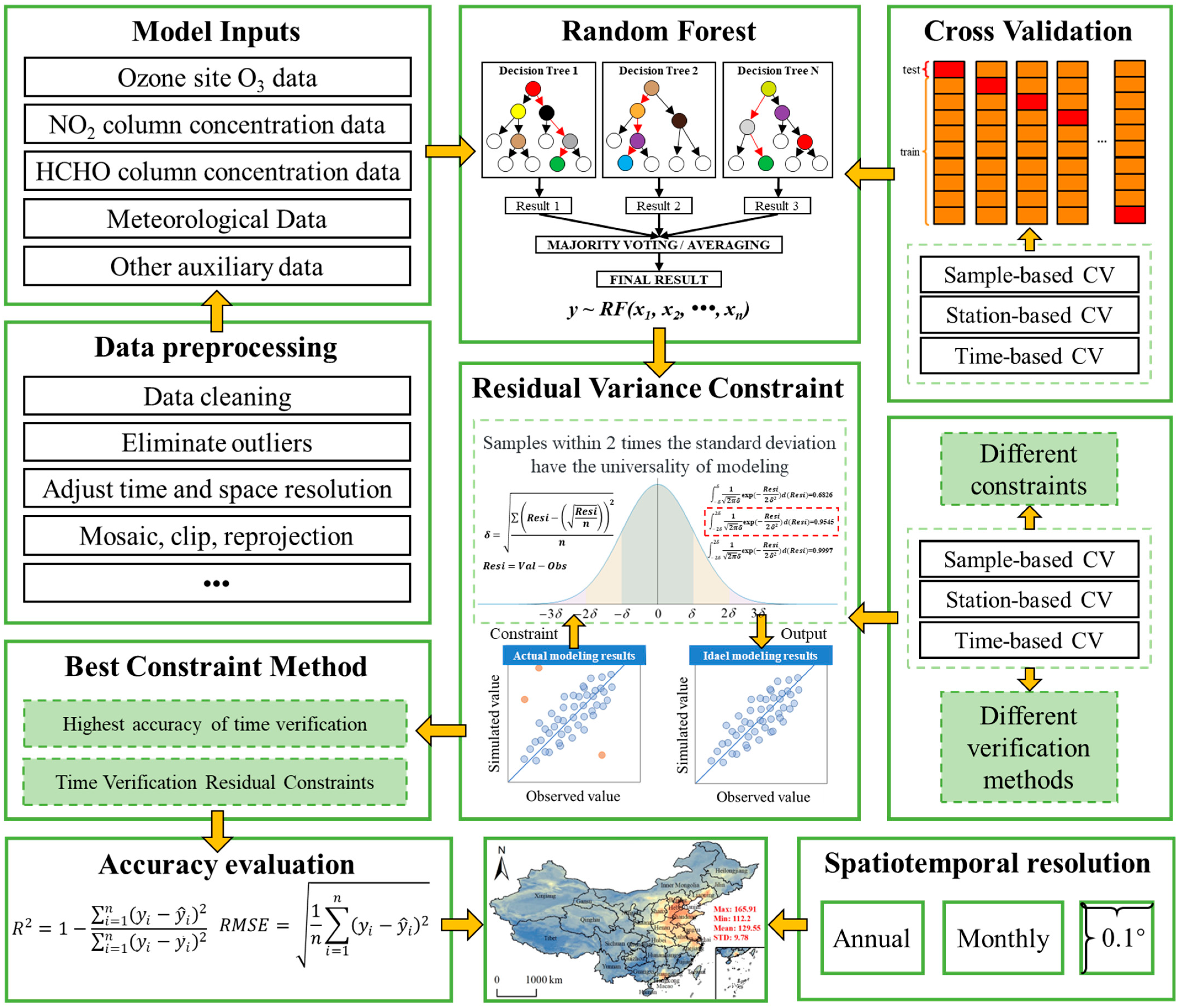
2.2. Method
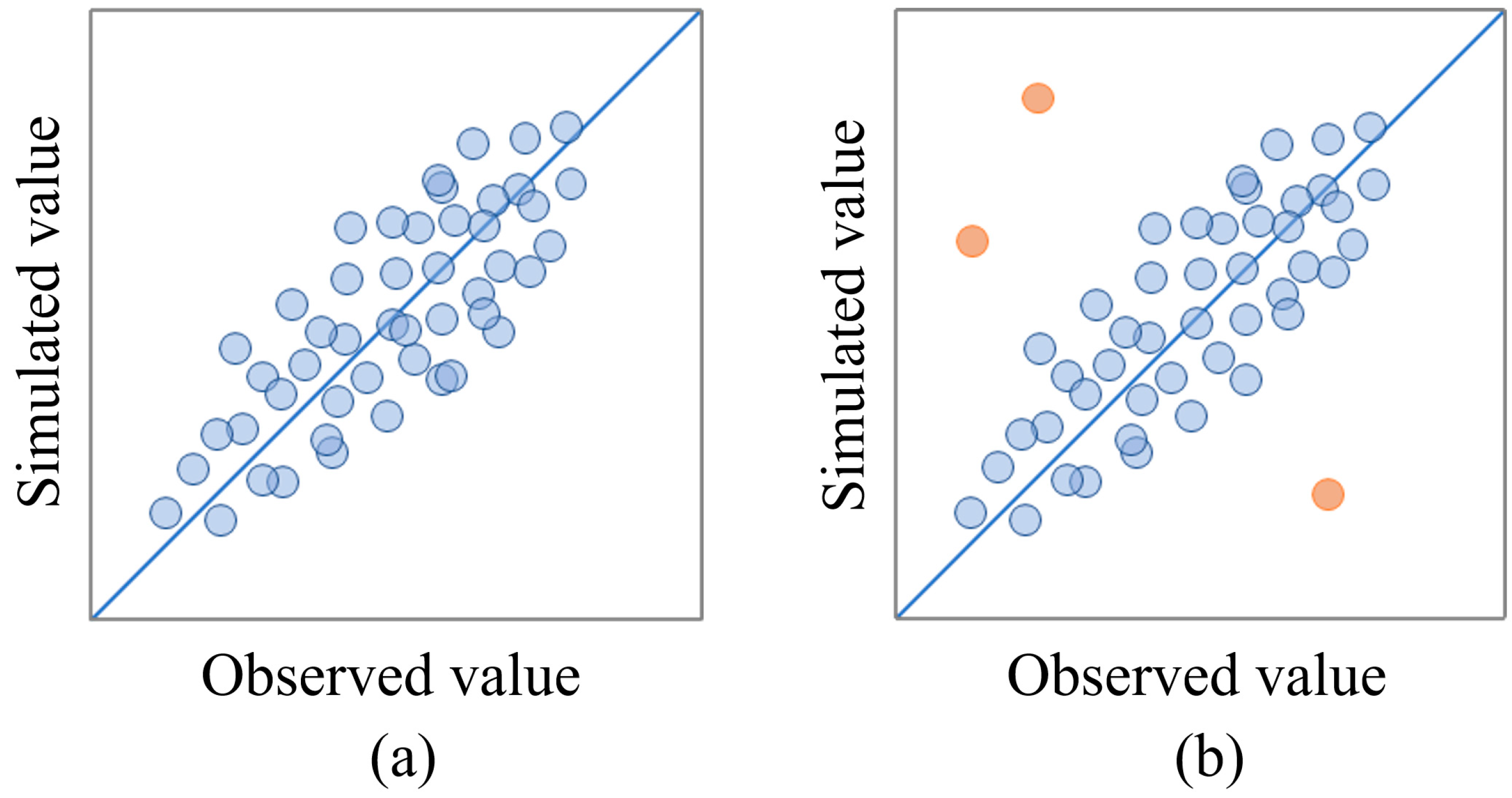
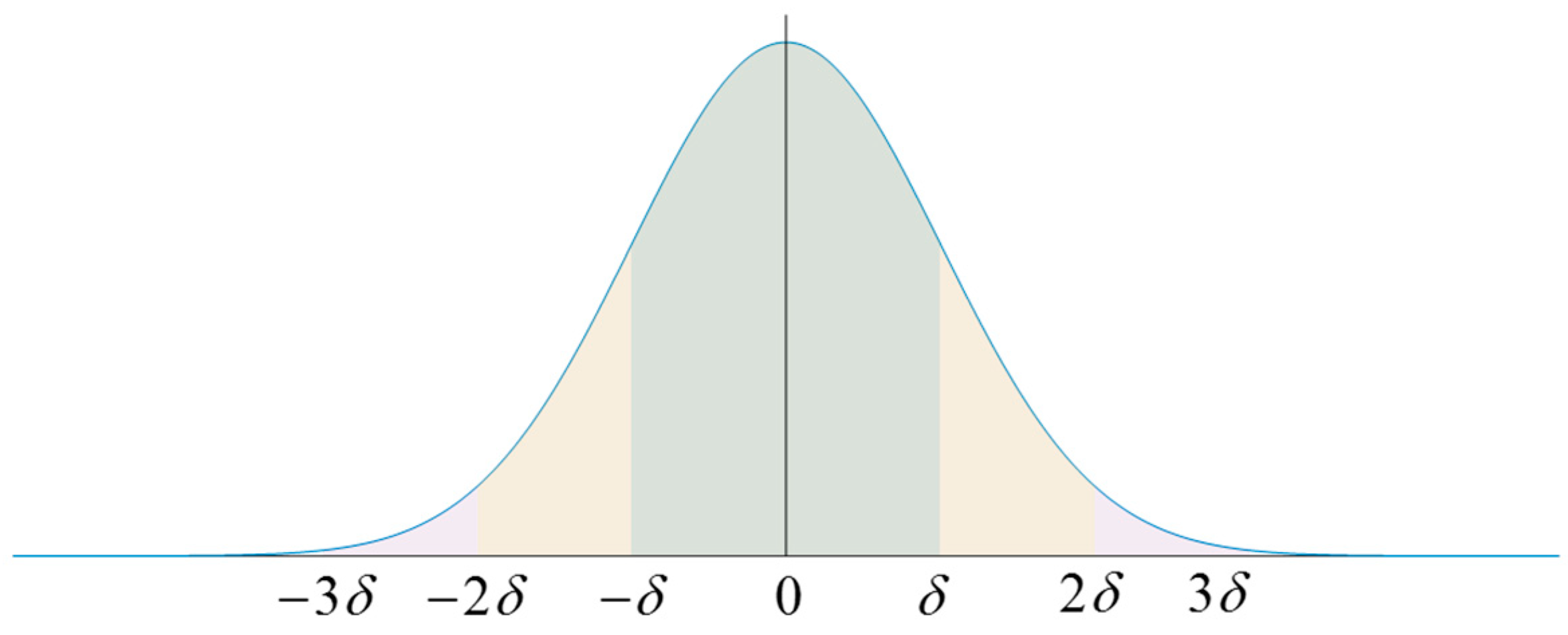
2.2.1. The Concept of Residual Constraint Theory
2.2.2. Construction of RF-RVC Model
2.2.3. RF-RVC Model Verification
2.2.4. Ozone Exposure Evaluation Index
3. Results
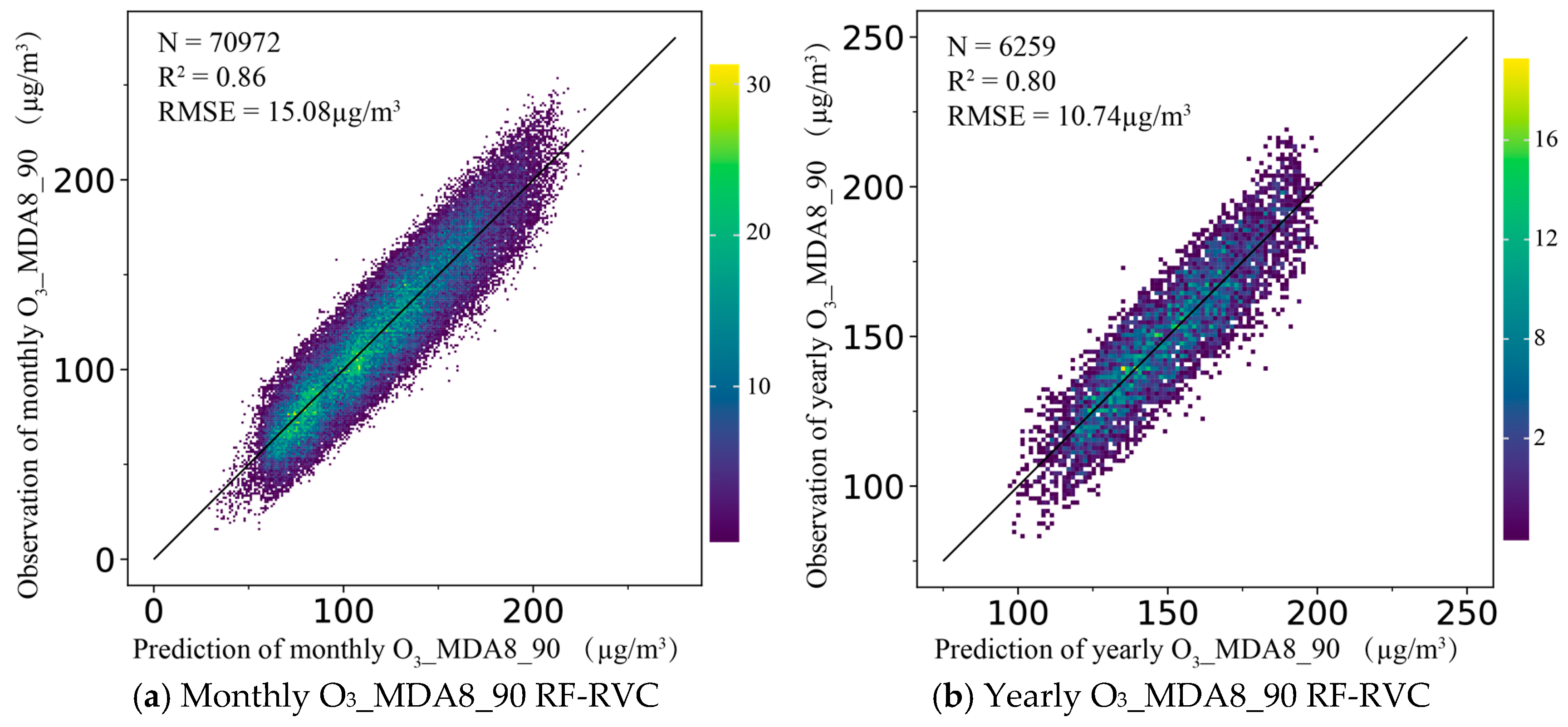
3.1. Evaluation of Model Accuracy
Comparison of Accuracy Between RF-RVC and RF-WRVC
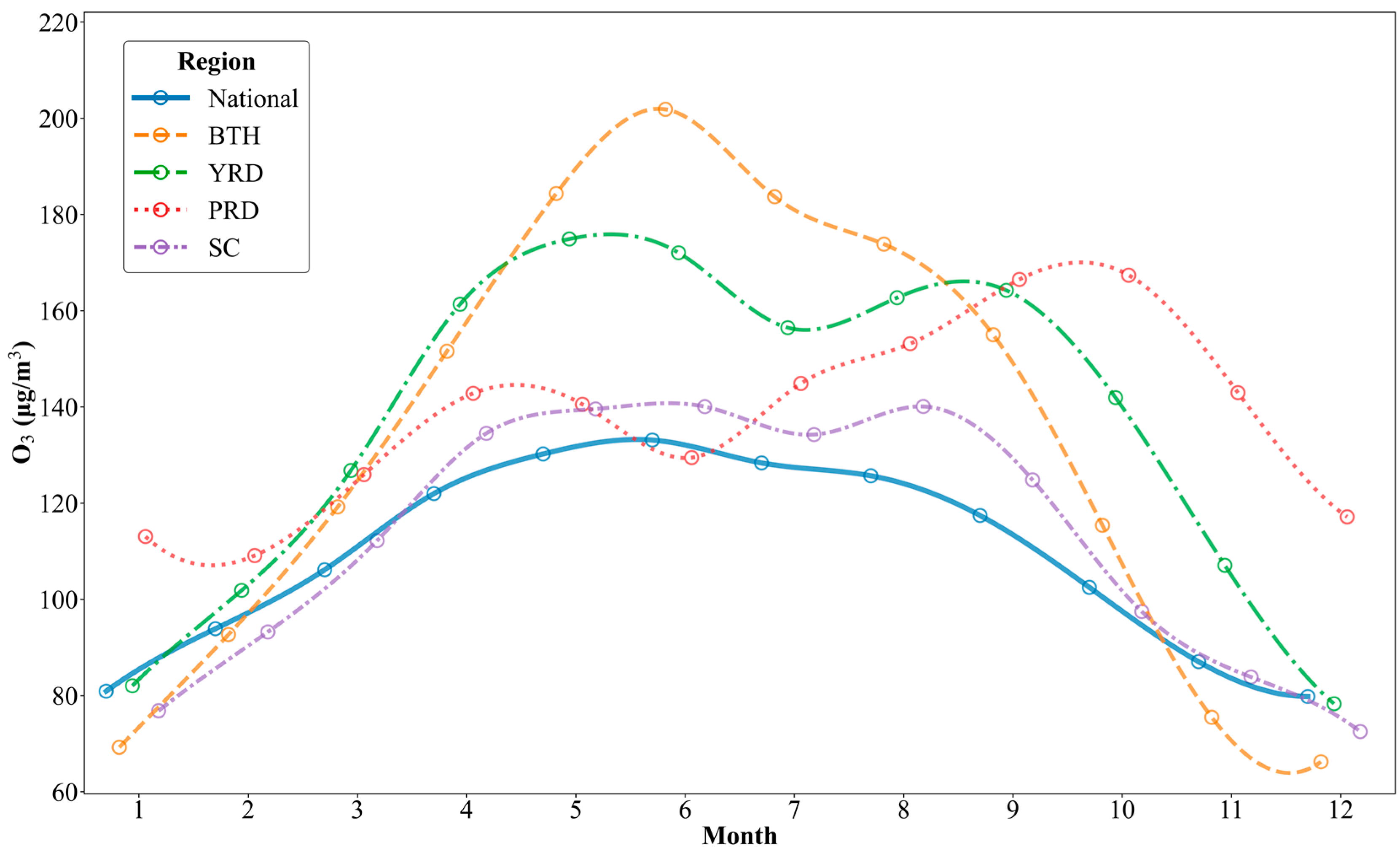
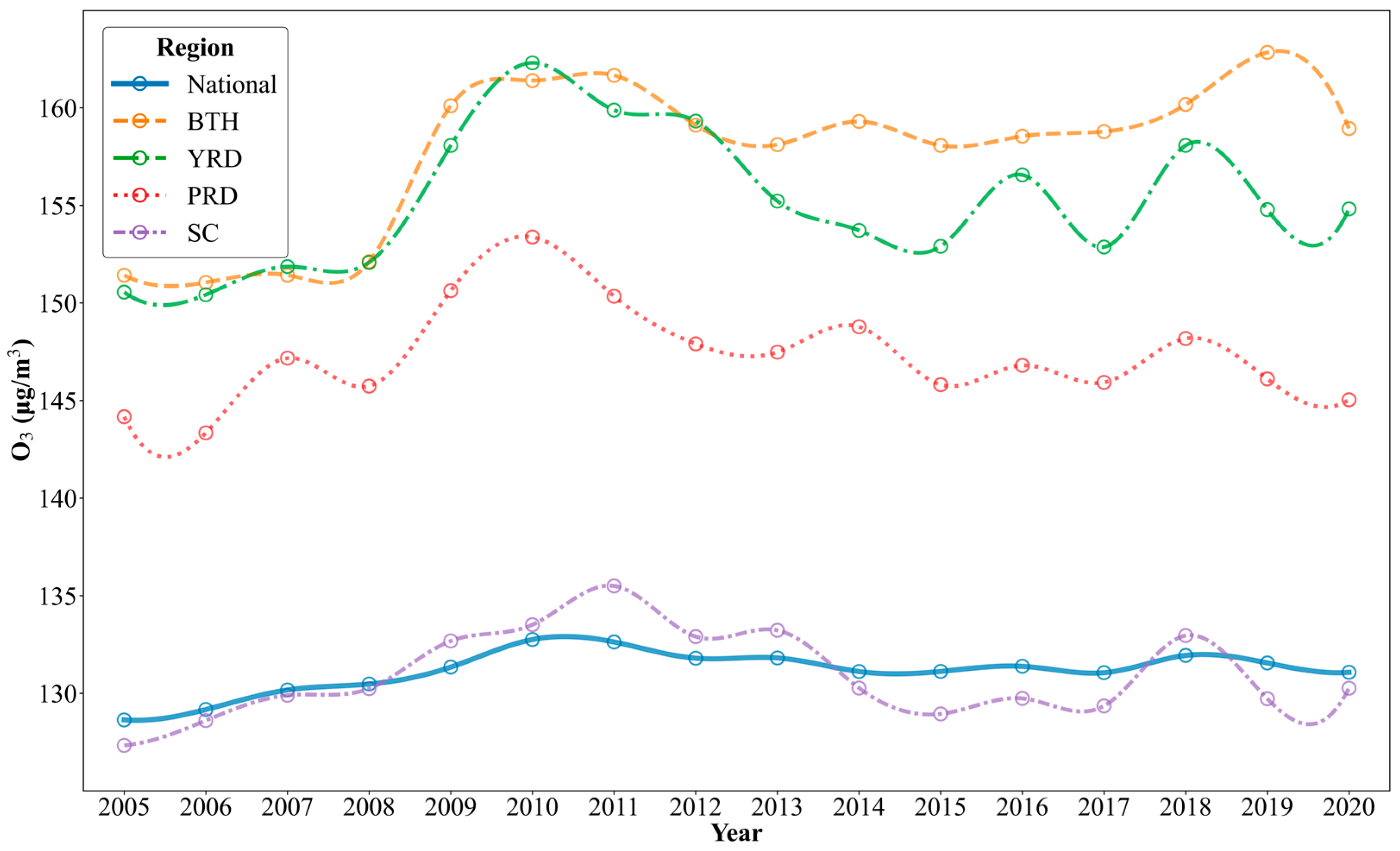
3.2. Time Variation of Ozone Concentrations
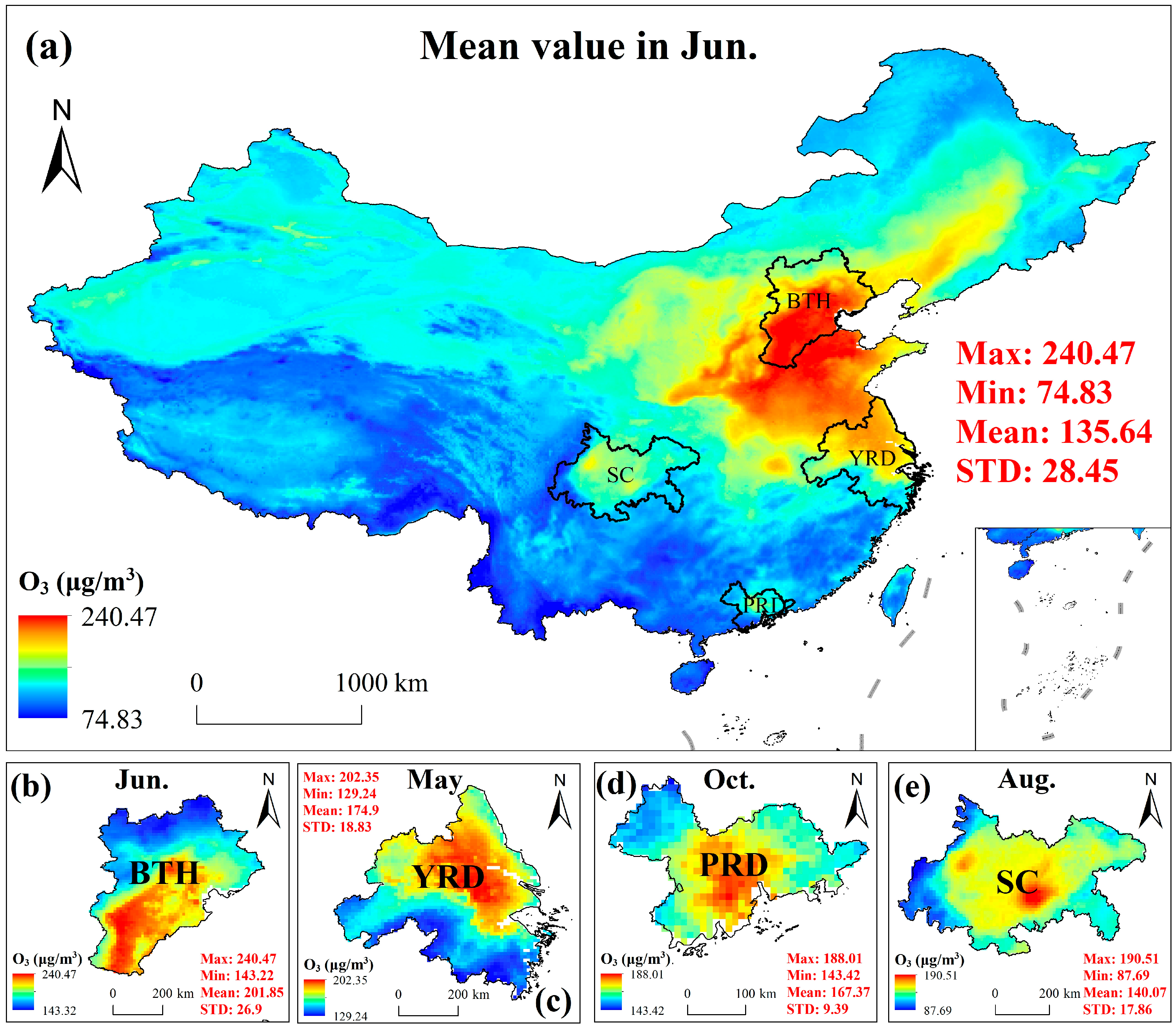
3.3. Spatial Distribution of Ozone Concentration
3.4. Spatial Variation of O3 Concentration
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, G.; Xing, J.; Yang, J.; Dong, L.; Lin, H.; Teng, M.; Hu, S.; Qin, Y.; Zeng, X. Surface UV-assisted retrieval of spatially continuous surface ozone with high spatial transferability. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 274, 112996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrer, J.; Booker, F. Ecological issues related to ozone: Agricultural issues. Environ. Int. 2003, 29, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurston, G.D.; Ito, K. Epidemiological studies of acute ozone exposures and mortality. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2001, 11, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malashock, D.A.; Delang, M.N.; Becker, J.S.; Serre, M.L.; West, J.J.; Chang, K.-L.; Cooper, O.R.; Anenberg, S.C. Global trends in ozone concentration and attributable mortality for urban, peri-urban, and rural areas between 2000 and 2019: A modelling study. Lancet Planet. Health 2022, 6, e958–e967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Ma, Z.; Liu, Y.; Shao, Y.; Zhao, W.; Bi, J. Spatiotemporal distributions of surface ozone levels in China from 2005 to 2017: A machine learning approach. Environ. Int. 2020, 142, 105823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Yang, Q.; Yuan, Q.; Zhu, L. Estimation of high spatial resolution ground-level ozone concentrations based on Landsat 8 TIR bands with deep forest model. Chemosphere 2022, 301, 134817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, P.; Yu, Y.; Hu, T. Development History and Future Prospects of Eco-environment Monitoring—From “Following” and “Running” to “Leading”. Environ. Prot. 2022, 50, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Madaniyazi, L.; Nagashima, T.; Guo, Y.; Pan, X.; Tong, S. Projecting ozone-related mortality in East China. Environ. Int. 2016, 92–93, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Wang, W.; Chen, C.; Ban, J.; Xu, D.; Zhu, P.; He, M.Z.; Li, T. Acute effect of multiple ozone metrics on mortality by season in 34 Chinese counties in 2013–2015. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 283, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Tang, J.; Zhou, X.; Li, P.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zou, Z.; Li, T.; Peng, C. Research progress, challenges, and prospects of PM2.5 concentration estimation using satellite data. Environ. Rev. 2023, 31, 605–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Gao, C.; Ren, X.; Zhang, F.; Cao, S.; Zhang, S.; Chen, T.; Liu, M.; Ni, B.; Liu, M. Understanding the spatial representativeness of air quality monitoring network and its application to PM2.5 in the mainland China. Geosci. Front. 2022, 13, 101370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, L. Spatiotemporal estimation of hourly 2-km ground-level ozone over China based on Himawari-8 using a self-adaptive geospatially local model. Geosci. Front. 2022, 13, 101286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyle, M.; Smith, R.; Stedman, J.; Weston, K.; Fowler, D. Quantifying the spatial distribution of surface ozone concentration in the UK. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, D.; Tian, H.; Pan, N.; Yang, R.; Tang, W.; Yang, J.; Lu, F.; Dayananda, B.; Mei, H.; et al. Parsimonious estimation of hourly surface ozone concentration across China during 2015–2020. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skipper, T.N.; Hogrefe, C.; Henderson, B.H.; Mathur, R.; Foley, K.M.; Russell, A.G. Source-specific bias correction of US background and anthropogenic ozone modeled in CMAQ. Geosci. Model Dev. 2024, 17, 8373–8397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayahi, T.; Garff, A.; Quah, T.; Lê, K.; Becnel, T.; Powell, K.M.; Gaillardon, P.-E.; Butterfield, A.E.; Kelly, K.E. Long-term calibration models to estimate ozone concentrations with a metal oxide sensor. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liang, S.; Li, X.; Mao, J.; Gao, S.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Y.; Vedal, S.; Bai, Z.; Ma, Z.; et al. A hybrid approach to estimating long-term and short-term exposure levels of ozone at the national scale in China using land use regression and Bayesian maximum entropy. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaan, J.; Hsu, F.-T.; Wong, P.-Y.; Chen, P.-C.; Guo, Y.-L.; Lung, S.-C.C.; Chen, Y.-C.; Wu, C.-D. A Geo-AI-based ensemble mixed spatial prediction model with fine spatial-temporal resolution for estimating daytime/nighttime/daily average ozone concentrations variations in Taiwan. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 446, 130749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, Y.; Osornio-Vargas, Á.R.; O’Neill, M.S.; Hystad, P.; Texcalac-Sangrador, J.L.; Ohman-Strickland, P.; Meng, Q.; Schwander, S. Land use regression models to assess air pollution exposure in Mexico City using finer spatial and temporal input parameters. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, W.; He, Q.; Chen, X.; Huang, J.; Zhang, M. Estimating ground-level high-resolution ozone concentration across China using a stacked machine-learning method. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2024, 15, 102114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Zhao, L.M.; Cheng, M.M.; Chen, D.M. Estimating Ground-Level Ozone Concentrations in Eastern China Using Satellite-Based Precursors. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 4754–4763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, S.; Hasunuma, H.; Yamamoto, K.; Shima, M.; Michikawa, T.; Nitta, H.; Nakayama, S.F.; Yamazaki, S. Estimating monthly concentrations of ambient key air pollutants in Japan during 2010–2015 for a national-scale birth cohort. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 284, 117483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sihag, P.; Pandhiani, S.M.; Sangwan, V.; Kumar, M.; Angelaki, A. Estimation of ground-level O3 using soft computing techniques: Case study of Amritsar, Punjab State, India. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 19, 5563–5570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zhang, H.; Yang, F.; Tan, W.; Wu, R.; Song, Y. First estimation of hourly full-coverage ground-level ozone from Fengyun-4A Satellite using machine learning. Environ. Res. Lett. 2024, 19, 024040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-Y.; Lee, R.-Q.; Wong, P.-Y.; Candice Lung, S.-C.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chen, P.-C.; Adamkiewicz, G.; Wu, C.-D. Estimating morning and evening commute period O3 concentration in Taiwan using a fine spatial-temporal resolution ensemble mixed spatial model with Geo-AI technology. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Li, K.; Dickerson, R.R.; Pinker, R.T.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Sun, L.; Xue, W.; Cribb, M. Full-coverage mapping and spatiotemporal variations of ground-level ozone (O3) pollution from 2013 to 2020 across China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 270, 112775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zheng, Q.; Sun, W.; Yang, G.; Feng, T.; Wang, Y. Geo-STO3Net: A deep neural network integrating geographical spatiotemporal information for surface ozone estimation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Huang, B. Satellite-based mapping of daily high-resolution ground PM2.5 in China via space-time regression modeling. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 206, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Hu, X.; Sayer, A.M.; Levy, R.; Zhang, Q.; Xue, Y.; Tong, S.; Bi, J.; Huang, L.; Liu, Y. Satellite-Based Spatiotemporal Trends in PM2.5 Concentrations: China, 2004–2013. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Zou, B.; Liu, X.; Sternberg, T.; Zhai, L. Satellite-based ground PM2.5 estimation using timely structure adaptive modeling. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 186, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Liu, Y.; Coull, B.A.; Schwartz, J.; Koutrakis, P. A novel calibration approach of MODIS AOD data to predict PM2.5 concentrations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 7991–8002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zou, B.; Fang, X.; Lin, Y. Time series modeling of PM2.5 concentrations with residual variance constraint in eastern mainland China during 2013–2017. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 135755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Hu, X.; Huang, L.; Bi, J.; Liu, Y. Estimating Ground-Level PM2.5 in China Using Satellite Remote Sensing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 7436–7444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment (MEE). Revision of the Ambient Air Quality Standards (GB 3095-2012). 2018. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/gkml/sthjbgw/sthjbgg/201808/t20180815_451398.htm (accessed on 11 April 2025). (In Chinese)
- Lamsal, L.N.; Krotkov, N.A.; Vasilkov, A.; Marchenko, S.; Qin, W.; Yang, E.-S.; Fasnacht, Z.; Joiner, J.; Choi, S.; Haffner, D.; et al. Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) Aura nitrogen dioxide standard product version 4.0 with improved surface and cloud treatments. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2021, 14, 455–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levelt, P.F.; Van Den Oord, G.H.; Dobber, M.R.; Malkki, A.; Visser, H.; De Vries, J.; Stammes, P.; Lundell, J.O.; Saari, H. The ozone monitoring instrument. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Jacob, D.J.; Shen, L.; Lu, X.; De Smedt, I.; Liao, H. Increases in surface ozone pollution in China from 2013 to 2019: Anthropogenic and meteorological influences. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 11423–11433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Gong, S.; Yu, Y.; Yu, L.; Wu, L.; Mao, H.; Song, C.; Zhao, S.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; et al. Air pollution characteristics and their relation to meteorological conditions during 2014–2015 in major Chinese cities. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meleux, F.; Solmon, F.; Giorgi, F. Increase in summer European ozone amounts due to climate change. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 7577–7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickerson, R.R.; Li, C.; Li, Z.; Marufu, L.T.; Stehr, J.W.; McClure, B.; Krotkov, N.; Chen, H.; Wang, P.; Xia, X.; et al. Aircraft observations of dust and pollutants over northeast China: Insight into the meteorological mechanisms of transport. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, D24S90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, F.J.; Gaughan, A.E.; Stevens, F.R.; Yetman, G.; Sorichetta, A.; Tatem, A.J. Gridded Population Maps Informed by Different Built Settlement Products. Data 2018, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, J.C.; Duncan, B.N.; Douglass, A.R.; Kurosu, T.P.; Chance, K.; Retscher, C. The unique OMI HCHO/NO2 feature during the 2008 Beijing Olympics: Implications for ozone production sensitivity. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 3103–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shith, S.; Ramli, N.A.; Awang, N.R.; Ismail, M.R.; Latif, M.T.; Zainordin, N.S. Does Light Pollution Affect Nighttime Ground-Level Ozone Concentrations? Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, B.; Yang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, S.; Qian, X.; Wang, C.; Wu, B.; Wu, J. An extended time series (2000–2018) of global NPP-VIIRS-like nighttime light data from a cross-sensor calibration. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 889–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Zou, B.; Zhang, H. Uncertainty measuring and constraining method for geographic weighted regression model results. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2023, 52, 307–317. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Some Infinity Theory for Predictor Ensembles. University of California at Berkeley Papers. 2000. Available online: https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&opi=89978449&url=https://www.stat.berkeley.edu/~breiman/some_theory2000.pdf&ved=2ahUKEwiP9dD9pfOMAxWas1YBHXUQKjgQFnoECCAQAQ&usg=AOvVaw0cirbK88sm1LYVgxZ2e0zp (accessed on 11 April 2025).
- Kang, Y.; Choi, H.; Im, J.; Park, S.; Shin, M.; Song, C.-K.; Kim, S. Estimation of surface-level NO2 and O3 concentrations using TROPOMI data and machine learning over East Asia. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Cui, L.; Hongbo, F.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, J. Satellite-based estimation of full-coverage ozone (O3) concentration and health effect assessment across Hainan Island. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Shi, J.; Tan, J.; Duan, Y.; Lin, Y.; Xu, W. Characteristics of Aerosol Particulate Concentrations and Their Climate Background in Shanghai During 2007–2016. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 14–22. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Y.; Xu, B.; Xia, L.; Chen, Y.; Deng, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, G. Characteristics of Ozone Pollution and Relationships with Meteorological Factors in Jiangxi Province. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 2190–2201. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Chen, B.; Ouyang, J.; Mu, Y.; Zhen, L.; Yang, L.; Xu, W.; Tang, L. Causal-inference machine learning reveals the drivers of China’s 2022 ozone rebound. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2025, 24, 100524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Li, X.; Zhu, S. High-resolution estimation of near-surface ozone concentration and population exposure risk in China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam-Poupart, A.; Brand, A.; Fournier, M.; Jerrett, M.; Smargiassi, A. Spatiotemporal Modeling of Ozone Levels in Quebec (Canada): A Comparison of Kriging, Land-Use Regression (LUR), and Combined Bayesian Maximum Entropy–LUR Approaches. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Xue, L.; Desai, A.R.; Wang, H. Cluster-Enhanced Ensemble Learning for Mapping Global Monthly Surface Ozone From 2003 to 2019. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL097947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Shindell, D.T.; Faluvegi, G.; Wenig, M.; Lam, Y.F.; Ning, Z.; Hao, S.; Lai, C.S. Increase of ozone concentrations, its temperature sensitivity and the precursor factor in South China. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2014, 66, 23455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antón, M.; Loyola, D.; Clerbaux, C.; López, M.; Vilaplana, J.M.; Bañón, M.; Hadji-Lazaro, J.; Valks, P.; Hao, N.; Zimmer, W.; et al. Validation of the MetOp-A total ozone data from GOME-2 and IASI using reference ground-based measurements at the Iberian Peninsula. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1380–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; He, J.; Liu, D. Investigating the biophysical and socioeconomic determinants of China tropospheric O3 pollution based on a multilevel analysis approach. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 2835–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.; Wang, H.; Li, L.; Lu, X.; Liu, Y.; Fan, S. Fast spreading of surface ozone in both temporal and spatial scale in Pearl River Delta. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 137, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tong, L.; Yu, W.; Jin, S.; Yuhong, Z.; Siqi, Y.; Duohong, C.; Jingyang, C. Characteristics of Ozone Pollution in Guangdong Province from 2016 to 2020. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2022, 31, 2374–2381. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Xin, J.; Dongsheng, J.; Bin, Z. Variation Analysis of Background Atmospheric Pollutants in North China During the Summer of 2008 to 2011. Environ. Sci. 2012, 33, 3693–3704. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, Y.; Li, L.; Qiong, L.; Yonghang, C.; Yingying, S.; Xiaozheng, L.; Liping, Q. Spatial-Temporal Distribution of Ozone and Its Precursors over Central and Eastern China based on OMI Data. Res. Environ. Sci. 2016, 29, 1128–1136. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, S.; Wei, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhao, R. Uncovering the evolution of ozone pollution in China: A spatiotemporal characteristics reconstruction from 1980 to 2021. Atmos. Res. 2024, 307, 107472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Tong, D.; Li, M.; Liu, F.; Hong, C.; Geng, G.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Peng, L.; Qi, J.; et al. Trends in China’s anthropogenic emissions since 2010 as the consequence of clean air actions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 14095–14111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Xu, K.; Chen, R.; Chen, W.; Li, F.; Lv, C. Heat waves in summer 2022 and increasing concern regarding heat waves in general. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2023, 16, 100290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, P.; Yuan, X.; Ma, F.; Xu, Q. Drivers of long-term changes in summer compound hot extremes in China: Climate change, urbanization, and vegetation greening. Atmos. Res. 2024, 310, 107632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascal, M.; Wagner, V.; Alari, A.; Corso, M.; Le Tertre, A. Extreme heat and acute air pollution episodes: A need for joint public health warnings? Atmos. Environ. 2021, 249, 118249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Desai, A.R. Significant Reductions in Crop Yields From Air Pollution and Heat Stress in the United States. Earth Future 2021, 9, e2021EF002000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, B.; You, J.; Lin, Y.; Duan, X.; Zhao, X.; Fang, X.; Campen, M.J.; Li, S. Air pollution intervention and life-saving effect in China. Environ. Int. 2019, 125, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
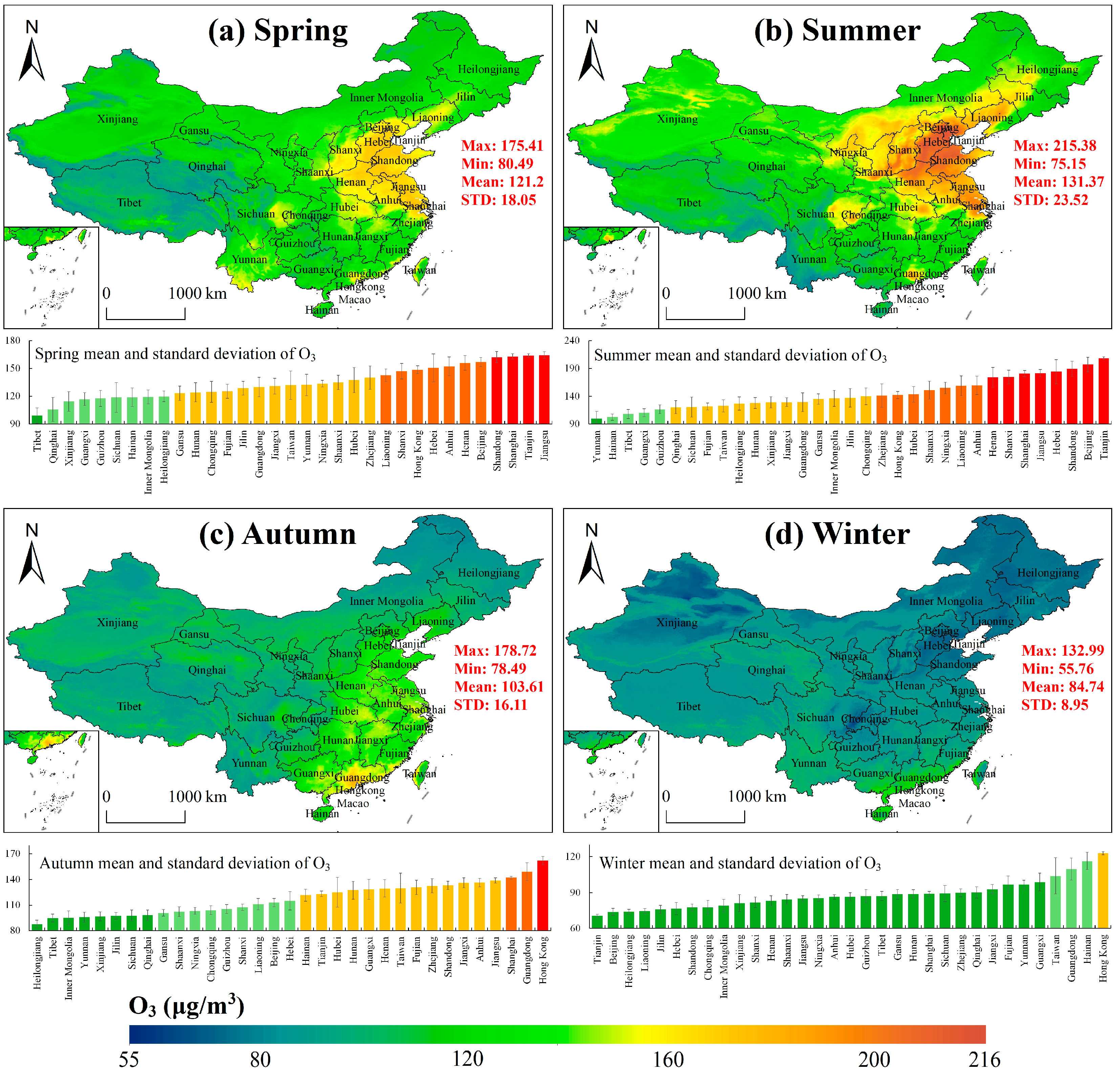
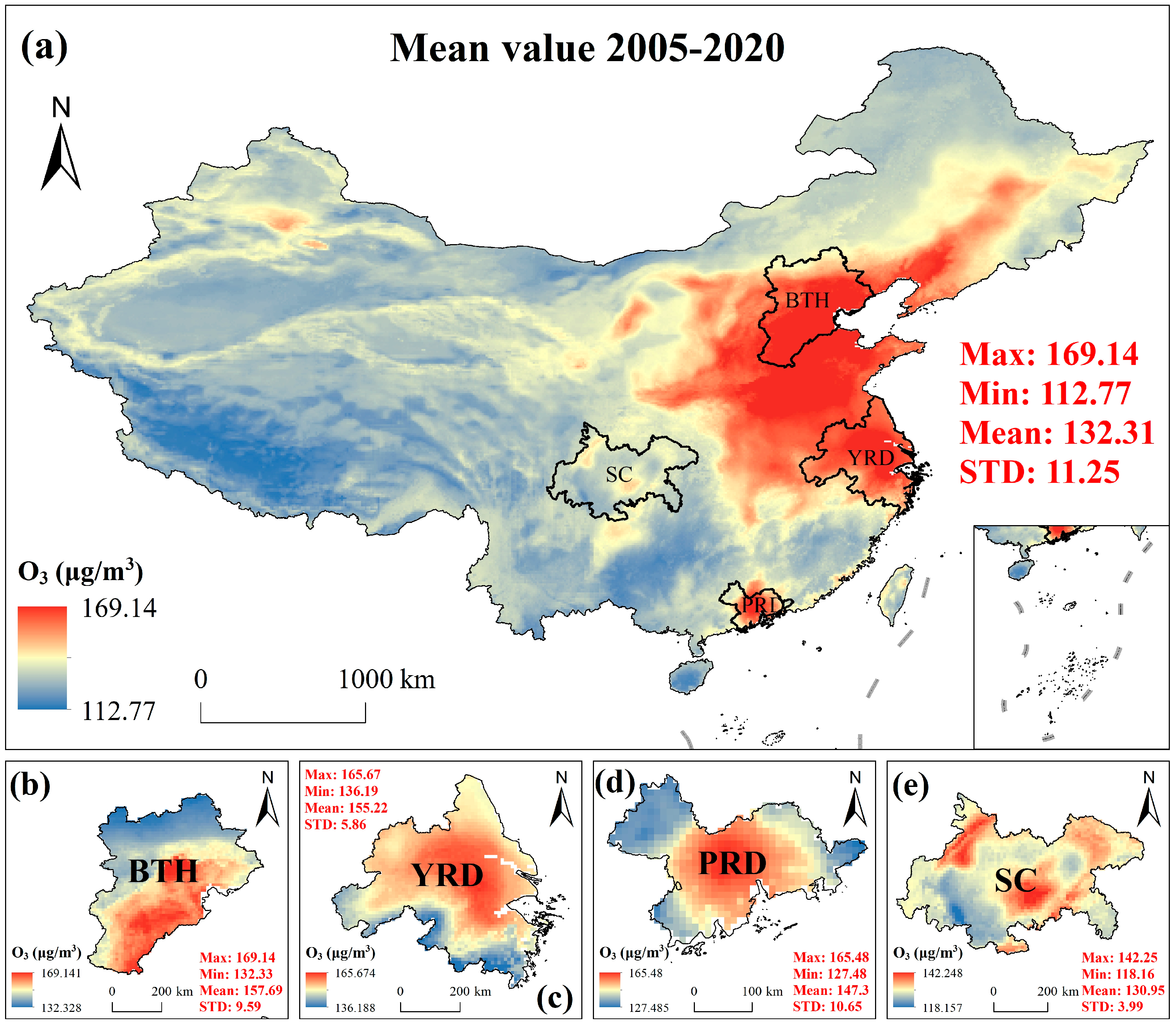
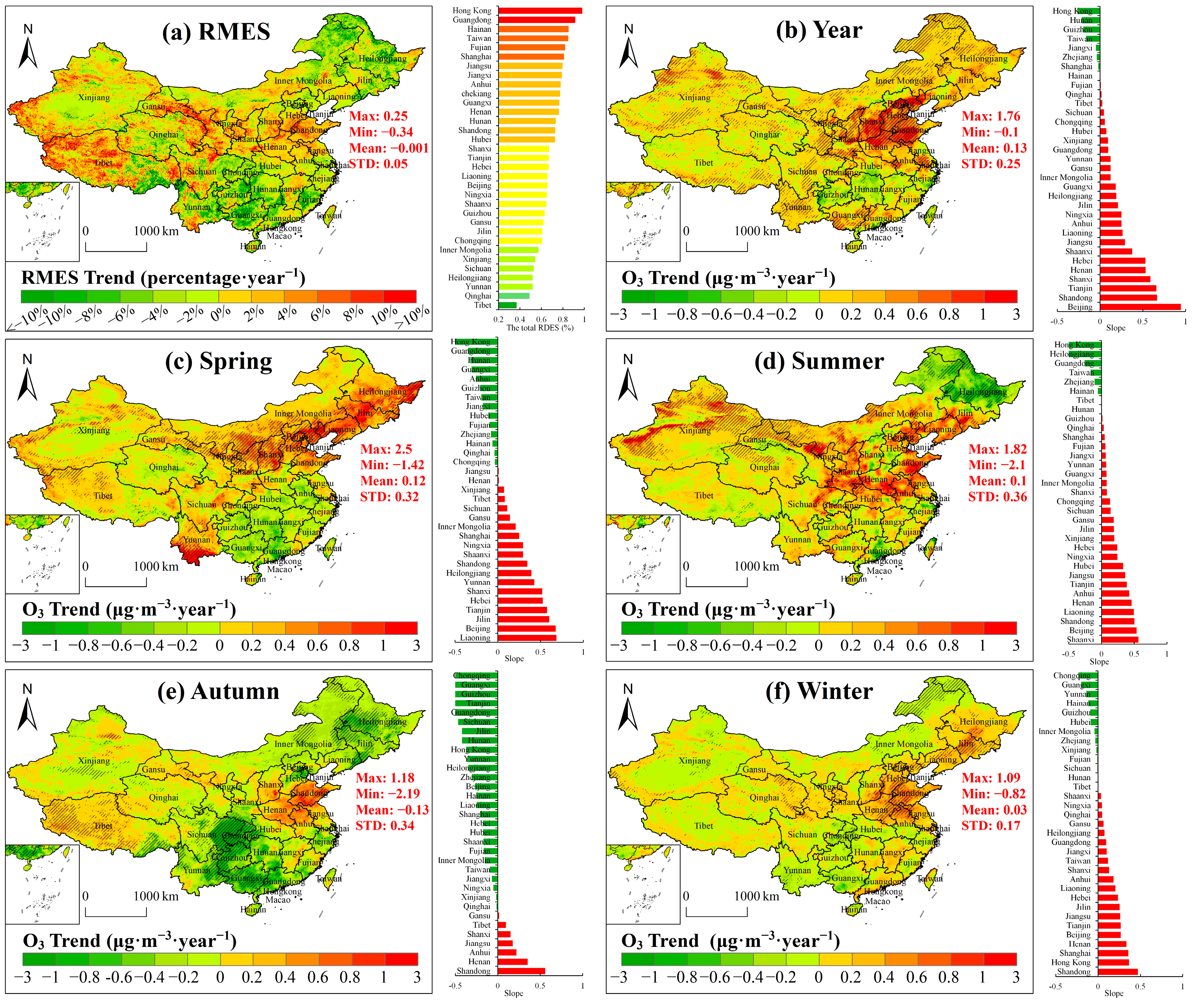
| Time Scale | Restraint Mode | Number of Samples | R2 | RMSE (µg/m3) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample-Based | Station-Based | Time-Based | Sample-Based | Station-Based | Time-Based | |||
| Monthly scale | Absence of restriction | 82,453 | 0.83 | 0.82 | 0.69 | 18.50 | 18.93 | 24.70 |
| Sample validation residuals | 73,156 | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.82 | 12.07 | 12.30 | 17.92 | |
| Station verification residuals | 73,070 | 0.92 | 0.92 | 0.82 | 12.08 | 12.21 | 18.00 | |
| Time verification residuals | 70,972 | 0.91 | 0.90 | 0.86 | 12.31 | 12.67 | 15.08 | |
| Annual scale | Absence of restriction | 7232 | 0.79 | 0.77 | 0.59 | 12.35 | 12.95 | 17.24 |
| Sample validation residuals | 6357 | 0.89 | 0.87 | 0.73 | 8.40 | 8.82 | 12.91 | |
| Station verification residuals | 6335 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.72 | 8.51 | 8.63 | 13.06 | |
| Time verification residuals | 6259 | 0.87 | 0.85 | 0.80 | 8.76 | 9.36 | 10.74 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, S.; Zou, B.; Huang, X.; Liu, N.; Li, S. Time-Series Modeling of Ozone Concentrations Constrained by Residual Variance in China from 2005 to 2020. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091534
Zhu S, Zou B, Huang X, Liu N, Li S. Time-Series Modeling of Ozone Concentrations Constrained by Residual Variance in China from 2005 to 2020. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(9):1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091534
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Shoutao, Bin Zou, Xinyu Huang, Ning Liu, and Shenxin Li. 2025. "Time-Series Modeling of Ozone Concentrations Constrained by Residual Variance in China from 2005 to 2020" Remote Sensing 17, no. 9: 1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091534
APA StyleZhu, S., Zou, B., Huang, X., Liu, N., & Li, S. (2025). Time-Series Modeling of Ozone Concentrations Constrained by Residual Variance in China from 2005 to 2020. Remote Sensing, 17(9), 1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091534







