Comparative Analysis of Novel View Synthesis and Photogrammetry for 3D Forest Stand Reconstruction and Extraction of Individual Tree Parameters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- Comparing the practical application of NVS techniques and photogrammetric reconstruction methods in complex urban forest stands;
- (2)
- Evaluating the ability of different NVS methods (one based on implicit neural networks: NeRF; another on explicit Gaussian point clouds: 3DGS) in reconstructing trees and generating dense point clouds;
- (3)
- Comparing tree parameters extracted from various 3D point cloud models and assessing whether NVS techniques can replace or supplement photogrammetric methods, potentially becoming a new tool for forest scene reconstruction and forest resource surveys.
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Study Area
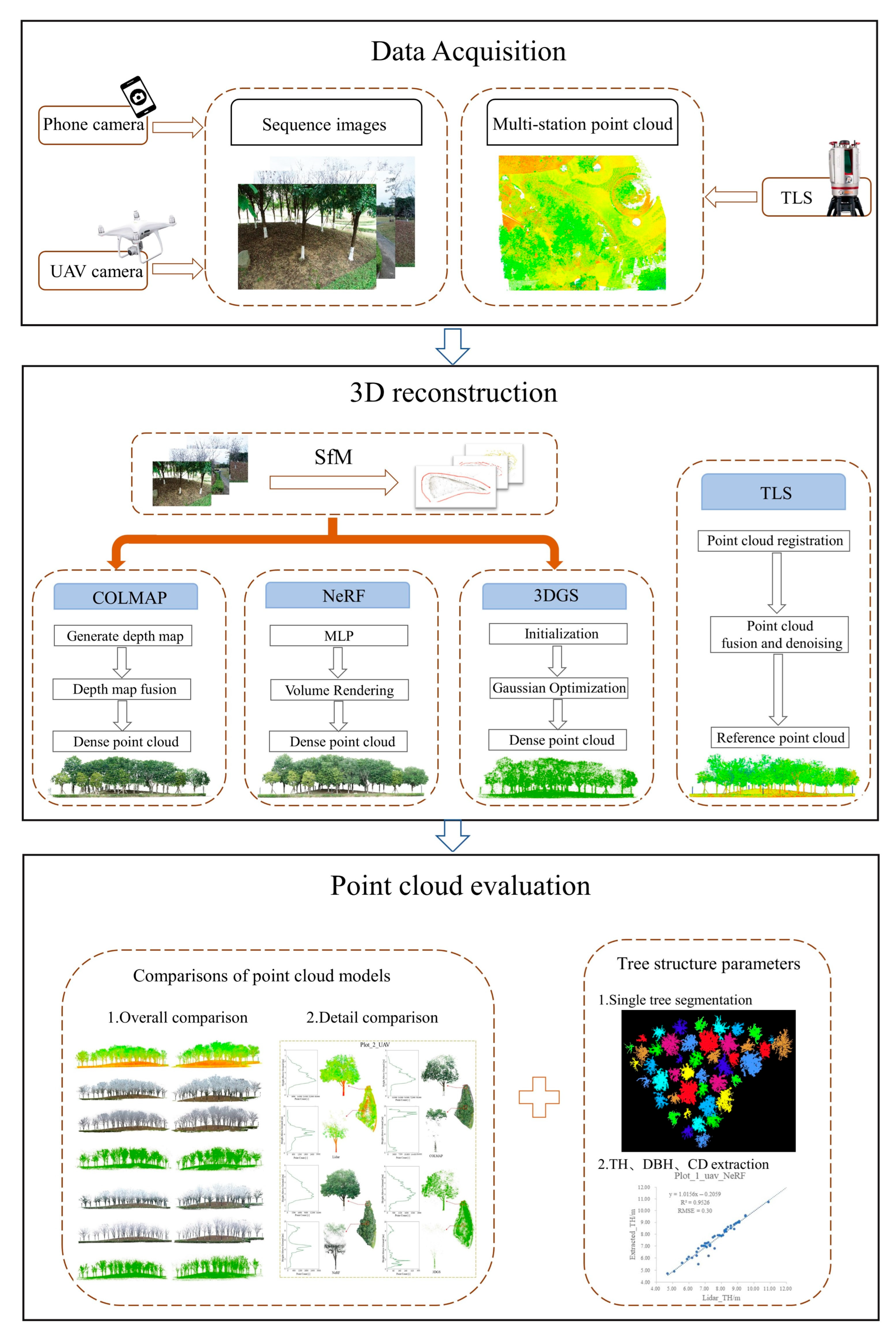
2.2. Research Method
2.2.1. Photogrammetric Reconstruction
2.2.2. Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF)
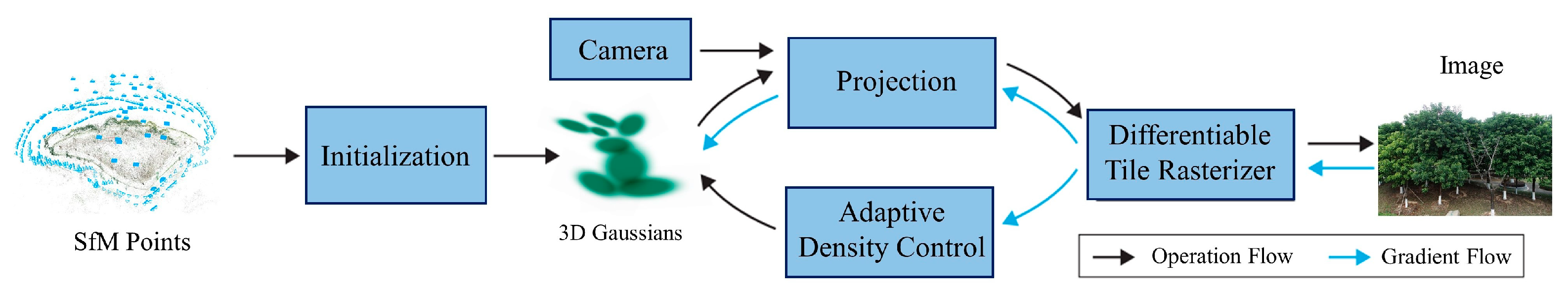
2.2.3. 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS)
2.3. Data Acquisition and Processing
2.3.1. Data Acquisition
2.3.2. Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Reconstruction Efficiency Comparison
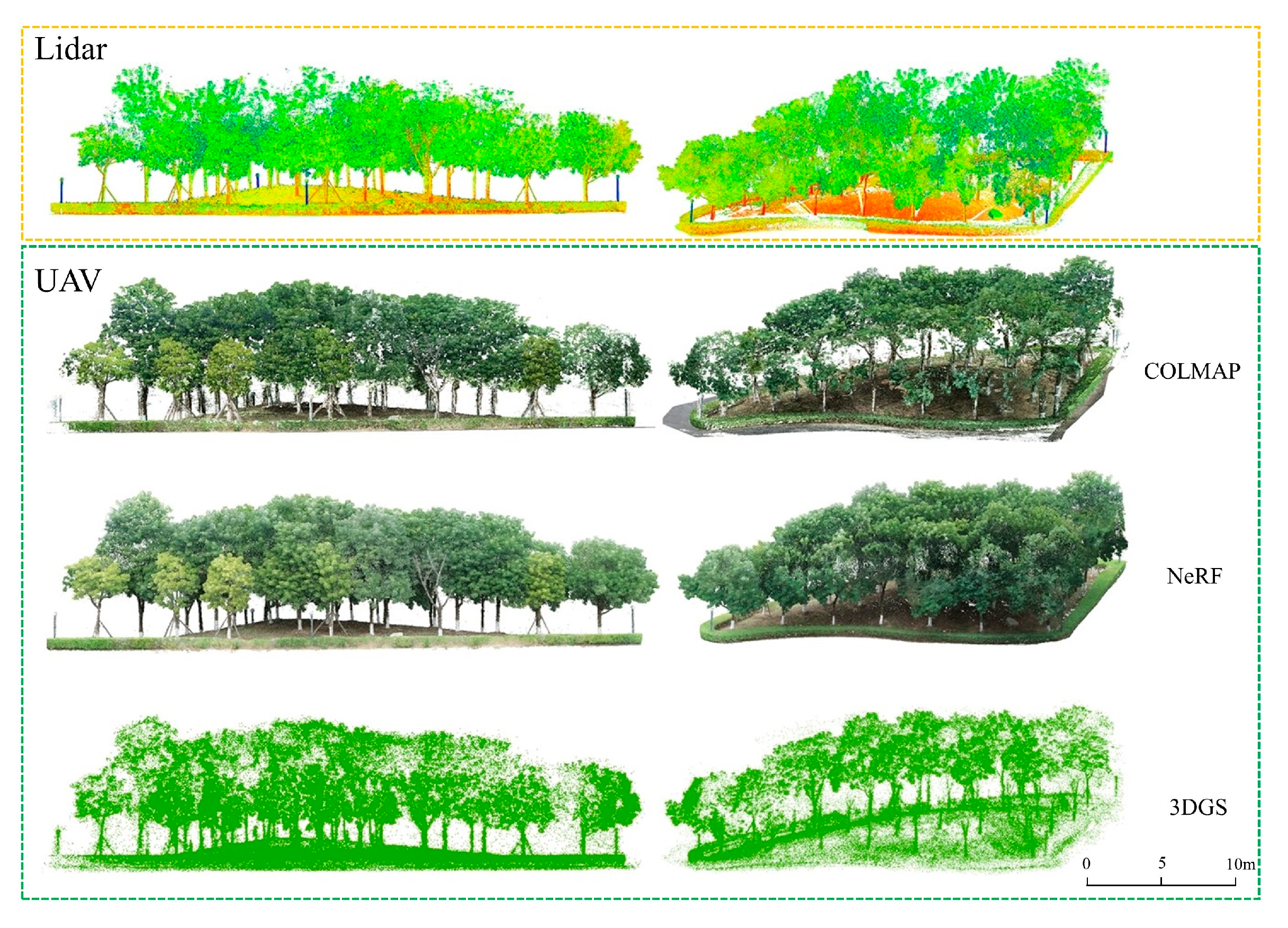
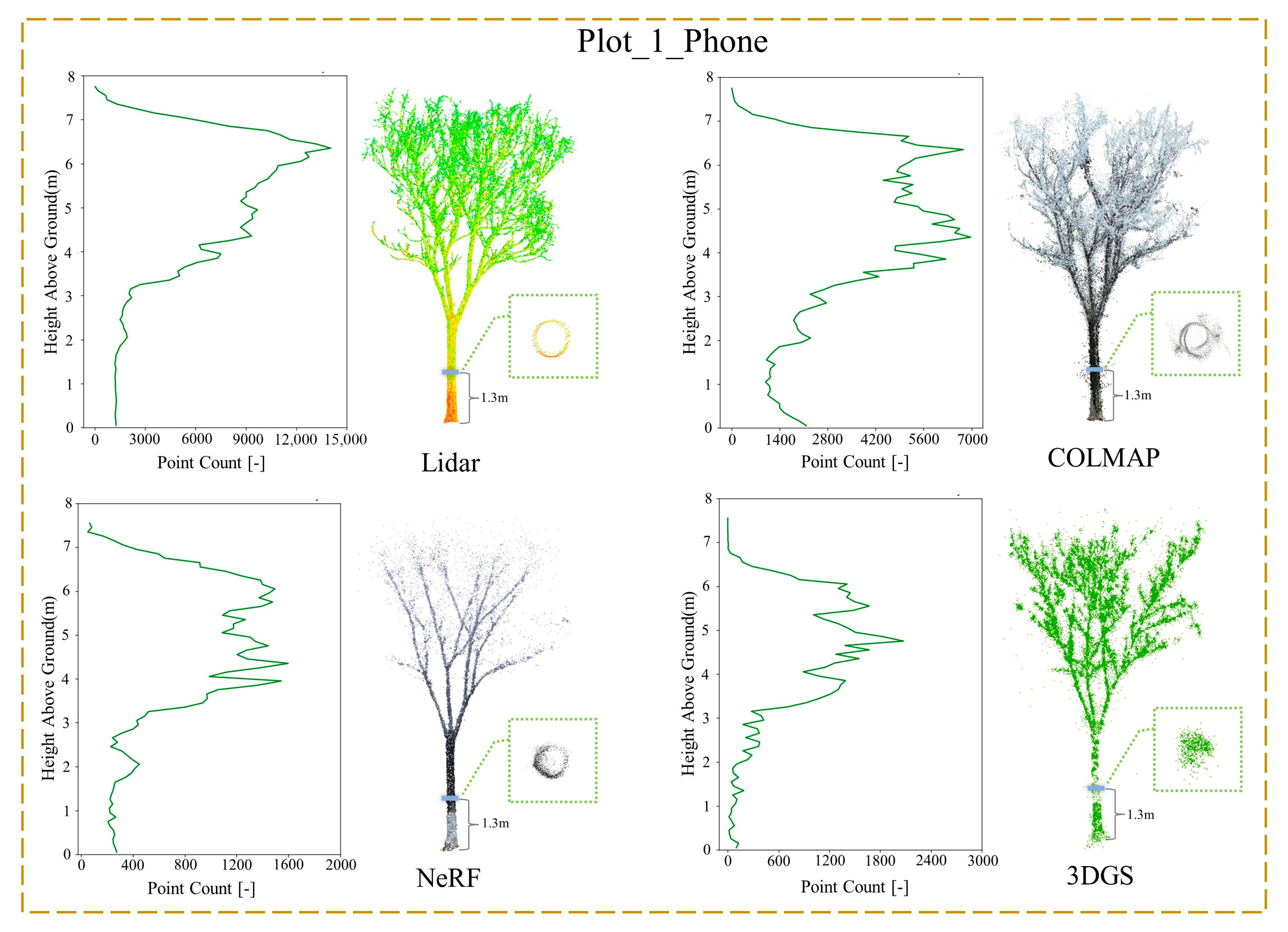
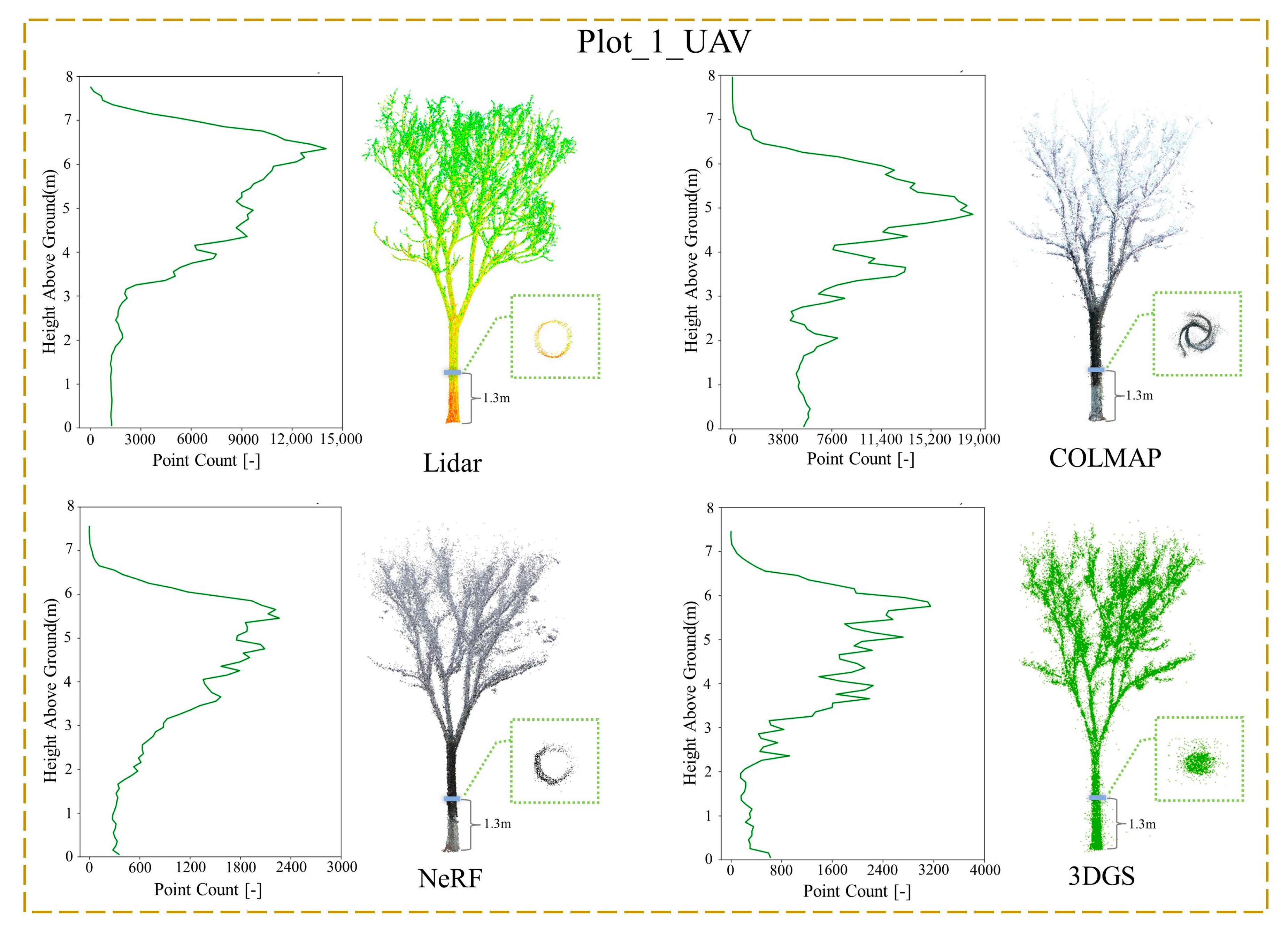
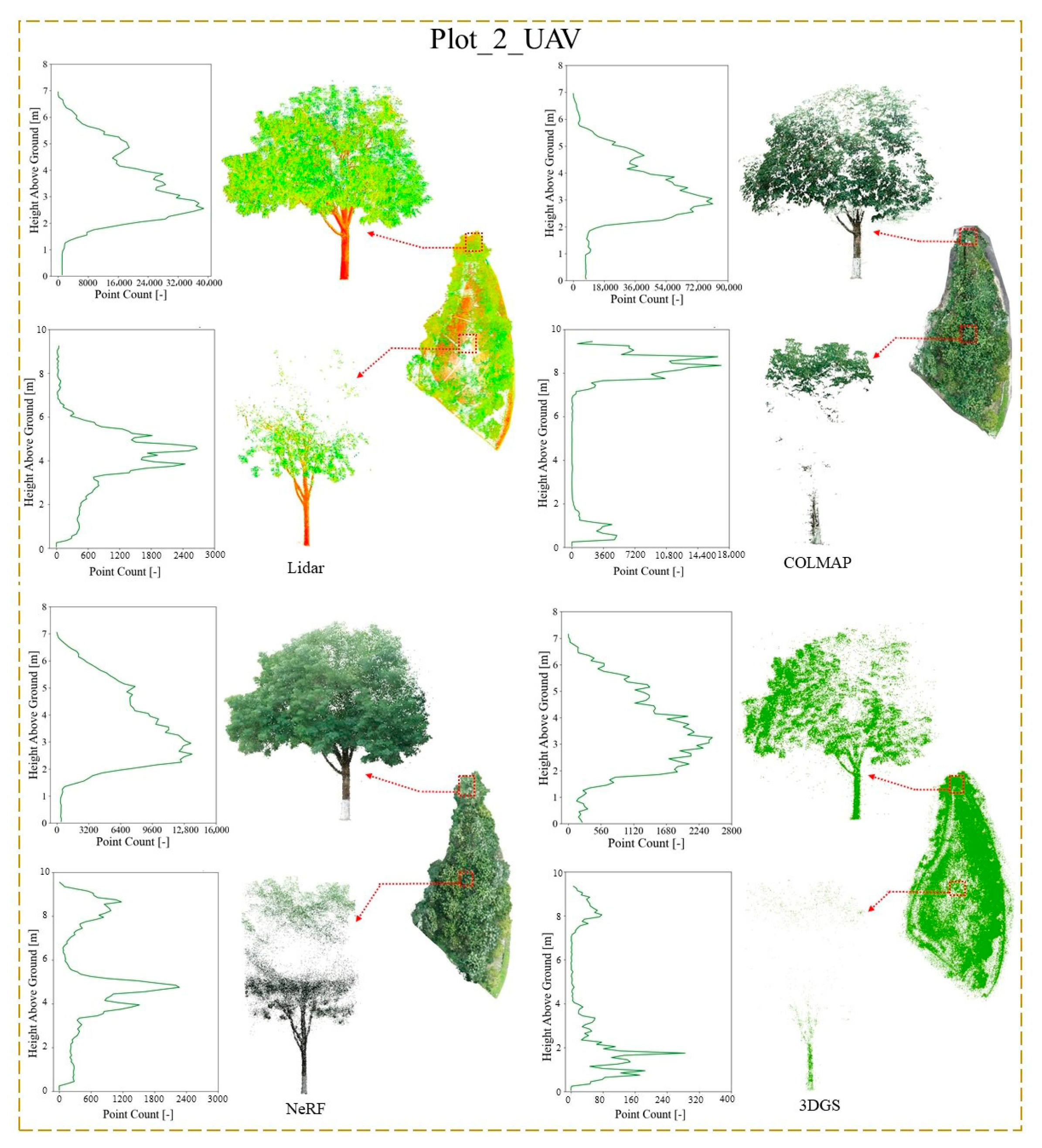
3.2. Point Cloud Comparison
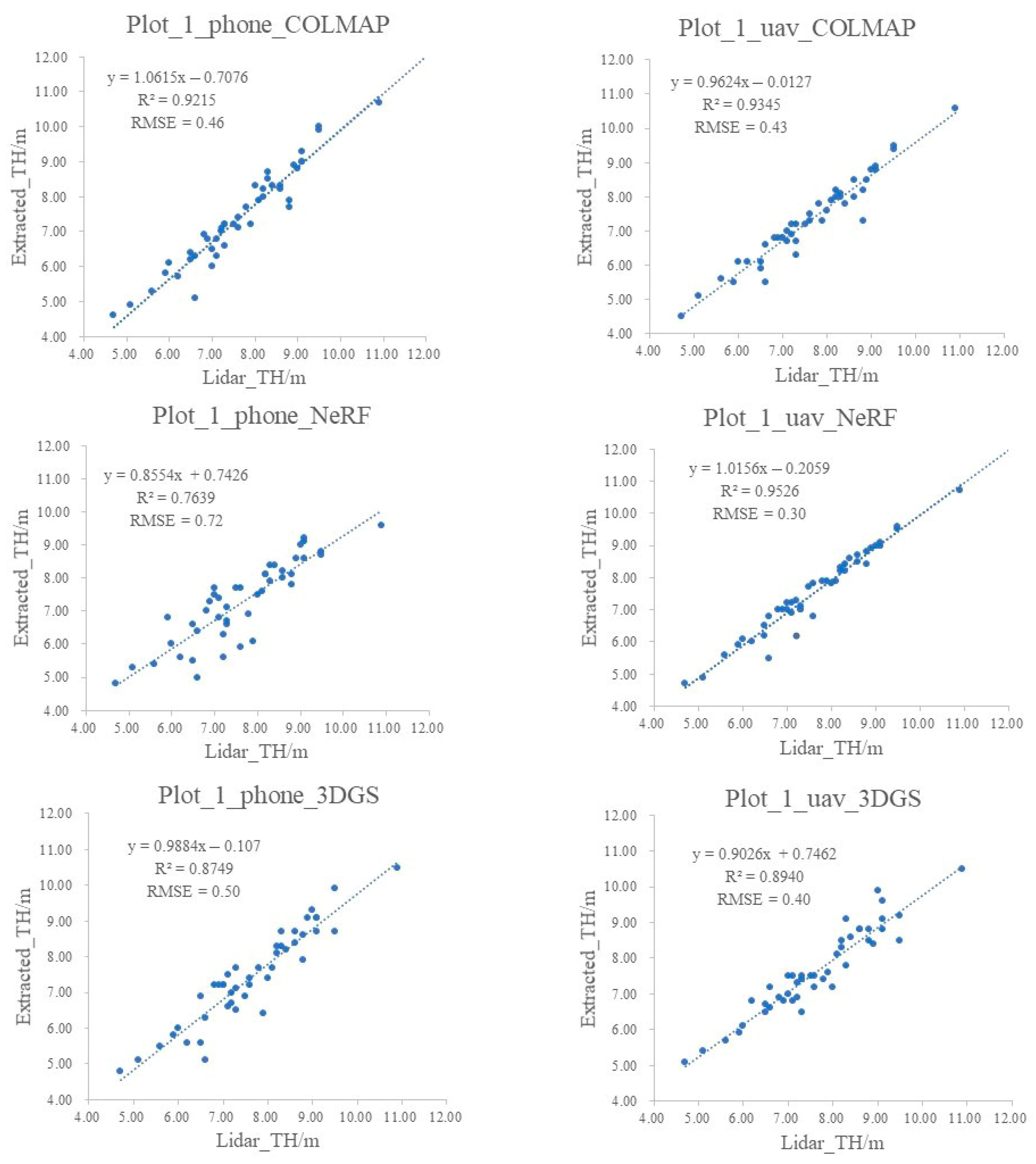
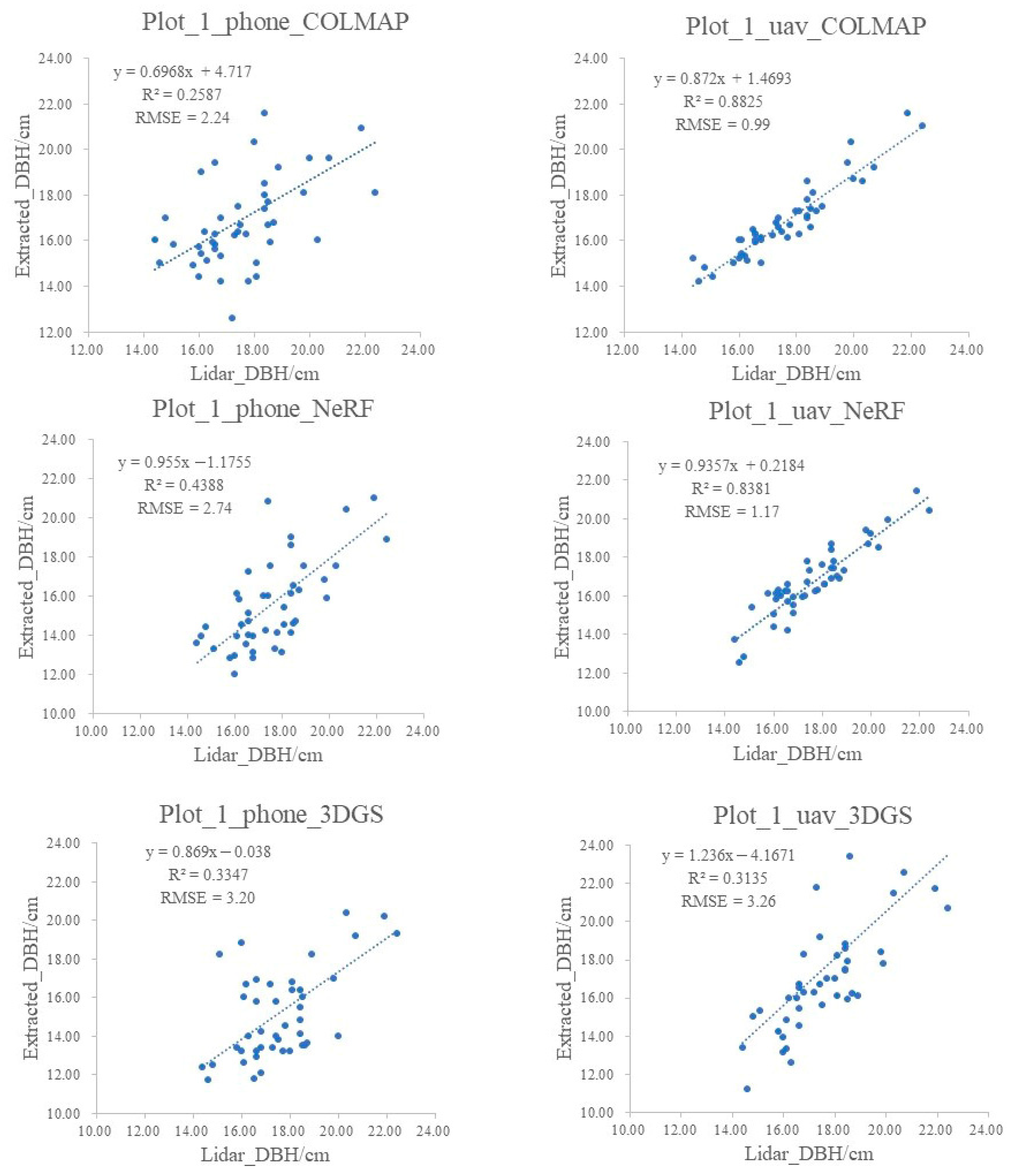
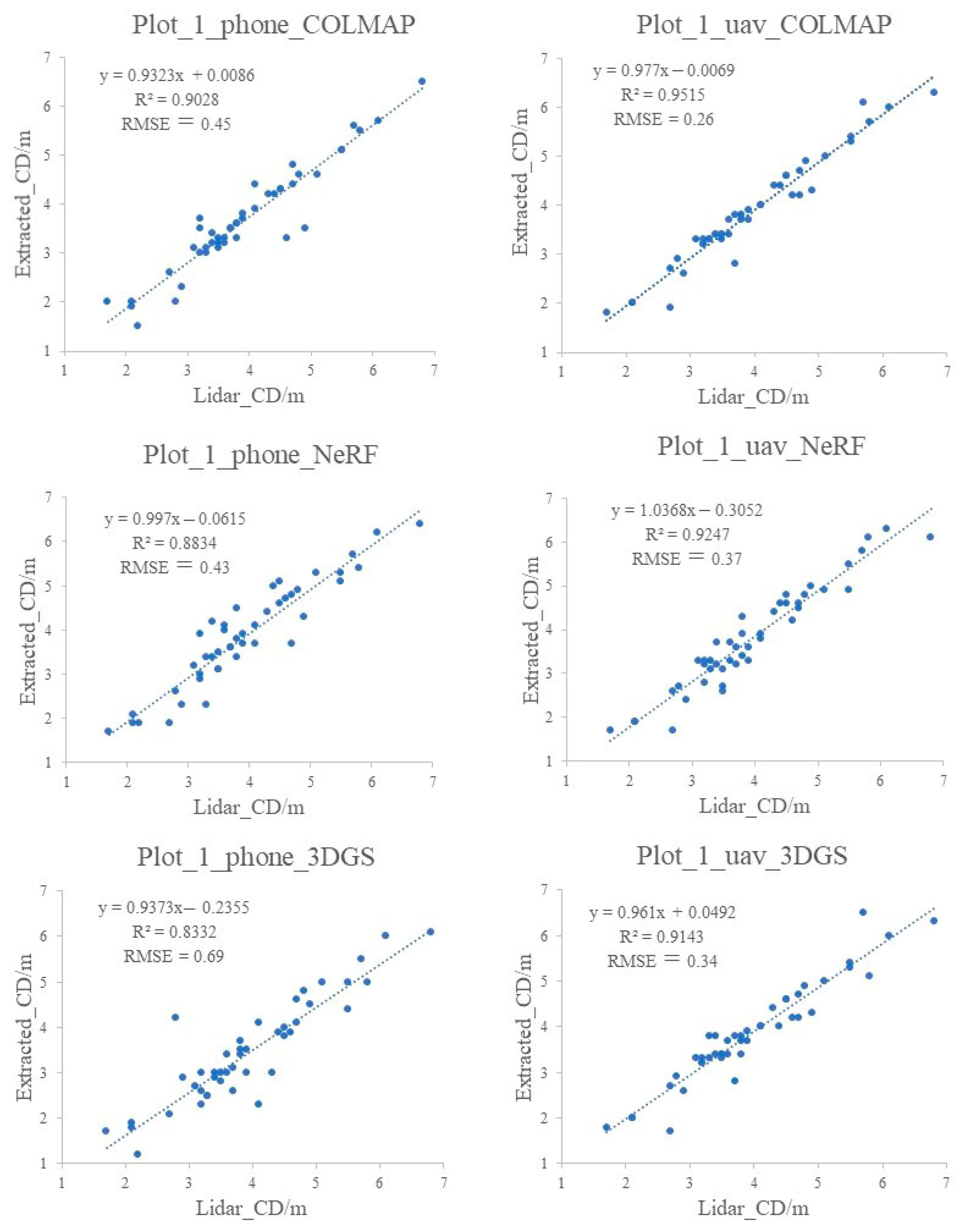
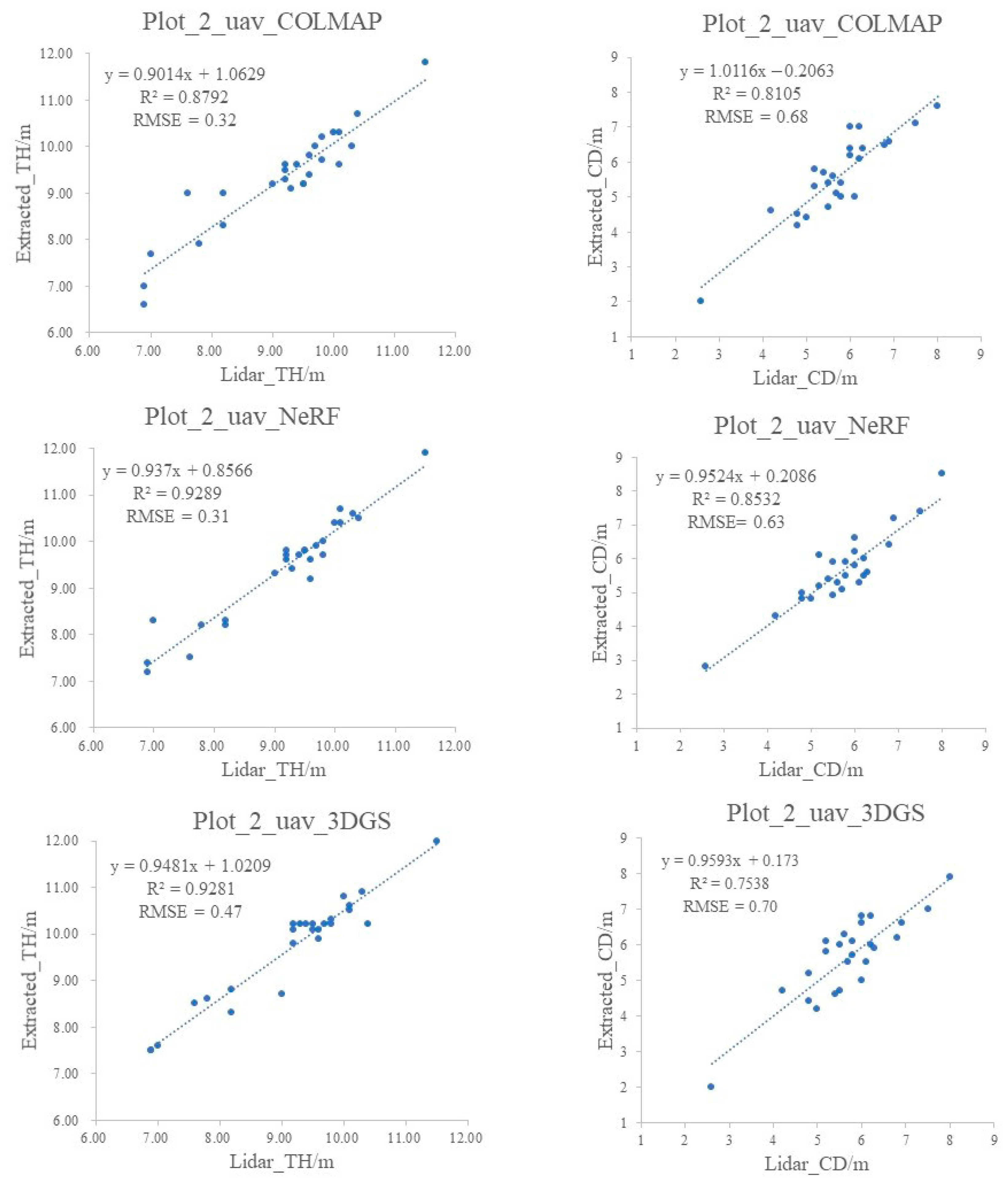
3.3. Extraction of Tree Parameters from Stand Plot Point Cloud
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The new view synthesis methods (NeRF and 3DGS) achieve significantly higher efficiency in dense reconstruction compared to classic photogrammetry methods;
- The 3DGS method’s capability to generate dense 3D point clouds is inferior to that of NeRF and photogrammetry methods, with 3DGS models often exhibiting sparser point densities and being inadequate for single-tree diameter estimation;
- For forest stands with dense foliage, NeRF provides superior reconstruction quality, while photogrammetry methods tend to produce poorer results, including issues such as tree trunk overlap and multiple tree duplications;
- All three methods achieve high accuracy in extracting single-tree height and crown diameter parameters, with NeRF providing the highest precision for tree height. Photogrammetry methods offer better accuracy in diameter estimation compared to NeRF and 3DGS;
- Image resolution and the completeness of viewpoints also impact the quality of the reconstruction results and the accuracy of tree structure parameter extraction.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baumeister, C.F.; Gerstenberg, T.; Plieninger, T.; Schraml, U. Exploring cultural ecosystem service hotspots: Linking multiple urban forest features with public participation mapping data. Urban For. Urban Green. 2020, 48, 126561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobedo, F.J.; Nowak, D. Spatial heterogeneity and air pollution removal by an urban forest. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 90, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, X.; Du, H.; Zhou, G.; Mao, F.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, L.; Xuan, J.; Gong, Y.; Chen, C. Estimation of urban forest characteristic parameters using UAV-Lidar coupled with canopy volume. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Chen, D.; Wu, W.; Liao, X. Estimating aboveground biomass of urban forest trees with dual-source UAV acquired point clouds. Urban For. Urban Green. 2022, 69, 127521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isibue, E.W.; Pingel, T.J. Unmanned aerial vehicle based measurement of urban forests. Urban For. Urban Green. 2020, 48, 126574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakir, G.Y.; Post, C.J.; Mikhailova, E.A.; Schlautman, M.A. 3D LiDAR scanning of urban forest structure using a consumer tablet. Urban Sci. 2021, 5, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobrowski, R.; Winczek, M.; Zięba-Kulawik, K.; Wężyk, P. Best practices to use the iPad Pro LiDAR for some procedures of data acquisition in the urban forest. Urban For. Urban Green. 2023, 79, 127815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luoma, V.; Saarinen, N.; Wulder, M.A.; White, J.C.; Vastaranta, M.; Holopainen, M.; Hyyppä, J. Assessing precision in conventional field measurements of individual tree attributes. Forests 2017, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Kankare, V.; Hyyppä, J.; Wang, Y.; Kukko, A.; Haggrén, H.; Yu, X.; Kaartinen, H.; Jaakkola, A.; Guan, F. Terrestrial laser scanning in forest inventories. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 115, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, D.; Wang, D. Towards the digital twin of urban forest: 3D modeling and parameterization of large-scale urban trees from close-range laser scanning. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 127, 103695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holopainen, M.; Kankare, V.; Vastaranta, M.; Liang, X.; Lin, Y.; Vaaja, M.; Yu, X.; Hyyppä, J.; Hyyppä, H.; Kaartinen, H. Tree mapping using airborne, terrestrial and mobile laser scanning–A case study in a heterogeneous urban forest. Urban For. Urban Green. 2013, 12, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’hont, B.; Calders, K.; Bartholomeus, H.; Lau, A.; Terryn, L.; Verhelst, T.; Verbeeck, H. Evaluating airborne, mobile and terrestrial laser scanning for urban tree inventories: A case study in Ghent, Belgium. Urban For. Urban Green. 2024, 99, 128428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, R.C.; Da Silva, M.F.; Tommaselli, A.M.G.; Galo, M. Automatic Tree Detection/Localization in Urban Forest Using Terrestrial Lidar Data. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2024-2024 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Athens, Greece, 7–12 July 2024; pp. 4522–4525. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, S.; Fararoda, R.; Jha, C.S.; Rajan, K.S. Automatic estimation of tree stem attributes using terrestrial laser scanning in central Indian dry deciduous forests. Curr. Sci. 2018, 114, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnuson, R.; Erfanifard, Y.; Kulicki, M.; Gasica, T.A.; Tangwa, E.; Mielcarek, M.; Stereńczak, K. Mobile Devices in Forest Mensuration: A Review of Technologies and Methods in Single Tree Measurements. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Hyyppä, J.; Kaartinen, H.; Lehtomäki, M.; Pyörälä, J.; Pfeifer, N.; Holopainen, M.; Brolly, G.; Francesco, P.; Hackenberg, J. International benchmarking of terrestrial laser scanning approaches for forest inventories. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 144, 137–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaskierniak, D.; Lucieer, A.; Kuczera, G.; Turner, D.; Lane, P.; Benyon, R.; Haydon, S. Individual tree detection and crown delineation from Unmanned Aircraft System (UAS) LiDAR in structurally complex mixed species eucalypt forests. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 171, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, K.; Li, Y.; Zou, B.; Li, D.; Lu, D. Examining the role of UAV Lidar data in improving tree volume calculation accuracy. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghian, H.; Naghavi, H.; Maleknia, R.; Soosani, J.; Pfeifer, N. Estimating the attributes of urban trees using terrestrial photogrammetry. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yun, T.; Liang, F.; Li, W.; Zhang, T.; Sun, Y. Study of Obtain of Key Parameters of Forest Stand Based on Close Range Photogrammetry. Sci. Technol. Eng 2017, 17, 85–92. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, J.; Koeser, A.; Abd-Elrahman, A.; Wilkinson, B.; Hansen, G.; Landry, S.; Perez, A. Mobile terrestrial photogrammetry for street tree mapping and measurements. Forests 2019, 10, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, T.; Qu, Y.; Du, J. A low-cost integrated sensor for measuring tree diameter at breast height (DBH). Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 199, 107140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schonberger, J.L.; Frahm, J.-M. Structure-from-motion revisited. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 4104–4113. [Google Scholar]
- Seitz, S.M.; Curless, B.; Diebel, J.; Scharstein, D.; Szeliski, R. A comparison and evaluation of multi-view stereo reconstruction algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’06), New York, NY, USA, 17–22 June 2006; pp. 519–528. [Google Scholar]
- Kameyama, S.; Sugiura, K. Estimating Tree Height and Volume Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Photography and SfM Technology, with Verification of Result Accuracy. Drones 2020, 4, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayati, H.; Najafi, A.; Vahidi, J.; Gholamali Jalali, S. 3D reconstruction of uneven-aged forest in single tree scale using digital camera and SfM-MVS technique. Scand. J. For. Res. 2021, 36, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Shen, X.; Cao, L. Extraction of Forest Structural Parameters by the Comparison of Structure from Motion (SfM) and Backpack Laser Scanning (BLS) Point Clouds. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, X. Forest 3D reconstruction and individual tree parameter extraction combining close-range photo enhancement and feature matching. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mildenhall, B.; Srinivasan, P.P.; Tancik, M.; Barron, J.T.; Ramamoorthi, R.; Ng, R. Nerf: Representing scenes as neural radiance fields for view synthesis. Commun. ACM 2021, 65, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, T.; Evans, A.; Schied, C.; Keller, A. Instant neural graphics primitives with a multiresolution hash encoding. ACM Trans. Graph. 2022, 41, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, J.T.; Mildenhall, B.; Tancik, M.; Hedman, P.; Martin-Brualla, R.; Srinivasan, P.P. Mip-nerf: A multiscale representation for anti-aliasing neural radiance fields. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 5855–5864. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Han, Q.; Habermann, M.; Daniilidis, K.; Theobalt, C.; Liu, L. Neus2: Fast learning of neural implicit surfaces for multi-view reconstruction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 3295–3306. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, N.; Ma, C. Lightning NeRF: Efficient Hybrid Scene Representation for Autonomous Driving. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.05907. [Google Scholar]
- Tancik, M.; Casser, V.; Yan, X.; Pradhan, S.; Mildenhall, B.; Srinivasan, P.P.; Barron, J.T.; Kretzschmar, H. Block-nerf: Scalable large scene neural view synthesis. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 8248–8258. [Google Scholar]
- Croce, V.; Caroti, G.; De Luca, L.; Piemonte, A.; Véron, P. Neural radiance fields (nerf): Review and potential applications to digital cultural heritage. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2023, 48, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Ying, W.; Pan, Y.; Kang, H.; Chen, C. High-fidelity 3D reconstruction of plants using Neural Radiance Fields. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 220, 108848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Ni, X.; Dong, F.; Tang, L.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y. Neural radiance fields for multi-scale constraint-free 3D reconstruction and rendering in orchard scenes. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 217, 108629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Tian, G.; Chen, C. Evaluating the point cloud of individual trees generated from images based on Neural Radiance fields (NeRF) method. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerbl, B.; Kopanas, G.; Leimkühler, T.; Drettakis, G. 3D Gaussian Splatting for Real-Time Radiance Field Rendering. ACM Trans. Graph. 2023, 42, 139:1–139:14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Qi, Y. A Brief Review on Differentiable Rendering: Recent Advances and Challenges. Electronics 2024, 13, 3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lee, I.-K. Is 3DGS Useful?: Comparing the Effectiveness of Recent Reconstruction Methods in VR. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR), Bellevue, WA, USA, 21–25 October 2024; pp. 71–80. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, K.; Jiang, L.; Lu, T.; Yu, M.; Xu, L.; Ni, Z.; Dai, B. Octree-gs: Towards consistent real-time rendering with lod-structured 3d gaussians. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.17898. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Z.; Cong, W.; Wen, K.; Wang, K.; Zhang, J.; Ding, X.; Xu, D.; Ivanovic, B.; Pavone, M.; Pavlakos, G.; et al. Instantsplat: Unbounded sparse-view pose-free gaussian splatting in 40 seconds. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.20309. [Google Scholar]
- Tancik, M.; Weber, E.; Ng, E.; Li, R.; Yi, B.; Wang, T.; Kristoffersen, A.; Austin, J.; Salahi, K.; Ahuja, A. Nerfstudio: A modular framework for neural radiance field development. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH 2023 Conference Proceedings, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 6–10 August 2023; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Srinivasan, P.P.; Deng, B.; Debevec, P.; Freeman, W.T.; Barron, J.T. Nerfactor: Neural factorization of shape and reflectance under an unknown illumination. ACM Trans. Graph. 2021, 40, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.; Charatan, D.; Tewari, A.; Sitzmann, V. FlowMap: High-Quality Camera Poses, Intrinsics, and Depth via Gradient Descent. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.15259. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Chen, A.; Huang, B.; Sattler, T.; Geiger, A. Mip-splatting: Alias-free 3d gaussian splatting. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 19447–19456. [Google Scholar]
- Brachmann, E.; Wynn, J.; Chen, S.; Cavallari, T.; Monszpart, Á.; Turmukhambetov, D.; Prisacariu, V.A. Scene Coordinate Reconstruction: Posing of Image Collections via Incremental Learning of a Relocalizer. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.14351. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, L.; Baráth, D.; Pollefeys, M.; Schönberger, J.L. Global Structure-from-Motion Revisited. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Shen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Bao, H.; Zhou, X. LoFTR: Detector-free local feature matching with transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 8922–8931. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Du, S. Raising the Ceiling: Conflict-Free Local Feature Matching with Dynamic View Switching. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024. [Google Scholar]

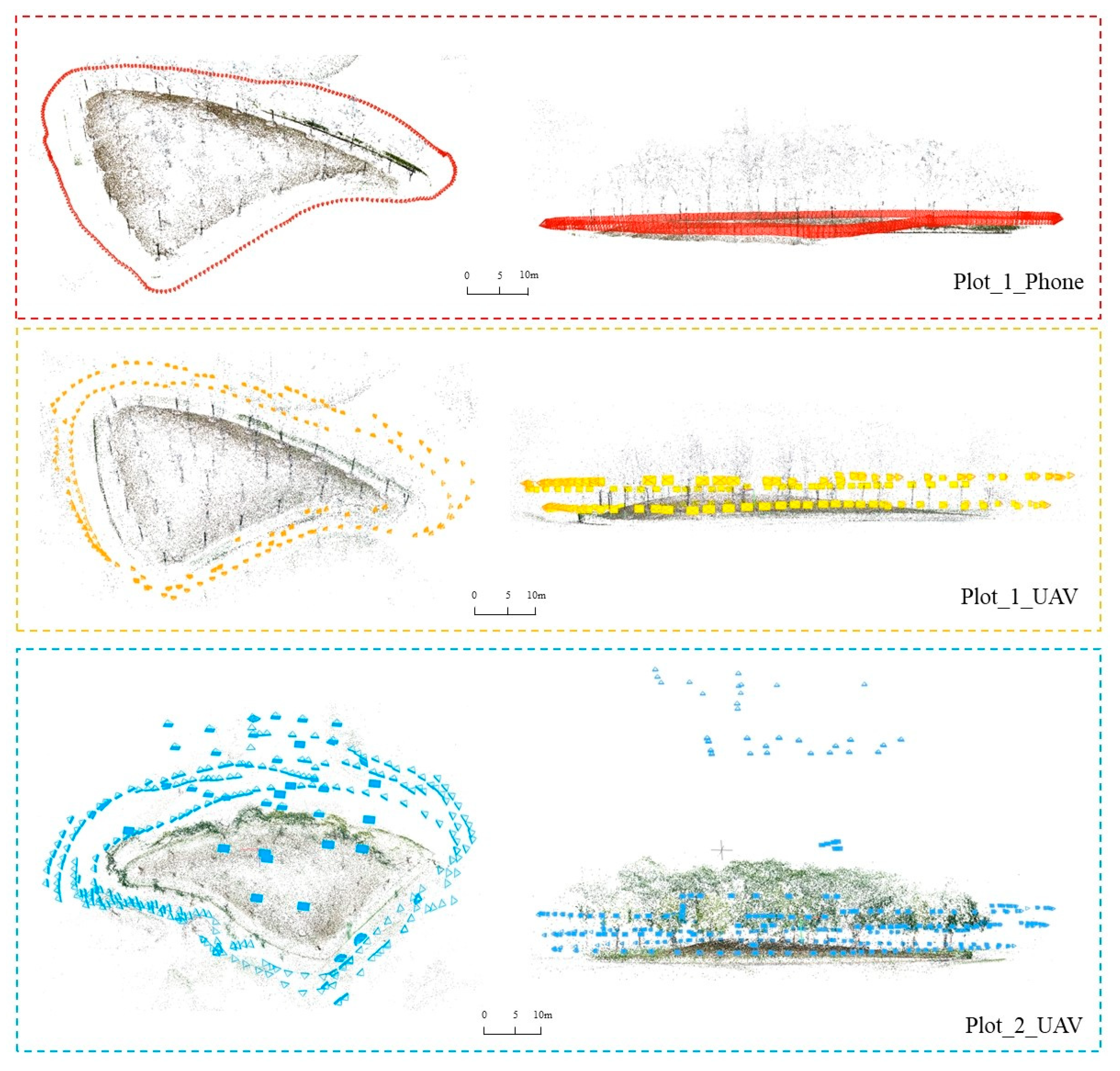



| Image Dataset | Number of Images | Image Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| Plot_1_Phone | 279 | 3840 × 2160 |
| Plot_1_UAV | 268 | 5472 × 3648 |
| Plot_2_UAV | 322 | 5472 × 3648 |
| Plot_1_Phone | Plot_1_UAV | Plot_2_UAV | |
|---|---|---|---|
| COLMAP | 544.292 | 724.495 | 453.834 |
| NeRF | 15.0 | 14.0 | 12.0 |
| 3DGS | 18.23 | 17.39 | 17.46 |
| Plot ID | Model ID | Number of Points |
|---|---|---|
| Plot_1 | Plot_1_Lidar | 25,617,648 |
| Plot_1_Phone_COLMAP | 20,200,476 | |
| Plot_1_Phone_NeRF | 4,548,307 | |
| Plot_1_Phone_3DGS | 1,555,984 | |
| Plot_1_UAV_COLMAP | 53,153,623 | |
| Plot_1_UAV_NeRF | 2,573,330 | |
| Plot_1_UAV_3DGS | 806,149 | |
| Plot_2 | Plot_2_Lidar | 9,053,897 |
| Plot_2_UAV_COLMAP | 55,861,268 | |
| Plot_2_UAV_NeRF | 5,465,952 | |
| Plot_2_UAV_3DGS | 831,164 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, G.; Chen, C.; Huang, H. Comparative Analysis of Novel View Synthesis and Photogrammetry for 3D Forest Stand Reconstruction and Extraction of Individual Tree Parameters. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091520
Tian G, Chen C, Huang H. Comparative Analysis of Novel View Synthesis and Photogrammetry for 3D Forest Stand Reconstruction and Extraction of Individual Tree Parameters. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(9):1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091520
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Guoji, Chongcheng Chen, and Hongyu Huang. 2025. "Comparative Analysis of Novel View Synthesis and Photogrammetry for 3D Forest Stand Reconstruction and Extraction of Individual Tree Parameters" Remote Sensing 17, no. 9: 1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091520
APA StyleTian, G., Chen, C., & Huang, H. (2025). Comparative Analysis of Novel View Synthesis and Photogrammetry for 3D Forest Stand Reconstruction and Extraction of Individual Tree Parameters. Remote Sensing, 17(9), 1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091520






