HiDRA-DCDNet: Dynamic Hierarchical Attention and Multi-Scale Context Fusion for Real-Time Remote Sensing Small-Target Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
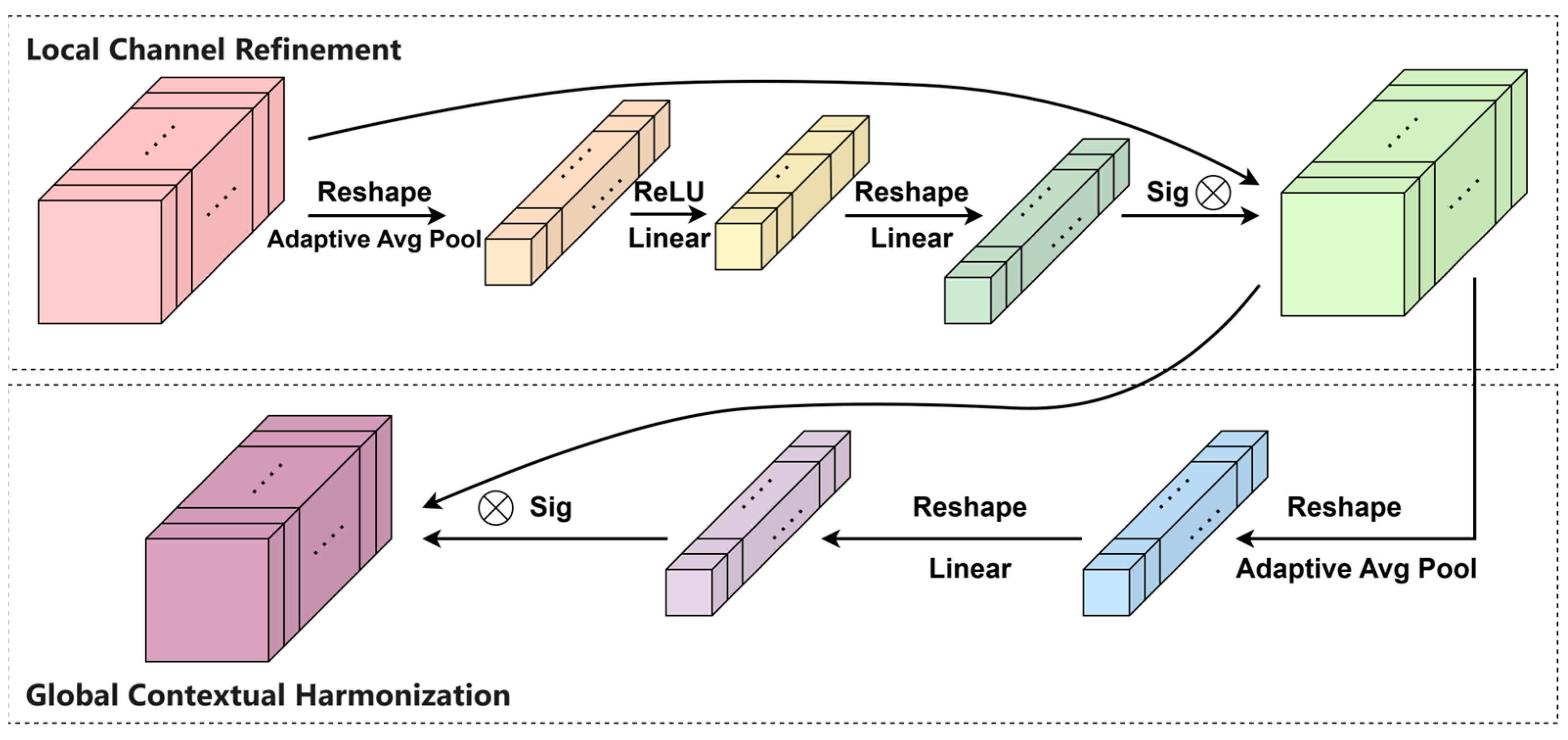
- HiDRA Mechanism: A dual-resolution attention paradigm combining competitive channel selection (via adaptive bottlenecking) and global contextual reweighting. Unlike conventional single-stage attention, HiDRA prevents feature over-smoothing by decoupling channel competition from cross-feature dependency modeling;
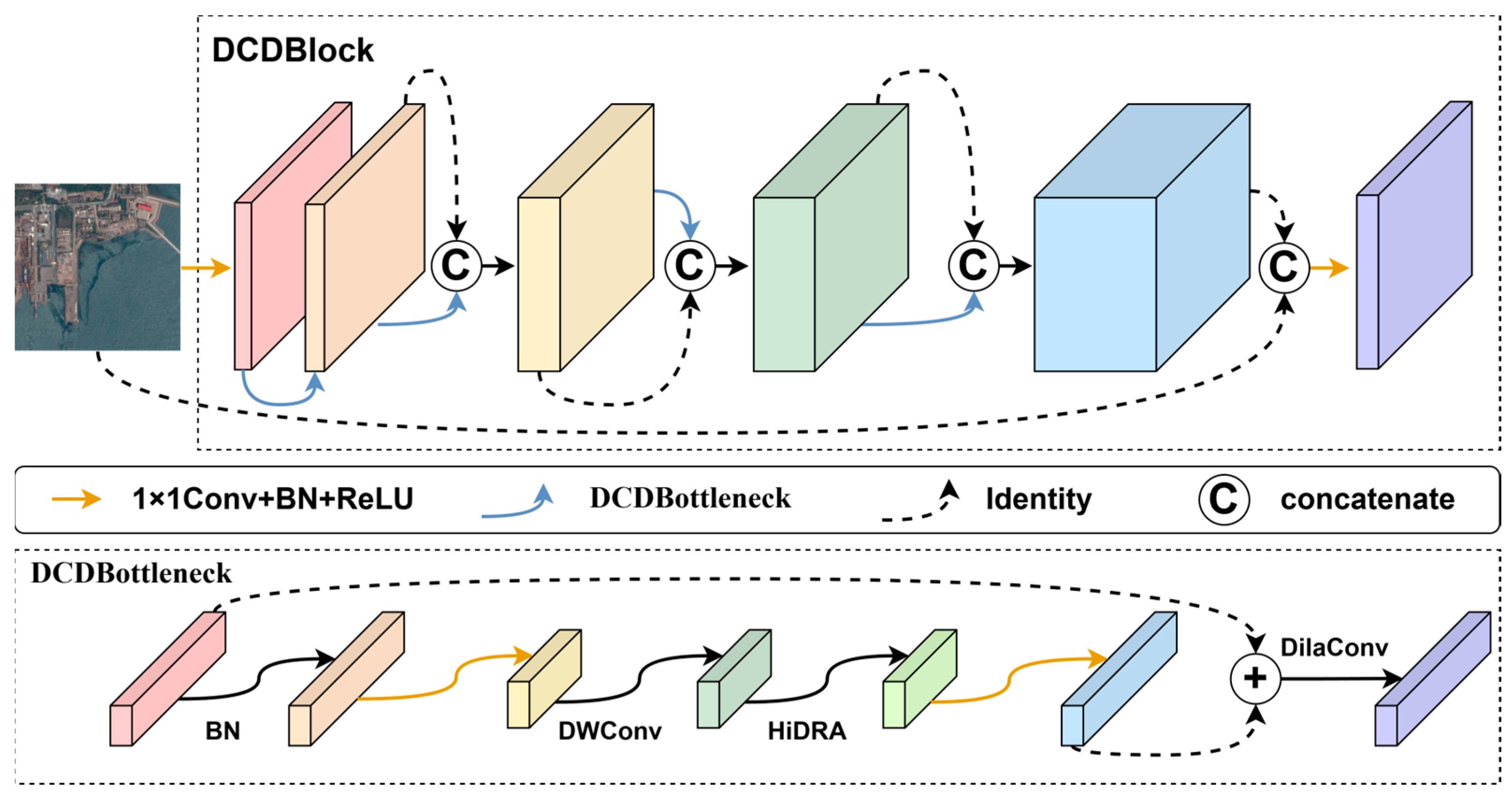
- DCDBlock Architecture: A feature extraction module unifying dilated convolutions, dense cross-stage connections, and embedded HiDRA units. This design achieves multi-scale context aggregation without spatial downsampling, explicitly addressing the resolution-preservation versus receptive field trade-off;
- Empirical Validation: Extensive experiments on the AI-TOD, VisDrone, MAR20, and DOTA-v1.0 datasets demonstrate our method’s consistent superiority, achieving average absolute gains of +1.16% (mAP50), +0.93% (mAP95), and +1.83% (F1-score) over prior state-of-the-art approaches across all benchmarks, with HiDRA alone contributing 63% of the mAP gains in ablation studies.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Main Challenges and Solutions for Small-Target Detection in Remote Sensing
2.1.1. Complex Backgrounds and High-Resolution Images
2.1.2. Small-Target Diversity and Scale Variation
2.1.3. Computing Resources and Real-Time Requirements
2.2. Attention Mechanism in Object Detection
2.3. Proposed Method
2.3.1. Contextual Motivation and HiDRA Architecture
2.3.2. Design and Implementation of the Feature Extraction Module DCDBlock
3. Results
3.1. Experimental Dataset and Evaluation Metrics
3.2. Training and Test Details
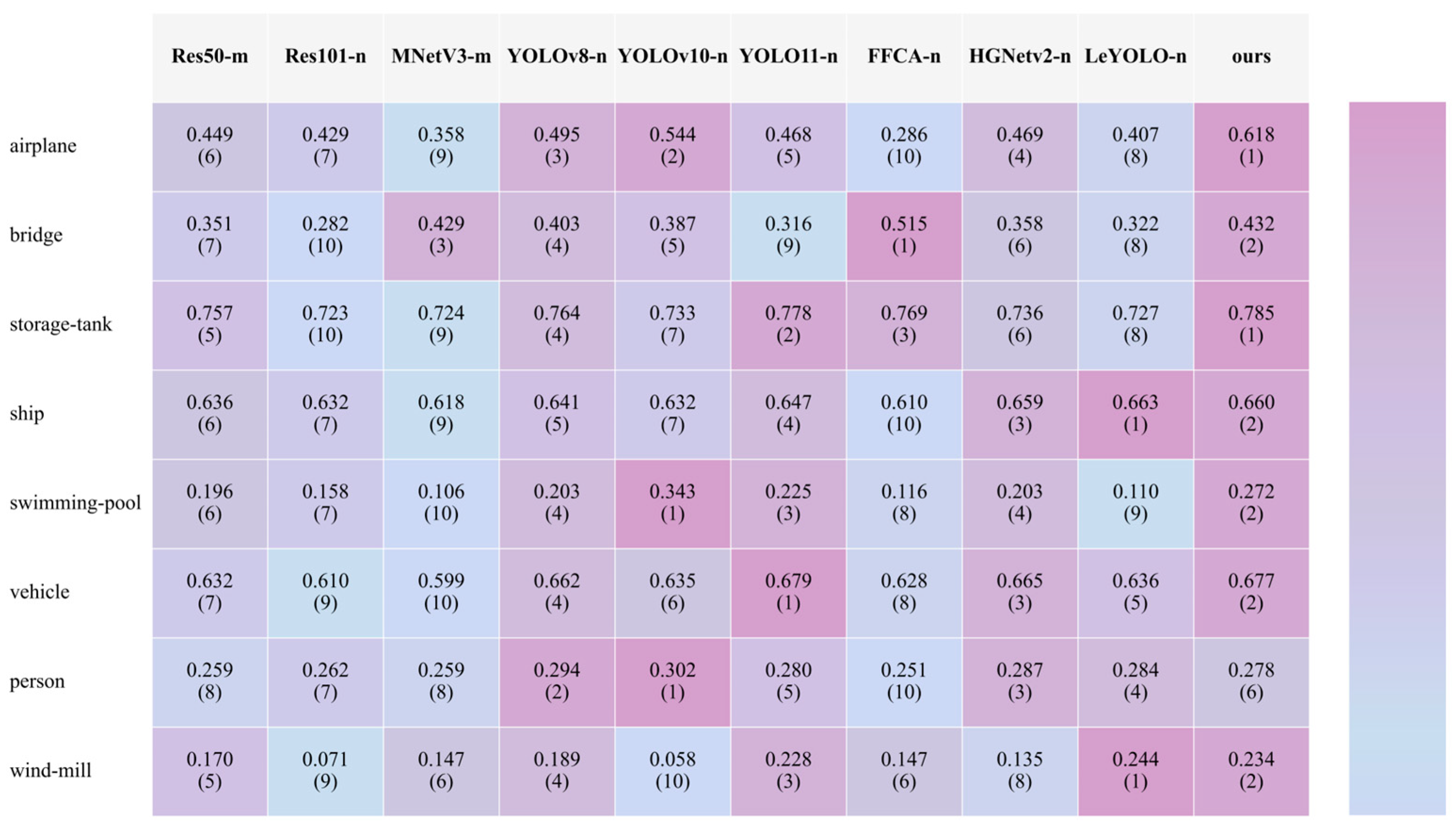
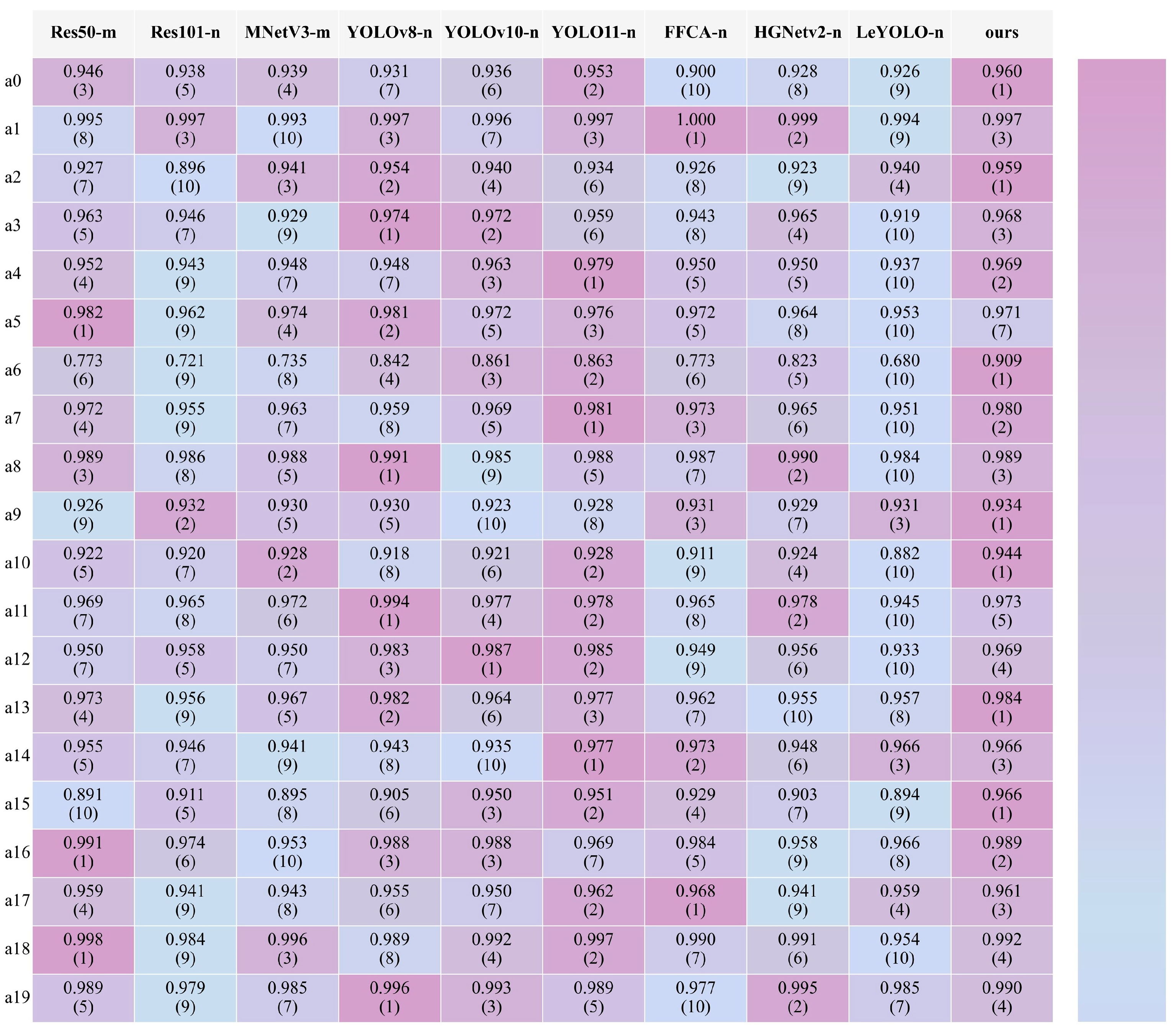
3.3. Main Results and Analysis
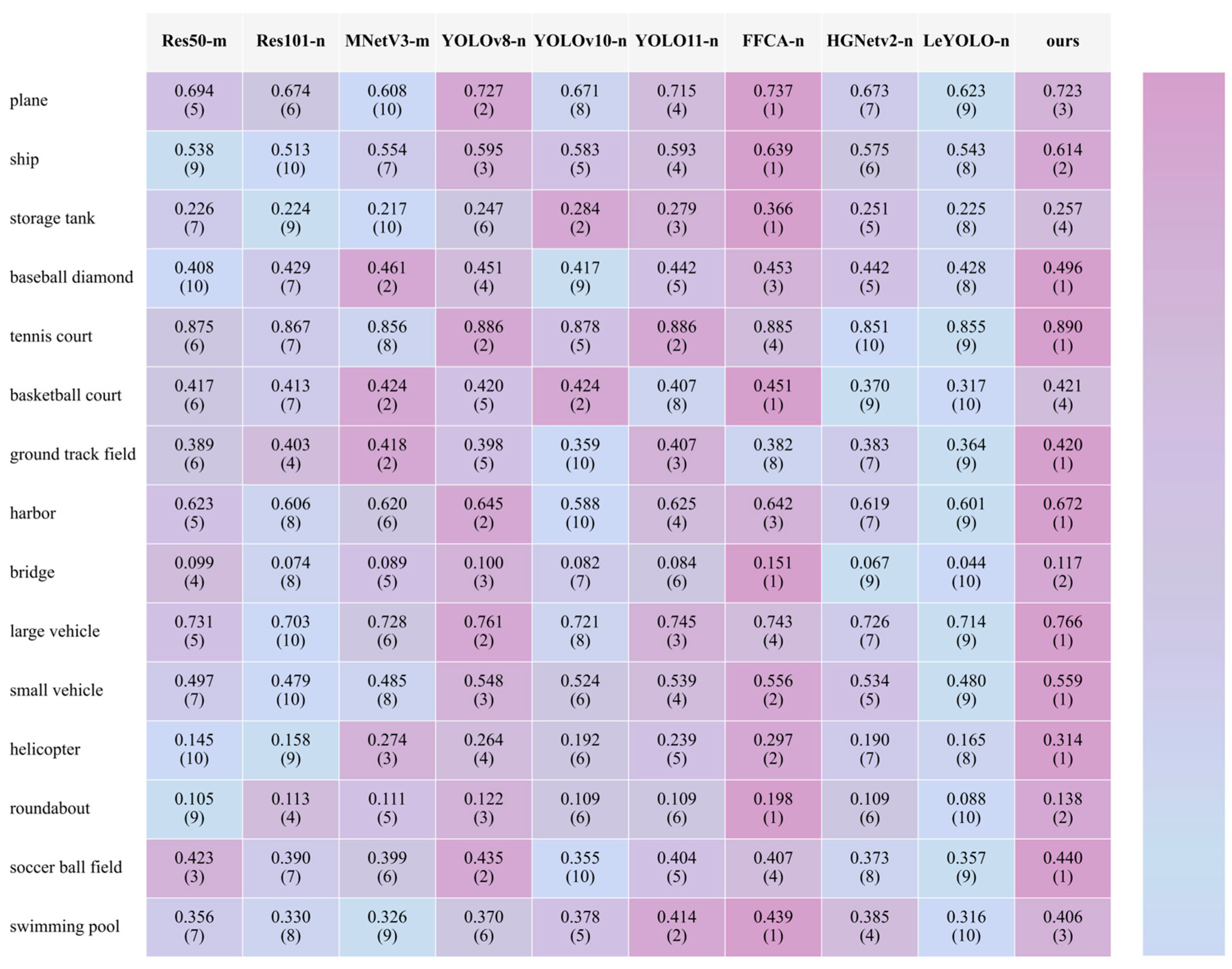
3.3.1. The Comparison of All Networks
3.3.2. F1 Score Comparison of All Networks Across AI-TOD, VisDrone, MAR20, and DOTA-v1.0 Datasets
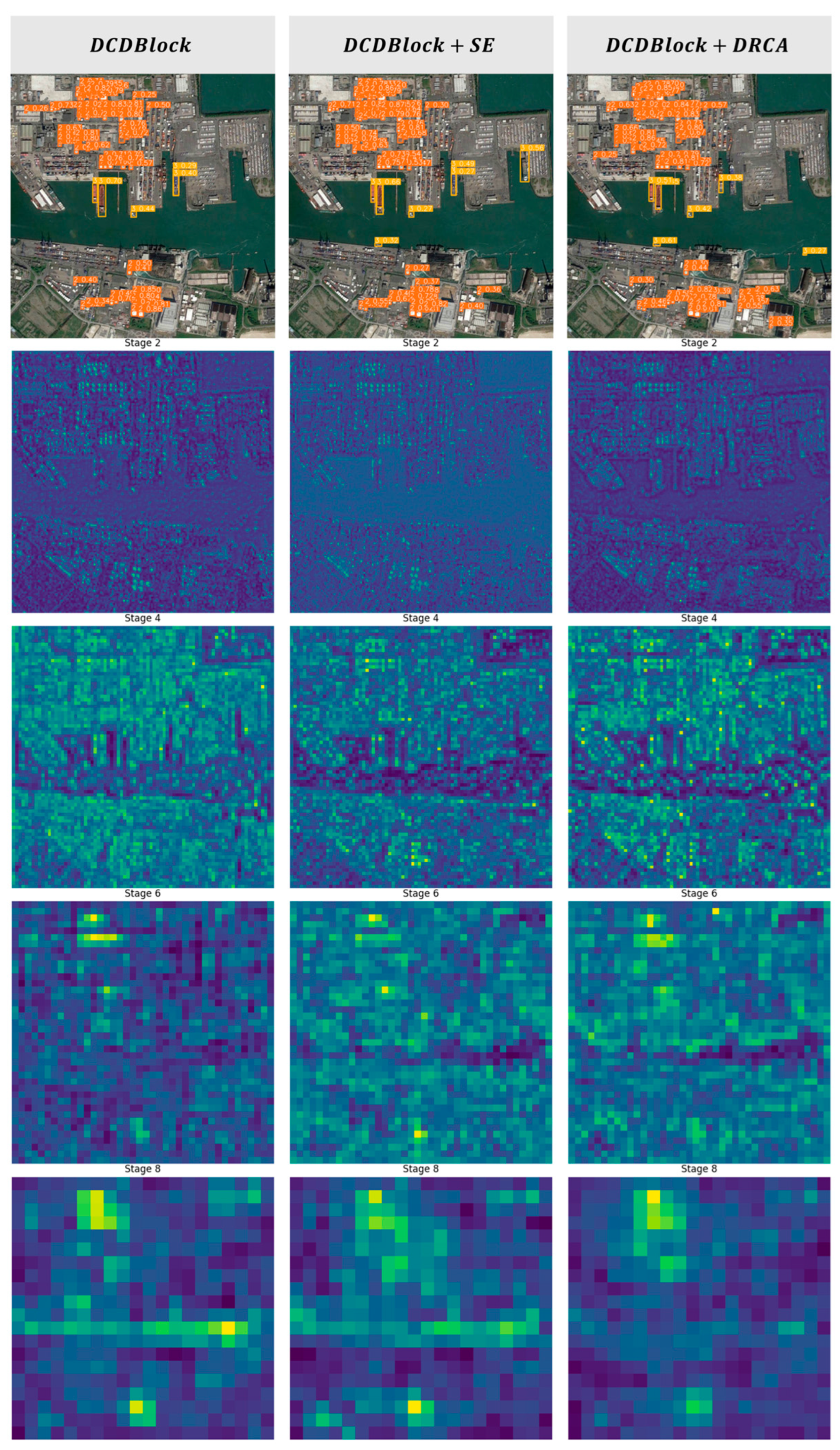
3.3.3. Ablation Experiments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, L.; Zhi, X.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, S.; Hu, J.; Zhang, W.; Huang, Y. A Method for Detecting Aircraft Small Targets in Remote Sensing Images by Using CNNs Fused with Hand-crafted Features. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 6010105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Xiong, W.; Chen, X.; Lu, Y. Experimental study of maritime moving target detection using hitchhiking bistatic radar. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lei, J.; Xie, W.; Fang, Z.; Li, Y.; Du, Q. SuperYOLO: Super resolution assisted object detection in multimodal remote sensing imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5605415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Luo, J.; Zhou, M.; Pi, Y. EFLNet: Enhancing Feature Learning Network for Infrared Small Target Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5906511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Ding, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y. Inshore ship detection based on multi-modality saliency for synthetic aperture radar images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ye, M.; Zhu, G.; Liu, Y.; Guo, P.; Yan, J. FFCA-YOLO for small object detection in remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5611215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Etten, A. You only look twice: Rapid multi-scale object detection in satellite imagery. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.09512. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, S.; Wu, H.; Zhen, L.; Hua, Q.; Garg, S.; Kaddoum, G.; Hassan, M.M.; Yu, K. Edge YOLO: Real-time intelligent object detection system based on edge-cloud cooperation in autonomous vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 25345–25360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.-Y.; Liu, W.; Ranga, A.; Tyagi, A.; Berg, A.C. Dssd: Deconvolutional single shot detector. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1701.06659. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1904–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papa, L.; Alati, E.; Russo, P.; Amerini, I. Speed: Separable pyramidal pooling encoder-decoder for real-time monocular depth estimation on low-resource settings. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 44881–44890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Lei, J.; Zhu, Z.; Cheng, S.; Feng, Z.; Liang, R. AFPN: Asymptotic feature pyramid network for object detection. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Maui, HI, USA, 1–4 October 2023; pp. 2184–2189. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Xu, F.; Yong, X.; Chen, D.; Xia, R.; Ye, B.; Gao, H.; Chen, Z.; Lyu, X. SSCNet: A spectrum-space collaborative network for semantic segmentation of remote sensing images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Xiao, L.; Wei, Z.; Liu, H.; Tang, S. A new pan-sharpening method with deep neural networks. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 1037–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Li, Z.; Deng, J.; Huang, Y.a.; Peng, Z. TFCD-Net: Target and False Alarm Collaborative Detection Network for Infrared Imagery. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Lin, M.; Sun, J. Shufflenet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6848–6856. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, N.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, H.-T.; Sun, J. Shufflenet v2: Practical guidelines for efficient cnn architecture design. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 116–131. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.-C. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Koonce, B.; Koonce, B. MobileNetV3. Convolutional Neural Networks with Swift for Tensorflow: Image Recognition and Dataset Categorization; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2021; pp. 125–144. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Guo, J.; Xu, C.; Xu, C. Ghostnet: More features from cheap operations. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 1580–1589. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Han, K.; Guo, J.; Xu, C.; Xu, C.; Wang, Y. GhostNetv2: Enhance cheap operation with long-range attention. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 9969–9982. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, T.; Wang, J.; Ning, H.; Wang, X.; Xue, D.; Wang, Q.; Nandi, A.K. Difference enhancement and spatial–spectral nonlocal network for change detection in VHR remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 4507013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, L.; Gong, C.; Huang, S.; Zheng, F. Infrared Small Target Detection Based on Weighted Improved Double Local Contrast Measure. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhu, P.; Li, P.; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q. ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11534–11542. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.; Zhou, D.; Feng, J. Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 13713–13722. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, H.; Xie, W.; Long, K. Yolo-former: Marrying yolo and transformer for foreign object detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 5026114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, Y.; Zhao, S.; Song, L.; Yue, X.; Shan, Y. UniRepLKNet: A Universal Perception Large-Kernel ConvNet for Audio Video Point Cloud Time-Series and Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 5513–5524. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C.; Yang, W.; Yu, L. A Normalized Gaussian Wasserstein Distance for Tiny Object Detection. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.13389. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, P.; Wen, L.; Du, D.; Bian, X.; Fan, H.; Hu, Q.; Ling, H. Detection and tracking meet drones challenge. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 7380–7399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenqi, Y.; Gong, C.; Meijun, W.; Yanqing, Y.; Xingxing, X.; Xiwen, Y.; Junwei, H. MAR20: A benchmark for military aircraft recognition in remote sensing images. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2024, 27, 2688–2696. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, G.-S.; Bai, X.; Ding, J.; Zhu, Z.; Belongie, S.; Luo, J.; Datcu, M.; Pelillo, M.; Zhang, L. DOTA: A large-scale dataset for object detection in aerial images. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 3974–3983. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 580–587. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, G.J.A.C.Q. Ultralytics YOLO. Available online: https://ultralytics.com (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- Wang, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, K.; Lin, Z.; Han, J. Yolov10: Real-time end-to-end object detection. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2025, 37, 107984–108011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Lv, W.; Xu, S.; Wei, J.; Wang, G.; Dang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J. Detrs beat yolos on real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 16965–16974. [Google Scholar]
- Hollard, L.; Mohimont, L.; Gaveau, N.; Steffenel, L.-A. LeYOLO, New Scalable and Efficient CNN Architecture for Object Detection. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.14239. [Google Scholar]

| Input Size | Output Size | Parameters | FLOPs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conv1 | H × W × C | H × W × C′ | 0.25C2 + 0.5C | 0.5C2HW + 0.5CHW |
| DCDBottleneck1 | H × W × C′ | H × W × C′ | 0.25C2 + 4.25C | 0.125C2HW + 4.25CHW + 0.25C2 |
| DCDBottleneck2 | H × W × C′ | H × W × C′ | 0.25C2 + 4.25C | 0.125C2HW + 4.25CHW + 0.25C2 |
| Concat1 | [C′, C′] | H × W × 2C′ | 0 | 0 |
| DCDBottleneck3 | H × W × 2C′ | H × W × 2C′ | C2 + 8.5C | 0.5C2HW + 8.5CHW + C2 |
| Concat2 | [2C′, 2C′] | H × W × 4C′ (C) | 0 | 0 |
| DCDBottleneck4 | H × W × 4C′ | H × W × 4C′ (C) | 4C2 + 17C | 2C2HW + 17CHW + 4C2 |
| Concat3 | [4C′, 4C′] | H × W × 8C′ (2C) | 0 | 0 |
| Concat4 | [8C′, 4C′] | H × W × 12C′ (3C) | 0 | 0 |
| Conv2 | H × W × 12C′ (3C) | H × W × C | 3C2 + 2C | 3C2HW + 2CHW |
| Total | H × W × C | H × W × C | 8.75C2 + 36.5C | 6C2HW + 36.5CHW + 5.5C2 |
| GFLOPs | Detection Time | AI-TOD | VisDrone (Static Images) | Mar20 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mAP50 | mAP95 | F1 | mAP50 | mAP95 | F1 | mAP50 | mAP95 | F1 | |||
| Resnet50-m [37] | 9.1 | 2.7 ms | 0.381 | 0.163 | 0.442 | 0.319 | 0.184 | 0.370 | 0.973 | 0.772 | 0.951 |
| Resnet101-n [37] | 9.6 | 3.3 ms | 0.358 | 0.154 | 0.406 | 0.304 | 0.175 | 0.356 | 0.967 | 0.765 | 0.941 |
| MobileNetV3-m [24] | 8.4 | 3.3 ms | 0.367 | 0.157 | 0.410 | 0.31 | 0.176 | 0.358 | 0.972 | 0.768 | 0.945 |
| YOLOv8-n [38] | 8.1 | 1.9 ms | 0.413 | 0.18 | 0.467 | 0.352 | 0.205 | 0.397 | 0.98 | 0.785 | 0.958 |
| YOLOv10-n [39] | 8.4 | 2.0 ms | 0.416 | 0.176 | 0.468 | 0.351 | 0.206 | 0.400 | 0.987 | 0.776 | 0.959 |
| YOLO11-n [38] | 6.5 | 2.3 ms | 0.41 | 0.176 | 0.466 | 0.349 | 0.204 | 0.394 | 0.984 | 0.788 | 0.964 |
| FFCA-YOLO-n [8] | 10.3 | 3.4 ms | 0.369 | 0.16 | 0.458 | 0.362 | 0.215 | 0.402 | 0.975 | 0.77 | 0.948 |
| HGNetv2-n [40] | 7.7 | 3.7 ms | 0.395 | 0.174 | 0.444 | 0.314 | 0.18 | 0.364 | 0.979 | 0.775 | 0.95 |
| LeYOLO-n [41] | 8.9 | 5.2 ms | 0.375 | 0.16 | 0.432 | 0.316 | 0.182 | 0.363 | 0.965 | 0.764 | 0.934 |
| Ours | 8.1 | 2.6 ms | 0.45 | 0.193 | 0.503 | 0.367 | 0.216 | 0.412 | 0.983 | 0.799 | 0.969 |
| GFLOPs | Detection Time | DOTA-v1.0 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mAP50 | mAP95 | F1 | |||
| Resnet50-m [37] | 9.1 | 2.7 ms | 0.394 | 0.237 | 0.471 |
| Resnet101-n [37] | 9.6 | 3.3 ms | 0.383 | 0.228 | 0.468 |
| MobileNetV3-m [24] | 8.4 | 3.3 ms | 0.396 | 0.234 | 0.476 |
| YOLOv8-n [38] | 8.1 | 1.9 ms | 0.426 | 0.261 | 0.498 |
| YOLOv10-n [39] | 8.4 | 2.0 ms | 0.405 | 0.245 | 0.472 |
| YOLO11-n [38] | 6.5 | 2.3 ms | 0.424 | 0.263 | 0.492 |
| FFCA-YOLO-n [8] | 10.3 | 3.4 ms | 0.435 | 0.262 | 0.507 |
| HGNetv2-n [40] | 7.7 | 3.7 ms | 0.402 | 0.238 | 0.477 |
| LeYOLO-n [41] | 8.9 | 5.2 ms | 0.366 | 0.214 | 0.446 |
| Ours | 8.1 | 2.6 ms | 0.443 | 0.271 | 0.515 |
| Dataset | Settings | mAP50 | mAP95 | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI-TOD | DCDBlock | 0.393 | 0.169 | 0.448 |
| DCDBlock-SE | 0.414 | 0.174 | 0.47 | |
| DCDBlock-HiDRA | 0.45 | 0.193 | 0.503 | |
| VisDrone | DCDBlock | 0.338 | 0.198 | 0.383 |
| DCDBlock-SE | 0.342 | 0.198 | 0.384 | |
| DCDBlock-HiDRA | 0.367 | 0.216 | 0.412 | |
| MAR20 | DCDBlock | 0.947 | 0.778 | 0.947 |
| DCDBlock-SE | 0.979 | 0.779 | 0.958 | |
| DCDBlock-HiDRA | 0.983 | 0.799 | 0.969 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Bai, Z.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, Y.; Bu, F.; Shao, Y. HiDRA-DCDNet: Dynamic Hierarchical Attention and Multi-Scale Context Fusion for Real-Time Remote Sensing Small-Target Detection. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17132195
Wang J, Bai Z, Zhang X, Qiu Y, Bu F, Shao Y. HiDRA-DCDNet: Dynamic Hierarchical Attention and Multi-Scale Context Fusion for Real-Time Remote Sensing Small-Target Detection. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(13):2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17132195
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jiale, Zhe Bai, Ximing Zhang, Yuehong Qiu, Fan Bu, and Yuancheng Shao. 2025. "HiDRA-DCDNet: Dynamic Hierarchical Attention and Multi-Scale Context Fusion for Real-Time Remote Sensing Small-Target Detection" Remote Sensing 17, no. 13: 2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17132195
APA StyleWang, J., Bai, Z., Zhang, X., Qiu, Y., Bu, F., & Shao, Y. (2025). HiDRA-DCDNet: Dynamic Hierarchical Attention and Multi-Scale Context Fusion for Real-Time Remote Sensing Small-Target Detection. Remote Sensing, 17(13), 2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17132195






