Brain-Inspired Synergistic Adversarial Framework for Style Transfer-Guided Semantic Segmentation in Cross-Domain Remote Sensing Imagery
Abstract
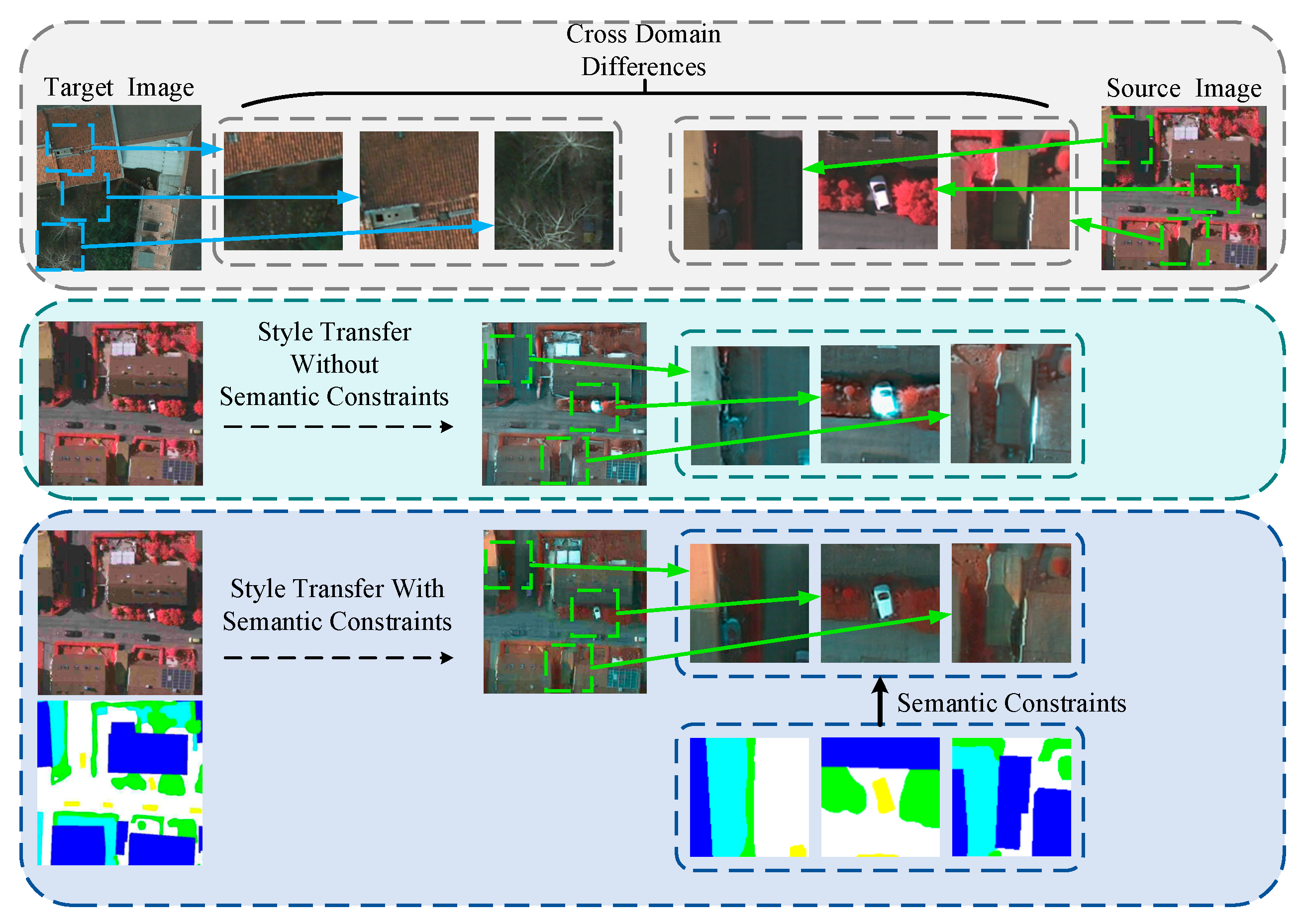
1. Introduction
- We propose a brain-inspired synergistic adversarial framework (SAF) that integrates style transfer and semantic segmentation into a unified learning process. This framework enhances domain generalization by jointly optimizing style alignment and semantic consistency.
- We propose a Semantic-Aware Style Transfer Network (STGAN) equipped with a lightweight Semantic-Aware Transformer Module (SATM), which mimics the brain’s top–down and bottom–up information flow to guide style transformation while preserving semantic structure.
- We introduce a Semantic-Driven Multi-Feature Memory Mechanism (SMM) and a Domain-Invariant Style-Semantic Space (DSCS), which collaboratively support the storage, retrieval, and alignment of semantic and style features across domains, enabling effective style adaptation and cross-domain feature synergy.
2. Related Work
2.1. Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Cross-Domain Semantic Segmentation
2.2. Style Transfer for Cross-Domain Adaptation
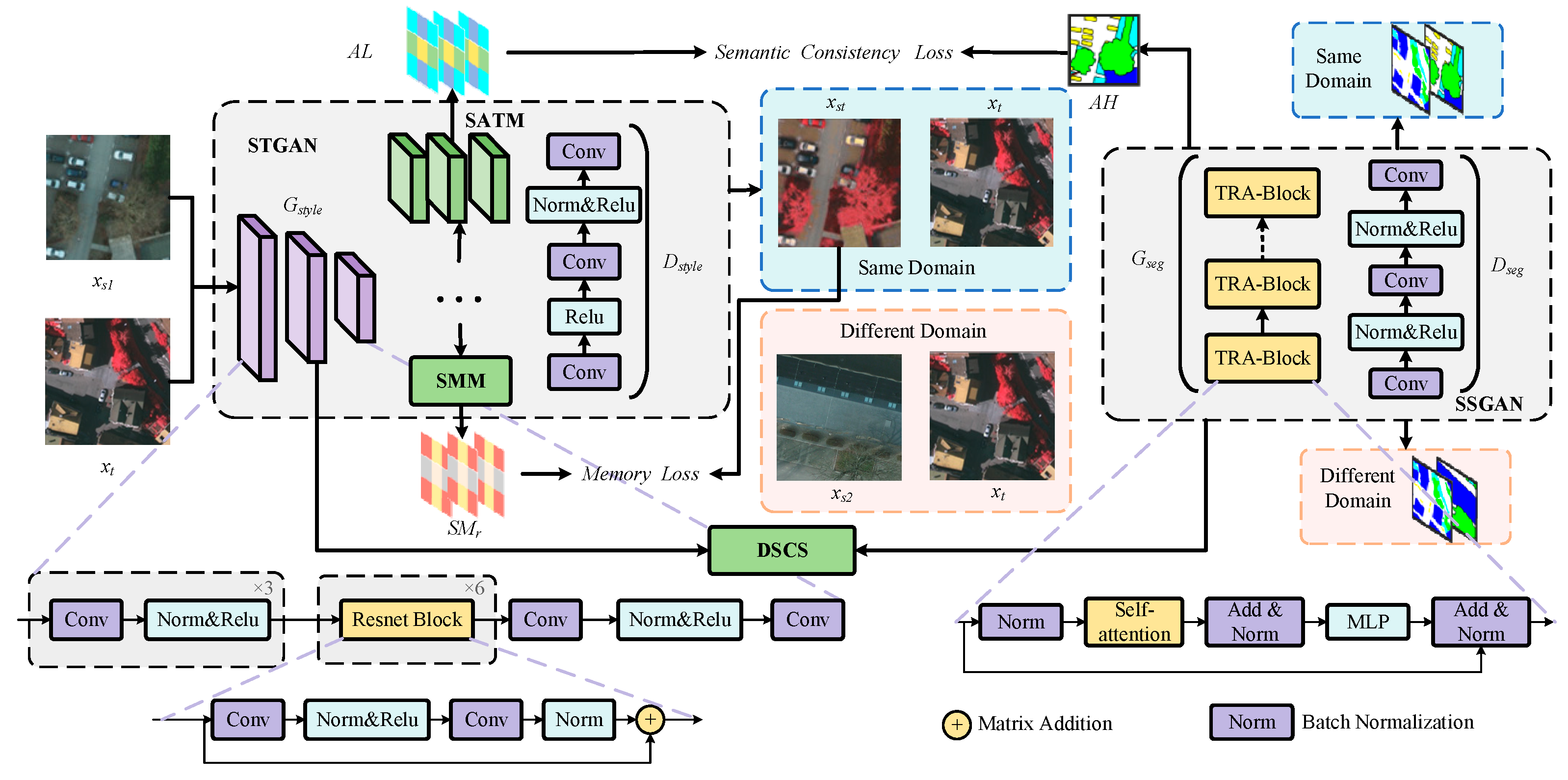
3. Methodology
3.1. Overview Framework
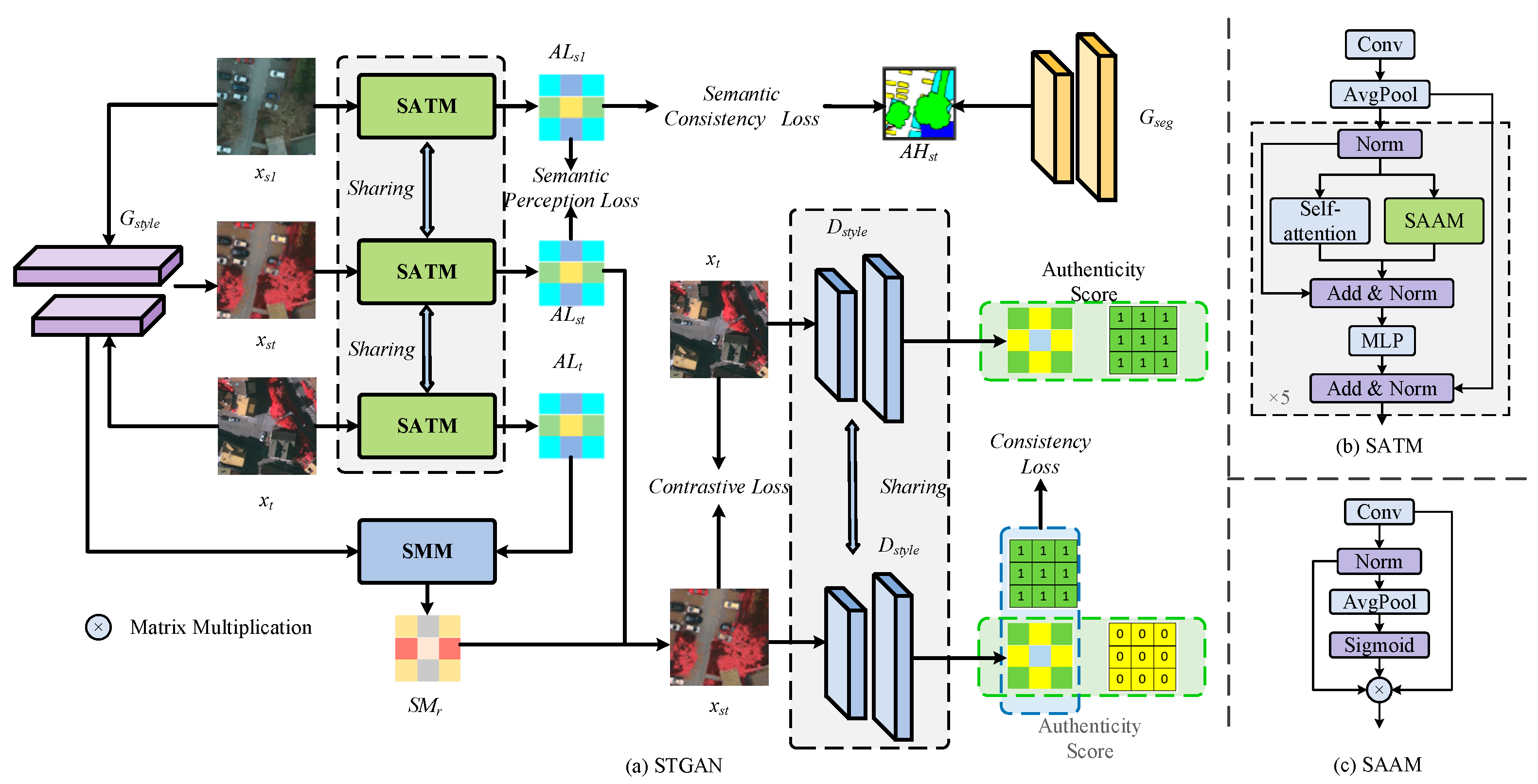
3.2. Style Transfer Generative Adversarial Network with Semantically Aware Modules
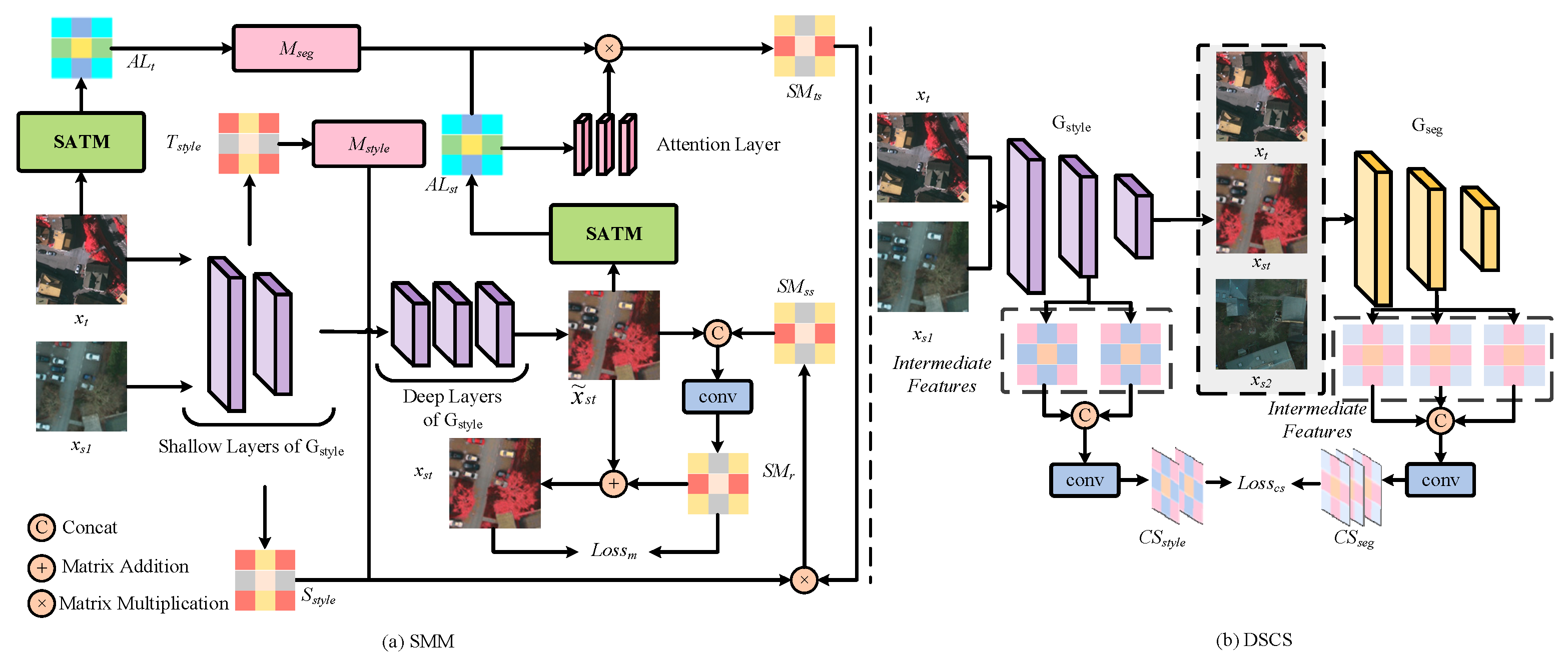
3.3. Semantic-Driven Multi-Feature Memory Module for Style Transfer
3.4. Domain-Invariant Style-Semantic Center Space
3.5. Overall Objective Function
- (1)
- Style Transfer GAN
- (2)
- Semantic Segmentation GAN
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Experimental Settings
- (1)
- Evaluation Metrics
- (2)
- Comparison Method
- (3)
- Implementation Details
- (4)
- Cross-Domain Task Setup
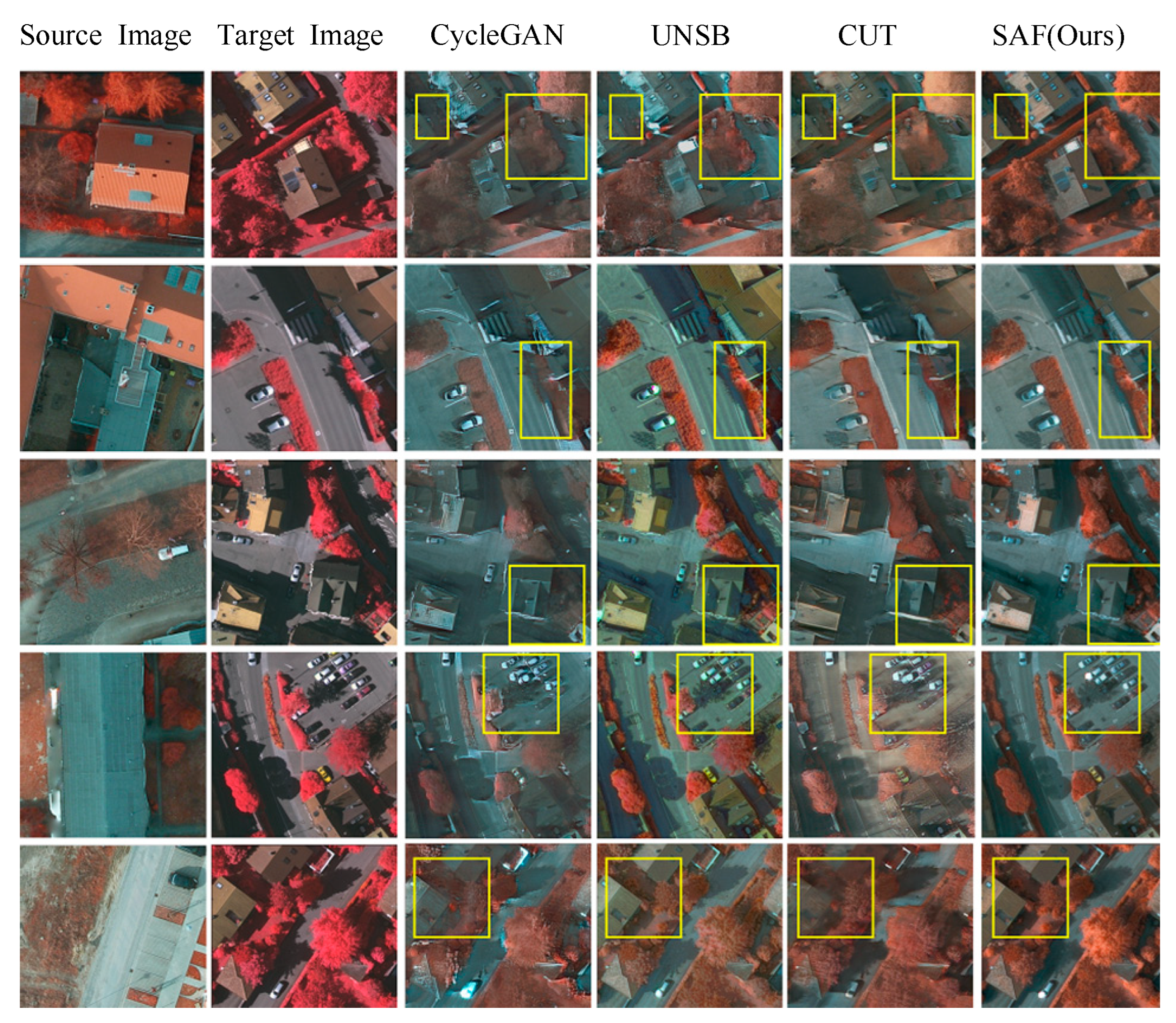
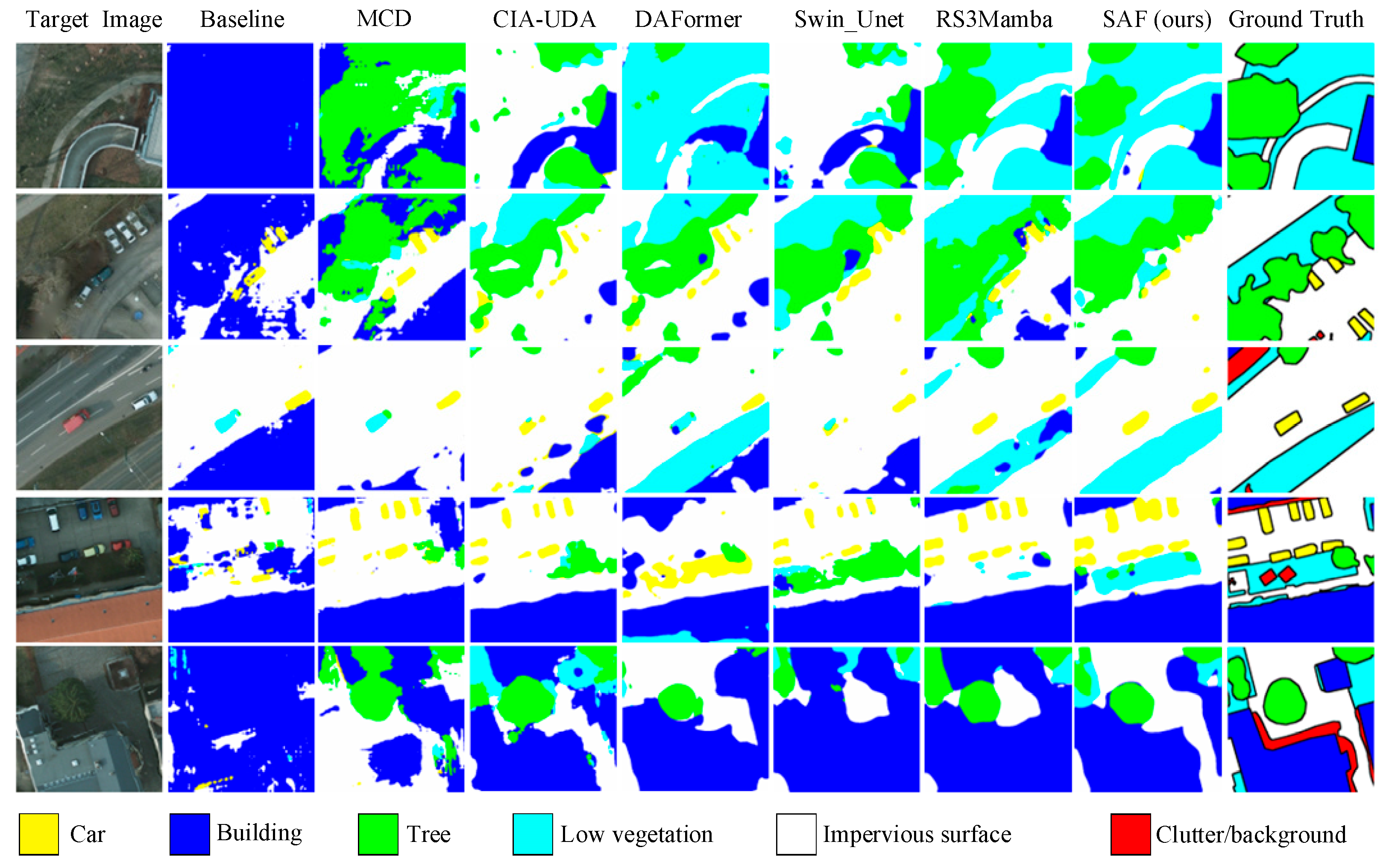
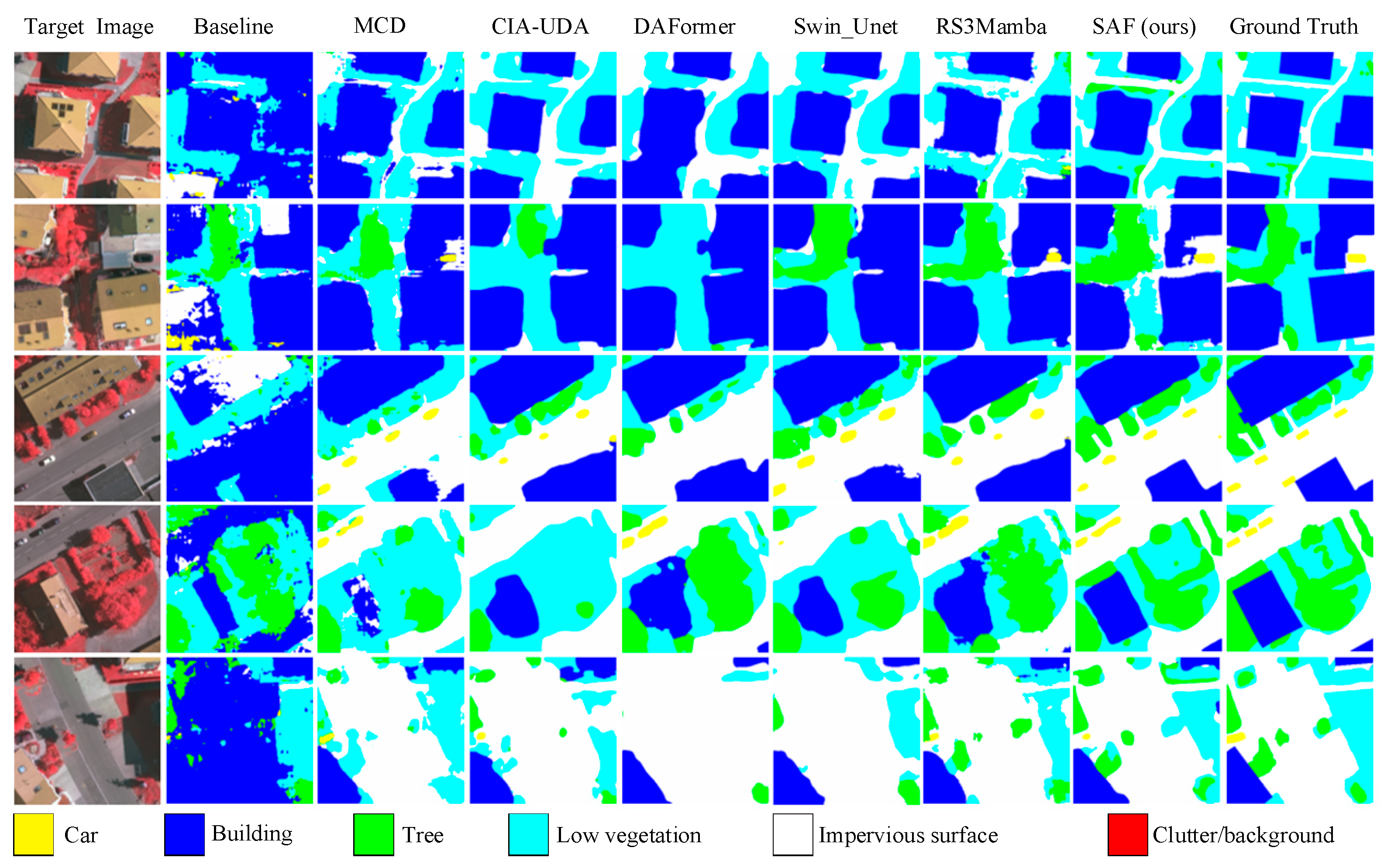
4.3. Cross-Domain Semantic Segmentation Task Between Vai and Potsdam Irrg
4.4. Cross-Domain Semantic Segmentation Task Between Potsdam Rgb and Vai
5. Discussion
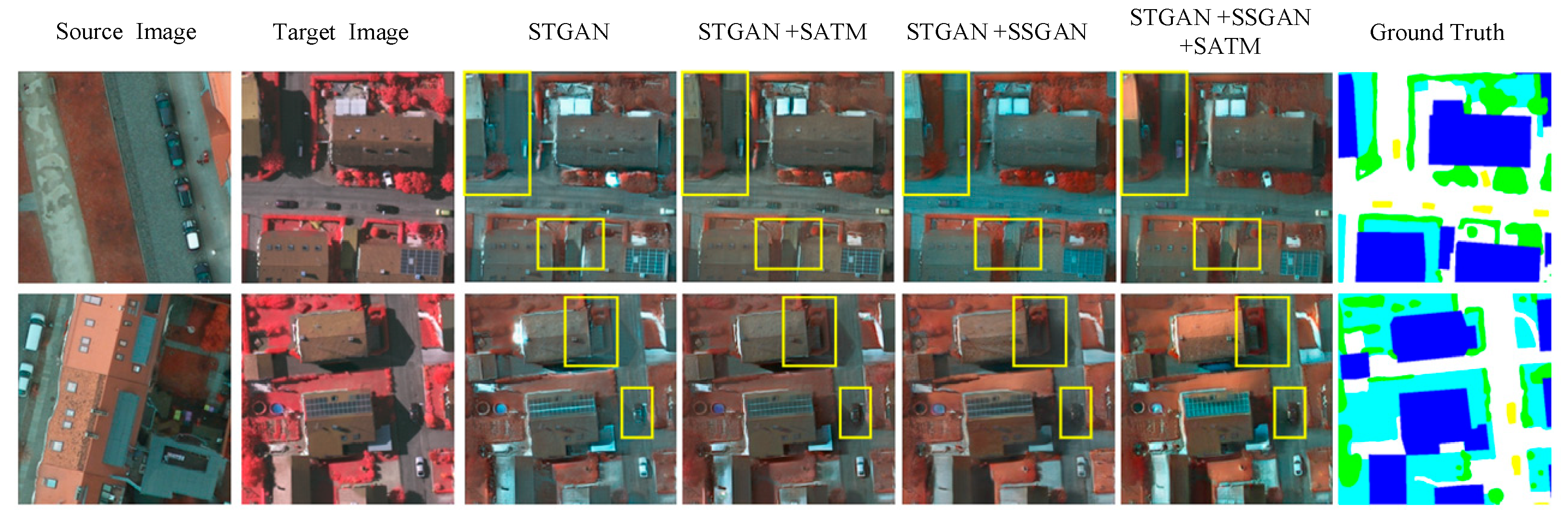
5.1. Ablation Study
5.2. Impact of Semantic Guidance on Style Transfer
5.3. Impact of Style Transfer on Semantic Segmentation
5.4. Cross-Domain Task Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, H.; Peng, M.; Zhong, Y.; Xie, H.; Hao, Z.; Lin, J.; Ma, X.; Hu, X. A Survey on Deep Learning-Based Change Detection from High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhu, D. Study of land cover classification based on knowledge rules using high-resolution remote sensing images. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 3647–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, F.; Liao, Y. Review the state-of-the-art technologies of semantic segmentation based on deep learning. Neurocomputing 2022, 493, 626–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, Z.; Zheng, G.; Yao, X. Semantic Segmentation of High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images with Improved U-Net Based on Transfer Learning. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2023, 16, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zheng, L.; Guan, T.; Yu, J.; Yang, Y. Taking a Closer Look at Domain Shift: Category-Level Adversaries for Semantics Consistent Domain Adaptation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 2502–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yoo, C.; Xing, F.; Oh, H.; El Fakhri, G.; Kang, J.W.; Woo, J. Deep Unsupervised Domain Adaptation: A Review of Recent Advances and Perspectives. APSIPA Trans. Signal Inf. Process. 2022, 11, e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganin, Y.; Lempitsky, V. Unsupervised Domain Adaptation by Backpropagation. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 7–9 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Guan, D.; Xiao, A.; Lu, S. Model Adaptation: Historical Contrastive Learning for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation without Source Data. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 3635–3649. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Guo, Y.; Sun, G.; Yang, L.; Deng, M.; Chen, J. Unsupervised domain adaptation semantic segmentation of high-resolution remote sensing imagery with invariant domain-level prototype memory. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5603518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-H.; Hung, W.-C.; Schulter, S.; Sohn, K.; Yang, M.-H.; Chandraker, M. Learning to adapt structured output space for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7472–7481. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Kim, D.; Feris, R.; Betke, M. CDAC: Cross-domain attention consistency in transformer for domain adaptive semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 11519–11529. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Q. A dual-channel network for cross-domain one-shot semantic segmentation via adversarial learning. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2023, 275, 110698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chen, H.; Ma, X.; Xie, C.; Xing, W.; Zhao, L.; Song, W. Image Style Transfer Algorithm Based on Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 54518–54529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettedgui, S.; Abu-Hussein, S.; Giryes, R.J.A. ProCST: Boosting Semantic Segmentation using Progressive Cyclic Style-Transfer. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.11891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Yang, Y.; Feng, Z.; Ye, J.; Yu, Y.; Song, M. Neural style transfer: A review. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2019, 26, 3365–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madokoro, H.; Takahashi, K.; Yamamoto, S.; Nix, S.; Chiyonobu, S.; Saruta, K.; Saito, T.K.; Nishimura, Y.; Sato, K. Semantic Segmentation of Agricultural Images Based on Style Transfer Using Conditional and Unconditional Generative Adversarial Networks. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, E.; Bala, R.; Price, B.; Susstrunk, S. Editing in Style: Uncovering the Local Semantics of GANs. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 5770–5779. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Yang, M. Semantic GAN: Application for Cross-Domain Image Style Transfer. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Shanghai, China, 8–12 July 2019; pp. 910–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Xia, F. Brain-inspired Artificial Intelligence: A Comprehensive Review. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.14811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.S.; Sumari, A.D.W. Cognitive artificial intelligence: Brain-inspired intelligent computation in artificial intelligence. In Proceedings of the 2017 Computing Conference (2017), London, UK, 18–20 July 2017; pp. 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Zhao, D.; Zhao, F.; Shen, G.; Dong, Y.; Lu, E.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Liang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; et al. BrainCog: A spiking neural network based, brain-inspired cognitive intelligence engine for brain-inspired AI and brain simulation. Patterns 2022, 4, 100789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Pang, X.; Hu, Y. Bio-inspired multi-level interactive contour detection network. Digit. Signal Process. 2023, 141, 104155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Howard, C.M.; Hovhannisyan, M.; Ritchey, M.; Cabeza, R.; Davis, S.W. Hippocampal Functions Modulate Transfer-Appropriate Cortical Representations Supporting Subsequent Memory. J. Neurosci. 2023, 44, e1135232023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, A.T.; Bzdok, D.; Langner, R.; Fox, P.T.; Laird, A.R.; Amunts, K.; Eickhoff, S.B.; Eickhoff, C.R. Multimodal connectivity mapping of the human left anterior and posterior lateral prefrontal cortex. Brain Struct. Funct. 2016, 221, 2589–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.; Kim, Y. Cross-Domain Semantic Segmentation on Inconsistent Taxonomy using VLMs. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2024. ECCV 2024; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Leonardis, A., Ricci, E., Roth, S., Russakovsky, O., Sattler, T., Varol, G., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; Volume 15123, pp. 18–35. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Feng, Z.; Gu, Q.; Cheng, G.; Lu, X.; Shi, J.; Ma, L. Uncertainty-Aware Consistency Regularization for Cross-Domain Semantic Segmentation. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2020, 221, 103448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shi, T.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, Z.; Li, H. Learning deep semantic segmentation network under multiple weakly-supervised constraints for cross-domain remote sensing image semantic segmentation. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 175, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; He, F.; Du, B.; Tao, D.; Zhang, L. Self-Ensembling GAN for Cross-Domain Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2023, 25, 7837–7850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Todorovic, S. Attention Decomposition for Cross-Domain Semantic Segmentation. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2024. ECCV 2024; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Leonardis, A., Ricci, E., Roth, S., Russakovsky, O., Sattler, T., Varol, G., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; Volume 15072, pp. 414–431. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.; Chen, W.; Liang, Z.; Yang, L.; Wang, S.; Li, C. Crots: Cross-Domain Teacher–Student Learning for Source-Free Domain Adaptive Semantic Segmentation. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2024, 132, 20–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, W.; Ren, M.; Zhang, H. Unsupervised cross domain semantic segmentation with mutual refinement and information distillation. Neurocomputing 2024, 586, 127641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, W. Inter-Class and Inter-Domain Semantic Augmentation for Domain Generalization. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2024, 33, 1338–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Lyu, S.; Zhao, H.; Liu, B.; Chen, L.; Cheng, G. Self-training guided disentangled adaptation for cross-domain remote sensing image semantic segmentation. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 127, 103646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Liu, Q.; Guan, H.; Tang, H.; Chanussot, J. Category-level assignment for cross-domain semantic segmentation in remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5608416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shi, T.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, J. SPGAN-DA: Semantic-preserved generative adversarial network for domain adaptive remote sensing image semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5406717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psychogyios, K.; Leligou, H.C.; Melissari, F.; Bourou, S.; Anastasakis, Z.; Zahariadis, T. SAMStyler: Enhancing Visual Creativity with Neural Style Transfer and Segment Anything Model (SAM). IEEE Access 2023, 11, 100256–100267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Liu, C.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhou, H. Multi-style transfer and fusion of image’s regions based on attention mechanism and instance segmentation. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2023, 110, 116871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Tian, Y. Shape robustness in style enhanced cross domain semantic segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 135, 109143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toldo, M.; Michieli, U.; Zanuttigh, P. Learning with Style: Continual Semantic Segmentation Across Tasks and Domains. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 46, 7434–7450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Roy, S.; Zhou, H.; Lu, H.; Lathuilière, S. Contrast, Stylize and Adapt: Unsupervised Contrastive Learning Framework for Domain Adaptive Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 4869–4879. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Sun, P.; Li, J.; Zhang, A.; Liu, W.; Jiang, N. AdvST: Generating Unrestricted Adversarial Images via Style Transfer. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2024, 26, 4846–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Jing, Y.; Yang, X.; Chu, J. A Bio-Inspired Visual Perception Transformer for Cross-Domain Semantic Segmentation of High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heusel, M.; Ramsauer, H.; Unterthiner, T.; Nessler, B.; Klambauer, G.; Hochreiter, S. GANs Trained by a Two Time-Scale Update Rule Converge to a Nash Equilibrium. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30: Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2017, December 4–9, 2017, Long Beach, CA, USA; Neural Information Processing Systems Foundation, Inc. (NeurIPS): La Jolla, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, L.; Fan, B.; Liu, H.; Huo, C.; Xiang, S.; Pan, C. Triplet Adversarial Domain Adaptation for Pixel-Level Classification of VHR Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 3558–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Watanabe, K.; Ushiku, Y.; Harada, T. Maximum Classifier Discrepancy for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 3723–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Guo, P.; Sun, Z.; Chen, X.; Gao, H. ResiDualGAN: Resize-Residual DualGAN for Cross-Domain Remote Sensing Images Semantic Segmentation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyer, L.; Dai, D.; Gool, L.V. DAFormer: Improving Network Architectures and Training Strategies for Domain-Adaptive Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 9914–9925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Q.; Wang, M. Swin-Unet: Unet-like Pure Transformer for Medical Image Segmentation. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 205–218. [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer, L.; Dai, D.; Van Gool, L. HRDA: Context-Aware High-Resolution Domain-Adaptive Semantic Segmentation. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2022. ECCV 2022; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 13690. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, X.; Pun, M. RS3Mamba: Visual State Space Model for Remote Sensing Image Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 6011405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Tian, X.; Zhang, F.; Wen, X.; Gao, Z.; Chen, S. CACP: Covariance-Aware Cross-Domain Prototypes for Domain Adaptive Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2025, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Liang, Z.; Wang, L.; Tian, G.; Long, Q. Unsupervised domain adaptation segmentation algorithm with cross-domain data augmentation and category contrast. Neurocomputing 2025, 623, 129393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Xie, L.; Lin, J.; Zhang, S. Exploring Semantic Consistency and Style Diversity for Domain Generalized Semantic Segmentation. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2025, 39, 6245–6253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.-Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation Using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2242–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.; Efros, A.A.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, J.-Y. Contrastive Learning for Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2020. ECCV 2020; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 12354. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.; Kwon, G.; Kim, K.; Ye, J.-C. Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation via Neural Schrödinger Bridge. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.15086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Method | Car | Building | Tree | Low Veg | Surface | Average Results | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IoU | F1 | IoU | F1 | IoU | F1 | IoU | F1 | IoU | F1 | mIoU | mF1 | |
| Baseline | 40.1 | 52.5 | 44.3 | 53.1 | 20.9 | 44.6 | 29.5 | 46.2 | 40.8 | 60.2 | 35.1 | 51.3 |
| MCD | 41.4 | 55.1 | 42.8 | 50.3 | 35.6 | 56.2 | 43.7 | 58.2 | 53.7 | 66.7 | 43.4 | 57.7 |
| TriADA | 59.9 | 69.1 | 71.5 | 81.2 | 48.6 | 66.8 | 57.9 | 72.1 | 68.3 | 81.9 | 61.2 | 74.2 |
| ResiDualGAN | 58.7 | 68.5 | 72.9 | 82.9 | 46.9 | 65.1 | 53.2 | 67.9 | 61.7 | 77.1 | 58.7 | 72.3 |
| CIA-UDA | 57.5 | 67.6 | 71.3 | 82.8 | 47.6 | 66.2 | 55.3 | 68.0 | 65.1 | 78.5 | 59.4 | 72.6 |
| DAFormer | 58.6 | 69.9 | 71.2 | 82.5 | 47.4 | 66.3 | 56.6 | 69.9 | 67.1 | 81.7 | 60.2 | 74.1 |
| Swin_Unet | 57.1 | 70.6 | 70.6 | 81.3 | 46.0 | 64.8 | 53.6 | 67.8 | 63.2 | 78.1 | 58.1 | 72.5 |
| HRDA | 55.8 | 64.3 | 72.4 | 83.5 | 49.1 | 67.5 | 52.1 | 66.4 | 64.8 | 78.9 | 58.8 | 72.1 |
| RS3Mamba | 59.5 | 69.4 | 72.7 | 81.6 | 48.9 | 67.4 | 54.9 | 68.3 | 66.7 | 80.5 | 60.5 | 73.4 |
| CACP | 58.2 | 68.7 | 71.9 | 82.0 | 47.2 | 65.5 | 55.8 | 68.6 | 65.5 | 79.7 | 59.7 | 72.9 |
| CSI | 56.1 | 66.3 | 70.2 | 81.5 | 46.7 | 65.0 | 54.5 | 67.1 | 64.2 | 78.6 | 58.3 | 71.7 |
| CACC | 57.6 | 68.0 | 71.0 | 82.2 | 47.5 | 66.0 | 57.0 | 70.0 | 68.1 | 80.3 | 60.2 | 73.3 |
| DGSS | 58.9 | 69.2 | 71.6 | 82.7 | 48.0 | 66.5 | 56.2 | 69.0 | 66.2 | 80.0 | 60.2 | 73.5 |
| SAF (ours) | 61.4 | 72.5 | 73.5 | 83.9 | 50.5 | 68.7 | 58.3 | 72.2 | 71.9 | 82.5 | 63.1 | 75.9 |
| Method | Vaihingen IRRG →Potsdam IRRG | Potsdam IRRG →Vaihingen IRRG | Vaihingen IRRG →Potsdam RGB | Potsdam RGB →Vaihingen IRRG |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CycleGAN | 121.5 | 135.1 | 118.9 | 134.6 |
| CUT | 70.9 | 75.6 | 68.8 | 88.1 |
| UNSB | 79.2 | 86.1 | 75.4 | 76.8 |
| SAF (ours) | 62.1 | 69.7 | 62.7 | 61.9 |
| Method | Car | Building | Tree | Low Veg | Surface | Average Results | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IoU | F1 | IoU | F1 | IoU | F1 | IoU | F1 | IoU | F1 | mIoU | mF1 | |
| Baseline | 8.5 | 25.8 | 41.9 | 50.5 | 36.2 | 50.0 | 24.6 | 47.1 | 26.5 | 34.3 | 27.5 | 41.5 |
| MCD | 17.1 | 35.6 | 57.4 | 70.2 | 47.5 | 68.8 | 32.7 | 49.9 | 58.5 | 72.6 | 42.6 | 59.4 |
| TriADA | 27.1 | 41.5 | 74.1 | 81.6 | 54.8 | 72.3 | 40.2 | 59.7 | 65.2 | 77.9 | 52.3 | 66.6 |
| ResiDualGAN | 28.3 | 43.0 | 73.9 | 81.2 | 54.6 | 71.9 | 41.5 | 58.8 | 64.8 | 76.8 | 52.6 | 66.3 |
| CIA-UDA | 29.8 | 44.9 | 74.6 | 82.0 | 55.1 | 71.5 | 41.3 | 58.4 | 65.9 | 78.1 | 53.3 | 66.9 |
| DAFormer | 29.5 | 44.6 | 74.2 | 81.5 | 55.3 | 72.1 | 42.4 | 59.0 | 63.7 | 75.2 | 53.0 | 66.5 |
| Swin_Unet | 28.4 | 43.8 | 70.6 | 81.4 | 53.1 | 70.7 | 36.3 | 57.8 | 64.1 | 75.5 | 50.5 | 65.8 |
| HRDA | 30.2 | 45.7 | 74.5 | 82.4 | 56.7 | 73.4 | 43.8 | 59.1 | 62.3 | 74.4 | 53.5 | 67.0 |
| RS3Mamba | 30.5 | 45.8 | 73.0 | 81.1 | 56.0 | 72.5 | 42.9 | 58.5 | 65.8 | 77.4 | 53.6 | 67.1 |
| CACP | 29.0 | 44.0 | 73.3 | 81.7 | 54.2 | 71.2 | 41.8 | 58.6 | 64.5 | 76.5 | 52.6 | 66.4 |
| CSI | 28.7 | 43.5 | 72.5 | 81.2 | 53.6 | 70.5 | 41.0 | 57.5 | 63.9 | 75.8 | 51.9 | 65.7 |
| CACC | 30.2 | 44.3 | 73.8 | 81.9 | 54.7 | 71.6 | 42.2 | 58.9 | 65.0 | 76.9 | 53.2 | 66.7 |
| DGSS | 29.6 | 44.7 | 74.0 | 82.0 | 55.0 | 71.9 | 42.5 | 59.2 | 65.4 | 77.3 | 53.3 | 67.0 |
| SAF (ours) | 31.8 | 46.8 | 75.2 | 83.9 | 57.9 | 74.8 | 44.5 | 60.8 | 66.6 | 79.4 | 55.2 | 69.1 |
| Task | STGAN | SATM | SMM | DSCS | SSGAN | FID | mIoU | mF1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vaihingen IR-R-G ↓ Potsdam IR-R-G | √ | / | 52.1 | 62.8 | ||||
| √ | 115.8 | / | / | |||||
| √ | √ | 80.6 | 59.4 | 72.3 | ||||
| √ | √ | √ | 70.4 | 61.2 | 73.4 | |||
| √ | √ | √ | √ | 65.3 | 62.7 | 74.6 | ||
| √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 62.1 | 63.1 | 75.9 | |
| Potsdam R-G-B ↓ Vaihingen IR-R-G | √ | / | 43.5 | 58.0 | ||||
| √ | 110.5 | / | / | |||||
| √ | √ | 77.2 | 51.3 | 65.2 | ||||
| √ | √ | √ | 71.8 | 52.4 | 67.1 | |||
| √ | √ | √ | √ | 64.9 | 53.9 | 68.5 | ||
| √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 61.9 | 55.2 | 69.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Jing, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, X. Brain-Inspired Synergistic Adversarial Framework for Style Transfer-Guided Semantic Segmentation in Cross-Domain Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17111834
Wang X, Wang H, Jing Y, Li X, Yang X. Brain-Inspired Synergistic Adversarial Framework for Style Transfer-Guided Semantic Segmentation in Cross-Domain Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(11):1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17111834
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xinyao, Haitao Wang, Yuqian Jing, Xiaodong Li, and Xianming Yang. 2025. "Brain-Inspired Synergistic Adversarial Framework for Style Transfer-Guided Semantic Segmentation in Cross-Domain Remote Sensing Imagery" Remote Sensing 17, no. 11: 1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17111834
APA StyleWang, X., Wang, H., Jing, Y., Li, X., & Yang, X. (2025). Brain-Inspired Synergistic Adversarial Framework for Style Transfer-Guided Semantic Segmentation in Cross-Domain Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sensing, 17(11), 1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17111834







