Quantifying Time-Lag and Time-Accumulation Effects of Climate Change and Human Activities on Vegetation Dynamics in the Yarlung Zangbo River Basin of the Tibetan Plateau
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
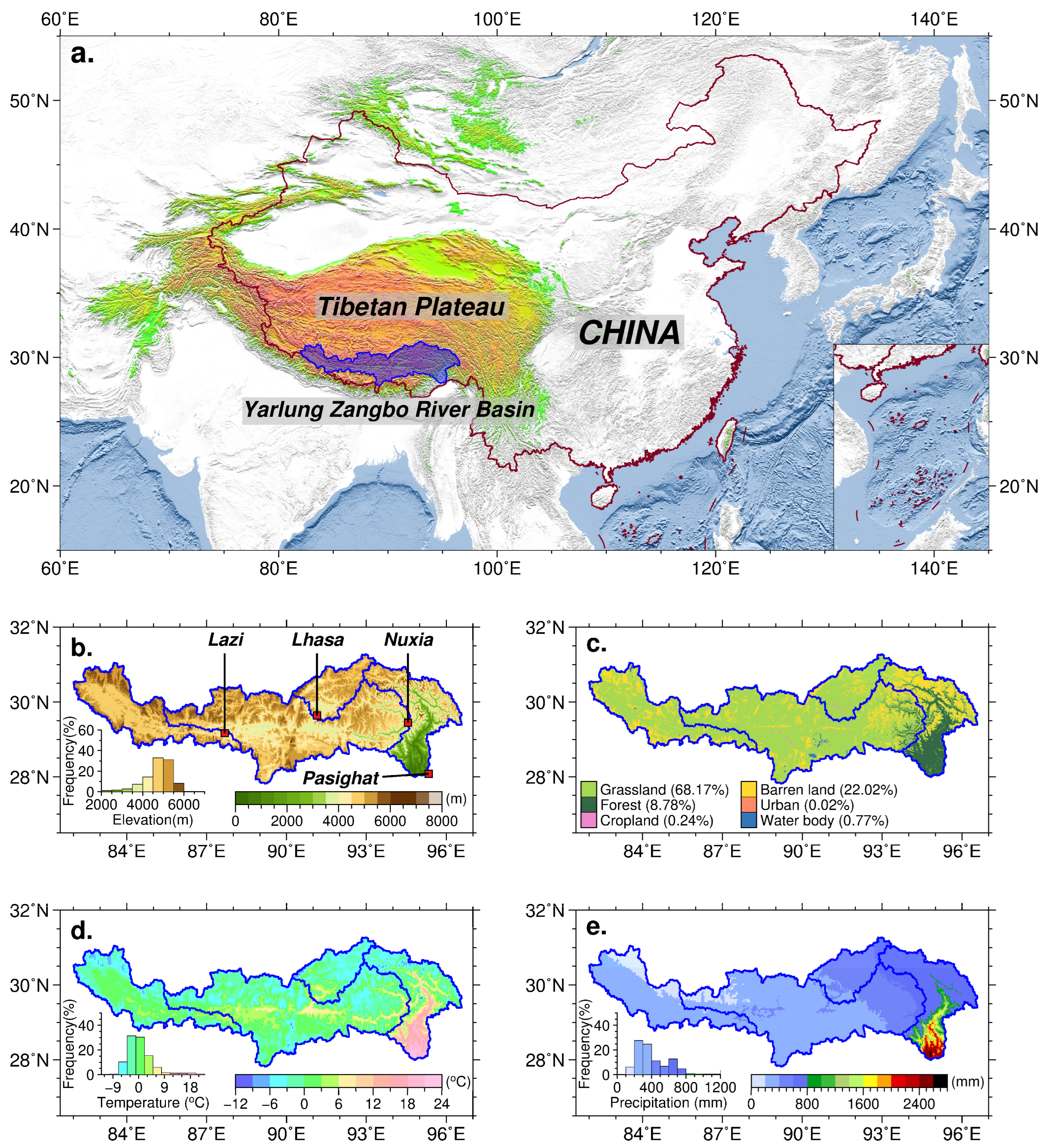
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Datasets
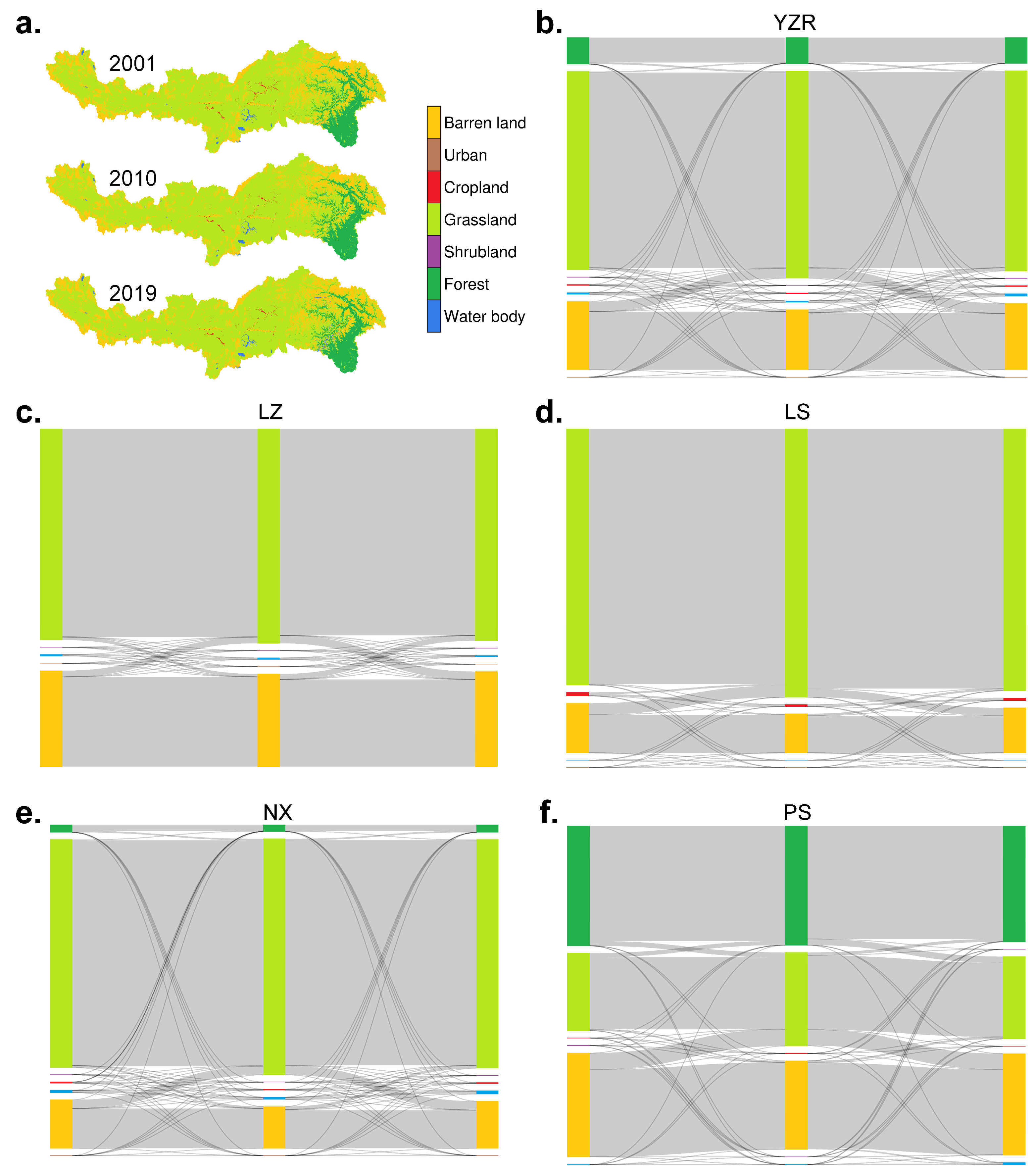
2.2.1. Vegetation Datasets
2.2.2. Meteorological Datasets
2.2.3. Data Preprocessing
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Analysis of Temporal Trend
2.3.2. Analysis of Temporal Effects of Climatic Factors on Vegetation Dynamics
2.3.3. Residual Trend Analysis
3. Results
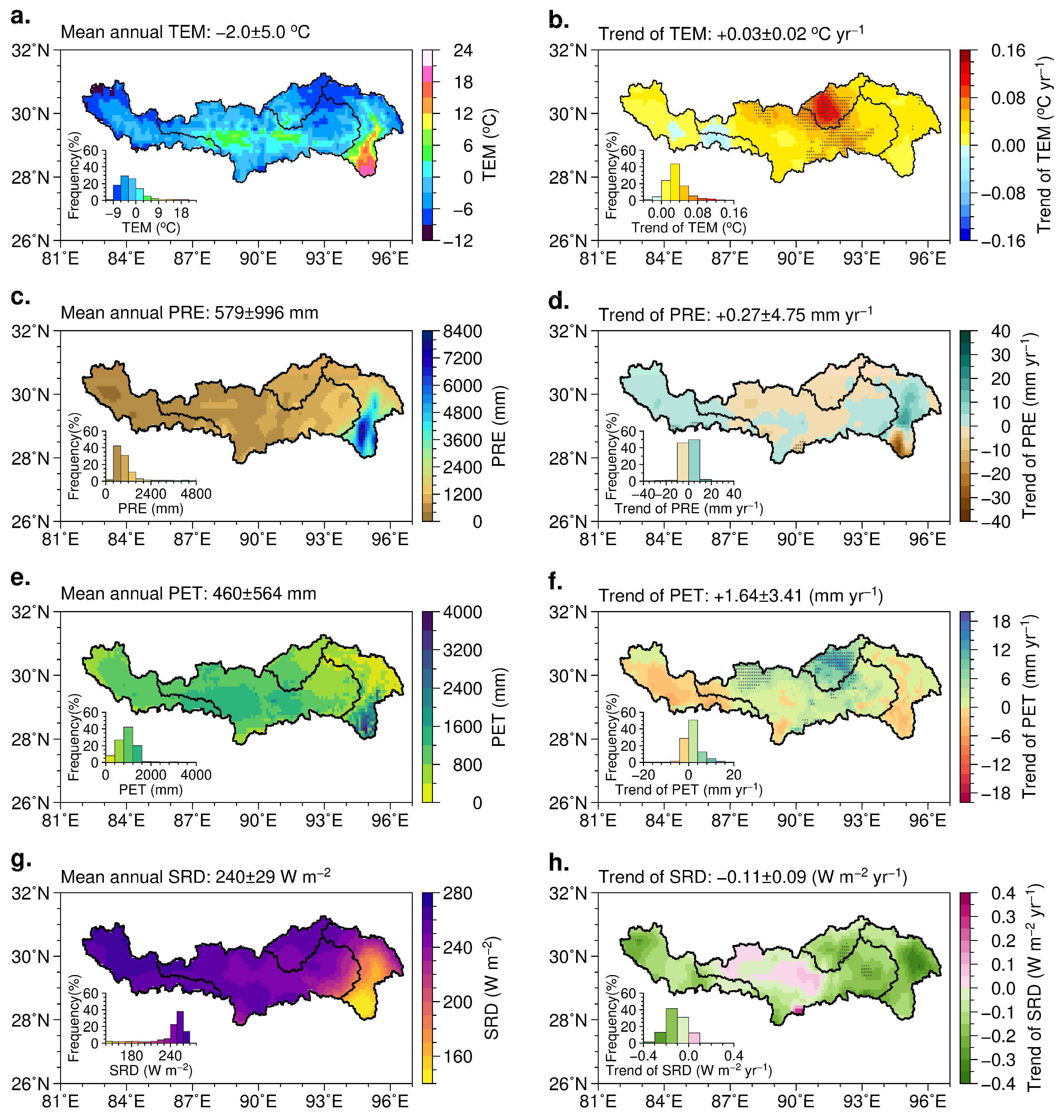
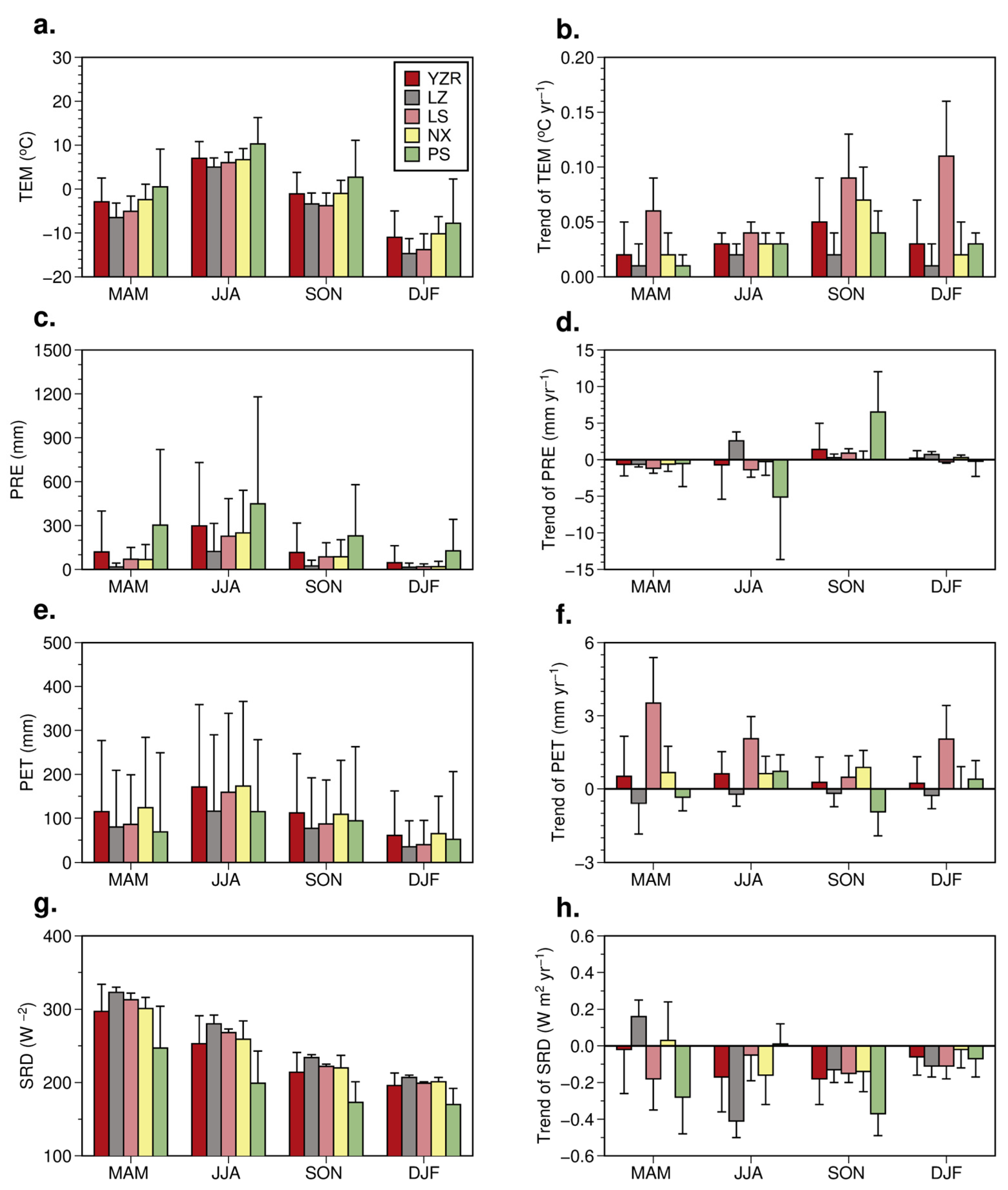
3.1. Spatiotemporal Variability of Climate Factors
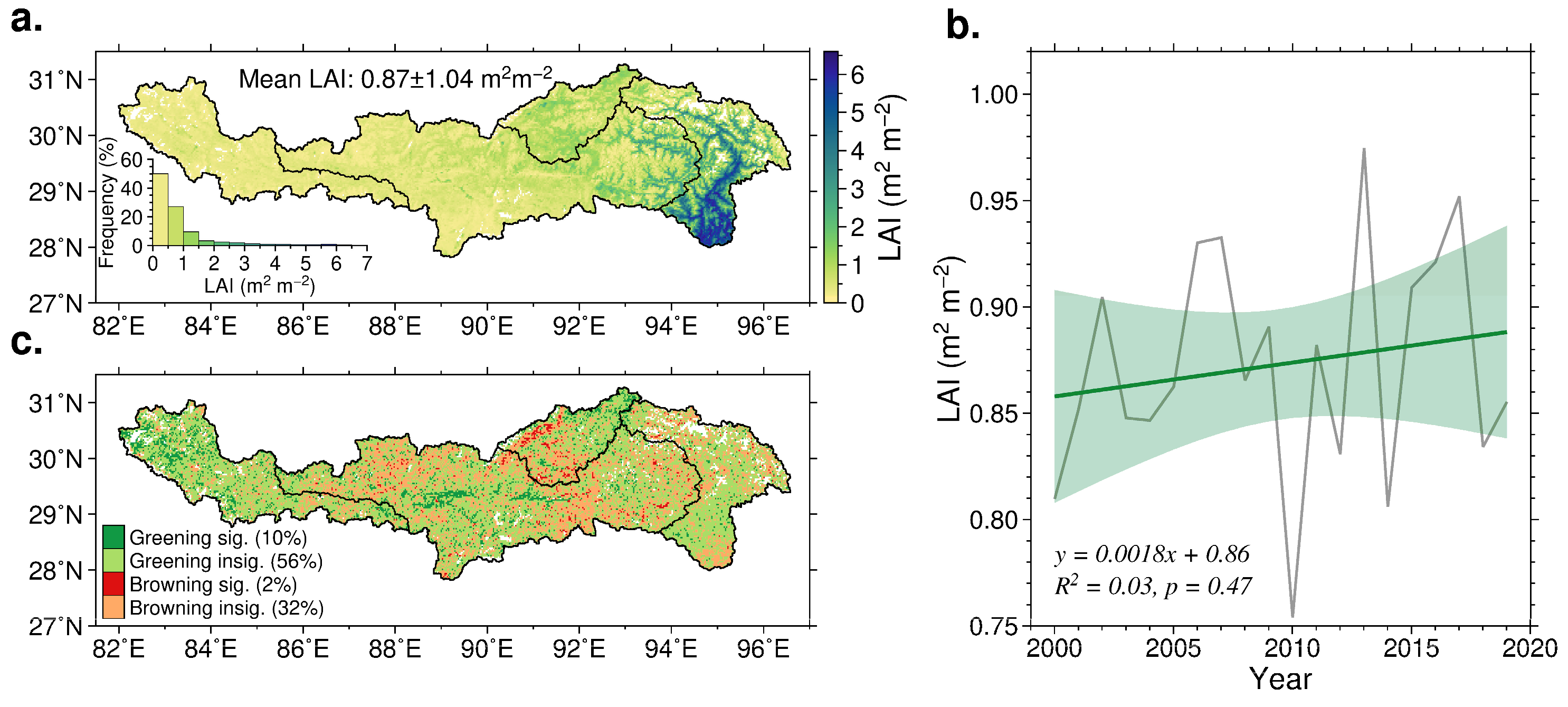
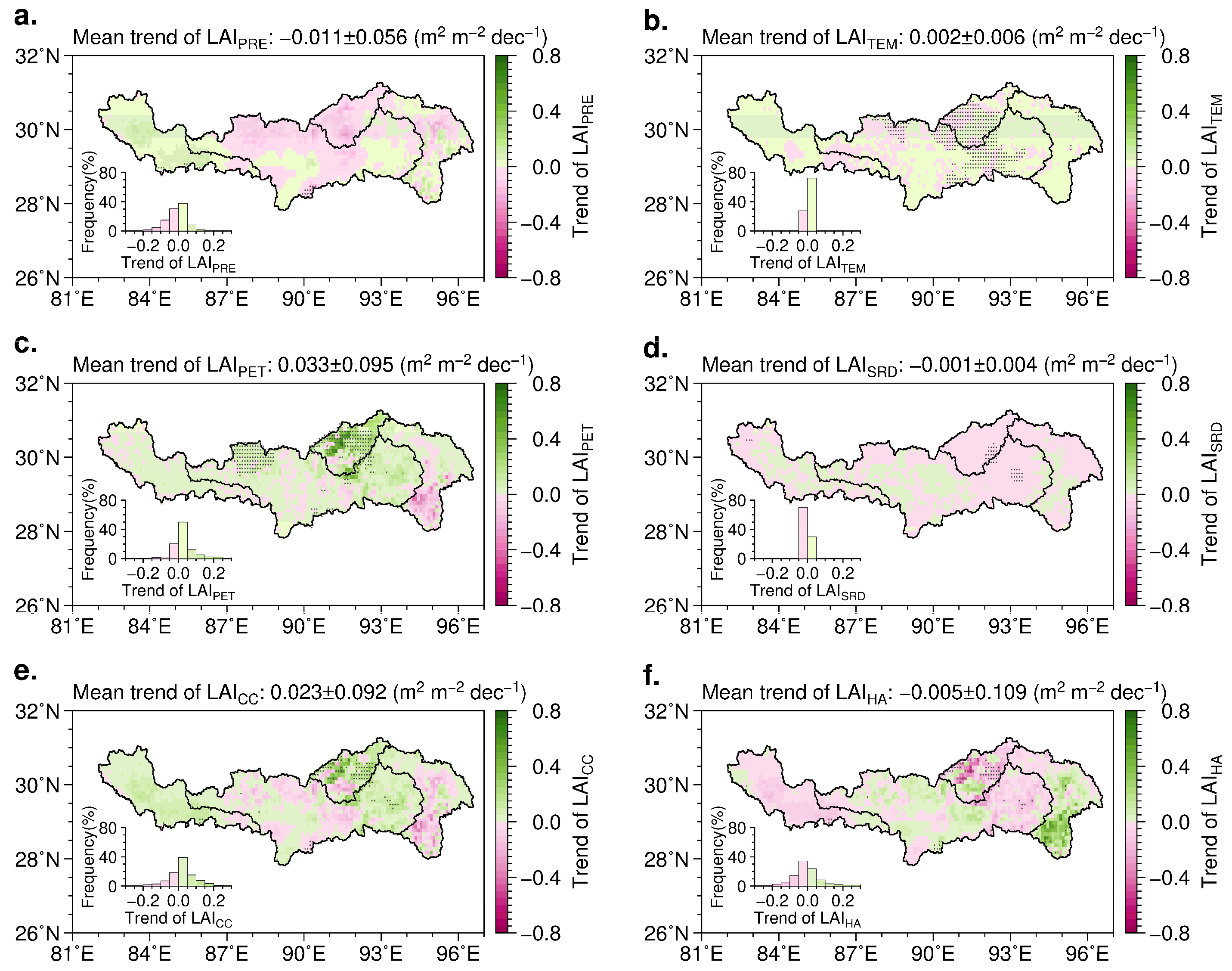
3.2. Vegetation Change
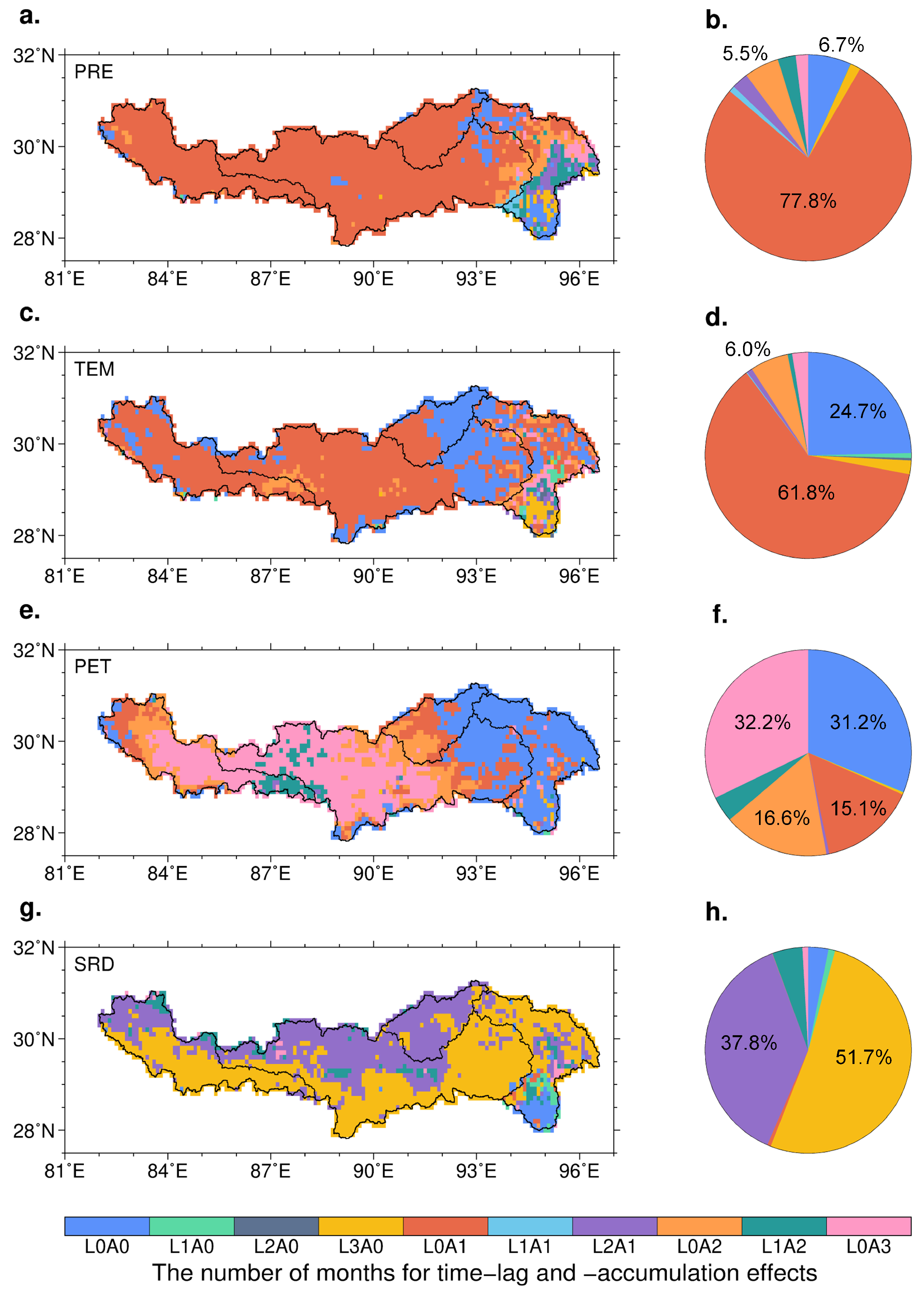
3.3. Temporal Inflences of Climatic Factors on LAI Variability
3.4. Relative Contributions of Climate Change and Human Activities to Vegetation Change
4. Discussion
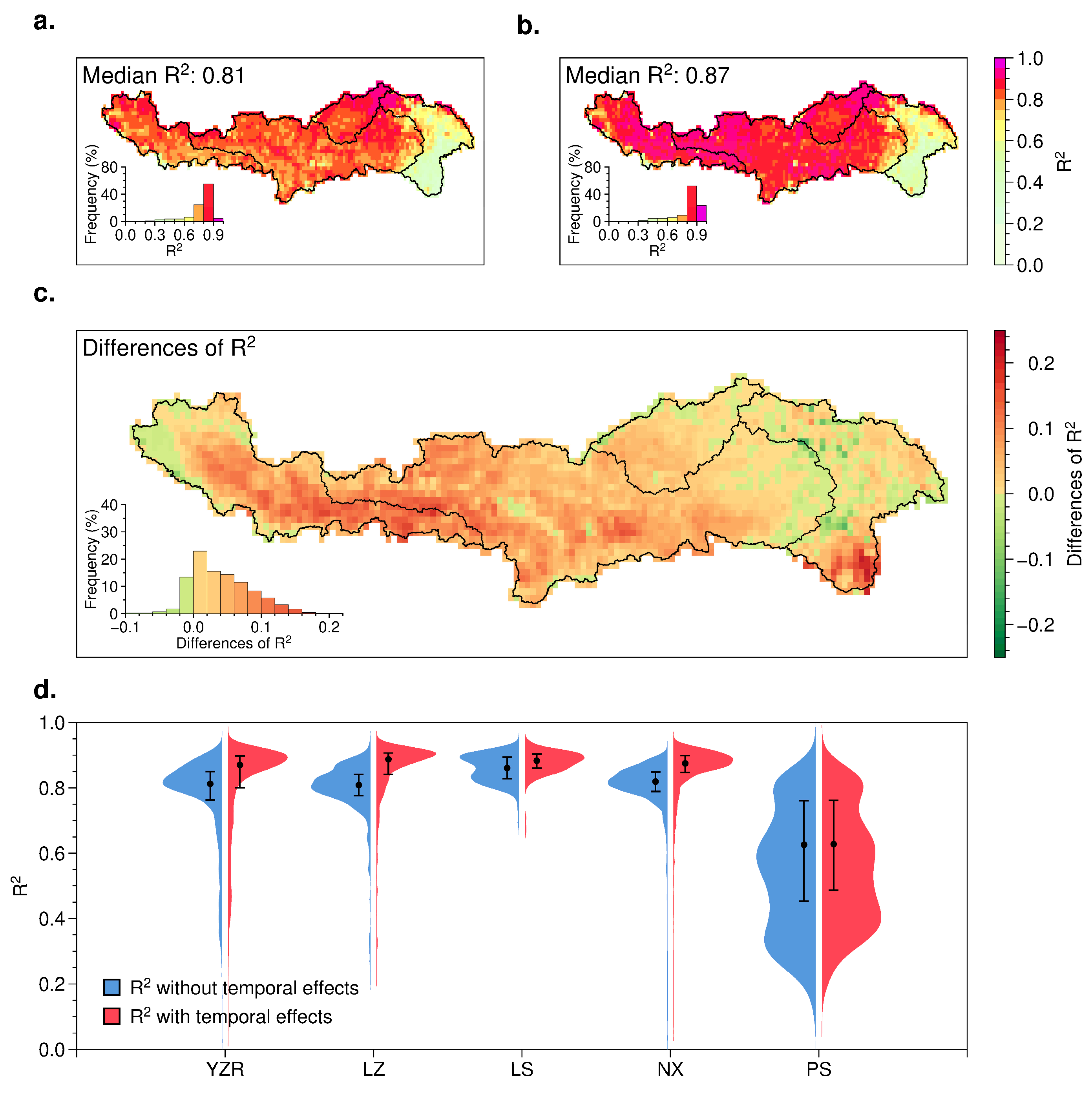
4.1. Advancements in the Enhanced Residual Trend Analysis
4.2. Impacts of Climate Change on Vegetation Dynamics
4.3. Impacts of Human Activities on Vegetation Dynamics
4.4. Limitations and Future Prospects
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abera, T.A.; Heiskanen, J.; Pellikka, P.; Rautiainen, M.; Maeda, E.E. Clarifying the role of radiative mechanisms in the spatio-temporal changes of land surface temperature across the Horn of Africa. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 221, 210–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bright, R.M.; Davin, E.; O’Halloran, T.; Pongratz, J.; Zhao, K.; Cescatti, A. Local temperature response to land cover and management change driven by non-radiative processes. Nat. Clim. Change 2017, 7, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.Z.; Piao, S.L.; Li, L.Z.X.; Zhou, L.M.; Ciais, P.; Wang, T.; Li, Y.; Lian, X.; Wood, E.F.; Friedlingstein, P.; et al. Climate mitigation from vegetation biophysical feedbacks during the past three decades. Nat. Clim. Change 2017, 7, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Park, T.; Wang, X.H.; Piao, S.L.; Xu, B.D.; Chaturvedi, R.K.; Fuchs, R.; Brovkin, V.; Ciais, P.; Fensholt, R.; et al. China and India lead in greening of the world through land-use management. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Wang, X.; Park, T.; Chen, C.; Lian, X.; He, Y.; Bjerke, J.W.; Chen, A.; Ciais, P.; Tommervik, H.; et al. Characteristics, drivers and feedbacks of global greening. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.C.; Piao, S.L.; Myneni, R.B.; Huang, M.T.; Zeng, Z.Z.; Canadell, J.G.; Ciais, P.; Sitch, S.; Friedlingstein, P.; Arneth, A.; et al. Greening of the Earth and its drivers. Nat. Clim. Change 2016, 6, 791–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Odorico, P.; Caylor, K.; Okin, G.S.; Scanlon, T.M. On soil moisture-vegetation feedbacks and their possible effects on the dynamics of dryland ecosystems. J. Geophys. Res.-Biogeosci. 2007, 112, G04010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Piao, S.; Li, L.Z.; Chen, A.; Wang, X.; Ciais, P.; Huang, L.; Lian, X.; Peng, S.; Zeng, Z. Divergent hydrological response to large-scale afforestation and vegetation greening in China. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Peng, L.; Piao, S. Response of terrestrial evapotranspiration to Earth’s greening. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2018, 33, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Roderick, M.L.; Guo, H.; Miralles, D.G.; Zhang, L.; Fatichi, S.; Luo, X.; Zhang, Y.; McVicar, T.R.; Tu, Z. Evapotranspiration on a greening Earth. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 626–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, S.; Bai, X.; Luo, G.; Wu, L.; Chen, F.; Wang, J.; Li, C.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Z.; et al. Vegetation greening intensified soil drying in some semi-arid and arid areas of the world. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 292–293, 108103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Harper, R.J.; Smettem, K.R.J.; Dell, B.; Liu, S. Responses of streamflow to vegetation and climate change in southwestern Australia. J. Hydrol. 2019, 572, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, L.; Chen, D. Vegetation greening amplifies shallow soil temperature warming on the Tibetan Plateau. Npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2024, 7, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, G.; Chen, D.; Wang, X.; Lai, H.-W. Spatiotemporal variations of land surface albedo and associated influencing factors on the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 804, 150100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J. Decreased surface albedo driven by denser vegetation on the Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 104001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.B.; Whittaker, R.J.; Malhi, Y. ET come home: Potential evapotranspiration in geographical ecology. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2011, 20, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, B.; Li, H.; Zhai, J. Spatio-temporal variation of potential evapotranspiration and climatic drivers in the Jing-Jin-Ji region, North China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 256, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Iturbe, I.; D’odorico, P.; Porporato, A.; Ridolfi, L. On the spatial and temporal links between vegetation, climate, and soil moisture. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 3709–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, F.; Lomas, M. Vegetation dynamics–simulating responses to climatic change. Biol. Rev. 2004, 79, 643–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Li, Z.; Peng, S. Global analysis of time-lag and -accumulation effects of climate on vegetation growth. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 92, 102179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyakov, Y.; Gavrichkova, O. Time lag between photosynthesis and carbon dioxide efflux from soil: A review of mechanisms and controls. Glob. Change Biol. 2010, 16, 3386–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Wang, Q.; Liu, R.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, D. Effects of climate change and human activities on vegetation coverage change in northern China considering extreme climate and time-lag and -accumulation effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 860, 160527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Liu, X.; Pei, F.; Li, X.; Du, G. Non-uniform time-lag effects of terrestrial vegetation responses to asymmetric warming. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 252, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Qian, K.; Yang, X.; Ma, X. Evaluating the cumulative and time-lag effects of vegetation response to drought in Central Asia under changing environments. J. Hydrol. 2023, 627, 130455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.D.; Keenan, T.F.; Migliavacca, M.; Ryu, Y.; Sonnentag, O.; Toomey, M. Climate change, phenology, and phenological control of vegetation feedbacks to the climate system. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 169, 156–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, D.P.; Han, Y.N.; Xu, Z.X.; Li, P.J.; Ban, C.G.; Sun, W.C.; Pang, B.; Peng, D.Z.; Kan, G.Y.; Zhang, R.; et al. Time-lag effects of climatic change and drought on vegetation dynamics in an alpine river basin of the Tibet Plateau, China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 600, 126532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zhao, X.; Liang, S.; Zhou, T.; Huang, K.; Tang, B.; Zhao, W. Time-lag Effects of Global Vegetation Responses to Climate Change. Glob. Change Biol. 2015, 21, 3520–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Liu, X.; Xin, Q.; Wu, J.; Xu, X.; Pei, F.; Li, X.; Du, G.; Cai, Y.; Lin, K. Cumulative effects of climatic factors on terrestrial vegetation growth. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosc. 2019, 124, 789–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Liu, Q.; Chen, A.; Janssens, I.A.; Fu, Y.; Dai, J.; Liu, L.; Lian, X.; Shen, M.; Zhu, X. Plant phenology and global climate change: Current progresses and challenges. Glob. Change Biol. 2019, 25, 1922–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenka, N.K.; Lal, R. Soil-related constraints to the carbon dioxide fertilization effect. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2012, 31, 342–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, J.A.; DeFries, R.; Asner, G.P.; Barford, C.; Bonan, G.; Carpenter, S.R.; Chapin, F.S.; Coe, M.T.; Daily, G.C.; Gibbs, H.K. Global consequences of land use. Science 2005, 309, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.-P.; Hansen, M.C.; Stehman, S.V.; Potapov, P.V.; Tyukavina, A.; Vermote, E.F.; Townshend, J.R. Global land change from 1982 to 2016. Nature 2018, 560, 639–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, A.; Martins, I.S.; Kastner, T.; Plutzar, C.; Theurl, M.C.; Eisenmenger, N.; Huijbregts, M.A.; Wood, R.; Stadler, K.; Bruckner, M. Increasing impacts of land use on biodiversity and carbon sequestration driven by population and economic growth. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 3, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S. Impact of China’s large-scale ecological restoration program on the environment and society in arid and semiarid areas of China: Achievements, problems, synthesis, and applications. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 41, 317–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, J.; Chokkalingam, U.; Poulsen, J. The restoration of forest biodiversity and ecological values. For. Ecol. Manag. 2004, 201, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worlanyo, A.S.; Jiangfeng, L. Evaluating the environmental and economic impact of mining for post-mined land restoration and land-use: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 279, 111623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, J. The third pole. Nature 2008, 454, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, T.; Xue, Y.; Chen, D.; Chen, F.; Thompson, L.; Cui, P.; Koike, T.; Lau, W.K.M.; Lettenmaier, D.; Mosbrugger, V.; et al. Recent Third Pole’s Rapid Warming Accompanies Cryospheric Melt and Water Cycle Intensification and Interactions between Monsoon and Environment: Multidisciplinary Approach with Observations, Modeling, and Analysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 100, 423–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immerzeel, W.W.; Lutz, A.F.; Andrade, M.; Bahl, A.; Biemans, H.; Bolch, T.; Hyde, S.; Brumby, S.; Davies, B.J.; Elmore, A.C.; et al. Importance and vulnerability of the world’s water towers. Nature 2020, 577, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Ouyang, Z.; Shi, P.; Fan, J.; Wang, X.; Zheng, H.; Zhao, W.; Wu, F. Current Condition and Protection Strategies of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Ecological Security Barrier. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2021, 36, 1298–1306. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, T.; Bolch, T.; Chen, D.; Gao, J.; Immerzeel, W.; Piao, S.; Su, F.; Thompson, L.; Wada, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. The imbalance of the Asian water tower. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 618–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Piao, S.; Bao, W.; Wang, S.; Wang, G.; Sun, H.; Luo, T.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, P.; et al. Ecological change on the Tibetan Plateau. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 3048–3056. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Xu, B.; Yao, T.; Guo, Z.; Cui, P.; Chen, F.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, J.; et al. Assessment of past, present and future environmental changes on the Tibetan Plateau. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 3025–3035. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.; Wu, H.; Qin, J.; Lin, C.G.; Tang, W.J.; Chen, Y.Y. Recent climate changes over the Tibetan Plateau and their impacts on energy and water cycle: A review. Glob. Planet. Change 2014, 112, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Thompson, L.; Yang, W.; Yu, W.; Gao, Y.; Guo, X.; Yang, X.; Duan, K.; Zhao, H.; Xu, B.; et al. Different glacier status with atmospheric circulations in Tibetan Plateau and surroundings. Nat. Clim. Change 2012, 2, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lv, W.; Xue, K.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Hu, R.; Zeng, H.; Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Jiang, L.; et al. Grassland changes and adaptive management on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 668–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Lu, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Sun, J. Dual influence of climate change and anthropogenic activities on the spatiotemporal vegetation dynamics over the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau from 1981 to 2015. Earth’s Future 2022, 10, e2021EF002566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, T.; Wang, X.M. Temporal and Spatial Variations in the Climate Controls of Vegetation Dynamics on the Tibetan Plateau during 1982–2011. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 35, 1337–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.P.; Wu, J.S.; Niu, B.; He, Y.T.; Zu, J.X.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.Z. Vegetation Expansion on the Tibetan Plateau and Its Relationship with Climate Change. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, T.; Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Ni, F.; Han, X.; Qiao, X.; Sun, X. Elevation-dependent patterns of temporally asymmetrical vegetation response to climate in an alpine basin on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 159, 111736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.H.; Liu, A.Q.; Tian, Z.H.; Wu, L.L.; Zhou, G.S. Response of Vegetation Phenology to Climate Change on the Tibetan Plateau Considering Time-Lag and Cumulative Effects. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Guo, Z.; Xi, G. Effects of Climate Variability and Human Activities on Vegetation Dynamics across the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau from 1982 to 2020. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.X.; Zhao, W.W.; Yao, Y.; Pereira, P. The rising human footprint in the Tibetan Plateau threatens the effectiveness of ecological restoration on vegetation growth. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, T.; Wang, X.; Ci, Z.; Lang, L.; Zhang, C. Responses of vegetation activity to climate variation on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau (China) from 1982 to 2011. Clim. Res. 2015, 66, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weatherhead, E.C.; Reinsel, G.C.; Tiao, G.C.; Meng, X.L.; Choi, D.; Cheang, W.K.; Keller, T.; DeLuisi, J.; Wuebbles, D.J.; Kerr, J.B. Factors affecting the detection of trends: Statistical considerations and applications to environmental data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 17149–17161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N. Characteristics of maximum-value composite images from temporal AVHRR data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1986, 7, 1417–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.; Geerken, R. Discrimination between climate and human-induced dryland degradation. J. Arid Environ. 2004, 57, 535–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geerken, R.; Ilaiwi, M. Assessment of rangeland degradation and development of a strategy for rehabilitation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 90, 490–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z. The relative roles of climate variations and human activities in vegetation change in North China. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2015, 87, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Pattey, E.; Jégo, G. Assessment of vegetation indices for regional crop green LAI estimation from Landsat images over multiple growing seasons. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 123, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhe, M.; Zhang, X. Time-lag effects of NDVI responses to climate change in the Yamzhog Yumco Basin, South Tibet. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 124, 107431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Y.H.; Xue, B.; Wang, G.; Yu, J.; Zuo, D.; Xu, Z. Spatial heterogeneity of changes in vegetation growth and their driving forces based on satellite observations of the Yarlung Zangbo River Basin in the Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2019, 574, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Mohammat, A.; Fang, J.; Cai, Q.; Feng, J. NDVI-based increase in growth of temperate grasslands and its responses to climate changes in China. Glob. Environ. Change 2006, 16, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Ma, Y.; Fu, Y.; Pan, X.; Hu, W.; Su, Z.; Salama, M.S.; Feng, L. Assessment of soil water deficit for the middle reaches of Yarlung-Zangbo River from optical and passive microwave images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 142, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, Y.; Li, H.; Jiang, S.; He, X.; Liu, K. Attribution analyses of reference evapotranspiration changes in China incorporating surface resistance change response to elevated CO2. J. Hydrol. 2021, 599, 126387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Chen, W.; Zhang, X.; Bi, P.; Yang, Z.; Shi, X.; Wang, Z. Spatiotemporal dynamics of vegetation in China from 1981 to 2100 from the perspective of hydrothermal factor analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 14219–14230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, G.; Yan, S.; Chen, H.; Yang, J.; Wen, Y. Intra-Annual Cumulative Effects and Mechanisms of Climatic Factors on Global Vegetation Biomes’ Growth. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.S.; Ramachandran, R.M.; Paul, O.; Thakur, P.K.; Ravan, S.; Behera, M.D.; Sarangi, C.; Kanawade, V.P. Anthropogenic land use and land cover changes—A review on its environmental consequences and climate change. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2022, 50, 1615–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seneviratne, S.I.; Zhang, X.; Adnan, M.; Badi, W.; Dereczynski, C.; Luca, A.D.; Ghosh, S.; Iskandar, I.; Kossin, J.; Lewis, S. Weather and climate extreme events in a changing climate. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis: Working Group I Contribution to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V.P., Zhai, A., Pirani, S.L., Connors, C., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021; pp. 1513–1766. [Google Scholar]
- D’Odorico, P.; Bhattachan, A.; Davis, K.F.; Ravi, S.; Runyan, C.W. Global desertification: Drivers and feedbacks. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 326–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayiah, M.; Dong, S.; Khomera, S.W.; Ur Rehman, S.A.; Yang, M.; Xiao, J. Status and challenges of Qinghai–Tibet Plateau’s grasslands: An analysis of causes, mitigation measures, and way forward. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomiero, T. Soil degradation, land scarcity and food security: Reviewing a complex challenge. Sustainability 2016, 8, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aradottir, A.L.; Hagen, D. Ecological restoration: Approaches and impacts on vegetation, soils and society. Adv. Agron. 2013, 120, 173–222. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; Ding, Q.; Niu, B.; He, Y. Declining human activity intensity on alpine grasslands of the Tibetan Plateau. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 296, 113198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuo, L.; Li, N.; Liu, Z.; Ding, J.; Liang, L.Q.; Zhang, Y.X.; Gong, T.L. Warming and human activities induced changes in the Yarlung Tsangpo basin of the Tibetan plateau and their influences on streamflow. J. Hydrol.-Reg. Stud. 2019, 25, 100625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Hao, J.; Zhang, G.; Fang, H.; Wang, Y.; Lu, H. Runoff variations affected by climate change and human activities in Yarlung Zangbo River, southeastern Tibetan Plateau. CATENA 2023, 230, 107184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, L.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Xu, Z. Greening Implication Inferred from Vegetation Dynamics Interacted with Climate Change and Human Activities over the Southeast Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gong, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, B. NDVI-Based Greening of Alpine Steppe and Its Relationships with Climatic Change and Grazing Intensity in the Southwestern Tibetan Plateau. Land 2022, 11, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Jia, J.; Liu, H.; Lin, Z. Relative importance of climate change and human activities for vegetation changes on China’s silk road economic belt over multiple timescales. CATENA 2019, 180, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Yu, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, K. Quantitative contributions of climate change and human activities to vegetation changes over multiple time scales on the Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hong, S.; Liu, D.; Piao, S. Susceptibility of vegetation low-growth to climate extremes on Tibetan Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2023, 331, 109323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

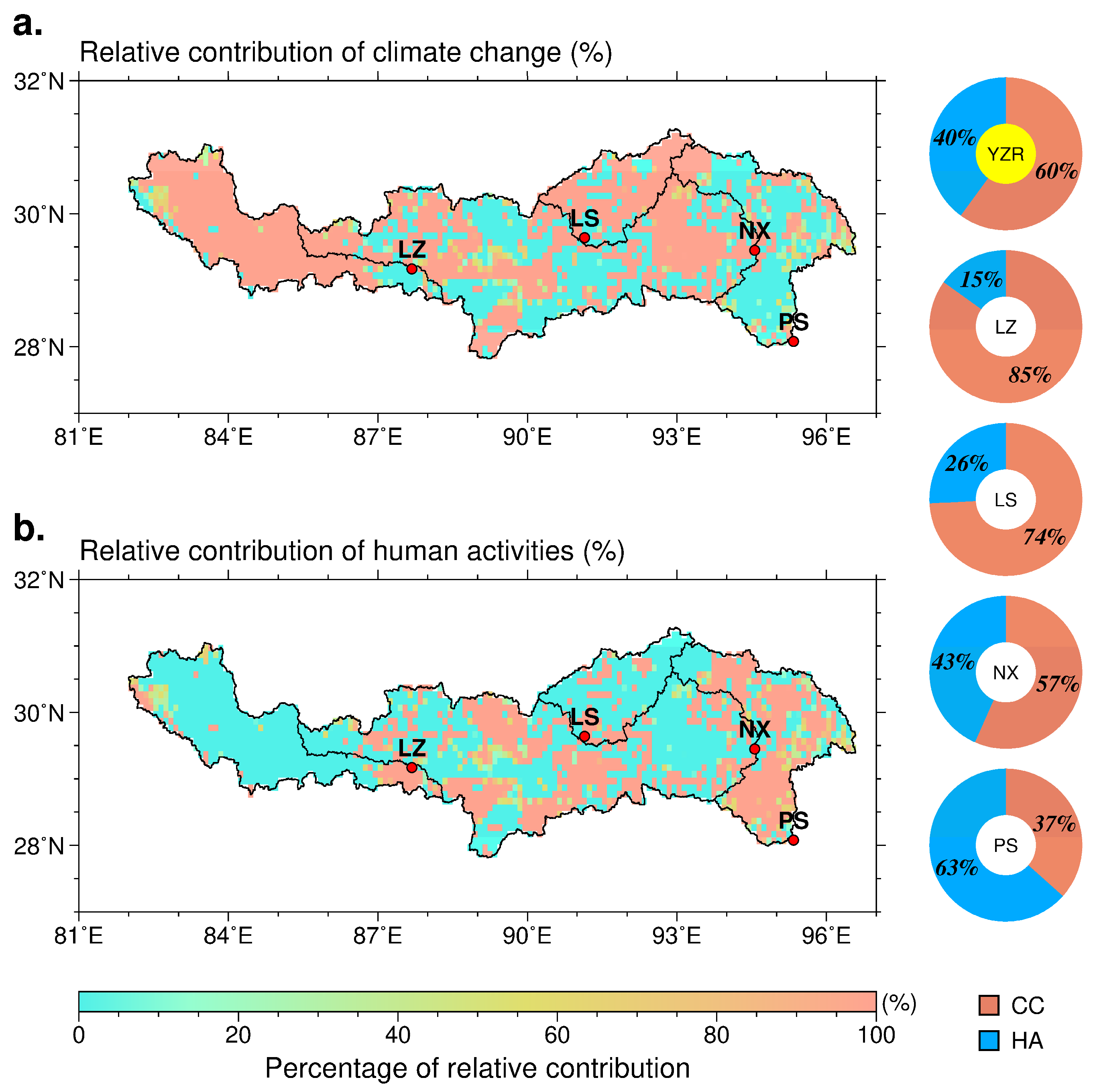
| Relative Contribution Rate (%) | Description | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC | HAs | ||||
| >0 | >0 | >0 | Both CC and HAs contributed to the increase in LAI. | ||
| >0 | <0 | 100 | 0 | CC contributed to the increase in LAI. | |
| <0 | >0 | 0 | 100 | HAs contributed to the increase in LAI. | |
| <0 | <0 | <0 | Both CC and HAs contributed to the decrease in LAI. | ||
| >0 | <0 | 0 | 100 | HAs contributed to the decrease in LAI. | |
| <0 | >0 | 100 | 0 | CC contributed to the decrease in LAI. | |
| Climatic Factors | Basins | Time-Lag Months | Time-Accumulation Months |
|---|---|---|---|
| PRE | YZR | 0.14 ± 0.52 | 1.04 ± 0.49 |
| LZ | 0.00 ± 0.09 | 0.99 ± 0.24 | |
| LS | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.90 ± 0.30 | |
| NX | 0.02 ± 0.15 | 1.03 ± 0.33 | |
| PS | 0.65 ± 0.97 | 1.20 ± 0.92 | |
| TEM | YZR | 0.11 ± 0.50 | 0.84 ± 0.65 |
| LZ | 0.01 ± 0.16 | 0.94 ± 0.50 | |
| LS | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.45 ± 0.50 | |
| NX | 0.01 ± 0.13 | 0.82 ± 0.53 | |
| PS | 0.49 ± 0.99 | 1.02 ± 0.99 | |
| PET | YZR | 0.06 ± 0.29 | 1.53 ± 1.24 |
| LZ | 0.11 ± 0.37 | 2.07 ± 0.95 | |
| LS | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.93 ± 0.81 | |
| NX | 0.06 ± 0.26 | 1.92 ± 1.19 | |
| PS | 0.05 ± 0.36 | 0.26 ± 0.65 | |
| SRD | YZR | 2.37 ± 0.79 | 0.51 ± 0.63 |
| LZ | 2.52 ± 0.67 | 0.47 ± 0.65 | |
| LS | 2.20 ± 0.41 | 0.80 ± 0.41 | |
| NX | 2.48 ± 0.66 | 0.49 ± 0.61 | |
| PS | 2.04 ± 1.19 | 0.36 ± 0.69 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, N.; Wang, D. Quantifying Time-Lag and Time-Accumulation Effects of Climate Change and Human Activities on Vegetation Dynamics in the Yarlung Zangbo River Basin of the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17010160
Li N, Wang D. Quantifying Time-Lag and Time-Accumulation Effects of Climate Change and Human Activities on Vegetation Dynamics in the Yarlung Zangbo River Basin of the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(1):160. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17010160
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ning, and Di Wang. 2025. "Quantifying Time-Lag and Time-Accumulation Effects of Climate Change and Human Activities on Vegetation Dynamics in the Yarlung Zangbo River Basin of the Tibetan Plateau" Remote Sensing 17, no. 1: 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17010160
APA StyleLi, N., & Wang, D. (2025). Quantifying Time-Lag and Time-Accumulation Effects of Climate Change and Human Activities on Vegetation Dynamics in the Yarlung Zangbo River Basin of the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sensing, 17(1), 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17010160





