Optimal and Multi-View Strategic Hybrid Deep Learning for Old Landslide Detection in the Loess Plateau, Northwest China
Abstract
1. Introduction
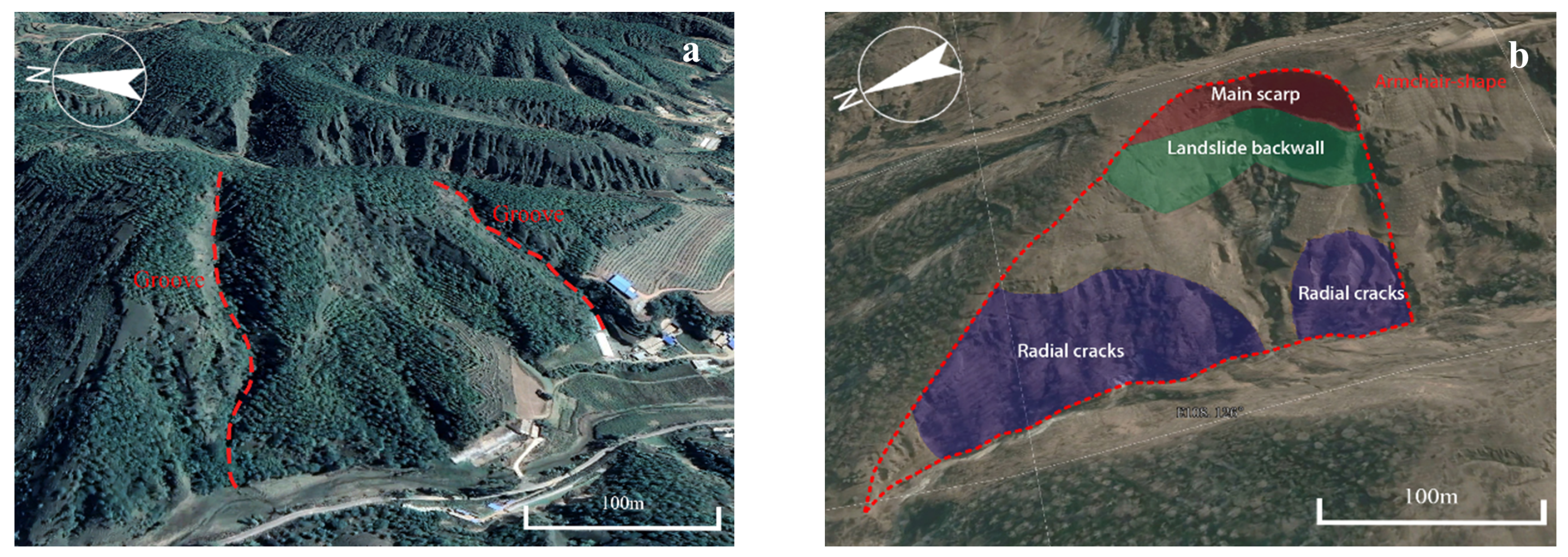
- Old loess landslides occurred over a relatively long period, and due to the loose and porous character of loess, the shapes of landslides have been changed for a long time, and may be covered with vegetation, which make it difficult to recognize them in high-resolution remote sensing images.
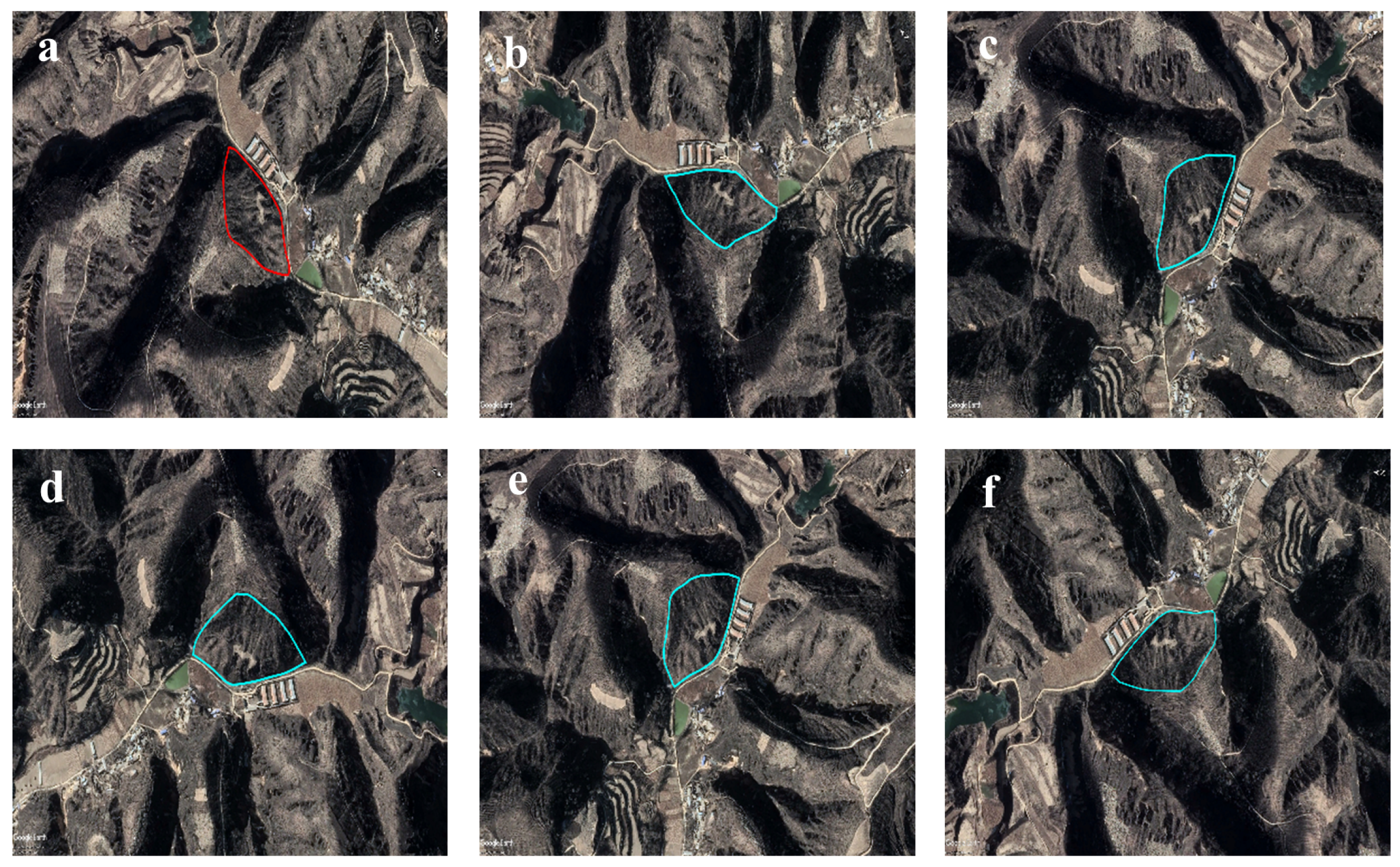
- The high-resolution remote sensing image only contains the orthophoto-view of old loess landslides, which is difficult for training models to recognize. Actually, experts usually interpret old landslides by rotating the view angle in order to find more features and recognize them (Figure 1). There is still no effective automatic method to simulate this process to detect old loess landslides intelligently.
- Detection models based on CNNs or transformers only extract local or global features of remote sensing images, respectively. They cannot utilize various features in the image effectively, which makes detection more difficult.
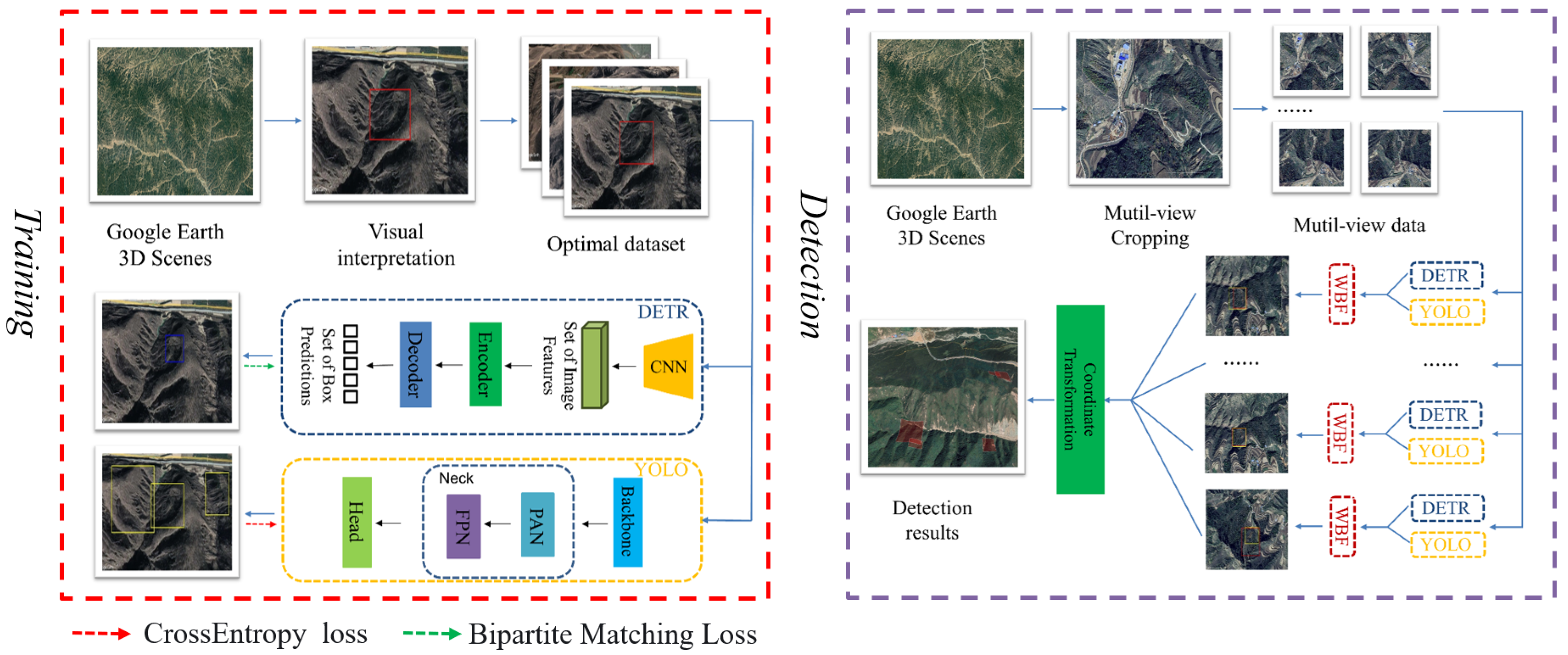
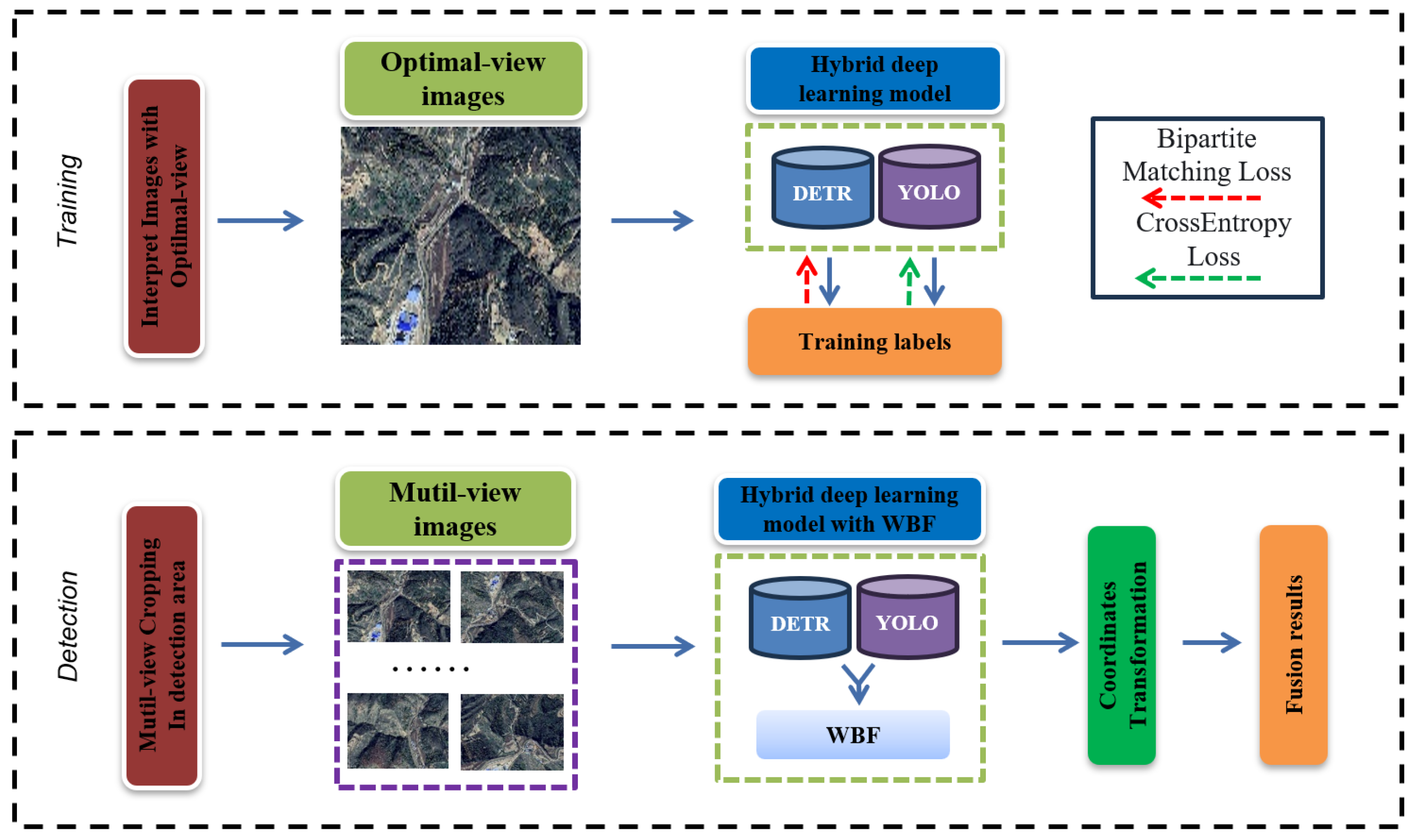
- A HDL model which combines the advantages of CNNs and transformers was proposed, and it can extract global and local features of images at the same time. As such, it can detect old loess landslides effectively. The proposed method consists of the YOLOv5 object detection model based on CNNs and the detection transformer (DETR) model, and weighted boxes fusion (WBF) was introduced to fuse the results of the proposed hybrid deep learning model and to obtain comprehensive detection results.
- The optimal and multi-view (OMV) strategy was proposed to detect old landslides effectively and efficiently. During the training process, more obvious features of old landslides can be learned from optimal-view images, while traditional learning methods only use orthophoto images, in which old landslides cannot be observed clearly. During detection in a new area, because the optimal view is unknown, we propose the multi-view strategy instead to detect old landslides with a trained model, which can be implemented in parallel without increasing detection time.
- An optical remote sensing dataset with optimal images from the Yan’an area (YA-OP) was constructed as a benchmark for old landslide detection, and it can be used for related research about old landslides in the Loess Plateau.
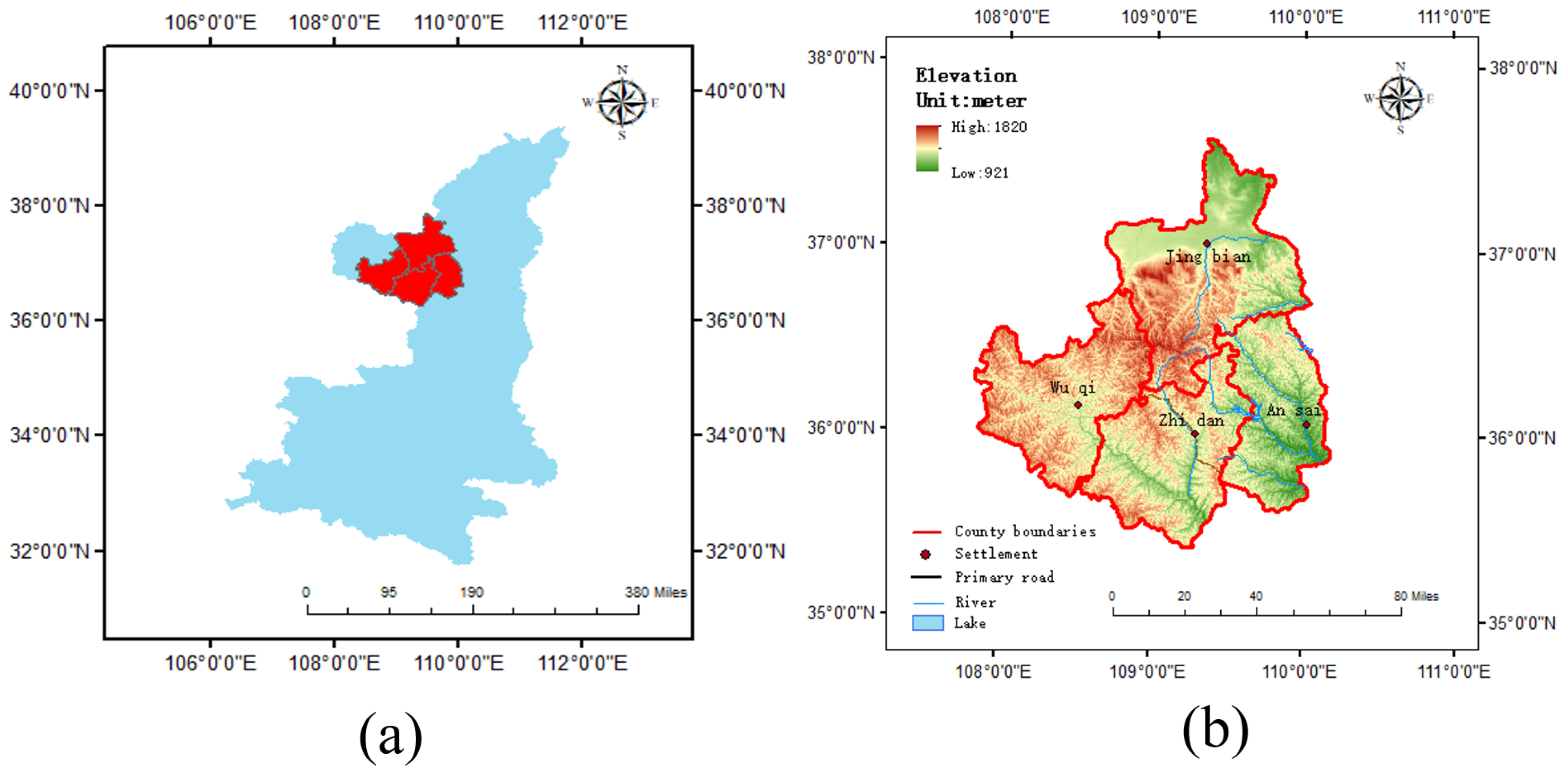
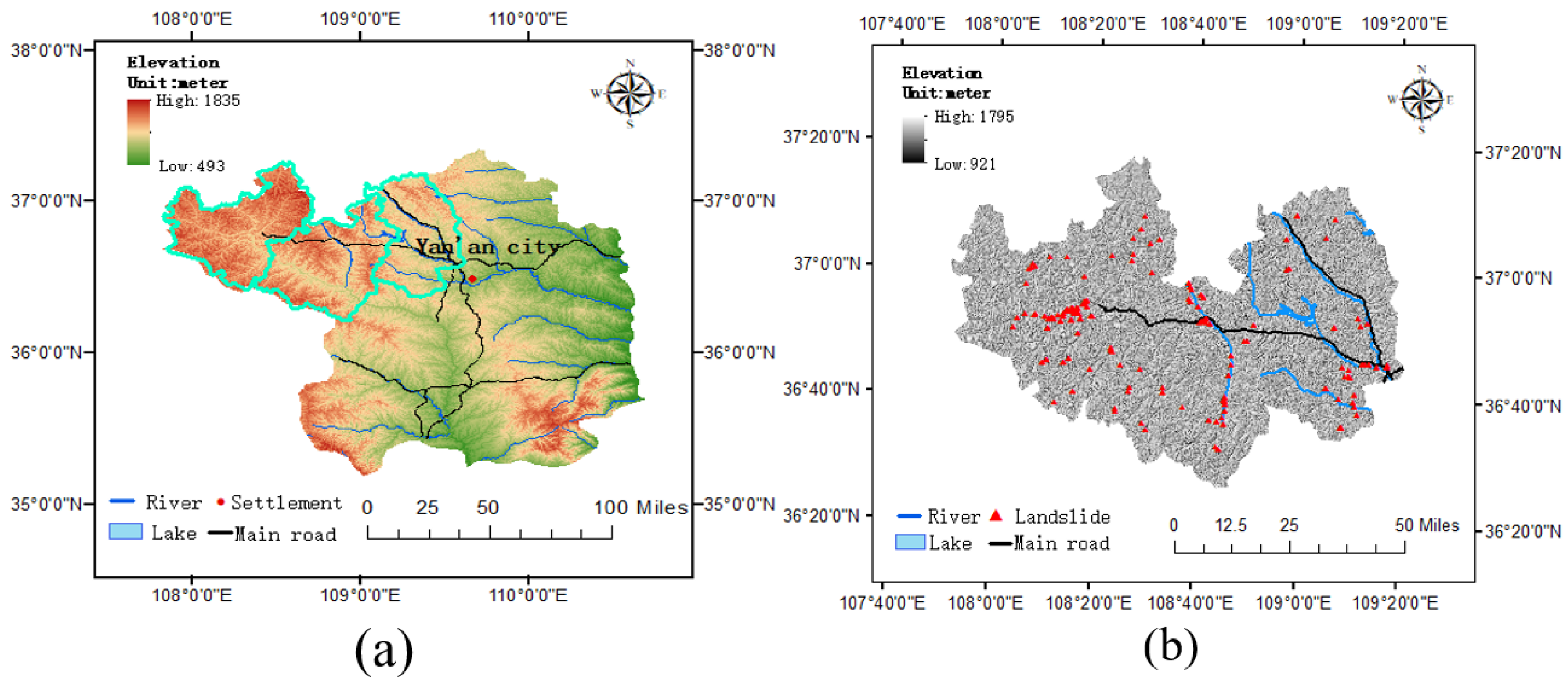
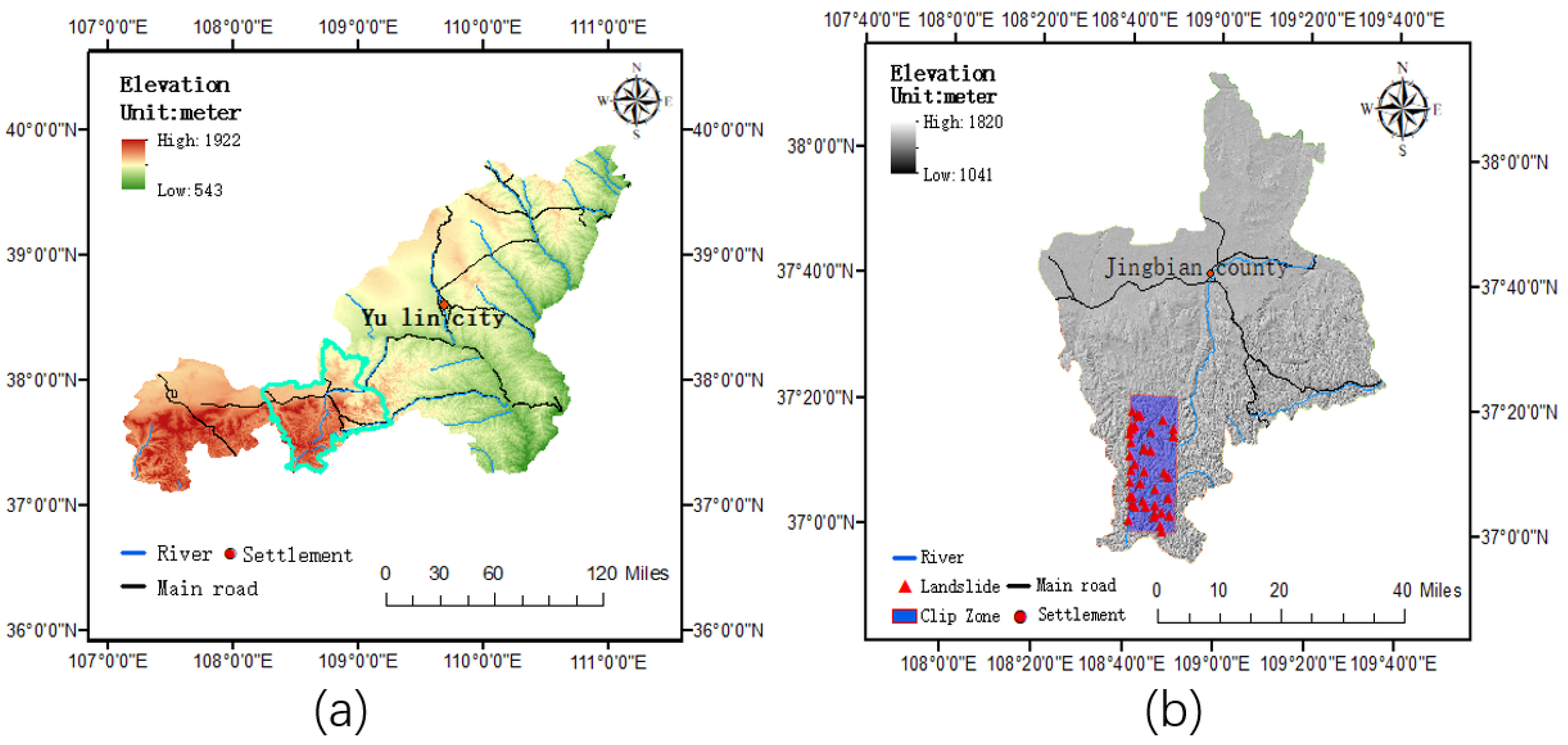
2. Description of the Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data for Training and Detection
3.1.1. Optimal-View Dataset for Training
3.1.2. Multi-View Images for Detection
3.2. Optimal-View and Multi-View Strategic Hybrid Deep Learning Method
3.2.1. Optimal-View and Multi-View Strategy
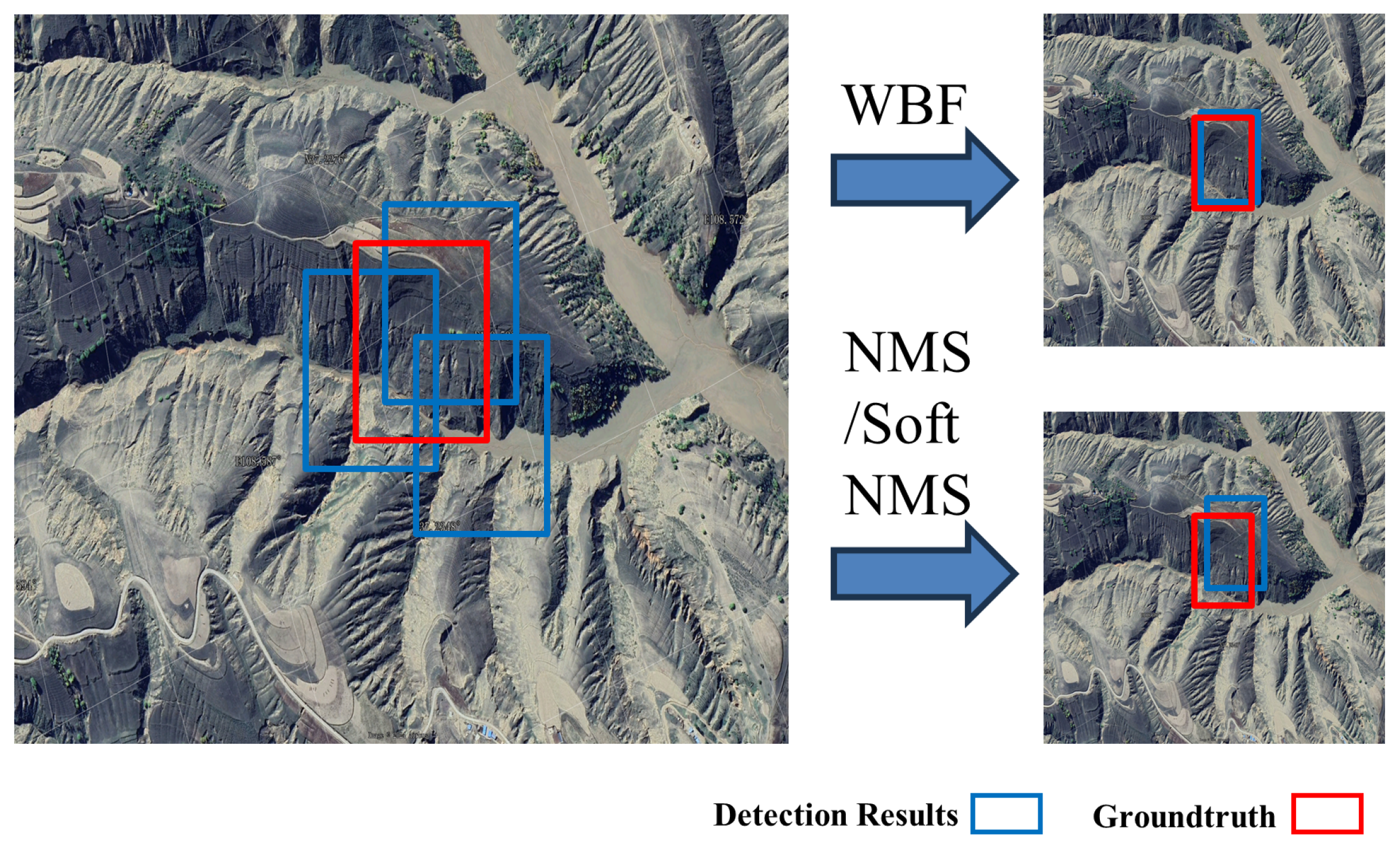
3.2.2. Hybrid Deep Learning Model with Weighted Boxes Fusion
- Create a new List B. The prediction boxes for each model are added to the List B, and elements (each box) of the list are sorted in descending order according to confidence.
- Create two empty lists: List L is used to store all the prediction boxes belonging to the same target, and List F is used to store the fusion prediction boxes of each target.
- Iterate over all of the prediction boxes of List B. Find the matching box in List F (the IoU of two boxes is greater than the threshold).
- If no matching box is found, then the prediction box in List B is added as a new box to the end of Lists L and F, and then the next box in List B is iterated.
- If a match is found, add the box to the same position in List L that corresponds to the matching box in List F.
- Using the following fusion formula, the new coordinates and confidence scores for all T boxes at each location in the List L are recalculated. In these formulas, C represents the confidence scores of the resulting fusion box, and and represent the upper-left and lower-right corner coordinates of the resulting fusion box, and i is the number of prediction boxes for the same target.
- After processing all the boxes in List B, the confidence score in List F is recalculated using Formula (5), where N is the total number of models.
4. Experimental Results and Analysis
4.1. Evaluation Indices and Experimental Settings
4.1.1. Evaluation Indices
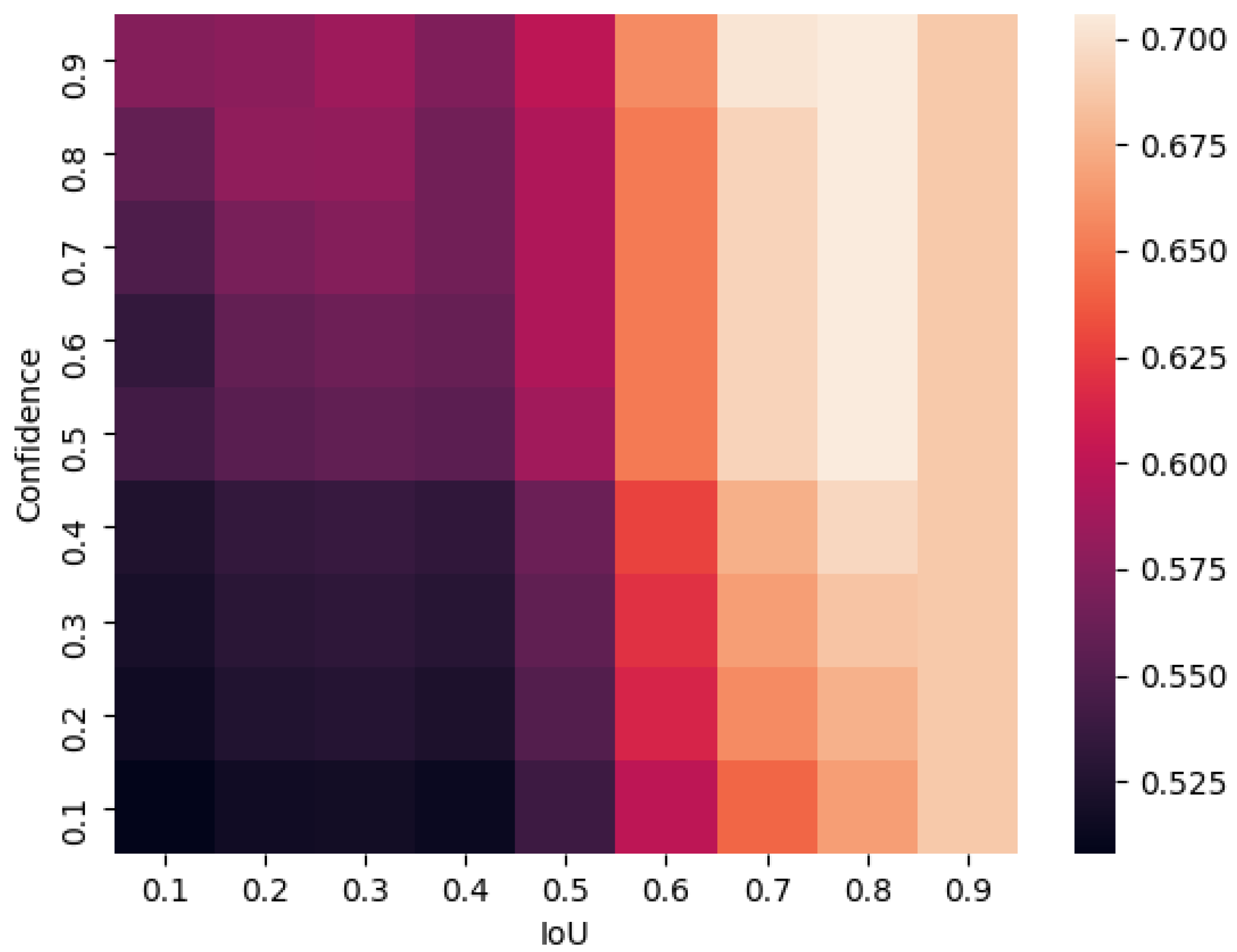
4.1.2. Experimental Settings
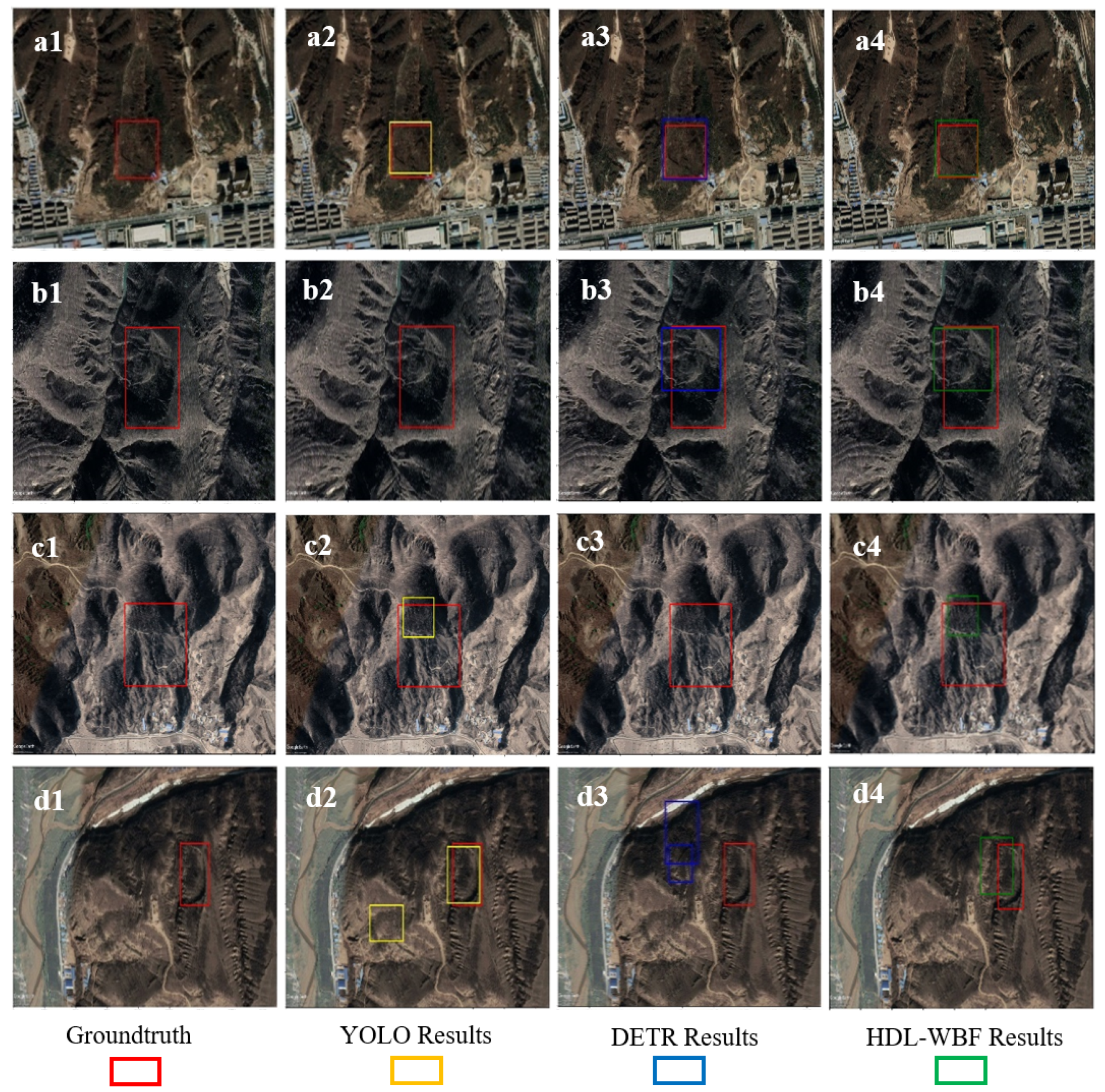
4.2. Performance of HDL-WBF on Yan’an Optimal-View Dataset
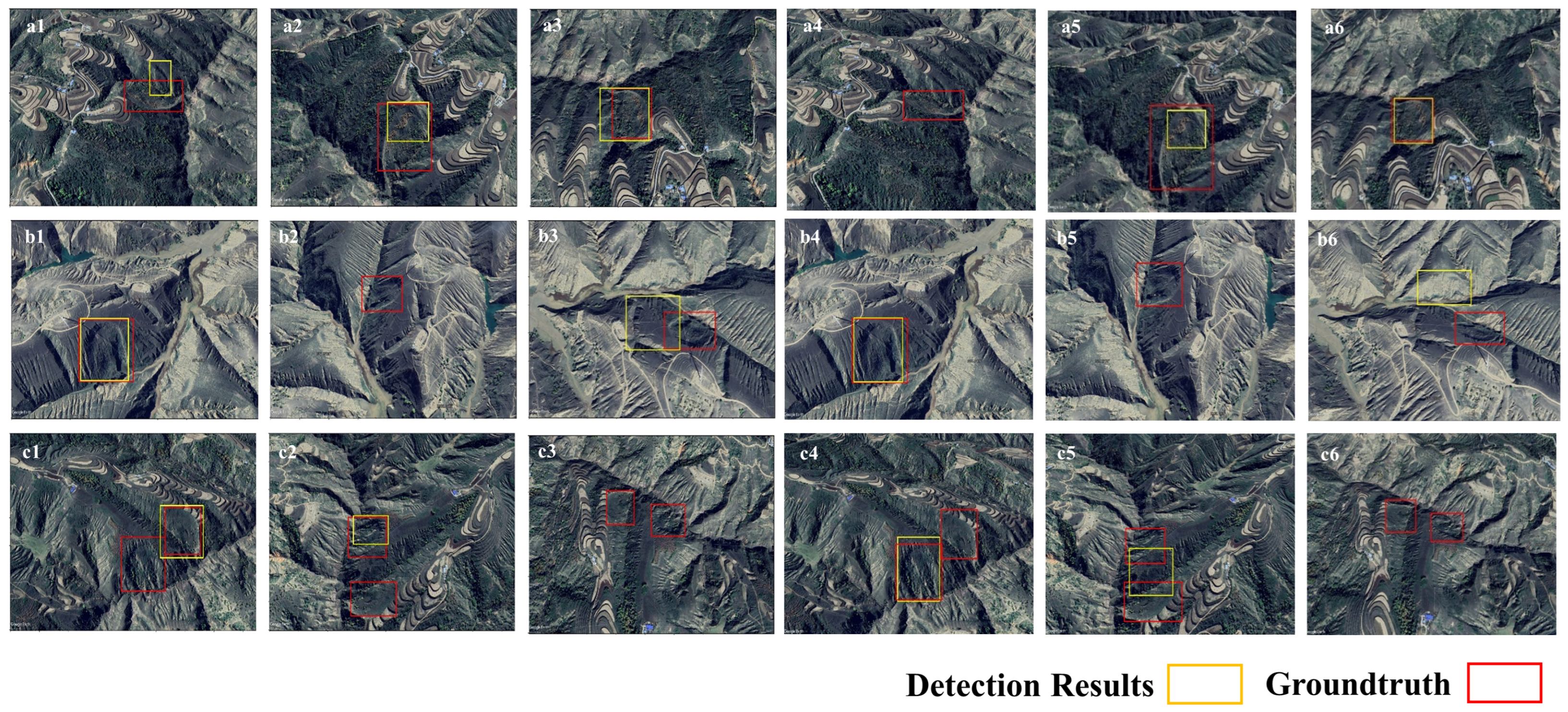
4.3. Verification of HDL-WBF Using Multi-View Images in Jingbian County
4.4. Experiments of WBF
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, S.; Peng, J.; Zhuang, J.; Kang, C.; Jia, Z. Underlying mechanisms of the geohazards of macro Loess discontinuities on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Eng. Geol. 2019, 263, 105357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Xu, C.; Xu, S.; Chai, S.; Fu, G.; Bao, P. Small-scale catastrophic landslides in loess areas of China: An example of the March 15, 2019, Zaoling landslide in Shanxi Province. Landslides 2020, 17, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Shao, X.; Xu, C.; Xu, Y. Insight from a Physical-Based Model for the Triggering Mechanism of Loess Landslides Induced by the 2013 Tianshui Heavy Rainfall Event. Water 2023, 15, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, T.; Xing, X.; Zou, Y. Research on loess flow-slides induced by rainfall in July 2013 in Yan’an, NW China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 7933–7944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhuang, J.; Huang, W.; Zhu, X.; Leng, Y.; Ma, P. Distribution and genetic types of loess landslides in China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2019, 170, 329–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen-jiang, M.; Peng-hui, M.; Jian-bing, P. Characteristics of loess landslides triggered by different factors in the Chinese Loess Plateau. J. Mt. Sci. 2021, 18, 3218–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ren, S.; Liu, X.; Guo, C.; Li, J.; Bi, J.; Ran, L. Reactivation mechanism of old landslide triggered by coupling of fault creep and water infiltration: A case study from the east Tibetan Plateau. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2023, 82, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guanglao, H. The Historical Transformation of the Landsliding Causes and Factors in the Border Slopes of Loessial Highland in the Baoji-Changxing Area. J. Chang. Univ. Earth Sci. Ed. 1986, 8, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.; Qiu, H.; Wang, N.; Wang, X.; Ma, S.; Yang, D.; Wei, N.; Liu, Z.; Shen, Y.; Cao, M.; et al. Movement process, geomorphological changes, and influencing factors of a reactivated loess landslide on the right bank of the middle of the Yellow River, China. Landslides 2022, 19, 1265–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zeng, P.; Li, T.; Zhang, L.; Jimenez, R.; Dong, X.; Xu, Q. A Bayesian approach to develop simple run-out distance models: Loess landslides in Heifangtai Terrace, Gansu Province, China. Landslides 2023, 20, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumma, M.K.; Thenkabail, P.S.; Panjala, P.; Teluguntla, P.; Yamano, T.; Mohammed, I. Multiple agricultural cropland products of South Asia developed using Landsat-8 30 m and MODIS 250 m data using machine learning on the Google Earth Engine (GEE) cloud and spectral matching techniques (SMTs) in support of food and water security. Giscience Remote Sens. 2022, 59, 1048–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wu, L.; Pei, L.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, D.; Wang, G.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y. Identifying Crop Growth Stages from Solar-Induced Chlorophyll Fluorescence Data in Maize and Winter Wheat from Ground and Satellite Measurements. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Jiang, J.; Liu, Z.; Pan, Y. Combining a Crop Growth Model with CNN for Underground Natural Gas Leakage Detection Using Hyperspectral Imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 1846–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zang, Z.; Lin, H.; Wang, X.; Wen, Z. Using a Vegetation Index to Monitor the Death Process of Chinese Fir Based on Hyperspectral Data. Forests 2023, 14, 2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Liu, M.; Man, W.; Chen, L. Annually Spatial Pattern Dynamics of Forest Types under a Rapid Expansion of Impervious Surfaces: A Case Study of Hangzhou City. Forests 2024, 15, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Guan, J.; Zhang, F.; Wang, X.; Long, Z. Attention-Unet-Based Near-Real-Time Precipitation Estimation from Fengyun-4A Satellite Imageries. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tichý, O.; Eckhardt, S.; Balkanski, Y.; Hauglustaine, D.; Evangeliou, N. Decreasing trends of ammonia emissions over Europe seen from remote sensing and inverse modelling. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 15235–15252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Deng, M.; Chen, K.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, B.; Liu, Q. A spatial hierarchical learning module based cellular automata model for simulating urban expansion: Case studies of three Chinese urban areas. Giscience Remote Sens. 2024, 61, 2290352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Qi, Z.; Shi, Z. Remote Sensing Image Change Detection with Transformers. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5607514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, A.; Navarro, G.; Caballero, I.; Tovar-Sanchez, A. High-spatial resolution UAV multispectral data complementing satellite imagery to characterize a chinstrap penguin colony ecosystem on deception island (Antarctica). Giscience Remote Sens. 2022, 59, 1159–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Liao, K.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Lu, L.; Jian, S.; Qin, R.; Fu, X. Extraction of Tobacco Planting Information Based on UAV High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Li, Y.; Du, Y.; Wang, W.; Chen, G. Noncontact detection of earthquake-induced landslides by an enhanced image binarization method incorporating with Monte-Carlo simulation. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2019, 10, 219–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorucci, F.; Ardizzone, F.; Mondini, A.C.; Viero, A.; Guzzetti, F. Visual interpretation of stereoscopic NDVI satellite images to map rainfall induced landslides. Landslides 2019, 16, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Chow, J.K.; Tan, P.S.; Wu, J.; Ho, Y.K.; Wang, Y.H. Deep convolutional neural network-based pixel-wise landslide inventory mapping. Landslides 2021, 18, 1421–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.P.; Hasegawa, H.; Fujiwara, S.; Tobita, M.; Koarai, M.; Une, H.; Iwahashi, J. Interpretation of landslide distribution triggered by the 2005 Northern Pakistan earthquake using SPOT 5 imagery. Landslides 2007, 4, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, D.T.; Shahabi, H.; Shirzadi, A.; Chapi, K.; Alizadeh, M.; Chen, W.; Mohammadi, A.; Bin Ahmad, B.; Panahi, M.; Hong, H.; et al. Landslide Detection and Susceptibility Mapping by AIRSAR Data Using Support Vector Machine and Index of Entropy Models in Cameron Highlands, Malaysia. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, J.; Yunus, A.P.; Bui, D.T.; Merghadi, A.; Sahana, M.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, C.W.; Han, Z.; Pham, B.T. Improved landslide assessment using support vector machine with bagging, boosting, and stacking ensemble machine learning framework in a mountainous watershed, Japan. Landslides 2020, 17, 641–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakkoli Piralilou, S.; Shahabi, H.; Jarihani, B.; Ghorbanzadeh, O.; Blaschke, T.; Gholamnia, K.; Meena, S.R.; Aryal, J. Landslide Detection Using Multi-Scale Image Segmentation and Different Machine Learning Models in the Higher Himalayas. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, A.; Kerle, N. Object-oriented mapping of landslides using Random Forests. Remote Sens. Environ. Interdiscip. J. 2011, 115, 2564–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Ersoy, O.K.; Cong, M.; Zhao, C.; Qu, W.; Wu, T. Wide and Deep Fourier Neural Network for Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Image Classification. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Cong, M.; Ersoy, O.K.; Zou, W.; Zhao, C.; Li, Z.; Gu, J.; Wu, T. Dynamic Wide and Deep Neural Network for Hyperspectral Image Classification. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Ersoy, O.K.; Fang, J.; Wu, T.; Wei, X.; Zhao, C. Parallel Multistage Wide Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 34, 4019–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Xi, J.; Li, Z.; Ding, M.; Yang, L.; Xie, D. Landslide Detection and Segmentation Using Mask R-CNN with Simulated Hard Samples. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2023, 48, 1931–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Xi, J.; Li, Z.; Zang, M.; Chen, B.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Z.; Gao, S.; Zhu, W. Deep Learning for Landslide Detection and Segmentation in High-Resolution Optical Images along the Sichuan-Tibet Transportation Corridor. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, C.; Lu, Z.; Xi, J. Landslide Inventory Mapping Based on Independent Component Analysis and UNet3+: A Case of Jiuzhaigou, China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 2213–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, C.; Xi, J.; Lu, Z.; Ji, S.; Chen, L. Deep Learning Method of Landslide Inventory Map with Imbalanced Samples in Optical Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habumugisha, J.M.; Chen, N.; Rahman, M.; Islam, M.M.; Ahmad, H.; Elbeltagi, A.; Sharma, G.; Liza, S.N.; Dewan, A. Landslide Susceptibility Mapping with Deep Learning Algorithms. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Li, Y.; Cui, P.; Liang, L.; Pirasteh, S.; Marcato, J., Jr.; Goncalves, W.N.; Li, J. Landslide Detection of Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Data Based on Deep Learning with Constrains. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 5047–5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Yu, D.; Shen, C.; Li, W.; Xu, Q. Landslide detection from an open satellite imagery and digital elevation model dataset using attention boosted convolutional neural networks. Landslides 2020, 17, 1337–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; He, Y.; Xu, Q.; Deng, J.; Li, W.; Wei, Y. Detection and segmentation of loess landslides via satellite images: A two-phase framework. Landslides 2022, 19, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Zeng, S.; Xiao, K.; Yang, D.; Yao, G.; Yang, R. A novel landslide identification method for multi-scale and complex background region based on multi-model fusion: YOLO + U-Net. Landslides 2024, 21, 901–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.03762. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1706.03762 (accessed on 12 June 2017).
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929 (accessed on 22 October 2020).
- Tang, X.; Tu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, D.; Fan, X. Automatic Detection of Coseismic Landslides Using a New Transformer Method. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, P.; Ma, L.; Li, Q.; Du, F. ShapeFormer: A Shape-Enhanced Vision Transformer Model for Optical Remote Sensing Image Landslide Detection. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 2681–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Allen, M.B.; Zhang, W.; Li, W.; He, H. Landslide characteristics in the Loess Plateau, northern China. Geomorphology 2020, 359, 107150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gool, L.V.; Neubeck, A. Efficient Non-Maximum Suppression. In Proceedings of the 2006 18th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Los Alamitos, CA, USA, 20–24 August 2006; Volume 3, pp. 850–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodla, N.; Singh, B.; Chellappa, R.; Davis, L.S. Soft-NMS—Improving Object Detection with One Line of Code. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovyev, R.; Wang, W.; Gabruseva, T. Weighted boxes fusion: Ensembling boxes from different object detection models. Image Vis. Comput. 2021, 107, 104117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
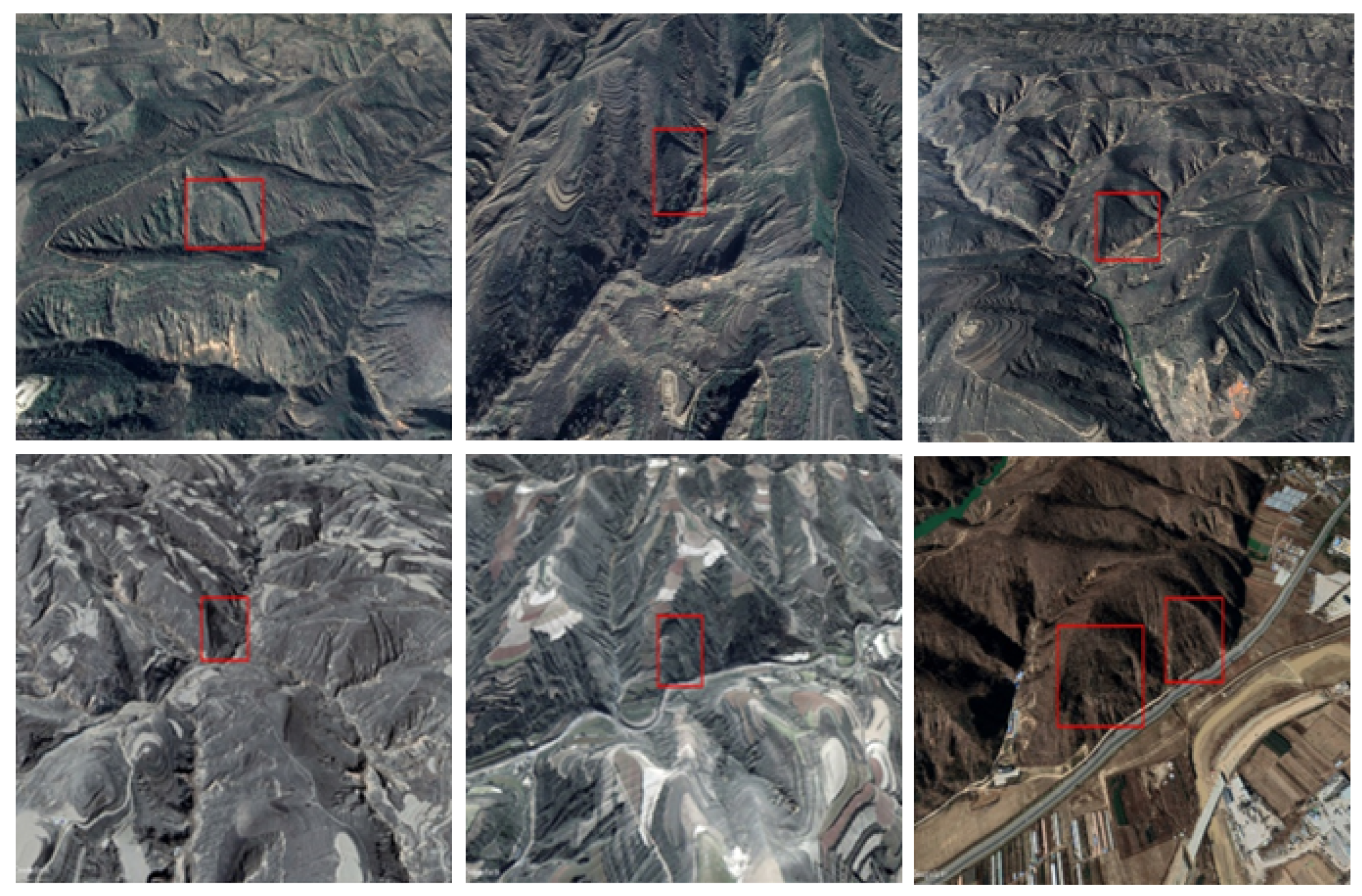


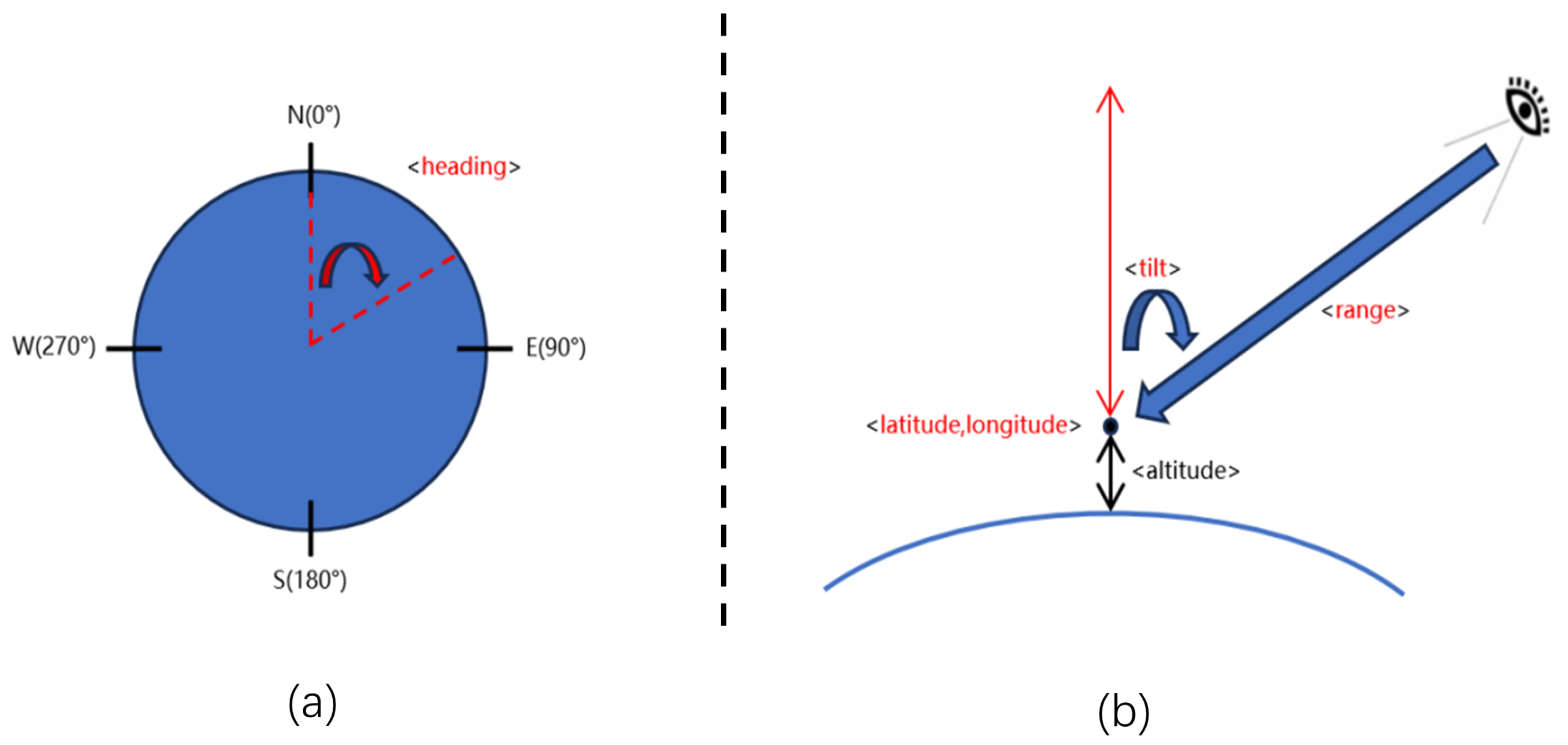





| Heading | 0° | 0° | 120° | 120° | 240° | 240° |
| Tilt | 30° | 45° | 30° | 45° | 30° | 45° |
| Model | Precision | Recall | F1 Score | AP (Mean) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5 (OR) | 0.754 | 0.533 | 0.625 | 0.564 | 0.537 | 0.415 | 0.505 |
| DETR (OR) | 0.814 | 0.846 | 0.830 | 0.879 | 0.877 | 0.710 | 0.822 |
| HDL-WBF (OR) | 0.826 | 0.934 | 0.877 | 0.936 | 0.937 | 0.758 | 0.877 |
| YOLOv5 (OP) | 0.769 | 0.588 | 0.666 | 0.639 | 0.595 | 0.675 | 0.636 |
| DETR (OP) | 0.865 | 0.889 | 0.877 | 0.948 | 0.928 | 0.901 | 0.926 |
| HDL-WBF (OP) | 0.857 | 1.0 | 0.923 | 0.946 | 0.932 | 0.932 | 0.937 |
| TOTAL | Detected (TP) | Missed (FN) | Recall |
|---|---|---|---|
| 43 | 35 | 8 | 81.4% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, S.; Xi, J.; Li, Z.; Ge, D.; Guo, Z.; Yu, J.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, J. Optimal and Multi-View Strategic Hybrid Deep Learning for Old Landslide Detection in the Loess Plateau, Northwest China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16081362
Gao S, Xi J, Li Z, Ge D, Guo Z, Yu J, Wu Q, Zhao Z, Xu J. Optimal and Multi-View Strategic Hybrid Deep Learning for Old Landslide Detection in the Loess Plateau, Northwest China. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(8):1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16081362
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Siyan, Jiangbo Xi, Zhenhong Li, Daqing Ge, Zhaocheng Guo, Junchuan Yu, Qiong Wu, Zhe Zhao, and Jiahuan Xu. 2024. "Optimal and Multi-View Strategic Hybrid Deep Learning for Old Landslide Detection in the Loess Plateau, Northwest China" Remote Sensing 16, no. 8: 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16081362
APA StyleGao, S., Xi, J., Li, Z., Ge, D., Guo, Z., Yu, J., Wu, Q., Zhao, Z., & Xu, J. (2024). Optimal and Multi-View Strategic Hybrid Deep Learning for Old Landslide Detection in the Loess Plateau, Northwest China. Remote Sensing, 16(8), 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16081362








