Testing the Limits of Atmospheric Correction over Turbid Norwegian Fjords
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
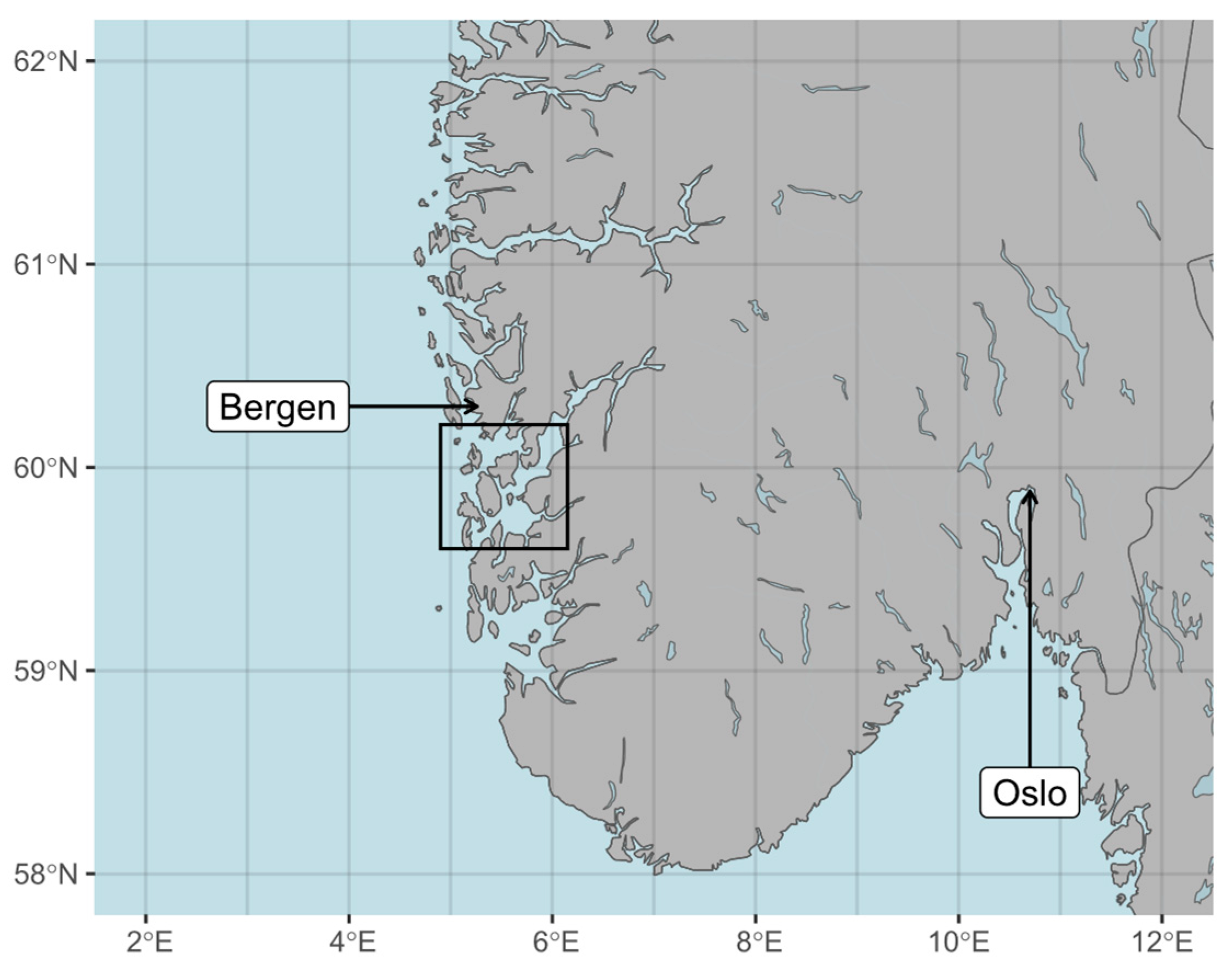
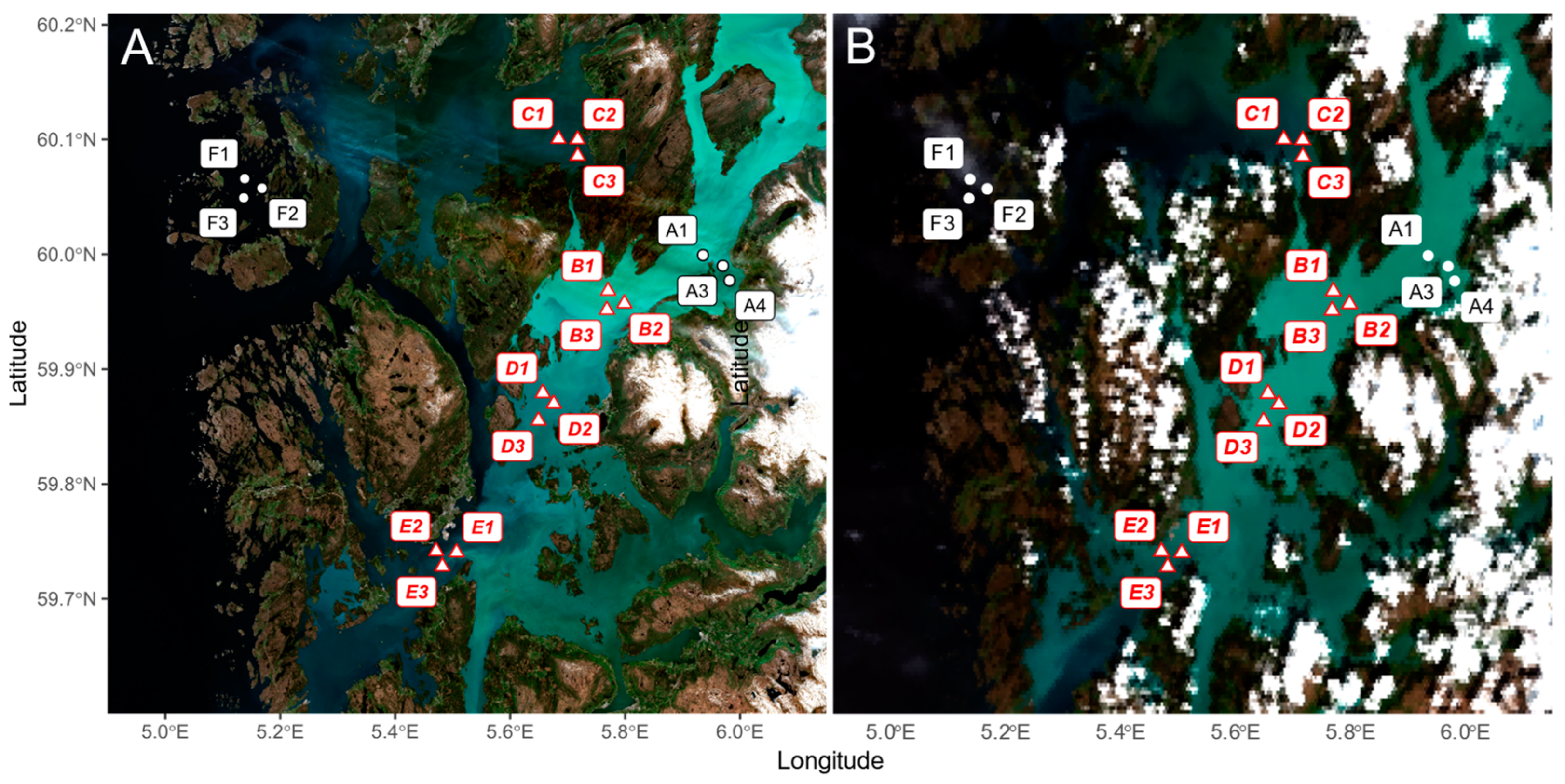
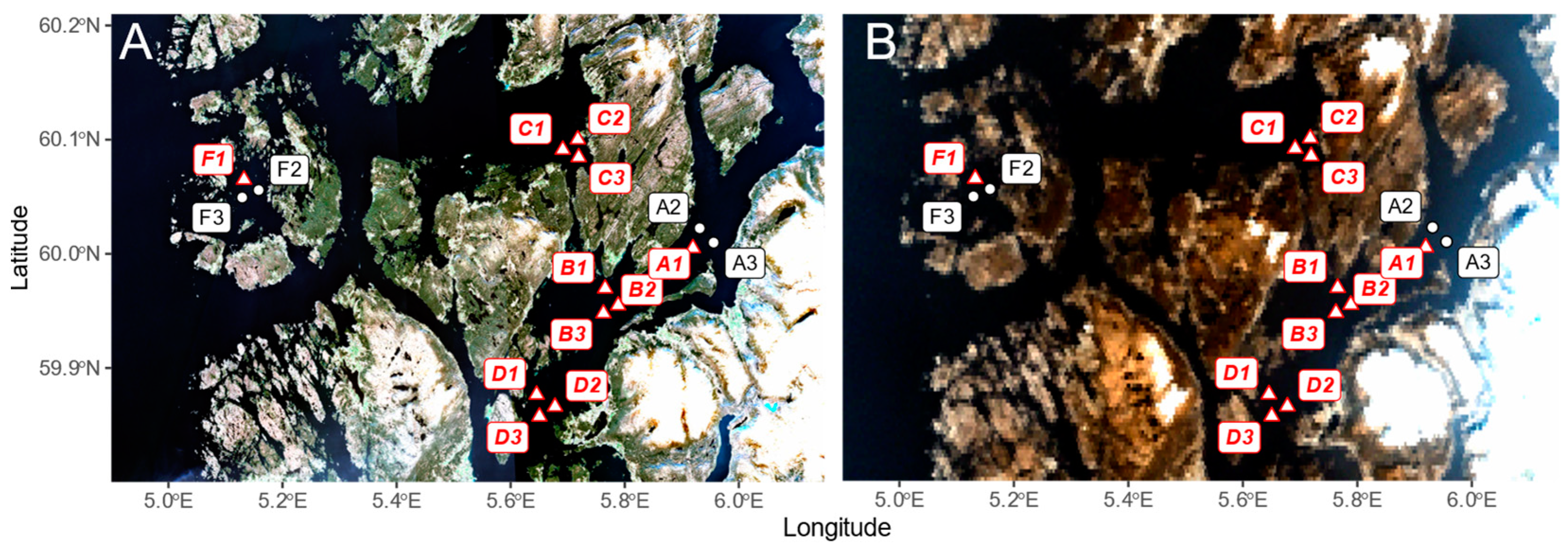
2.1. Study Area
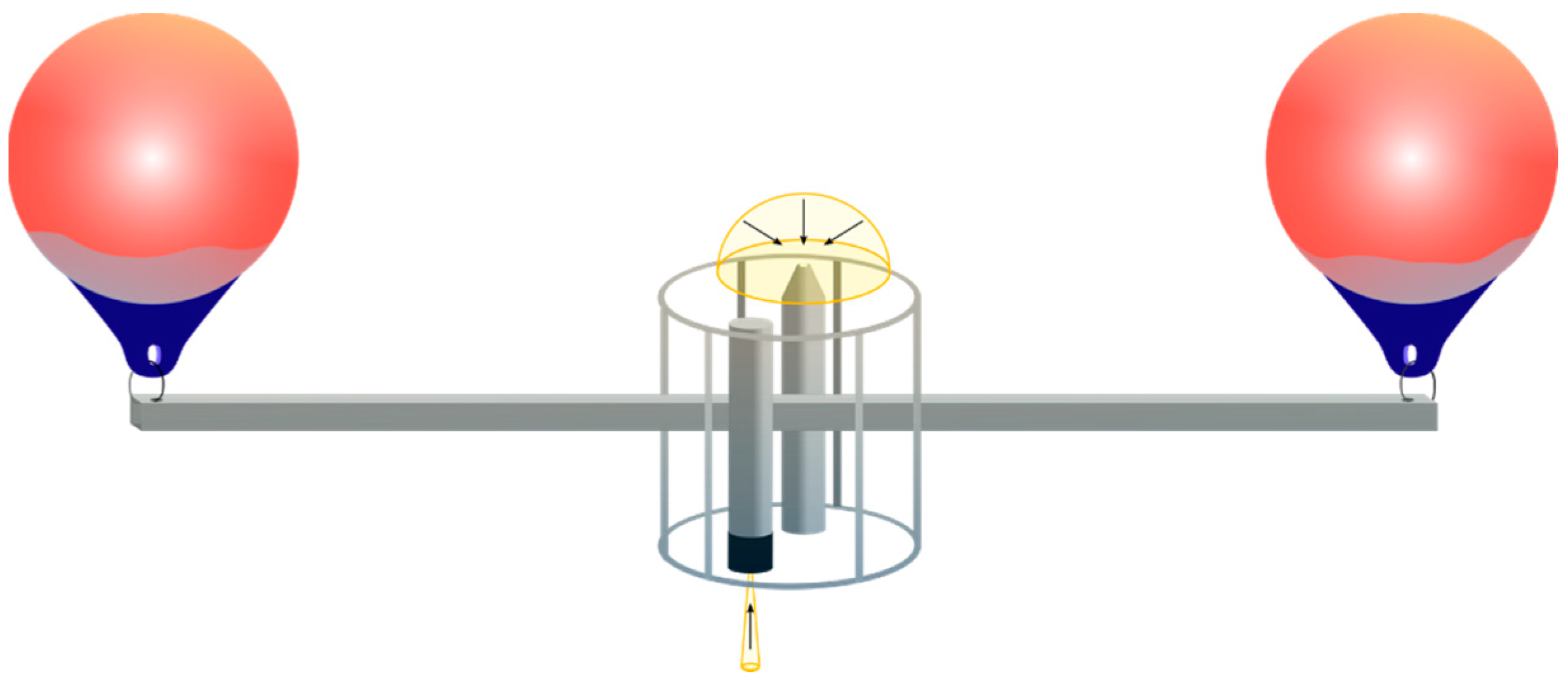
2.2. In Situ Data Collection
2.3. Satellite Data
2.4. Flags
2.5. Atmospheric Correction
2.6. Chlorophyll-a Retrieval Algorithms
2.7. Analysis
3. Results
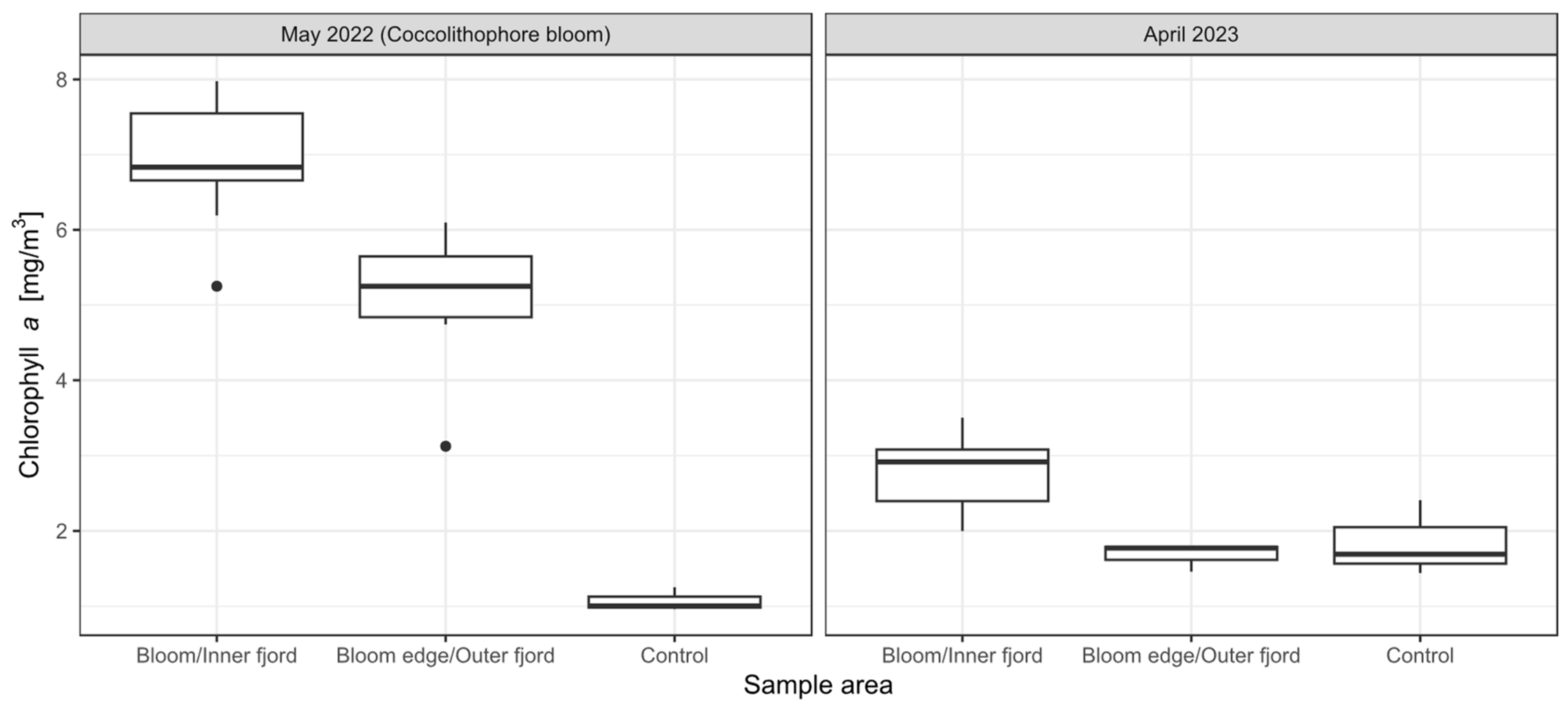
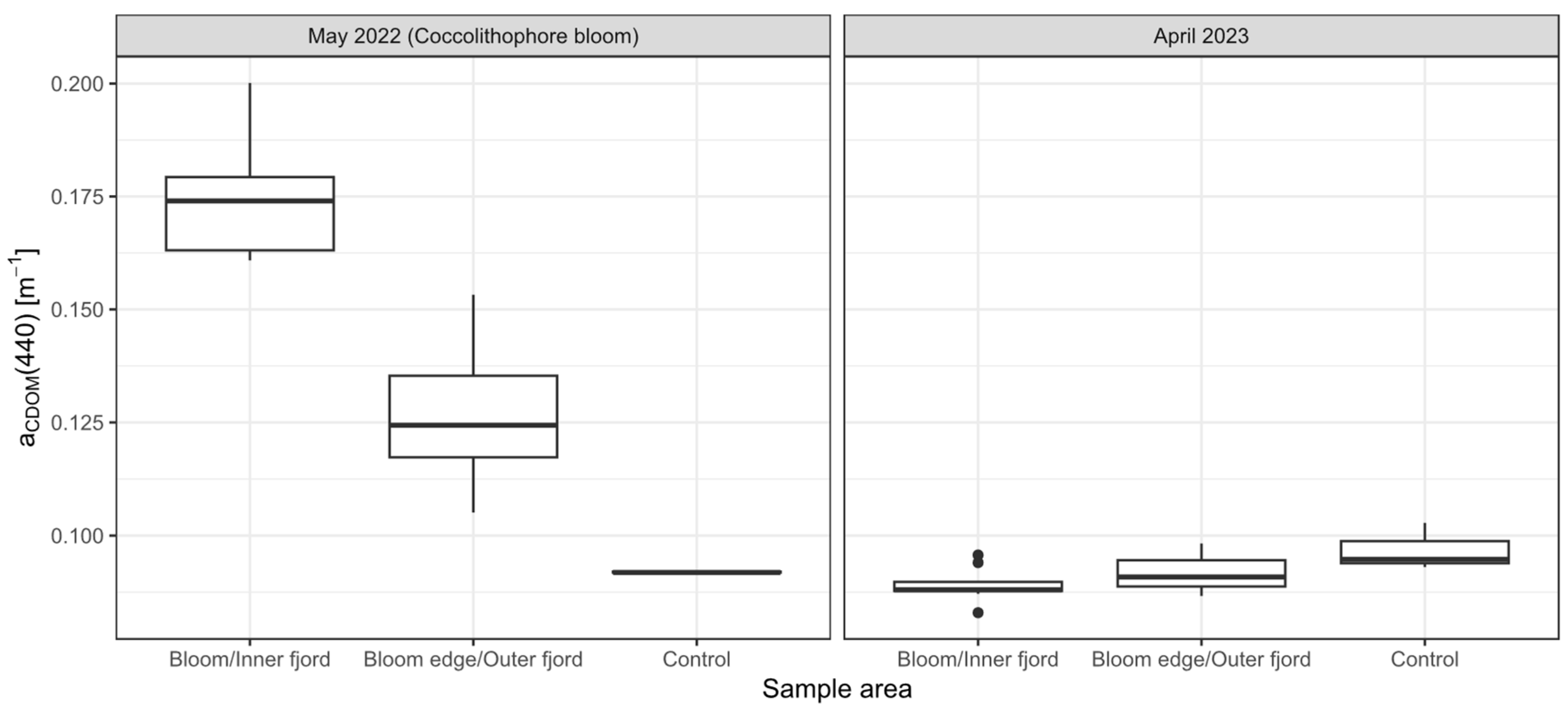
3.1. In Situ Chlorophyll-a, aCDOM(440) and Cell Counts
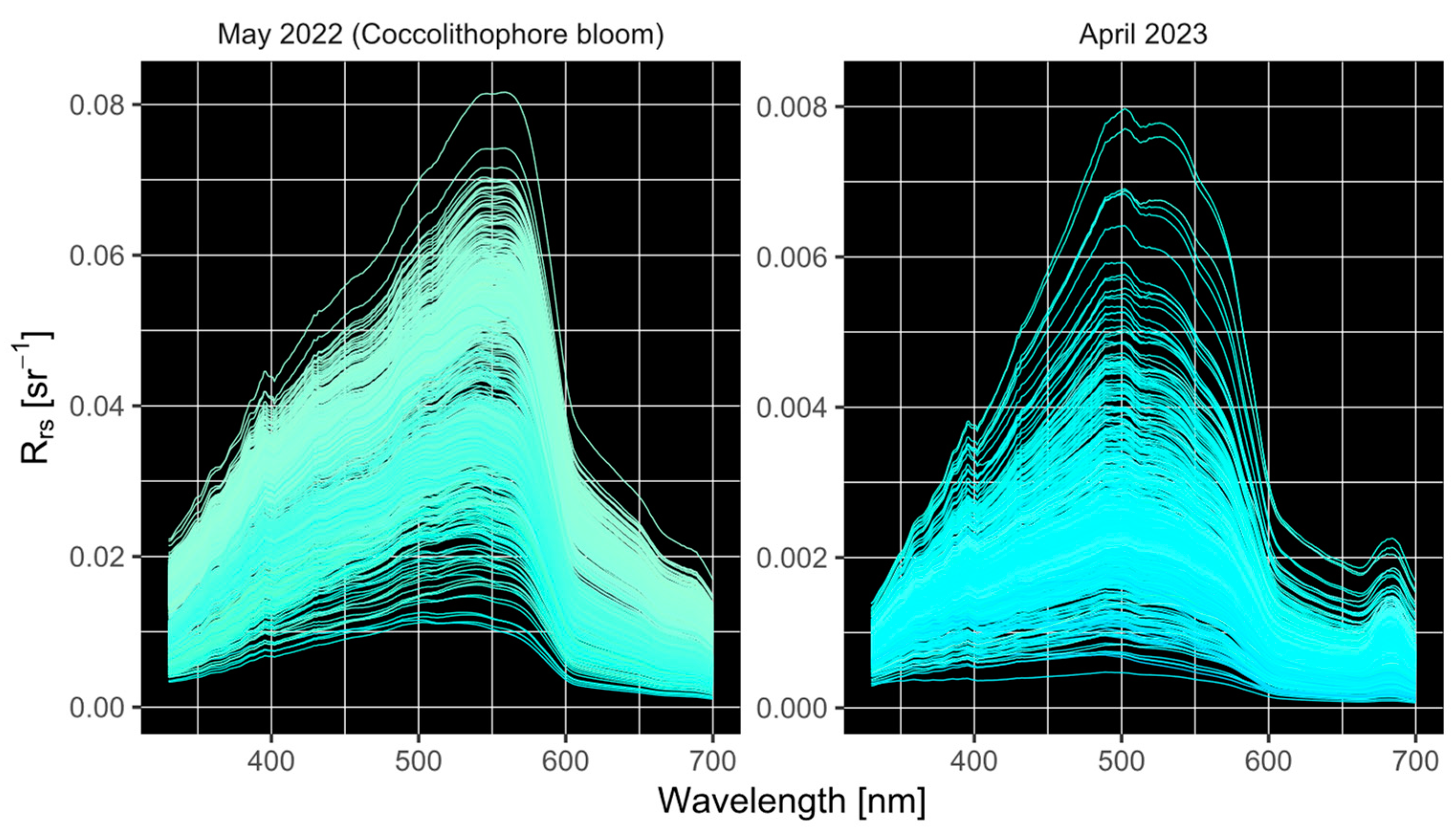
3.2. In Situ Reflectances
3.3. Remote Sensing
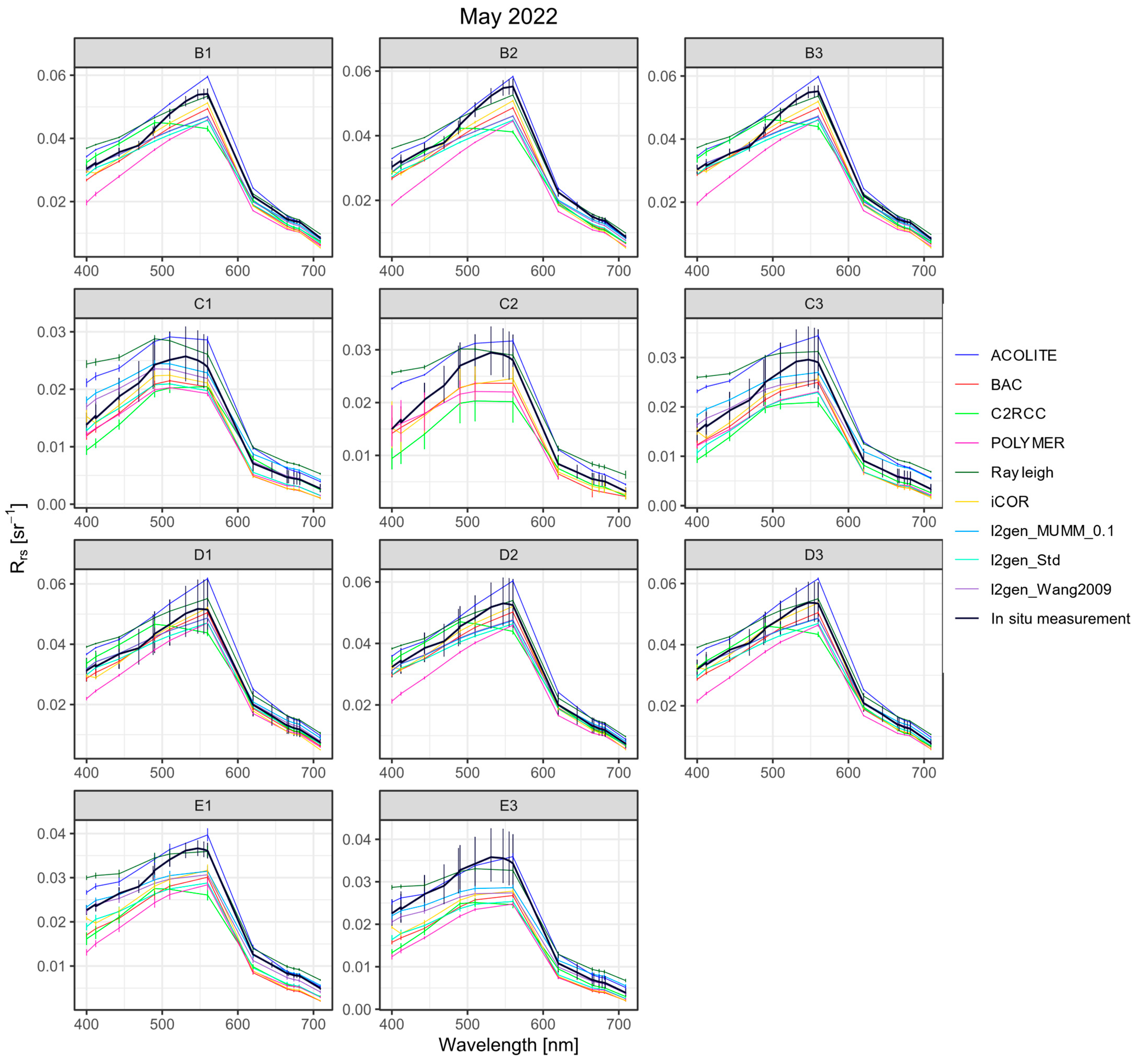
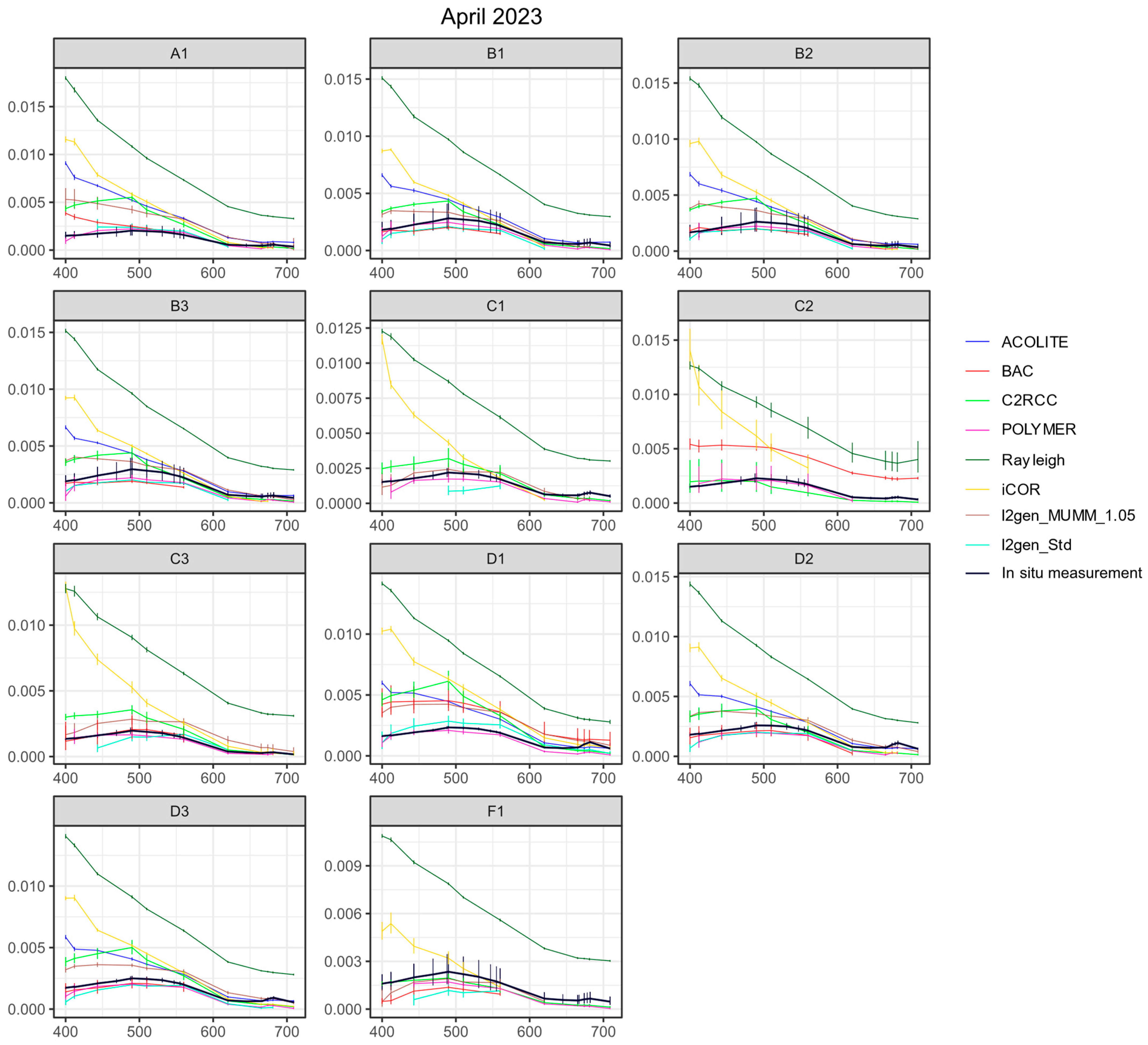
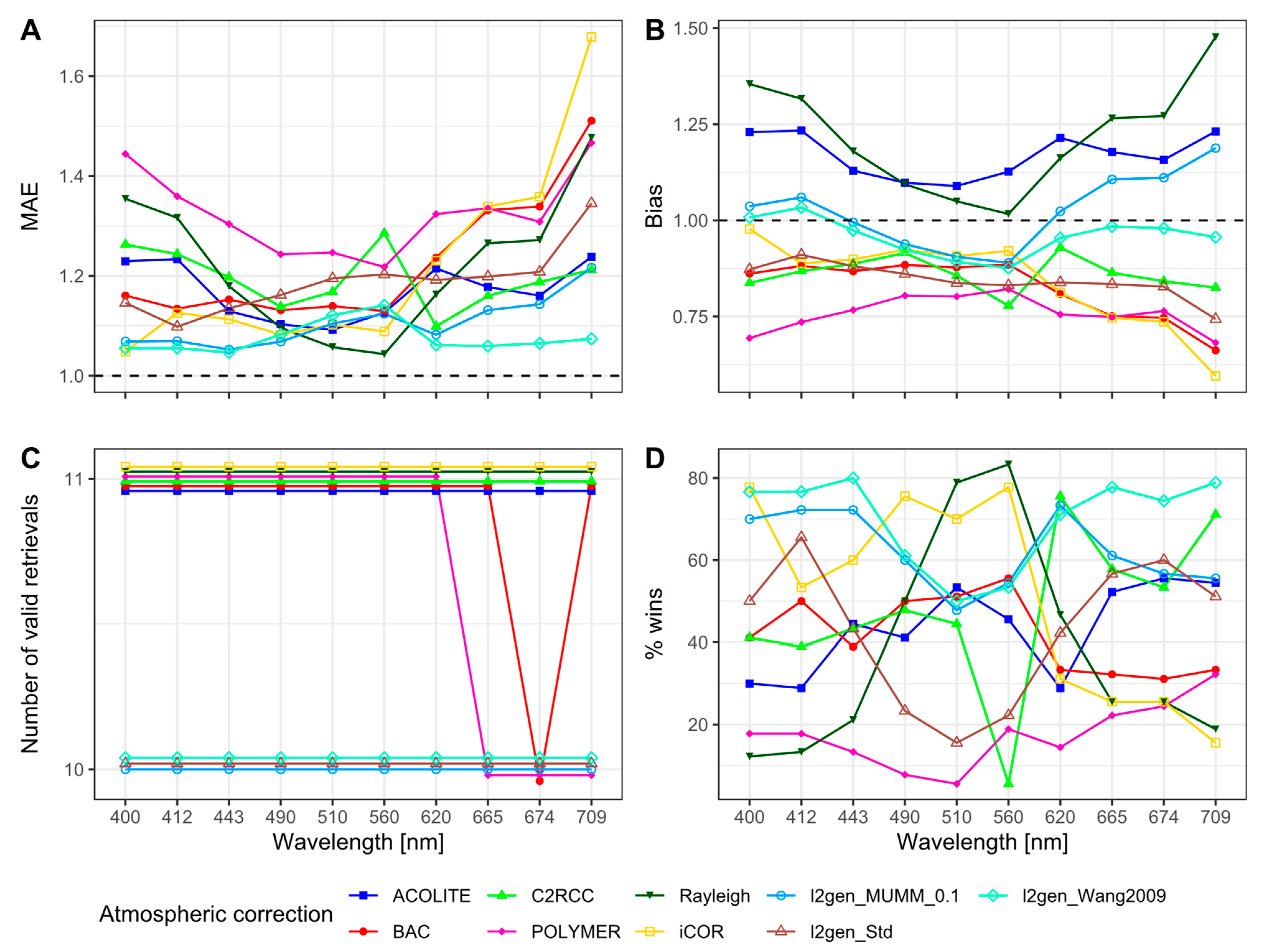
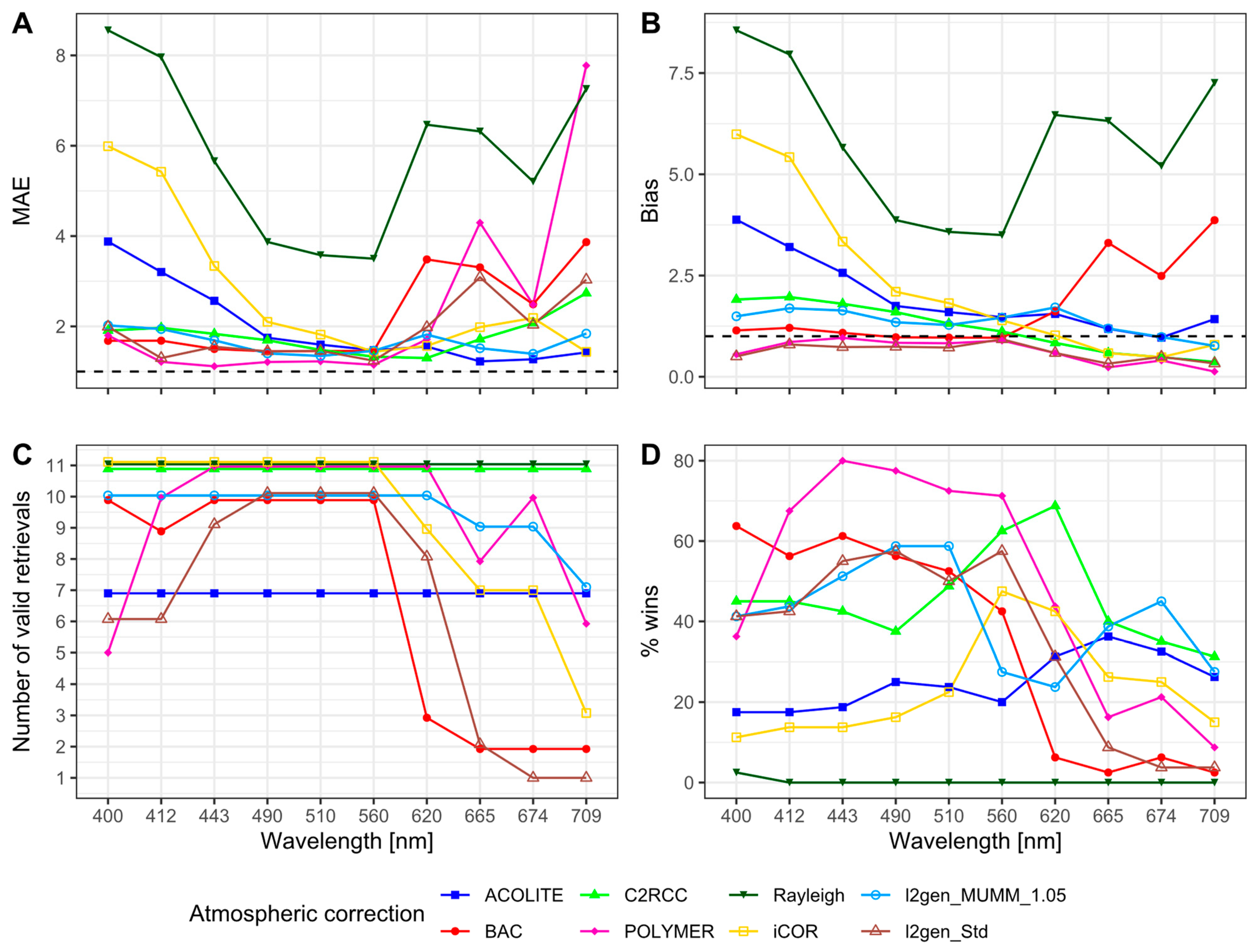
3.3.1. Remote Sensing Reflectances
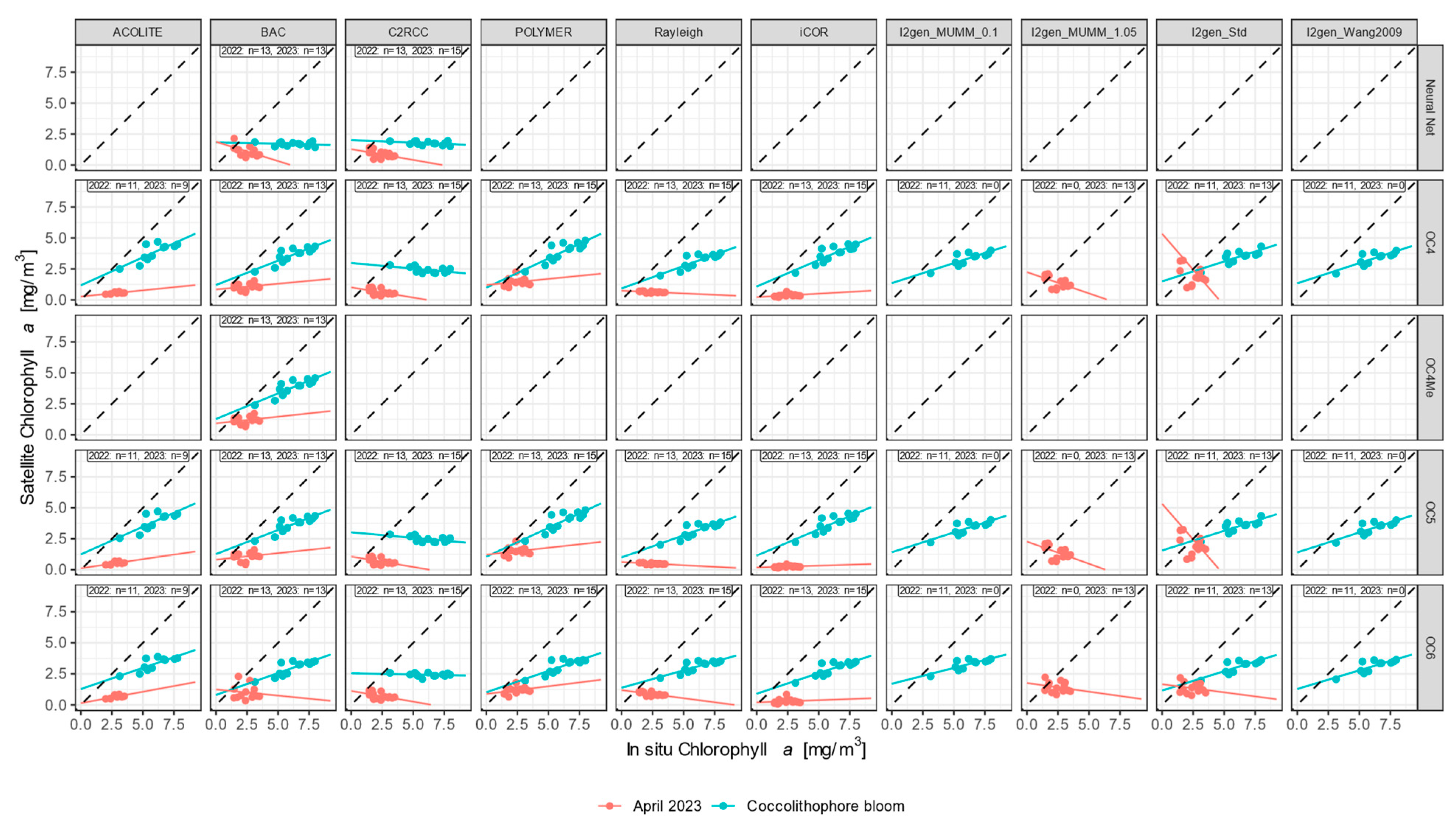
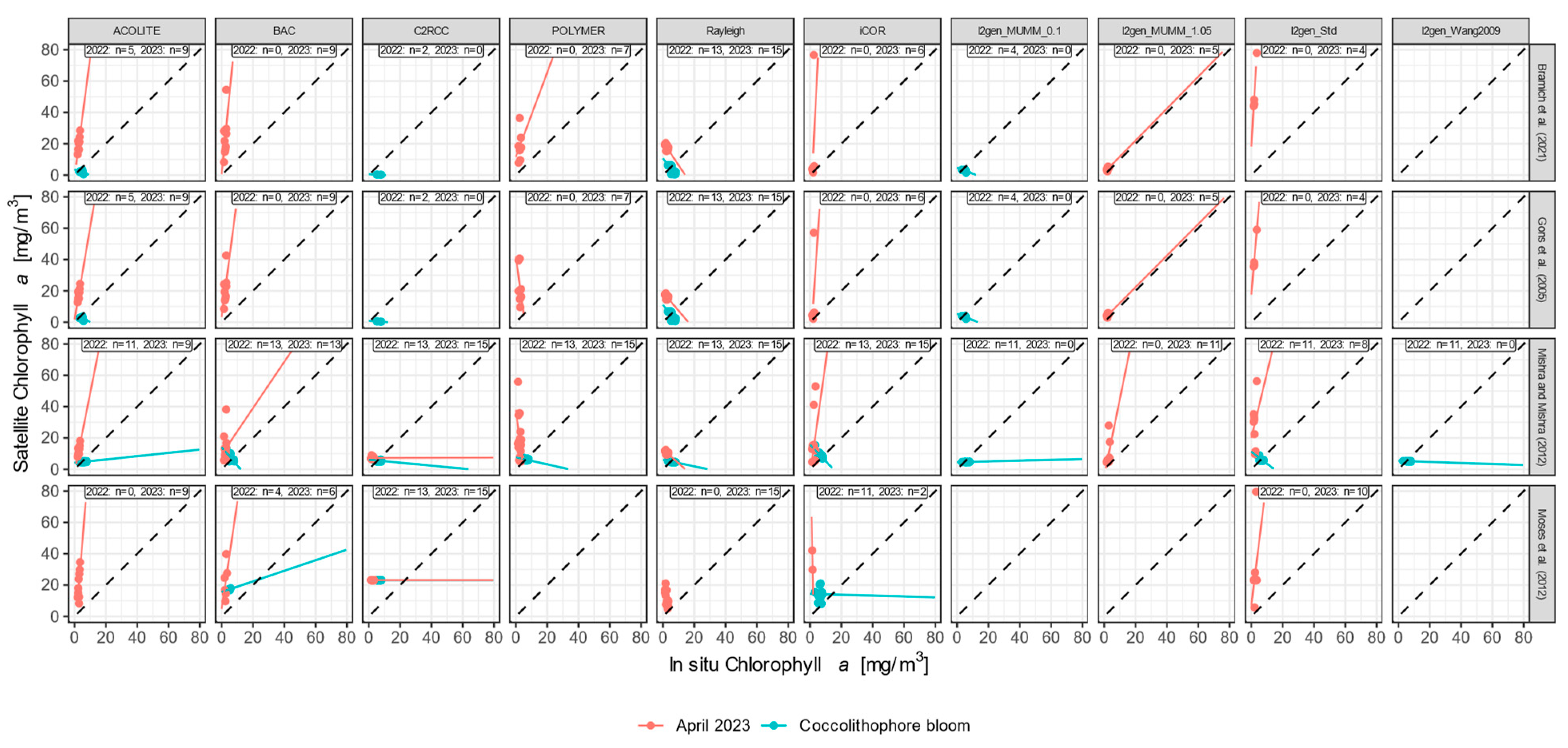
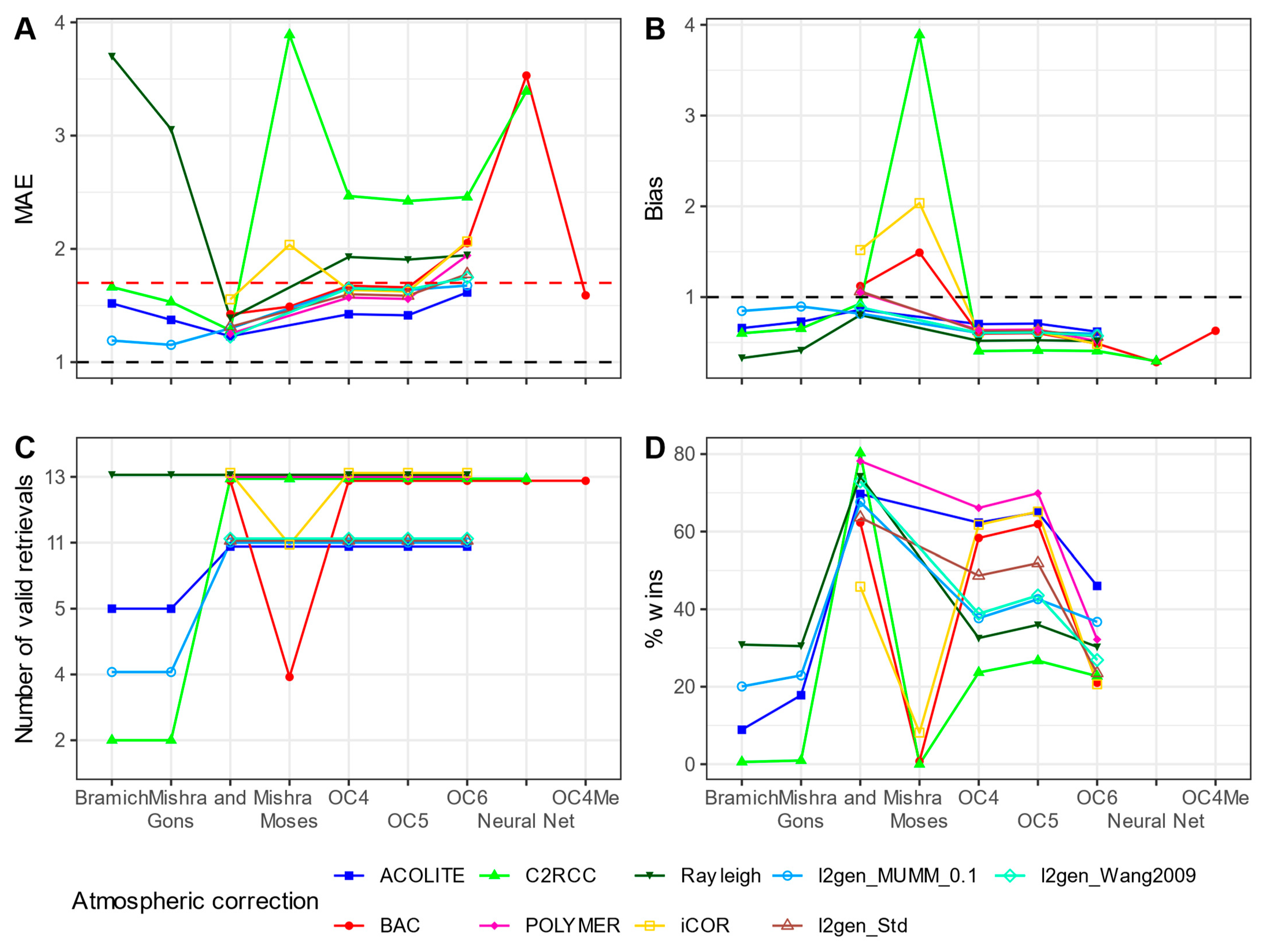
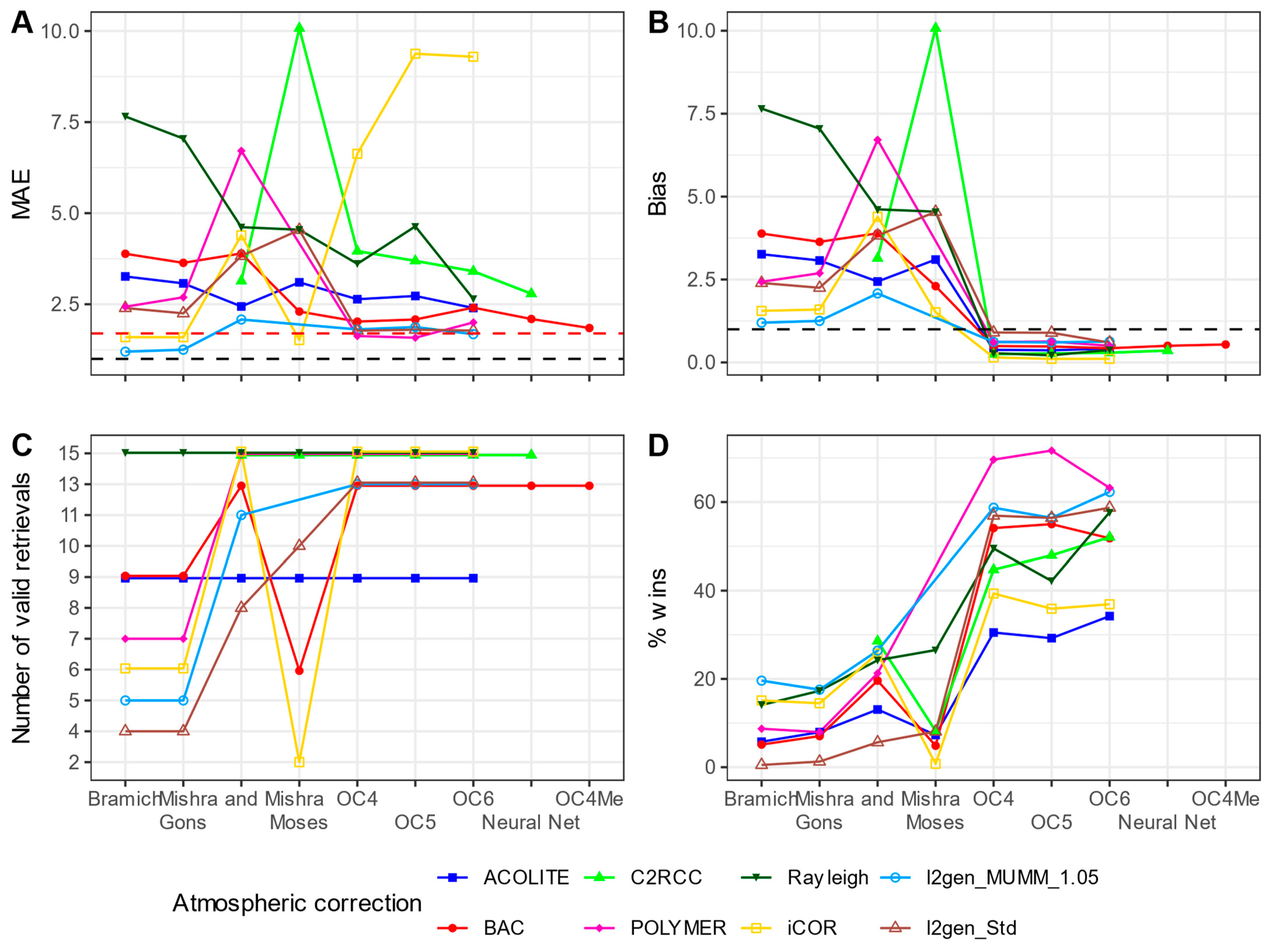
3.3.2. Chlorophyll-a
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hovis, W.A.; Clark, D.K.; Anderson, F.; Austin, R.W.; Wilson, W.H.; Baker, E.T.; Ball, D.; Gordon, H.R.; Mueller, J.L.; El-Sayed, S.Z.; et al. Nimbus-7 Coastal Zone Color Scanner: System Description and Initial Imagery. Science 1980, 210, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buhl-Mortensen, P.; Buhl-Mortensen, L. Diverse and Vulnerable Deep-Water Biotopes in the Hardangerfjord. Mar. Biol. Res. 2014, 10, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzetti, S.; Stenersen, J.H.V. A Critical View of the Environmental Condition of the Sognefjord. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 2167–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlson, B.; Andersen, P.; Arneborg, L.; Cembella, A.; Eikrem, W.; John, U.; West, J.J.; Klemm, K.; Kobos, J.; Lehtinen, S.; et al. Harmful Algal Blooms and Their Effects in Coastal Seas of Northern Europe. Harmful Algae 2021, 102, 101989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, R.M.; Salehi, B.; Mahdianpari, M.; Mohammadimanesh, F.; Mountrakis, G.; Quackenbush, L.J. A Meta-Analysis on Harmful Algal Bloom (Hab) Detection and Monitoring: A Remote Sensing Perspective. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IOCCG. Observation of Harmful Algal Blooms with Ocean Colour Radiometry; Bernard, S., Lain, L.R., Kudela, R., Pitcher, G., Eds.; Reports of the International Ocean Colour Coordinating Group; IOCCG: Dartmouth, NS, Canada, 2021; Volume 20. [Google Scholar]
- IOCCG. Atmospheric Correction for Remotely-Sensed Ocean-Colour Products; Wang, M., Ed.; Reports of the International Ocean Colour Coordinating Group; IOCCG: Dartmouth, NS, Canada, 2010; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, H.R. Evolution of Ocean Color Atmospheric Correction: 1970–2005. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werdell, P.J.; McKinna, L.I.W.; Boss, E.; Ackleson, S.G.; Craig, S.E.; Gregg, W.W.; Lee, Z.; Maritorena, S.; Roesler, C.S.; Rousseaux, C.S.; et al. An Overview of Approaches and Challenges for Retrieving Marine Inherent Optical Properties from Ocean Color Remote Sensing. Prog. Oceanogr. 2018, 160, 186–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobley, C.D.; Stramski, D.; Paul Bissett, W.; Boss, E. Optical Modeling of Ocean Waters: Is the Case 1–Case 2 Classification Still Useful? Oceanography 2004, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, H.R.; Wang, M. Retrieval of Water-Leaving Radiance and Aerosol Optical Thickness over the Oceans with SeaWiFS: A Preliminary Algorithm. Appl. Opt. 1994, 33, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoine, D. OLCI Level 2 Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document: Atmospheric Corrections over Case 1 Waters (CWAC). Ref S3-L2-SD-03-C07-LOV-ATBD Version 22. 2010. Available online: https://sentiwiki.copernicus.eu/__attachments/1672112/S3-L2-SD-03-C07-LOV-ATBD%20-%20OLCI%20L2%20ATBD%20Atmospheric%20Corrections%20case%201%20waters%202010%20-%2002.pdf?inst-v=d105f701-8f35-4a57-9bd3-983ac5f50bca (accessed on 28 October 2024).
- Mazeran, C.; Hieronymi, M.; Steinmetz, F. Ocean Colour Bright Pixel Correction–Algorithm Theoretical Basis. EUM/18/BPC/ATBD. 2021. Available online: https://www-cdn.eumetsat.int/files/2021-10/S3-OLCI_OC-BPC_ATBD.pdf (accessed on 28 October 2024).
- Vanhellemont, Q.; Ruddick, K. Atmospheric Correction of Metre-Scale Optical Satellite Data for Inland and Coastal Water Applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 216, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockmann, C.; Doerffer, R.; Peters, M.; Stelzer, K.; Embacher, S.; Ruescas, A. Evolution of the C2RCC Neural Network for Sentinel 2 and 3 for the Retrieval of Ocean Colour Products in Normal and Extreme Optically Complex Waters; European Space Agency: Paris, France, 2016; Volume SP-740. [Google Scholar]
- De Keukelaere, L.; Sterckx, S.; Adriaensen, S.; Knaeps, E.; Reusen, I.; Giardino, C.; Bresciani, M.; Hunter, P.; Neil, C.; Van der Zande, D.; et al. Atmospheric Correction of Landsat-8/OLI and Sentinel-2/MSI Data Using iCOR Algorithm: Validation for Coastal and Inland Waters. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 51, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.W.; Franz, B.A.; Werdell, P.J. Estimation of Near-Infrared Water-Leaving Reflectance for Satellite Ocean Color Data Processing. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 7521–7527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Son, S.; Shi, W. Evaluation of MODIS SWIR and NIR-SWIR Atmospheric Correction Algorithms Using SeaBASS Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruddick, K.G.; Ovidio, F.; Rijkeboer, M. Atmospheric Correction of SeaWiFS Imagery for Turbid Coastal and Inland Waters. Appl. Opt. 2000, 39, 897–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinmetz, F.; Ramon, D. Sentinel-2 MSI and Sentinel-3 OLCI Consistent Ocean Colour Products Using POLYMER. In Remote Sensing of the Open and Coastal Ocean and Inland Waters; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2018; Volume 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, F.; Deschamps, P.-Y.; Ramon, D. Atmospheric Correction in Presence of Sun Glint: Application to MERIS. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 9783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.-J.; Ruddick, K. Model of Remote-Sensing Reflectance Including Bidirectional Effects for Case 1 and Case 2 Waters. Appl. Opt. 2005, 44, 1236–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhellemont, Q.; Ruddick, K. Atmospheric Correction of Sentinel-3/OLCI Data for Mapping of Suspended Particulate Matter and Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Belgian Turbid Coastal Waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 256, 112284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourg, L. MERIS Level 2 Detailed Processing Model. In Document no. PO-TN-MEL-GS-0006; ACRI-ST, 2011; Available online: https://earth.esa.int/eogateway/documents/20142/37627/MERIS-Level-2-Detailed-Processing-Model.pdf/075b5eb1-7b3b-52f5-28a4-9fbb5d8e0fb7?t=1703157756360 (accessed on 28 October 2024).
- Brewin, R.J.W.; Sathyendranath, S.; Müller, D.; Brockmann, C.; Deschamps, P.-Y.; Devred, E.; Doerffer, R.; Fomferra, N.; Franz, B.; Grant, M.; et al. The Ocean Colour Climate Change Initiative: III. A Round-Robin Comparison on in-Water Bio-Optical Algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 162, 271–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balch, W.M.; Gordon, H.R.; Bowler, B.C.; Drapeau, D.T.; Booth, E.S. Calcium Carbonate Measurements in the Surface Global Ocean Based on Moderate-Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer Data. J. Geophys. Res. C Oceans 2005, 110, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansper, A.; Alikas, K. Retrieval of Chlorophyll a from Sentinel-2 MSI Data for the European Union Water Framework Directive Reporting Purposes. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlevan, N.; Mangin, A.; Balasubramanian, S.V.; Smith, B.; Alikas, K.; Arai, K.; Barbosa, C.; Bélanger, S.; Binding, C.; Bresciani, M.; et al. ACIX-Aqua: A Global Assessment of Atmospheric Correction Methods for Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 over Lakes, Rivers, and Coastal Waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 258, 112366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Ma, R.; Xue, K.; Loiselle, S.A. The Assessment of Landsat-8 OLI Atmospheric Correction Algorithms for Inland Waters. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windle, A.E.; Evers-King, H.; Loveday, B.R.; Ondrusek, M.; Silsbe, G.M. Evaluating Atmospheric Correction Algorithms Applied to OLCI Sentinel-3 Data of Chesapeake Bay Waters. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel, F.P.; Pedocchi, F. Evaluation of ACOLITE Atmospheric Correction Methods for Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 in the Río de La Plata Turbid Coastal Waters. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2022, 43, 215–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendif, E.M.; Nevado, B.; Wong, E.L.Y.; Hagino, K.; Probert, I.; Young, J.R.; Rickaby, R.E.M.; Filatov, D.A. Repeated Species Radiations in the Recent Evolution of the Key Marine Phytoplankton Lineage Gephyrocapsa. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrrell, T.; Merico, A. Emiliania Huxleyi: Bloom Observations and the Conditions That Induce Them. In Coccolithophores: From Molecular Processes to Global Impact; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 75–97. [Google Scholar]
- Berge, G. Discoloration of the Sea Due to Coccolithus Huxleyi “Bloom”. Sarsia 1962, 6, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramich, J.; Bolch, C.J.S.; Fischer, A. Improved Red-Edge Chlorophyll-a Detection for Sentinel 2. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 120, 106876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gons, H.J.; Rijkeboer, M.; Ruddick, K.G. Effect of a Waveband Shift on Chlorophyll Retrieval from MERIS Imagery of Inland and Coastal Waters. J. Plankton Res. 2005, 27, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Mishra, D.R. Normalized Difference Chlorophyll Index: A Novel Model for Remote Estimation of Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Turbid Productive Waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, W.J.; Saprygin, V.; Gerasyuk, V.; Povazhnyy, V.; Berdnikov, S.; Gitelson, A.A. OLCI-Based NIR-Red Models for Estimating Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Productive Coastal Waters—A Preliminary Evaluation. Environ. Res. Commun. 2019, 1, 011002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, J.E.; Werdell, P.J. Chlorophyll Algorithms for Ocean Color Sensors–OC4, OC5 & OC6. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 229, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamre, B.; Stamnes, S.; Stamnes, K.; Stamnes, J. AccuRT: A Versatile Tool for Radiative Transfer Simulations in the Coupled Atmosphere-Ocean System. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1810, 120002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burggraaff, O. Biases from Incorrect Reflectance Convolution. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 13801–13816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tassan, S.; Ferrari, G.M. A Sensitivity Analysis of the ‘Transmittance–Reflectance’Method for Measuring Light Absorption by Aquatic Particles. J. Plankton Res. 2002, 24, 757–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Heukelem, L.; Thomas, C.S. Computer-Assisted High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Method Development with Applications to the Isolation and Analysis of Phytoplankton Pigments. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 910, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm-Hansen, O.; Riemann, B. Chlorophyll a Determination: Improvements in Methodology. Oikos 1978, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seegers, B.N.; Stumpf, R.P.; Schaeffer, B.A.; Loftin, K.A.; Werdell, P.J. Performance Metrics for the Assessment of Satellite Data Products: An Ocean Color Case Study. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 7404–7422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUMETSAT. Recommendations for Sentinel-3 OLCI Ocean Colour Product Validations in Comparison with in Situ Measurements – Matchup Protocols. 2022. Available online: https://user.eumetsat.int/s3/eup-strapi-media/Recommendations_for_Sentinel_3_OLCI_Ocean_Colour_product_validations_in_comparison_with_in_situ_measurements_Matchup_Protocols_V8_B_e6c62ce677.pdf (accessed on 28 October 2024).
- Ahmad, Z.; Franz, B.A.; McClain, C.R.; Kwiatkowska, E.J.; Werdell, J.; Shettle, E.P.; Holben, B.N. New Aerosol Models for the Retrieval of Aerosol Optical Thickness and Normalized Water-Leaving Radiances from the SeaWiFS and MODIS Sensors over Coastal Regions and Open Oceans. Appl. Opt. 2010, 49, 5545–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shi, W. The NIR-SWIR Combined Atmospheric Correction Approach for MODIS Ocean Color Data Processing. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 15722–15733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doerffer, R. OLCI L2 ATBD Ocean Colour Turbid Water. Ref S3-L2-SD-03-C11-GKSS-ATBD Version 20. 2010. Available online: https://step.esa.int/docs/extra/OLCI_L2_ATBD_Ocean_Colour_Turbid_Water.pdf (accessed on 28 October 2024).
- Sterckx, S.; Knaeps, S.; Kratzer, S.; Ruddick, K. SIMilarity Environment Correction (SIMEC) Applied to MERIS Data over Inland and Coastal Waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 157, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berk, A.; Anderson, G.P.; Acharya, P.K.; Bernstein, L.S.; Muratov, L.; Lee, J.; Fox, M.; Adler-Golden, S.M.; Chetwynd, J.H., Jr.; Hoke, M.L. MODTRAN5: 2006 Update. In Algorithms and Technologies for Multispectral, Hyperspectral, and Ultraspectral Imagery XII; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2006; Volume 6233, pp. 508–515. [Google Scholar]
- Morel, A.; Antoine, D.; Gentili, B. Bidirectional Reflectance of Oceanic Waters: Accounting for Raman Emission and Varying Particle Scattering Phase Function. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 6289–6306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EUMETSAT. Sentinel-3 OLCI L2 Report for Baseline Collection OL_L2M_003. 2021. Available online: https://user.eumetsat.int/s3/eup-strapi-media/Sentinel_3_OLCI_L2_report_for_baseline_collection_OL_L2_M_003_2_B_c8bbc6d986.pdf (accessed on 28 October 2024).
- Franz, B.A.; Bailey, S.W.; Werdell, P.J.; McClain, C.R. Sensor-Independent Approach to the Vicarious Calibration of Satellite Ocean Color Radiometry. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 5068–5082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gons, H.J.; Rijkeboer, M.; Ruddick, K.G. A Chlorophyll-Retrieval Algorithm for Satellite Imagery (Medium Resolution Imaging Spectrometer) of Inland and Coastal Waters. J. Plankton Res. 2002, 24, 947–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gons, H.J.; Auer, M.T.; Effler, S.W. MERIS Satellite Chlorophyll Mapping of Oligotrophic and Eutrophic Waters in the Laurentian Great Lakes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 4098–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricaud, A.; Morel, A.; Prieur, L. Absorption by Dissolved Organic Matter of the Sea (Yellow Substance) in the UV and Visible Domains. Limnol Ocean. 1981, 26, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, W.J.; Gitelson, A.A.; Berdnikov, S.; Saprygin, V.; Povazhnyi, V. Operational MERIS-Based NIR-Red Algorithms for Estimating Chlorophyll-a Concentrations in Coastal Waters–The Azov Sea Case Study. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drinkwater, M.; Rebhan, H. Sentinel-3: Mission Requirements Document. Ref EOP-SMO1151MD-Md 2007. Available online: https://earth.esa.int/eogateway/documents/20142/1564943/Sentinel-3-Mission-Requirements-Document-MRD.pdf (accessed on 28 October 2024).
- Moore, T.S.; Dowell, M.D.; Franz, B.A. Detection of Coccolithophore Blooms in Ocean Color Satellite Imagery: A Generalized Approach for Use with Multiple Sensors. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.W.; Yoder, J.A. Coccolithophorid Blooms in the Global Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1994, 99, 7467–7482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.A.E.; Garcia, V.M.T.; Dogliotti, A.I.; Ferreira, A.; Romero, S.I.; Mannino, A.; Souza, M.S.; Mata, M.M. Environmental Conditions and Bio-optical Signature of a Coccolithophorid Bloom in the Patagonian Shelf. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, H.; Ohde, T.; Gerth, M.; Lavik, G.; Leipe, T. Identification of Coccolithophore Blooms in the SE Atlantic Ocean off Namibia by Satellites and In-Situ Methods. Cont. Shelf Res. 2007, 27, 258–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renosh, P.R.; Doxaran, D.; Keukelaere, L.D.; Gossn, J.I. Evaluation of Atmospheric Correction Algorithms for Sentinel-2-MSI and Sentinel-3-OLCI in Highly Turbid Estuarine Waters. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, M.A.; Simis, S.G.H.; Martinez-Vicente, V.; Poser, K.; Bresciani, M.; Alikas, K.; Spyrakos, E.; Giardino, C.; Ansper, A. Assessment of Atmospheric Correction Algorithms for the Sentinel-2A MultiSpectral Imager over Coastal and Inland Waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 225, 267–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Algorithm | References | Method | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACOLITE | [14,23] | Dark spectrum fitting with sun-glint correction | Needs dark pixels; assumes atmospheric homogeneity if used on subset/tiles |
| BAC | [12,13] | Bright pixel correction | Assumes zero water-leaving reflectance in NIR, flags very bright water pixels, limitations of training dataset for neural net products |
| C2RCC | [15] | Neural network | Limitations of training dataset |
| iCOR | [16] | Dark spectrum fitting with adjacency correction | Needs dark land pixels; assumes atmospheric homogeneity |
| L2gen_Std | [17,47] | Relative humidity-based model selection and iterative NIR | Fails in environments outside scope of empirical optical models |
| L2gen_MUMM | [19] | Aerosol model choice based on user-determined calibration parameters | Requires input of calibration parameters; assumes spatial heterogeneity of 765:865 nm ratio for aerosol and water-leaving reflectance over scene or subscene |
| L2gen_Wang2009 | [18,48] | NIR-SWIR switching | OLCI has no SWIR band; low signal-to-noise ratio of 1020 nm band |
| POLYMER | [20,21] | Spectral matching with sun-glint correction | Neglects CDOM absorption variability, based on the Park and Ruddick (2005) water reflectance model [22] |
| Rayleigh correction | [24] | Molecular scattering estimated from air pressure and sensor geometry | No aerosol correction |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tessin, E.; Hamre, B.; Kristoffersen, A.S. Testing the Limits of Atmospheric Correction over Turbid Norwegian Fjords. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4082. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16214082
Tessin E, Hamre B, Kristoffersen AS. Testing the Limits of Atmospheric Correction over Turbid Norwegian Fjords. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(21):4082. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16214082
Chicago/Turabian StyleTessin, Elinor, Børge Hamre, and Arne Skodvin Kristoffersen. 2024. "Testing the Limits of Atmospheric Correction over Turbid Norwegian Fjords" Remote Sensing 16, no. 21: 4082. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16214082
APA StyleTessin, E., Hamre, B., & Kristoffersen, A. S. (2024). Testing the Limits of Atmospheric Correction over Turbid Norwegian Fjords. Remote Sensing, 16(21), 4082. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16214082






