Study and Analysis of the Thunder Source Location Error Based on Acoustic Ray-Tracing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
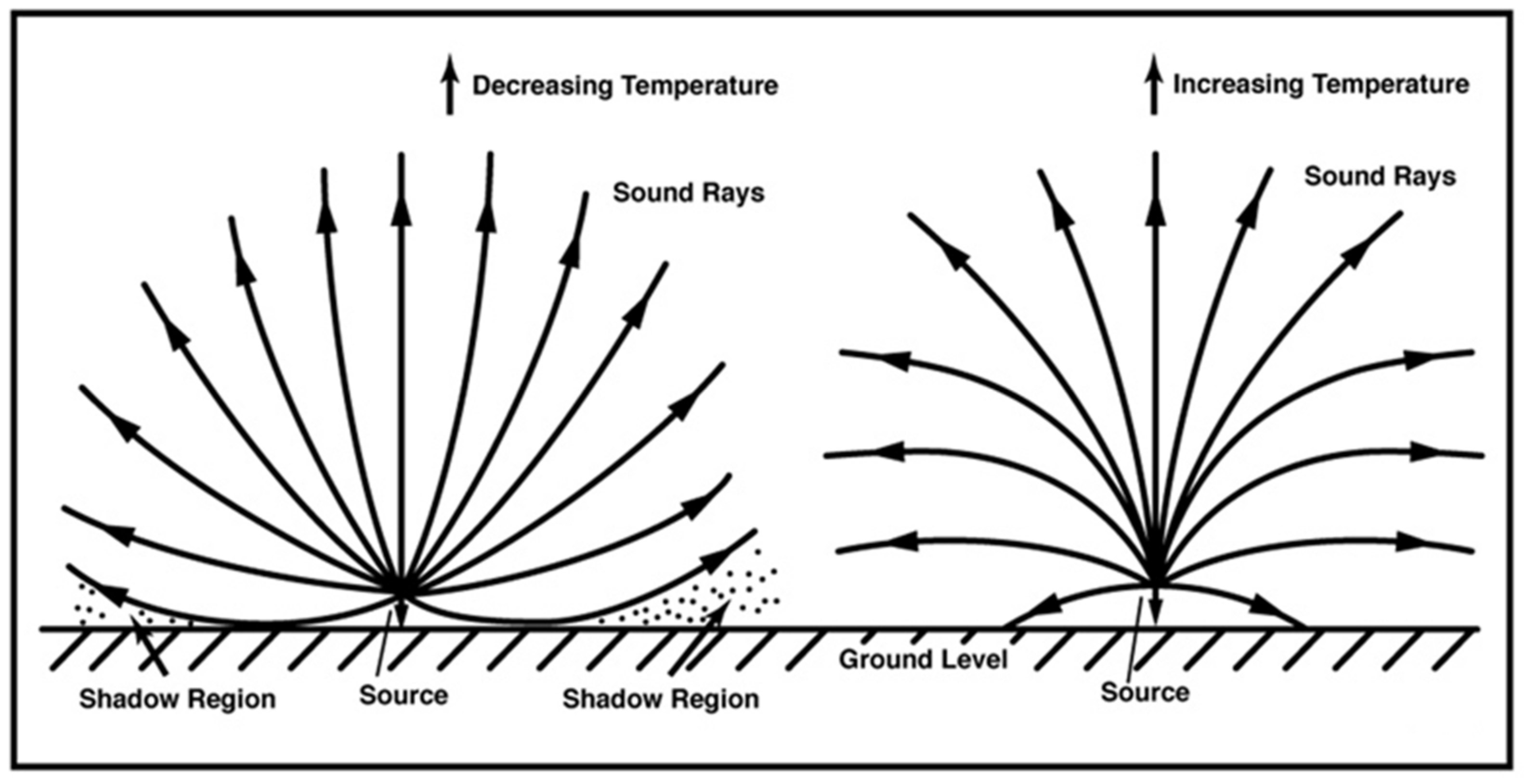
2.1. Vertical Distribution of Acoustic Velocity in the Atmosphere
2.2. Theory of Acoustic Ray Transmission
2.2.1. The Eikonal Equation
2.2.2. Snell’s Law of Refraction for Acoustic Ray Transmission
2.3. Principle of RLE Calculation for Three Models
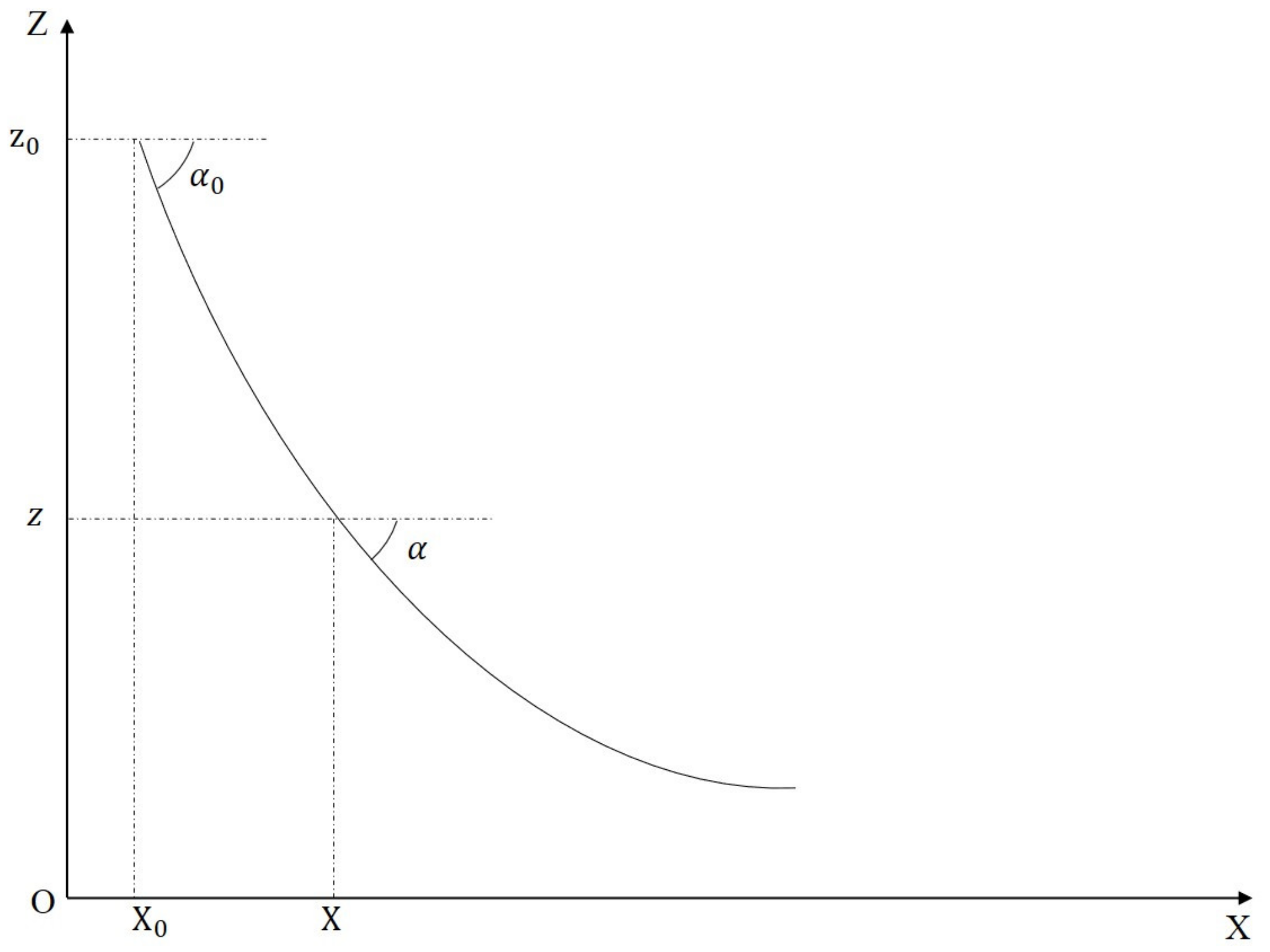
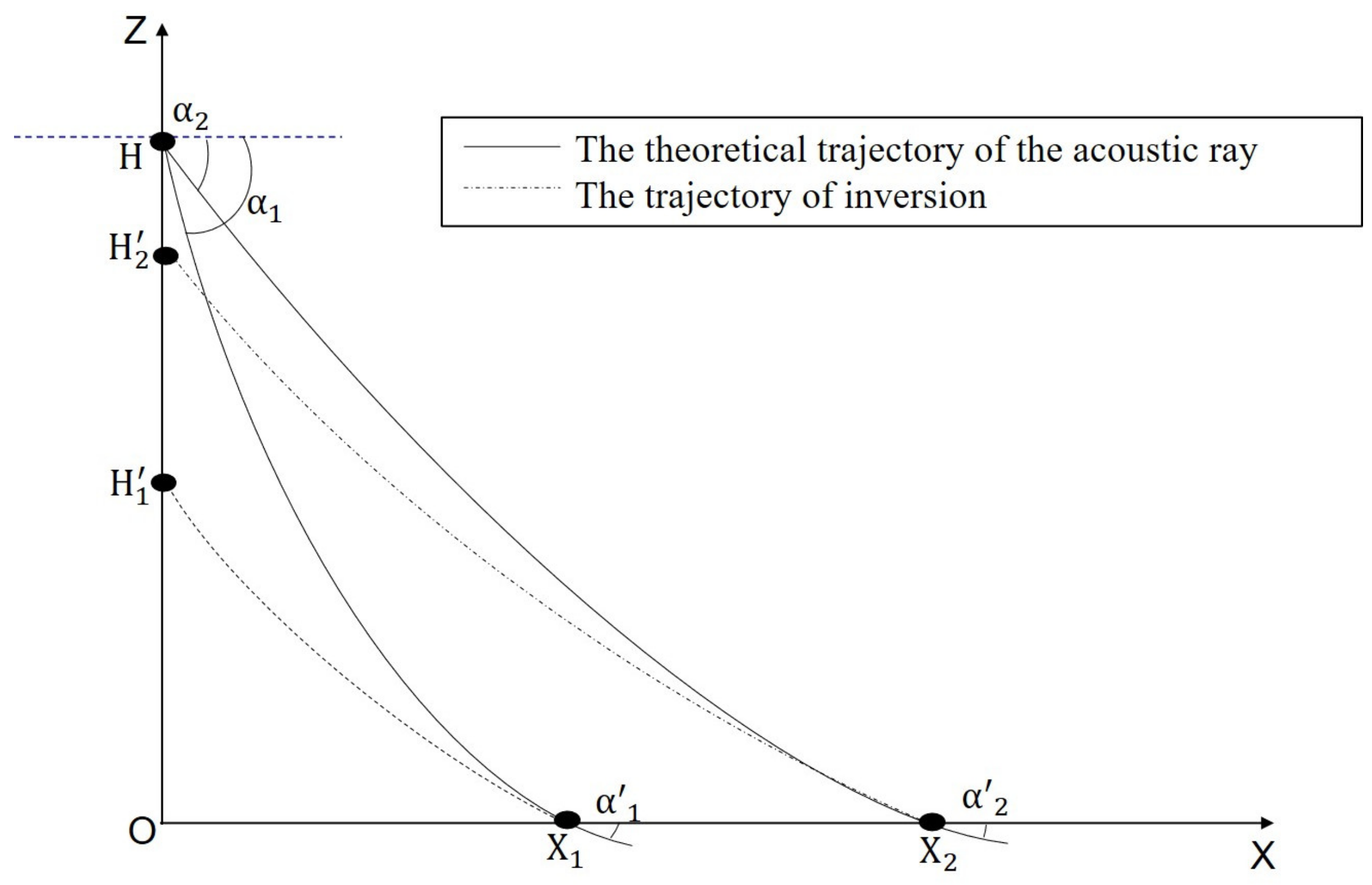
2.3.1. Calculation of the RLE in Straight-Line Propagation Model
2.3.2. Calculation of RLE in Uniform Vertical Distribution of Temperature Only
2.3.3. Calculation of RLE in Uniform Vertical Distribution of Humidity Only
3. Simulation Results and Analysis
3.1. Location Error of Straight-Line Propagation Model
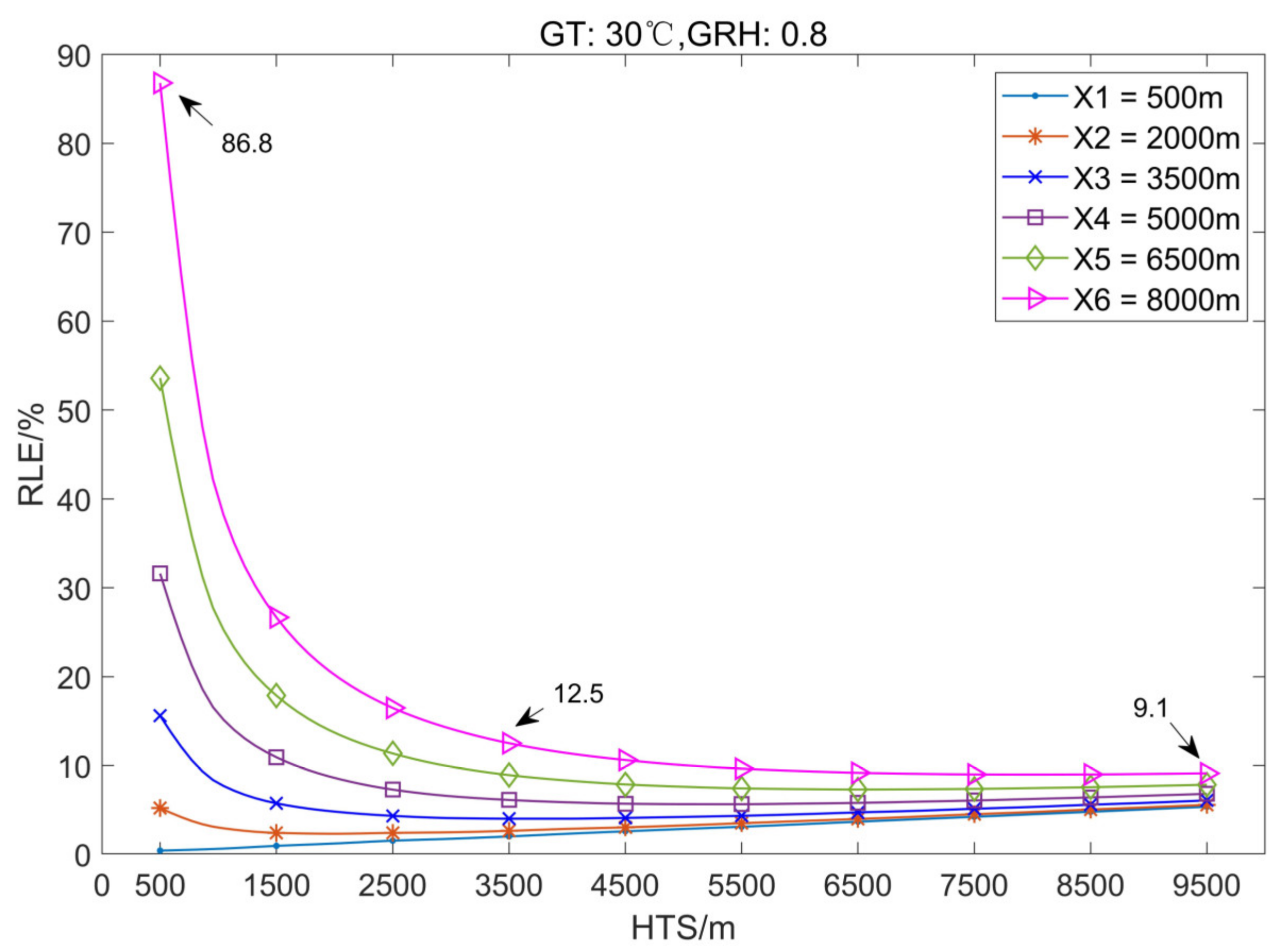
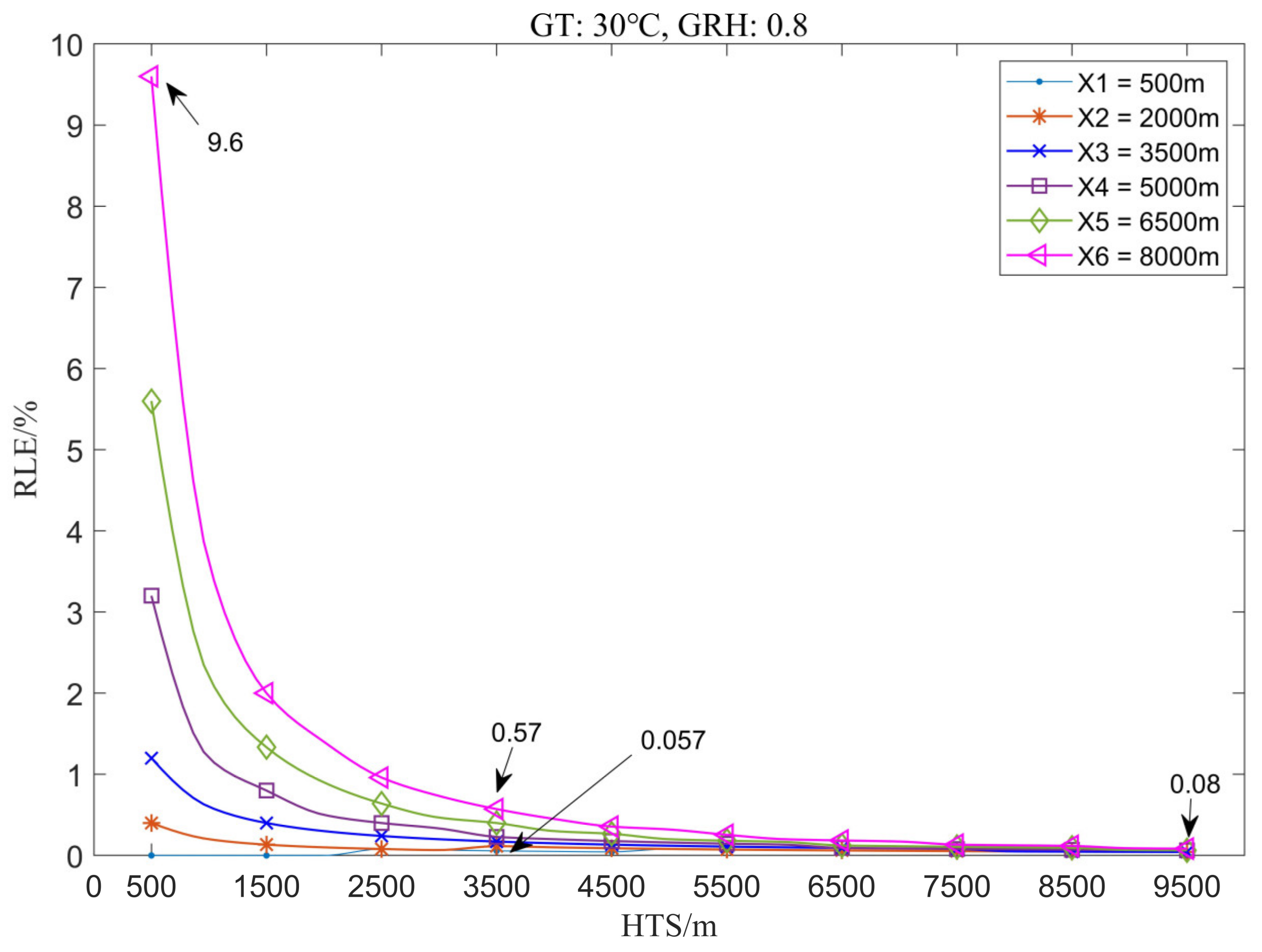
3.1.1. The Variation Law of Location Error with the Height of Thunder Source
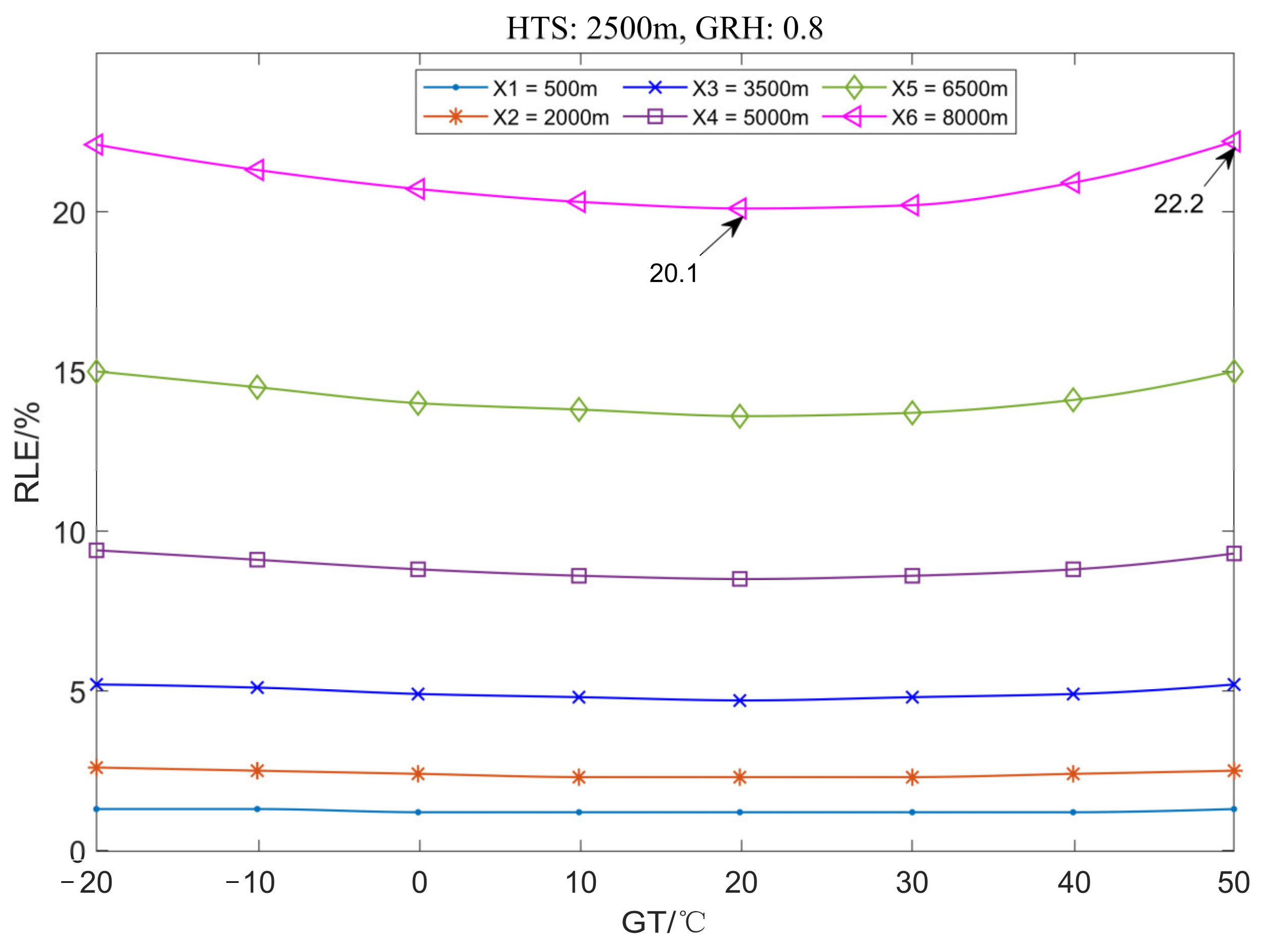
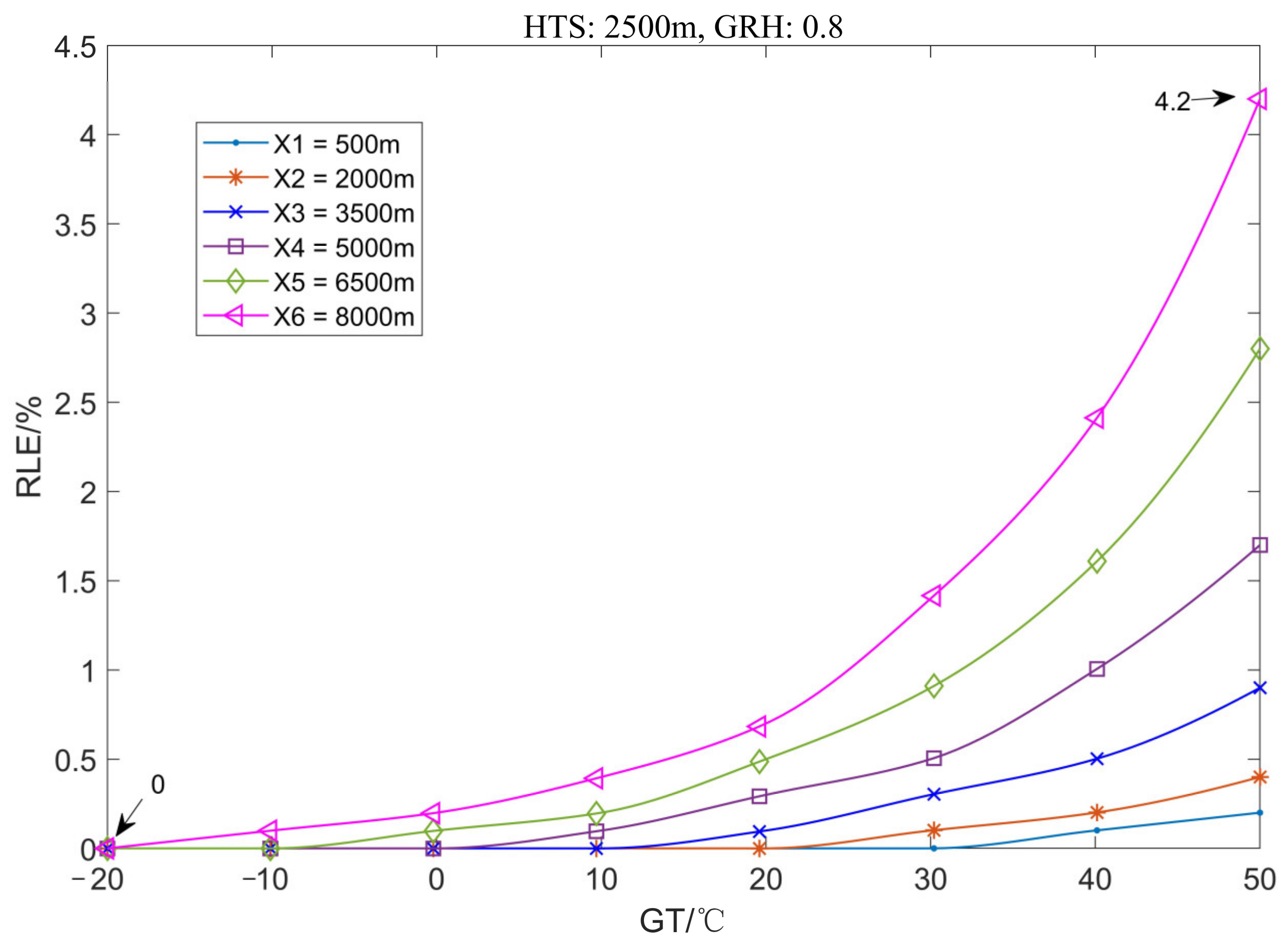
3.1.2. The Variation Law of Location Error with Ground Temperature
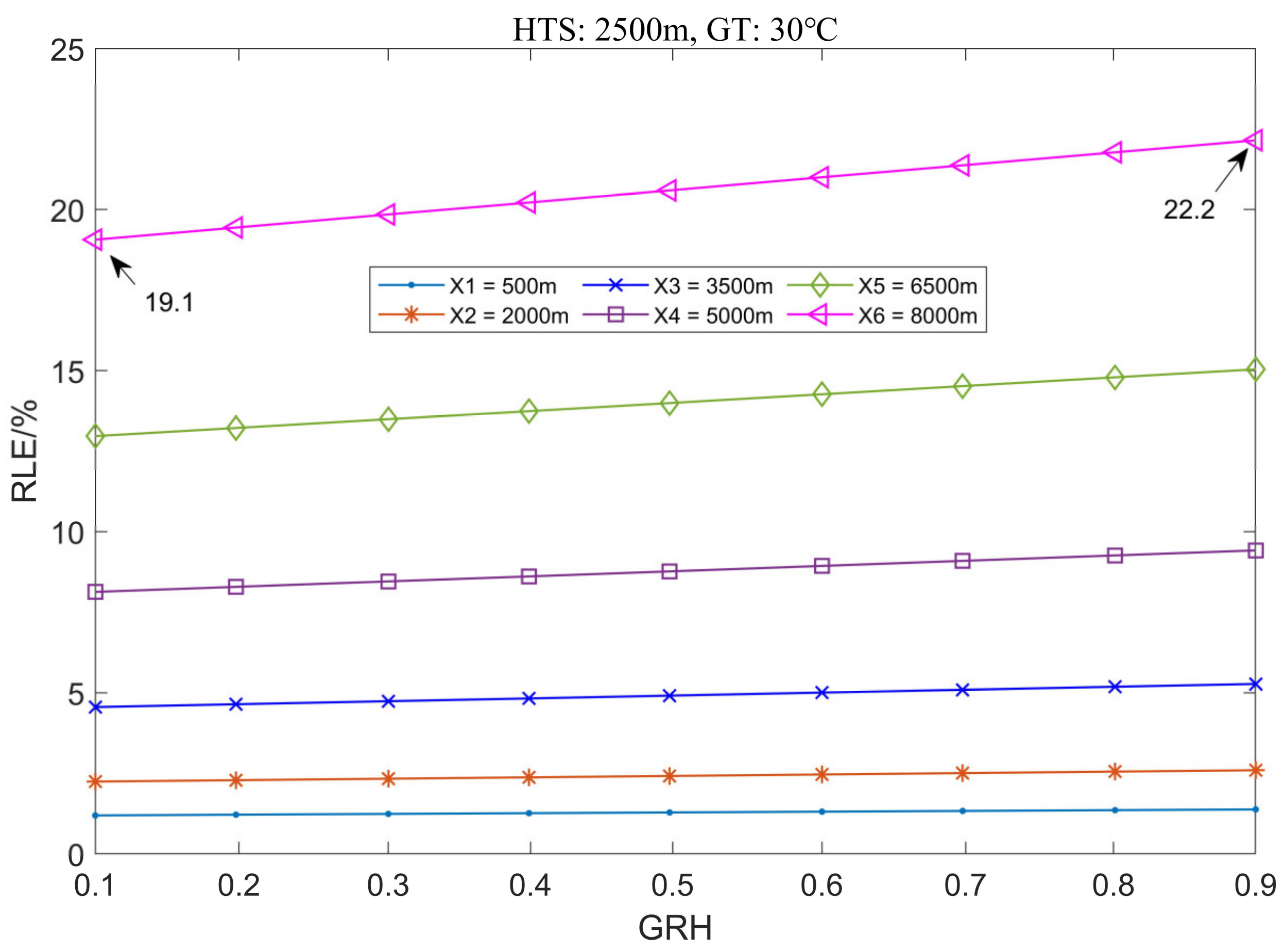
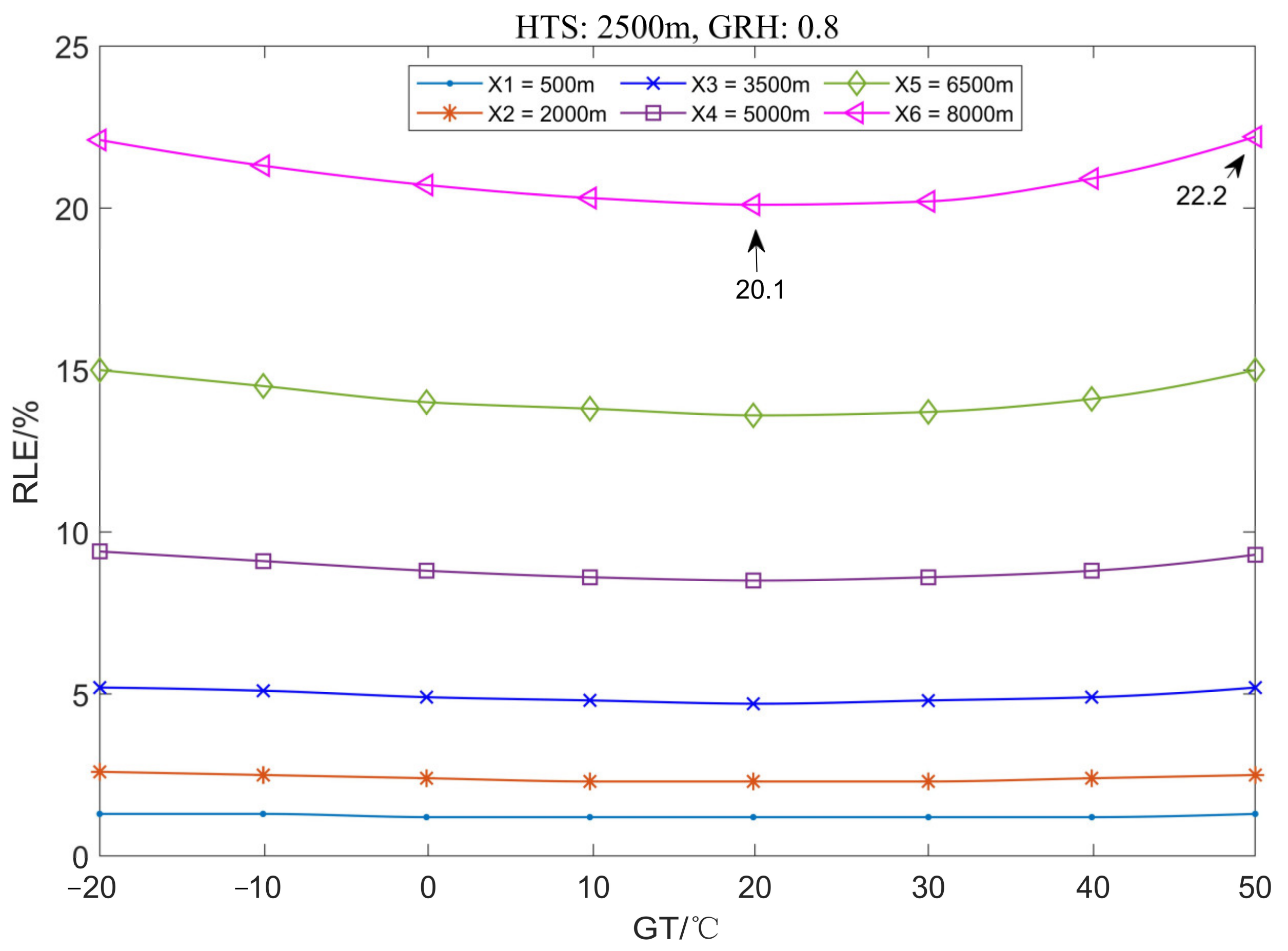
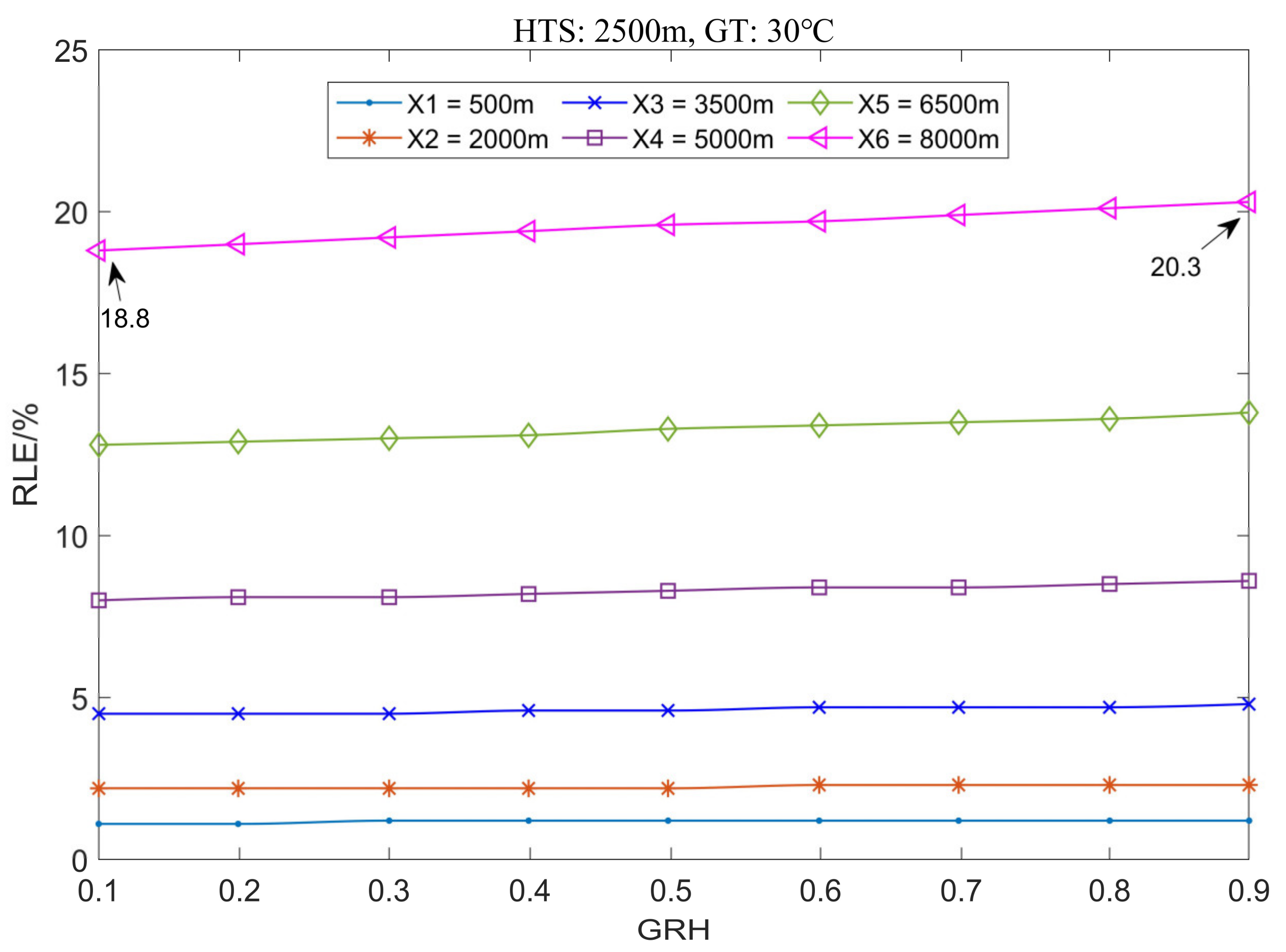
3.1.3. The Variation Law of Location Error with Ground Humidity
3.2. Location Error of the Model of Uniform Vertical Distribution of Temperature Only
3.2.1. The Variation Law of Location Error with the Height of the Thunder Source
3.2.2. The Variation Law of Location Error with Ground Temperature
3.2.3. The Variation Law of Location Error with Ground Humidity
3.3. Location Error of the Model of Uniform Vertical Distribution of Humidity Only
3.3.1. The Variation Law of Location Error with the Height of Thunder Source
3.3.2. The Variation Law of Location Error with Ground Temperature
3.3.3. The Variation Law of Location Error with Ground Humidity
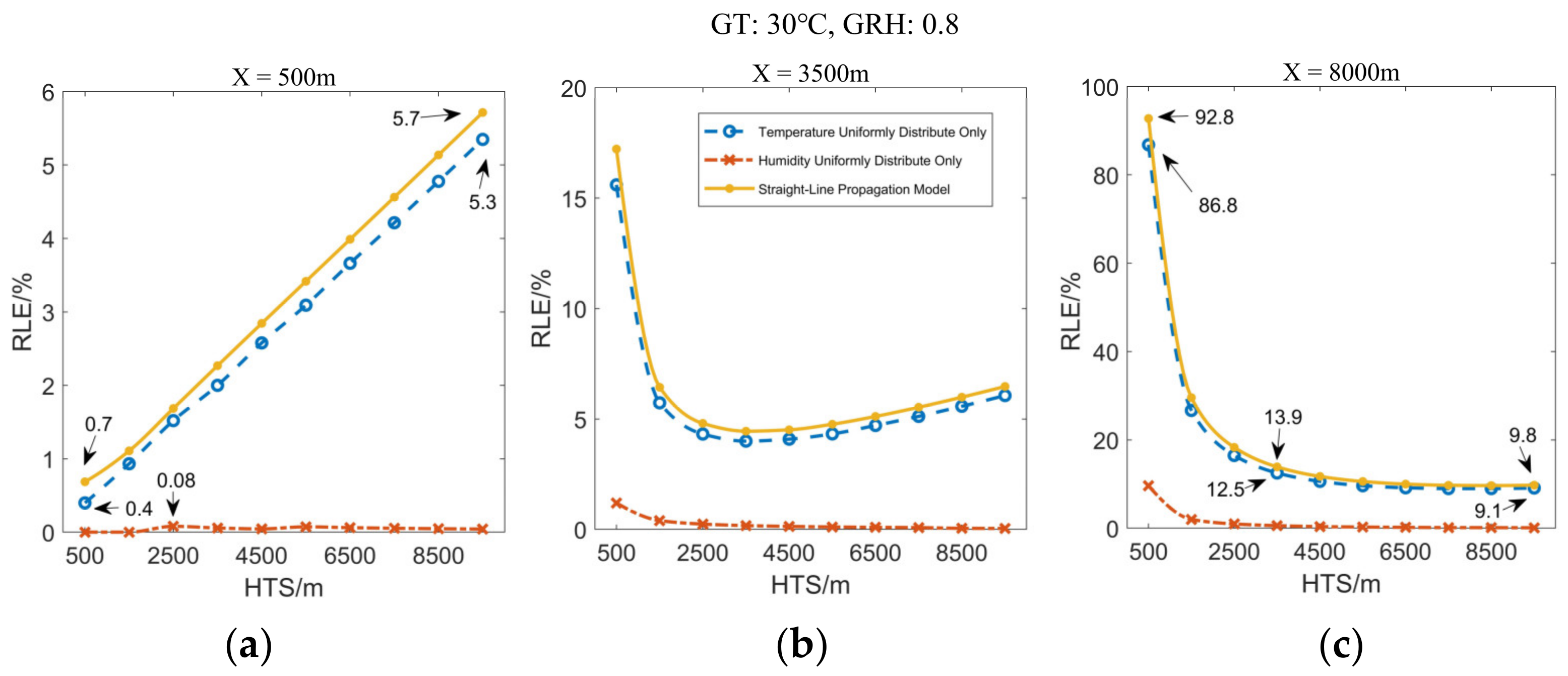
3.4. Comparison of the Main Factors Affecting the Location Results
3.4.1. Effect of the Height of the Thunder Source on Location Error
3.4.2. Effect of the Ground Temperature on Location Error
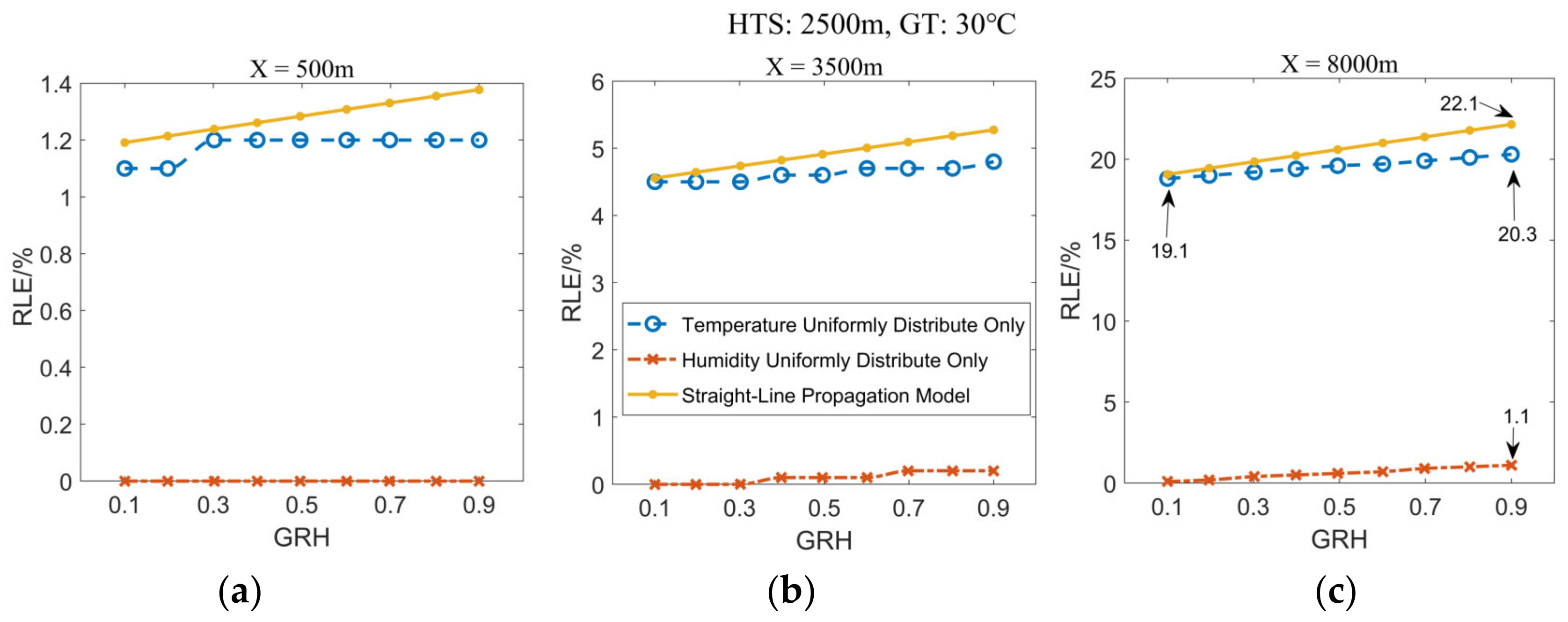
3.4.3. Effect of the Ground Humidity on Location Error
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qie, X.S.; Qie, K.; Wei, L.; Zhu, K.X.; Sun, Z.L.; Yuan, S.F.; Jiang, R.B.; Zhang, H.B.; Xu, C. Significantly increased lightning activity over the Tibetan Plateau and its relation to thunderstorm genesis. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL099894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterpka, C.; Dwyer, J.; Liu, N.; Demers, N.; Demers, N.; Hare, B.M.; Scholten, O.; ter Veen, S. Ultra-Slow Discharges That Precede Lightning Initiation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL101597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.G.; Cao, J.X.; Cai, L.; Su, R.; Zhou, M.; Fan, Y.D.; Li, Q.X. Thunder acoustic signature for channel reconstruction in triggered lightning. J. Appl. Phys. 2022, 132, 123301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.Y.; Loboda, T.V.; Chen, D.; French, N.H.F. Cloud-to-ground lightning and near-surface fire weather control wildfire occurrence in Arctic tundra. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2021GL096814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessilt, T.D.; Abatzoglou, J.T.; Chen, Y.; Randerson, J.T.; Scholten, R.C.; van der Werf, G.; Veraverbeke, S. Future increases in lightning ignition efficiency and wildfire occurrence expected from drier fuels in boreal forest ecosystems of western North America. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 054008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.G.; Cao, J.X.; Cai, L.; Fan, Y.D.; Zhou, M.; Li, Q.X. Characteristics of Acoustic Response from Simulated Impulsive Lightning Current Discharge. High. Voltage 2019, 4, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallin, L.J.; Farges, T.; Marchiano, R.; Coulouvrat, F.; Defer, E.; Rison, W.; Schulz, W.; Nuret, M. Statistical analysis of storm electrical discharges reconstituted from a lightning mapping system, a lightning location system, and an acoustic array. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 3929–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.T.; Wang, B.S.; Lu, G.P.; Li, X.; Ge, Q.S.; Xie, A.; Wu, Y.; Qiu, X.X.; Chen, J. Tracking Lightning Through 3D Thunder Source Location with Distributed Acoustic Sensing. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2024, 129, e2023JD038882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Qie, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, J.; Kong, X. Characteristics and simulation of lightning current waveforms during one artificially triggered lightning. Atmos. Res. 2009, 91, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qie, X.S.; Wu, X.K.; Yuan, T.; Bian, J.C.; Lu, D.R. Comprehensive pattern of deep convective systems over the Tibetan Plateau-south Asian monsoon region based on TRMM data. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 6612–6626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakov, V.A.; Uman, M.A. Lightning: Physics and Effects, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003; pp. 374–389. [Google Scholar]
- Bodhika, J.A.P.; Dharmarathna, W.G.D.; Fernando, M.; Cooray, V. A preliminary study on characteristics of thunder pulses of lightning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Lightning Protection, Shanghai, China, 11–18 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bodhika, J.A.P.; Dharmarathna, W.G.D.; Fernando, M.; Cooray, V. Localization of thunder source and reconstruction of lightning channel geometry using sound data. In Proceedings of the Asia-Pacific International Conference on Lightning, Chengdu, China, 1–4 November 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Gu, S.Q.; Chen, J.H.; Zhao, C.; Wu, M.; Yan, B.W.; Wang, Y. Single-Station-Based Lightning Mapping System with Electromagnetic and Thunder Signals. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 47, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bestard, D.; Coulouvrat, F.; Farges, T.; Mlynarczyk, J. Acoustical power of lightning flashes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2023, 128, e2023JD038714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. A Single-Station-Based 3D Lightning Channel Location Method by Using Differential Arrival Time of Thunder. Master’s Thesis, Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences, Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Few, A.A. Lightning channel reconstruction from thunder measurement. Geophys. Res. 1970, 75, 7515–7523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, M. Characteristic of lightning channel in thunderclouds determined by thunder. J. Meteorol. Soc. JPN 1976, 54, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bohannon, J.L. Infrasonic Pulses from Thunderstorms. Master’s Thesis, Rise University, Houston, TX, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Arechiga, R.O.; Johnson, J.B.; Edens, H.E.; Thomas, R.J.; Rison, W. Acoustic localization of triggered lightning. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D09103-1–D09103-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.B.; Arechiga, R.O.; Thomas, R.J.; Edens, H.E.; Anderson, J.; Johnson, R. Imaging thunder. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, D.H.; Lu, W.T.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, Y.J. A single station-based 3D lightning channel location system by using differential arrival time of thunder. Plateau Meteorol. 2012, 31, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Zhou, B.H.; Shi, L.H. Synchronized observations of cloud-to-ground lightning using VHF broadband interferometer and acoustic arrays. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.M. Absorption of Sound in Air versus Humidity and Temperature. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1966, 40, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacroix, A.; Coulouvrat, F.; Marchiano, R.; Farges, T.; Ripoll, J.F. Acoustical Energy of Return Strokes: A Comparison Between a Statistical Model and Measurements. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 11479–11489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.K.; Park, S.; Chung, D.C.; Kim, B. Inversion of acoustic thunder source spectral model from thunder-induced seismic waves in megacity. Geophys. J. Int. 2023, 233, 107–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.T. Research on Thunder Acoustic Signal Characteristics. Master’s Thesis, Shaanxi Normal University, Xi’an, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Few, A.A.; Teer, T.L. The accuracy of acoustic reconstructions of lightning channels. J. Geophys. Res. 1974, 79, 5007–5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacGorman, D.R. Lightning Location in a Colorado Thunderstorm. Master’s Thesis, Rice University, Houston, TX, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- MacGorman, D.R. Lightning Location in a Storm with Strong Wind Shear. Ph.D. Thesis, Rice University, Houston, TX, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, P.X.; Mao, J.T.; Li, J.G.; Zhang, A.C.; Sang, J.G.; Pan, N.X. Atmospheric Physics, 1st ed.; Peking University Press: Beijing, China, 2003; pp. 486–495. [Google Scholar]
- Simanek, D. Sound Reasons: The Answers. Available online: https://www.spsnational.org/the-sps-observer/winter/2015/sound-reasons-answers (accessed on 27 June 2024).
- Wong, G.S.K.; Embleton, T.F.W. Variation of the speed of sound in air with humidity and temperature. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1985, 77, 1710–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, D. The computation of equivalent potential temperature. Mon. Wea Rew 1980, 108, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.D.; Zuo, Z.G.; Yue, S.; Hong, P. Theoretical Model Analysis of the Effective Range of an Infrared Point Target Detection System. Infrared 2019, 40, 18–25. [Google Scholar]
- Kornhauser, E.T. Ray theory for moving fluids. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1953, 25, 945–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.J. Ray theory for an inhomogeneous moving medium. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1972, 51, 1675–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirley, J.W. An Early Experimental Determination of Snell’s Law. Am. J. Phys. 1951, 19, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, K.T.; Lee, C.C. Design and Reliability of Acoustic Wedge Transducer Assemblies for Outdoor Touch Panels. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 2011, 1, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohenwarter, D.; Jelinek, F. Snell’s Law of Refraction and Sound Rays for a Moving Medium. Acta Acust. United Acust. 1999, 86, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, J.; Wang, C.; Xu, J.; Jia, S.; Yang, H.; Sun, Z.; Wang, X. Study and Analysis of the Thunder Source Location Error Based on Acoustic Ray-Tracing. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4000. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16214000
Guo J, Wang C, Xu J, Jia S, Yang H, Sun Z, Wang X. Study and Analysis of the Thunder Source Location Error Based on Acoustic Ray-Tracing. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(21):4000. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16214000
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Jinyuan, Caixia Wang, Jia Xu, Song Jia, Hui Yang, Zhuling Sun, and Xiaobao Wang. 2024. "Study and Analysis of the Thunder Source Location Error Based on Acoustic Ray-Tracing" Remote Sensing 16, no. 21: 4000. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16214000
APA StyleGuo, J., Wang, C., Xu, J., Jia, S., Yang, H., Sun, Z., & Wang, X. (2024). Study and Analysis of the Thunder Source Location Error Based on Acoustic Ray-Tracing. Remote Sensing, 16(21), 4000. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16214000






