Trade-Off and Synergy Relationships and Driving Factor Analysis of Ecosystem Services in the Hexi Region
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Quantification of Ecosystem Service Functions
2.3.2. Trend Analysis
2.3.3. Analysis of ESs Trade-Offs/Synergies
2.3.4. Analysis of Factors Influencing ESs and Their Trade-Offs and Synergies
3. Results
3.1. Spatial and Temporal Distribution Characteristics of Ecosystem Service Functions
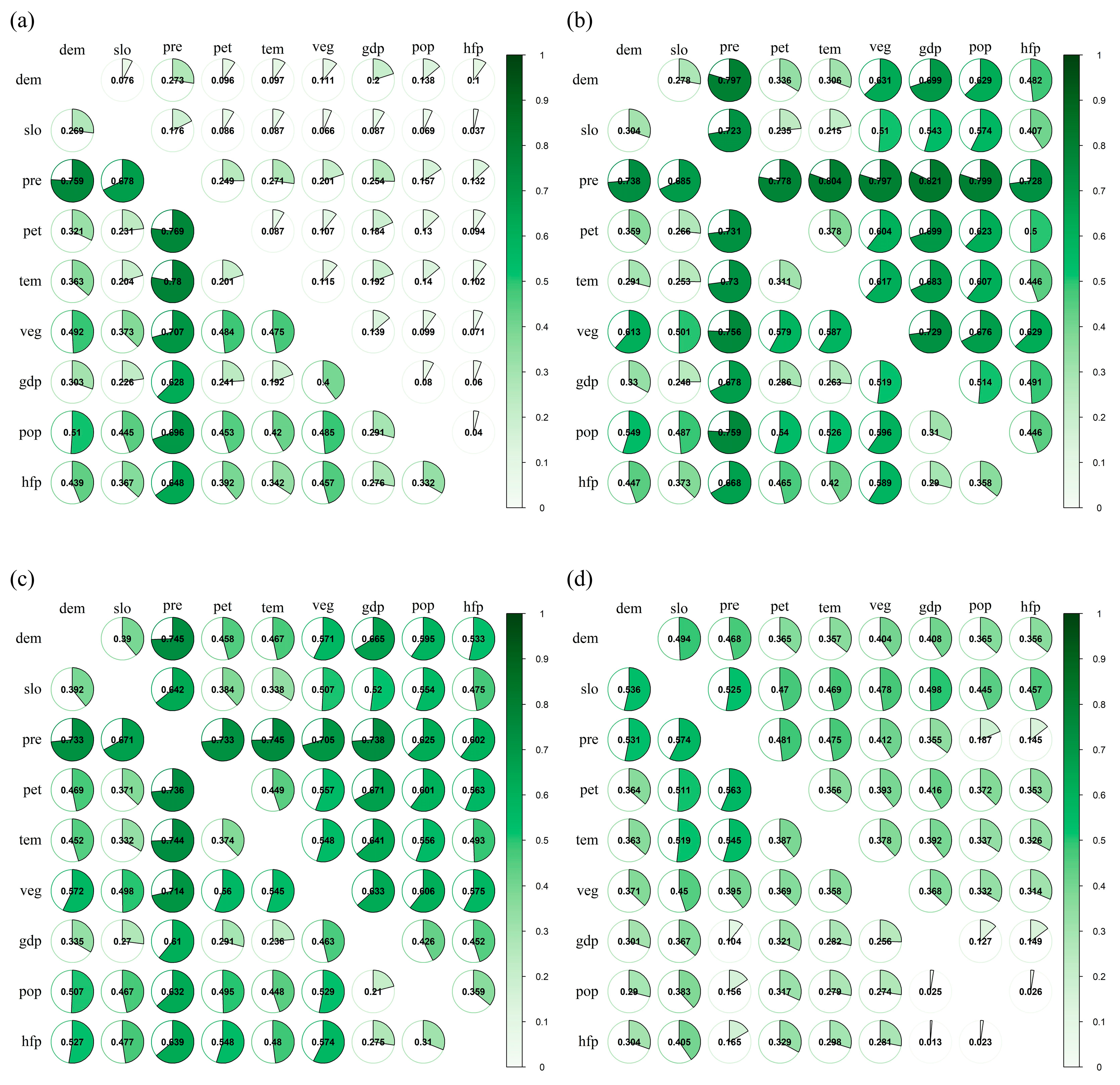
3.2. Analysis of Trade-Off and Synergy Relationships
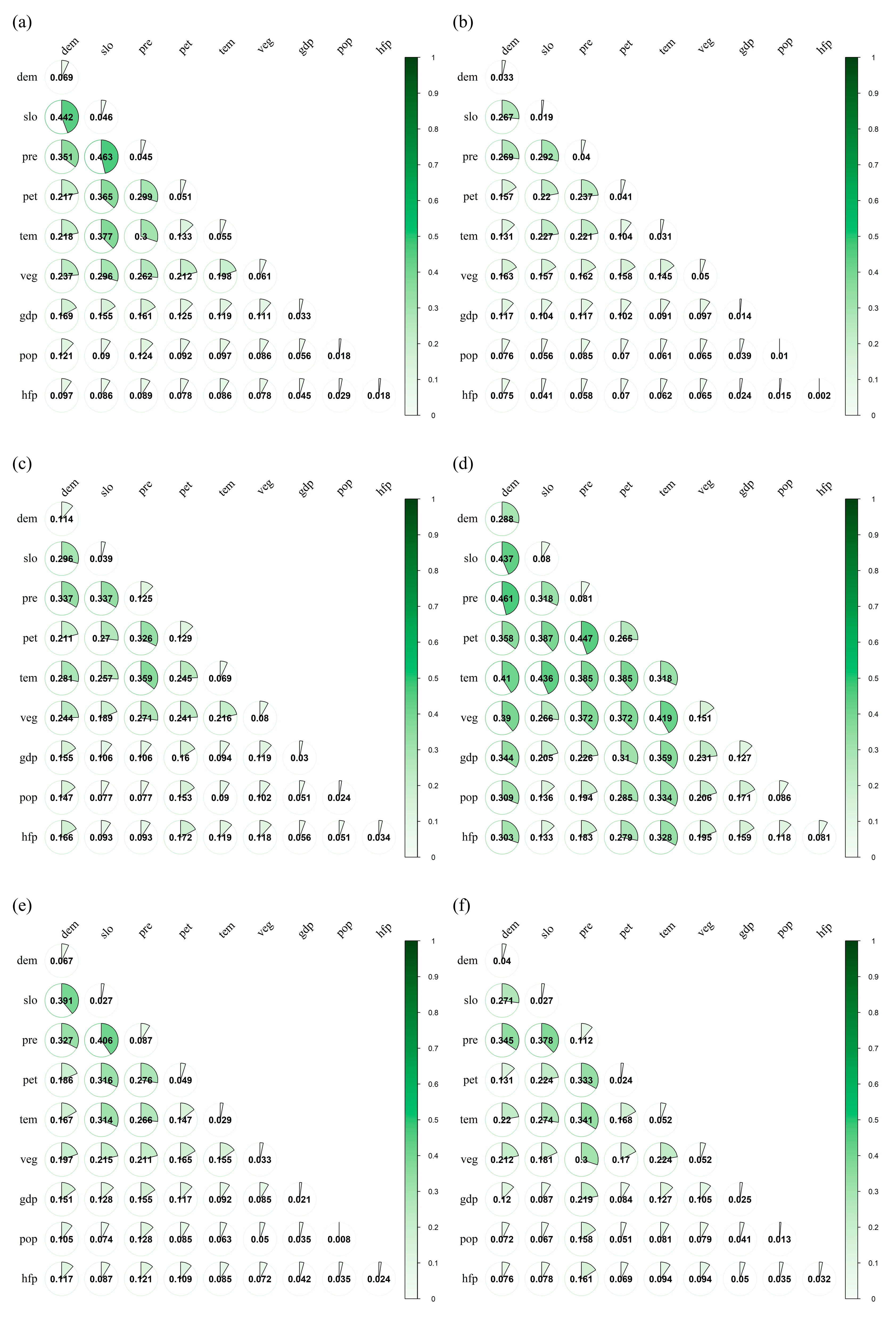
3.3. Analysis of Influencing Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, D.; Zheng, H.; Ouyang, Z. Ecosystem Services Supply and Consumption and Their Relationships with Human Well-Being. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2013, 24, 1747–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millennium Ecosystem Assessment, MEA. Ecosystems and Human Well-Being; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, S.; Hu, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; Xu, D.; Bai, T. Understanding Spatial-Temporal Interactions of Ecosystem Services and Their Drivers in a Multi-Scale Perspective of Miluo Using Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, H.J.; Gaul, W.; Sadykova, D.; León-Sánchez, L.; Caplat, P.; Emmerson, M.C.; Yearsley, J.M. Quantifying Large-scale Ecosystem Stability with Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 6, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Yang, L.; Mi, J. Detecting the Effects of Opencast Mining on Ecosystem Services Value in Arid and Semi-Arid Areas Based on Time-Series Remote Sensing Images and Google Earth Engine (GEE). BMC Ecol. Evol. 2024, 24, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Yang, J.; Liao, W.; Xiao, J.; Yan, S. Refined Assessment of Space-Time Changes, Influencing Factors and Socio-Economic Impacts of the Terrestrial Ecosystem Quality: A Case Study of the GBA. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, H.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ning, X. Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of Ecological Environment Quality in the Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan Urban Agglomeration. Remote Sens. Nat. Resour. 2023, 35, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Wei, W.; Li, S.; Ma, M.; Li, X.; Yang, H.; Jiang, Q.; Chai, P. GEE Based Evaluation on Spatial-Temporal Pattern and Drivers of Long-Term Water Body in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2023, 32, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, S. Spatial-Temporal Dynamics of Cropland Ecosystem Water-Use Efficiency and the Responses to Agricultural Water Management in the Shiyang River Basin, Northwestern China. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 237, 106176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, G.; Li, T.; Li, J.; Dou, J.; Fan, R. Remote Sensing Inversion and Application for Soil Fertility of Cultivated Land in the Hilly Areas of Central-South Shandong of China. Trans. CSAE 2020, 36, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, B.; Meng, Y.; Xue, C.; Su, F. Oceanic Primary Production Estimation Based on Machine Learning. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean 2023, 128, e2022JC018980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Li, C. An Empirical Algorithm for Retrieving Chlorophyll-a Concentration in the Sea Area near Palawan Island. Sci. Surv. Mapp. 2022, 47, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Zheng, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, H.; Zhang, B. Coupling Relationship between Urbanization and Water-Related Ecosystem Services in China’s Yangtze River Economic Belt and Its Socio-Ecological Driving Forces: A County-Level Perspective. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Qiao, J.; Li, M.; Huang, M. Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity of Ecosystem Service Interactions and Their Drivers at Different Spatial Scales in the Yellow River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Chen, W.; Pan, S.; GU, T.; Zeng, J. Identifying the Driving Forces of Global Ecosystem Services Balance, 2000–2020. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 426, 139019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, H.; Pei, X.; Wang, Y. Drivers of Ecosystem Service Trade-off and Synergy in Long-Term Sequence: A Case Study of the Extremely Important Ecosystem Service Function Area in Wuhu City. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 1780–1790. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Li, S.; Liu, L.; Liang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, S. Uncovering the Relationships between Ecosystem Services and Social-Ecological Drivers at Different Spatial Scales in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 290, 125193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, X.; Dou, H.; Dang, D.; Gong, J. Integrating Constraint Effects among Ecosystem Services and Drivers on Seasonal Scales into Management Practices. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anna, F. Cord; Bartosz Bartkowski; Michael Beckmann; Andreas Dittrich; Kathleen Hermans-Neumann; Andrea Kaim; Nele Lienhoop; Karla Locher-Krause; Jörg Priess; Christoph Schröter-Schlaack; et al. Towards Systematic Analyses of Ecosystem Service Trade-Offs and Synergies: Main Concepts, Methods and the Road Ahead. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 28, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Gao, Y.; Lu, P.; Zhou, J.; Wang, K.; Zhang, B.; Ma, Y.; Liu, M. Spatial Distribution and Tradeoff-Synergy-Independence Relationships of Ecosystem Services Based on Land Use and Topography. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2024, 31, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Pu, R.; Cao, L.; Zhang, H. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Urban Expansion and Trade-Offs and Synergies among Ecosystem Services in Urban Agglomerations of China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 110057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Jia, Y.; Wanng, H.; Wang, Z. Analysis of Trade-off and Synergy Effects of Ecosystem Services in Hebei Province from the Perspective of Ecological Function Area. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2023, 78, 2833–2849. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Zhao, M.; Tan, Z.; Zhu, L.; Guo, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, C. Ecosystem Service Trade-Offs and Synergies Relationships and Their Driving Factor Analysis Based on the Bayesian Belief Network: A Case Study of the Yellow River Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 163, 112070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Gu, Y.; Zou, C.; Wang, L.; Luo, J.; Huang, X. Trade-Offs and Synergies of Ecosystem Services in the Taihu Lake Basin of China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, D.; Xu, H. Trade-offs and Synergies Relationships of Ecosystem Services and Their Socio-ecological Driving Factors under Different Spatial Scales in Shaoguan City, Guangdong, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2023, 34, 3073–3084. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Jiao, L.; Wang, H.; Yan, J.; Lv, Y.; Fu, B. Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of the Trade-off and Synergy Relationships among Multiple Ecosystem Services in the Upper Reaches of Hanjiang River Basin. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 2064–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, J.D.; Corstanje, R.; Harris, J.A. Bundling Ecosystem Services at a High Resolution in the UK: Trade-Offs and Synergies in Urban Landscapes. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 1817–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S. Effects of Landscape Pattern Change on Ecosystem Services and Its Interactions in Karst Cities: A Case Study of Guiyang City in China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scowen, M.; Athanasiadis, I.N.; Bullock, J.M.; Eigenbrod, F.; Willcock, S. The Current and Future Uses of Machine Learning in Ecosystem Service Research. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 799, 149263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C. Geodetector: Principle and Prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhao, F.; Zhu, L.; He, S.; Ye, L. Geographical detection of ecosystem services trade-offs and their spatial variation mechanism in Qihe River Basin. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 7568–7578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Sun, G.; Liu, J. Spatial and temporal effect and driving factors of ecosystem service trade-off in the Qingjiang River Basin, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2023, 34, 1051–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yang, H.; Yang, Y.; Wei, W.; Pan, J. Spatial-temporal evolution of ecological environment quality in Hexi Corridor based on Coupled Coordination Model. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2020, 30, 102–112. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, H.; Qu, Z.; Liu, C.; He, Y. Spatio-temporal variation of landscape pattern and the response of windbreak and sand fixation service in Hexi corridor of northern sand fixation belt. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2023, 34, 2518–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Lv, R.; Pang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, N. Spatial-temporal variability of ecosystem services in Qilian Mountains from 2000 to 2020. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2023, 45, 1367–1378. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Cao, H.; Fan, Y.; Han, H.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y. Remote sensing estimation and analysis of net primary productivity (NPP) based on corrected CASA model: A case study of Hexi Corridor. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 1616–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Du, W.; Chen, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Sun, W.; Chai, X.; Ma, L.; Xu, Z. Climatic and Topographical Effects on the Spatiotemporal Variations of Vegetation in Hexi Corridor, Northwestern China. Diversity 2022, 14, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, N.; Guo, B.; Zhang, D.; Yang, Q.; Luo, W. Desert vegetation composition and spatial distribution of soil nutrients in the middle section of Hexi Corridor. Arid. Zone Res. 2024, 41, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhao, C.; Wen, J. Dynamic coupling and spatial pattern of urbanization and resource-environment carrying capacity in Hexi Corridor. Chin. J. Ecol. 2021, 40, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Geng, M.; Li, F.; Xie, Y.; Tian, T.; Chen, Q. Spatiotemporal Characteristics and Drivers of Ecosystem Service Interactions in the Dongting Lake Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 172012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, C.S.; Randerson, J.T.; Field, C.B.; Matson, P.A.; Vitousek, P.M.; Mooney, H.A.; Klooster, S.A. Terrestrial Ecosystem Production: A Process Model Based on Global Satellite and Surface Data. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1993, 7, 811–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, H.; Ren, H.; Pei, H. Spatiotemporal Variations of the Soil Conservation in the Agro-pastoral Ecotone of Northern China Under Grain for Green Program. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 28, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, C.W.; Foster, G.R.; Wright, D.A. Estimation of Erosion Index from Daily Rainfall Amount. Trans. ASAE 1983, 26, 0153–0156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H. A Soil Erodibility Nomograph for Farmland and Construction Sites. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1971, 26, 189–193. [Google Scholar]
- Renard, K.G. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; ISBN 978-0-16-048938-9.
- Cai, C.; Ding, S.; Shi, Z.; Huang, L.; Zhang, G. Study of Applying USLE and Geographical Information System IDRISI to Predict Soil Erosionin Small Watershed. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2000, 14, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Liu, L.; Wu, D. Soil Erosion Changes and Driving Factors in the Three-River Headwaters Region. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2018, 27, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Xiao, Y.; Zheng, H.; Xiao, Y.; Ouyang, Z. Spatial patterns of ecosystem water conservation in China and its impact factors analysis. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 2455–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ryu, D.; Webb, J.A.; Lintern, A.; Guo, D.; Waters, D.; Western, A.W. A Bayesian Approach to Understanding the Key Factors Influencing Temporal Variability in Stream Water Quality—A Case Study in the Great Barrier Reef Catchments. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 2663–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigel, B.J.; Douglas Robinson, W.; Sherry, T.W. Comparing Bird Community Responses to Forest Fragmentation in Two Lowland Central American Reserves. Biol. Conserv. 2010, 143, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Ding, W.; Pu, X.; Lyu, Y.; Wang, Y. Spatial-temporal Distribution of Carbon Storage in Qilian Mountain National Park Based on InVEST Model. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 42, 324–334+396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric Tests Against Trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farlie, D.J.G.; Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A (Gen.) 1971, 134, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhai, J.; Hou, P.; Gao, H.; He, Y.; Jin, D.; Xu, N. Divergent Trends of Ecosystem Status and Services in the Hexi Corridor. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1008441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, F.; Yuan, S.-S. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Evapotranspiration and Effects of Water and Heat on Water Use Efficiency. Water 2021, 13, 3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Fang, G.; Li, Z.; Wang, F.; Qin, J.; Sun, F. Potential Risks and Challenges of Climate Change in the Arid Region of Northwestern China. Reg. Sustain. 2020, 1, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Xi, H.; Si, J.; Li, A. Study of Evapotranspiration Estimation and Drought Characteristics of Watershed in Low Coteau Area of Hexi Inland River. Arid Zone Res. 2020, 37, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Q. Spatio-Temporal Terrestrial Water Storage Changes in the Hexi Corridor Derived by GRACE/GRACE-FO Gravity Satellites over the Past 20 Years. Prog. Geophys. 2024, 39, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Zhang, L. Changes in temperature and precipitation in the plain area of Hexi Corridor in 2000–2020. J. Desert Res. 2023, 43, 264–270. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhou, H.; Gui, J. Spatial and temporal variation of ecosystem service functions in the Hexi region from 2000 to 2020 and its influence factors analysis. Environ. Ecol. 2023, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Jiang, C.; Gao, Y.; Du, J. Natural Driving Mechanism and Trade-off and Synergy Analysis of the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Multiple Typical Ecosystem Services in Northeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 374, 134075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, D.; Damm, A.; Hein, L.; Petchey, O.L.; Schaepman, M.E. Spatio-Temporal Trends and Trade-Offs in Ecosystem Services: An Earth Observation Based Assessment for Switzerland between 2004 and 2014. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 828–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomscha, S.A.; Gergel, S.E. Ecosystem Service Trade-Offs and Synergies Misunderstood without Landscape History. E&S 2016, 21, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Dou, Y.X.; Wang, Y.Q.; An, S.S. Ecosystem service trade-offs and synergies in typical small watersheds of the hilly and gullied region of the Loess Plateau. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 8152–8168. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, X.; Sun, H.; Cao, L.; Zhang, L.; Lv, B.; Liu, T. Variation Characteristics and Climatic Factors of Vegetation NPP in Typical Arid Region. J. Northeast For. Univ. 2021, 49, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stirzaker, R.J.; Passioura, J.B.; Wilms, Y. Soil Structure and Plant Growth: Impact of Bulk Density and Biopores. Plant Soil 1996, 185, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Werner, A.D.; Li, Y.; Jiang, S.; Tan, Z. Root-Induced Changes of Soil Hydraulic Properties—A Review. J. Hydrol. 2020, 589, 125203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Xie, X.; Wang, Y.; Liang, S.; Zhu, B.; Meng, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y. Vegetation Greening Intensified Transpiration but Constrained Soil Evaporation on the Loess Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2022, 614, 128514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, P.; Wu, F.; Wang, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhang, L.; An, S.; Kuzyakov, Y. Large-Scale Ecosystem Carbon Stocks and Their Driving Factors across Loess Plateau. Carb Neutrality 2023, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, H.; Bai, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, R.; Xiang, Q.; Lv, L.; Ma, J. Dynamics of evapotranspiration and its relationship with drought in a grain-forage compound ecosystem on the Loess Plateau. Pratacultural Sci. 2023, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Bu, R.; Hong, G.; Li, W.; Shao, F.; Zhang, L. Soil Moisture Characteristics and Its Response to Precipitation of Typical Plantation in Mu Us Sandy Land. For. Grassl. Resour. Res. 2023, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudmundsson, L.; Greve, P.; Seneviratne, S.I. The Sensitivity of Water Availability to Changes in the Aridity Index and Other Factors—A Probabilistic Analysis in the Budyko Space. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 6985–6994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Deng, X.; Li, Z.; Xue, J.; Ma, L.; He, J.; Lu, S.; Shao, J.; Cai, S.; Zhao, P. Analysis of the spatial and temporal evolution of water resources conservation and human activity intensity in the Hexi region of Gansu Province. J. Desert Res. 2024, 44, 189–200. [Google Scholar]
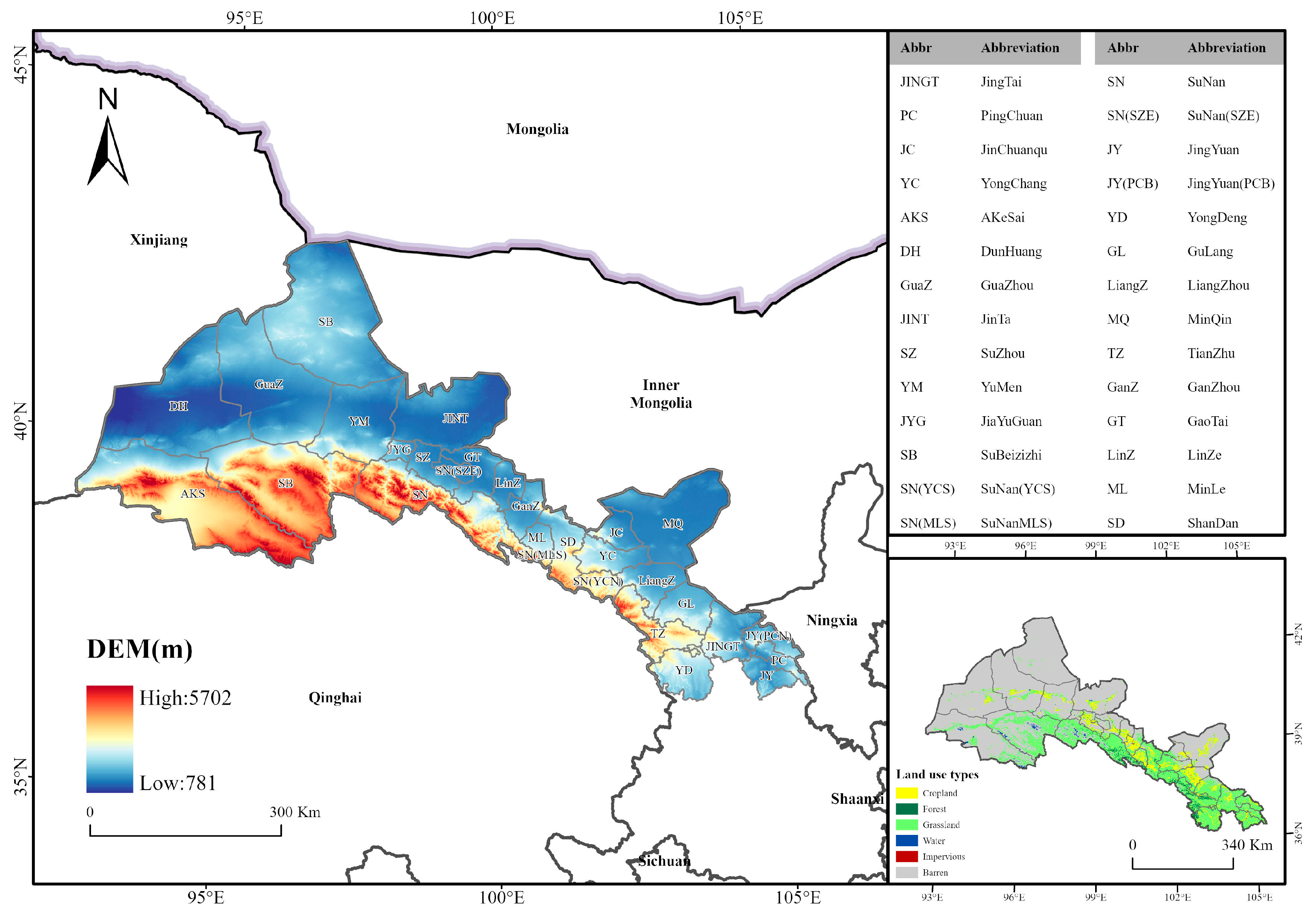
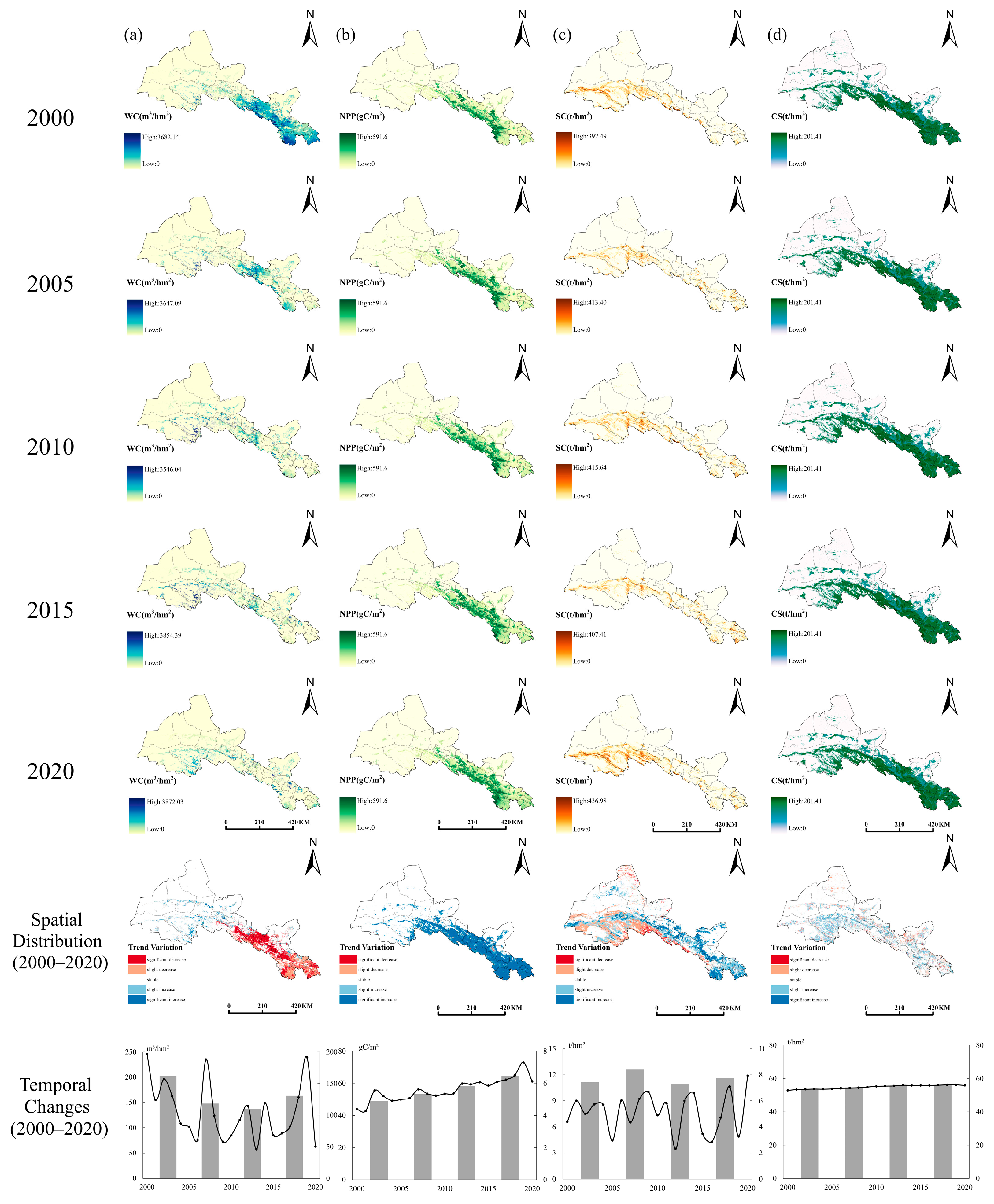
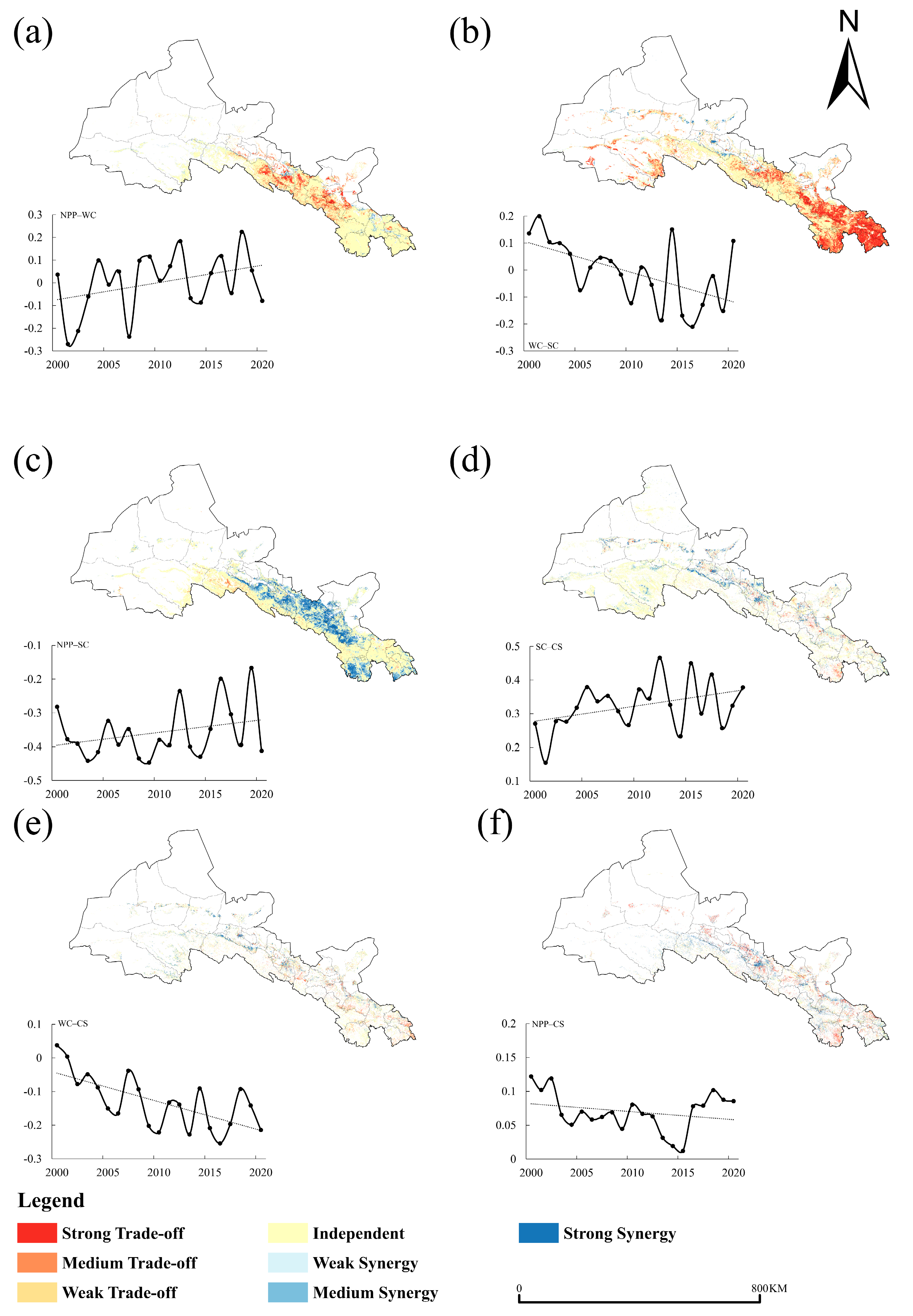
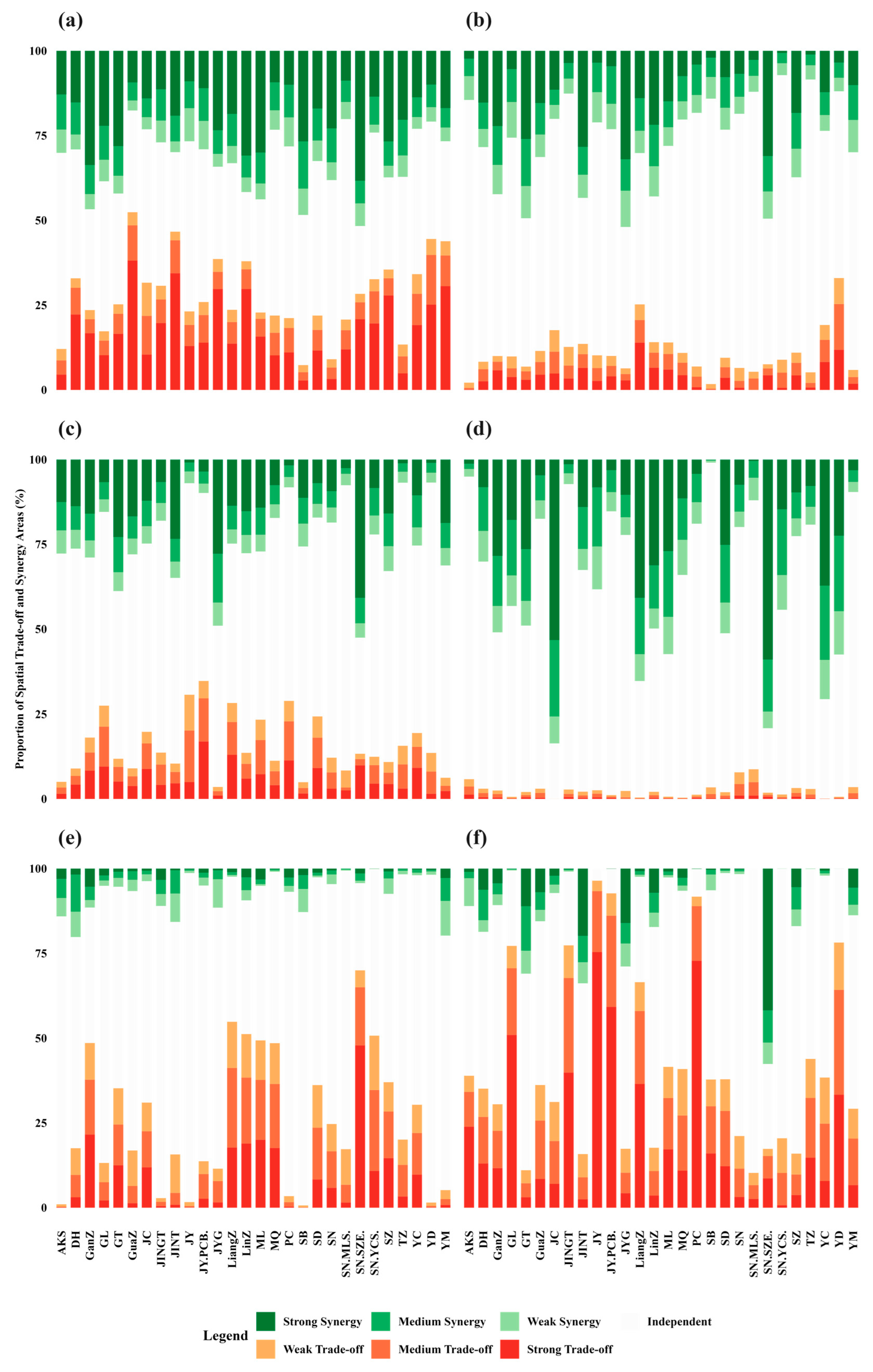
| Data Type | Data Format | Resolution | Data Description and Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| DEM | tif | 30 m | NASA SRTM Digital Elevation (https://earthengine.google.com/ accessed on 20 December 2023) |
| Land use\land cover | tif | 30 m/year | Annual land cover dataset (https://zenodo.org/records/8176941 accessed on 20 December 2023) |
| NPP | tif | 500 m/year | the MODIS MOD17A3 dataset (https://earthengine.google.com/ accessed on 20 December 2023) |
| Vegetational type | shp | / | China vegetation map (scale: 1:1,000,000) Resource and Environment Science and Data Center (https://www.resdc.cn/ accessed on 20 December 2023) |
| Gross domestic product (GDP) | tif | 1 km/year | China GDP Spatial Distribution Grid Dataset Resource and Environment Science and Data Center (https://www.resdc.cn/ accessed on 20 December 2023) |
| Precipitation | tif | 1 km/Month | 1 km Resolution Monthly Potential Evapotranspiration Dataset, 1 km Resolution Monthly Average Temperature Dataset, 1 km Resolution Monthly Precipitation Dataset. Loess Plateau SubCenter, National Earth System Science Data Center, National Science and Technology Infrastructure of China (http://loess.geodata.cn accessed on 20 December 2023) |
| Potential evapotranspiration | tif | 1 km/Month | |
| Temperature | tif | 1 km/Month | |
| Population density | tif | 1 km/year | Oak Ridge National Laboratory (https://landscan.ornl.gov accessed on 20 December 2023) |
| Soil data | tif | 1 km | Harmonized World Soil Database, HWSD (https://www.fao.org/home/en/ accessed on 20 December 2023) |
| Human Footprint | tif | 1 km/year | Human Footprint dataset (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-022-01284-8 accessed on 20 December 2023) |
| Ecosystem Service | Type | Equation | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Provisioning Services | Net primary productivity (NPP) | Net primary productivity (NPP) directly reflects the supply capacity of the ecosystem and can be used as an indicator for quantifying provisioning service directly [40]. In this context, APAR(x,t) and ε(x,t) represent the absorbed photosynthetically active radiation (MJ·m−2)and the actual light use efficiency (g·MJ−1) at time t, respectively [41]. | |
| Regulating Services | Soil conservation (SC) | This study applies the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) to calculate soil conservation [42]. Ss represents the soil conservation amount (t/hm2) of grid cell s. R is the rainfall erosivity factor, which is calculated based on the average monthly and annual rainfall amounts [43]; K is the soil erodibility factor, which was determined using the nomograph method [44]; L is the slope length factor; and S is the slope steepness factor, both of which were calculated using the formulas provided in the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) [45]. C and P are the vegetation cover and management factor and the soil conservation practice factor, respectively [46,47]. | |
| Water conservation (WC) | This study used the water balance equation to calculate water conservation capacity [48]. WC represents the water conservation capacity (m3), Pi is the rainfall (mm), Ri is the surface runoff (mm), ETi is the evapotranspiration (mm), Ai is the area of the i-th type of ecosystem (km2), and i denotes the i-th type of ecosystem in the region. j represents the number of ecosystem types within the study area [49,50]. | ||
| Carbon stock (CS) | The calculation of carbon storage is based on the carbon module in the INVEST model [51]. Sc represents the total carbon storage, Cabove is the carbon in aboveground biomass, Cbelow is the carbon in belowground biomass, Csoil is the carbon in the soil, and Cdead is the carbon in the litter layer. |
| Intensity of Trade-Off and Synergy Relationships | Basis for Determination |
|---|---|
| Strong Synergy | r > 0, p < 0.01 |
| Medium Synergy | r > 0, 0.01 < p < 0.05 |
| Weak Synergy | r > 0, 0.05 < p < 0.1 |
| Independent | p > 0.1 |
| Weak Trade-off | r < 0, p < 0.0 |
| Medium Trade-off | r < 0, 0.01 < p < 0.05 |
| Strong Trade-off | r < 0, 0.05 < p < 0.1 |
| WC | NPP | SC | CS | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 2020 | 2000 | 2020 | 2000 | 2020 | 2000 | 2020 | |
| DEM | 0.176 | 0.046 | 0.182 | 0.190 | 0.275 | 0.329 | 0.254 | 0.273 |
| SLO | 0.088 | 0.012 | 0.097 | 0.085 | 0.355 | 0.407 | 0.198 | 0.214 |
| PRE | 0.568 | 0.112 | 0.598 | 0.682 | 0.067 | 0.075 | 0.586 | 0.563 |
| PET | 0.094 | 0.051 | 0.135 | 0.145 | 0.304 | 0.332 | 0.203 | 0.241 |
| TEM | 0.048 | 0.054 | 0.102 | 0.102 | 0.268 | 0.299 | 0.137 | 0.164 |
| VEG | 0.299 | 0.044 | 0.465 | 0.482 | 0.248 | 0.281 | 0.438 | 0.451 |
| GDP | 0.101 | 0.042 | 0.116 | 0.331 | 0.006 | 0.107 | 0.061 | 0.271 |
| POP | 0.258 | 0.029 | 0.283 | 0.381 | 0.021 | 0.019 | 0.199 | 0.293 |
| HFP | 0.233 | 0.021 | 0.249 | 0.303 | 0.009 | 0.007 | 0.264 | 0.268 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, S.; Xia, H.; Zhai, J.; Jin, D.; Gao, H. Trade-Off and Synergy Relationships and Driving Factor Analysis of Ecosystem Services in the Hexi Region. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3147. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173147
Xiao S, Xia H, Zhai J, Jin D, Gao H. Trade-Off and Synergy Relationships and Driving Factor Analysis of Ecosystem Services in the Hexi Region. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(17):3147. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173147
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Sijia, Haonan Xia, Jun Zhai, Diandian Jin, and Haifeng Gao. 2024. "Trade-Off and Synergy Relationships and Driving Factor Analysis of Ecosystem Services in the Hexi Region" Remote Sensing 16, no. 17: 3147. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173147
APA StyleXiao, S., Xia, H., Zhai, J., Jin, D., & Gao, H. (2024). Trade-Off and Synergy Relationships and Driving Factor Analysis of Ecosystem Services in the Hexi Region. Remote Sensing, 16(17), 3147. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173147







