VCC-DiffNet: Visual Conditional Control Diffusion Network for Remote Sensing Image Captioning
Abstract
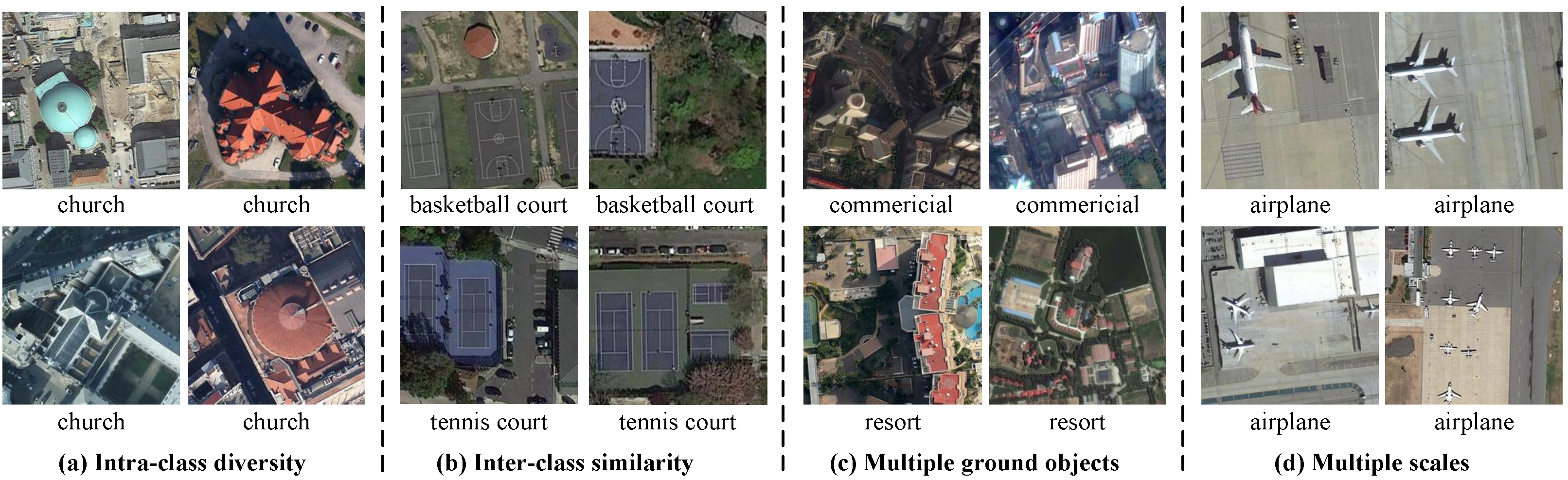
1. Introduction
- A Visual Conditional Control Diffusion Network (VCC-DiffNet) is proposed to address the subtitle delay problem in existing RSIC tasks. This is the first attempt, as far as we are aware, to apply a diffusion model-based non-autoregressive decoding paradigm to the RSIC task.
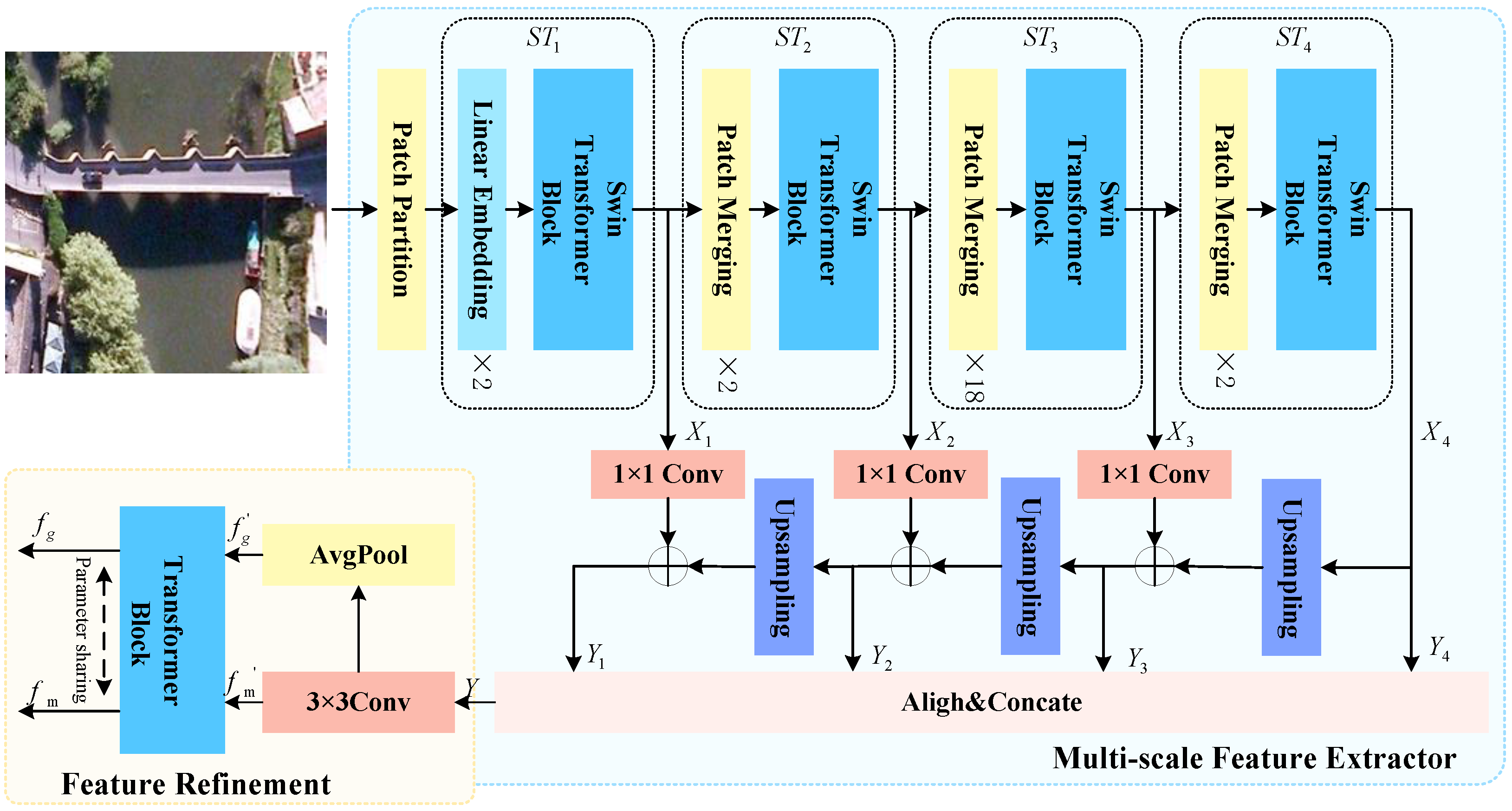
- A Refined Multi-scale Feature Extraction (RMFE) module is proposed as a means of obtaining more discernible visual features as the input of a diffusion model-based non-autoregressive decoder. The input visual features robustly represent the complex scenes and various ground objects by capitalizing on both global features and multi-scale grid features.
- An Interactive Enhanced Decoder (IE-Decoder) with dual interactions is proposed to focus on the accurate information pertaining to scenes and ground objects, thus ensuring the generation of accurate scene and ground object information from a description perspective.
2. Related Work
2.1. Autoregressive Remote Sensing Image Captioning
- RNN-based methods. In the pioneering work, Qu et al. [8] introduced the CNN plus RNN architecture to the RSIC task, which can produce more flexible and variable sentences compared to the template-based [9] and retrieval-based methods [10]. In subsequent research, long short-term memory (LSTM) [11], the special RNN variant, has been widely used in a significant number of studies [12,13,14,15] since it can better capture and handle long-term dependencies in sequential data. Until now, researchers have provided many ideas to enhance the description generation capability of LSTM. For instance, Fu et al. [16] devised a persistent memory mechanism component to expand the information storage capacity of LSTM, thereby reducing information loss at the decoding ends. Li et al. [17] introduced a semantic gate within the decoder with the aim of improving the comprehensiveness and accuracy of the description. Zhang et al. [18] proposed a novel approach to visual and textual feature fusion in the decoder, whereby linguistic state guidance was introduced to enhance the overall system’s performance. Wang et al. [19] proposed the integration of sequence attention and flexible word correlation within the decoder in order to generate accurate descriptions that were sufficiently detailed.
- Transformer-based methods. Another RSIC framework with Transformer instead of LSTM as decoder appears in [20]. The Transformer-based decoder employs a stacked structure devoid of recursive connections, exhibiting superior performance and reduced training time in comparison to traditional LSTM models. Thus, it is receiving more and more favor from researchers. Liu et al. [21] proposed a multi-layer aggregated Transformer architecture for text generation, which is capable of extracting information in a manner conducive to the generation of sentences of sufficient quality. Ren et al. [22] proposed a mask-guided Transformer network incorporating a topic token with the objective of enhancing the accuracy and variety of captioning. Zhao et al. [23] proposed a region attention Transformer model that integrates region features into the RSICD task. Subsequently, they proposed a cooperative connection Transformer [24], which employs both grid features and region features to improve the decoder’s perception.
2.2. Non-Autoregressive Image Captioning
3. Methodology
3.1. Diffusion Model for VCC-DiffNet
3.2. Refined Multi-Scale Feature Extraction (RMFE) Module
3.3. Interactive Enhanced Decoder (IE-Decoder)
4. Experiments and Analysis
4.1. Datasets and Evaluation Metric
4.2. Experimental Settings
4.3. Comparisons with State-of-the-Arts Models
- Soft-attention [12] proposes to integrate a “soft” attention mechanism with the LSTM decoder.
- MLCA-Net [37] dynamically gathers visual features by use of a multi-level attention module at the encoding ends. To explore the latent context, it integrates a contextual attention module within the decoder.
- Deformable Transformer [43] is outfitted with a deformable scaled dot-product attention mechanism that facilitates the acquisition of multi-scale features from both the foreground and background.
- Topic-Embed [44] proposes inputting topic-sensitive word embedding and multi-scale features into an adaptive attention-based decoder to generate novel captions.
- GLCM [45] proposes an attention-based global-local captioning model for the purpose of obtaining a representation of global and local visual features for RSICD.
- GVFGA [18] proposes a global visual feature-guided attention mechanism. In this mechanism, global visual features are introduced, and redundant feature components are removed, thus improving the overall performance of the system.
- CCT [24] suggests a cooperative connection Transformer to fully capitalize on the benefits of both area features and grid features.
- ClipCap [46] adopts the GPT-2 module as the autoregressive captioning decoder, and its architecture is the same as our suggested network, which acts as the AR baseline for runtime comparison.
- PNAIC [29] incorporates curriculum learning-based training tasks of group length prediction and invalid group deletion to generation accurate captions and prevent common incoherent errors.
- SATIC [31] introduce a semi-autoregressive model, which keeps the autoregressive property in global but generates words parallelly locally.
- EENAIC [28] presents a semantic retrieval module that retrieves semantic information from images using features, to reduce the performance difference between the autoregressive and non-autoregressive models.
- DDCap [5] adopts the GPT-2 module as the diffusion-based non-autoregressive decoder, and the structure is identical to both ClipCap and our proposed network.
| Method | B@1 | B@2 | B@3 | B@4 | M | R | C | Latency | Speedup |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Autoregressive Methods | |||||||||
| Soft-attention [12] | 73.22 | 66.74 | 62.23 | 58.20 | 39.42 | 71.27 | 249.93 | - | - |
| MLCA-Net [37] | 83.10 | 74.20 | 65.90 | 58.00 | 39.00 | 71.10 | 232.40 | - | - |
| Deformable Transformer [43] | 83.73 | 77.71 | 71.98 | 66.59 | 45.48 | 78.60 | 303.69 | - | - |
| Topic-Embed [44] | 82.2 | 74.1 | 66.2 | 59.4 | 39.7 | - | 270.5 | - | - |
| GLCM [45] | 80.41 | 73.05 | 67.45 | 62.59 | 44.21 | 69.65 | 243.37 | - | - |
| GVFGA [18] | 84.2 | 75.7 | 67.2 | 60.1 | 42.1 | 73.3 | 285.1 | - | - |
| CCT [24] | 86.6 | 79.9 | 74.7 | 69.1 | 46.0 | 79.1 | 286.7 | - | - |
| ClipCap † [46] | 78.47 | 67.52 | 57.69 | 49.22 | 38.45 | 72.38 | 218.30 | 370 ms | 1.00× |
| Partially Non-Autoregressive Methods | |||||||||
| PNAIC [29] | 71.40 | 52.54 | 41.23 | 34.18 | 27.20 | 57.61 | 156.23 | 46 ms | 8.04× |
| SATIC [31] | 72.16 | 53.14 | 42.51 | 34.95 | 27.40 | 57.48 | 157.14 | 49 ms | 7.55× |
| Non-Autoregressive Methods | |||||||||
| EENAIC [28] | 71.30 | 51.87 | 40.61 | 32.95 | 27.20 | 56.30 | 154.25 | 2 ms | 185.00× |
| DDCap † [5] | 81.77 | 71.35 | 62.13 | 54.20 | 39.86 | 73.70 | 216.44 | 50 ms | 7.40× |
| VCC-DiffNet † (Ours) | 80.11 | 72.83 | 65.98 | 59.81 | 42.16 | 74.90 | 274.42 | 45 ms | 8.22× |
| Method | B@1 | B@2 | B@3 | B@4 | M | R | C | Latency | Speedup |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Autoregressive Methods | |||||||||
| Soft-attention [12] | 74.54 | 65.45 | 58.55 | 52.50 | 38.86 | 72.37 | 261.24 | - | - |
| MLCA-Net [37] | 82.60 | 77.00 | 71.70 | 66.80 | 43.50 | 77.20 | 324.00 | - | - |
| Deformable Transformer [43] | 82.30 | 77.00 | 72.28 | 67.92 | 44.39 | 78.39 | 346.29 | - | - |
| Topic-Embed [44] | 83.9 | 76.9 | 71.5 | 67.5 | 44.6 | - | 323.1 | - | - |
| GLCM [45] | 81.82 | 75.40 | 69.86 | 64.68 | 46.19 | 75.24 | 302.79 | - | - |
| GVFGA [18] | 84.3 | 77.5 | 71.1 | 65.1 | 45.3 | 78.5 | 338.1 | - | - |
| CCT [24] | 92.2 | 89.0 | 86.4 | 83.3 | 57.3 | 88.3 | 415.6 | - | - |
| ClipCap † [46] | 83.74 | 77.64 | 72.29 | 67.53 | 44.75 | 78.90 | 337.37 | 418 ms | 1.00× |
| Partially Non-Autoregressive Methods | |||||||||
| PNAIC [29] | 77.22 | 66.57 | 58.76 | 53.25 | 40.10 | 71.93 | 280.24 | 36 ms | 11.61× |
| SATIC [31] | 77.85 | 67.13 | 58.98 | 53.88 | 40.61 | 72.00 | 280.53 | 38 ms | 11.00× |
| Non-Autoregressive Methods | |||||||||
| EENAIC [28] | 76.94 | 66.00 | 58.29 | 52.44 | 39.12 | 71.05 | 279.87 | 1 ms | 418.00× |
| DDCap † [5] | 81.48 | 73.67 | 66.26 | 59.44 | 41.85 | 77.64 | 305.81 | 46 ms | 9.09× |
| VCC-DiffNet † (Ours) | 87.12 | 81.77 | 76.95 | 72.43 | 47.77 | 82.10 | 366.31 | 36 ms | 11.61× |
| Method | B@1 | B@2 | B@3 | B@4 | M | R | C | Latency | Speedup |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Autoregressive Methods | |||||||||
| Soft-attention [12] | 67.53 | 53.08 | 43.33 | 36.17 | 32.55 | 61.09 | 196.43 | - | - |
| MLCA-Net [37] | 75.70 | 63.40 | 53.90 | 46.10 | 35.10 | 64.60 | 235.60 | - | - |
| Deformable Transformer [43] | 75.81 | 64.16 | 55.85 | 49.23 | 35.50 | 65.23 | 258.14 | - | - |
| Topic-Embed [44] | 79.8 | 64.7 | 56.9 | 48.9 | 28.5 | - | 240.4 | - | - |
| GLCM [45] | 77.67 | 64.92 | 56.42 | 49.37 | 36.27 | 67.79 | 254.91 | - | - |
| GVFGA [18] | 79.3 | 68.1 | 57.7 | 49.8 | 37.4 | 68.2 | 279.3 | - | - |
| CCT [24] | 79.8 | 69.3 | 60.8 | 53.3 | 38.3 | 69.2 | 288.1 | - | - |
| ClipCap † [46] | 71.65 | 58.6 | 48.3 | 40.26 | 35.7 | 62.91 | 222.8 | 456 ms | 1.00× |
| Partially Non-Autoregressive Methods | |||||||||
| PNAIC [29] | 68.50 | 53.10 | 42.95 | 35.12 | 31.34 | 57.22 | 180.37 | 35 ms | 13.03× |
| SATIC [31] | 68.61 | 53.24 | 43.00 | 35.68 | 31.98 | 57.98 | 180.53 | 36ms | 12.67× |
| Non-Autoregressive Methods | |||||||||
| EENAIC [28] | 68.20 | 52.67 | 42.48 | 34.95 | 30.2 | 56.66 | 179.32 | 2 ms | 228.00× |
| DDCap † [5] | 69.40 | 56.65 | 46.70 | 39.08 | 34.47 | 63.32 | 201.58 | 44 ms | 10.36× |
| VCC-DiffNet † (Ours) | 78.85 | 68.07 | 59.29 | 52.02 | 39.47 | 70.18 | 290.74 | 30 ms | 15.20× |
| Method | B@1 | B@2 | B@3 | B@4 | M | R | C | Latency | Speedup |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Autoregressive Methods | |||||||||
| Soft-attention [12] | 73.10 | 60.90 | 52.50 | 46.20 | 33.90 | 59.90 | 113.60 | - | - |
| MLCA-Net [37] | 74.50 | 62.40 | 54.10 | 47.80 | 33.70 | 60.10 | 126.40 | - | - |
| Deformable Transformer [43] | 75.15 | 62.91 | 54.57 | 48.28 | 31.87 | 58.58 | 120.71 | - | - |
| ClipCap † [46] | 74.07 | 60.05 | 49.44 | 41.32 | 28.52 | 58.04 | 108.70 | 374ms | 1.00× |
| Partially Non-Autoregressive Methods | |||||||||
| PNAIC [29] | 71.63 | 55.27 | 44.15 | 35.69 | 27.54 | 56.64 | 100.23 | 47 ms | 7.96× |
| SATIC [31] | 71.89 | 55.75 | 44.87 | 36.28 | 28.46 | 57.13 | 101.86 | 49ms | 7.63× |
| Non-Autoregressive Methods | |||||||||
| EENAIC [28] | 71.37 | 55.11 | 43.58 | 34.84 | 26.21 | 55.39 | 99.99 | 3ms | 124.67× |
| DDCap † [5] | 76.73 | 62.98 | 51.86 | 42.95 | 30.09 | 61.36 | 110.48 | 53 ms | 7.06× |
| VCC-DiffNet † (Ours) | 79.72 | 66.35 | 56.04 | 47.93 | 30.59 | 61.82 | 123.24 | 46ms | 8.13× |
4.4. Effect of Iterative Steps
4.5. Ablation Study
5. Conclusions and Outlooks
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, B. A Systematic Survey of Remote Sensing Image Captioning. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 154086–154111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhang, R.; Hinton, G.E. Analog Bits: Generating Discrete Data using Diffusion Models with Self-Conditioning. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.04202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Z. Fast Image Caption Generation with Position Alignment. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1912.06365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, K.; Zhao, W.X.; Wen, J.-R. Diffusion Models for Non-autoregressive Text Generation: A Survey. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.06574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wei, Y.; Wang, J.; Gan, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Hua, G.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Hu, H. Exploring Discrete Diffusion Models for Image Captioning. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.11694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Li, Y.; Pan, Y.; Yao, T.; Feng, J.; Chao, H.; Mei, T. Semantic-Conditional Diffusion Networks for Image Captioning. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 23359–23368. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S. CLIP-Diffusion-LM: Apply Diffusion Model on Image Captioning. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.04559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, B.; Li, X.; Tao, D.; Lu, X. Deep semantic understanding of high-resolution remote sensing image. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Computer, Information and Telecommunication Systems (CITS), Kunming, China, 6–8 July 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Zou, Z. Can a Machine Generate Humanlike Language Descriptions for a Remote Sensing Image? IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 3623–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lu, X.; Zheng, X.; Li, X. Semantic Descriptions of High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 1274–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long Short-Term Memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wang, B.; Zheng, X.; Li, X. Exploring Models and Data for Remote Sensing Image Caption Generation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 56, 2183–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Tang, X.; Zhou, H.; Li, C. Description generation for remote sensing images using attribute attention mechanism. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Diao, W.; Yan, M.; Gao, X.; Sun, X. VAA: Visual Aligning Attention Model for Remote Sensing Image Captioning. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 137355–137364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Diao, W.; Zhang, W.; Yan, M.; Gao, X.; Sun, X. LAM: Remote Sensing Image Captioning with Label-Attention Mechanism. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yu, H.; Sun, X. Boosting Memory with a Persistent Memory Mechanism for Remote Sensing Image Captioning. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Gu, J.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Tang, X.; Jiao, L. Recurrent Attention and Semantic Gate for Remote Sensing Image Captioning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5608816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yan, M.; Gao, X.; Fu, K.; Sun, X. Global Visual Feature and Linguistic State Guided Attention for Remote Sensing Image Captioning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5615216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, B.; Xi, J.; Bai, X.; Ersoy, O.K.; Cong, M.; Gao, S.; Zhao, Z. Remote Sensing Image Captioning With Sequential Attention and Flexible Word Correlation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 6004505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Liu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, J. Remote sensing image caption generation via transformer and reinforcement learning. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 26661–26682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, R.; Shi, Z.X. Remote-Sensing Image Captioning Based on Multilayer Aggregated Transformer. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 6506605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Gou, S.; Guo, Z.; Mao, S.; Li, R. A Mask-Guided Transformer Network with Topic Token for Remote Sensing Image Captioning. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Xiong, W. Exploring region features in remote sensing image captioning. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 127, 103672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Xiong, W. Cooperative Connection Transformer for Remote Sensing Image Captioning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5607314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Mansimov, E.; Cho, K. Deterministic Non-Autoregressive Neural Sequence Modeling by Iterative Refinement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.06901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Meng, X.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Ma, S.; Gao, W. Masked Non-Autoregressive Image Captioning. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.00717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Liu, J.; Zhu, X.; He, X.; Jiang, J.; Lu, H. Non-Autoregressive Image Captioning with Counterfactuals-Critical Multi-Agent Learning. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI-20), Yokohama, Japan, 11–17 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Liu, Y.; Qi, B.; Hu, Z.; Liu, H. End-to-End Non-Autoregressive Image Captioning. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2023—2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes Island, Greece, 4–10 June 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Z. Partially Non-Autoregressive Image Captioning. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2021, 35, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Fei, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Huang, Q.; Tian, Q. Semi-autoregressive image captioning. In Proceedings of the MM ’21: Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Virtual, 20–24 October 2021; pp. 2708–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Wang, M. Semi-autoregressive transformer for image captioning. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 3139–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Cai, Z.; Gan, X.; Chang, B. DiffCap: Exploring Continuous Diffusion on Image Captioning. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.12144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, Y.; Fei, Z.; Fu, H.; Luo, X.; Guo, Y. Prefix-diffusion: A Lightweight Diffusion Model for Diverse Image Captioning. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.04965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, J.; Johnson, D.D.; Ho, J.; Tarlow, D.; van den Berg, R. Structured Denoising Diffusion Models in Discrete State-Spaces. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.03006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.B.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S.J. Feature Pyramid Networks for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, A.; Wu, J.; Child, R.; Luan, D.; Amodei, D.; Sutskever, I. Language models are unsupervised multitask learners. OpenAI Blog 2019, 1, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Q.; Huang, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, Z. NWPU-captions dataset and MLCA-net for remote sensing image captioning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5629419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papineni, K.; Roukos, S.; Ward, T.; Zhu, W.J. Bleu: A method for automatic evaluation of machine translation. In Proceedings of the ACL ’02: Proceedings of the 40th Annual Meeting on Association for Computational Linguistics, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 7–12 July 2002; pp. 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Lavie, A. METEOR: An automatic metric for MT evaluation with improved correlation with human judgments. In Proceedings of the ACL Workshop on Intrinsic and Extrinsic Evaluation Measures for Machine Translation and/or Summarization, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 29 June 2005; pp. 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.Y. Rouge: A package for automatic evaluation of summaries. In Proceedings of the Text Summarization Branches Out, Post-Conference Workshop of ACL 2004, Barcelona, Spain, 4–10 July 2004; pp. 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Vedantam, R.; Zitnick, C.L.; Parikh, D. CIDEr: Consensus-based image description evaluation. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 4566–4575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; Cao, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhi, G.; Sun, X.; Li, S.; Li, J. From Plane to Hierarchy: Deformable Transformer for Remote Sensing Image Captioning. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 7704–7717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, U.; Riaz, M.M.; Ghafoor, A. Transforming remote sensing images to textual descriptions. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 108, 102741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Huang, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, X. GLCM: Global–Local Captioning Model for Remote Sensing Image Captioning. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2023, 53, 6910–6922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokady, R.; Hertz, A. ClipCap: CLIP Prefix for Image Captioning. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.09734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| DATASET | METHOD | B@1 | B@2 | B@3 | B@4 | M | R | C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSICD | Baseline | 75.32 | 63.67 | 54.32 | 46.77 | 37.51 | 66.86 | 259.77 |
| +Fea-Refine | 76.53 | 65.08 | 55.88 | 48.25 | 37.94 | 68.72 | 264.31 | |
| +Inter-Enhance | 77.67 | 66.14 | 56.55 | 48.61 | 37.99 | 68.66 | 260.36 | |
| VCC-DiffNet | 78.85 | 68.07 | 59.29 | 52.02 | 39.47 | 70.18 | 290.74 | |
| UCM-Captions | Baseline | 86.11 | 79.20 | 72.85 | 67.12 | 44.60 | 80.32 | 341.64 |
| +Fea-Refine | 86.38 | 81.05 | 76.21 | 71.45 | 46.66 | 81.88 | 356.09 | |
| +Inter-Enhance | 87.04 | 81.11 | 75.59 | 70.28 | 46.56 | 82.47 | 355.31 | |
| VCC-DiffNet | 87.12 | 81.77 | 76.95 | 72.43 | 47.77 | 82.10 | 366.31 | |
| Sydney-Captions | Baseline | 80.70 | 67.98 | 57.34 | 48.22 | 39.42 | 73.09 | 216.89 |
| +Fea-Refine | 82.60 | 73.62 | 64.50 | 55.96 | 42.19 | 75.13 | 241.66 | |
| +Inter-Enhance | 83.43 | 75.07 | 66.78 | 58.63 | 41.61 | 75.96 | 243.70 | |
| VCC-DiffNet | 80.11 | 72.83 | 65.98 | 59.81 | 42.16 | 74.90 | 274.42 | |
| NWPU-Captions | Baseline | 73.98 | 59.89 | 49.33 | 41.47 | 28.06 | 57.76 | 107.94 |
| +Fea-Refine | 75.84 | 62.16 | 51.58 | 43.31 | 28.79 | 58.93 | 112.50 | |
| +Inter-Enhance | 75.75 | 62.84 | 52.67 | 44.71 | 29.46 | 59.96 | 116.30 | |
| VCC-DiffNet | 79.72 | 66.35 | 56.04 | 47.93 | 30.59 | 61.82 | 123.24 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, Q.; Xu, Y.; Huang, Z. VCC-DiffNet: Visual Conditional Control Diffusion Network for Remote Sensing Image Captioning. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2961. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16162961
Cheng Q, Xu Y, Huang Z. VCC-DiffNet: Visual Conditional Control Diffusion Network for Remote Sensing Image Captioning. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(16):2961. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16162961
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Qimin, Yuqi Xu, and Ziyang Huang. 2024. "VCC-DiffNet: Visual Conditional Control Diffusion Network for Remote Sensing Image Captioning" Remote Sensing 16, no. 16: 2961. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16162961
APA StyleCheng, Q., Xu, Y., & Huang, Z. (2024). VCC-DiffNet: Visual Conditional Control Diffusion Network for Remote Sensing Image Captioning. Remote Sensing, 16(16), 2961. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16162961






