Inversion of Farmland Soil Moisture Based on Multi-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar Data and Optical Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
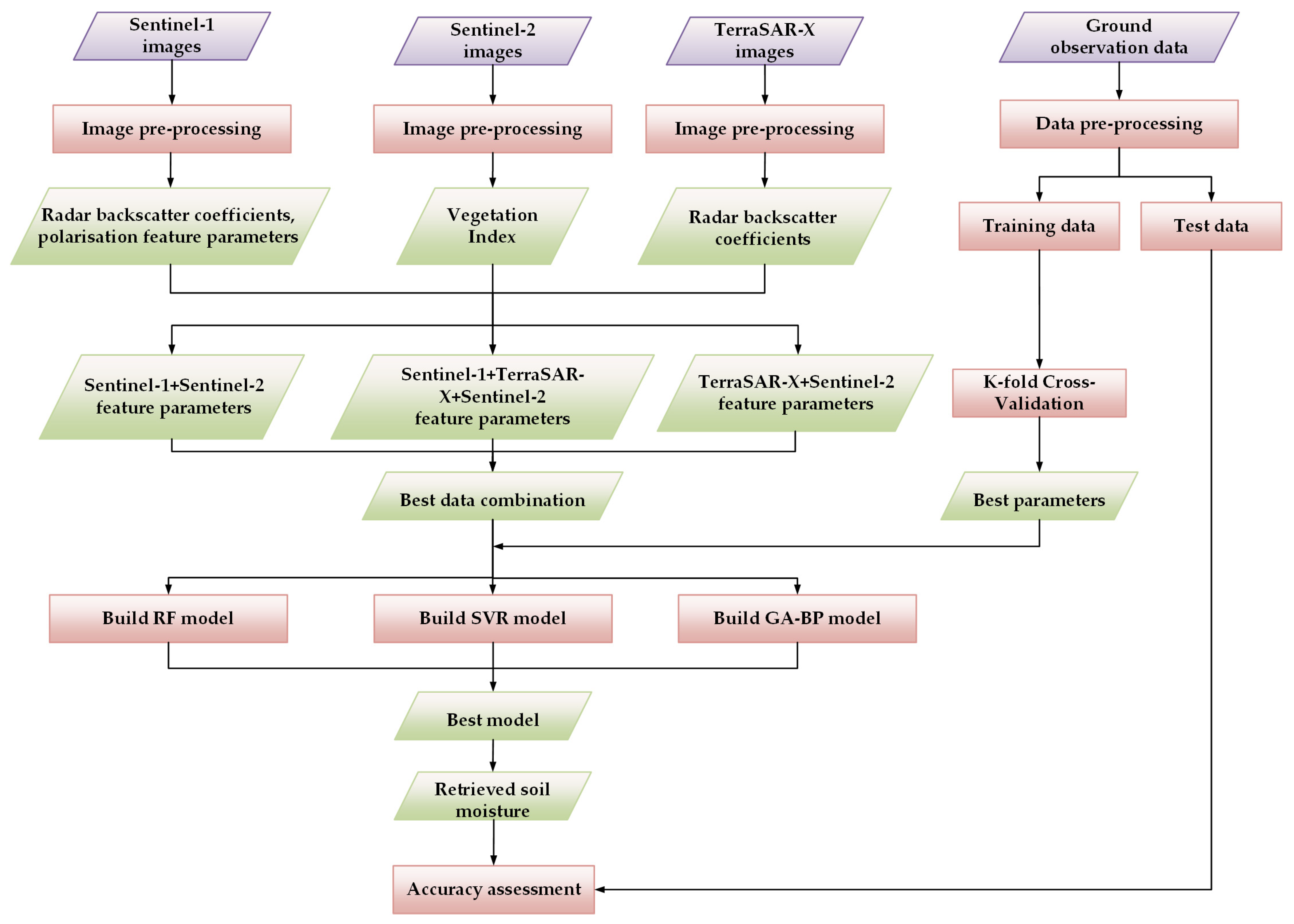
2. Materials and Methods
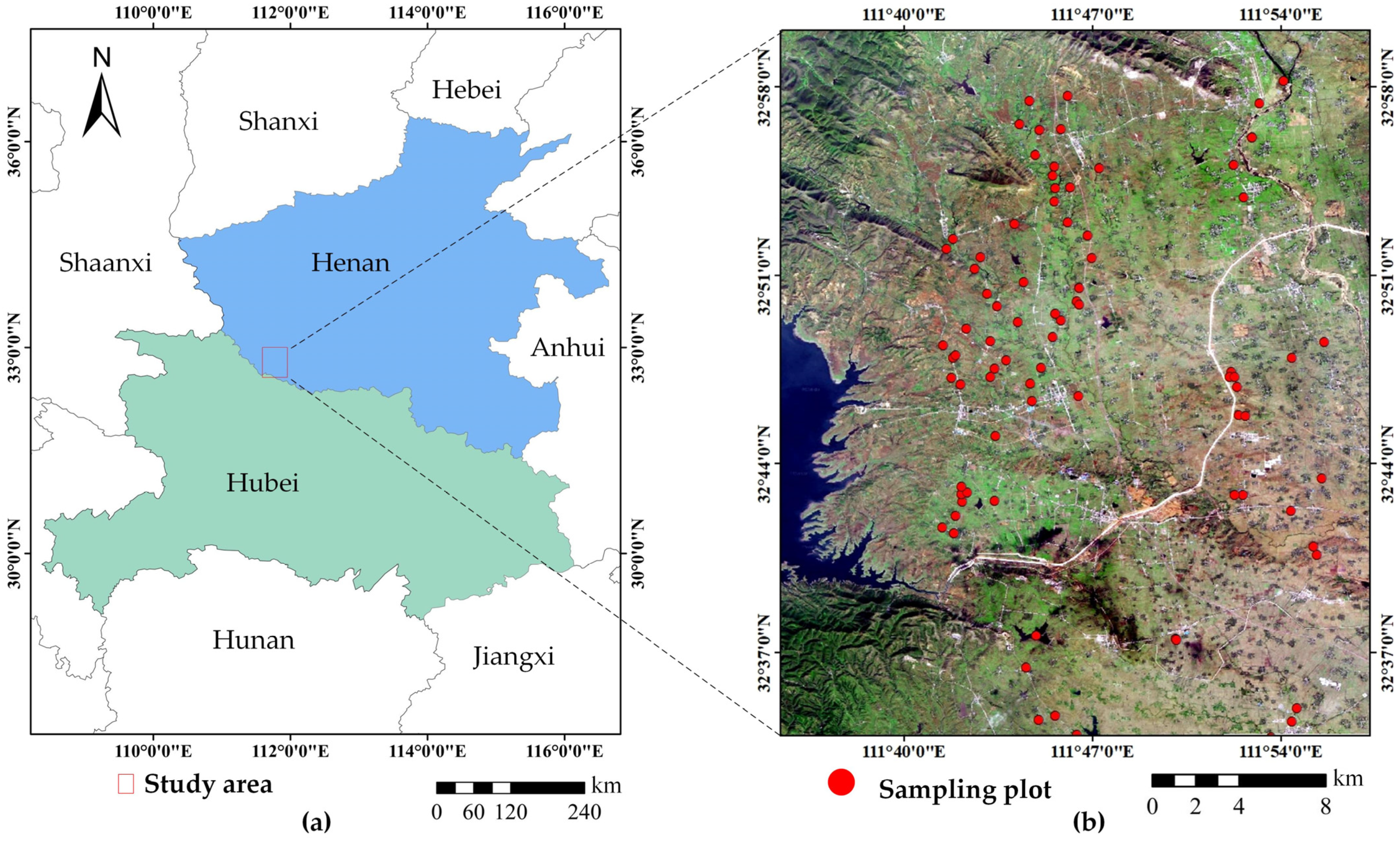
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Dataset and Image Preprocessing
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Feature Parameters Extraction
- Feature Parameters Extracted from SAR Data
- Feature Parameters Extracted from Optical Images
2.3.2. Machine Learning Model Building
- GA-BP model
- SVR model
- RF model
2.3.3. Data Combination Selection
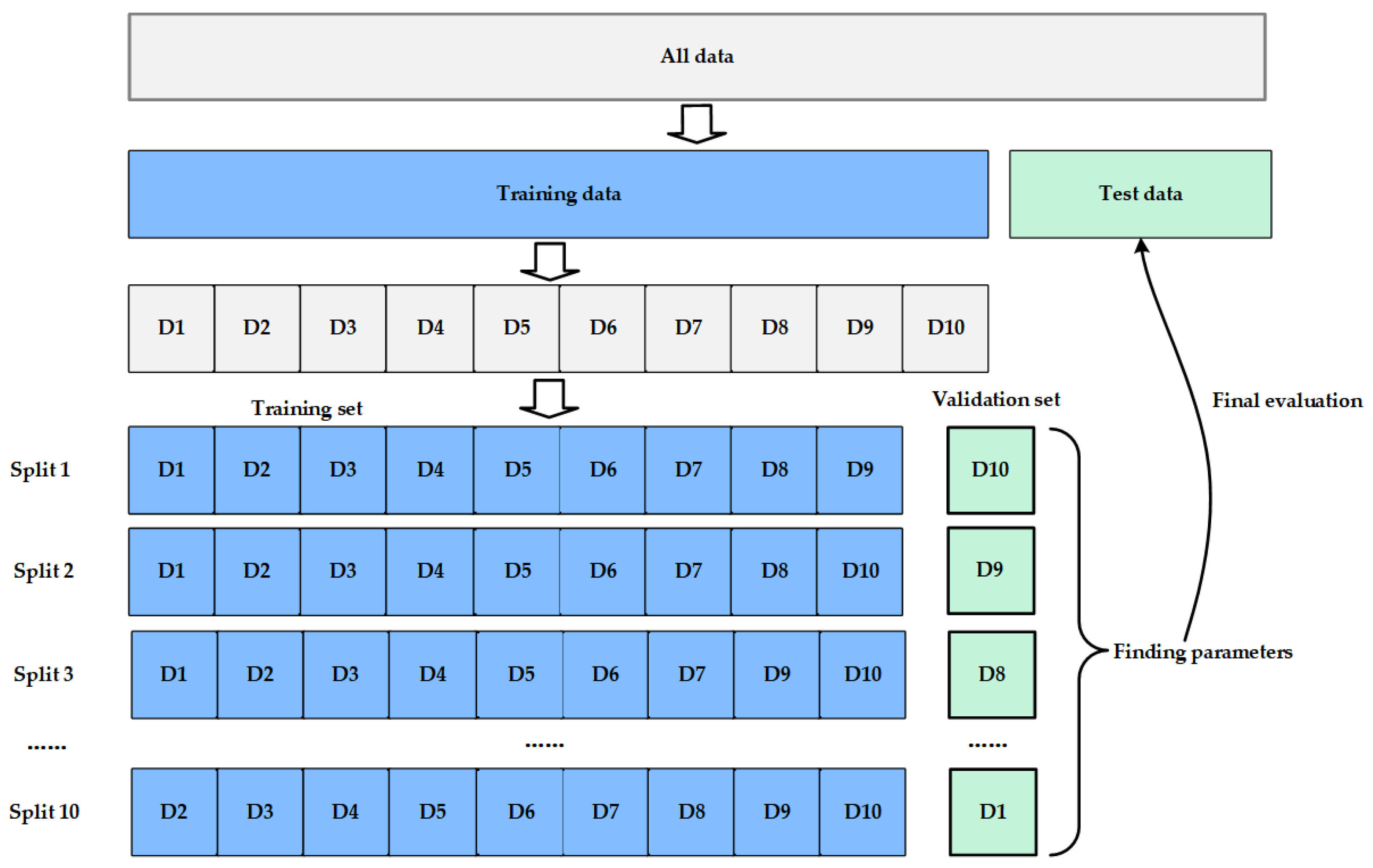
2.3.4. K-Fold Cross-Validation
2.3.5. SSM Result Prediction and Accuracy Assessment
3. Results
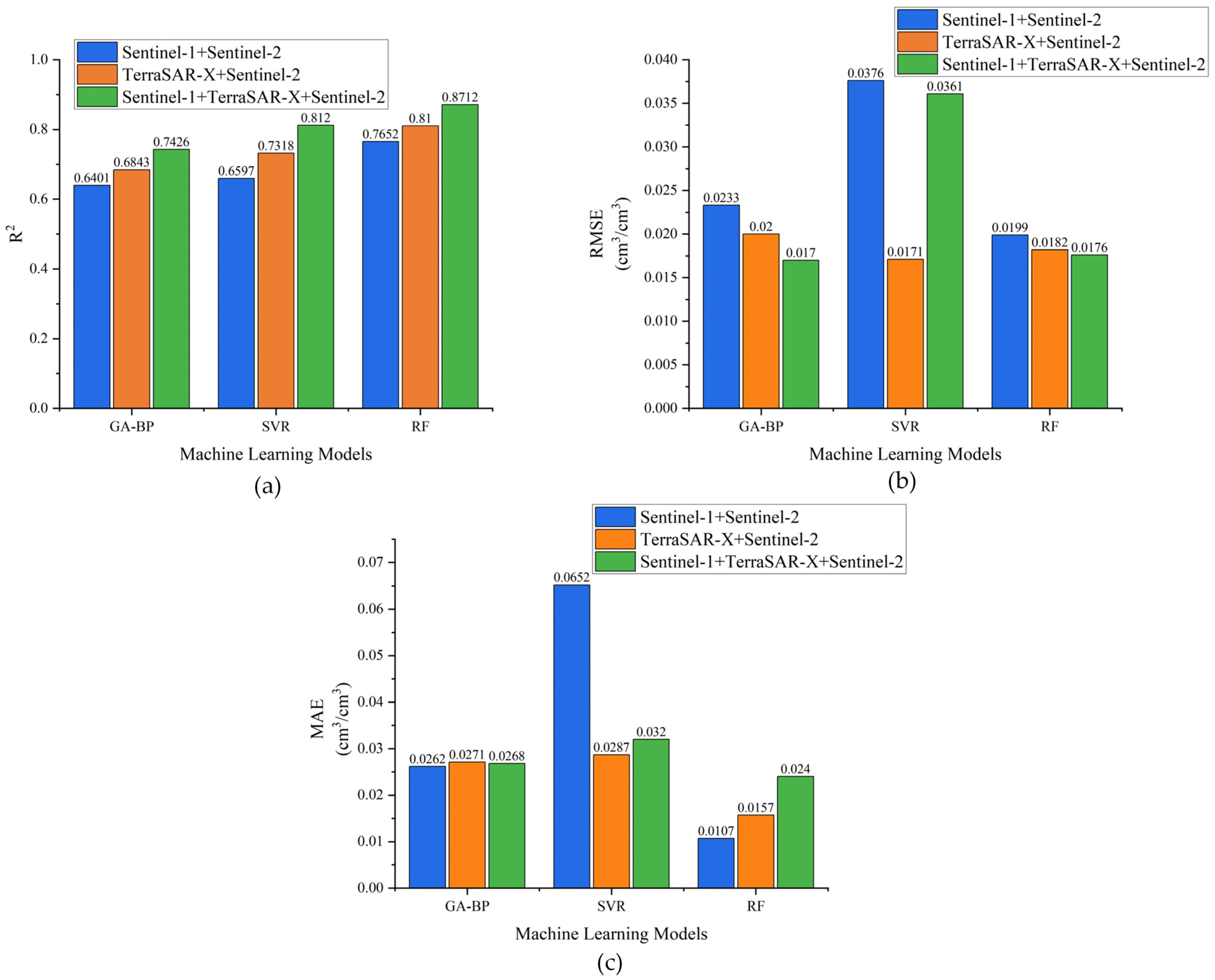
3.1. Multi-Band Data Accuracy Analysis
3.2. Cross-Validation Accuracy Analysis
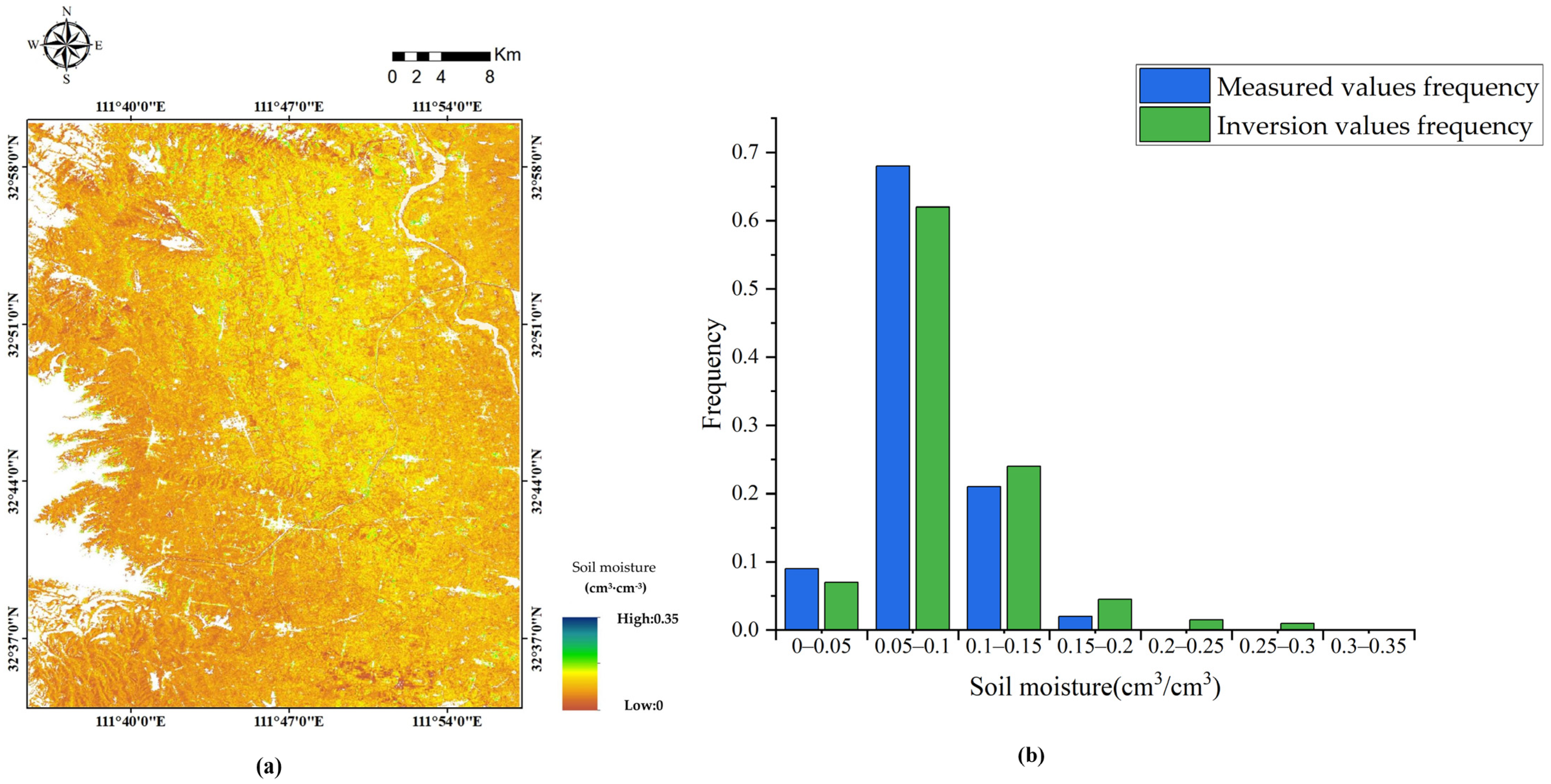
3.3. Analysis of Spatial Distribution of SSM in the Study Area
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Applicability during Late Vegetation Growth
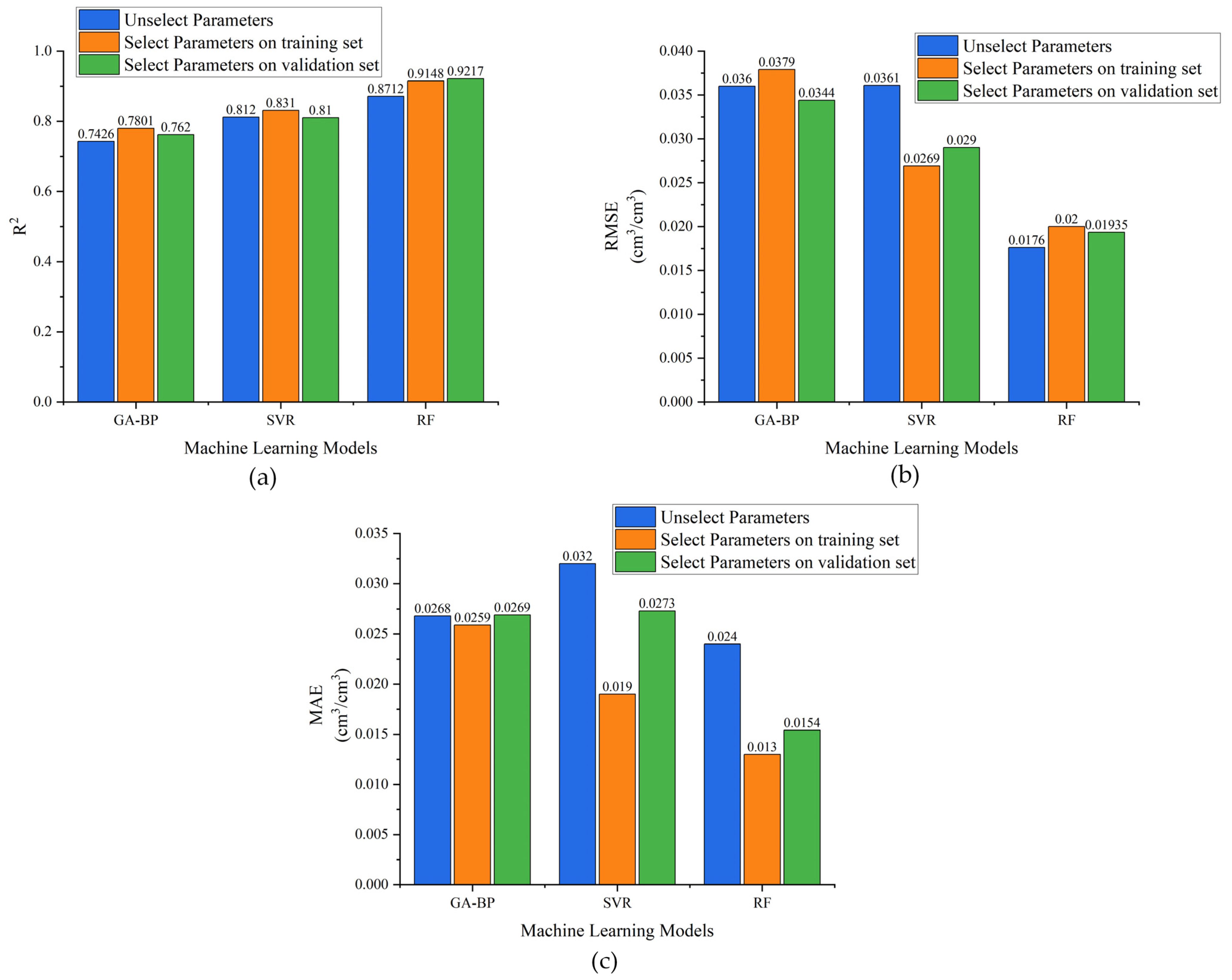
4.2. Analysis of the Effectiveness of Model Parameters
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, H.; Magagi, R.; Goïta, K. Potential of a two-component polarimetric decomposition at C-band for soil moisture retrieval over agricultural fields. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 217, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, R.; Chai, H.; Lv, X. A polarimetric decomposition and copula quantile regression approach for soil moisture estimation from Radarsat-2 data over vegetated areas. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 3405–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocca, L.; Tarpanelli, A.; Filippucci, P.; Dorigo, W.; Zaussinger, F.; Gruber, A.; Fernández-Prieto, D. How much water is used for irrigation? A new approach exploiting coarse resolution satellite soil moisture products. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 73, 752–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohaib, M.; Kim, H.; Choi, M. Detecting global irrigated areas by using satellite and reanalysis products. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 677, 679–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zohaib, M.; Choi, M. Satellite-based global-scale irrigation water use and its contemporary trends. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, C.; Min, L.; Guo, Z.; Li, N. Retrieval of farmland surface soil moisture based on feature optimization and machine learning. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.N.; Li, R.P.; Wu, Y.J.; Zhao, S.X.; Wang, X.Q. Soil moisture inversion based on environmental variables and machine learning. J. Agric. Mach. 2022, 53, 332–341. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.Z.; Liu, S.M.; Peng, A.H.; Sun, L.; Sun, G.Y. Active and passive cooperative algorithm at L-Band for bare soil moisture inversion. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2016, 32, 133–138. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.G.; Ma, C.F.; Zhao, Z.B.; Wei, L. Estimation of Soil Moisture of Agriculture Field in the Middle Reaches of the Heihe River Basin based on Sentinel-1 and Landsat 8 Imagery. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2020, 35, 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.T. Remote Sensing Retrieval of Soil Moisture in Ordos Blown-Sand Region Based on SVR. Master’s Thesis, Chang’an University, Xi’an, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Mishra, A.K.; Yu, Z. Evaluating uncertainties in multi-layer soil moisture estimation with support vector machines and ensemble Kalman filtering. J. Hydrol. 2016, 538, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Roo, R.D.; Du, Y.; Ulaby, F.T.; Dobson, M.C. A semi-empirical backscattering model at L-band and C-band for a soybean canopy with soil moisture inversion. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoest, N.E.; Lievens, H.; Wagner, W.; Álvarez-Mozos, J.; Moran, M.S.; Mattia, F. On the soil roughness parameterization problem in soil moisture retrieval of bare surfaces from synthetic aperture radar. Sensors 2008, 8, 4213–4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzahn, P.; Ludwig, R. On the derivation of soil surface roughness from multi parametric PolSAR data and its potential for hydrological modeling. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wu, Z.; Cui, N.; Jin, X.; Zhu, S.; Jiang, S.; Zhao, L.; Gong, D. Estimation of Soil Moisture Using Multi-Source Remote Sensing and Machine Learning Algorithms in Farming Land of Northern China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhao, J.; Yang, H.; Li, N. Inversion of Soil Moisture on Farmland Areas Based on SSA-CNN Using Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, P.; Li, Z.L.; Duan, S.B.; Gao, M.F.; Huo, H.Y. A Practical Approach for Deriving All-Weather Soil Moisture Content Using Combined Satellite and Meteorological Data. ISPRS J. Photogrammetry Remote Sens. 2017, 131, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Yaari, A.; Wigneron, J.P.; Ducharne, A.; Kerr, Y.; De Rosnay, P.; De Jeu, R.; Mialon, A. Global-scale evaluation of two satellite-based passive microwave soil moisture datasets (SMOS and AMSR-E) with respect to Land Data Assimilation System estimates. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 149, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, H.; Guo, J. Soil Moisture Retrieval in Farmland Areas with Sentinel Multi-Source Data Based on Regression Convolutional Neural Networks. Sensors 2021, 21, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Li, X.; McCabe, M.F. Retrieval of High-Resolution Soil Moisture through Combination of Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qian, J.; Yue, H. Combined Sentinel-1A with Sentinel-2A to estimate soil moisture in farmland. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 14, 1292–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, B.; Fan, H.; Huang, J.; Zhao, H. The Potential Use of Multi-Band SAR Data for Soil Moisture Retrieval over Bare Agricultural Areas: Hebei, China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.P.; Prasad, R.; Bala, R.; Vishwakarma, A.K. An improved inversion algorithm for spatio-temporal retrieval of soil moisture through modified water cloud model using C-band Sentinel-1A SAR data. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 173, 105447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.; Yang, L.; Yang, W.; Xu, T.; Gao, F.; Lu, Y.; Sun, B.; Yang, D.; Hong, X.; Wang, N.; et al. Robust Kalman Filter Soil Moisture Inversion Model Using GPS SNR Data—A Dual-Band Data Fusion Approach. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidoo, L.; Mathieu, R.; Main, R.; Kleynhans, W.; Wessels, K.; Asner, G.; Leblon, B. Savannah woody structure modelling and map** using multi-frequency (X-, C-and L-band) Synthetic Aperture Radar data. ISPRS J. Photogrammetry Remote Sens. 2015, 105, 234–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-J.; Choi, C.; Kim, J.; Choi, M.; Cho, J.; Lee, Y. Estimation of High-Resolution Soil Moisture in Canadian Croplands Using Deep Neural Network with Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 Images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Xue, Z.; Li, H. Sensitive Feature Evaluation for Soil Moisture Retrieval Based on Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data with Few In-Situ Measurements: A Case Study of the Continental US. Water 2021, 13, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, F.; Shang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Ahmad, I.; Zhou, G. Saline soil moisture mapping using Sentinel-1A synthetic aperture radar data and machine learning algorithms in humid region of China’s east coast. Catena 2022, 213, 106189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Li, M.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, C. An ensemble learning approach for land use/land cover classification of arid regions for climate simulation: A case study of Xinjiang, Northwest China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 2413–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Kalra, A.; Stephen, H. Estimating soil moisture using remote sensing data: A machine learning approach. Adv. Water Resour. 2010, 33, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaby, F.T.; Moore, R.K.; Fung, A.K. Microwave Remote Sensing: Active and Passive. Volume 2-Radar Remote Sensing and Surface Scattering and Emission Theory; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, L.; Li, J.; Jiang, J.; Chen, X.; Cai, Q. A modified vegetation backscattering model for leaf area index retrieval from SAR time series. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 5884–5901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghdadi, N.N.; El Hajj, M.; Zribi, M.; Fayad, I. Coupling SAR C-band and optical data for soil moisture and leaf area index retrieval over irrigated grasslands. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2015, 9, 1229–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balenzano, A.; Mattia, F.; Satalino, G.; Davidson, M.W.J. Dense temporal series of C-and L-band SAR data for soil moisture retrieval over agricultural crops. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2010, 4, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kseneman, M.; Gleich, D. Soil-moisture estimation from X-band data using Tikhonov regularization and neural net. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 3885–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Dai, J.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, S.; Qin, T.; Walker, J.P. A cross-resolution transfer learning approach for soil moisture retrieval from Sentinel-1 using limited training samples. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 301, 113944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, Q.; Hui, J.; Long, Z. Soil moisture estimation with SVR and data augmentation based on alpha approximation method. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 58, 3190–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xing, M.; He, B.; Wang, J.; Shang, J.; Huang, X.; Xu, M. Estimating soil moisture over winter wheat fields during growing season using machine-learning methods. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 3706–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, P.; Xiong, C.; Li, K.; Song, Y.; Gong, S.; Yue, Z. Effect of Data Characteristics Inconsistency on Medium and Long-Term Runoff Forecasting by Machine Learning. IEEE Access. 2023, 11, 11601–11612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Jiao, D.; Chen, T.; Gui, G. Medium-and long-term precipitation forecasting method based on data augmentation and machine learning algorithms. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 1000–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ye, C.; Zhang, Q. 11-Year change in water chemistry of large freshwater Reservoir Danjiangkou, China. J. Hydrol. 2017, 551, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Yang, P.; Ren, J.; Chen, Z.; Liu, C.; Li, H. Winter wheat LAI inversion considering morphological characteristics at different growth stages coupled with microwave scattering model and canopy simulation model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 240, 111681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lin, H.; Huang, C.; Fang, C. The relationship between the leaf area index (LAI) of rice and the C-band SAR vertical/horizontal (VV/HH) polarization ratio. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 2149–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, J.; Shang, J.; Liao, C.; Liu, J. Application of polarization signature to land cover scattering mechanism analysis and classification using multi-temporal C-band polarimetric RADARSAT-2 imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 193, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Chehbouni, A.; Huete, A.R.; Kerr, Y.H.; Sorooshian, S. A modified soil adjusted vegetation index. Remote Sens. Environ. 1994, 48, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Lin, L.; Wu, S.; Deng, K.A.; Petropoulos, G.P. Surface soil moisture retrievals over partially vegetated areas from the synergy of Sentinel-1 and Landsat 8 data using a modified water-cloud model. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 72, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yuan, Q.; Zhang, L. Geo-intelligent retrieval framework based on machine learning in the cloud environment: A case study of soil moisture retrieval. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Liu, C.; Tang, Y.; Gong, C. A GA-BP Neural Network Regression Model for Predicting Soil Moisture in Slope Ecological Protection. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brereton, R.G.; Lloyd, G.R. Support vector machines for classification and regression. Analyst 2010, 135, 230–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Z.; Yu, Y.; Samali, B.; Rashidi, M.; Mohammadi, M.; Nguyen, T.N.; Nguyen, A. Back-Propagation Neural Network Optimized by K-Fold Cross-Validation for Prediction of Torsional Strength of Reinforced Concrete Beam. Materials 2022, 15, 1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasternak, M.; Pawłuszek-Filipiak, K. Evaluation of C and X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar Derivatives for Tracking Crop Phenological Development. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Jiao, X.; Liu, Y.; Shao, M.; Yu, X.; Bai, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; Tuohuti, N.; Liu, S.; et al. Estimation of soil moisture content under high maize canopy coverage from UAV multimodal data and machine learning. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 264, 107530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Data Source | Acquisition Date | Band | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution | Product Type | Polarization Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sentinel-1 | 23 September 2021 | C | 10 m | 12 d | IW | VV/VH |
| 16 December 2021 | ||||||
| TerraSAR | 24 September 2021 | X | 18 m | 11 d | ScanSAR | HH |
| 21 December 2021 | ||||||
| Sentinel-2 | 22 September 2021 21 December 2021 | Band 1 | 60 m | 10 d | L2A | - |
| Band 2 | 10 m | |||||
| Band 3 | 10 m | |||||
| Band 4 | 10 m | |||||
| Band 5 | 20 m | |||||
| Band 6 | 20 m | |||||
| Band 7 | 20 m | |||||
| Band 8 | 10 m | |||||
| Band 8A | 20 m | |||||
| Band 9 | 60 m | |||||
| Band 10 | 60 m | |||||
| Band 11 | 20 m | |||||
| Band 12 | 20 m | |||||
| Ground observation data | 23 September 2021 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 21 December 2021 |
| No. | Parameter | Note |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sentinel-1 incident angle | |
| 2 | VV backscatter coefficients | |
| 3 | VH backscatter coefficients | |
| 4 | HH backscatter coefficients | |
| 5 | NDVI | Normalized Difference Vegetation Index |
| 6 | NDWI | Normalized Difference Water Index |
| No. | Data Type | Data |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | C-Band + Optical | Sentinel-1 + Sentinel-2 |
| 2 | X-Band + Optical | TerraSAR-X + Sentinel-2 |
| 3 | C-Band+X-Band + Optical | Sentinel-1 + TerraSAR-X + Sentinel-2 |
| Machine Learning Model | Input Data Source | R2 | RMSE (cm3/cm3) | MAE (cm3/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GA-BP | Sentinel-1 + Sentinel-2 | 0.6286 | 0.0282 | 0.0281 |
| TerraSAR-X + Sentinel-2 | 0.6719 | 0.0241 | 0.0265 | |
| Sentinel-1 + TerraSAR-X + Sentinel-2 | 0.7208 | 0.037 | 0.0309 | |
| SVR | Sentinel-1 + Sentinel-2 | 0.6822 | 0.0254 | 0.0269 |
| TerraSAR-X + Sentinel-2 | 0.7126 | 0.0235 | 0.0292 | |
| Sentinel-1 + TerraSAR-X + Sentinel-2 | 0.7984 | 0.0304 | 0.0276 | |
| RF | Sentinel-1 + Sentinel-2 | 0.7535 | 0.0192 | 0.0134 |
| TerraSAR-X + Sentinel-2 | 0.8306 | 0.0190 | 0.0144 | |
| Sentinel-1 + TerraSAR-X + Sentinel-2 | 0.8812 | 0.0169 | 0.0131 |
| Machine Learning Model | Parameter | Parameter Value before Selection | Parameter Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| GA-BP | Hidden Layers | 1 | 1 |
| Number of nodes | 10 | 9 | |
| Population size | 100 | 50 | |
| Number of iterations | 100 | 100 | |
| SVR | Penalty parameter | 5 | 6 |
| Kernel function coefficients | 0.5 | 0.1 | |
| RF | Number of trees | 50 | 100 |
| Maximum depth of the tree | 10 | 5 |
| Machine Learning Model | R2 | RMSE (cm3/cm3) | MAE (cm3/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GA-BP | 0.7346 | 0.0357 | 0.0276 |
| SVR | 0.8247 | 0.0279 | 0.0218 |
| RF | 0.9186 | 0.0153 | 0.0122 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, C.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Sun, X.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, J.; Li, N. Inversion of Farmland Soil Moisture Based on Multi-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar Data and Optical Data. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16132296
Xu C, Liu Q, Wang Y, Chen Q, Sun X, Zhao H, Zhao J, Li N. Inversion of Farmland Soil Moisture Based on Multi-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar Data and Optical Data. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(13):2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16132296
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Chongbin, Qingli Liu, Yinglin Wang, Qian Chen, Xiaomin Sun, He Zhao, Jianhui Zhao, and Ning Li. 2024. "Inversion of Farmland Soil Moisture Based on Multi-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar Data and Optical Data" Remote Sensing 16, no. 13: 2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16132296
APA StyleXu, C., Liu, Q., Wang, Y., Chen, Q., Sun, X., Zhao, H., Zhao, J., & Li, N. (2024). Inversion of Farmland Soil Moisture Based on Multi-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar Data and Optical Data. Remote Sensing, 16(13), 2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16132296








