Dominant Modes of Tibetan Plateau Summer Surface Sensible Heating and Associated Atmospheric Circulation Anomalies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Surface Energy Balance Analysis
2.2.2. Wave Activity Flux
2.2.3. Empirical Orthogonal Functions (EOF) Analysis
2.2.4. Linear Regression Analysis and Composite Analysis
3. Results
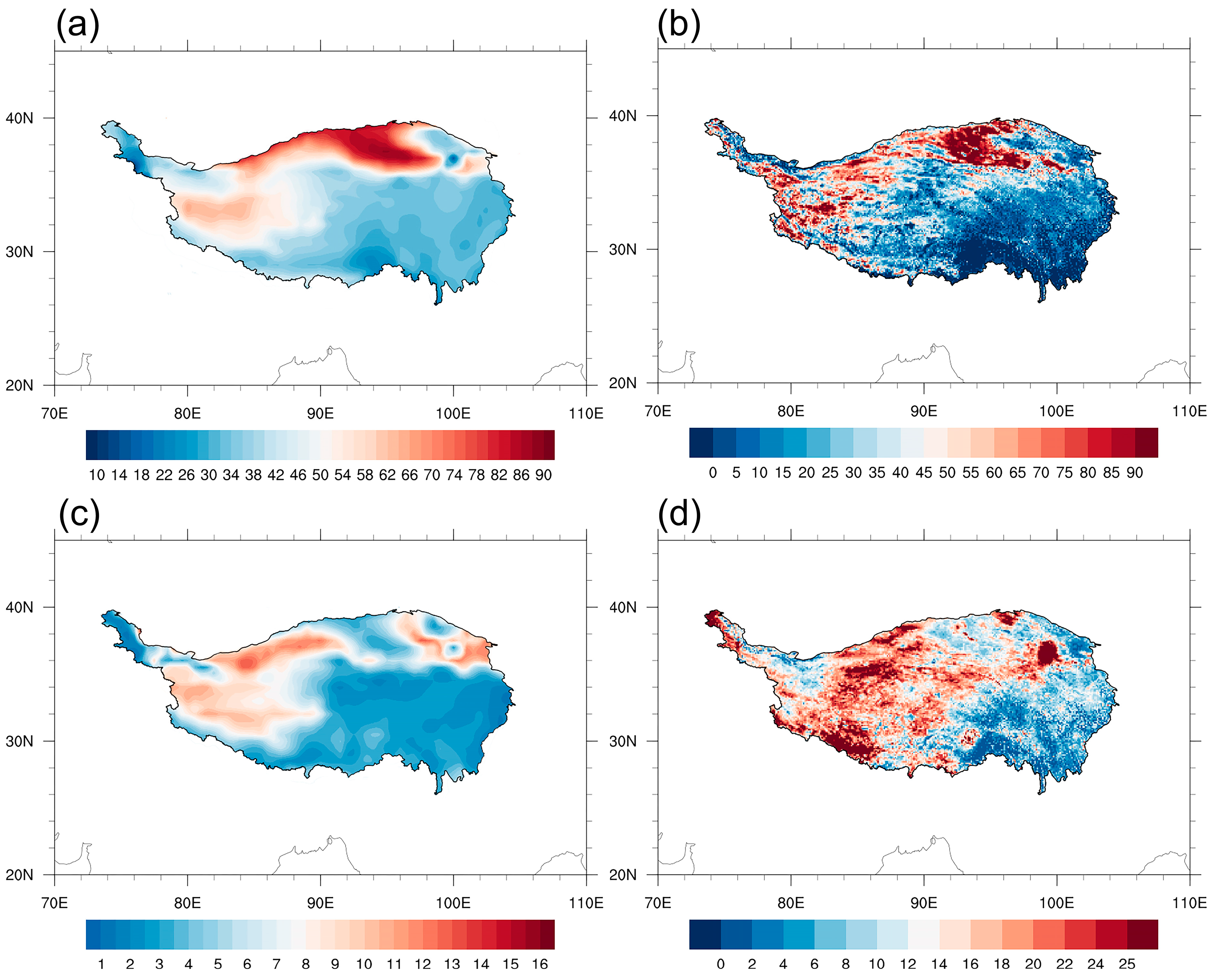
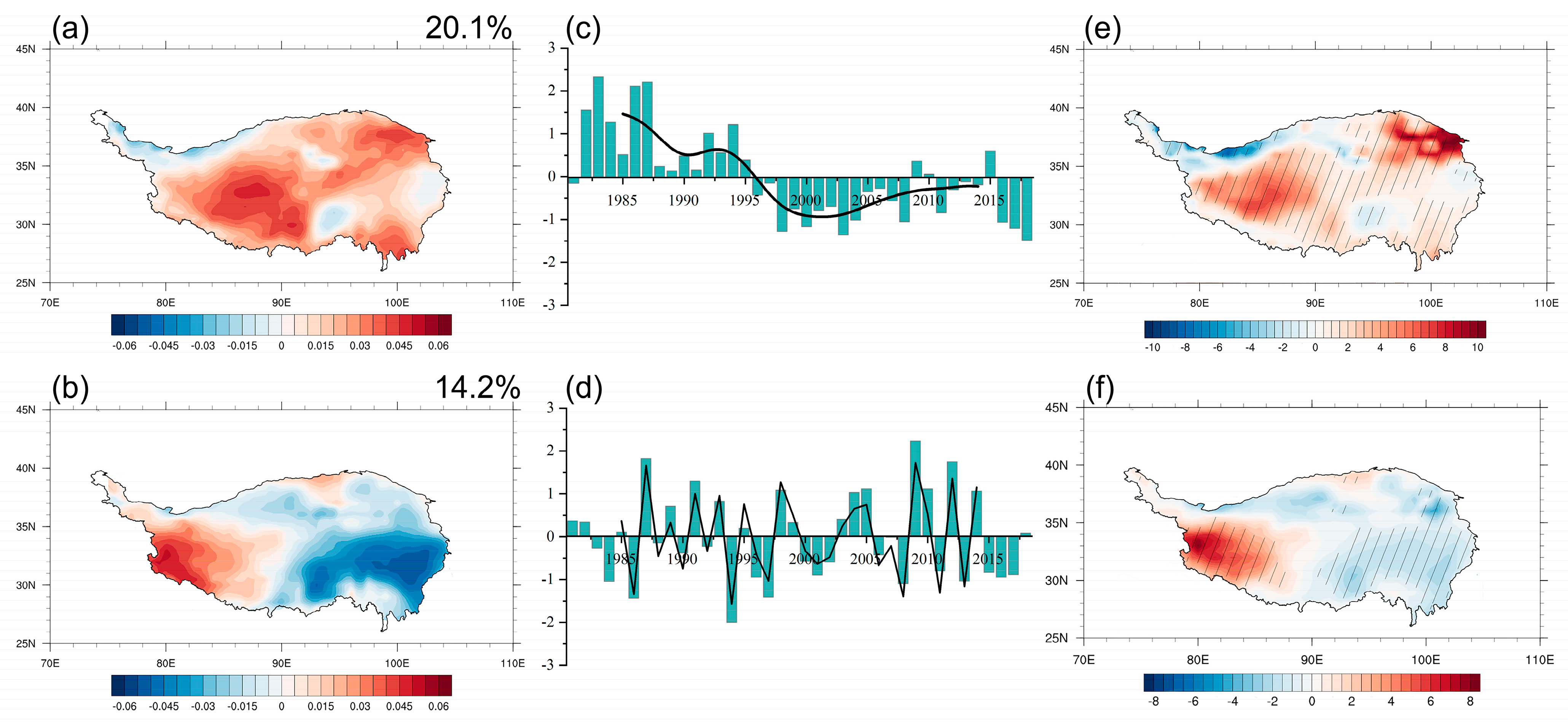
3.1. Dominant Modes of Variation in Summer SH over the TP
3.2. Physical Mechanisms of Variations in Summer SH
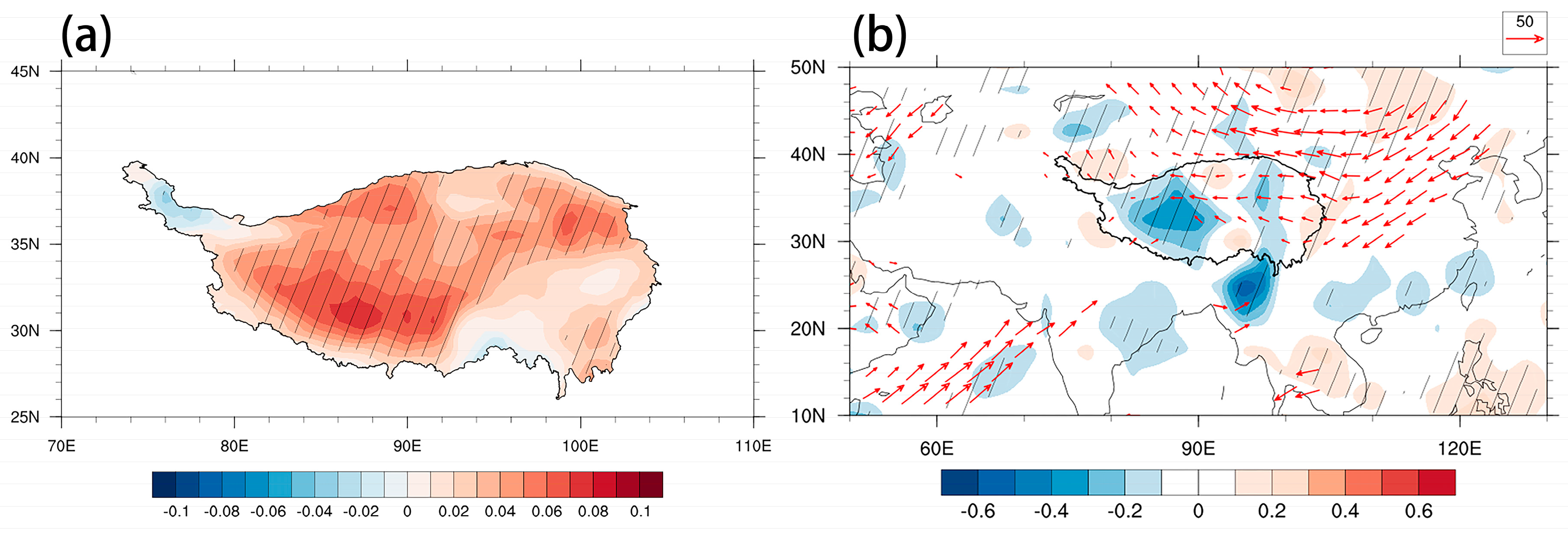
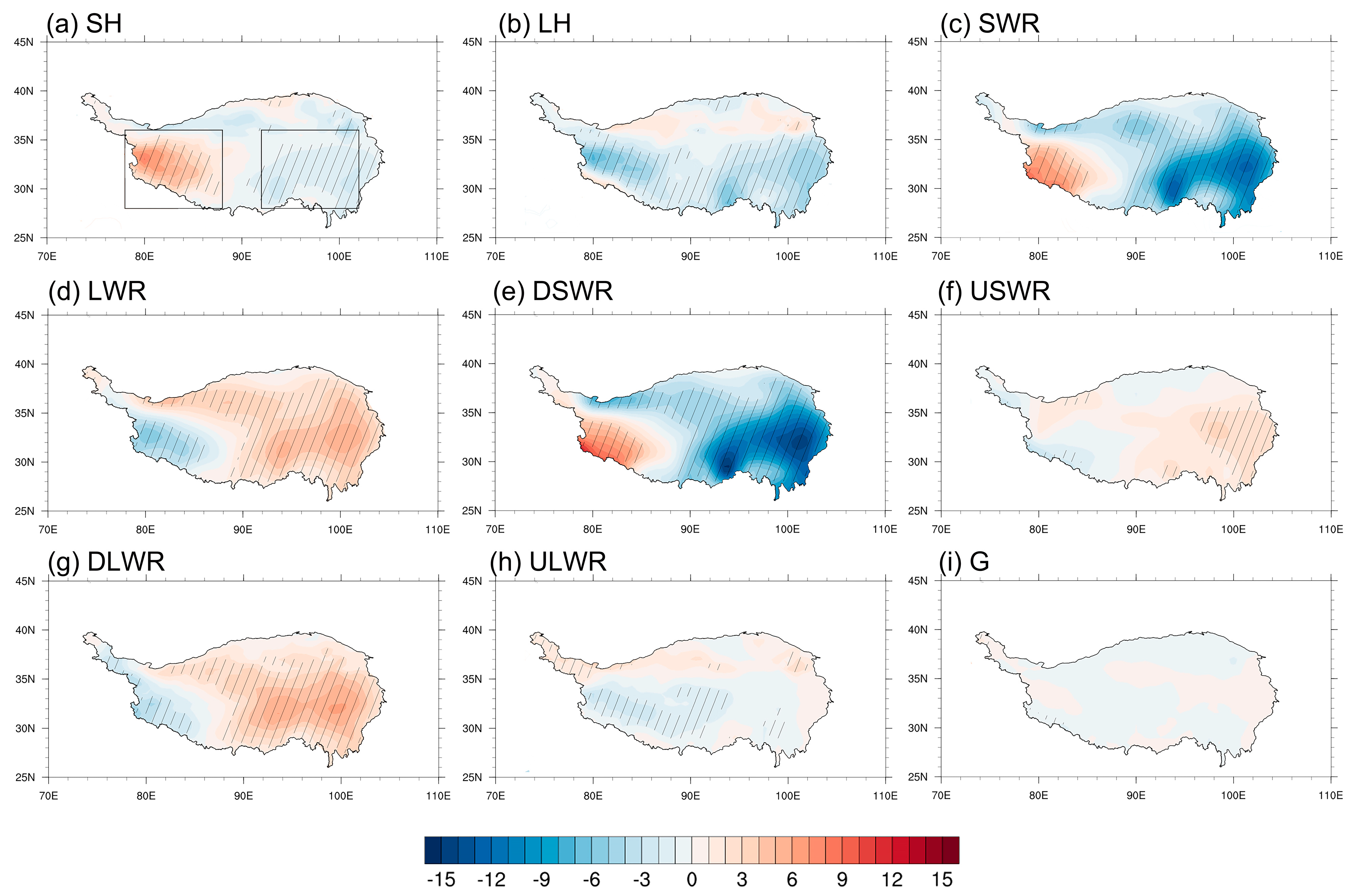
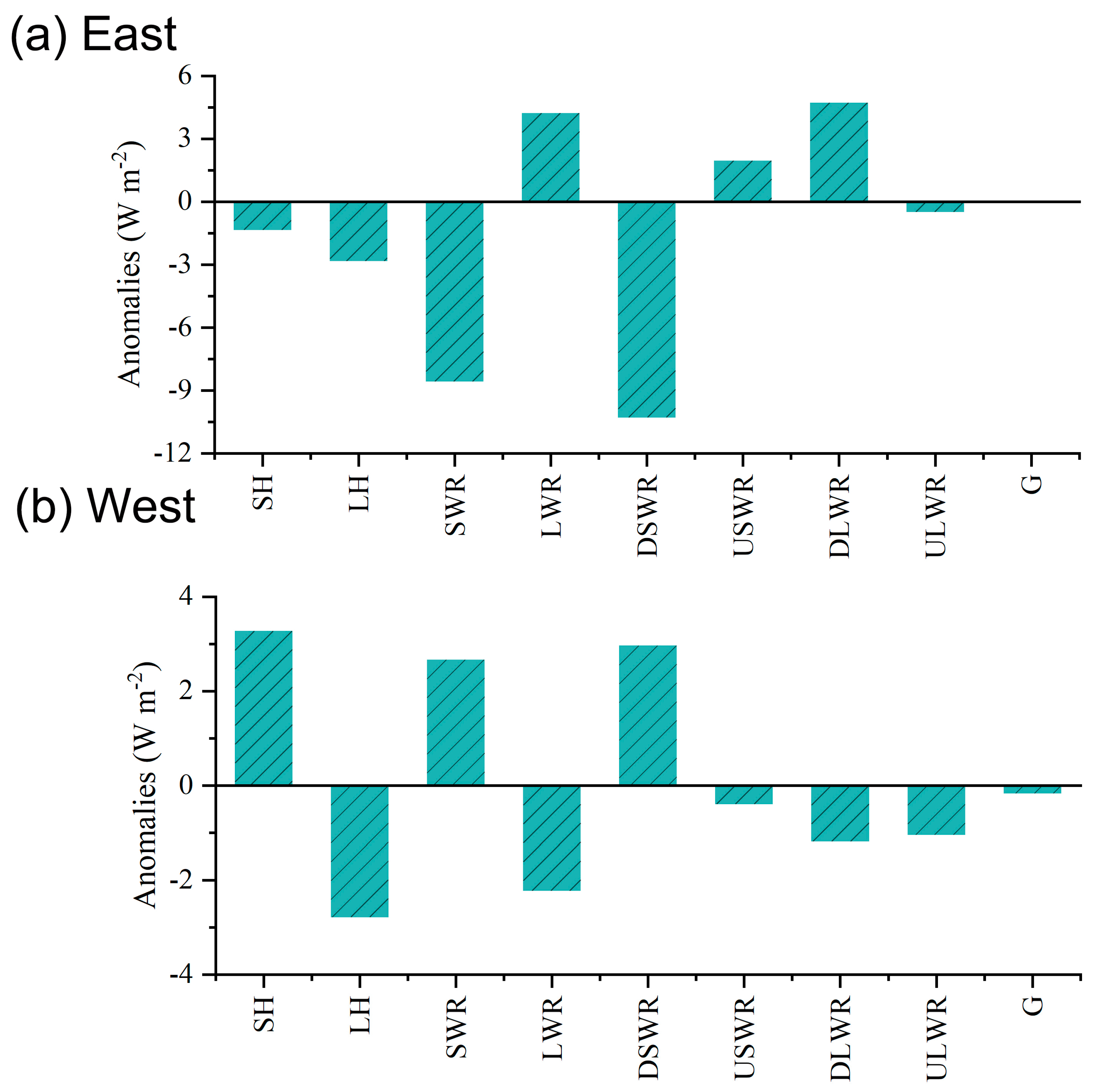
3.2.1. First Dominant Mode of Variation in Summer SH
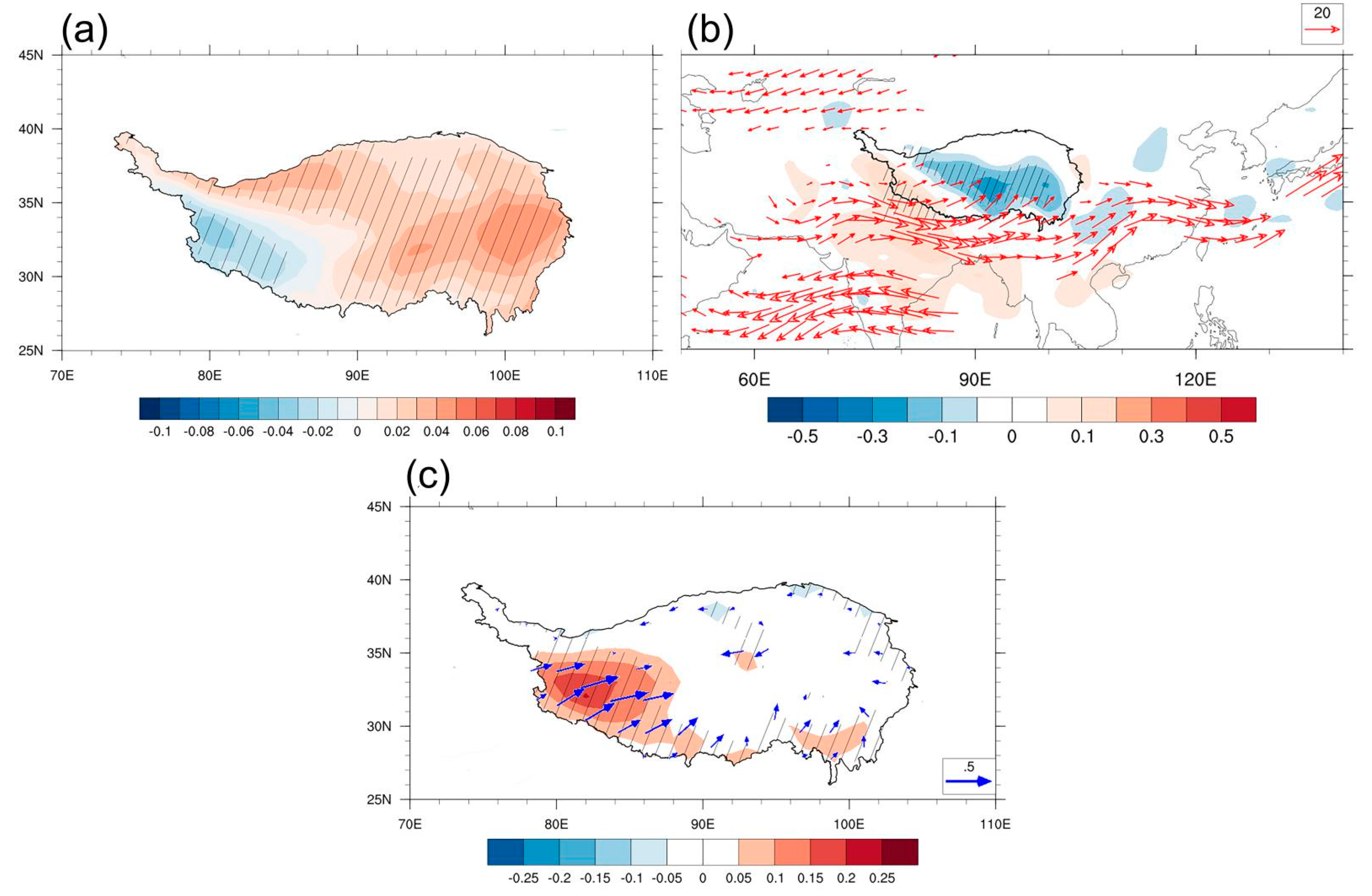
3.2.2. Second Dominant Mode of Variation in Summer SH
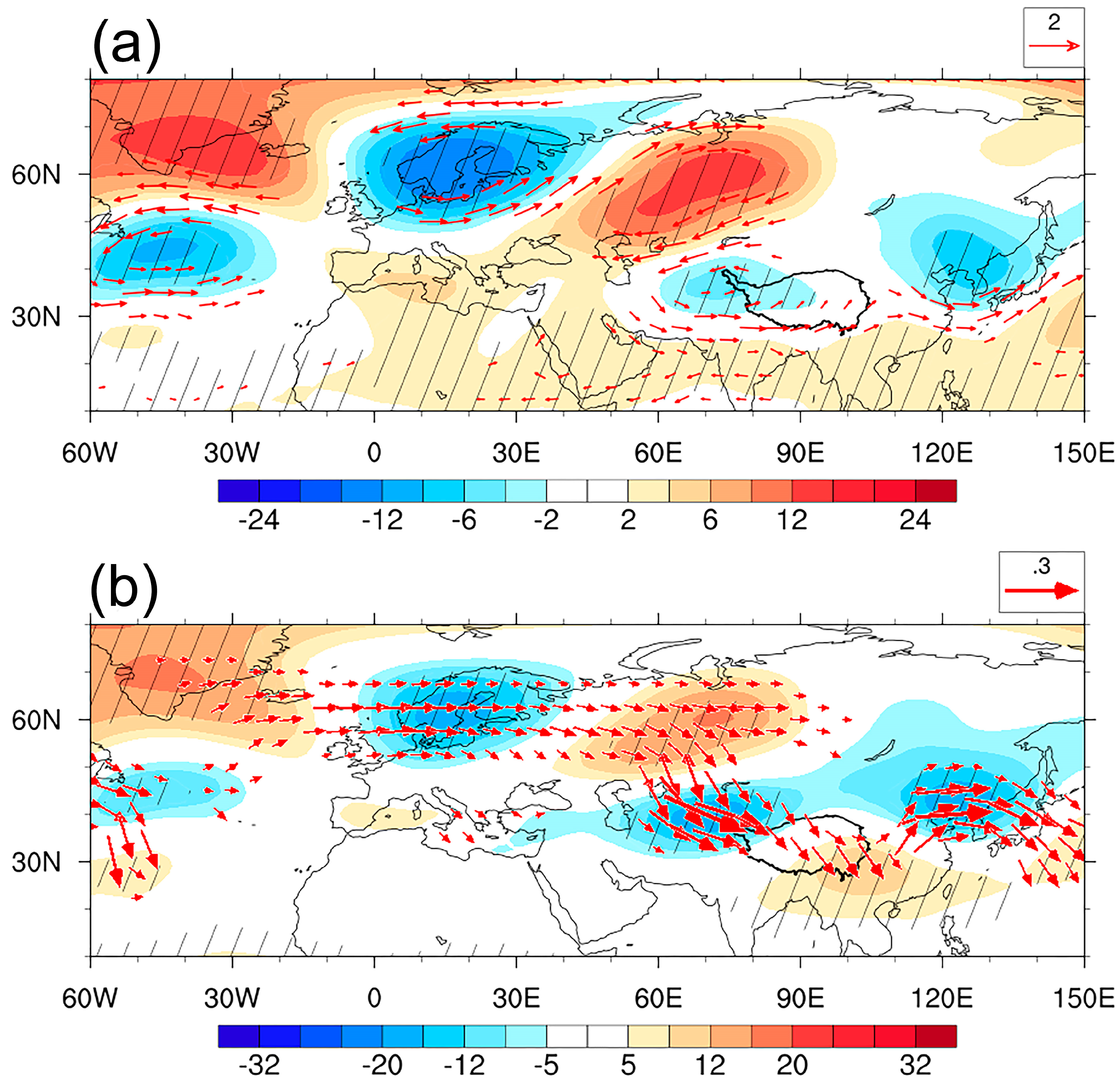
3.2.3. Association between Variations in Summer SH and Atmospheric Wave Trains
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
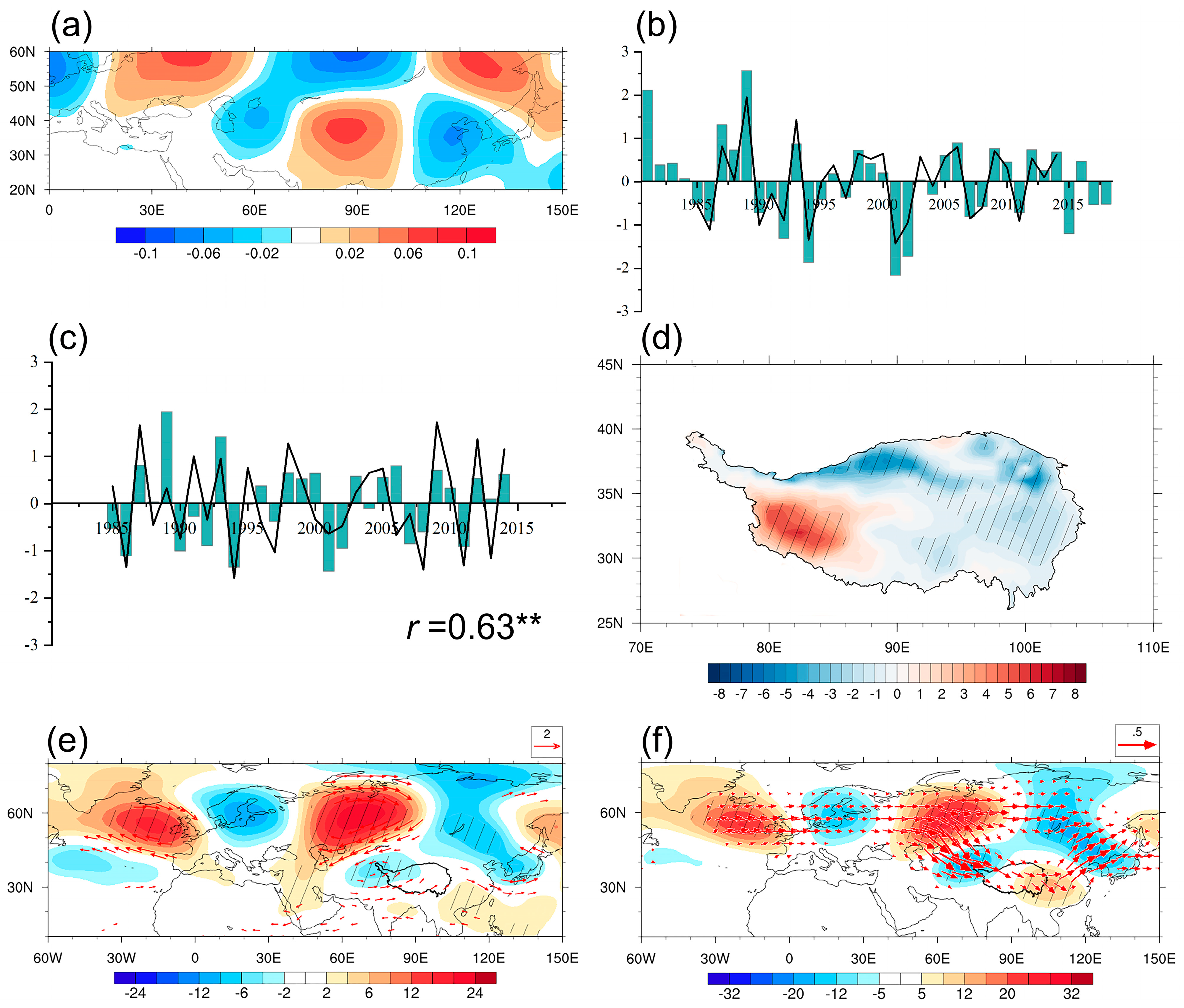
- The large value area in SH and its standard deviation was concentrated in the north and west of the TP. The first leading mode of the TP summer SH during the period 1981–2018 presented a decadal shift from a positive phase to a negative phase after around 1996. The second leading mode was characterized by a zonal dipole pattern with enhanced (weakened) SH anomalies in the western (eastern) TP on the interannual time scale.
- (2)
- The interannual variation of summer SH was dominated by anomalies in DSWR, which was associated with the anomalous cloud cover over the TP. An atmospheric pattern referred to as NAENA induced an anticyclone anomaly to the west of the TP, leading to anomalous water vapor convergence (divergence) and more (less) cloud cover in the eastern (western) TP. Corresponding to the increase (decrease) in cloud cover, DSWR presented anomalous enhancement (reduction) and resulted in a zonal dipole pattern with strengthened (weakened) SH in the western (eastern) TP.
- (3)
- Interdecadal weakening of summer SH was associated with the interdecadal variation of DSWR induced by the enhancement of cloud cover. The decadal change in cloud cover over the TP was mainly due to the variation of water vapor transport as a result of the decadal phase shift of SRP. An anticyclone circulation to the northeast of the TP associated with SRP led to enhanced water vapor supply and convergence of the TP, which resulted in an increase in cloud cover and a reduction in DSWR, contributing to the interdecadal decrease in SH over the TP.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, X.; Lu, C.; Shi, X.; Gao, S. World water tower: An atmospheric perspective. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L20815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Xu, Y.; You, Q.; Flügel, W.A.; Pepin, N.; Yao, T. Review of climate and cryospheric change in the Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 015101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ma, Y.; Su, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ma, W. Quantifying the evaporation amounts of 75 high-elevation large dimictic lakes on the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay8558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhou, T. Asian water tower evinced in total column water vapor: A comparison among multiple satellite and reanalysis data sets. Clim. Dyn. 2020, 54, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cuo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, F.; Liang, L. Characteristics and changes of streamflow on the Tibetan Plateau: A review. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2014, 2, 49–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Zhao, T.; Lu, C.; Guo, Y.; Chen, B.; Liu, R.; Li, Y.; Shi, X. An important mechanism sustaining the atmospheric “water tower” over the Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 11287–11295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yanai, M.; Li, C. Mechanism of heating and the boundary layer over the Tibetan Plateau. Mon. Weather Rev. 1994, 122, 305–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Zhang, Y. Tibetan Plateau forcing and the timing of the monsoon onset over South Asia and the South China Sea. Mon. Weather Rev. 1998, 126, 913–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Duan, A.; Wang, T.; Wan, R.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; et al. The influence of mechanical and thermal forcing by the Tibetan Plateau on Asian climate. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 770–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Zhang, R.; Wen, M.; Liu, L. Effect of the atmospheric heat source on the development and eastward movement of the Tibetan Plateau vortices. Tellus A Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 2014, 66, 24451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yanai, M.; Li, C.; Song, Z. Seasonal heating of the Tibetan Plateau and its effects on the evolution of the Asian summer monsoon. J. Meteorol. Soc. Japan. Ser. II 1992, 70, 319–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, A.; Li, F.; Wang, M.; Wu, G. Persistent weakening trend in the spring sensible heat source over the Tibetan Plateau and its impact on the Asian summer monsoon. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 5671–5682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, D.; Wu, G. The role of the heat source of the Tibetan plateau in the general circulation. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 1998, 67, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.; Liu, X. Relationship between the Tibetan Plateau heating and East Asian summer monsoon rainfall. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 30, 2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Duan, A.; Wu, G. Time-lagged impact of spring sensible heat over the Tibetan Plateau on the summer rainfall anomaly in East China: Case studies using the WRF model. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 42, 2885–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Duan, A.; Shi, Z.; Li, X.; Sun, H.; Liu, X.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, T.; Che, H.; Liu, Y. Modulation of springtime surface sensible heating over the Tibetan Plateau on the interannual variability of East Asian dust cycle. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics. 2020, 20, 11143–11159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, A.; Wu, G. Weakening trend in the atmospheric heat source over the Tibetan Plateau during recent decades. Part I: Observations. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 3149–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, L.; Huang, G.; Fan, G.; Qu, X.; Zhao, G.; Hua, W. Evolution of surface sensible heat over the Tibetan Plateau under the recent global warming hiatus. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2017, 34, 1249–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Chen, D.; Duan, A.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Guo, D.; Wang, H.; Ju, W. Recent recovery of the boreal spring sensible heating over the Tibetan Plateau will continue in CMIP6 future projections. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 124066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, L.; Huang, G.; Fan, G.; Qü, X.; Wang, Z.; Hua, W. Elevation-dependent sensible heat flux trend over the Tibetan Plateau and its possible causes. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 52, 3997–4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Duan, A.; Liu, Y.; Wu, G. Interannual variability of the spring atmospheric heat source over the Tibetan Plateau forced by the North Atlantic SSTA. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 45, 1617–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Wu, G.; He, B.; Li, J.; Bao, Q. Impact of North Atlantic SST and Tibetan Plateau forcing on the seasonal transition of springtime South Asian monsoon circulation. Clim. Dyn. 2021, 56, 559–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Han, C. Regionalization of land surface heat fluxes over the heterogeneous landscape: From the Tibetan Plateau to the Third Pole region. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 5872–5890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yao, Y. The effects of the thermal anomalies over the Tibetan Plateau and its vicinities on climate variability in China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2004, 21, 369–381. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Qian, Z.; Zhang, L. Numerical simulation of formation and development of vortices over the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau in summer. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 1996, 20, 491–502. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, L.; Li, Y.; Hu, H.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, E. Numerical study of the influence of sensible heat anomalies in summer over Qinghai-Xizang Plateau on rainfall in Sichuan-Chongqing regions. Plateau Meteorol. 2013, 32, 1538–1545. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, M.; Hu, Z.; Ding, Z. Assessment of reanalysis flux products based on eddy covariance observations over the Tibetan Plateau. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019, 138, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Ma, Y.; Chen, X.; Su, Z. Trends of land surface heat fluxes on the Tibetan Plateau from 2001 to 2012. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 4757–4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Ma, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhong, L.; Ma, W.; Chen, X.; Su, Z. Long-term variations in actual evapotranspiration over the Tibetan Plateau. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3513–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z. The Surface Energy Balance System (SEBS) for estimation of turbulent heat fluxes. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2002, 6, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaya, K.; Nakamura, H. A formulation of a phase-independent wave-activity flux for stationary and migratory quasigeostrophic eddies on a zonally varying basic flow. J. Atmos. Sci. 2001, 58, 608–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, G.; Bell, T.; Cahalan, R.; Moeng, F.J. Sampling errors in the estimation of empirical orthogonal functions. Mon. Weather Rev. 1982, 110, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wu, R.; Liu, Y. Dominant modes of interannual variability in Eurasian surface air temperature during boreal spring. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 1109–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhao, P.; Chen, J. The interdecadal change of summer water vapor over the Tibetan Plateau and associated mechanisms. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 4103–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, P.; Chen, W.; Liu, Y. Interdecadal variations of the Silk Road pattern. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 9915–9932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lu, R.; Ahn, J.B. Combined effects of the British-Baikal Corridor pattern and the Silk Road pattern on Eurasian surface air temperatures in summer. J. Clim. 2021, 34, 3707–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Ma, W.; Yang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Xie, Z.; Sun, G.; Menenti, M.; Su, B. Impacts of the Silk Road pattern on the interdecadal variations of the atmospheric heat source over the Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Res. 2021, 260, 105696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Ma, W.; Hu, Z.; Ma, Y. Recovery of sensible heating and its elevation amplification over and around the Tibetan Plateau since the 2000s. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2021, 146, 617–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Zhou, T. Skillful prediction of summer rainfall in the Tibetan Plateau on multiyear time scales. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabf9395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Variables | Data Source | Availability | Temporal Resolution | Spatial Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensible heat flux (Reanalysis) | ERA-Interim | 1981–2018 | Daily | 0.5° × 0.5° |
| Sensible heat flux (Remote Sensing) | Han et al. [28,29] | 2001–2018 | Monthly | 0.1° × 0.1° |
| Surface wind speed Total cloud cover Latent heat flux Surface radiation | ERA-Interim | 1981–2018 | Monthly | 0.5° × 0.5° |
| Geopotential height Zonal wind Meridional wind | NCEP/NCAR | 1981–2018 | Monthly | 2.5° × 2.5° |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, W.; Hu, Z.; Ma, W.; Ma, Y.; Han, C.; Han, X.; Yang, Y.; Yu, H.; Fu, C.; Wu, D. Dominant Modes of Tibetan Plateau Summer Surface Sensible Heating and Associated Atmospheric Circulation Anomalies. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 956. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14040956
Fan W, Hu Z, Ma W, Ma Y, Han C, Han X, Yang Y, Yu H, Fu C, Wu D. Dominant Modes of Tibetan Plateau Summer Surface Sensible Heating and Associated Atmospheric Circulation Anomalies. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(4):956. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14040956
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Weiwei, Zeyong Hu, Weiqiang Ma, Yaoming Ma, Cunbo Han, Xiang Han, Yaoxian Yang, Haipeng Yu, Chunwei Fu, and Di Wu. 2022. "Dominant Modes of Tibetan Plateau Summer Surface Sensible Heating and Associated Atmospheric Circulation Anomalies" Remote Sensing 14, no. 4: 956. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14040956
APA StyleFan, W., Hu, Z., Ma, W., Ma, Y., Han, C., Han, X., Yang, Y., Yu, H., Fu, C., & Wu, D. (2022). Dominant Modes of Tibetan Plateau Summer Surface Sensible Heating and Associated Atmospheric Circulation Anomalies. Remote Sensing, 14(4), 956. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14040956








