Mapping Soil Erosion Dynamics (1990–2020) in the Pearl River Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
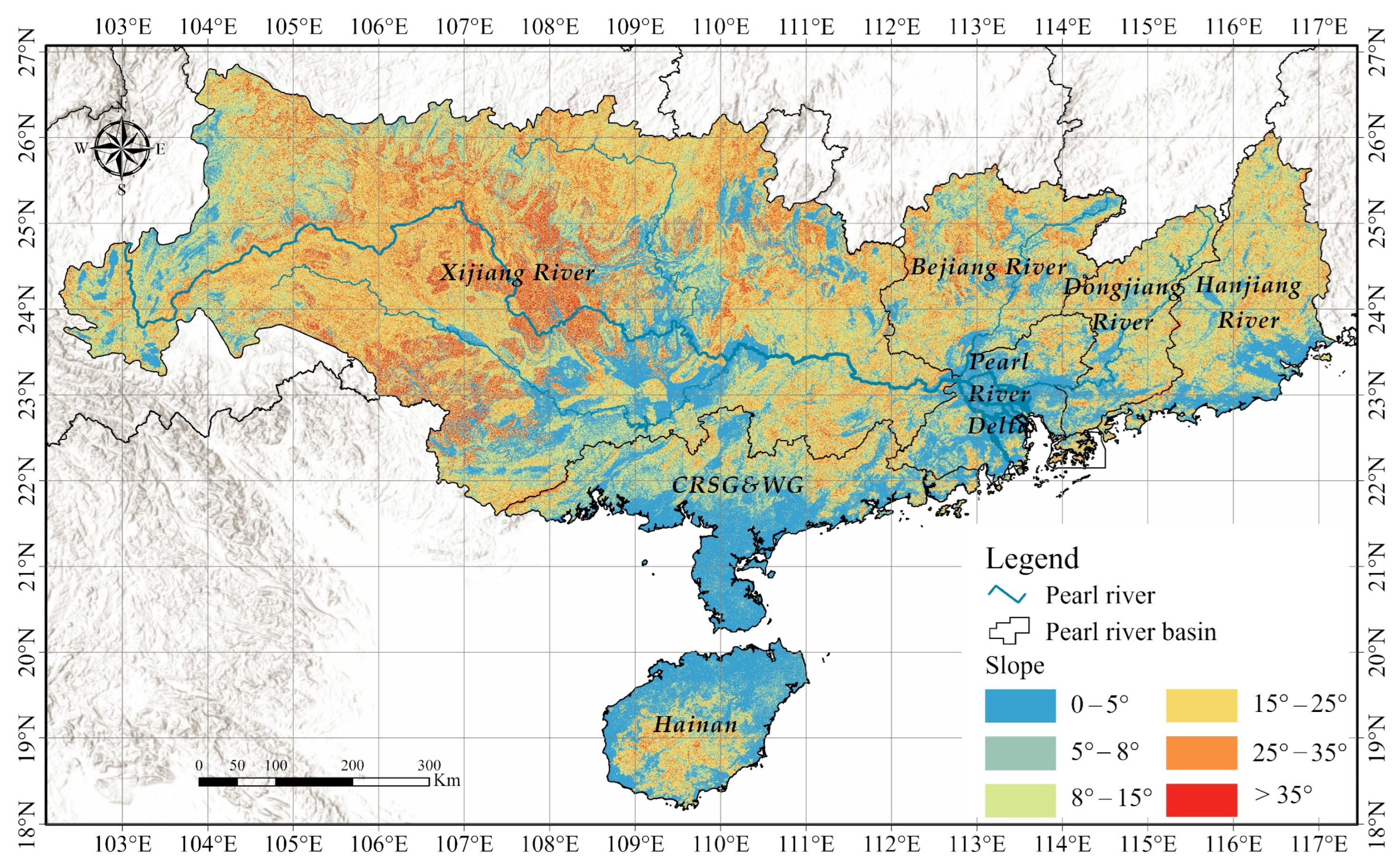
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Dataset
2.3. RUSLE Model
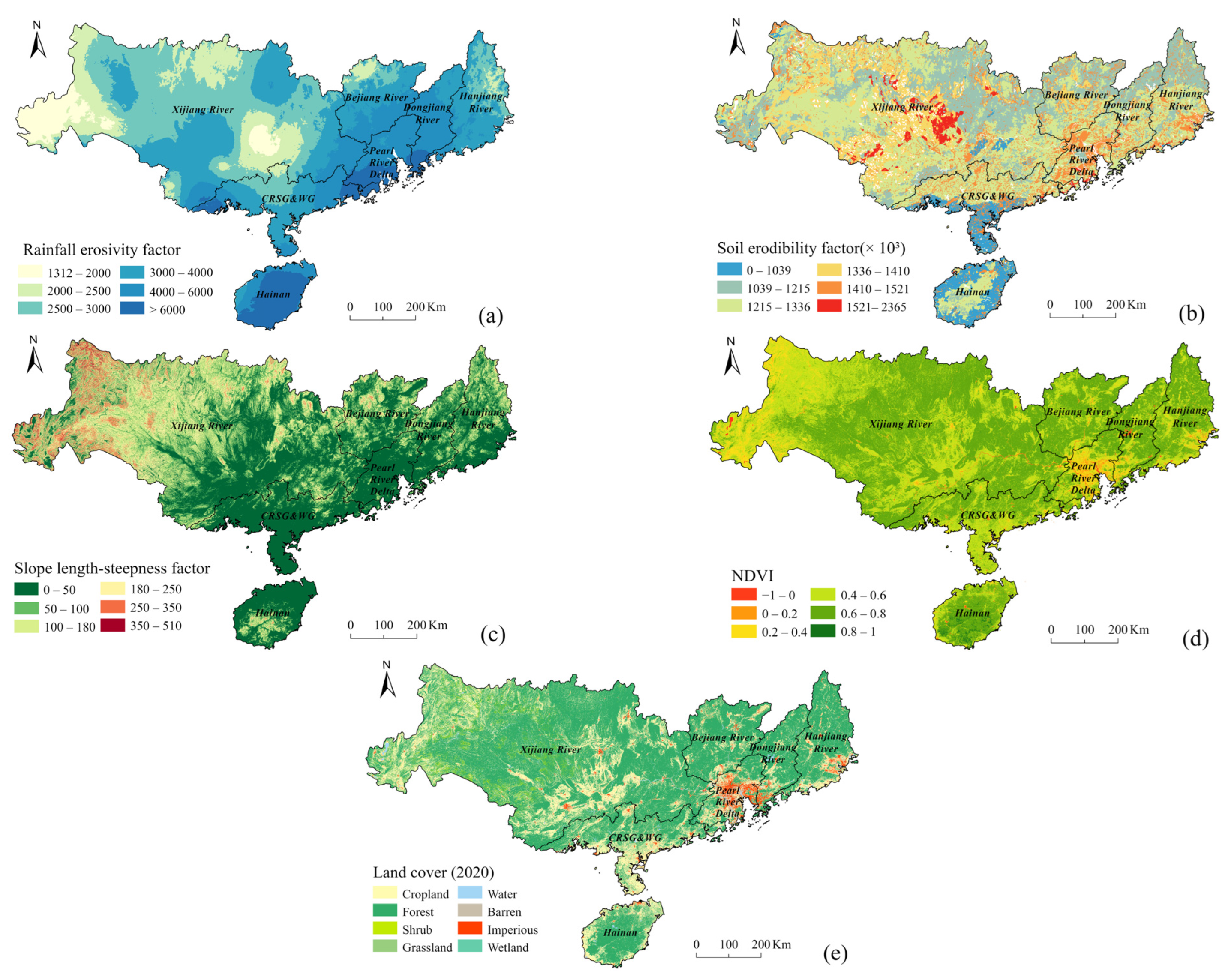
2.3.1. Rainfall Erosivity () Factor
2.3.2. Soil Erodibility () Factor
2.3.3. Slope Length and Steepness () Factor
2.3.4. Cover-Management () Factor
2.3.5. Conservation Practices (P) Factor
3. Results
3.1. Spatial Distribution Pattern of Subfactors
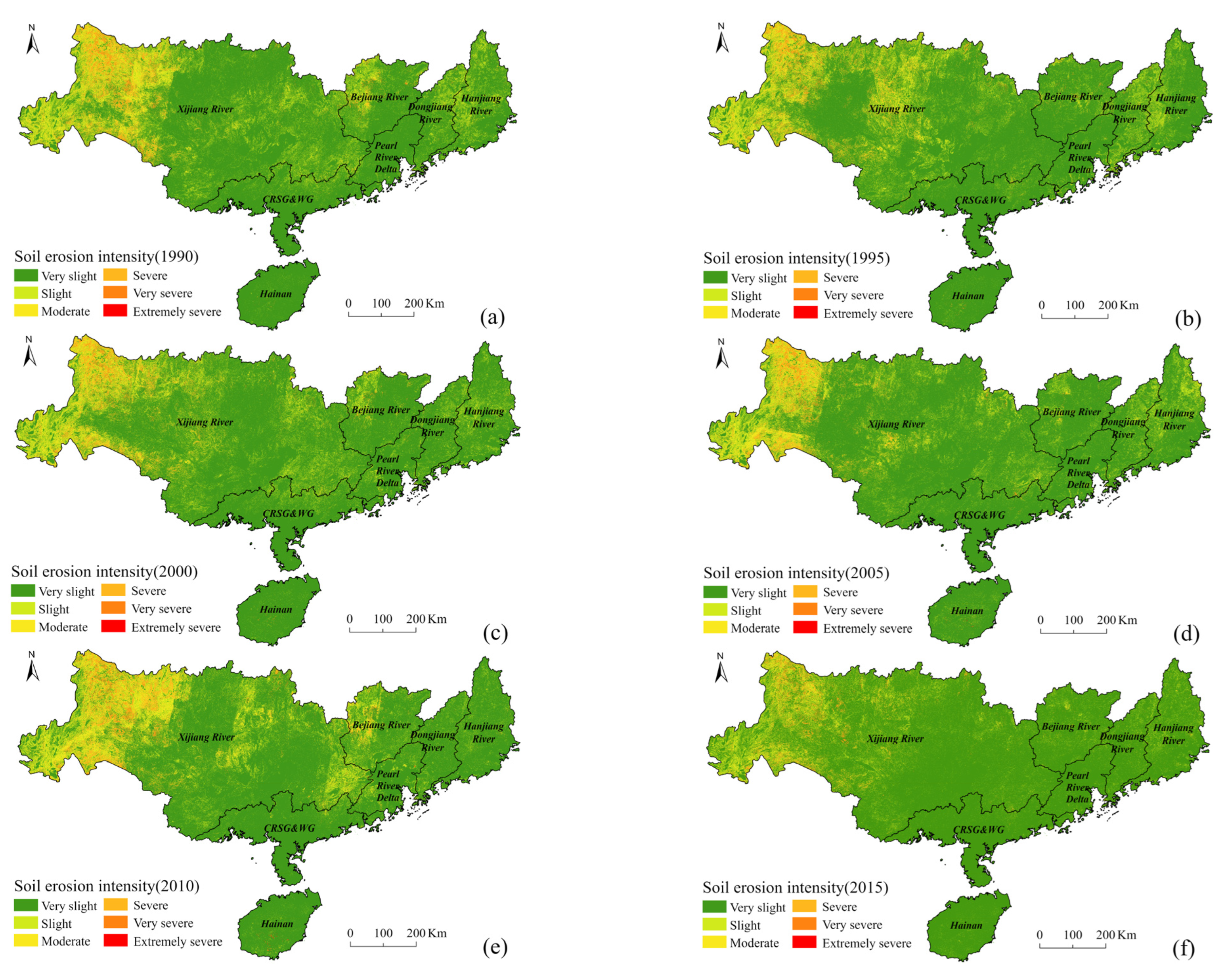
3.2. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Soil Erosion in PRB
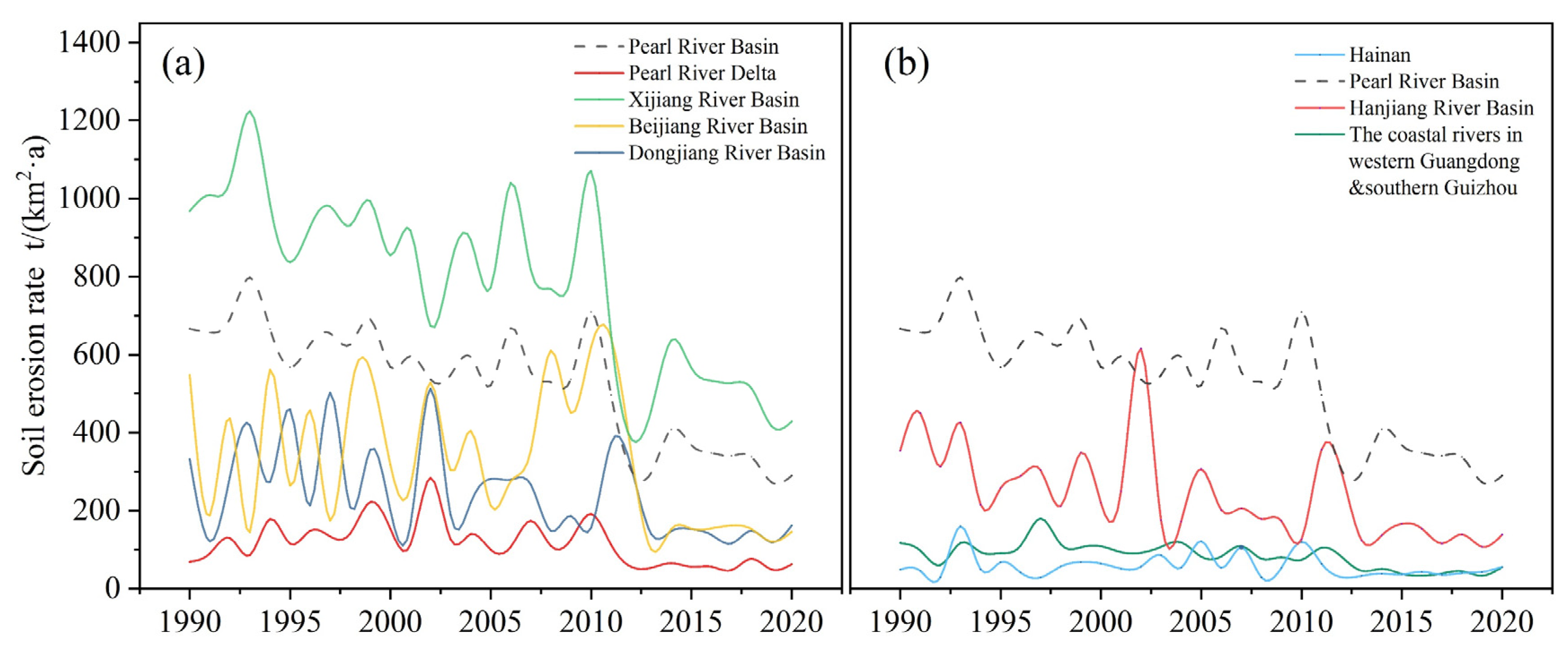
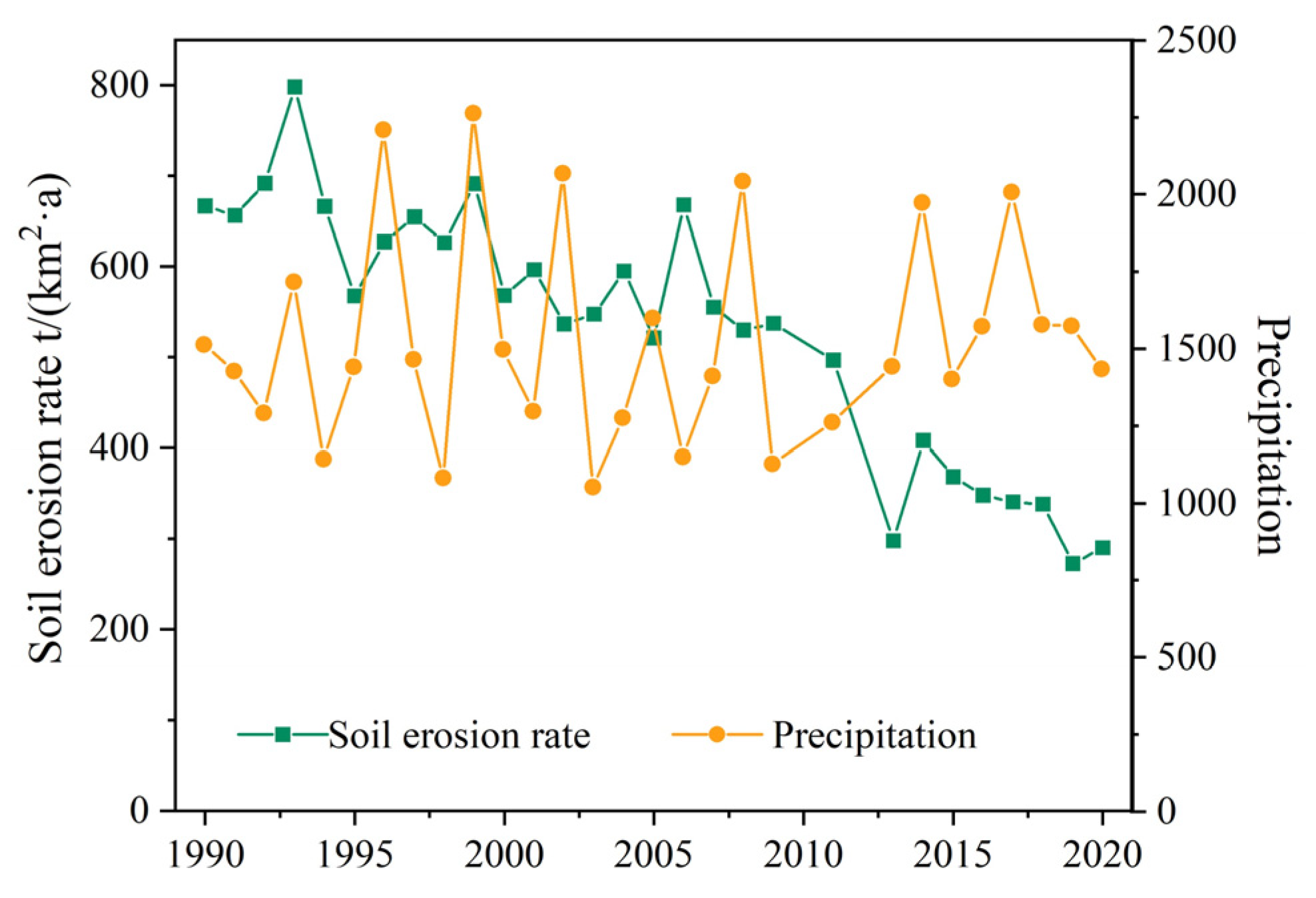
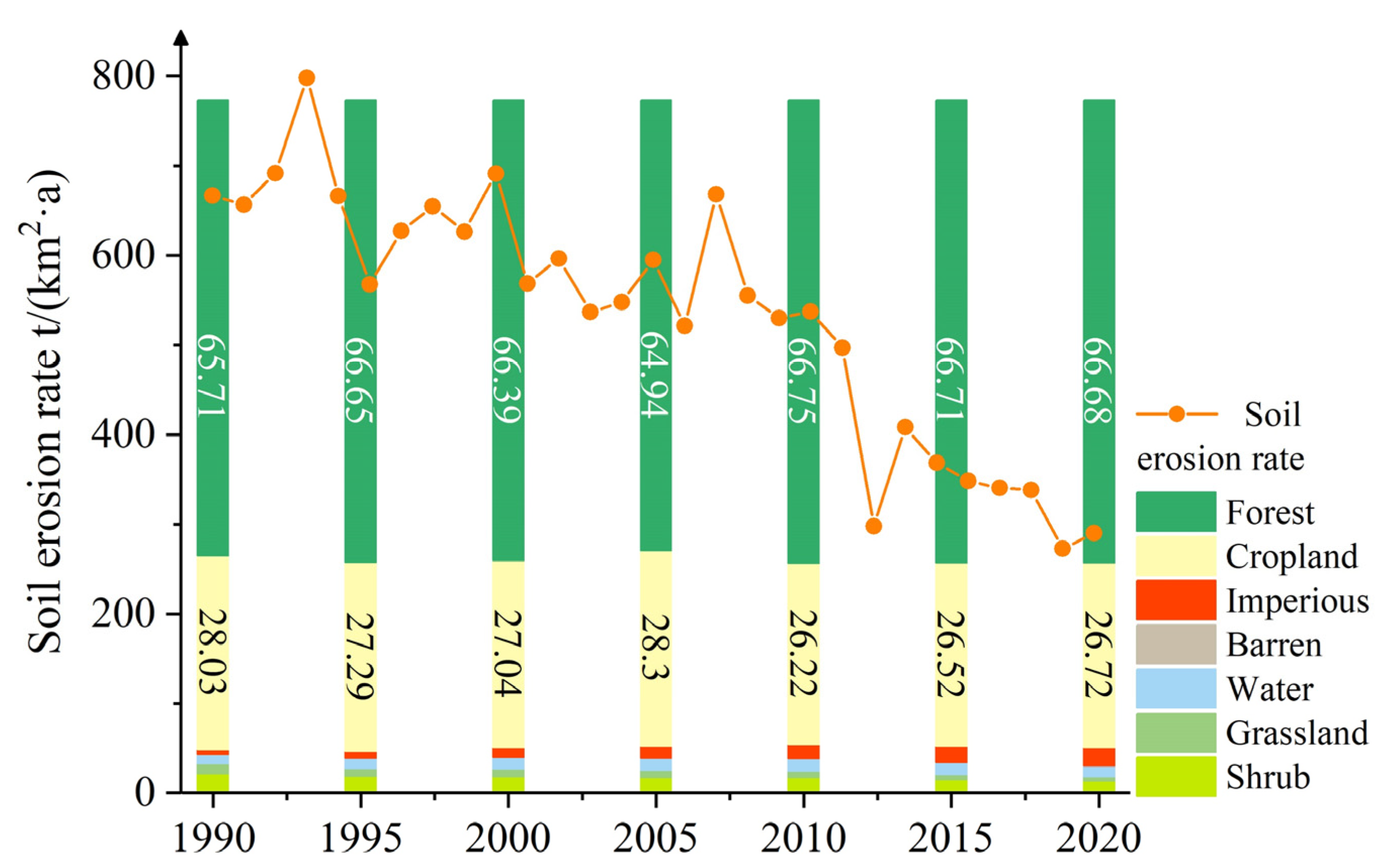
3.3. Temporal Fluctuation in Soil Erosion in the GPRB
3.4. Analysis of Influencing Factors
3.4.1. Precipitation
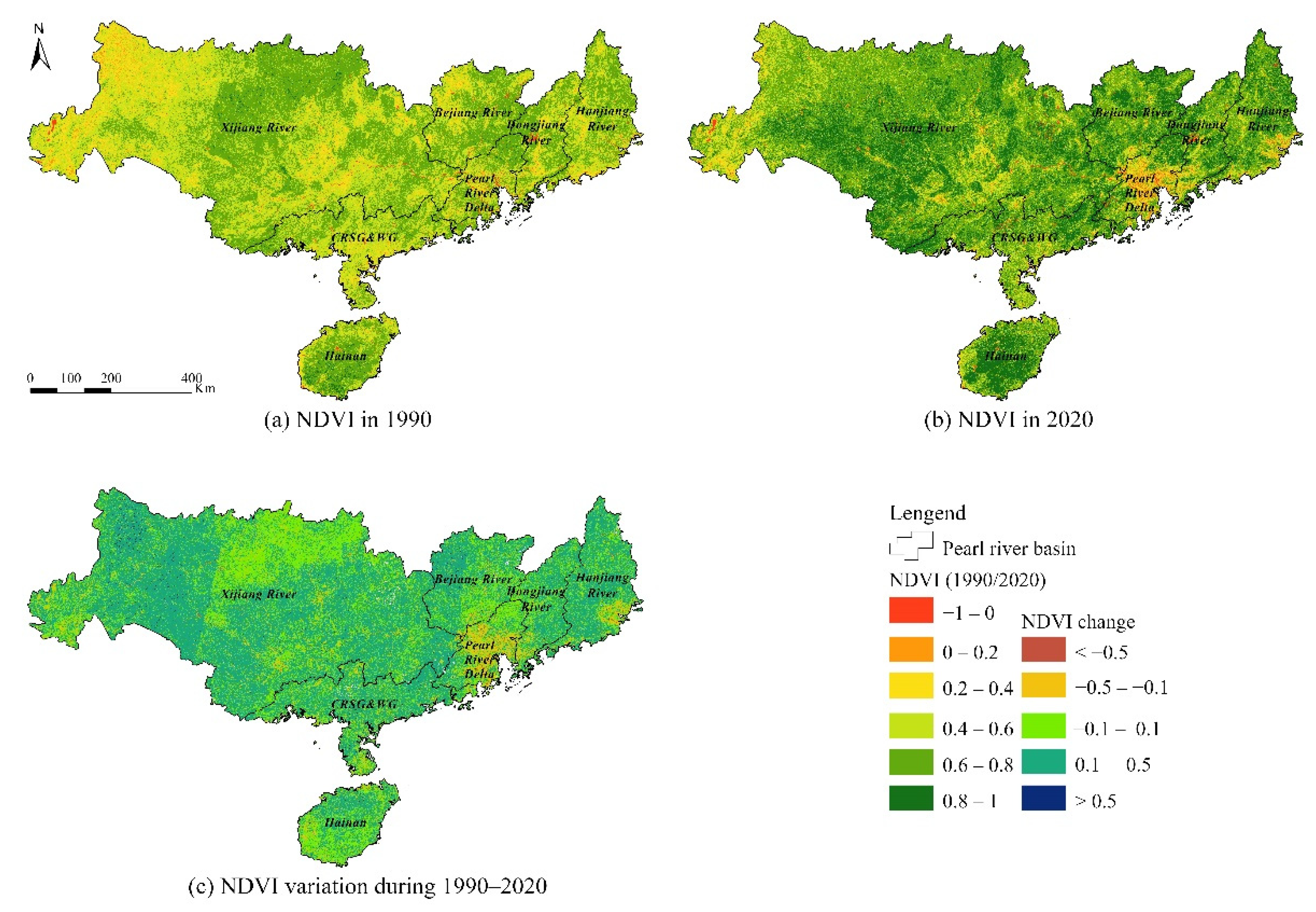
3.4.2. NDVI
3.4.3. Land Cover
4. Discussion
4.1. Satellite Sensor Calibration
4.2. Uncertainty Analysis
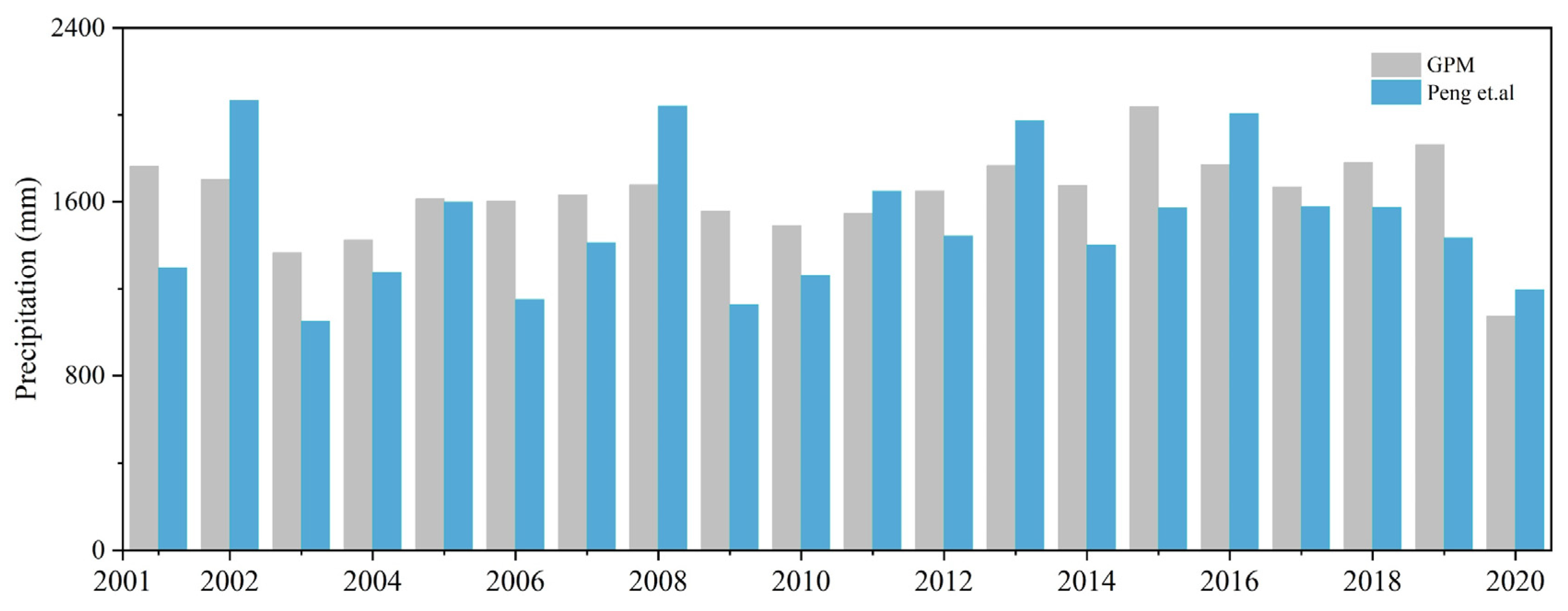
4.3. Comparison with Previous Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marcinkowski, P.; Szporak-Wasilewska, S.; Kardel, I. Assessment of Soil Erosion under Long-Term Projections of Climate Change in Poland. J. Hydrology 2022, 607, 127468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amundson, R.; Berhe, A.A.; Hopmans, J.W.; Olson, C.; Sztein, A.E.; Sparks, D.L. Soil and Human Security in the 21st Century. Science 2015, 348, 1261071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO. Status of the World’s Soil Resources (SWSR)—Main Report; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and Intergovernmental Technical Panel on Soils: Rome, Italy, 2016; 650p. [Google Scholar]
- Wuepper, D.; Borrelli, P.; Finger, R. Countries and the Global Rate of Soil Erosion. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lu, P.; Valente, D.; Petrosillo, I.; Babu, S.; Xu, S.; Li, C.; Huang, D.; Liu, M. Analysis of Soil Erosion Characteristics in Small Watershed of the Loess Tableland Plateau of China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issaka, S.; Ashraf, M.A. Impact of Soil Erosion and Degradation on Water Quality: A Review. Geol. Ecol. Landsc. 2017, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossio, D.; Geheb, K.; Critchley, W. Managing Water by Managing Land: Addressing Land Degradation to Improve Water Productivity and Rural Livelihoods. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, W.E.; Pierce, F.J.; Dowdy, R.H. The Threat of Soil Erosion to Long-Term Crop Production. Science 1983, 219, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zelm, R.; van der Velde, M.; Balkovic, J.; Čengić, M.; Elshout, P.M.F.; Koellner, T.; Núñez, M.; Obersteiner, M.; Schmid, E.; Huijbregts, M.A.J. Spatially Explicit Life Cycle Impact Assessment for Soil Erosion from Global Crop Production. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 30, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Lu, X.X.; Yang, X.; Chen, L.; Lin, L. Sediment Load Responses to Climate Variation and Cascade Reservoirs in the Yangtze River: A Case Study of the Jinsha River. Geomorphology 2018, 322, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, B.; Maskey, S.; Babel, M.S.; van Griensven, A.; Uhlenbrook, S. Sediment Related Impacts of Climate Change and Reservoir Development in the Lower Mekong River Basin: A Case Study of the Nam Ou Basin, Lao PDR. Clim. Chang. 2018, 149, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S. Soil Erosion, Sediment Yield and Sedimentation of Reservoir: A Review. Modeling Earth Syst. Environ. 2016, 2, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Cao, B.; Park, E.; Yang, X.; Zhang, W.; Tarolli, P. Flood Monitoring in Rural Areas of the Pearl River Basin (China) Using Sentinel-1 SAR. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldeman, L.R.; Hakkeling, R.T.A.; Sombroek, W.G. World Map of the Status of Human-Induced Soil Degradation: An Explanatory Note; International Soil Reference and Information Centre: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1990; ISBN 90-6672-042-5. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, M.; Huang, C.; Wang, P.; Zeng, L.; Zhou, Z.; Xiao, W.; Huang, Z.; Liu, C. Impacts of Forest Restoration on Soil Erosion in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, H.; Lal, R. Principles of Soil Conservation and Management; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Volume 167169. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, H.H. A Permanent Loss to New England: Soil Erosion Resulting from the Hurricane. Geogr. Rev. 1939, 29, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beasley, D.B.; Huggins, L.F. Monke, ampEJ ANSWERS: A Model for Watershed Planning. Trans. ASAE 1980, 23, 938–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laflen, J.M.; Lane, L.J.; Foster, G.R. WEPP: A New Generation of Erosion Prediction Technology. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1991, 46, 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.; Rose, C.W.; Ciesiolka, C.A.A.; Coughlan, K.J.; Fentie, B. Toward a Framework for Runoff and Soil Loss Prediction Using GUEST Technology. Soil Res. 1997, 35, 1191–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.P.C.; Quinton, J.N.; Smith, R.E.; Govers, G.; Poesen, J.W.A.; Auerswald, K.; Chisci, G.; Torri, D.; Styczen, M.E. The European Soil Erosion Model (EUROSEM): A Dynamic Approach for Predicting Sediment Transport from Fields and Small Catchments. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. J. Br. Geomorphol. Group 1998, 23, 527–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NALDC.US. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning. Available online: https://naldc.nal.usda.gov/download/CAT79706928/PDF (accessed on 22 November 2022).
- Renard, K.G. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); United States Government Printing: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; ISBN 0-16-048938-5. [Google Scholar]
- Baoyuan, L.; Keli, Z.; Yun, X. An Empirical Soil Loss Equation. In Proceedings of the 12th International Soil Conservation Organization Conference, Beijing, China, 26–31 May 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Borrelli, P.; Robinson, D.A.; Fleischer, L.R.; Lugato, E.; Ballabio, C.; Alewell, C.; Meusburger, K.; Modugno, S.; Schütt, B.; Ferro, V. An Assessment of the Global Impact of 21st Century Land Use Change on Soil Erosion. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Katsoyiannis, A. Soil Erosion Modelling: The New Challenges as the Result of Policy Developments in Europe. Environ. Res. 2019, 172, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olorunfemi, I.E.; Komolafe, A.A.; Fasinmirin, J.T.; Olufayo, A.A.; Akande, S.O. A GIS-Based Assessment of the Potential Soil Erosion and Flood Hazard Zones in Ekiti State, Southwestern Nigeria Using Integrated RUSLE and HAND Models. CATENA 2020, 194, 104725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue-Qing, X.; Xiao-Mei, S.; Xiang-Bin, K.; Jian, P.; Yun-Long, C. Adapting the RUSLE and GIS to Model Soil Erosion Risk in a Mountains Karst Watershed, Guizhou Province, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 141, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Fu, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Wang, S. Vulnerability Assessment of the Global Water Erosion Tendency: Vegetation Greening Can Partly Offset Increasing Rainfall Stress. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naipal, V.; Reick, C.; Pongratz, J.; Van Oost, K. Improving the Global Applicability of the RUSLE Model–Adjustment of the Topographical and Rainfall Erosivity Factors. Geosci. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 2893–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostovari, Y.; Ghorbani-Dashtaki, S.; Bahrami, H.-A.; Naderi, M.; Dematte, J.A.M. Soil Loss Estimation Using RUSLE Model, GIS and Remote Sensing Techniques: A Case Study from the Dembecha Watershed, Northwestern Ethiopia. Geoderma Reg. 2017, 11, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, K.; Qiu, J.; Cai, S.; Zhang, W.; Mu, X.; Park, E.; Yang, X. Use of a MODIS Satellite-Based Aridity Index to Monitor Drought Conditions in the Pearl River Basin from 2001 to 2021. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F. The stressed area to harness and the basic coutermeasures to soil and water loss in the Zhujiang watershed. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 1990, 3, 25–29. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luk, S.H.; Yao, Q.Y.; Gao, J.Q.; Zhang, J.Q.; He, Y.G.; Huang, S.M. Environmental Analysis of Soil Erosion in Guangdong Province: A Deqing Case Study. CATENA 1997, 29, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Chen, H.; Polyakov, V.O.; Wang, K.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W. Soil Erosion Rates in Two Karst Peak-Cluster Depression Basins of Northwest Guangxi, China: Comparison of the RUSLE Model with 137Cs Measurements. Geomorphology 2016, 253, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Lu, Y.; Liu, B.; Xu, G. Estimation and Characteristics Analysis of Soil Erosion in Xijiang River Basin of Guangxi. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 25, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Cao, w.; He, T.; Wu, D.; Jiang, H. Analysis on spatial-temporal variation of soil loss and its driving factors in North-south Pan River watershed. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2019, 17, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, Q.; Liu, B.; Huang, C.; Wang, C.; Pang, G. Assessment of soil erosion intensity in Pearl River Basin based on CSLE model. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 19, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, C.B.; Barros, V.R.; Mastrandrea, M.D.; Mach, K.J.; Abdrabo, M.-K.; Adger, N.; Anokhin, Y.A.; Anisimov, O.A.; Arent, D.J.; Barnett, J. Summary for Policymakers. In Climate change 2014: Impacts, adaptation, and vulnerability. Part A: Global and sectoral aspects. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 1–32. ISBN 1-107-64165-9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Cheng, Z.; Qiu, J.; Park, E.; Ran, L.; Xie, X.; Yang, X. Spatiotemporal Changes in Mulberry-Dyke-Fish Ponds in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area over the Past 40 Years. Water 2021, 13, 2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, W.; Xie, X.; Lu, X.; Yang, X.; Li, H. Retrieval of Suspended Sediment Concentrations in the Pearl River Estuary Using Multi-Source Satellite Imagery. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Yang, X.; Cao, B.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y. Effects of Urbanization on Regional Extreme-Temperature Changes in China, 1960–2016. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Ding, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, Z. 1 Km Monthly Temperature and Precipitation Dataset for China from 1901 to 2017. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 1931–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RESDC.CN.A China Data Set of Soil Properties for Land Surface Modeling. Available online: https://www.resdc.cn/data.aspx?DATAID=260 (accessed on 22 November 2022).
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. 30 m Annual Land Cover and Its Dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data Discuss. 2021, 2021, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NTPC.CN. Peng 1-Km Monthly Precipitation Dataset for China (1901–2020). Available online: https://www.tpdc.ac.cn/zh-hans/data/faae7605-a0f2-4d18-b28f-5cee413766a2/?q=%E4%B8%AD%E5%9B%BD1km (accessed on 22 November 2022).
- Wu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, W. Comparison of Different Methods for Estimating Average Annual Rainfall Erosivity. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2001, 3, 31–34. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Fu, J. Rainfall erosivity estimation under different rainfall amount. Resour. Sci. 2003, 1, 35–41. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Meyer, L.D. Soil Erodibility on Construction Areas. Soil Erosion: Causes, Mechanisms, Prevention and Control. US Highw. Res. Board Spec. Rep. 1973, 135, 20–29. [Google Scholar]
- EPIC: The Erosion-Productivity Impact Calculator. Available online: http://agrilife.org/epicapex/files/2015/05/EpicModelDocumentation.pdf (accessed on 22 November 2022).
- Shirazi, M.A.; Boersma, L. A Unifying Quantitative Analysis of Soil Texture. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1984, 48, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Peng, W.; Yang, H. Soil erodibility and its estimation for agricultural soil in china. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2007, 6, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.Y.; Nearing, M.A.; Risse, L.M. Slope Gradient Effects on Soil Loss for Steep Slopes. Trans. ASAE 1994, 37, 1835–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmet, P.J.J.; Govers, G. A GIS Procedure for Automatically Calculating the USLE LS Factor on Topographically Complex Landscape Units. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1996, 51, 427–433. [Google Scholar]
- McCool, D.K.; Brown, L.C.; Foster, G.R.; Mutchler, C.K.; Meyer, L.D. Revised Slope Steepness Factor for the Universal Soil Loss Equation. Trans. ASAE 1987, 30, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutman, G.; Ignatov, A. The Derivation of the Green Vegetation Fraction from NOAA/AVHRR Data for Use in Numerical Weather Prediction Models. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 1533–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Ding, S.; Shi, Z.; Huang, L.; Zhang, G. Study of Applying USLE and Geographical Information System IDRISI to Predict Soil Erosion in Small Watershed. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2000, 2, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wu, B.; Yan, C.; Zhou, W. Estimation of Vegetation Fraction in the Upper Basin of Miyun Reservoir by Remote Sensing. Resour. Sci. 2004, 4, 153–159. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, R.; Xiong, M.; Yang, G. Estimation of soil erosion based on the RUSLE model in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 3473–3485. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Wu, X.; Yu, H. Spatial and temporal variations of rainfall erosivity on Pearl River basin during 1960–2012. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, X.; Zhao, S.; Wu, X.; Bai, W. Spatio-Temporal Variation in Rainfall Erosivity during 1960–2012 in the Pearl River Basin, China. CATENA 2016, 137, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MEE.CN, Standards for Classification and Gradation of Soil Erosion. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/stzl/202106/W020210910459257234201.pdf (accessed on 22 November 2022).
- Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C. Effects of Land Use Changes on Soil Erosion in a Fast Developing Area. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 11, 1549–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NDRC.CN. Pearl River Basin Flood Protection Plan. Available online: https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/fggz/fzzlgh/gjjzxgh/200804/P020191104623802066146.pdf (accessed on 22 November 2022).
- MWR.CN. Pearl River Basin Soil and Water Conservation Bulletin. Available online: http://www.pearlwater.gov.cn/zwgkcs/lygb/stbc/202109/P020210914335796341337.pdf (accessed on 22 November 2022).
- Roy, D.P.; Kovalskyy, V.; Zhang, H.K.; Vermote, E.F.; Yan, L.; Kumar, S.S.; Egorov, A. Characterization of Landsat-7 to Landsat-8 Reflective Wavelength and Normalized Difference Vegetation Index Continuity. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Datasets | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution | Data Source | Explanation/Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRTM DEM | 30 m | N/A | USGS | Calculation of the slope length and steepness factor in RUSLE |
| 1 km monthly precipitation dataset for China | 1 km | Monthly | TPDC [46] | Calculation of the rainfall erosivity factor in RUSLE |
| Soil properties | 1 km | N/A | RESDC (soil texture data) TPDC (soil organic data) | Calculation of the soil erodibility factor in RUSLE |
| Land Cover data | 30 m | Yearly | Yang J. et al. [45] | Calculation of the conservation practices factor in RUSLE |
| Land Cover Type | 1990 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cropland | 28.03 | 27.29 | 27.04 | 28.30 | 26.22 | 26.52 | 26.72 |
| Forest | 65.71 | 66.65 | 66.39 | 64.94 | 66.75 | 66.71 | 66.68 |
| Shrub | 2.80 | 2.45 | 2.40 | 2.28 | 2.24 | 1.97 | 1.78 |
| Grassland | 1.42 | 1.09 | 1.10 | 1.06 | 0.94 | 0.73 | 0.63 |
| Water | 1.36 | 1.51 | 1.67 | 1.71 | 1.79 | 1.72 | 1.54 |
| Barren | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Impervious | 0.67 | 0.99 | 1.40 | 1.71 | 2.06 | 2.35 | 2.64 |
| Wetland | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Dataset | Dataset Provider | Temporal Domain | Spatial Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|
| TerraClimate | University of California Merced | Monthly (1958–2021) | 0.5° (lat-lon) |
| APHRODITE | Yatagai; Hamada | Daily (1951–2007) | 0.5° (lat-lon) |
| TRMM 3B43 | NASA GES DISC at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center | Monthly (1998–2019) | 0.25° (lat-lon) |
| PERSIANN-CDR | NOAA NCDC | Daily (1983–present) | 0.25° (lat-lon) |
| ERA5 | Climate Data Store | 1 hourly (1981–present) | 0.1° (lat-lon) |
| GPM V6 | NASA GES DISC at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center | 3 hourly (2000–present) | 0.1° (lat-lon) |
| 1-km monthly precipitation dataset for China | Peng et al. | Monthly (1901–2020) | 0.00833° (~1 km) |
| Global precipitation station data | NOAA | 1 hourly (1942–present) | N/A |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mu, X.; Qiu, J.; Cao, B.; Cai, S.; Niu, K.; Yang, X. Mapping Soil Erosion Dynamics (1990–2020) in the Pearl River Basin. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5949. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14235949
Mu X, Qiu J, Cao B, Cai S, Niu K, Yang X. Mapping Soil Erosion Dynamics (1990–2020) in the Pearl River Basin. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(23):5949. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14235949
Chicago/Turabian StyleMu, Xiaolin, Junliang Qiu, Bowen Cao, Shirong Cai, Kunlong Niu, and Xiankun Yang. 2022. "Mapping Soil Erosion Dynamics (1990–2020) in the Pearl River Basin" Remote Sensing 14, no. 23: 5949. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14235949
APA StyleMu, X., Qiu, J., Cao, B., Cai, S., Niu, K., & Yang, X. (2022). Mapping Soil Erosion Dynamics (1990–2020) in the Pearl River Basin. Remote Sensing, 14(23), 5949. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14235949







