Empirical Examinations of Whether Rural Population Decline Improves the Rural Eco-Environmental Quality in a Chinese Context
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
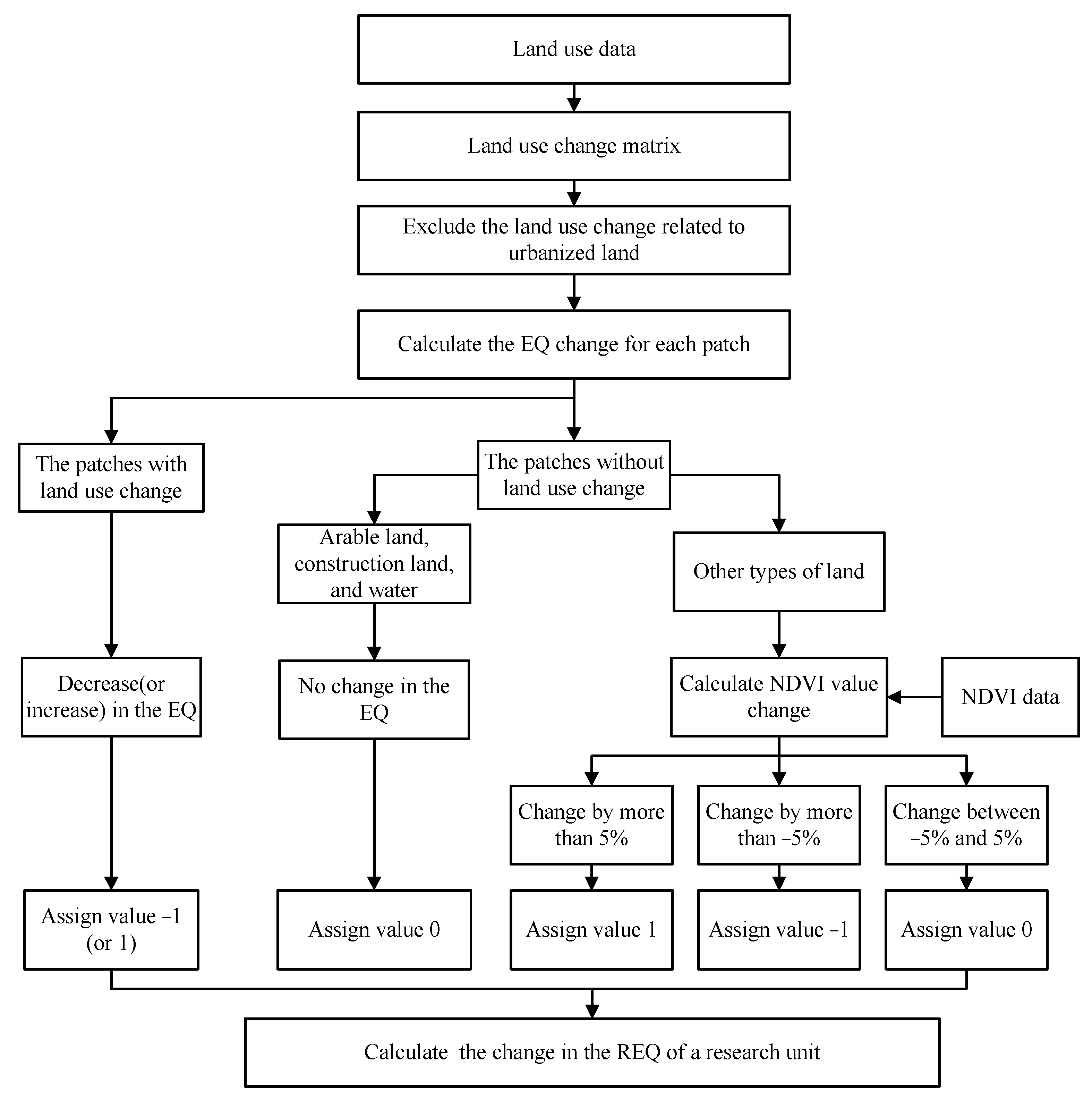
2.1. The Measurement of Change in Rural Environmental Quality
2.1.1. The EQI Method
2.1.2. A Revised EQI Method
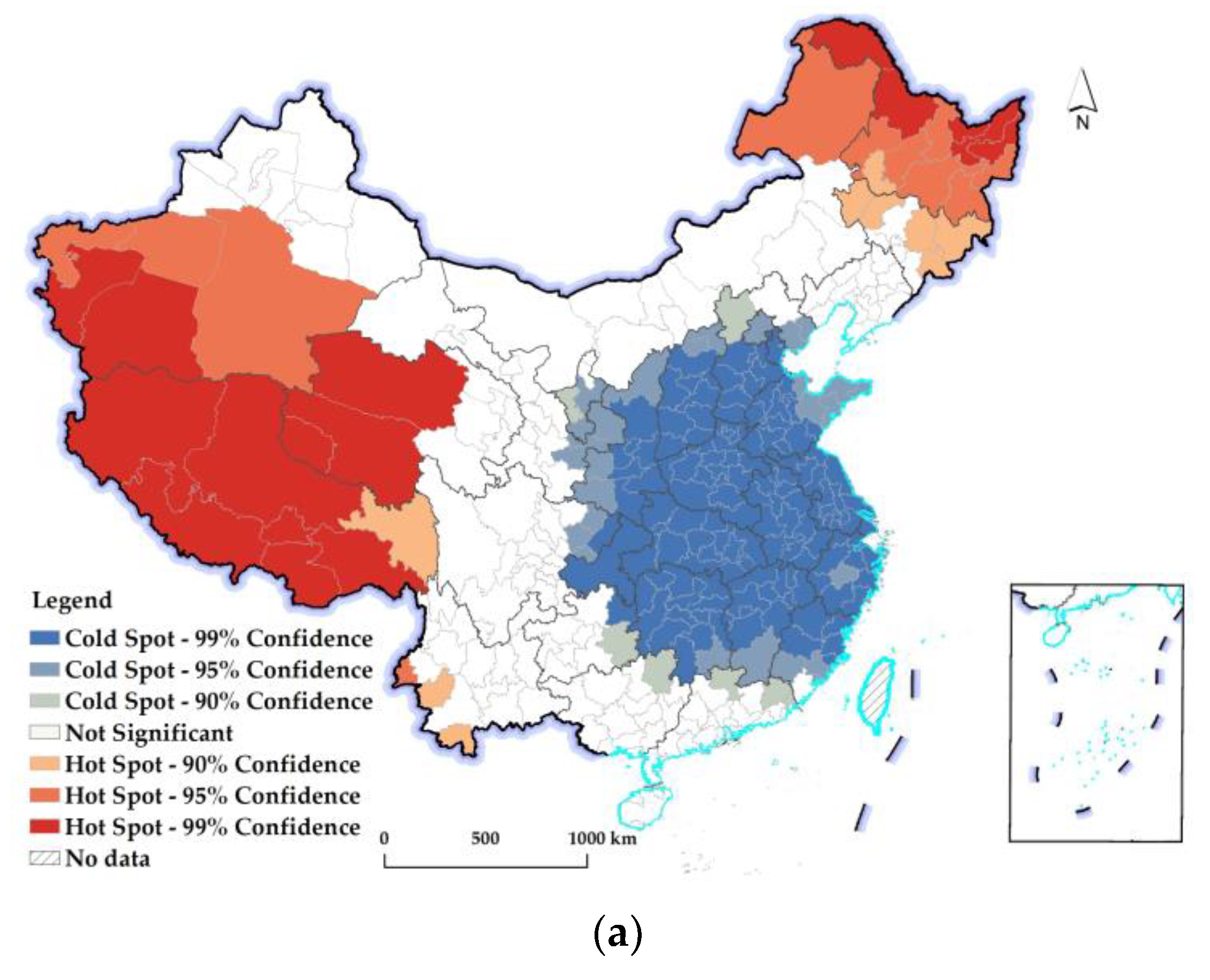
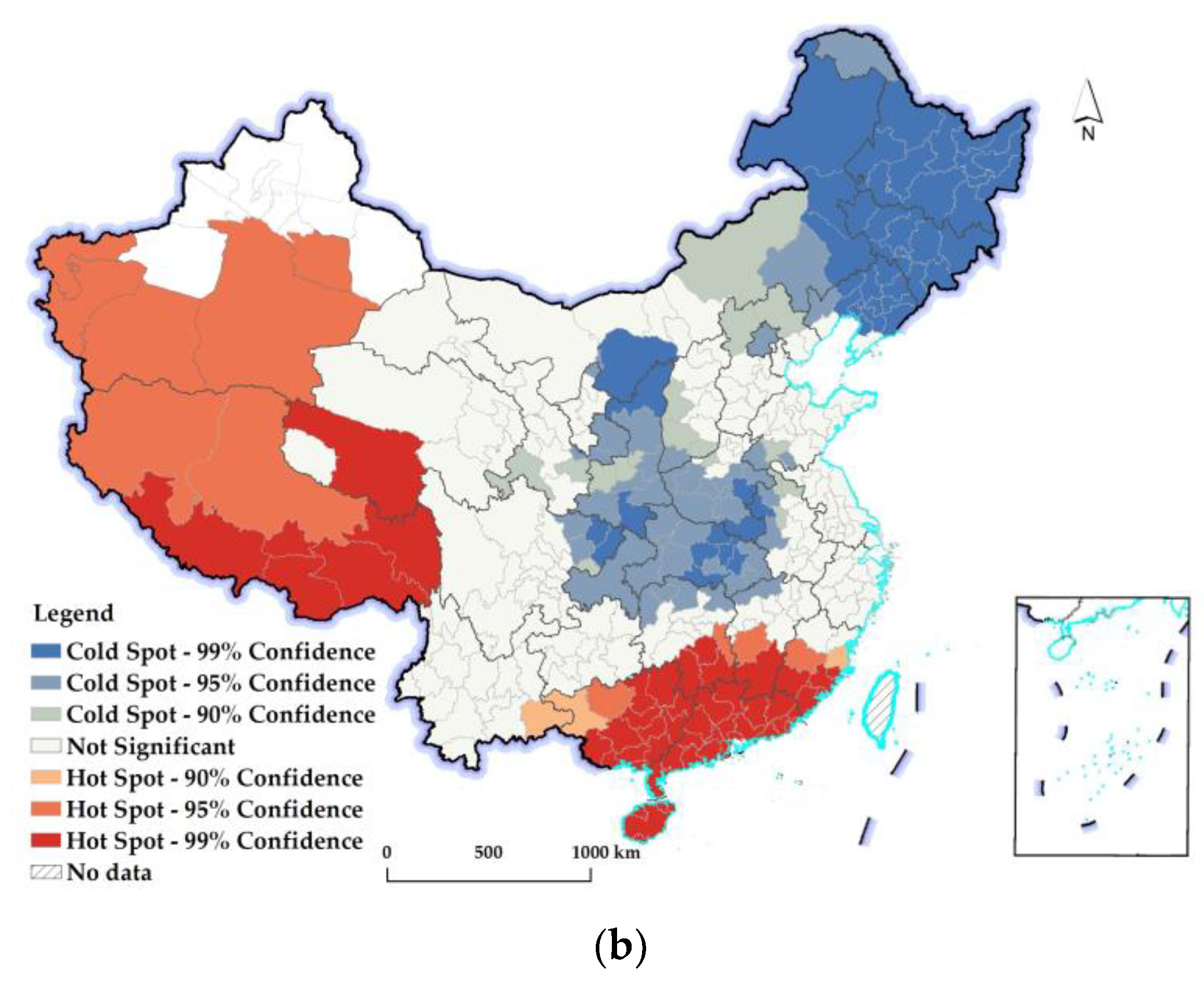
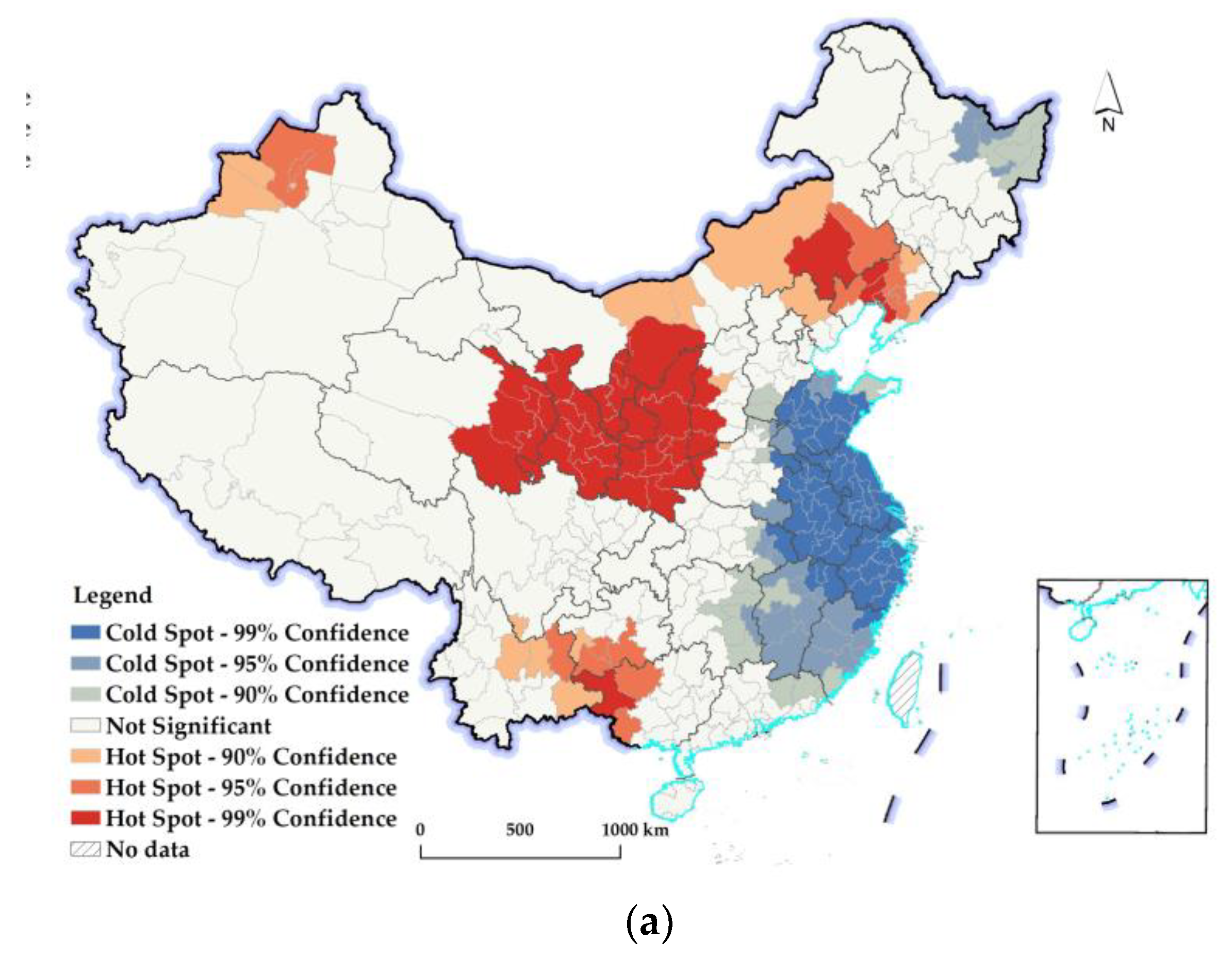
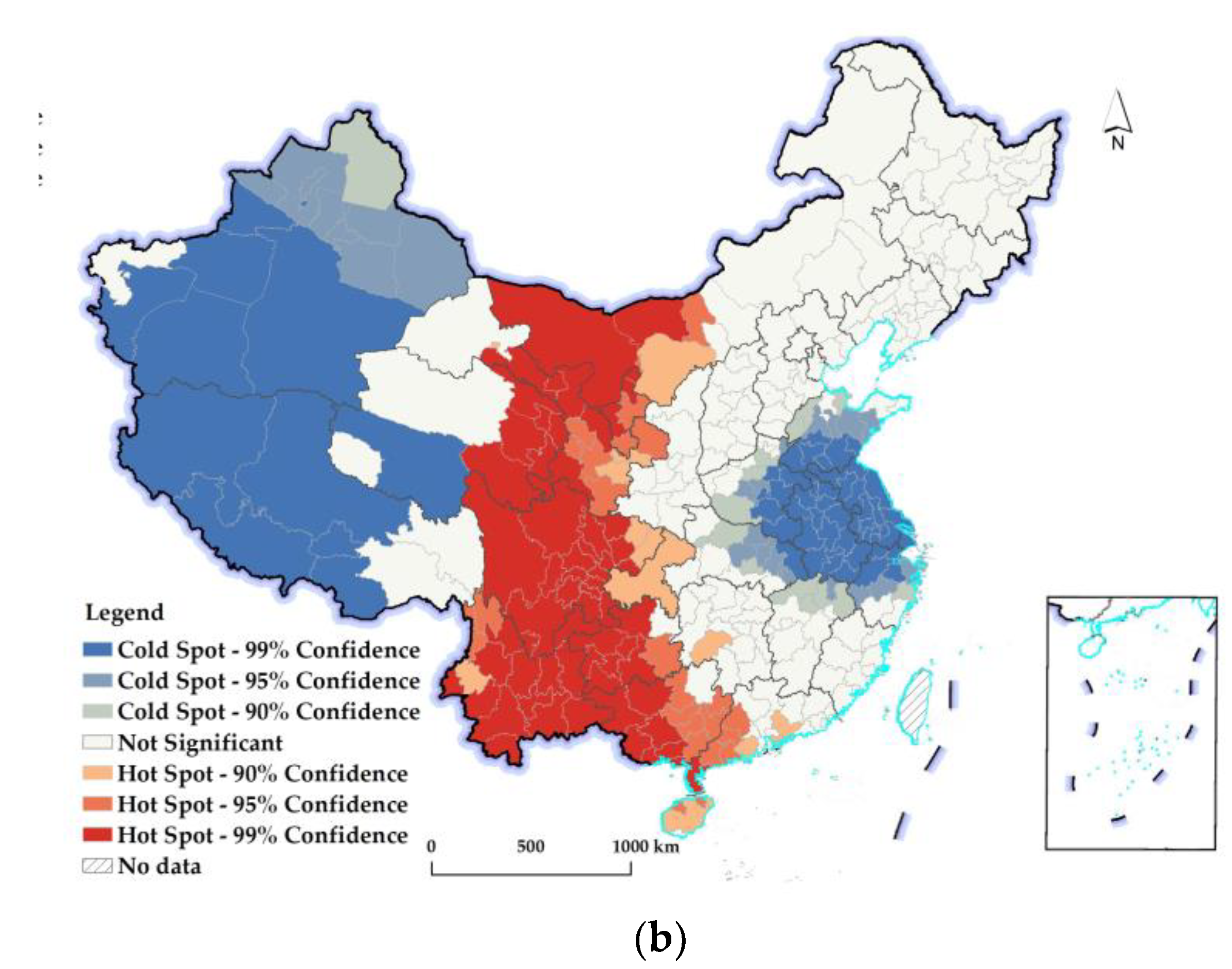
2.2. Hot–Cold-Spot Analysis
2.3. Empirical Models and Variables
2.4. Data Sources and Processing
3. Results
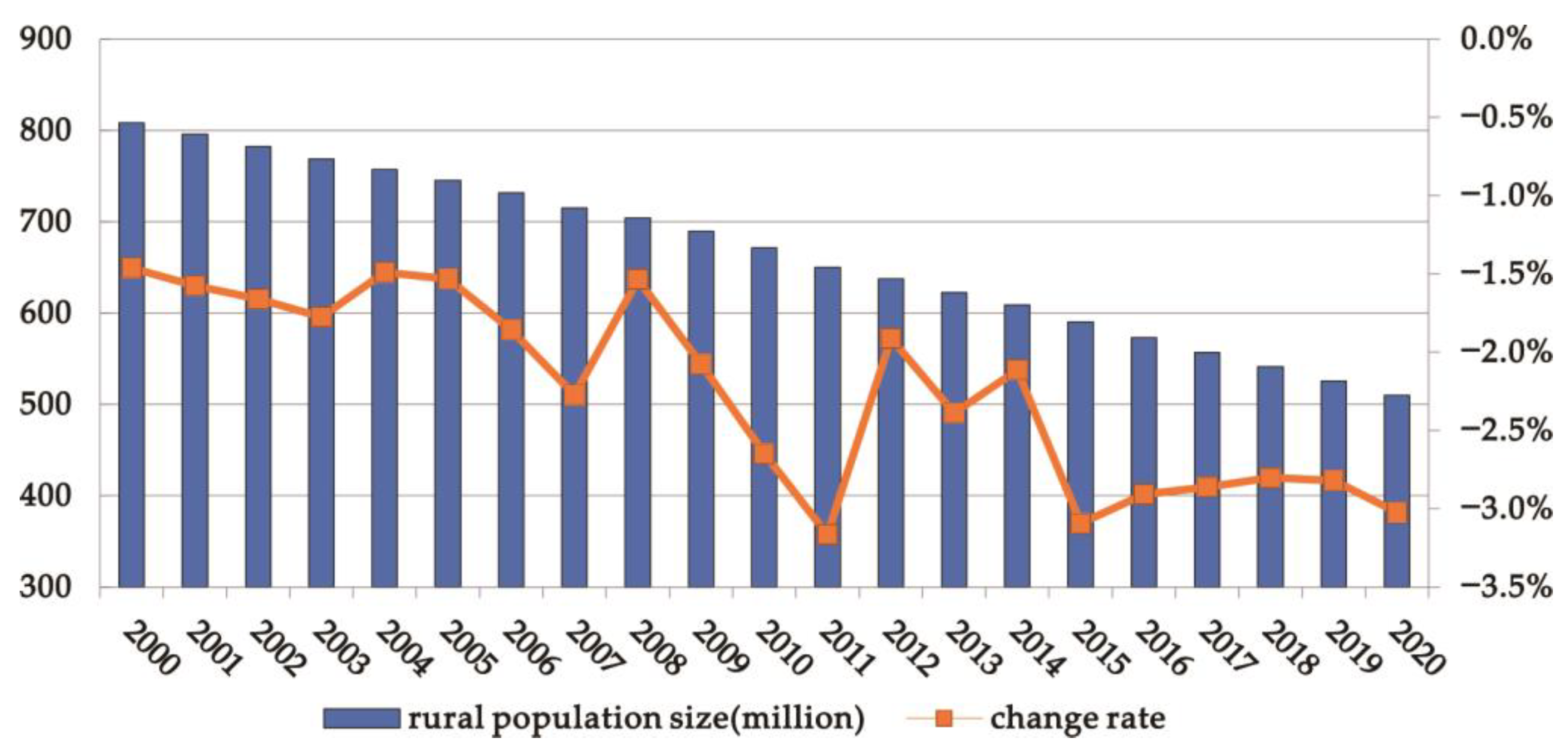
3.1. Rural Population Decline in China from 2000 to 2020
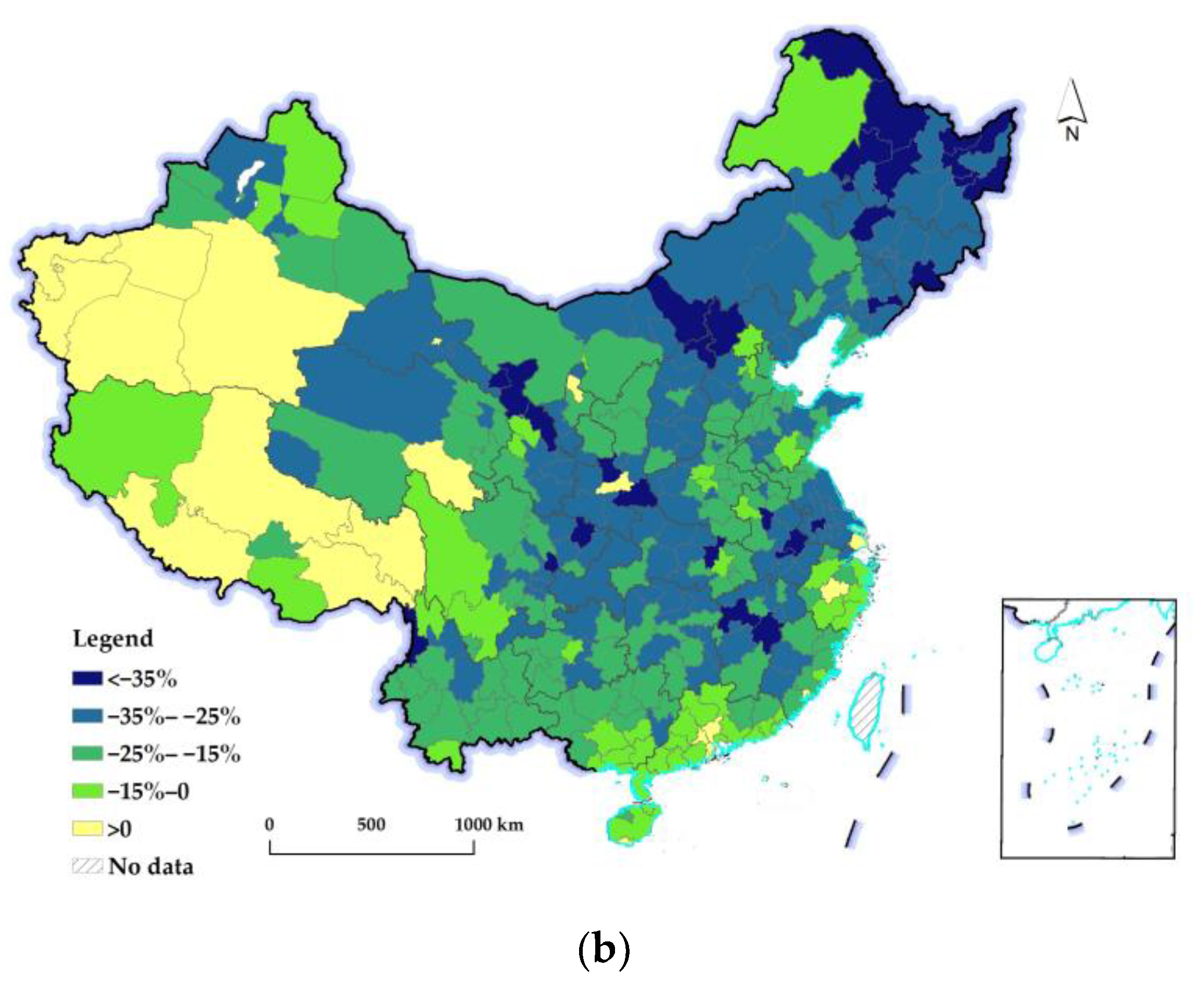
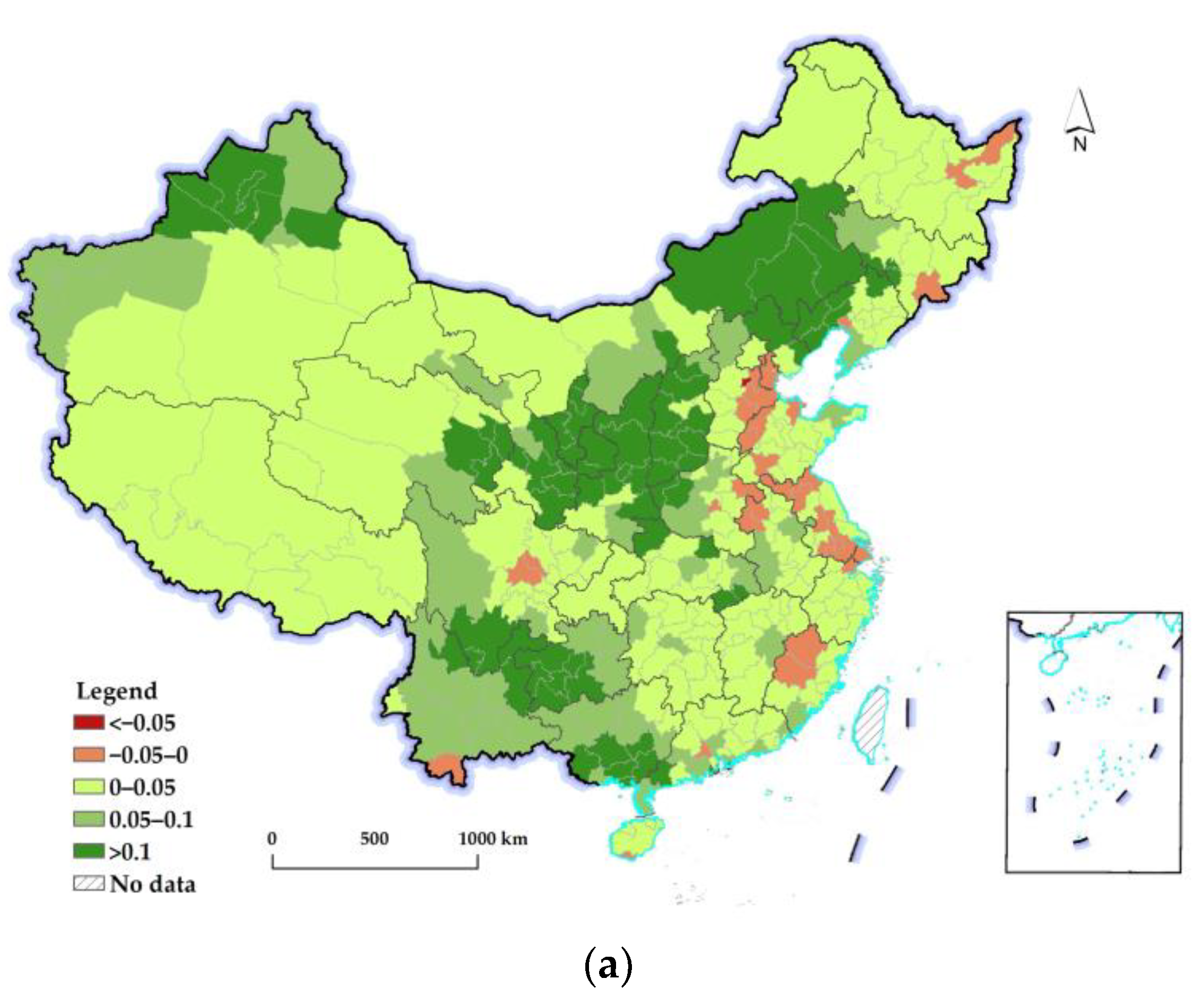
3.2. Spatiotemporal Differences of Changes in the REQ
3.2.1. An Overall Picture of the Change in the REQ at the National Level
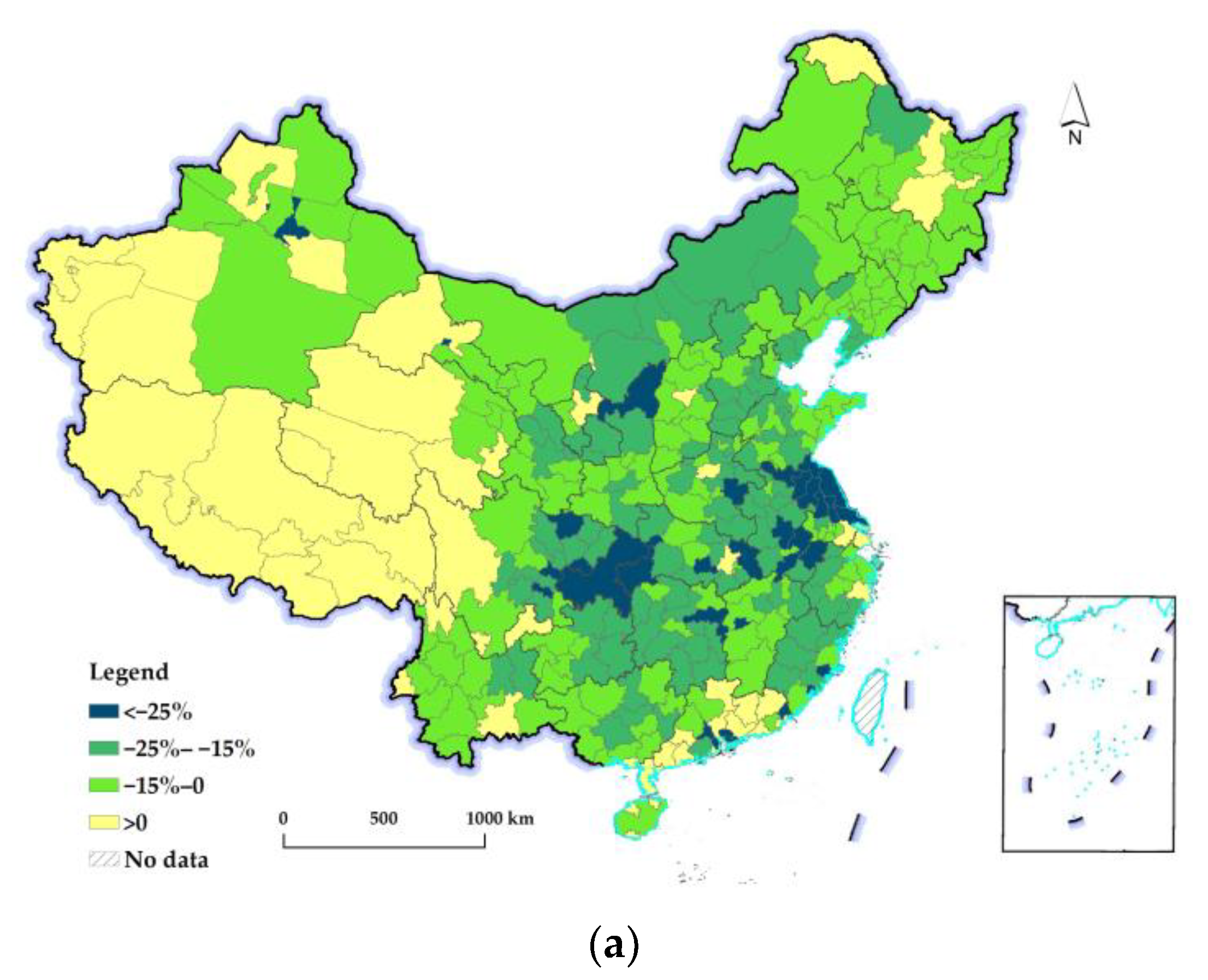
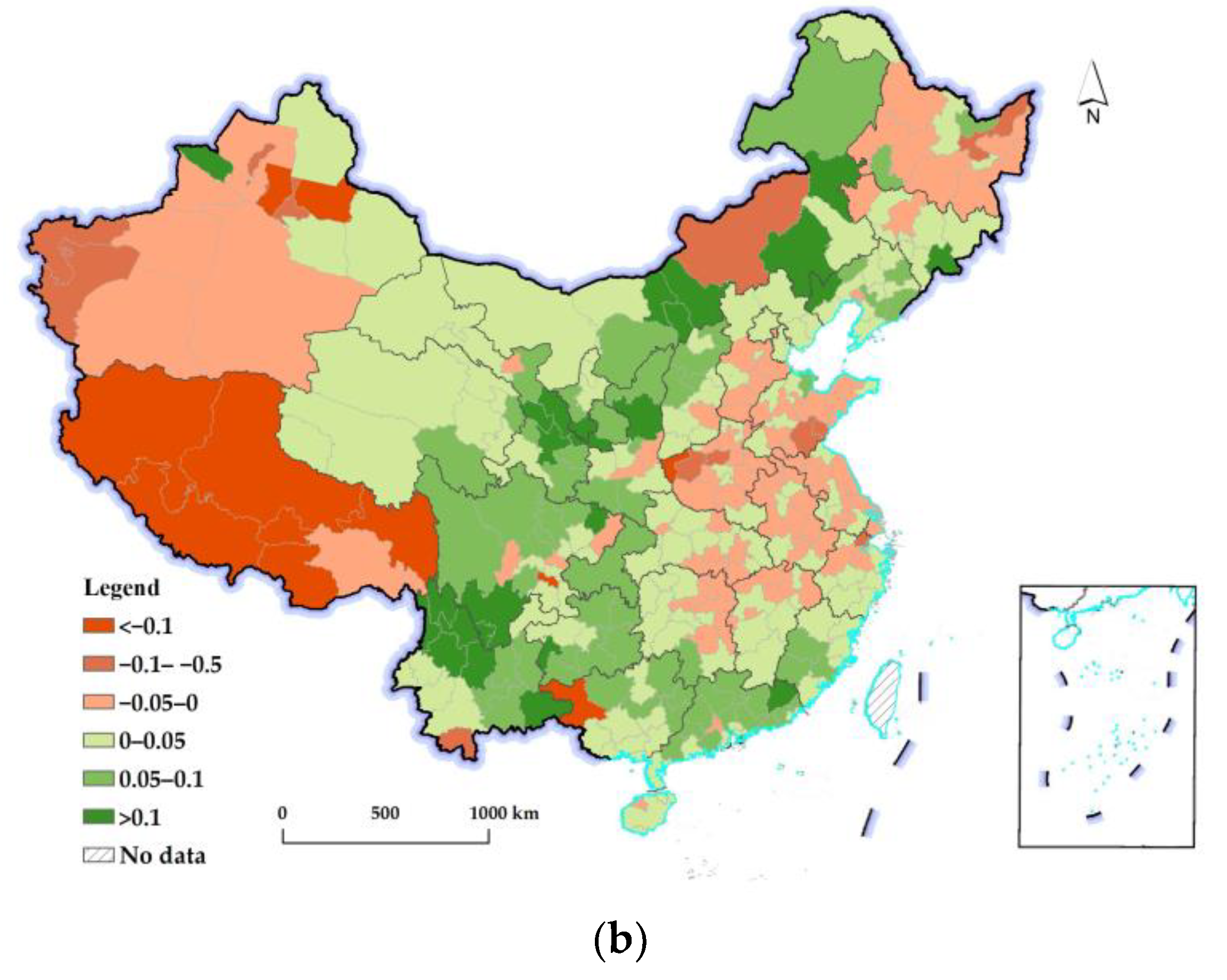
3.2.2. Spatiotemporal Differences in Changes in the REQ at the Prefectural Level
3.3. Examining the Impacts of the Rural Population Decline on the Changes in the REQ
3.3.1. Results for All Samples
3.3.2. Results for Different Regions
4. Discussion
4.1. Performance Evaluation of the Revised EQI Method for Measuring Changes in the REQ
4.2. REQ Changes and the Factors
4.3. Policy Implications
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations. World Urbanization Prospects—Population Division; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mukerji, S.; Gupta, R.B. Population Change and Economic Development in Rural India. Rele J. 2011, 30, 241–243. [Google Scholar]
- Anríquez, G.; Stloukal, L. Rural Population Change in Developing Countries: Lessons for Policymaking. Eur. View 2008, 7, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Jin, H.; Qi, W. Rural Population Change in China: Spatial Differences, Driving Forces and Policy Implications. J. Rural Stud. 2017, 51, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y. Progress and Prospect on the Study of Rural Hollowing in China. Geogr. Res. 2010, 29, 25–42. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Y.; Long, H. The Economic and Environmental Effects of Land Use Transitions under Rapid Urbanization and the Implications for Land Use Management. Habitat Int. 2018, 82, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z. Rural Population Decline, Cultivated Land Expansion, and the Role of Land Transfers in the Farming-Pastoral Ecotone: A Case Study of Taibus, China. Land 2022, 11, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Shao, H.; Xian, W.; Yin, Z.; You, M.; Zhong, J.; Qi, J. Monitoring Cropland Abandonment in Hilly Areas with Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 Timeseries. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Gu, X.; Sun, Q.; Hu, X.; Gao, Y. Analysis of the Spatial and Temporal Pattern of Changes in Abandoned Farmland Based on Long Time Series of Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Yan, J.; Zhou, H.; Li, X. The Factors Influencing Rural Household Firewood Consumption: A Theoretical Model and Empirical Research of a Typical Area in Chongqing Municipality. Shengtai Xuebao 2016, 36, 1369–1379. [Google Scholar]
- Knight, K.W.; Rosa, E.A. Household Dynamics and Fuelwood Consumption in Developing Countries: A Cross-National Analysis. Popul. Environ. 2012, 33, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Wu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Z.; Marinello, F. Exploration of Eco-Environment and Urbanization Changes in Coastal Zones: A Case Study in China over the Past 20 Years. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 119, 106847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, R.I.; Marcotullio, P.J.; Güneralp, B. Urbanization and Global Trends in Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. In Urbanization, Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services: Challenges and Opportunities: A Global Assessment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Robson, J.P.; Berkes, F. Exploring Some of the Myths of Land Use Change: Can Rural to Urban Migration Drive Declines in Biodiversity? Glob. Environ. Change 2011, 21, 844–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Zarzoso, I.; Bengochea-Morancho, A.; Morales-Lage, R. The Impact of Population on CO2 Emissions: Evidence from European Countries. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2007, 38, 497–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hospers, G.-J.; Reverda, N. Managing Population Decline in Europe’s Urban and Rural Areas; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Song, G.; Liu, S. Factors Influencing Farmers’ Willingness and Behavior Choices to Withdraw from Rural Homesteads in China. Growth Change 2022, 53, 112–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, L. Quantifying the Influences of Driving Factors on Vegetation EVI Changes Using Structural Equation Model: A Case Study in Anhui Province, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, Y.; Zhang, L.; Feng, X.; Zeng, Y.; Fu, B.; Yao, X.; Li, J.; Wu, B. Recent Ecological Transitions in China: Greening, Browning, and Influential Factors. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, X.; Tan, M.; Wang, Y. Influences of Population Pressure Change on Vegetation Greenness in China’s Mountainous Areas. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 9041–9053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; D’Arge, R.; de Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The Value of the World’s Ecosystem Services and Natural Capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Shi, Y.; Chen, C.; Yu, M. Monitoring Cropland Transition and Its Impact on Ecosystem Services Value in Developed Regions of China: A Case Study of Jiangsu Province. Land Use Policy 2017, 69, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Fang, C.; Wang, S. Exploring Spatiotemporal Changes in Ecosystem-Service Values and Hotspots in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 545–546, 609–620. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, X.; Hu, M.; Tan, M.; Li, X.; Li, W. Changes in the Ecological Footprint of Rural Populations in the Taihang Mountains, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3741. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q. Impact of Livelihood Diversification of Rural Households on Their Ecological Footprint in Agro-Pastoral Areas of Northern China. J. Arid Land 2015, 7, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Dai, X.; Li, W.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Qu, G.; Liu, W.; Ren, J.; Li, C.; Liang, S.; et al. Detecting Spatial-Temporal Changes of Urban Environment Quality by Remote Sensing-Based Ecological Indices: A Case Study in Panzhihua City, Sichuan Province, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, T.; Ding, Z.; Zhang, X.; Han, L. Uncertainty Analysis of Impact Factors of Eco-Environmental Vulnerability Based on Cloud Theory. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 110, 105864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Sun, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Xiang, Z.; Tan, R.; Chen, X.; Xian, W.; Qi, J. A Method to the Impact Assessment of the Returning Grazing Land to Grassland Project on Regional Eco-Environmental Vulnerability. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2016, 56, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shi, Z.H.; Yin, W.; Zhu, D.; Ng, S.L.; Cai, C.F.; Lei, A.L. A Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process (FAHP) Approach to Eco-Environmental Vulnerability Assessment for the Danjiangkou Reservoir Area, China. Ecol. Model. 2009, 220, 3439–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhai, S.; Liu, H.; Chen, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z. Multi-Scenario Simulation of Production-Living-Ecological Space and Ecological Effects Based on Shared Socioeconomic Pathways in Zhengzhou, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Bao, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z. Land Use Transition and Its Eco-Environmental Effects in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration: A Production-Living-Ecological Perspective. Land 2020, 9, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, J.; Zeng, J.; Ran, D.; Yang, B. Spatial Heterogeneity and Formation Mechanism of Eco-Environmental Effect of Land Use Change in China. Geogr. Res. 2019, 38, 2173–2187. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, R.; Hu, N.; Zhou, J.; Sun, D.; Ye, H. Study on Eco-Environmental Effects of Land-Use Transitions and Their Influencing Factors in the Central and Southern Liaoning Urban Agglomeration: A Production-Living-Ecological Perspective. Land 2022, 11, 937. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Chi, G.; Li, J. The Spatial Association of Ecosystem Services with Land Use and Land Cover Change at the County Level in China, 1995–2015. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yu, B.; Chen, F.; Wang, N.; Li, C. An Analysis of Eco-Environmental Changes in Rural Areas in China Based on Sustainability Indicators between 2000 and 2015. Land 2022, 11, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Qin, K.; Jia, Y.; Yuan, X.; Yang, S. Land Use Transition and Eco-Environmental Effects in Karst Mountain Area Based on Production-Living-Ecological Space: A Case Study of Longlin Multinational Autonomous County, Southwest China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Fan, F. Developing an Enhanced Ecological Evaluation Index (EEEI) Based on Remotely Sensed Data and Assessing Spatiotemporal Ecological Quality in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau Greater Bay Area, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Liu, M.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Su, H.; Mao, X.; Li, X.; Fan, J.; Chen, J.; Lv, Y.; et al. Assessing Land Cover and Ecological Quality Changes in the Forest-Steppe Ecotone of the Greater Khingan Mountains, Northeast China, from Landsat and MODIS Observations from 2000 to 2018. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Wu, Z.; Chen, B.; Yang, C.; Qi, D.; Lan, G.; Fraedrich, K. Effects of Land-Use Change on Eco-Environmental Quality in Hainan Island, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 109, 105777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Huang, Z. Ecological and Environmental Effects of Land Use Change in Rapid Urbanization: The Case of Hangzhou, China. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 81, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Lu, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, X. Measurement of the Eco-Environmental Effects of Urban Sprawl: Theoretical Mechanism and Spatiotemporal Differentiation. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 105, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asabere, S.B.; Acheampong, R.A.; Ashiagbor, G.; Beckers, S.C.; Keck, M.; Erasmi, S.; Schanze, J.; Sauer, D. Urbanization, Land Use Transformation and Spatio-Environmental Impacts: Analyses of Trends and Implications in Major Metropolitan Regions of Ghana. Land Use Policy 2020, 96, 104707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintas-Soriano, C.; Castro, A.J.; Castro, H.; García-Llorente, M. Impacts of Land Use Change on Ecosystem Services and Implications for Human Well-Being in Spanish Drylands. Land Use Policy 2016, 54, 534–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawler, J.J.; Lewis, D.J.; Nelson, E.; Plantinga, A.J.; Polasky, S.; Withey, J.C.; Helmers, D.P.; Martinuzzi, S.; Penningtonh, D.; Radeloff, V.C. Projected Land-Use Change Impacts on Ecosystem Services in the United States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7492–7497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuissl, H.; Haase, D.; Lanzendorf, M.; Wittmer, H. Environmental Impact Assessment of Urban Land Use Transitions—A Context-Sensitive Approach. Land Use Policy 2009, 26, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, B.L.; Lambin, E.F.; Reenberg, A. The Emergence of Land Change Science for Global Environmental Change and Sustainability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20666–20671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Deng, X.; Guo, S.; Liu, S. Labor Migration and Farmland Abandonment in Rural China: Empirical Results and Policy Implications. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 232, 738–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, B.B. Migration, Land Use and Forest Change in St. Lucia, West Indies. Land Use Policy 2016, 51, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grau, H.R.; Aide, T.M. Are Rural-Urban Migration and Sustainable Development Compatible in Mountain Systems? Mt. Res. Dev. 2007, 27, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Bai, C.; Wang, H.; Xue, Q. The Land System and the Rise and Fall of China’s Rural Industrialization: Based on the Perspective of Institutional Change of Rural Collective Construction Land. Land 2022, 11, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Du, G.; Zhang, H. Temporal and Spatial Changes of Rural Settlements and Their Influencing Factors in Northeast China from 2000 to 2020. Land 2022, 11, 1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Liu, Q.; Wang, S.; Huang, C. Vegetation Dynamics and Their Influencing Factors in China from 1998 to 2019. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Land Type | Arable Land | Forestland | Shrubland | Open Woodland | Other Woodland | HC Grassland | MC Grassland | LC Grassland | Water | Construction Land | Unused Land |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arable land | N | ||||||||||
| Forestland | D | A | |||||||||
| Shrubland | D | G | A | ||||||||
| Open woodland | D | G | G | A | |||||||
| Other woodland | D | G | G | G | A | ||||||
| HC grassland | D | G | D | D | D | A | |||||
| MC grassland | D | G | G | N | D | G | A | ||||
| LC grassland | D | G | G | G | G | G | G | A | |||
| Water | D | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | ||
| Construction land | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | N | |
| Unused land | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | D | A |
| Categories | Variables | Definition and Description | Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural | Terrain | The average terrain of a research unit | Terrain |
| Temperature | The average annual temperature during a certain period | Temp | |
| Precipitation | The average annual precipitation during a certain period | Precipitation | |
| Economic | Rural land average GDP | The average GDP value within the rural scope of a unit | LGDP |
| Change in the rural land average GDP | The change rate of the rural land average GDP | RLGDP | |
| Road network density | The ratio between the total mileage of the main road and the area in a research unit | RND | |
| Demographic | Rural population density | The ratio between the number of the rural population and the area in a research unit | RPD |
| Rural population density change | The change rate of the rural population density | CRPD | |
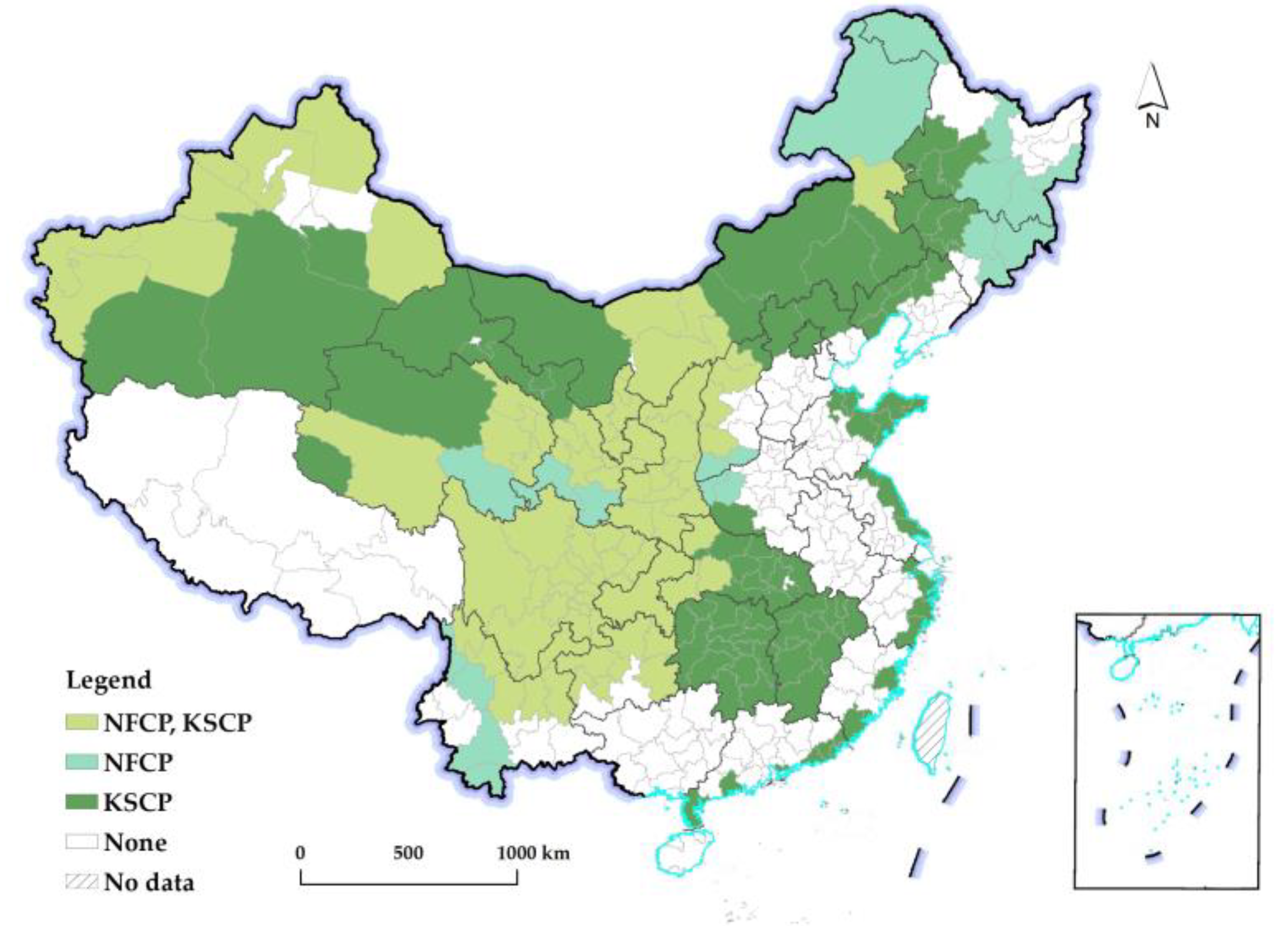
| State policy | Forest conservation | The Natural Forest Conservation Program | NFCP |
| Forest construction | The Key Shelterbelt Construction Program | KSCP |
| Arable Land | Woodland | Grassland | Water | Construction | Unused Land | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The land-use change matrix for the improvement in the REQ (%) | |||||||
| Arable land | 0 (0) | 9.6 (12.0) | 8.7 (12.0) | 7.2 (8.2) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 25.5 (32.2) |
| Woodland | 0 (0) | 16.4 (4.7) | 1.1 (2.5) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 17.5 (7.1) |
| Grassland | 0 (0) | 5.7 (7.2) | 26.6 (7.9) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 32.3 (15.1) |
| Construction | 5.8 (2.3) | 0.1 (1.4) | 0.1 (1.8) | 0.2 (1.2) | 0 (0) | 0 (0.2) | 6.3 (6.8) |
| Unused land | 7.9 (4.9) | 0.9 (6.3) | 7.5 (19.0) | 1.6 (4.9) | 0 (0) | 0.5 (3.6) | 18.5 (38.7) |
| Total | 13.7 (7.2) | 32.6 (31.6) | 44.0 (43.1) | 9.0 (14.3) | 0 (0) | 0.6 (3.8) | 100 (100) |
| The land-use change matrix for the decline in the REQ (%) | |||||||
| Arable land | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 4.3 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (4.6) | 2.4 (3.9) | 6.6 (8.5) |
| Woodland | 7.8 (7.1) | 8.6 (5.7) | 4.8 (8.3) | 0 (0) | 0.9 (1.8) | 1.2 (4.9) | 23.3 (27.7) |
| Grassland | 19.5 (7.8) | 6.7 (4.2) | 14.5 (10.0) | 0 (0) | 0.9 (2.3) | 15.0 (20.7) | 56.7 (44.9) |
| Water | 7.3 (7.4) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1.0 (1.6) | 4.4 (5.6) | 12.6 (14.6) |
| Unused land | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0.2) | 0.7 (4.1) | 0.8 (4.3) |
| Total | 34.6 (22.3) | 15.3 (9.8) | 23.6 (18.3) | 0 (0) | 2.8 (10.6) | 23.7 (39.1) | 100 (100) |
| Categories | Variables | 2000–2010 | 2010–2020 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural | Terrain | 0.220 *** | 0.229 *** |
| Temp | 0.388 *** | 0.325 *** | |
| Precipitation | 0.408 *** | 0.266 ** | |
| Economic | LGDP | −0.112 | −0.120 |
| RLGDP | −0.027 | −0.133 *** | |
| RND | −0.156 ** | −0.097 ** | |
| Demographic | RPD | −0.309 *** | −0.231 *** |
| CRPD | −0.126 ** | −0.143 *** | |
| State policy | NFCP | 0.161 *** | 0.315 *** |
| KSCP | 0.134 *** | 0.141 ** | |
| Constant | 0.255 *** | 0.086 *** | |
| F-value | 11.39 | 11.69 | |
| Adjusted R2 | 0.47 | 0.52 | |
| Sample | 340 | 340 | |
| Categories | Variables | Coastal Region | Central Region | Western Region | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000–2010 | 2010–2020 | 2000–2010 | 2010–2020 | 2000–2010 | 2010–2020 | ||
| Natural | Terrain | 0.023 ** | 0.255 ** | −0.095 | 0.651 | 0.253 *** | 0.176 ** |
| Temp | 0.475 *** | 0.215 ** | |||||
| Precipitation | 0.106 ** | 0.187 ** | 0.268 ** | 0.162 | 0.118 | 0.340 *** | |
| Economic | LGDP | −0.099 ** | −0.227 ** | −0.088 | −0.150 | −0.331 | −0.326 |
| RLGDP | −0.014 ** | −0.065 ** | 0.170 | −0.072 ** | −0.092 ** | −0.236 ** | |
| RND | −0.017 ** | −0.071 ** | −0.101 ** | −0.112 ** | −0.276 *** | −0.299 *** | |
| Demographic | RPD | −0.145 | −0.083 | −0.586 ** | −0.297 ** | −0.446 *** | −0.350 ** |
| CRPD | −0.054 | −0.152 | −0.057 | −0.053 | −0.205 ** | −0.160 ** | |
| State policy | NFCP | 0.230 ** | 0.203 ** | 0.101 | 0.326 ** | ||
| KSCP | 0.342 *** | 0.144 ** | 0.024 | 0.349 ** | 0.283 *** | 0.239 *** | |
| Constant | 0.029 *** | 0.042 *** | 0.560 *** | 0.931 *** | 1.344 *** | 1.511 *** | |
| F-value | 9.53 | 10.56 | 16.25 | 17.01 | 16.58 | 15.76 | |
| Adjusted R2 | 0.39 | 0.38 | 0.49 | 0.49 | 0.44 | 0.41 | |
| Sample | 90 | 90 | 83 | 83 | 133 | 133 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z. Empirical Examinations of Whether Rural Population Decline Improves the Rural Eco-Environmental Quality in a Chinese Context. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5217. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14205217
Liu Z. Empirical Examinations of Whether Rural Population Decline Improves the Rural Eco-Environmental Quality in a Chinese Context. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(20):5217. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14205217
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zhen. 2022. "Empirical Examinations of Whether Rural Population Decline Improves the Rural Eco-Environmental Quality in a Chinese Context" Remote Sensing 14, no. 20: 5217. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14205217
APA StyleLiu, Z. (2022). Empirical Examinations of Whether Rural Population Decline Improves the Rural Eco-Environmental Quality in a Chinese Context. Remote Sensing, 14(20), 5217. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14205217





