An Efficient MUSIC Algorithm Enhanced by Iteratively Estimating Signal Subspace and Its Applications in Spatial Colored Noise
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Problem Formulation
2.2. Proposed Algorithm
2.2.1. Enhanced MUSIC Algorithm
| Algorithm 1: Efficient MUSIC |
| Input data: , ε, P; Output data: 1: , , initial n = 1 2: 3: , and arrange the diagonal elements of in descending order. 4: 5: If , end loop; else, jump to step 2. 6: , then the first few largest peaks of are particularly sharp, and is obtained. |
2.2.2. Computational Complexity
3. Results
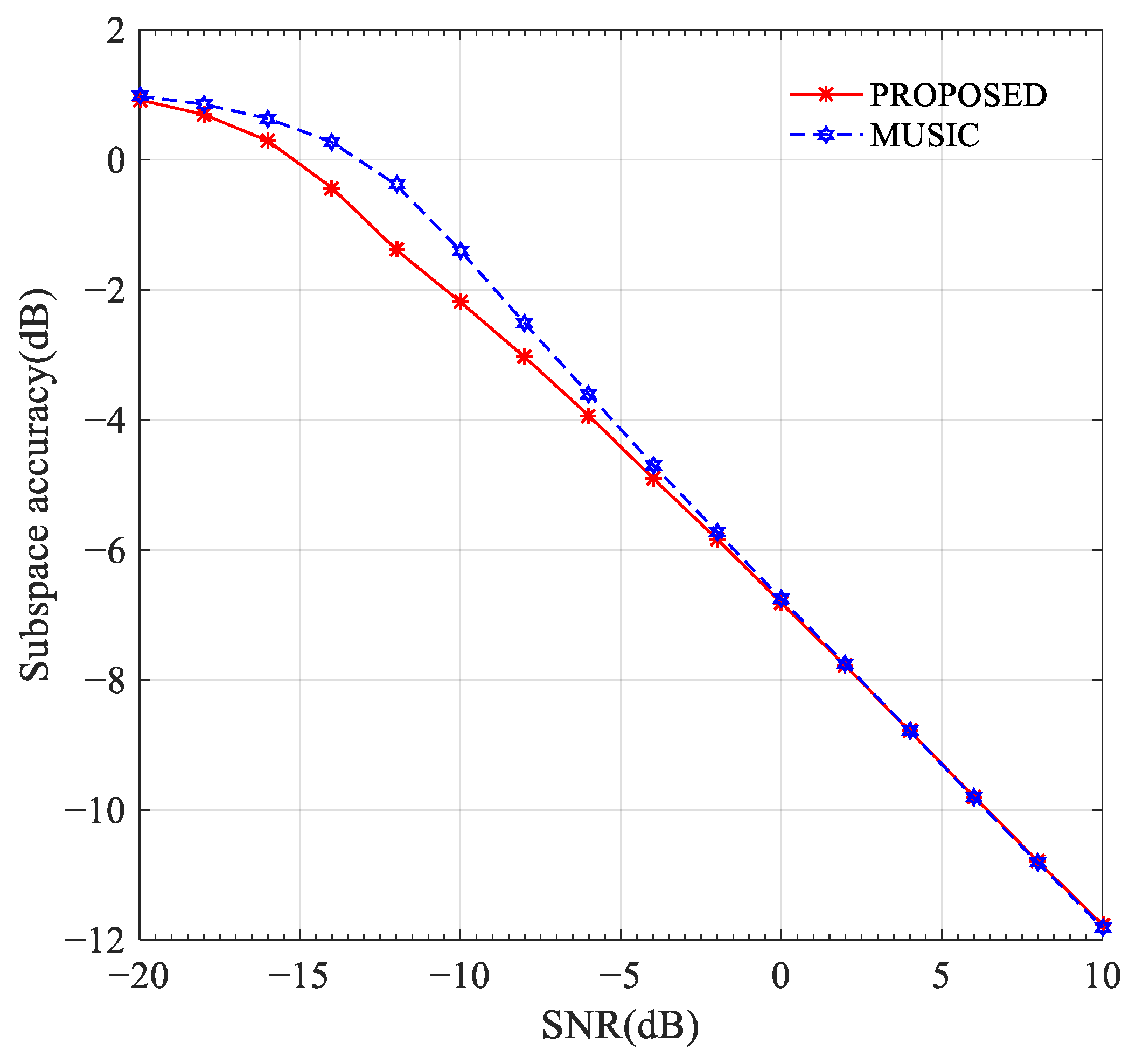
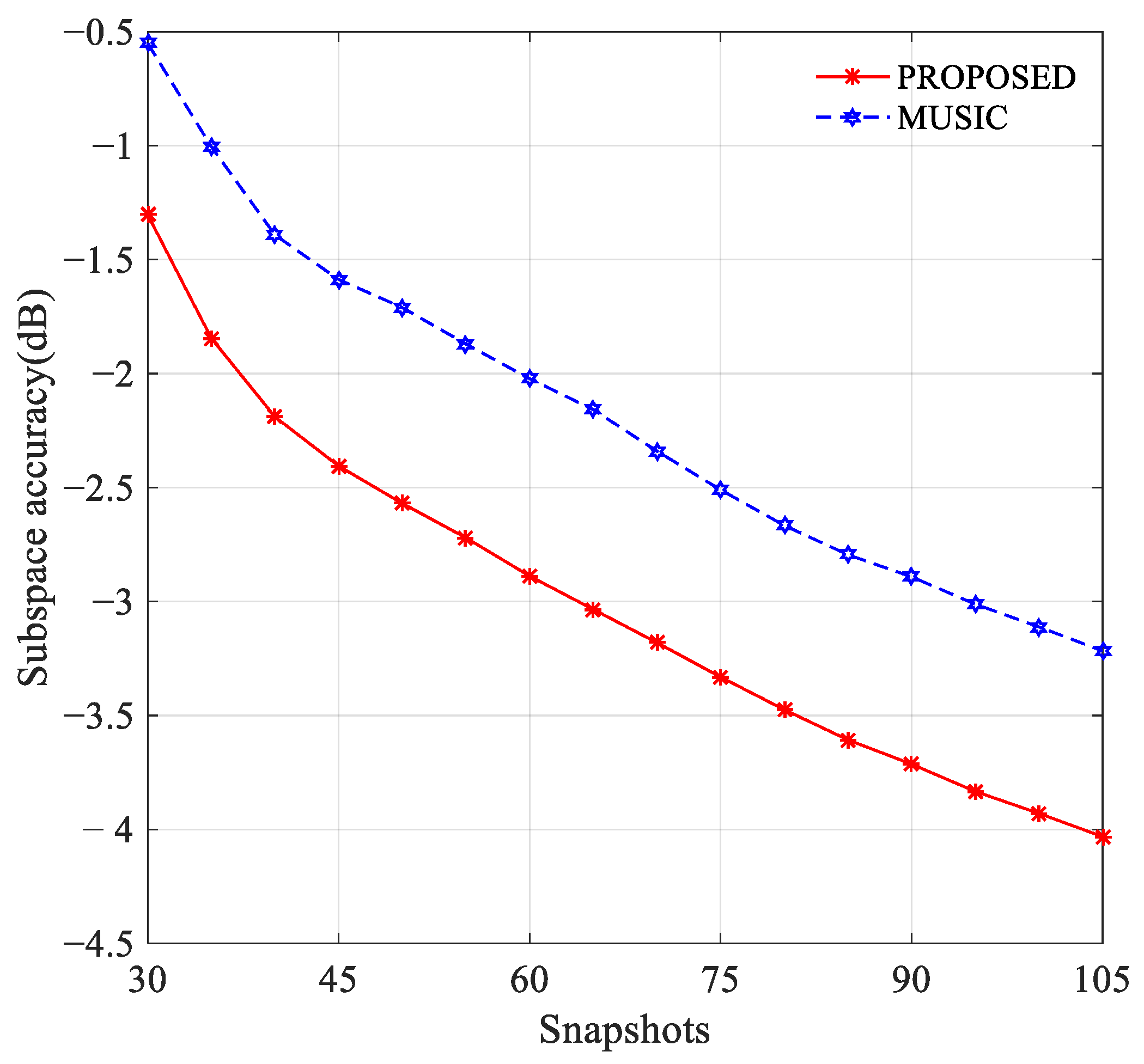
3.1. Experiment 1: Subspace Accuracy
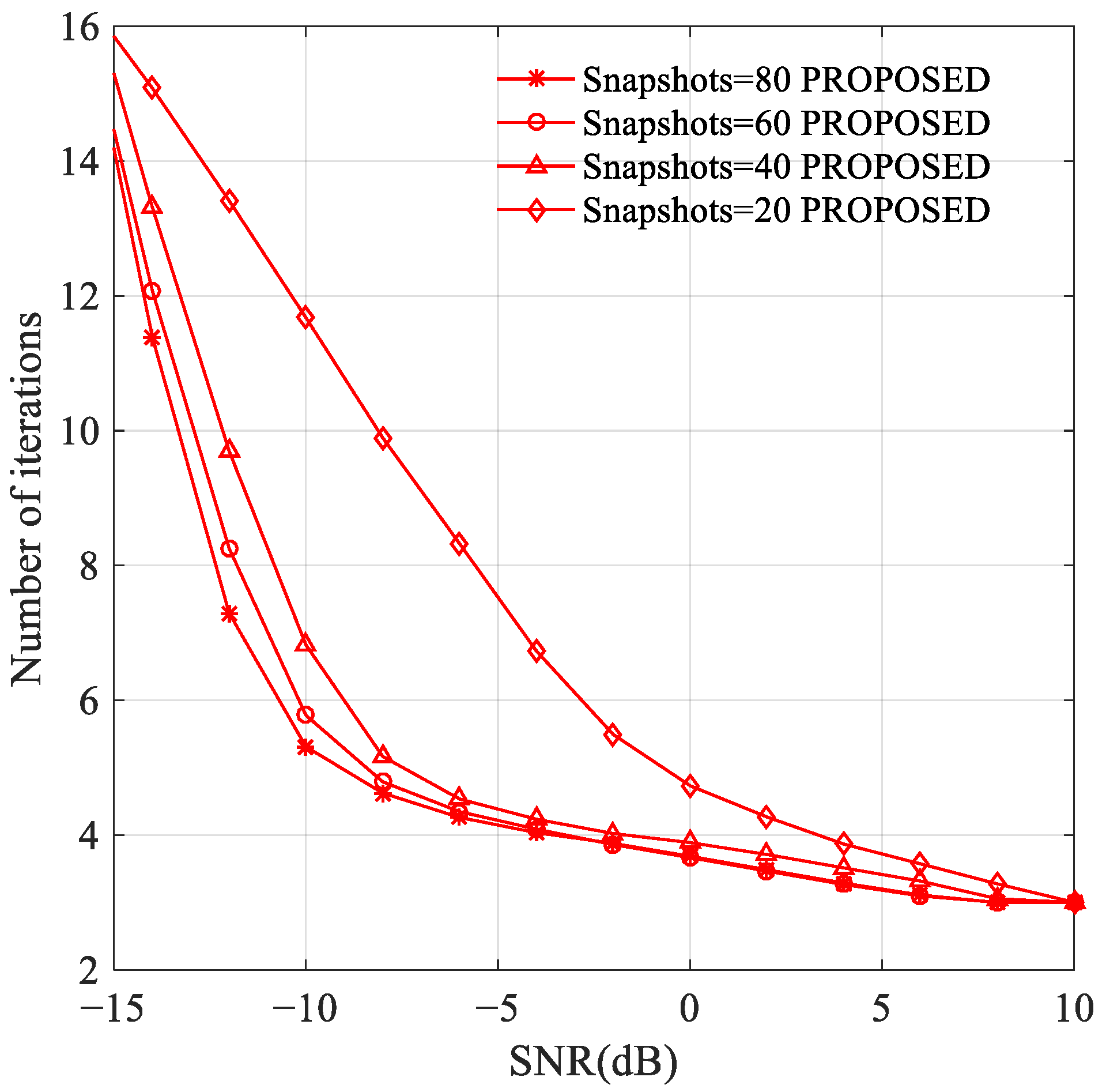
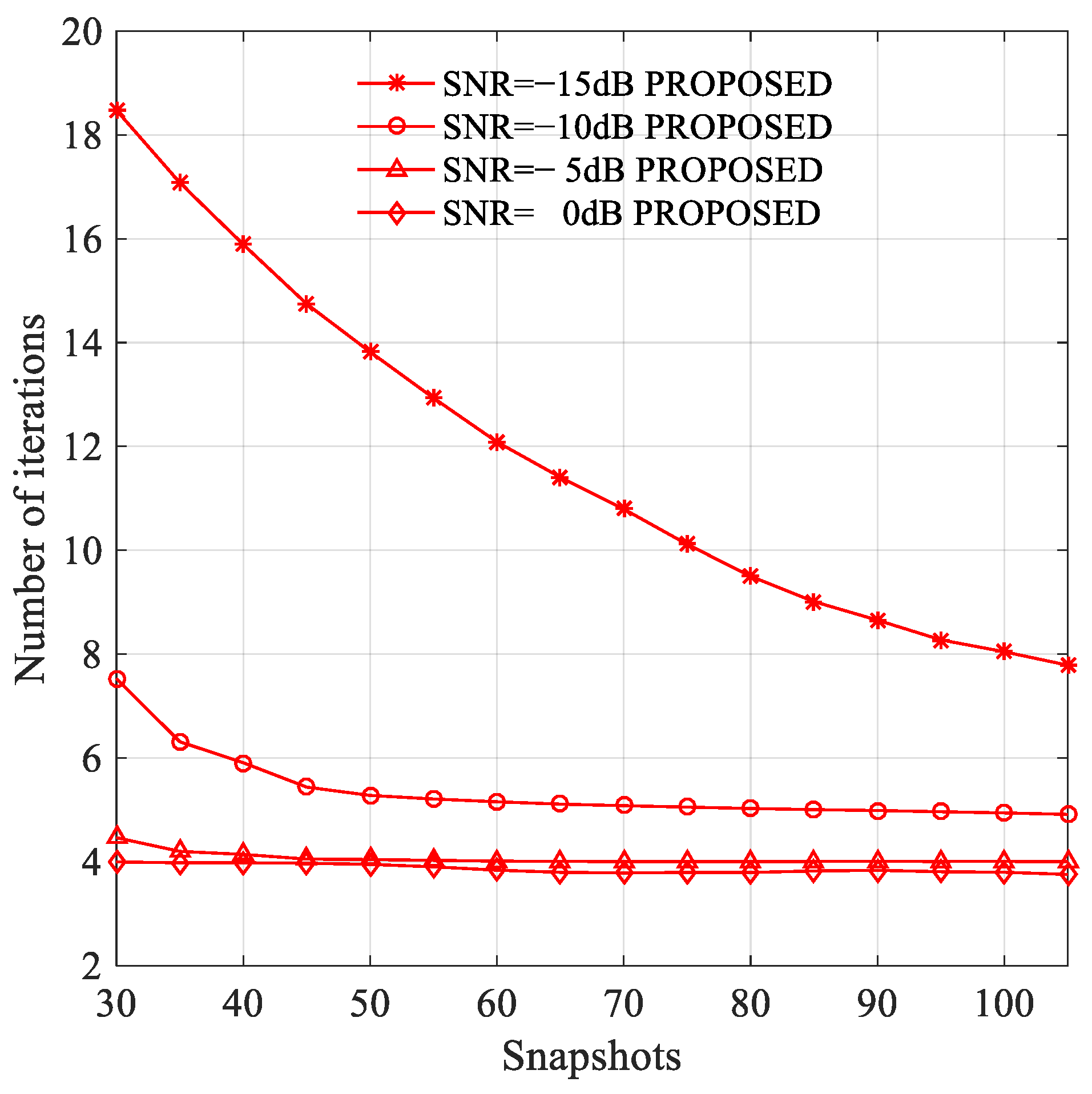
3.2. Experiment 2: The Number of Iterations of the Proposed Algorithm
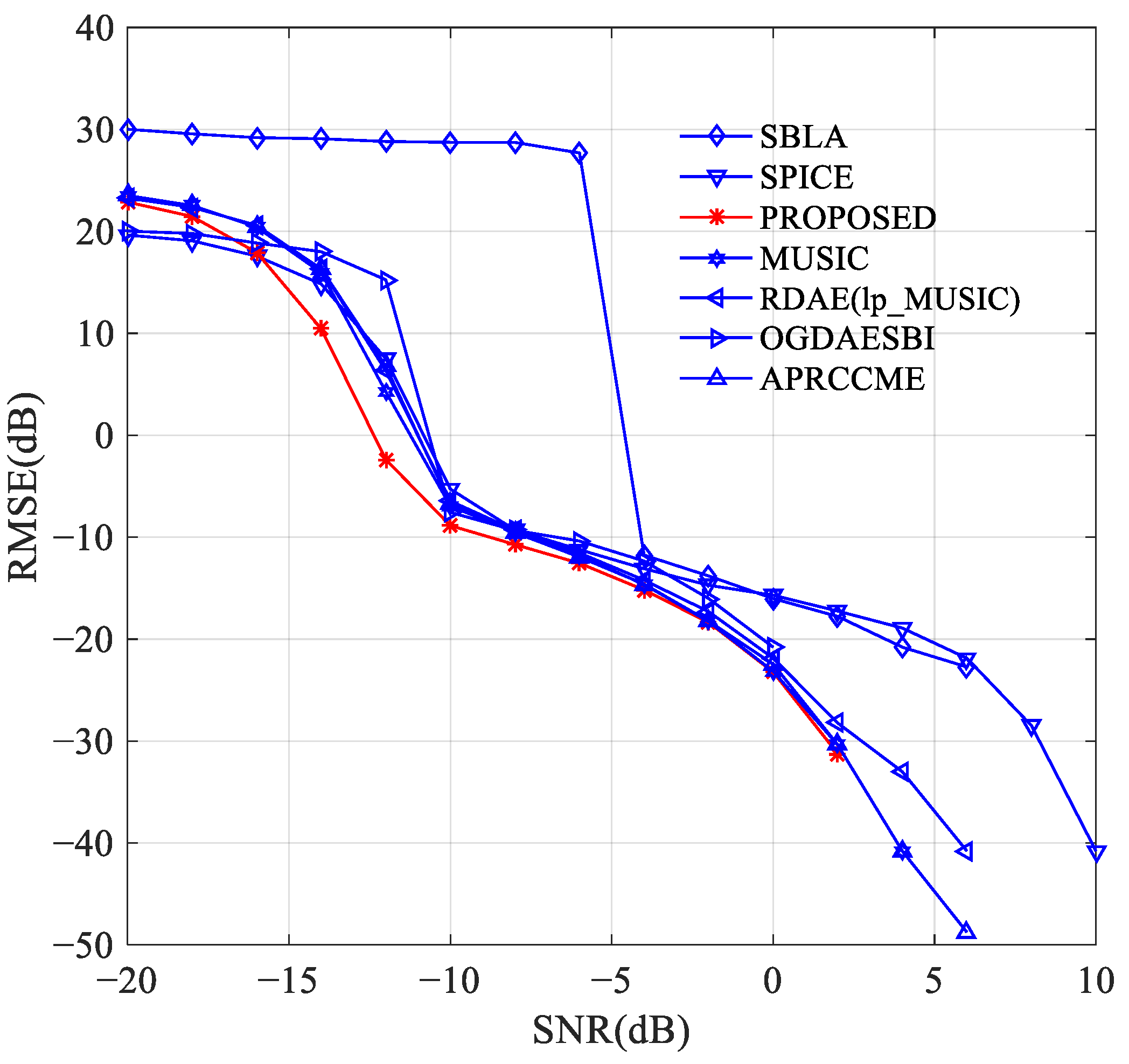
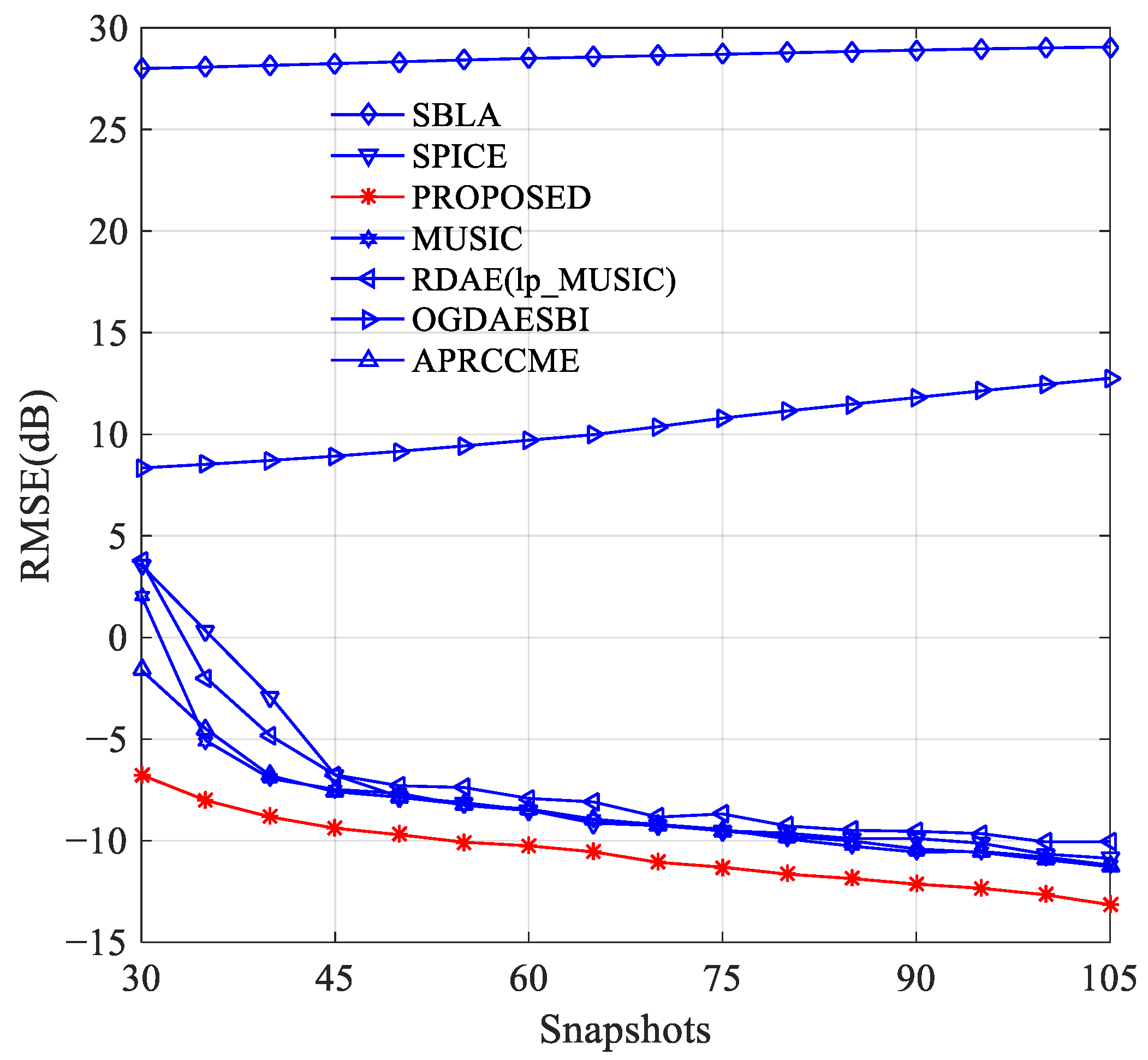
3.3. Experiment 3: Root Mean Square Error
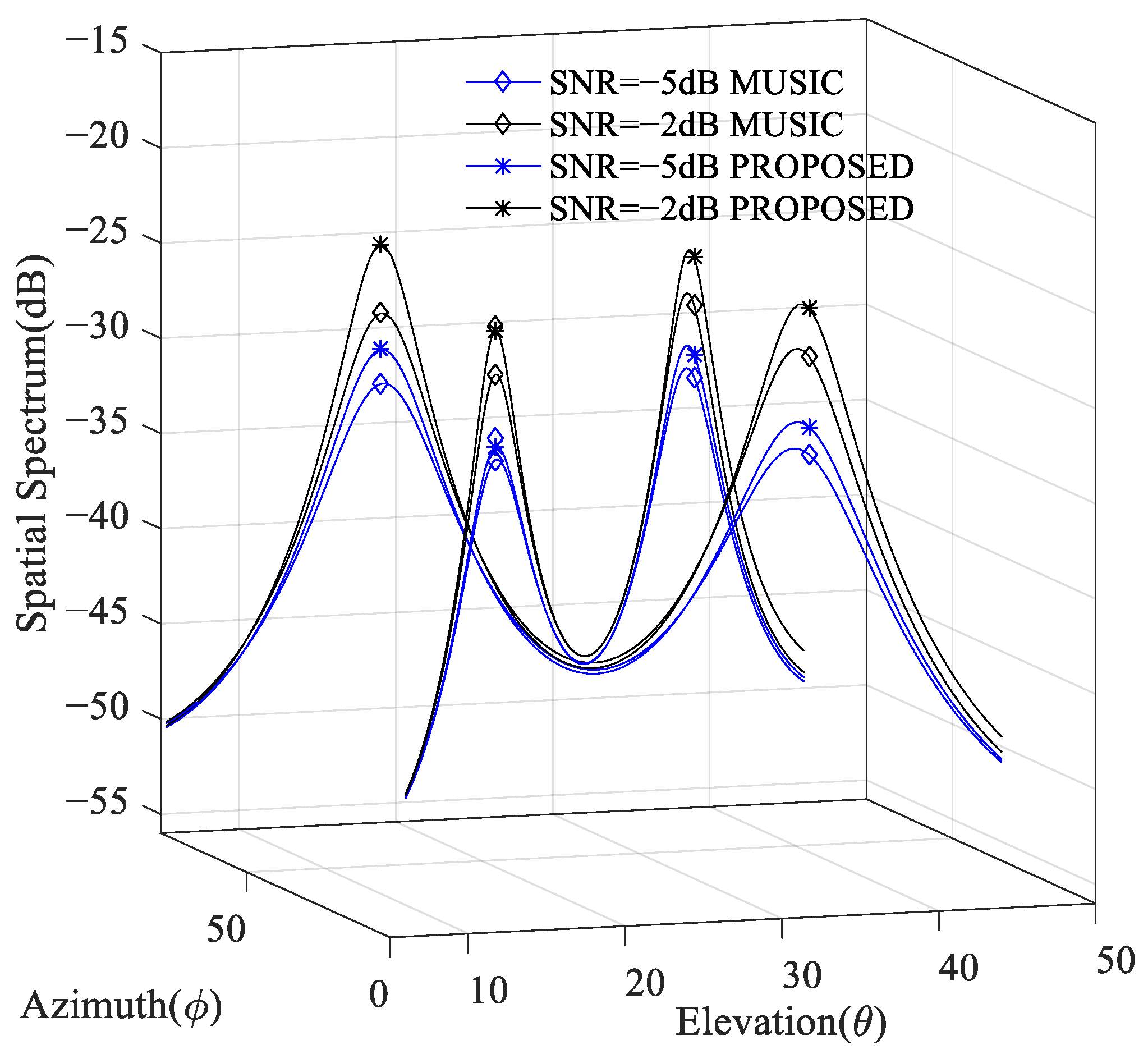
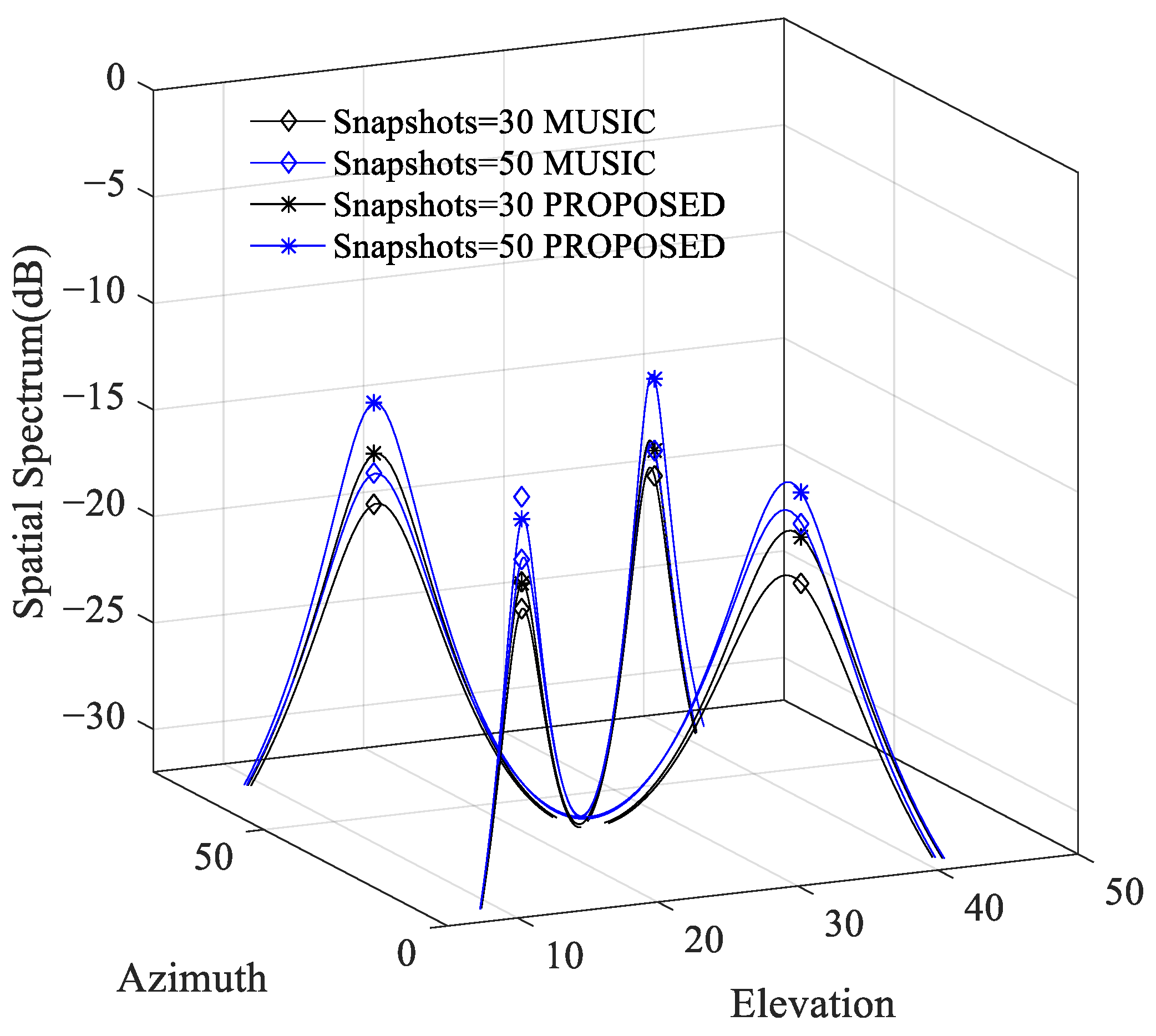
3.4. Experiment 4: Spatial Spectrum
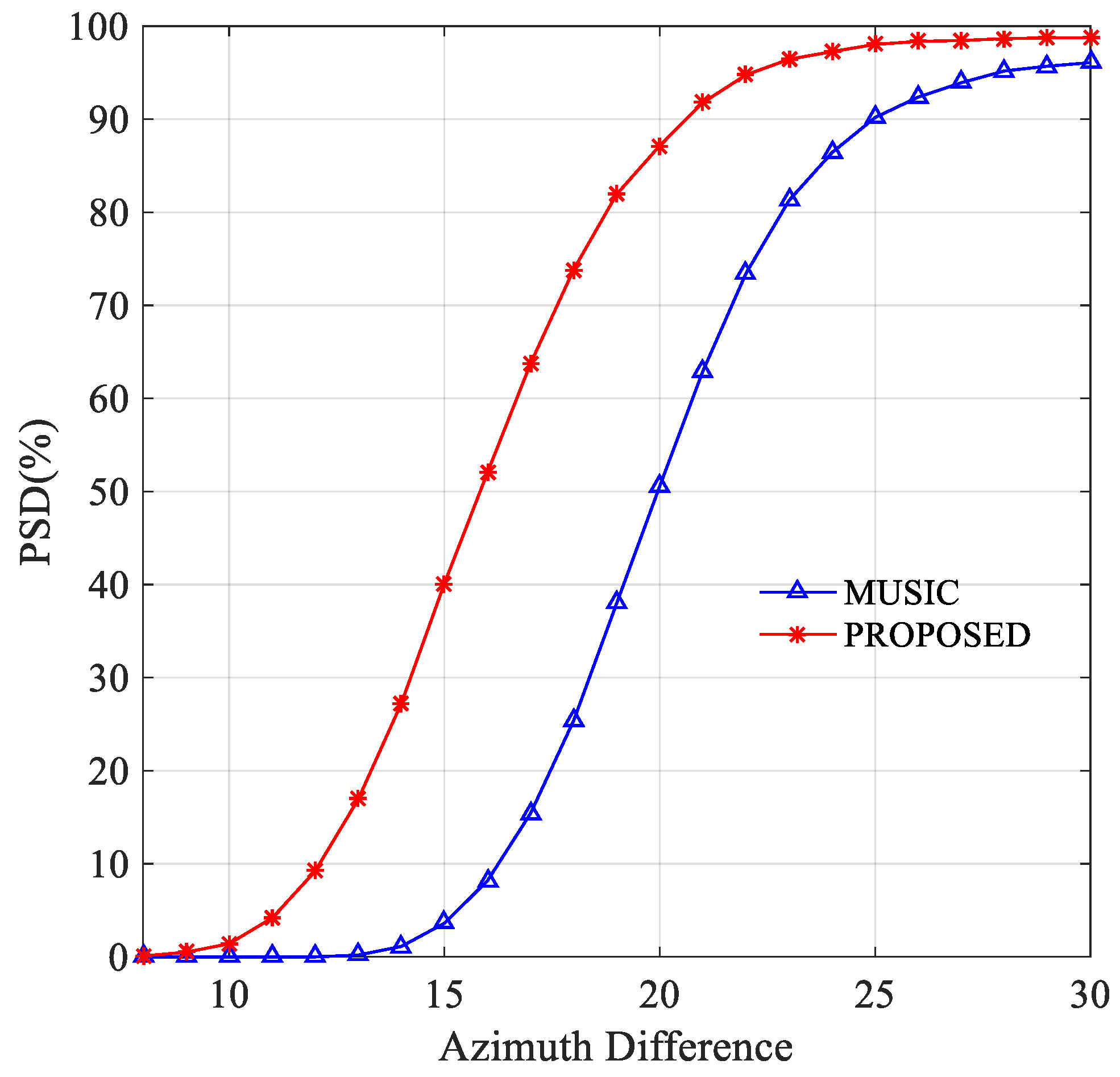
3.5. Experiment 5: Probabilities of Successful Discrimination (PSD)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wen, F.; Wan, Q.; Fan, R.; Wei, H. Improved MUSIC Algorithm for Multiple Noncoherent Subarrays. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2014, 21, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, B.D.; Hari, K.V.S. Performance analysis of ESPRIT and TAM in determining the direction of arrival of plane waves in noise. IEEE Signal Proc. Lett. 1989, 40, 1990–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, W.-K.; Feng, D.-Z.; Xie, H. Improved MUSIC algorithm for high resolution angle estimation. Signal Process. 2016, 122, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhao, Y.P.; Liu, J.J. Mixed-Order MUSIC Algorithm for Localizations in of Far-Field and Near-Field Sources. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2013, 20, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-M.; Zhang, C.; Yu, P.S. Direction-of-Arrival Estimation Based on Deep Neural Networks With Robustness to Array Imperfections. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 66, 7315–7327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.-L.; Liu, Z.-M.; Huang, Z.-T. Deep Convolution Network for Direction of Arrival Estimation With Sparse Prior. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2019, 26, 1688–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Peng, Y.; Yang, J.; Xia, W.; Gui, G. Fast Beamforming Design via Deep Learning. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 1065–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Yang, J. Data-Driven Deep Learning for Automatic Modulation Recognition in Cognitive Radios. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 4074–4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbir, M.; Mishra, K.V. Joint antenna selection and hybrid beamformer design using unquantized and quantized deep learning networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel Commun. 2020, 19, 1677–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.Y.; Guo, Y. Efficient 2D-DOA estimation algorithm for multi-FH signals. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2018, 465, 180–187. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, D. Online Sparse DOA Estimation Based on Sub–Aperture Recursive LASSO for TDM–MIMO Radar. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Sarkar, T.K.; Weiner, D.D. An L-shaped array for estimating 2-D directions of wave arrival. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1991, 39, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Huang, D.; Liu, S. 2D-DOA estimation for uniform rectangular array using non-circular HOSVD method. In Proceedings of the 2016 11th International Symposium on Antennas, Propagation and EM Theory (ISAPE), GuiLin, China, 18–22 October 2016; pp. 617–620. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Rao, Z. An Adaptive Lp Norm Minimization Algorithm for Direction of Arrival Estimation. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, E. A RARE Algorithm for 2D DOA Estimation Based on Nested Array in Massive MIMO System. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 3806–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y. Estimating two-dimensional frequencies by matrix enhancement and matrix pencil. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1992, 40, 2267–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouquette, S.; Najim, M. Estimation of frequencies and damping factors by two-dimensional ESPRIT type methods. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2000, 49, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.-J.; Fung, C.C.; Kok, C. Estimation of Two-Dimensional Frequencies Using Modified Matrix Pencil Method. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2007, 55, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.-Y. 2-D DOA Estimation for L-Shaped Array With Array Aperture and Snapshots Extension Techniques. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2017, 24, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayem, N.; Majeed, K.; Hussain, A.A. Two-Dimensional DOA Estimation Using Cross-Correlation Matrix With L-Shaped Array. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2016, 15, 1077–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wu, R.H.; Zhang, X.F. Joint Two-Dimensional DOA and Frequency Estimation for L-Shaped Array via Compressed Sensing PARAFAC Method. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 37204–37213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xie, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Qi, C. Dynamic Antenna Selection for Collocated MIMO Radar. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W. DOA Estimation for UCA in the Presence of Gain-Phase Errors. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2019, 23, 446–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.; Zhang, X.; Hassan, W.U. A Higher-Order Propagator Method for 2D-DOA Estimation in Massive MIMO Systems. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2020, 24, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.-Q. Joint diagonalization based 2D-DOD and 2D-DOA estimation for bistatic MIMO radar. Signal Process. 2015, 116, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chintagunta, S.; Ponnusamy, P. 2D-DOD and 2D-DOA estimation using the electromagnetic vector sensors. Signal Process. 2018, 147, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.-J.; Nie, W.-K.; Feng, D. A multi-direction virtual array transformation algorithm for 2D DOA estimation. Signal Process. 2016, 125, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.Z.; Kooij, B.J.; Yarovoy, A. Joint Doppler and DOA estimation using (Ultra-)Wideband FMCW signals. Signal Process. 2020, 168, 107259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, X.W.; Liu, Y.; Feng, Q.X. Adaptive DOA estimation with low complexity for wideband signals of massive MIMO systems. Signal Process. 2020, 176, 107702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. Extended DOA-Matrix Method for DOA Estimation via Two Parallel Linear Arrays. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2019, 23, 1981–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Mu, S. Two-Dimensional DOA Estimation Using Two Parallel Nested Arrays. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2020, 24, 568–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q. Two-Dimensional Angular Parameter Estimation for Noncircular Incoherently Distributed Sources Based on an L-Shaped Array. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 13704–13715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Shen, J. 2D-DOA Estimation of Strictly Non-circular Sources Utilizing Connection-Matrix for L-Shaped Array. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2021, 10, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Cao, Z.X.; Chen, Z.M. Sparse off-grid DOA estimation method with unknown mutual coupling effect. Digit. Signal Process. 2019, 90, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guldogan, M.B.; Arikan, O. Cross-ambiguity function domain multipath channel parameter estimation. Digit. Signal Process. 2012, 22, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liang, J.L.; Liu, D. Joint estimation of source number and DOA using simulated annealing algorithm. Digit. Signal Process. 2010, 20, 887–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Zhang, G.; Liu, W.; Wang, X. Off-grid sparse DOA estimation based iterative reweighted linear interpolation in spatial coloured noise. Electron. Lett. 2020, 56, 573–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Liao, G.S.; Li, J. Joint DOD and DOA estimation for bistatic MIMO radar. Signal Process. 2009, 89, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gu, H.; Su, W.M. A new method for joint DOD and DOA estimation in bistatic MIMO radar. Signal Process. 2010, 90, 714–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, J.-K.; Wong, K.M. Joint DOD and DOA Estimation for Bistatic MIMO Radar in Unknown Correlated Noise. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2015, 64, 5113–5125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, W.; Li, X. A Tensor-Based Subspace Approach for Bistatic MIMO Radar in Spatial Colored Noise. Sensors 2014, 14, 3897–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Du, J.; Shao, H. A Nyström-Based Low-Complexity Algorithm with Improved Effective Array Aperture for Coherent DOA Estimation in Monostatic MIMO Radar. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.Q.; Xiong, X.D.; Su, J. Angle estimation for bistatic MIMO radar in the presence of spatial colored noise. Signal Process. 2017, 134, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, K.; Yu, Z.; Xie, N.; Jiang, J. Joint Estimation of Azimuth and Distance for Far-Field Multi Targets Based on Graph Signal Processing. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Tang, J.; Zhang, Y. Maximum likelihood estimation of DOD and DOA for bistatic MIMO radar. Signal Process. 2012, 93, 1349–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, G. A Tensor-Based Covariance Differencing Method for Direction Estimation in Bistatic MIMO Radar with Unknown Spatial Colored Noise. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 18451–18458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D. A bi-iteration instrumental variable noise-subspace tracking algorithm. Signal Process. 2001, 81, 2215–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; So, H.C.; Huang, L. lp-MUSIC: Robust Direction-of-Arrival Estimator for Impulsive Noise Environments. IEEE Trans. Signal Process 2013, 61, 4296–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; So, H.C. Sparse Bayesian Learning Approach for Outlier-Resistant Direction-of-Arrival Estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process 2018, 66, 744–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Hu, X.; Feng, W.; Gong, J. Low-Complexity 2D DOA Estimation and Self-Calibration for Uniform Rectangle Array with Gain-Phase Error. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xie, L.; Zhang, C. Off-Grid Direction of Arrival Estimation Using Sparse Bayesian Inference. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2013, 61, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahot, M.; Pascal, F.; Forster, P.; Ovarlez, J. Asymptotic Properties of Robust Complex Covariance Matrix Estimates. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2013, 61, 3348–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoica, P.; Babu, P.; Li, J. SPICE: A Sparse Covariance-Based Estimation Method for Array Processing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2011, 59, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Zhao, Y.; Liao, W. Nonlocal Low-Rank Regularized Tensor Decomposition for Hyperspectral Image Denoising. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 5174–5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Xie, X.; Cui, H. Hyperspectral Image Restoration via Global L Spatial-Spectral Total Variation Regularized Local Low-Rank Tensor Recovery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2020, 99, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Feng, D. An Efficient MUSIC Algorithm Enhanced by Iteratively Estimating Signal Subspace and Its Applications in Spatial Colored Noise. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4260. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14174260
Zhang X, Feng D. An Efficient MUSIC Algorithm Enhanced by Iteratively Estimating Signal Subspace and Its Applications in Spatial Colored Noise. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(17):4260. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14174260
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xuejun, and Dazheng Feng. 2022. "An Efficient MUSIC Algorithm Enhanced by Iteratively Estimating Signal Subspace and Its Applications in Spatial Colored Noise" Remote Sensing 14, no. 17: 4260. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14174260
APA StyleZhang, X., & Feng, D. (2022). An Efficient MUSIC Algorithm Enhanced by Iteratively Estimating Signal Subspace and Its Applications in Spatial Colored Noise. Remote Sensing, 14(17), 4260. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14174260





