Relative Effects of the Greenhouse Gases and Stratospheric Ozone Increases on Temperature and Circulation in the Stratosphere over the Arctic
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Model
2.2. Numerical Simulations
2.3. Methods
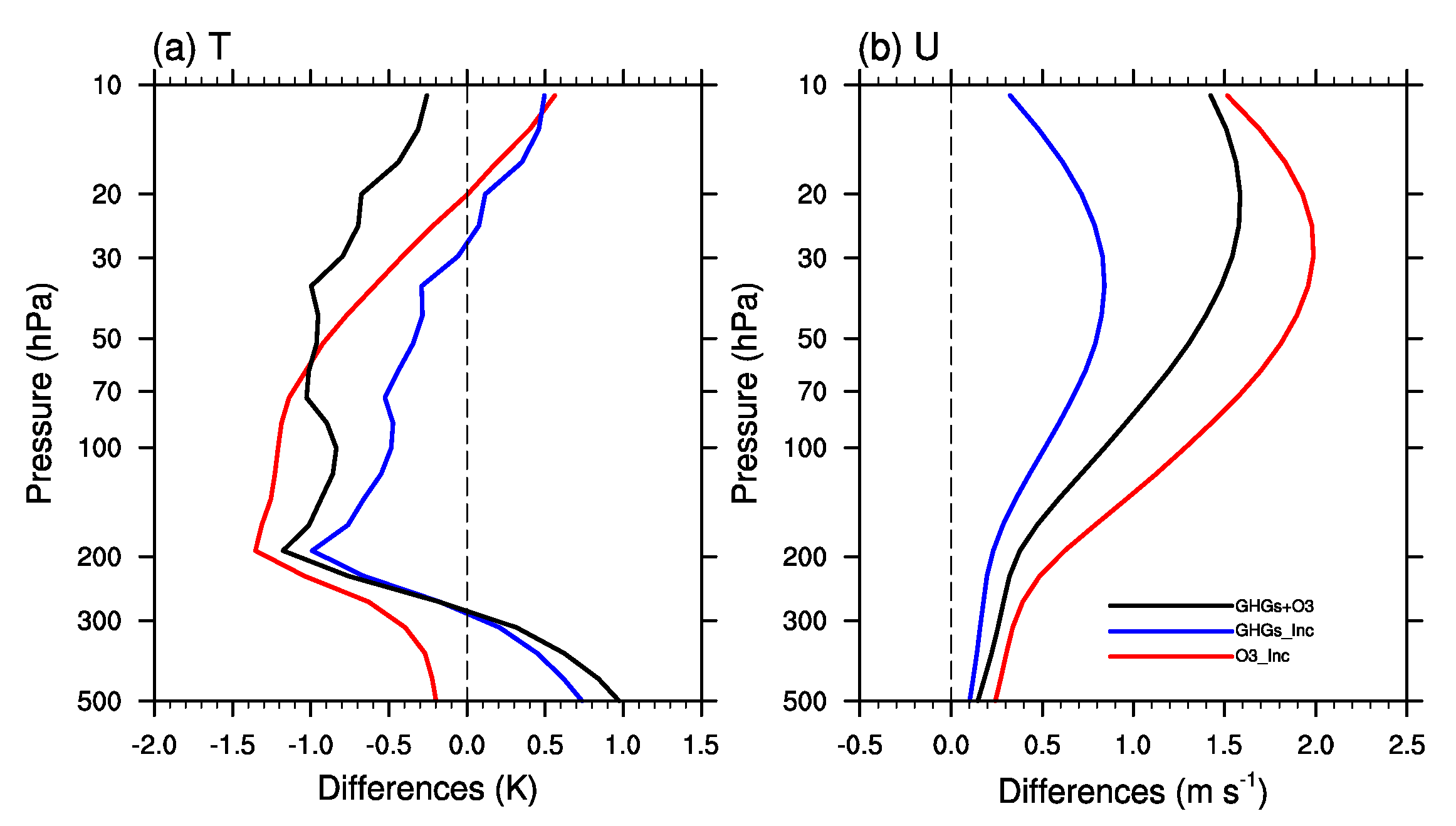
3. Results
3.1. Relative Contributions of Ozone and GHGs Increase
3.2. Possible Dynamic Mechanisms
3.2.1. Wave Activity Responses
3.2.2. Anomalies in the Wave Fluxes
3.2.3. Wave Propagation Responses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xie, F.; Tian, W.S.; Chipperfield, M.P. Radiative effect of ozone change on stratosphere-troposphere exchange. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D00B09. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shu, J.C.; Tian, W.S.; Austin, J.; Chipperfield, M.P.; Xie, F.; Wang, W. Effects of sea surface temperature and greenhouse gas changes on the transport between the stratosphere and troposphere. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, D02124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baldwin, M.P.; Dunkerton, T.J. Stratospheric Harbingers of Anomalous Weather Regimes. Science 2001, 294, 581–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haynes, P. Stratospheric Dynamics. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2005, 37, 263–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, M.P.; Dameris, M.; Shepherd, T.G. How will the stratosphere affect climate change? Science 2007, 316, 1576–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, F.; Li, J.; Tian, W.; Fu, Q.; Jin, F.F.; Hu, Y.; Ding, R. A connection from Arctic stratospheric ozone to El Niño-Southern oscillation. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 124026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hannachi, A.; Straus, D.M.; Franzke, C.L.; Corti, S.; Woollings, T. Low-frequency nonlinearity and regime behavior in the Northern Hemisphere extratropical atmosphere. Rev. Geophys. 2017, 55, 199–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Tian, W.; Zhang, J.; Huang, J.; Xie, F.; Xu, M. The corresponding tropospheric environments during downward-extending and nondownward-extending events of stratospheric northern annular mode anomalies. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 1857–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beerli, R.; Wernli, H.; Grams, C.M. Does the lower stratosphere provide predictability for month-ahead wind electricity generation in Europe? Q. J. R. Meteor. Soc. 2017, 143, 3025–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigmond, M.; Scinocca, J.F.; Kharin, V.V.; Shepherd, T.G. Enhanced seasonal forecast skill following stratospheric sudden warmings. Nat. Geosci. 2013, 6, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitchcock, P.; Simpson, I.R. The downward influence of stratospheric sudden warmings. J. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 71, 3856–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, O.P.; Charlton-Perez, A.; Sigmond, M.; Vitart, F. Enhanced long-range forecast skill in boreal winter following stratospheric strong vortex conditions. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 104007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scaife, A.A.; Karpechko, A.Y.; Baldwin, M.P.; Brookshaw, A.; Butler, A.H.; Eade, R.; Smith, D. Seasonal winter forecasts and the stratosphere. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2016, 17, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karpechko, A.Y. Improvements in statistical forecasts of monthly and two-monthly surface air temperatures using a stratospheric predictor. Q. J. R. Meteor. Soc. 2015, 141, 2444–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.W.; Polvani, L.M.; Waugh, D.W.; Akiyoshi, H.; Garcia, R.; Kinnison, D.; Shibata, K. The impact of stratospheric ozone recovery on the southern hemisphere westerly jet. Science 2008, 320, 1486–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garfinkel, C.I.; Waugh, D.W.; Gerber, E.P. The effect of tropospheric jet latitude on coupling between the stratospheric polar vortex and the troposphere. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 2077–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, Y. Role of the stratosphere on the predictability of medium-range weather forecast: A case study of winter 2003–2004. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L19701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WMO. Scientific assessment of ozone depletion: 2006, Report No. 50, Global Ozone Research and Monitoring Project, Geneva, Assessment Cochairs Ayité-Lô Nohende Ajavon, Daniel L. Albritton, and Robert T. Watson. 2007. Available online: https://csl.noaa.gov/assessments/ozone/2006/chapters/contentsprefaceexecutivesummary.pdf (accessed on 6 June 2022).
- Ramaswamy, V.; Schwarzkopf, M.D.; Randel, W.J.; Santer, B.D.; Soden, B.J.; Stenchikov, G.L. Anthropogenic and natural influences in the evolution of lower stratospheric cooling. Science 2006, 311, 1138–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasseur, G.P.; Hitchman, M.A. Stratospheric response to trace gas perturbations: Changes in ozone and temperature distributions. Science 1988, 240, 634–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, J.T. The Physics of Atmospheres; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002; p. 320. [Google Scholar]
- Kodama, C.; Iwasaki, T.; Shibata, K.; Yukimoto, S. Changes in the stratospheric mean meridional circulation due to increased CO2: Radiation- and sea surface temperature induced effects. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D16103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Tian, W.; Xie, F.; Shu, J.; Dhomse, S. Effects of meridional sea surface temperature gradients on the stratospheric temperature and circulation. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 31, 888–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, T.G.; McLandress, C. A robust mechanism for strengthening of the Brewer-Dobson circulation in response to climate change: Critical-Layer control of subtropical wave breaking. J. Atmos. Sci. 2011, 68, 784–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasseur, G.P.; Solomon, S. Aeronomy of the Middle Atmosphere: Chemistry and Physics of the Stratosphere and Mesosphere; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; p. 644. [Google Scholar]
- Coy, L.; Nash, E.R.; Newman, P.A. Meteorology of the polar vortex: Spring 1997. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1997, 24, 2693–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, P.A.; Nash, E.R.; Rosenfield, J.E. What controls the temperature of the Arctic stratosphere during the spring? J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 19999–20010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.; Tung, K.K. Possible ozone-induced long-term changes in planetary wave activity in late winter. J. Clim. 2003, 16, 3027–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S. Stratospheric ozone depletion. a review of concepts and history. Rev. Geophys. 1999, 37, 275–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.W.; Solomon, S.; Kushner, P.J.; England, M.H.; Grise, K.M.; Karoly, D.J. Signatures of the Antarctic ozone hole in Southern Hemisphere surface climate change. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.W.; Gerber, E.P.; Perlwitz, J.; Polvani, L.M.; Gillett, N.P.; Seo, K.H.; Yamashita, Y. Impact of stratospheric ozone on Southern Hemisphere circulation change: A multi-model assessment. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D00M07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polvani, L.M.; Waugh, D.W.; Correa, G.J.; Son, S.W. Stratospheric ozone depletion: The main driver of 20th Century atmospheric circulation changes in the Southern Hemisphere. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 795–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.M.; Polvani, L.M.; Fyfe, J.C.; Sigmond, M. Impact of polar ozone depletion on subtropical precipitation. Science 2011, 332, 951–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bitz, C.M.; Polvani, L.M. Antarctic climate response to stratospheric ozone depletion in a fine resolution ocean climate model. Geophy. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, 20705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weatherhead, E.C.; Andersen, S.B. The search for signs of recovery of the ozone layer. Nature 2006, 441, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randel, W.J.; Shine, K.P.; Austin, J.; Barnett, J.; Claud, C.; Gillett, N.P.; Yoden, S. An update of observed stratospheric temperature trends. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D02107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forster, P.G.; Bodeker, R.S.; Solomon, S.; Thompson, D. Effects of ozone cooling in the tropical lower stratosphere and upper troposphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L23813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polvani, L.M.; Solomon, S. The signature of ozone depletion on tropical temperature trends, as revealed by their seasonal cycle in model integrations with single forcings. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D17102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, D.; Tian, W.; Xie, F.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J. Impacts of stratospheric ozone depletion and recovery on wave propagation in the boreal winter stratosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 2015, 120, 8299–8317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collins, W.D.; Bitz, C.M.; Blackmon, M.L.; Bonan, G.B.; Bretherton, C.S.; Carton, J.A.; Smith, R.D. The Community Climate System Model version 3 (CCSM3). J. Clim. 2006, 19, 2122–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyring, V.; Waugh, D.W.; Bodeker, G.E.; Cordero, E.; Akiyoshi, H.; Austin, J.; Yoshiki, M. Multi-model projections of stratospheric ozone in the 21st century. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D16303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shangguan, M.; Tian, W.; Schmidt, T.; Ding, A. Large uncertainties in estimation of tropical tropopause temperature variabilities due to model vertical resolution. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 10043–10052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, R.R.; Marsh, D.R.; Kinnison, D.E.; Boville, B.A.; Sassi, F. Simulation of secular trends in the middle atmosphere, 1950–2003. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D09301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oman, L.; Waugh, D.W.; Pawson, S.; Stolarski, R.S.; Newman, P.A. On the influence of anthropogenic forcing on changes in the stratospheric mean age. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D03105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- SPARC CCMVal. SPARC Report on the Evaluation of Chemistry-Climate Models, SPARC Rep. 5, edited by Eyring, V.; Shepherd, T.G.; Waugh, D.W. WCRP-132, WMO/TD-No. 152, Univ. of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, 2010. Available online: https://www.sparc-climate.org/publications/sparc-reports/ (accessed on 6 June 2022).
- Andrews, D.G.; Holton, J.R.; Leovy, C.B. Middle Atmosphere Dynamics; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1987; 489p. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, D.; Guan, Z. Decadal relationship between the stratospheric arctic vortex and pacific decadal oscillation. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 3371–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Robinson, W.A. Propagation of planetary waves between the troposphere and stratosphere. J. Atmos. Sci. 1992, 49, 2533–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jadin, E.A.; Wei, K.; Zyulyaeva, Y.A.; Chen, W.; Wang, L. Stratospheric wave activity and the Pacific Decadal Oscillation. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2010, 72, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.H.; Sung, M.K.; Son, S.W.; Kug, J.S. Connection between weak stratospheric vortex events and the Pacific Decadal Oscillation. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 45, 3481–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Guan, Z.; Tian, W.; Ren, R. Recent strengthening of the stratospheric Arctic vortex response to warming in the central North Pacific. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charney, J.G.; Drazin, P.G. Propagation of planetary scale disturbances from the lower into the upper atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 1961, 66, 83–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, I.R.; Blackburn, M.; Haigh, J.D. The role of eddies in driving the tropospheric response to stratospheric heating perturbations. J. Atmos. Sci. 2009, 66, 1347–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, T.C. A North Pacific short-wave train during the extreme phases of ENSO. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 2359–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Tung, K.K. Interannual and decadal variations of planetary wave activity, stratospheric cooling, and northern hemisphere annular model. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 1659–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Graf, H.F.; Giorgetta, M.A. Stationary planetary wave propagation in Northern Hemisphere winter-climatological analysis of the refractive index. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WMO. Scientific Assessment of Ozone Depletion. In Global Ozone Research and Monitoring Project (Report No. 58); Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; p. 588. Assessment Co-chairs: David W. Fahe, Paul A. Newman, John A. Pyle, Bonfils Safari. Available online: https://ozone.unep.org/sites/default/files/2019-05/SAP-2018-Assessment-report.pdf (accessed on 6 June 2022).
- Manzini, E.; Steil, B.; Bruhl, C.; Giorgetta, M.A.; Kruger, K. A new interactive chemistry-climate model: 2. Sensitivity of the middle atmosphere to ozone depletion and increase in greenhouse gases and implications for recent stratospheric cooling. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ball, W.T.; Alsing, J.; Mortlock, D.J.; Staehelin, J.; Haigh, J.D.; Peter, T.; Rozanov, E.V. Evidence for a continuous decline in lower stratospheric ozone offsetting ozone layer recovery. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 1379–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wargan, K.; Orbe, C.; Pawson, S.; Ziemke, J.R.; Oman, L.D.; Olsen, M.A.; Emma Knowland, K. Recent decline in extratropical lower stratospheric ozone attributed to circulation changes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 5166–5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipperfield, M.P.; Dhomse, S.; Hossaini, R.; Feng, W.; Santee, M.L.; Weber, M.; Coldewey-Egbers, M. On the cause of recent variations in lower stratospheric ozone. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 5718–5726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Guan, Z.; Liu, M.; Feng, W. Dynamical mechanisms for the recent ozone depletion in the Arctic stratosphere linked to North Pacific sea surface temperatures. Clim. Dyns. 2021, 58, 2663–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tian, W.; Xie, F.; Sang, W.; Guo, D.; Chipperfield, M.; Hu, D. Zonally asymmetric trends of winter total column ozone in the northern middle latitudes. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 52, 4483–4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bednarz, E.M.; Maycock, A.C.; Abraham, N.L.; Braesicke, P.; Dessens, O.; Pyle, J.A. Future Arctic ozone recovery: The importance of chemistry and dynamics. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 12159–12176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhomse, S.S.; Kinnison, D.; Chipperfield, M.P.; Salawitch, R.J.; Cionni, I.; Hegglin, M.I.; Zeng, G. Estimates of ozone return dates from Chemistry-Climate Model Initiative simulations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 8409–8438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Lei, Y. Diagnostic analysis of the impact of tropical QBO on the general circulation in the Northern Hemisphere winter. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2004, 28, 161–173. [Google Scholar]
- Labitzke, K. On the solar cycle-QBO relationship: A summary. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2005, 67, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Matthes, K.; Omrani, N.; Latif, M. Decadal variability of tropical tropopause temperature and its relationship to the Pacific Decadal Oscillation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manzini, E.; Giorgetta, M.A.; Esch, M.; Kornblueh, L.; Roeckner, E. The influence of sea surface temperatures on the northern winter stratosphere: Ensemble simulations with the MAECHAM5 model. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 3863–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Matthes, K.; Tian, W.; Park, W.; Shangguan, M.; Ding, A. Solar impacts on decadal variability of tropopause temperature and lower stratospheric (LS) water vapour: A mechanism through ocean-atmosphere coupling. Clim. Dyns. 2018, 52, 5585–5604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Tian, W.; Xie, F.; Chipperfield, M.P.; Feng, W.; Son, S.W.; Zeng, G. Stratospheric ozone loss over the Eurasian continent induced by the polar vortex shift. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








| Experiments | Ozone | CO2 (ppmv) | CH4 (ppbv) | N2O (ppbv) | CFC-11 (pptv) | CFC-12 (pptv) | SSTs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF | 1998–2002 | 371 | 1757 | 316 | 267 | 535 | 1995–2004 |
| O3_Inc | 2018–2022 | 371 | 1757 | 316 | 267 | 535 | 1995–2004 |
| GHGs_Inc | 1998–2002 | 416 | 336 | 1930 | 214 | 486 | 2015–2024 |
| GHGs + O3 | 2018–2022 | 416 | 336 | 1930 | 214 | 486 | 2015–2024 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, D.; Guan, Z. Relative Effects of the Greenhouse Gases and Stratospheric Ozone Increases on Temperature and Circulation in the Stratosphere over the Arctic. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3447. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14143447
Hu D, Guan Z. Relative Effects of the Greenhouse Gases and Stratospheric Ozone Increases on Temperature and Circulation in the Stratosphere over the Arctic. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(14):3447. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14143447
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Dingzhu, and Zhaoyong Guan. 2022. "Relative Effects of the Greenhouse Gases and Stratospheric Ozone Increases on Temperature and Circulation in the Stratosphere over the Arctic" Remote Sensing 14, no. 14: 3447. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14143447
APA StyleHu, D., & Guan, Z. (2022). Relative Effects of the Greenhouse Gases and Stratospheric Ozone Increases on Temperature and Circulation in the Stratosphere over the Arctic. Remote Sensing, 14(14), 3447. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14143447






