Investigation of Atmospheric Dynamic and Thermodynamic Structures of Typhoon Sinlaku (2020) from High-Resolution Dropsonde and Two-Way Rawinsonde Measurements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
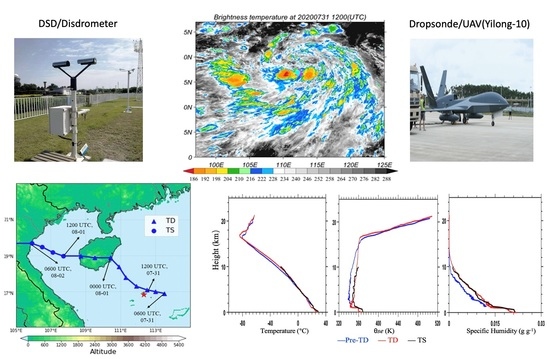
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
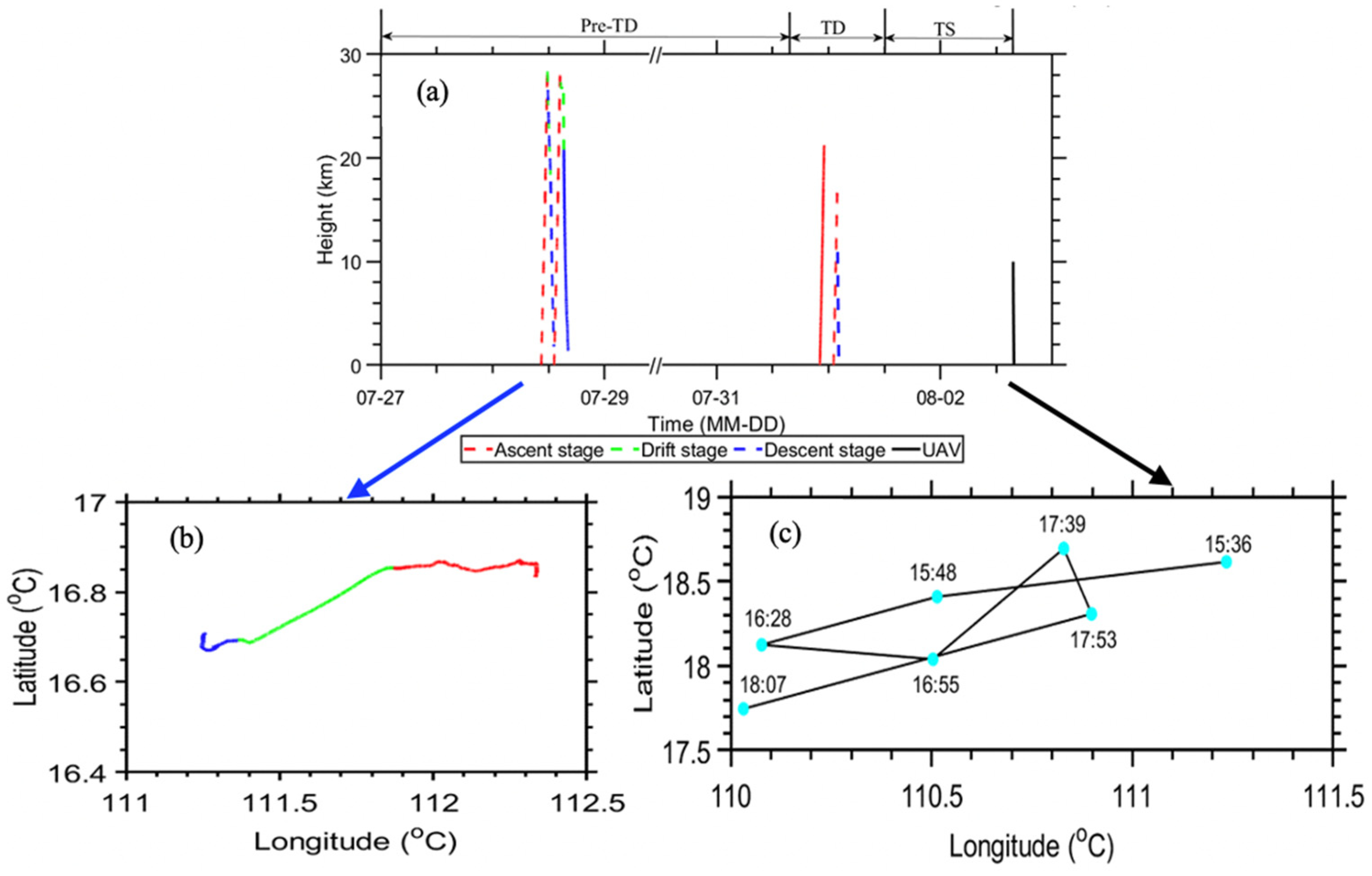
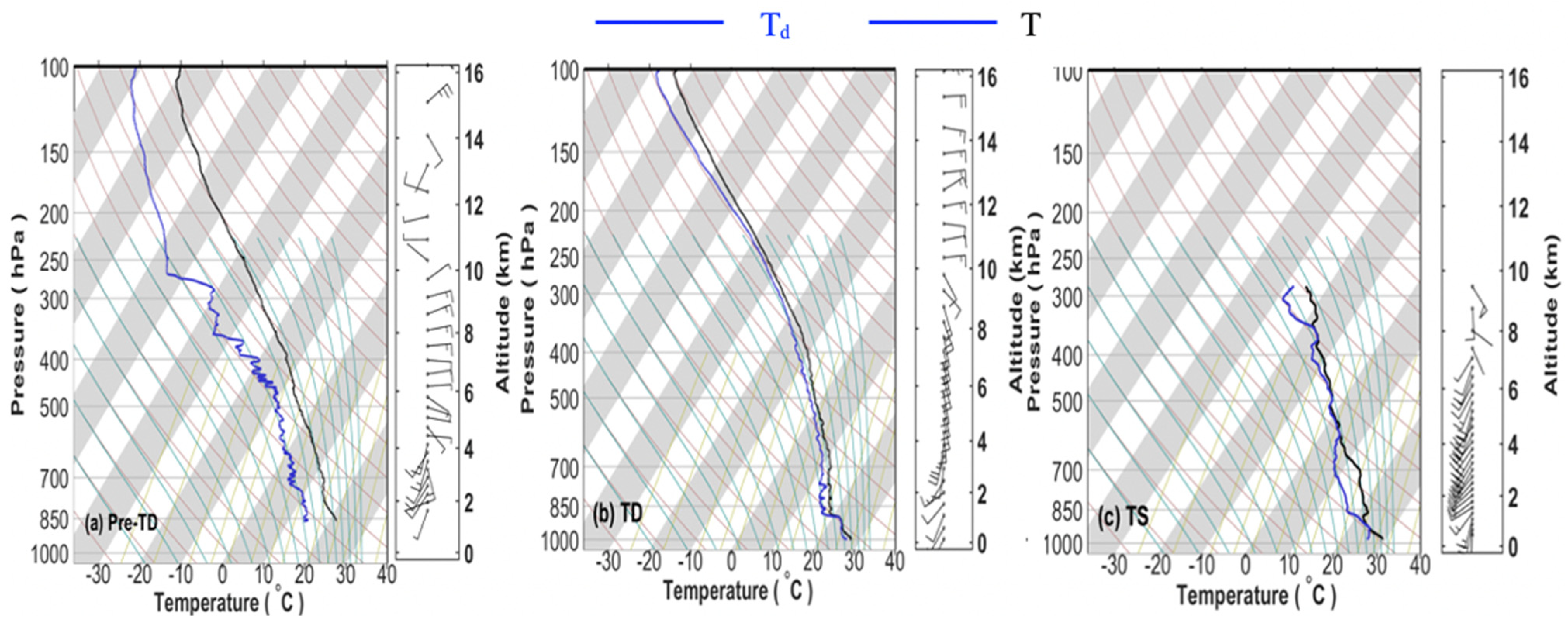
3.1. Determination of the Evolutionary Stages of Typhoon Sinlaku (2020)
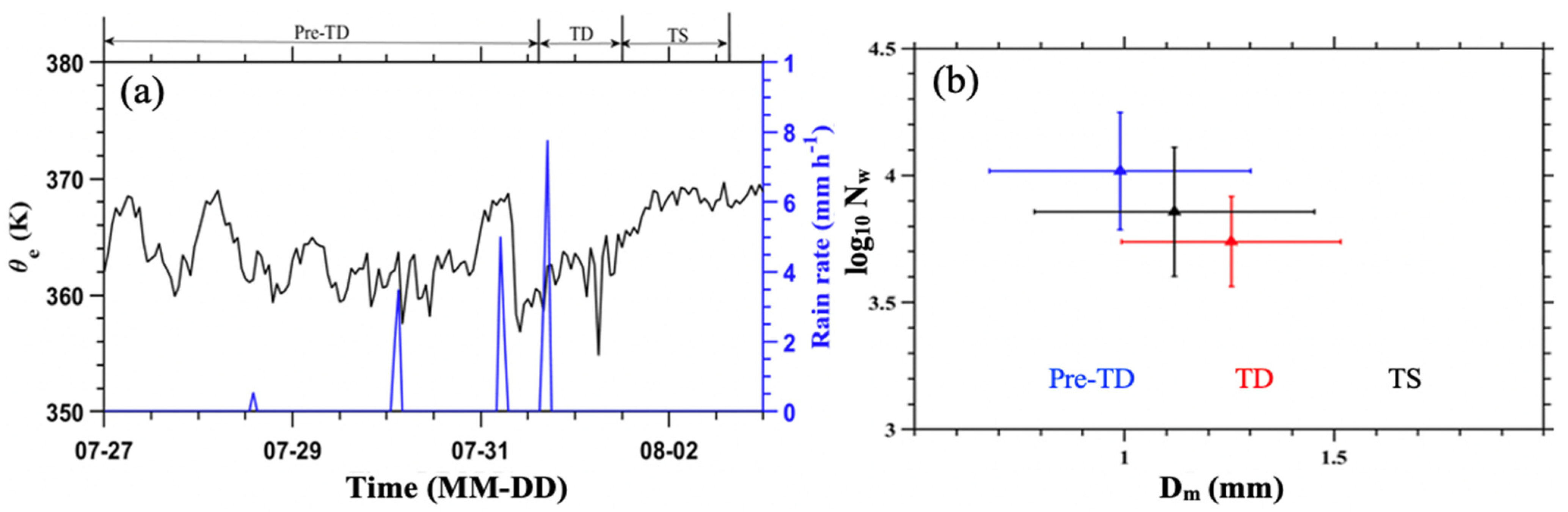
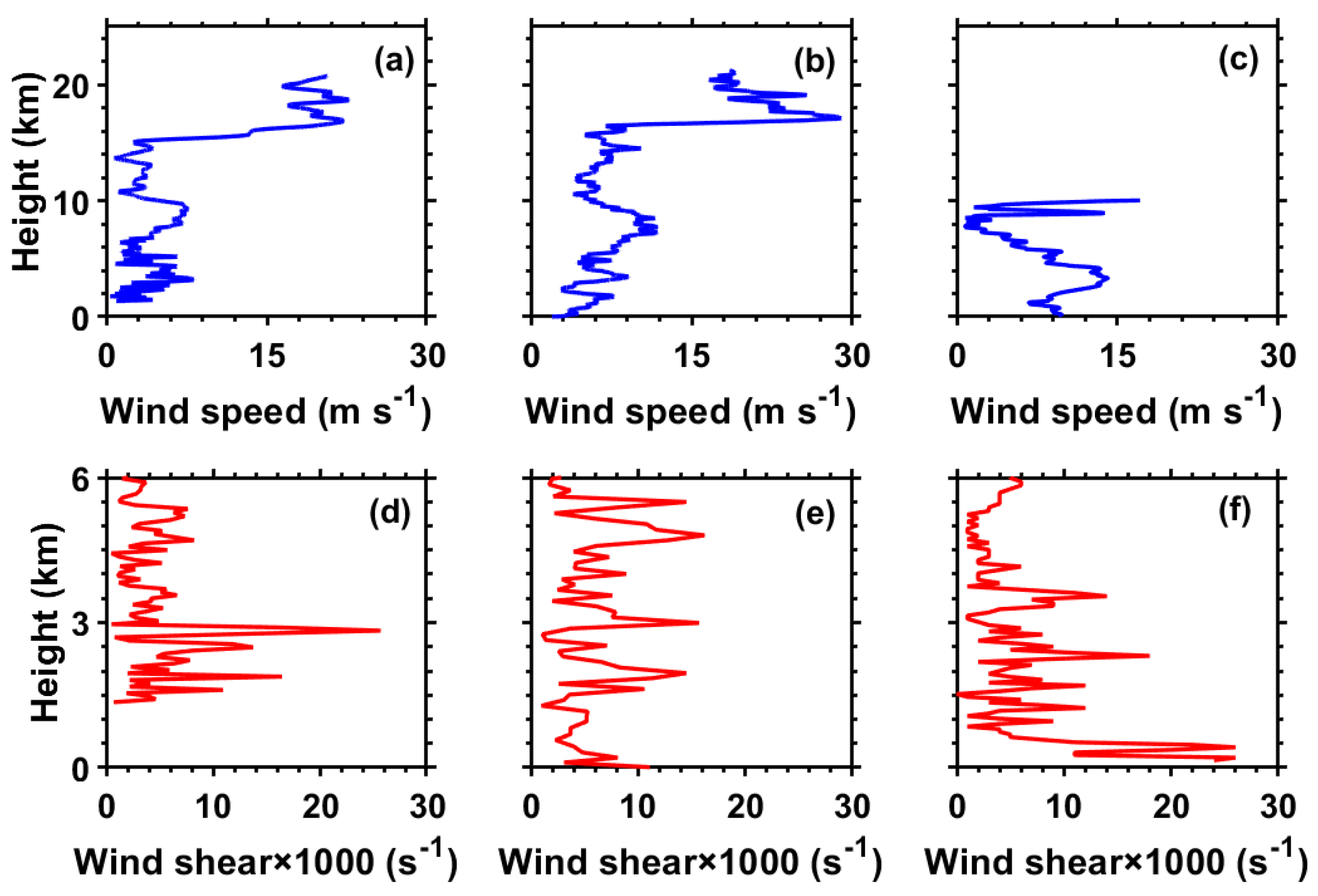
3.2. Atmospheric Profile Features for Different Evolutionary Stages of Typhoon Sinlaku (2020)
4. Discussion
5. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hendricks, E.A.; Montgomery, M.T.; Davis, C.A. The role of “vortical” hot towers in the formation of Tropical Cyclone Diana (1984). J. Atmos. Sci. 2004, 61, 1209–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tory, K.J.; Frank, W.M. Tropical cyclone formation. In Global Perspectives on Tropical Cyclones: From Science to Mitigation; World Scientific: Singapore, 2010; pp. 55–91. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, C.C. Current understanding of tropical cyclone structure and intensity changes—A review. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2004, 87, 257–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reason, C.J.C.; Keibel, A. Tropical cyclone Eline and its unusual penetration and impacts over the southern African mainland. Weather Forecast. 2004, 19, 789–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, M.; Chen, B.; Wu, G. Climate trends in tropical cyclone-induced wind and precipitation over mainland China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chu, P.C.; Cheng, K.F. South China Sea wave characteristics during Typhoon Muifa passage in winter 2004. J. Ocean. 2008, 64, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, M.; Onyejuruwa, A.; Wang, Y.; Wen, S.; Gao, A.E.; Li, Y. Tropical cyclone damages in Mainland China over 2005–2016: Losses analysis and implications. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2019, 21, 3077–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noji, E.K. Natural disasters. Crit. Care Clin. 1991, 7, 271–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peduzzi, P.; Chatenoux, B.; Dao, Q.-H.; De Bono, A.; Herold, C.; Kossin, J.; Mouton, F.; Nordbeck, O. Global trends in tropical cyclone risk. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, P.J. Understanding and forecasting tropical cyclone intensity change with the Typhoon Intensity Prediction Scheme (TIPS). Weather Forecast. 1997, 12, 826–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaff, J.A.; Sampson, C.R.; DeMaria, M. An operational statistical typhoon intensity prediction scheme for the western North Pacific. Weather Forecast. 2005, 20, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dvorak, V.F. Tropical cyclone intensity analysis and forecasting from satellite imagery. Mon. Weather Rev. 1975, 103, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Fu, B.; Ge, X.; Wang, B.; Peng, M. Satellite data analysis and numerical simulation of tropical cyclone formation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeMaria, M.; Sampson, C.R.; Knaff, J.A.; Musgrave, K.D. Is tropical cyclone intensity guidance improving? Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halverson, J.B.; Simpson, J.; Heymsfield, G.; Pierce, H.; Hock, T.; Ritchie, L. Warm core structure of Hurricane Erin diagnosed from high altitude dropsondes during CAMEX-4. J. Atmos. Sci. 2006, 63, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Su, J.; Ding, Y.; Chen, D. Tropical cyclone genesis over the South China Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2007, 68, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, J.D.; Irish, J.L.; Camargo, S.J. Coastal flooding by tropical cyclones and sea-level rise. Nature 2013, 504, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mitsuta, Y.; Fujii, T. Analysis and synthesis of typhoon wind pattern over Japan. Bull. Disast. Prev. Res. Inst. 1987, 37, 169–185. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Z.; Xiao, S.-G.; Hao, Y.-Q.; Zhang, D.-H. Morphological features of ionospheric response to typhoon. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phy. 2007, 112, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frank, W.M. The structure and energetics of the tropical cyclone I. Storm structure. Mon. Weather Rev. 1977, 105, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kepert, J.D. Observed boundary layer wind structure and balance in the hurricane core. Part I: Hurricane Georges. J. Atmos. Sci. 2006, 63, 2169–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodge, P.; Burpee, R.W.; Marks, F.D., Jr. The kinematic structure of a hurricane with sea level pressure less than 900 mb. Mon. Weather. Rev. 1999, 127, 987–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yan, J.; Wang, Q. A comprehensive analysis of the spiral structure features of typhoon Utor (2001). J. Trop. Meteor. 2007, 23, 365–375. [Google Scholar]
- Raymond, D.J.; Sessions, S.L.; López Carrillo, C. Thermodynamics of tropical cyclogenesis in the northwest Pacific. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, J.C.L. Decadal variations of intense typhoon occurrence in the western North Pacific. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2008, 464, 249–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Fu, B. Tropical cyclogenesis associated with Rossby wave energy dispersion of a preexisting typhoon. Part I: Satellite data analyses. J. Atmos. Sci. 2006, 63, 1377–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Houze, R.A., Jr.; Chen, S.S.; Smull, B.F.; Lee, W.C.; Bell, M.M. Hurricane intensity and eyewall replacement. Science 2007, 315, 1235–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Powell, M.D.; Murillo, S.; Dodge, P.; Uhlhorn, E.; Gamache, J.; Cardone, V.; Cox, A.; Otero, S.; Carrasco, N.; Annane, B.; et al. Reconstruction of Hurricane Katrina’s wind fields for storm surge and wave hindcasting. Ocean Eng. 2010, 37, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, S. Observational aspects including weather radar for tropical cyclone monitoring. Mausam 2013, 64, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fudeyasu, H.; Ito, K.; Miyamoto, Y. Characteristics of tropical cyclone rapid intensification over the western North Pacific. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 8917–8930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieper, M.E.; Jiang, H. Predicting tropical cyclone rapid intensification using the 37 GHz ring pattern identified from passive microwave measurements. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rogers, R. Convective-scale structure and evolution during a high-resolution simulation of tropical cyclone rapid intensification. J. Atmos. Sci. 2010, 67, 44–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Molinari, J. Rapid intensification of a sheared, fast-moving hurricane over the Gulf Stream. Mon. Weath Rev. 2013, 140, 3361–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Li, Y.; Cohen, J.; Li, J.; Chen, D.; Xu, H.; Liu, L.; Yin, J.; Hu, K.; Zhai, P. Shift in the temporal trend of boundary layer height trend in China using long-term (1979–2016) radiosonde data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 6080–6089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, J.; Cao, L.; Chen, T.; Wang, D.; Chen, D.; Han, Y.; Guo, X.; Xu, H.; et al. Spatiotemporal characteristics of atmospheric turbulence over China estimated using operational high-resolution soundings. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 054050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chan, P.; Wu, N.; Huang, Y.; Hon, K. The impact of dropsonde data on a numerical simulation of landfalling Typhoon Mangkhut. Meteorol. Appl. 2020, 27, e1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, R.; Barnes, G.M. Low-level kinematic, thermodynamic, and reflectivity fields associated with Hurricane Bonnie (1998) at landfall. Mon. Weather Rev. 2005, 133, 3243–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, K.H.; Wu, C.C. Typhoon initialization in a mesoscale model—Combination of the bogused vortex and the dropwindsonde data in DOTSTAR. Mon. Weather Rev. 2008, 136, 865–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ito, K.; Yamada, H.; Yamaguchi, M.; Nakazawa, T.; Nagahama, N.; Shimizu, K.; Ohigashi, T.; Shinoda, T.; Tsuboki, K. Analysis and forecast using dropsonde data from the inner-core region of Tropical Cyclone Lan (2017) obtained during the first aircraft missions of T-PARCII. SOLA 2018, 14, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Young, K.; Hock, T.; Lauritsen, D.; Behringer, D.; Black, M.; Black, P.G.; Franklin, J.; Halverson, J.; Molinari, J.; et al. A Long-Term, High-Quality, High-Vertical-Resolution GPS Dropsonde Dataset for Hurricane and Other Studies. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 961–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamada, H.; Ito, K.; Tsuboki, K.; Shinoda, T.; Ohigashi, T.; Yamaguchi, M.; Nakazawa, T.; Nagahama, N.; Shimizu, K. The Double Warm-Core Structure of Typhoon Lan (2017) as Observed through the First Japanese Eyewall-Penetrating Aircraft Reconnaissance. J. Meteorol. Soc. Japan Ser. II 2021, 99, 1297–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, S.; Ito, K.; Yamada, H.; Tsujino, S.; Tsuboki, K.; Wu, C. Deep Eye Clouds in Tropical Cyclone Trami (2018) during T-PARCII Dropsonde Observations. J. Atmos. Sci. 2022, 79, 683–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X. Overview of the development history of China’s typhoon research and operational work in the past century. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2020, 63, 362–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.Y.; Shu, Z.R.; Li, Q.S.; Chan, P.W.; Hon, K.K.; He, Y.C. Field measurements of Tropical Storm Aere (1619) via airborne GPS-dropsondes over the South China Sea. Meteorol. Appl. 2020, 27, e1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.W.; Wu, N.G.; Zhang, C.Z.; Deng, W.J.; Hon, K.K. The first complete dropsonde observation of a tropical cyclone over the South China Sea by the Hong Kong Observatory. Weather 2018, 73, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langland, R.H.; Toth, Z.; Gelaro, R.; Szunyogh, I.; Shapiro, M.A.; Majumdar, S.J.; Morss, R.E.; Rohaly, G.D.; Velden, C.; Bond, N.; et al. The North Pacific Experiment (NORPEX-98): Targeted observations for improved North American weather forecasts. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1999, 80, 1363–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szunyogh, I.; Toth, Z.; Morss, R.E.; Majumdar, S.J.; Etherton, B.J.; Bishop, C.H. The effect of targeted dropsonde observations during the 1999 Winter Storm Reconnaissance Program. Mon. Weather Rev. 2000, 128, 3520–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szunyogh, I.; Toth, Z.; Zimin, A.V.; Majumdar, S.J.; Persson, A. Propagation of the effect of targeted observations: The 2000 Winter Storm Reconnaissance Program. Mon. Weather Rev. 2002, 130, 1144–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aberson, S.D. Targeted observations to improve operational tropical cyclone track forecast guidance. Mon. Weather Rev. 2003, 131, 1613–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnisch, F.; Weissmann, M. Sensitivity of typhoon forecasts to different subsets of targeted dropsonde observations. Mon. Weather Rev. 2010, 138, 2664–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montgomery, M.T.; Bell, M.M.; Aberson, S.D.; Black, M.L. Hurricane ISABEL (2003): New insights into the physicas of intense storms. Part I: Mean vortex structure and maximum intensity estimates. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2006, 87, 1335–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.A.; Cione, J.J.; Kalina, E.A.; Uhlhorn, E.W.; Hock, T.; Smith, J.A. Observations of infrared sea surface temperature and air–sea interaction in Hurricane Edouard (2014) using GPS dropsondes. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2017, 34, 1333–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weatherford, C.L.; Gray, W.M. Typhoon structure as revealed by aircraft reconnaissance. Part I: Data analysis a, wind climatology. Mon. Weather Rev. 1988, 116, 1032–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marks, F.D.; Shay, L.K.; Barnes, G.; Black, P.; Demaria, M.; McCaul, B.; Mounari, J.; Montgomery, M.; Powell, M.; Smith, J.D.; et al. Landfalling tropical cyclones: Forecast problems and associated research opportunities. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 305–323. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, B.Y.J.; Kim, H.; Zhang, F.; Wu, C.-C. Effect of targeted dropsonde observations and best track data on the track forecasts of Typhoon Sinlaku (2008) using an ensemble Kalman filter. Tellus A Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 2012, 64, 14984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, J.; He, W.; Ma, S.; Wei, Y.; Pan, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hu, S. IAP’s Solar-Powered Unmanned Surface Vehicle Actively Passes through the Center of Typhoon Sinlaku (2020). Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 38, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, D.J.; Zhang, Y.; Beljaars, A.; Golaz, J.C.; Jacobson, A.R.; Medeiros, B. Climatology of the planetary boundary layer over the continental United States and Europe. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D17106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Chen, X.; Su, T.; Liu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, D.; Li, J.; Xu, H.; Lv, Y.; He, B.; et al. The climatology of lower tropospheric temperature inversions in China from radiosonde measurements: Roles of black carbon, local meteorology, and large-scale subsidence. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 9327–9350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; He, J.; Lou, M.; Yan, Y.; Bian, L.; et al. The climatology of planetary boundary layer height in China derived from radiosonde and reanalysis data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 13309–13319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, K.; Liao, H.; Zhang, S.; Huang, K.; Lv, Y.; Shao, J.; Yu, T.; Tong, B.; et al. Investigation of near-global daytime boundary layer height using high-resolution radiosondes: First results and comparison with ERA-5, MERRA-2, JRA-55, and NCEP-2 reanalyses. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 17079–17097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, J.; Zhang, S.; Shao, J. Inertia-gravity wave energy and instability drive turbulence, evidence from a near-global high-resolution radiosonde dataset. Clim. Dyn. 2022, 58, 2927–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Yang, R.; Guo, R.; Sun, X.; Luo, J.; Chen, H.; Liu, D.; Tang, K.; Peng, W.; et al. Comprehensive Marine Observing Experiment Based on High-Altitude Large Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (South China Sea Experiment 2020 of the “Petrel Project”). Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 38, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessho, K.; Date, K.; Hayashi, M.; Ikeda, A.; Imai, T.; Inoue, H.; Kumagai, Y.; Miyakawa, T.; Murata, H.; Ohno, T.; et al. An introduction to Himawari-8/9—Japan’s new-generation geostationary meteorological satellites. J. Meteorol. Soc. Japan. Ser. II 2016, 94, 151–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, D.; Guo, J.; Yao, D.; Lin, Y.; Zhao, C.; Min, M.; Xu, H.; Liu, L.; Huang, X.; Chen, T.; et al. Mesoscale convective systems in East Asia from Advanced Himawari Imager: Algorithms and preliminary results. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 2210–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ying, M.; Zhang, W.; Yu, H.; Lu, X.; Feng, J.; Fan, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, D. An overview of the China Meteorological Administration tropical cyclone database. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol. 2014, 31, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, X.Q.; Yu, H.; Ying, M.; Zhao, B.K.; Zhang, S.; Lin, L.M.; Bai, L.N.; Wan, R.J. Western North Pacific tropical cyclone database created by the China Meteorological Administration. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 38, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Krejci, R.; Giangrande, S.; Kuang, C.; Barbosa, H.M.; Brito, J.; Carbone, S.; Chi, X.; Comstock, J.; Ditas, F.; et al. Amazon boundary layer aerosol concentration sustained by vertical transport during rainfall. Nature 2016, 539, 416–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.H.; Kim, B.M.; Kim, K.Y.; Song, H.J.; Lim, G.H. The impact of the diurnal cycle on the MJO over the Maritime Continent: A modeling study assimilating TRMM rain rate into global analysis. Clim. Dyn. 2013, 40, 893–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Guo, J.; Yun, Y.; Li, J.; Guo, X.; Lv, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y. Regional variability of summertime raindrop size distribution from a network of disdrometers in Beijing. Atmos. Res. 2021, 257, 105591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Zhao, K.; Chen, G.; Wang, M.; Zhou, B.; Huang, H.; Hu, D.; Lee, W.-C.; Hu, H. Drop size distribution characteristics of seven typhoons in China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 123, 6529–6548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, J.L.; Black, M.L.; Valde, K. GPS dropwindsonde wind profiles in hurricanes and their operational implications. Weather Forecast. 2003, 18, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, D.P.; Zhang, F. How does the eye warm? Part II: Sensitivity to vertical wind shear and a trajectory analysis. J. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 70, 1849–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwood, S.C.; Roca, R.; Weckwerth, T.M.; Andronova, N.G. Tropospheric water vapor, convection, and climate. Rev. Geophys. 2010, 48, RG2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takemi, T. Impacts of global warming on extreme rainfall of a slow-moving typhoon: A case study for Typhoon Talas (2011). SOLA 2019, 15, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Yang, Q.; Yang, X.; Zhao, D. Changes in the tropopause height induced by landing typhoons in China during the last 50 years. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2013, 14, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.W.; Wilczak, J.M.; Choi, J.K.; Kantha, L.H. Numerical simulations of air–sea interaction under high wind conditions using a coupled model: A study of hurricane development. Mon. Weather Rev. 2000, 128, 2190–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Vortex Rossby waves in a numerically simulated tropical cyclone. Part I: Overall structure, potential vorticity, and kinetic energy budgets. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 1213–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.D.; Ming, J.; Wang, Y. Analysis of dynamic and thermodynamic structural characteristics of the super typhoon Jangmi (2008) using dropsonde data. Chin. J. Geophys. 2019, 62, 825–835. [Google Scholar]



| Date | Ascent Stage | Drift Stage | Descent Stage | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Start Time | Finish Time | Number of Samples | Start Time | Finish Time | Number of Samples | Start Time | Finish Time | Number of Samples | |
| 28 July | 10:27 | 11:45 | 4096 | 11:45 | 12:28 | 2573 | 11:51 | 13:09 | 4569 |
| 28 July | 13:11 | 14:36 | 5077 | 14:36 | 15:17 | 2484 | 15:17 | 16:12 | 3268 |
| 31 August | 22:09 | 23:05 | 3340 | ||||||
| 1 August | 01:06 | 01:52 | 2811 | 01:59 | 02:24 | 907 | |||
| Unmanned Aerial Vehicle | Start Time (hh:mm) | Finish Time (hh:mm) | Number of Dropsondes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leg I | 15:50 | 18:17 | 8 |
| Leg II | 15:38 | 18:01 | 10 |
| Leg III | 15:36 | 18:10 | 7 |
| Leg IV | 16:57 | 18:04 | 4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, L.; Han, Y.; Xia, Y.; Guo, Q.; Gao, W.; Guo, J. Investigation of Atmospheric Dynamic and Thermodynamic Structures of Typhoon Sinlaku (2020) from High-Resolution Dropsonde and Two-Way Rawinsonde Measurements. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2704. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14112704
Liu L, Han Y, Xia Y, Guo Q, Gao W, Guo J. Investigation of Atmospheric Dynamic and Thermodynamic Structures of Typhoon Sinlaku (2020) from High-Resolution Dropsonde and Two-Way Rawinsonde Measurements. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(11):2704. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14112704
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Lihui, Yi Han, Yuancai Xia, Qiyun Guo, Wenhua Gao, and Jianping Guo. 2022. "Investigation of Atmospheric Dynamic and Thermodynamic Structures of Typhoon Sinlaku (2020) from High-Resolution Dropsonde and Two-Way Rawinsonde Measurements" Remote Sensing 14, no. 11: 2704. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14112704
APA StyleLiu, L., Han, Y., Xia, Y., Guo, Q., Gao, W., & Guo, J. (2022). Investigation of Atmospheric Dynamic and Thermodynamic Structures of Typhoon Sinlaku (2020) from High-Resolution Dropsonde and Two-Way Rawinsonde Measurements. Remote Sensing, 14(11), 2704. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14112704