Abstract
One recent trend in optical remote sensing is to increase observation frequencies. However, there are still challenges on the night side when sunlight is not available. Due to their powerful capabilities in low-light sensing, nightlight satellite sensors have been deployed to capture nightscapes of Earth from space, observing anthropomorphic and natural activities at night. To date, the mainstream of nightlight remote sensing applications has mainly focused on artificial lights, especially within cities or self-luminous bodies, such as fisheries, oil, offshore rigs, etc. Observations taken under moonlight are often discarded or corrected to reduce lunar effects. Some researchers have discussed the possibility of using moonlight as a useful illuminating source at night for the detection of nocturnal features on Earth, but no quantitative analysis has been reported so far. This study aims to systematically evaluate the potential of moonlight remote sensing with mono-spectral Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite/Day-Night-Band (VIIRS/DNB) imagery and multi-spectral photos taken by astronauts from the International Space Station (ISS), as well as unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) night-time imagery. Using the VIIRS/DNB, ISS and UAV moonlight images, the possibilities of the moonlight remote sensing were first discussed. Then, the VIIRS/DNB, ISS, UAV images were classified over different non-self-lighting land surfaces to explore the potential of moonlight remote sensing. The overall accuracies (OA) and kappa coefficients are 79.80% and 0.45, 87.16% and 0.77, 91.49% and 0.85, respectively, indicating a capability to characterize land surface that is very similar to daytime remote sensing. Finally, the characteristics of current moonlight remote sensing are discussed in terms of bands, spatial resolutions, and sensors. The results confirm that moonlight remote sensing has huge potential for Earth observation, which will be of great importance to significantly increase the temporal coverage of optical remote sensing during the whole diurnal cycle. Based on these discussions, we further examined requirements for next-generation nightlight remote sensing satellite sensors.
1. Introduction
One recent trend in optical remote sensing is to increase observation frequencies to meet the urgent need for effectively monitoring of ephemeral events or phenomena on Earth from space. For example, Sentinel 2 can revisit the Earth every 10 days at the equator with one satellite, but 5 days with 2 satellites under cloud-free conditions, which results in 2–3 days revisiting time at mid-latitudes [1]. MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) sensors can visit the entire Earth surface twice a day through the constellation of Terra and Aqua, and commercial small or nano-satellite constellations, such as Jilin-1 [2] and Planet Labs’ Dove [3], enable even higher observation frequencies of up to hours. Increasing the number of satellites can surely help to increase the temporal resolution of remote sensing observations, but there are still challenges at the night side, when there is no sunlight available to illuminate the Earth surface. Such a situation can be even worse in the polar regions, where sunlight is not available for almost half the year [4].
Diurnality is a common ephemeral phenomenon, frequently observed in many animals, plants, as well as some natural processes. For example, many animals’ daily activities strictly depend on sunlight, and they are active during the day and sleeping at night or vice versa. Natural plants use photosynthesis to convert light energy into chemical energy during the day and uptake and transport of water through the process of transpiration at night. The ocean temperature often shows differences during the day and night cycles, mainly caused by the influences of the sun [5,6,7,8]. Diurnality (circadian rhythms for organisms) are mainly caused by day and night cycles, driven by Earth revolving both around the sun and on its own axis. Lunar rhythms are also embedded in the life cycles of many organisms. Fluctuating light levels reflected by the Moon also have a startling impact on life on Earth. For example, some animals prefer to live by the light of the Moon. For many animals, particularly birds, the Moon is essential to migration and navigation [9,10]. In addition, although coral reproduction is affected by weather, water temperature and other factors, it is also found that most corals choose to spawn during or near a full moon [11].
Human beings used to be a member of the diurnal club. During our early history, human activities at night were also greatly confined until they learned how to use fire to light up their living spaces. Artificial illumination thus has been allowing human beings to break through its natural diurnality so their social, cultural, and economic activities can extend into night, creating cities and a night-time economy [12]. Nowadays, lighting is essential for human beings, first for convenience and for safety. Artificial nightlight is thus an important and reliable indicator of human activities, directly at night and indirectly during daytime. The artificial illumination of buildings, transportation corridors, parking lots, and other elements of the built environment have become a hallmark of many contemporary urban settlements and urban activities [13].
With the advent of low-light detecting technologies, nightlight remote sensing makes it possible to detect artificial lights from space, forming a convenient and powerful tool to characterize and understand human being’s altered diurnality. Since the first night-time light scene was captured using the operational linescan system (OLS) aboard Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) satellites, detecting artificial light has become the main staple of nightlight remote sensing. Since then, whether it is mono-spectral (Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite/Day-Night-Band (VIIRS/DNB), Scientific Application Satellite-C High Sensitivity Technological Camera (SAC-C HSTC), Scientific Application Satellite-D High Sensitivity Camera (SAC-D HSC), CubeSat Multispectral Observing System (CUMULOS), Luojia1-01 (LJ 1-01), Earth Remote Observation System-B (EROS-B) or multi-spectral (Aerocube 4, International Space Station (ISS), Aerocube 5, Landsat-8, Jilin-1), new sensors have been developed with the main focus of detecting and identifying self-luminous objects at night [14].
Applications using these night-time remote sensing data include mapping urban areas [15,16,17,18,19], estimating population, GDP, and poverty [20,21,22,23], monitoring disasters and conflicts [24,25,26], as well as understanding the influence of light pollution [10,27,28,29]. These studies often focus on urban lights or self-luminous bodies, such as fisheries, oil, gas extraction, etc., with very few exploring the potential of nightlight remote sensing data to study natural processes.
Ironically, it seems to have long been ignored that the original purpose of DMSP/OLS was to detect clouds under moonlight illumination [30]. Although moonlight has been an important factor that affect many nocturnal animals and plants, mainstream nightlight remote sensing image processes either try their best to totally avoid moonlight, or to remove the moonlight component from observations with tuned algorithms. For example, to generate annual DMSP/OLS composites, only sunlit and moonlight-free observations have been used, and moonlit observations are simply discarded [31]. To produce the VIIRS/DNB daily black marble product, an algorithm was developed to remove moonlight components from daily nightlight observations [32].
With the recent development of low-light detection technology, the nightlight remote sensing community started to realize that moonlight can be a very useful illumination source for detecting weather and climate parameters at night, instead of being treated as a noise source for city light detection [33,34]. Miller et al. [4] made a detailed insight of many potential applications for nocturnal low-light visible satellite observations and presented a long list of key variables that could be obtained under moonlight using VIIRS/DNB from space. They found that sometimes night-time moonlight remote sensing even showed advantages over the daytime sunlight remote sensing. These include the detection of snow cover, rainfall distributions across arid/semi-arid surfaces, the ability to peer through optically thin clouds to reveal sea ice, and the detection of oceanic currents, etc. Although these studies demonstrated a comprehensive potential for night-time low-light measurements, quantitative assessment is still needed.
How to quantitatively assess the potential of moonlight remote sensing needs a thorough investigation and more questions must be addressed. Currently, there exist many different satellite sensors, as mentioned above, with different characteristics in terms of spectra and spatial resolutions. Furthermore, drones, as a new near-ground remote-sensing platform, also have great potential to study changes in lighting at night [14]. These sensors have not been discussed for Earth observation under moonlight, thus, it is of great significance to analyze and compare them in the context of radiometric correction of nightlight remote sensing data and for the design of next generation night-time sensors. Another important question is the quantitative characterization of non-self-lighting objects under night-time low-light environments, considering that there is no rigorous quantitative analysis to date, such as land cover classification under moonlight lighting conditions.
We first compare the differences in night-time observations under moonlight using different sensors, the mono-spectral VIIRS/DNB night-time image, the multi-spectral night-time photos taken by astronauts from the International Space Station, and UAVs. We then explore the potential of nightlight remote sensing through land cover classification under night-time low-light conditions, with a specific focus on detecting non-self-lighting features at night. Finally, we propose a new concept of nightlight remote sensing—moonlight remote sensing, which uses moonlight as a stable lighting source to observe the Earth’s surface, and which focuses on night-time remote sensing mechanisms and applications under lunar illumination. With these distinct characteristics, moonlight remote sensing is different than traditional nightlight remote sensing, as well as from daytime optical remote sensing.
2. Study Area and Data
The potentiality of moonlight remote sensing in this study was evaluated using two ISS multi-spectral moonlight images, acquired on 24 December 2010 and 28 November 2015; UAV moonlight imagery acquired on 20 June 2021; and VIIRS/DNB imagery acquired on 1 November 2015 (with a full moon). These images with different spatial and spectral resolutions covered three regions, Calgary in Canada, Komsomolsk-on-Amur in Russia, and a small part of the Guangming District, in Shenzhen, China. The Calgary images cover a land area of about 825.56 km2, located in the south of Alberta, Canada. Calgary is the fourth largest city in Canada and is one of the most livable cities in North America in both 2018 and 2019 and has high living standards. This region has a temperate continental climate, warm in summer, cold and dry in winter, and with four distinctive seasons [35,36]. Komsomolsk-on-Amur is a city in Khabarovsk Krai, Russia, located on the west bank of the Amur River in the Russian Far East, characterized by a humid continental climate. There is a long period of snow and ice coverage because of the high latitude [37]. The Guangming District, a recently developed area in Shenzhen, has been planned as the Shenzhen Science City in recent years and is one of the core areas for the construction of a comprehensive national science center in the Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Bay Area. After more than 40 years of reform and opening, the urbanization process of Shenzhen has reached a high-level with rapid economic and social development [38].
Figure 1 shows these three regions and the corresponding nightlight imagery, including information of sensor parameters. These parameters include spacecraft nadir points and altitudes, UAV height, moon altitudes, azimuths, and illumination, as well as cloud cover percentages. In addition, local times when the images were captured were also recorded. The ISS imagery was taken with digital single-lens reflex (DSLR) cameras since 2001, and was the first dataset providing colorful space-borne nightlight images with moderate spatial resolutions (often between 5 m and 200 m). The true-color images in this study were taken with Nikon D3S and D4 DSLR cameras. Both the Nikon D3S and Nikon D4 DSLR cameras were equipped with a Bayer filter in front of the sensor, and were comprised of red (R), green (G), and blue (B) microfilters. The focal lengths of the Nikon DSLR cameras in this study were 180 mm and 400 mm, respectively. These sensors, mounted on a specially designed device to compensate for the movement of the ISS, can take multi-spectral images in visible wavelengths, making it capable of detecting ground features under faint illumination from space [39,40,41,42]. In addition, a Hasselblad L1D-20c camera was mounted on a DJI MAVIC2 Pro UAV, with a focal length of 35 mm. Both Nikon and Hasselblad cameras are equipped with complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) sensors. VIIRS is a temperature-controlled charge coupled device (CCD) sensor, and is one of the key instruments aboard the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership (S-NPP) satellite. It is a passive whiskbroom scanning imaging spectroradiometer, taking measurements from 0.4 to 12.2 μm in 15 reflective solar bands (RSB), including a panchromatic DNB and seven thermal emissive bands [43]. VIIRS has gathered high-quality nightlight images since 28 October 2011, at a spatial resolution of 750 m and in a broad band, covering the 500 to 900 nm spectral region for the DNB [44,45] (Table 1).
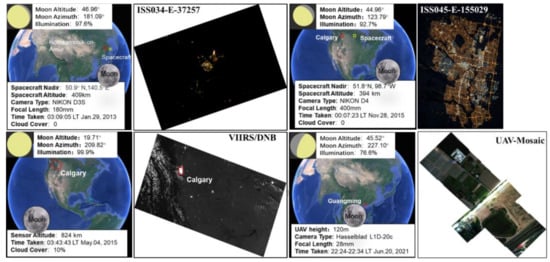
Figure 1.
Parameters of the moonlight remote sensing images in study areas.

Table 1.
Acquisition parameters of the moonlight imagery used in this study.
Since the ISS and UAV moonlight remote sensing images we obtained were not geo-referenced, we geometrically corrected them using Landsat-7/8 and SuperView-1 optical remote sensing data with accurate geo-referencing information. Moreover, the daytime Landsat-7/8 and Sentinel-2 and SuperView-1 optical remote sensing data were used as auxiliary data to examine the reliability of the moonlight remote sensing imagery. Landsat-7/8 and Sentinel-2 were accessed from the Google Earth Engine (GEE) platform [46], SuperView-1 constellation is China’s first commercial satellite constellation with high agility and multi-mode imaging capability(http://www.spacewillinfo.com/SuperView-1English/index.html#pos02 (accessed on 20 September 2021)).
3. Methodology
3.1. Assessment of the ISS Images
We quantitatively examined the potential of ISS imagery in land surface mapping at the current stage, with a specific focus on low-light suburban areas, through an image classification process. What must be pointed out here is that we did land surface mapping using the ISS imagery as a practical way to quantitatively assess the potential of moonlight remote sensing, considering the limitations of currently available data. The whole image classification process mainly consisted of four steps (Figure 2), the geometric correction, the thresholding method to distinguish the low-light suburban areas and the bright urban areas, the multi-resolution segmentation, and the final classification step with an object-oriented method and Random Forests (RF) algorithm.

Figure 2.
Scheme of the land surface classification with the ISS multi-spectral moonlight images.
3.1.1. Geometric Correction
The ISS moonlight images we obtained were not geo-referenced. We first carried out geometric correction for these images, using the Landsat-7/8 images that contain accurately geo-referenced information as the reference.
3.1.2. Retrieving the Low-Light Suburban Areas
Three different ISS image parts in the study areas were first selected to obtain the optimal thresholding values of brightness for separating bright urban areas and low-light suburban areas (Figure 3). We focused on only low-light suburban areas to avoid duplicating efforts, given that numerous studies have shown that ISS imagery is very useful to map lighting types and land surface within bright urban areas [45,47,48].

Figure 3.
Multi-spectral brightness values of transects of three different parts of the ISS nightlight scenes.
In the image of Calgary, the optimal thresholding values were found to be 35 for the red band, 30 for the yellow band, and 25 for the blue band, respectively. Areas with brightness values above these numbers are bright urban areas and the others are low-light suburban areas. Similarly, the optimal thresholding values in the Komsomolsk image were found to be 50 for the red band, 50 for the yellow band, and 45 for the blue band, respectively (Figure 4).

Figure 4.
The images of the Calgary and Komsomolsk-na-Amure after threshold segmentation.
3.1.3. Multi-Resolution Image Segmentation
We adopted an object-oriented image classification scheme, applying the multi-resolution segmentation algorithm on the ISS images first to delineate ground objects. Multi-resolution segmentation is an optimization procedure for minimizing the average heterogeneity and maximizing the homogeneity in a given number of image objects [49]. The multi-resolution segmentation scale parameter greatly influenced the segmentation results, and the optimal scale parameter is commonly determined using a heuristic process [50]. By setting different thresholds and combining real objects, results showed that there was a relatively large area of similar land parcels. The segmentation scales of the low-light areas in the ISS image after liner stretching were finally set to 50 for the Calgary image, and 40 for the Komsomolsk-na-Amure image, respectively.
3.1.4. Classification with the RF Algorithm
For low-light suburban areas, we chose three types of land surface, namely snowfields (Snow), trees/forests (Forest), and other types, city lights areas (Other types). We randomly selected 200 (100 samples for training, 100 samples for testing) and 160 (76 samples for training, 86 samples for testing) samples for the land-cover classification in the two study areas, respectively. Numerous classification methods, including decision trees (DTs), support vector machines (SVMs), and random forests (RFs), have been developed for land-type classification [51,52,53,54]. RF algorithms have been widely used in various studies due to their flexibility and practicality. Many studies have found that random forest algorithms could produce better results than DT and SVM algorithms [55]. Therefore, RF algorithms were adopted in this study for object-oriented classification on the ISS images. The multi-resolution image segmentation algorithm and RF algorithm implemented in eCognition Developer 64 9.01 software was used. Some key parameters of the entire procedure are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Parameters of the ISS image land surface classification.
3.2. Assessment of the UAV and VIIRS/DNB Images
As shown in Figure 1, we found that the UAV moonlight remote sensing mosaic eliminated the need for a linear stretching process to clearly distinguish the land surface features. Therefore, the whole image classification process mainly consisted of three steps, geometric correction, multi-resolution segmentation, and land surface classification using the RF algorithm. The coverage area of UAV moonlight remote sensing mosaic was relatively small, while each land surface type in the mosaic was too big, so that the multi-resolution segmentation in which the optimal segmentation scale was 200. We randomly selected 226 samples (113 samples for training, 113 samples for testing). Five different land surface classes (farmland, bare land, pond, vegetable greenhouses, and others) were used to map in this image.
Because the brightness ranges of VIIRS/DNB were small, numerical stretching (×1010) operations were performed on the entire image. Then, the image was also selected to obtain the optimal thresholding value (170.00 in this case) for separating the low-light suburban areas from the bright urban areas (Figure 5).

Figure 5.
The VIIRS/DNB image of Calgary before (left) and after (right, urban removed) linear preprocessing.
For the low-light suburban area, four types of land surface were selected, namely snowy mountains (Snow), farmlands (Farmland), rivers (River), as well as other types and city light areas (Other type). The optimal segmentation scale in the multi-resolution segmentation process was set as 20. We randomly selected 189 (93 samples for training, 96 samples for testing). Some parameters are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Parameters of the UAV and VIIRS/DNB image land surface classification.
4. Results
4.1. The Reliability of the Moonlight Remote Sensing Imagery
4.1.1. Visual Examination of the VIIRS/DNB Moonlight Image
Three types of moonlight imagery were used to assess the reliability of moonlight remote sensing. First, using the VIIRS/DNB image and Sentinel-2 mosaic (from 1 May 2015 to 31 December 2016) image on the Google Earth Engine platform (GEE), we first assessed the potential of multi-spectral data in land-surface classification under faint lunar illumination (Figure 6). Under a full moon and cloudless condition, the VIIRS/DNB data successfully obtained spatial distribution and spectral information of the land surface, such as snowy mountains, forests, farmlands, and rivers.

Figure 6.
Three cases of the VIIRS/DNB moonlight remote sensing and Sentinel-2 images. 1. snowy mountains, 2. forests, farmlands, and 3. rivers.
4.1.2. Visual Examination of the ISS Nightlight Imagery
Comparing the ISS imagery with the Landsat-7 optical remote sensing mosaic (1 January–31 March 2013, the limitations of Landsat-7 band strips and clouds) and the Google Earth imagery in low-light suburban areas of Komsomolsk-on-Amur, Russia (ISS034-E-37257), it is very obvious that the ISS nightlight imagery with three bands well captured the ground surface in the suburban area out of the city boundaries under faint lunar illumination, in addition to the bright urban areas with emitted lights (Figure 7). However, the ground was under heavy snow cover when the ISS photo was acquired, so distinguishing more surface types in the suburbs in this imagery is very difficult. To further check whether moonlight remote sensing images are valuable under faint lunar illumination, we selected three sub-areas (A, B, and C) with different brightness and colors in the ISS image, referenced to the Google Earth image taken in the daytime in summer. Part A is mainly covered by frigid coniferous forests, making it difficult to accumulate snow on tree crowns, due to the relatively high height of the trees, blowing winds, and the sunny sides of the mountains. Part B is almost fully covered by white snow, and in the ISS image it shows a bright blue color. Therefore, part B is much brighter than part A in the ISS image, even though it was under a similar faint lunar illumination. Part C is mainly located in the city of Komsomolsk, which is the brightest and most colorful part of the ISS image.

Figure 7.
The ISS nightlight image and Landsat-7 image of the Komsomolsk, Russia (above ISS and Landsat-7) and three sub-areas of the ISS nightlight image under faint lunar illumination with reference to the Google Earth images taken in summer daytime (below A, B and C).
4.1.3. Visual Examination of the UAV Moonlight Image
Finally, the spatial and spectral resolution features of the UAV moonlight remote-sensing images, obtained under a waxing gibbous moon and without any further image processing, are very vivid and comparable to the high-resolution optical images (SuperView-1) with a resolution of 1 m (Figure 8). More importantly, it is possible to obtain the same clear spatial distribution and texture characteristics of the ground surface as daytime optical remote sensing imagery, especially for non-self-lighting objects, such as fish ponds, bare ground, farmland, and even greenhouses. From part 1, although the timing of collecting data is different and the texture of the land surface changed, we could still clearly observe that both images clearly captured the spatial distribution and texture characteristics of farmland. Meanwhile, the characterization of water bodies and bare land is well reflected in the UAV moonlight remote sensing mosaic (Part2, Part3).

Figure 8.
Three cases of the UAV moonlight remote sensing image with reference to the high-resolution optical image (SuperView-1) taken on 17 December 2019.
In conclusion, it is now feasible to capture a non-self-lighting surface under weak lunar illumination at night.
4.2. Land Surface Classification Results
4.2.1. Result with the Mono-Spectral VIIRS/DNB Moonlight Image
The moonlight image of VIIRS/DNB was classified to systematically explore the potential of moonlight remote sensing. The overall accuracy (OA) and kappa coefficient are 79.80% and 0.45, respectively. From the confusion matrix table, although there are some misclassifications of snowy mountains and rivers, the results (Figure 9) still demonstrate a good performance of the mono-spectral moonlight remote sensing to characterize land surface in low-light areas under full moon illumination.

Figure 9.
The classification result obtained in the low-light areas of the VIIRS/DNB moonlight image.
4.2.2. Result with the Multi-Spectral ISS Moonlight Images
It is found that Calgary was covered by snow on 21 November and 27 November 2015. The snow-covered areas (Snow) and forests/trees (Forests) were accurately classified (Figure 10) with an overall accuracy of 87.16% and a kappa coefficient of 0.77. The classification results of the Komsomolsk-na-Amure imagery showed that the overall accuracy and kappa coefficients were 91.49% and 0.85, respectively (Figure 11). It is evident that moonlight remote sensing has tremendous potential in extracting land surfaces, such as snow-covered lands and forests, under faint lunar illumination in winter.

Figure 10.
The classification result in the low-light areas of the Calgary image.

Figure 11.
The classification result in the low-light areas of Komsomolsk-na-Amure.
Although astronauts aboard the ISS have taken numerous nightlight photos, we only found limited scenes with moonlight, mainly because their focus was on city lights. In the future, it would be very useful if astronauts aboard the ISS or China’s Tiangong space station in the near future could help to take photos while paying attention to moonlit areas that are apart from urban areas.
4.2.3. Results with the Multi-Spectral UAV Moonlight Image
Finally, land surface classification with the UAV moonlight image well reflected the spatial distribution characteristics of each land type (Figure 12). The overall accuracy and kappa coefficient are 82.33% and 0.77, respectively. While some parts of the results are misclassified because of similar spectral characteristics, such as ponds and farmlands, the results prove that UAV data taken under faint lunar illumination are useful for characterizing land surfaces, particularly those that cannot emit light.

Figure 12.
The classification result of the UAV moonlight mosaic.
The above results have shown that these moonlight remote-sensing data could be applied well to the classification of non-self-luminous land surfaces at night.
4.3. The Characteristics of Current Moonlight Remote Sensing
Finally, the characteristics of current moonlight remote sensing were compared in terms of bands, spatial resolutions, and sensors. The overall classification accuracy with the VIIIRS/DNB imagery was the lowest among the three sets of moonlight remote-sensing imagery. By comparing VIIRS/DNB with the Sentinel-2 images (Figure 13), there are many misclassifications of snowy mountains and rivers, possibly due to their similar backscatter values in the mono-spectral VIIRS/DNB image. The result is limited by the inadequate spectrum information and substantial noise in the mono-spectral data. Thereby, multi-spectral moonlight remote sensing is expected for Earth observations under complex environments at night.

Figure 13.
Comparison of snowy mountains from the VIIRS/DNB, Sentinel-2 and classification results.
In this study, three image sets with different resolutions (750 m, 30 m, 1 m) were analyzed. Comparing the classification parameters and results, we found that the higher the spatial resolutions were, the more details of the features in an image could be shown, and the UAV image showed unexpectedly vivid details that are even comparable to daytime high-resolution images. Even cars parked in parking lots could be clearly seen on the UAV moonlight image (Figure 14). However, the single-scene data only covered a small amount of land surface. To cover a larger area with more than one scene, the image quality of the multi-scene data could be reduced significantly. Small changes in georeferencing and the surrounding environment caused some land cover types to be misclassified.

Figure 14.
Cars in the UAV moonlight image acquired on 20 June 2021.
Finally, panchromatic VIIRS/DNB with a spectral coverage from 0.50 µm to 0.90 µm uses a unique detecting technology. DNB measures night lights, reflected solar, and/or moon light with a large dynamic range of 45,000,000:1, which allows the detection of reflected signals from as low as a quarter full moon illumination to the brightest daylight. To achieve this large dynamic range, it uses four charge coupled device (CCD) arrays in three gain stages.
As a comparison, consumer-level digital CMOS cameras from Nikon and Hasselblad are used to obtain land surface images under faint lunar illumination (Table 4). It was found that the further the imaging distances are, the larger the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) values are. The exposure time of the UAV imagery is the longest, while that of the ISS imagery is relatively short. The aperture value (AV) and white balance (WB) were F/2.8 and auto-adjustment, respectively. Compared with the VIIRS/DNB sensor, the cost of the UAV and ISS cameras were greatly reduced and they had additional advantages, such as more spectral bands (RGB color) and finer spatial resolutions. However, given the relatively long exposure time, it is impossible to apply a carpeting data acquisition mode to ISS cameras as what is currently implemented for VIIRS/DNB to collect land surface data without gaps under faint lunar illumination.

Table 4.
Parameters of different moonlight sensors.
5. Discussions
5.1. The Potential of Moonlight Remote Sensing to Increase Temporal Resolution
Undoubtedly, our study strongly demonstrates that moonlight remote sensing in the detection of non-self-emitting objects at night is feasible. For example, using either VIIRS/DNB or ISS moonlight data, moonlight remote sensing could be used to identify snow glaciers. In recent years, the continuous melting of glaciers has posed more serious problems for human habitats, as well as for climate change. Due to the limited night-time observation data, the melting rate of permanent glaciers at night has not been extensively studied [41,56,57]. Thus, there is a great potential for nightlight remote sensing in glacier studies.
Our findings further support calls for a newer generation of nightlight sensors [58,59], but also strongly suggest that attention should be paid to detecting reflected moonlight from land surface outside of urban areas. With advanced low light detecting capabilities, these sensors will help to fill the observation gaps on the night side of a full orbit cycle for optical satellites. Currently, Landsat and Sentinel-2 sensors apply a mechanism to shut down when the satellites enter the night side, leading to a huge waste of orbit resources.
To efficiently utilize moonlight as a useful remote sensing illuminating source, we must rely on the advent of light-sensing hardware technologies. As shown above, thanks to its improved sensitivity, VIIRS/DNB allows the detection of moonlit features out of urban areas. However, its band settings are still limited to a broad band and its spatial resolution is still relatively coarse (750 m), to guarantee enough light energy to be captured during a relatively short period of a single scan. The ISS and UAV sensors can capture photos in three bands and with finer spatial resolutions, but require much longer exposure times. These technical limitations are expected to be overcome soon with advancements in light-sensing hardware technology.
5.2. Technical Speculations for the New Generation of Nightlight Satellite Sensors
5.2.1. Spectral Resolution
Although, it is highly convincing that moonlight can be a very useful illuminating source for Earth observations via optical remote sensing. Our knowledge of utilizing moonlight for remote sensing purposes is still very limited. We have proposed some new views and ideas for future designs of nightlight satellite sensors. First, for detecting nightlight non-self-emitting objects, the current mono-spectral nightlight remote sensing data are very limited and more bands are required. We believe that the bands of future sensors must contain at least three bands in the visible range, as well as a near-infrared band (IR). With three bands, the ISS and UAV data can overcome the limitations of traditional mono-spectral VIIRS/DNB data [46,47,48]. Whether for urban lighting or light pollution, a single wide waveband is no longer able to meet our requirements. It has been discussed that the scotopic band from 0.454 to 0.549 mm, the photopic band from 0.51 to 0.61 mm, and a broad red and near-infrared band spanning from 0.61 to 0.9 mm are needed for future sensors. Additionally, IR bands are also needed to detect sodium vapor emission lines [57]. Combining the current experience of lightings in urban areas [58], the perspective of light pollution [59] and this study, the settings of a new generation of nightlight satellite mission should contain at least four-color channels in the visible light band (at 383–503, 493–619, 568–584, and 797–833 nm), and an additional ~10 µm thermal infrared band for cloud and fire detection.
5.2.2. Spatial Resolution
The optimal resolution settings of remote sensing sensors should be 30 m or 10 m, similar to those discussed in the Nightsat proposal [57]. The spatial resolution of UAV nightlight sensors and the Jilin-1 sensor are now able to achieve spatial resolutions finer than 1 m, which is significant for small-scale urban characterization, especially the extraction of street lights [60]. However, the higher the spatial resolution is, the smaller the field of view is. Based on previous analyses and discussions, we suggest setting the optimal resolution at 10 m or 30 m due to the following reasons: (1) there are now a large amount of daytime optical Landsat series and Sentinel-2 data, which could be well applied to both urban refinement mapping and global mapping; (2) traditional optical remote sensing, however, is not available for research with nightlight Earth observation; (3) nightlight imagery can be effectively combined with daytime optical imagery to increase the capability to characterize land surfaces [61,62]. Our future nocturnal and daytime optical data will be complementary, enabling more applications of circadian studies. Furthermore, setting similar spatial resolutions for both nightlight and daytime optical imagery will also reduce the burden of image processing.
5.2.3. Imaging Sensitivity Requirement
Both DMSP/OLS and VIIRS/DNB needed to apply the single wide spectral band strategy to gather as much light energy as possible during a single scan to increase the sensitivity. How to increase the number of bands and sensitivity at the same time might be a very large challenge for next generation nightlight remote sensing satellite sensors.
To face this challenge, ISS astronauts applied a specially designed tool to compensate the movement of the ISS to increase exposure time. However, such an imaging strategy obviously cannot take observations in a carpeting mode. That challenge is expected to be solved in the near future with the development of photo sensing materials and technology. On the other hand, the VIIRS DNB sensor is a temperature-controlled charge coupled device (CCD), provides global daily measurements in single nocturnal visible and near-infrared (NIR) band that is suitable for Earth system science and applications studies. One thing that must be pointed out is that VIIRS/DNB only has a mono-spectral band, which is still below the spectral band requirement for detecting all types of city lights with a diverse range of spectral characteristics. In addition, it takes 0.56 s for the instrument to scan across the width of the swath. During this time, the nadir point of the satellite moves 3.75 km (the satellite moves at ~6.7 km/s). In the future, if equipped with a multi-spectral sensor, how to maintain the same level of sensitivity with reduced light energy will be the primary problem to be solved.
6. Conclusions
Most nightlight remote-sensing studies focus on artificial lights that are emitted at night and can be observed from space, especially those of cities. Little attention has been paid to examine the potential use of reflected moonlight. The present study systematically evaluated the potential of moonlight remote sensing.
- (1)
- The reliability of the moonlight remote-sensing imagery.
Using VIIRS/DNB, ISS and UAV moonlight images, the possibilities of moonlight remote sensing were discussed. VIIRS/DNB data successfully acquired spatial distribution and spectral information of land surface, such as snowy mountains, forests, farmlands, and rivers. The ISS data successfully identified snow and forests in the wilderness. In addition, the spatial distribution and texture characteristics of the land surface could be obtained as clearly as optical data in the daytime, especially for the observation of non-self-luminous objects, such as fish ponds, bare land, farmland, and even greenhouses. Therefore, it is believable that moonlight remote sensing is feasible for obtaining non-luminous land surfaces under faint lunar illumination at night, providing a practical way to increase observation frequencies of optical remote sensing.
- (2)
- Land surface classification of moonlight remote-sensing imagery.
VIIRS/DNB, ISS, UAV images were classified to explore the potential of moonlight remote sensing. The overall accuracy (OA) and kappa coefficient of the VIIRS/DNB moonlight image are 79.80% and 0.45, respectively. In the low-light suburban areas of Calgary, the overall accuracy and kappa coefficient of the classification result are 87.16% and 0.77, respectively. While the overall accuracy and kappa coefficient of Komsomolsk-na-Amure are 91.49% and 0.85, respectively.
The land surface classification of UAV moonlight images well reflected the spatial distribution characteristics of each land type. The overall accuracy and kappa coefficient are 82.33% and 0.77, respectively. The above results show that these moonlight remote sensing data can be applied well to the classification of a non-self-luminous land surface at night.
- (3)
- The characteristics of current moonlight remote sensing.
Finally, the characteristics of current moonlight remote sensing were compared from three aspects of bands, spatial resolutions, and sensors. First of all, multi-spectral moonlight remote sensing is more suitable for Earth observation under complex environments at night. Then, the spatial resolution of the moonlight data directly affects the application scenario of moonlight sensors; both CCD and CMOS cameras have great potential to achieve night-time Earth observations under fine lunar illumination.
The present study has systematically proved the huge potential of moonlight remote sensing in detecting non-self-emitting objects at night, which has been overlooked in traditional applications of night-light remote sensing. Although moonlight remote sensing has great potential for Earth observations, there is still more work to be done to use moonlight as an illuminating source for nightlight remote sensing. It is more difficult for the nocturnal atmospheric radiative transfer model to establish that the moonlight irradiance is much smaller than the sunlight irradiance and atmospheric changes at night are more complicated. In addition, the irradiances of moonlight under different moon phases from a new moon to a full moon also need to be carefully measured and calculated in the future. Meanwhile, studies on the nocturnal atmospheric radiative transfer model and the influence of different moon phase irradiances on the quality of nightlight data are also the basis for promoting quantitative research of moonlight remote sensing.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.L. and Q.Z.; methodology, D.L. and Y.W.; writing—original draft preparation, D.L., Q.Z. and J.W.; writing—review and editing, D.L., J.W., Y.S. (Yanyun Shen) and Q.Z.; supervision, Q.Z.; project administration, Q.Z. and Y.S. (Yanmin Shuai); funding acquisition, Q.Z. and Y.S. (Yanmin Shuai). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2017YFB0504204; No. 2020YFA0608501); the Talents Recruitment Program of the Chinese Academy of Science (No. Y674141001; No. Y938091); and supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program, No. 42071351), the Liaoning Revitalization Talents Program (No. XLYC1802027), the Western Talents (No. 2018XBYJRC004), and the Discipline Innovation Team of Liaoning Technical University (No. LNTU20TD-23).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sentinel 2 User Handbook. 2015. Available online: https://sentinels.copernicus.eu/web/sentinel/user-guides/document-library/-/asset_publisher/xlslt4309D5h/content/sentinel-2-user-handbook (accessed on 20 September 2021).
- Guk, E.; Levin, N. Analyzing spatial variability in night-time lights using a high spatial resolution color Jilin-1 image—Je-rusalem as a case study. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 163, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dove Satellite Constellation. 2017. Available online: https://www.satimagingcorp.com/satellite-sensors/other-satellite-sensors/dove-3m/ (accessed on 20 September 2021).
- Miller, S.; Straka, W.; Mills, S.; Elvidge, C.; Lee, T.; Solbrig, J.; Walther, A.; Heidinger, A.; Weiss, S. Illuminating the capabilities of the Suomi National Polar-Orbiting partnership (NPP) visible infrared imaging radiometer suite (VIIRS) day/night band. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 6717–6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dvornyk, V.; Vinogradova, O.; Nevo, E. Origin and evolution of circadian clock genes in prokaryotes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 2495–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martino, T.; Arab, S.; Straume, M.; Belsham, D.D.; Tata, N.; Cai, F.; Liu, P.; Trivieri, M.; Ralph, M.; Sole, M.J. Day/night rhythms in gene expression of the normal murine heart. J. Mol. Med. 2004, 82, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, M.P.M.; Affholder, M. Descriptive Physical Oceanography: State of the Art; Taylor and Francis: Oxfordshire, UK, 2001; p. 249. ISBN 9054107065. [Google Scholar]
- DeCoursey, P.J.; Dunlap, J.C.; Loros, J.J. Chronobiology; Sinauer Associates Inc.: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2003; ISBN 978-0-87893-149-1. [Google Scholar]
- La Sorte, F.A.; Fink, D.; Buler, J.J.; Farnsworth, A.; Cabrera-Cruz, S.A. Seasonal associations with urban light pollution for nocturnally migrating bird populations. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 4609–4619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Cruz, S.A.; Smolinsky, J.A.; Buler, J.J. Light pollution is greatest within migration passage areas for nocturnally-migrating birds around the world. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, Y.; Hatta, M.; Furukawa, S.; Kawata, M.; Ueno, N.; Maruyama, S. Environmental factors explain spawning day deviation from full moon in the scleractinian coral Acropora. Biol. Lett. 2020, 16, 20190760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lovatt, A.; O’Connor, J. Cities and the night-time economy. Plan. Pr. Res. 1995, 10, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Levin, N.; Chalkias, C.; Letu, H. Nighttime Light Remote Sensing–Monitoring Human Societies from Outerspace; Thenkabail, P.S., Ed.; Taylor and Francis Inc.: London, UK, 2015; p. 289e310. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Levin, N.; Xie, J.; Li, D. Monitoring hourly night-time light by an unmanned aerial vehicle and its implications to satellite remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldblatt, R.; Stuhlmacher, M.F.; Tellman, B.; Clinton, N.; Hanson, G.; Georgescu, M.; Wang, C.; Serrano-Candela, F.; Khandelwal, A.K.; Cheng, W.-H.; et al. Using Landsat and nighttime lights for supervised pixel-based image classification of urban land cover. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 205, 253–275. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Weng, Q.; Fu, P. Temporal variations of artificial nighttime lights and their implications for urbanization in the conterminous United States, 2013–2017. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 225, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Cheng, W.; Zhou, C.; Ma, T.; Li, M.; Huang, K. Mapping urban dynamics (1992–2018) in Southeast Asia using consistent nighttime light data from DMSP and VIIRS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 248, 111980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Asrar, G.R.; Smith, S.; Imhoff, M. A global record of annual urban dynamics (1992–2013) from nighttime lights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 219, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Seto, K.C.; Stokes, E.C.; Deng, C.; Pickett, S.T.; Taubenböck, H. Understanding an urbanizing planet: Strategic directions for remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 228, 164–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Nordhaus, W.D. Using luminosity data as a proxy for economic statistics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8589–8594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keola, S.; Andersson, M.; Hall, O. Monitoring economic development from space: Using nighttime light and land cover data to measure economic growth. World Dev. 2015, 66, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, N.; Zhang, Q. A global analysis of factors controlling VIIRS nighttime light levels from densely populated areas. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 190, 366–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, B.; Shi, K.; Hu, Y.; Huang, C.; Chen, Z.; Wu, J. Poverty evaluation using NPP-VIIRS nighttime light composite data at the county level in China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 1217–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-H.K.; Prishchepov, A.V.; Fensholt, R.; Sabel, C. Detecting and monitoring long-term landslides in urbanized areas with nighttime light data and multi-seasonal Landsat imagery across Taiwan from 1998 to 2017. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 225, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, M.O.; Stokes, E.C.; Shrestha, R.; Wang, Z.; Schultz, L.; Carlo, E.A.S.; Sun, Q.; Bell, J.; Molthan, A.; Kalb, V.; et al. Satellite-based assessment of electricity restoration efforts in Puerto Rico after Hurricane Maria. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yu, B.; Liu, Y.; Yao, S.; Lian, T.; Chen, L.; Yang, C.; Chen, Z.; Wu, J. NPP-VIIRS DNB daily data in natural disaster assessment: Evidence from selected case studies. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kyba, C.C.M.; Aronson, K.J. Assessing exposure to outdoor lighting and health risks. Epidemiology 2015, 26, e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyba, C.C.M. Is light pollution getting better or worse? Nat. Astron. 2018, 2, 267–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunn, R.M.; Blask, D.E.; Coogan, A.N.; Figueiro, M.G.; Gorman, M.R.; Hall, J.E.; Hansen, J.; Nelson, R.J.; Panda, S.; Smolensky, M.H.; et al. Health consequences of electric lighting practices in the modern world: A report on the National Toxicology Program’s workshop on shift work at night, artificial light at night, and circadian disruption. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607, 1073–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Croft, T.A. Nighttime images of the earth from space. Sci. Am. 1978, 239, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.B.; Dietz, K.E.; Bland, J.B.; Sutton, T.; Kroehl, P.C. Radiance calibration of DMSP-OLS low-light imaging data of human settlements. Remote Sens. Environ. 1999, 68, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, M.O.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Q.; Kalb, V.; Miller, S.D.; Molthan, A.; Schultz, L.; Bell, J.; Stokes, E.C.; Pandey, B.; et al. NASA’s Black Marble nighttime lights product suite. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 210, 113–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.D.; Mills, S.P.; Elvidge, C.D.; Lindsey, D.; Lee, T.F.; Hawkins, J.D. Suomi satellite brings to light a unique frontier of nighttime environmental sensing capabilities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 15706–15711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miller, S.D.; Turner, R.E. A dynamic lunar spectral irradiance data set for NPOESS/VIIRS day/night band nighttime environmental applications. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 2316–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calgary Industries. Calgary Economic Development. Archived from the original on 18 February 2014. Retrieved 31 January 2014. Available online: https://www.calgaryeconomicdevelopment.com/industries (accessed on 20 September 2021).
- Population and Dwelling Counts, for Canada, Provinces and Territories, and Census Subdivisions (Municipalities), 2011 and 2006 censuses (Alberta). Statistics Canada. 8 February 2012. Available online: https://www12.statcan.gc.ca/census-recensement/2016/dp-pd/hlt-fst/pd-pl/Table.cfm?Lang=Eng&T=801&SR=1&S=3&O=D&RPP=100&PR=48&CMA=0#tPopDwell (accessed on 20 September 2021).
- Russian Federal State Statistics Service. Bcepoccийcкaя пepeпиcь нaceлeния 2010 гoдa. Toм 1. Bcepoccийcкaя пepeпиcь нaceлeния 2010 гoдa; Federal State Statistics Service: Moscow, Russia, 2011; Available online: http://government.ru/en/department/456/ (accessed on 20 September 2021).
- Guangming District. Retrieved 2018-05-25. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Guangming_District (accessed on 20 September 2021).
- Sánchez de Miguel, A.; Zamorano, J.; Pascual, S.; López Cayuela, M.; Ocaña, F.; Challupner, P.; de Miguel, E. ISS nocturnal images as a scientific tool against light pollution: Flux calibration and colors. In Highlights of Spanish Astrophysics VII; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 916–919. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, S.J.; Tuttle, B.T.; Powell, R.L.; Sutton, P. Characterizing relationships between population density and nighttime imagery for Denver, Colorado: Issues of scale and representation. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 5733–5746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Miguel, A.S.; Castaño, J.G.; Zamorano, J.; Pascual, S.; Ángeles, M.; Cayuela, L.; Martinez, G.M.; Challupner, P.; Kyba, C.C.M. Atlas of astronaut photos of Earth at night. Astron. Geophys. 2014, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotarba, A.Z.; Aleksandrowicz, S. Impervious surface detection with nighttime photography from the International Space Station. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 176, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schueler, C.F.; Clement, J.E.; Ardanuy, P.E.; Welsch, C.; Deluccia, F.; Swenson, H. NPOESS VIIRS sensor design overview. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Optical Science and Technology, San Diego, CA, USA, 29 July–3 August 2001; pp. 11–23. [Google Scholar]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.; Zhizhin, M.; Hsu, F.C.; Ghosh, T. VIIRS night-time lights. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 5860–5879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, N.; Kyba, C.C.; Zhang, Q.; de Miguel, A.S.; Román, M.O.; Li, X.; Portnov, B.A.; Molthan, A.L.; Jechow, A.; Miller, S.D.; et al. Remote sensing of night lights: A review and an outlook for the future. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelestov, A.; Lavreniuk, M.; Kussul, N.; Novikov, A.; Skakun, S. Exploring Google earth engine platform for big data processing: Classification of multi-temporal satellite imagery for crop mapping. Front. Earth Sci. 2017, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Miguel, A.S.; Kyba, C.C.; Aubé, M.; Zamorano, J.; Cardiel, N.; Tapia, C.; Bennie, J.; Gaston, K.J. Colour remote sensing of the impact of artificial light at night (I): The potential of the International Space Station and other DSLR-based platforms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 224, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Miguel, A.S.; Kyba, C.C.; Aubé, M.; Zamorano, J.; Cardiel, N.; Tapia, C.; Bennie, J.; Gaston, K.J. Colour remote sensing of the impact of artificial light at night (II): Calibration of DSLR-based images from the International Space Station. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 264, 112611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.; Kovacs, J.; Shang, J.; McNairn, H.; Walters, D.; Ma, B.; Geng, X. Object-oriented crop mapping and monitoring using multi-temporal polarimetric RADARSAT-2 data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 96, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baatz, M.; Benz, U.; Dehghani, S.; Heynen, M.; Höltje, A.; Hofmann, P.; Lingenfelder, I.; Mimler, M.; Sohlbach, M.; Weber, M. eCognition professional user guide. UNBC GIS Lab. 2004, 4, 72. [Google Scholar]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random forest in remote sensing: A review of applications and future directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Chen, J.; Imura, H.; Higashi, O. A SVM-based method to extract urban areas from DMSP-OLS and SPOT VGT data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2205–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Yeh, A.G.-O.; Li, X.; Lin, Z. A novel algorithm for land use and land cover classification using RADARSAT-2 polarimetric SAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 118, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Qi, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Yeh, A.G.O.; Wang, J. Investigation of the capability of multitemporal RADARSAT-2 fully polarimetric SAR images for land cover classification: A case of Panyu, Guangdong province. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 54, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Samat, A.; Waske, B.; Liu, S.; Li, Z. Random forest and rotation forest for fully polarized SAR image classification using polarimetric and spatial features. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 105, 38–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbatini, M. NightPod-Nodding Mechanism for the ISS. Technical Report; European Space Agency: Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Cinzano, P.; Pettit, D.R.; Arvesen, J.; Sutton, P.; Small, C.; Nemani, R.; Longcore, T.; Rich, C.; Safran, J.; et al. The Nightsat mission concept. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 2645–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meester, J.; Storch, T. Optimized performance parameters for nighttime multispectral satellite imagery to analyze lightings in urban areas. Sensors 2020, 20, 3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barentine, J.C.; Walczak, K.; Gyuk, G.; Tarr, C.; Longcore, T. A case for a new satellite mission for remote sensing of night lights. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Chen, Z.; Yu, B.; Li, Q.; Wang, C.; Li, B.; Wu, B.; Li, Y.; Wu, J. Automated extraction of street lights from JL1-3B nighttime light data and assessment of their solar energy potential. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, B.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Building a better urban picture: Combining day and night remote sensing imagery. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 11887–11913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pekel, J.-F.; Cottam, A.; Gorelick, N.; Belward, A.S. High-resolution mapping of global surface water and its long-term changes. Nature 2016, 540, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).