Estimation of Inter-System Biases between BDS-3/GPS/Galileo and Its Application in RTK Positioning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. RTK Positioning Models
2.1. GNSS Observations
2.2. LCM RTK
2.3. ISB and TCM RTK
3. Datasets and Experiments
3.1. Datasets
3.2. Quality of the Signals
3.2.1. Multipath Errors for Pseudo Range
3.2.2. Triple-Frequency Phase Combination
3.3. Stability of ISBs
3.3.1. Short-Term ISB
3.3.2. Long-Term ISB
3.4. Performance of RTK Positioning
3.4.1. Single System vs. Multi System
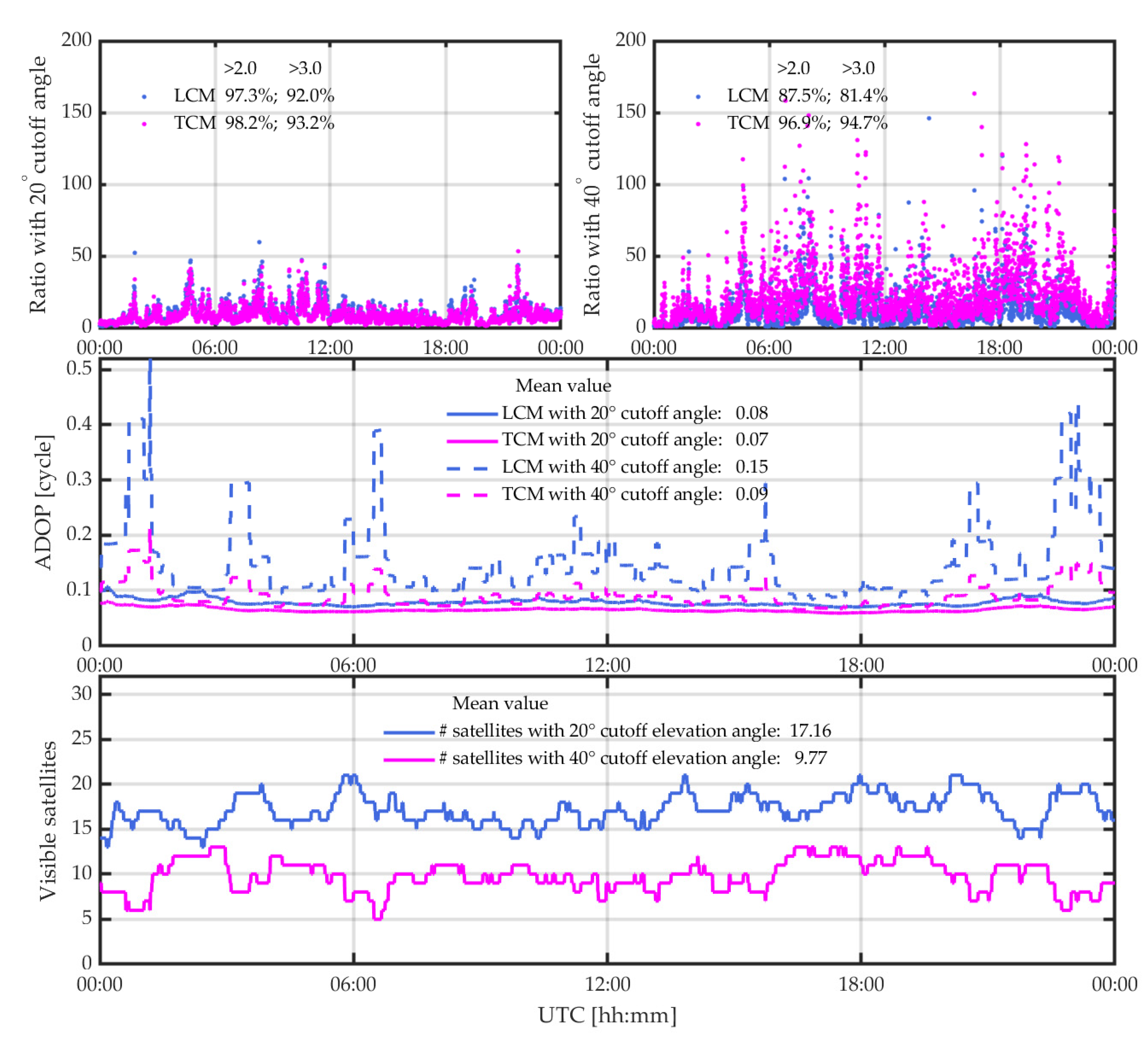
3.4.2. LCM RTK vs. TCM RTK
3.4.3. SR and Accuracy under Different Cutoff Elevation Angles
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P.; Khachikyan, R.; Weber, G.; Langley, R.; Mervart, L.; Hugentobler, U. IGS-MGEX: Preparing the Ground for Multi-Constellation. GNSS Sci. 2014, 9, 42–49. [Google Scholar]
- CSNO. Development of the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (Version 4.0); China Satellite Navigation Office Technical Report; CSNO: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, P.; Zhang, B.; Yuan, Y. Combined GPS+BDS instantaneous single- and dual-frequency RTK positioning: Stochastic modelling and performance assessment. J. Spat. Sci. 2019, 66, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, K.; Jin, S. Triple-frequency carrier phase precise time and frequency transfer models for BDS-3. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CSNO. BeiDou Navigation Satellite System Open Service Performance Stand (Version 3.0); China Satellite Navigation Office Technical Report; CSNO: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Kubo, N.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, H. Initial Positioning Assessment of BDS New Satellites and New Signals. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Gao, W.; Guo, S.; Mao, Y.; Yang, Y. Introduction to BeiDou-3 navigation satellite system. Navigation 2019, 66, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, M.; Liu, W.; Li, X.; Yu, S.; Lu, C.; Wickert, J. Initial assessment of the COMPASS/BeiDou-3: New-generation navigation signals. J. Geod. 2017, 91, 1225–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOAA. Space Segment. Available online: https://www.gps.gov/systems/gps/space/ (accessed on 5 August 2021).
- Centre, E.G.S. (European GNSS Service). Constellation Information. Available online: https://www.gsc-europa.eu/system-service-status/constellation-information (accessed on 5 August 2021).
- Kubo, N. Advantage of velocity measurements on instantaneous RTK positioning. GPS Solut. 2009, 13, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angelo, F.N.; Gianpaolo, C.; Carmine, G.; Antonino, M.; Annamaria, V. A Test on the Potential of a Low Cost Unmanned Aerial Vehicle RTK/PPK Solution for Precision Positioning. Sensors 2021, 21, 3882. [Google Scholar]
- Keshavarzi, H.; Lee, C.; Johnson, M.; Abbott, D.; Ni, W.; Campbell, D.L. Validation of Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) Devices on Sheep to Detect Grazing Movement Leaders and Social Networks in Merino Ewes. Sensors 2021, 21, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Gao, C.; Pan, S. A method of GPS/BDS/GLONASS combined RTK positioning for middle-long baseline with partial ambiguity resolution. Surv. Rev. 2016, 49, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann-Wellenhof, B.; Lichtenegger, H.; Wasle, E. GNSS—Global Navigation Satellite Systems: GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and More; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Odolinski, R.; Teunissen, P.J.G.; Odijk, D. First combined COMPASS/BeiDou-2 and GPS positioning results in Australia. Part II: Single- and multiple-frequency single-baseline RTK positioning. J. Spat. Sci. 2014, 59, 25–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, S.J.; Clarke, P.J.; Penna, N.T.; Goebell, S. An Examination of Network RTK GPS Services in Great Britain. Surv. Rev. 2013, 42, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lemmon, T.R.; Gerdan, G.P. The Influence of the Number of Satellites on the Accuracy of RTK GPS Positions. Aust. Surv. 2012, 44, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirti, A. Performance Analysis of the Real Time Kinematic GPS (RTK GPS) Technique in a Highway Project (Stake-Out). Surv. Rev. 2013, 39, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odolinski, R.; Teunissen, P.J.G. Single-frequency, dual-GNSS versus dual-frequency, single-GNSS: A low-cost and high-grade receivers GPS-BDS RTK analysis. J. Geod. 2016, 90, 1255–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odolinski, R.; Teunissen, P.J.G. Low-cost, high-precision, single-frequency GPS–BDS RTK positioning. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 1315–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G.; Odolinski, R.; Odijk, D. Instantaneous BeiDou+GPS RTK positioning with high cut-off elevation angles. J. Geod. 2013, 88, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Xu, J.; He, H.; Guo, H.; Wang, A. Performance Analysis of Single-Epoch Dual-Frequency RTK by BeiDou Navigation Satellite System. In China Satellite Navigation Conference (CSNC) 2013 Proceedings; Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 245, pp. 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odijk, D.; Teunissen, P.J.G. Characterization of between-receiver GPS-Galileo inter-system biases and their effect on mixed ambiguity resolution. GPS Solut. 2012, 17, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odijk, D.; Teunissen, P.J.G.; Huisman, L. First results of mixed GPS+GIOVE single-frequency RTK in Australia. J. Spat. Sci. 2012, 57, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odijk, D.; Nadarajah, N.; Zaminpardaz, S.; Teunissen, P.J.G. GPS, Galileo, QZSS and IRNSS differential ISBs: Estimation and application. GPS Solut. 2016, 21, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, X.; Zhang, B.; Yuan, Y.; Luo, X. Characteristics of GPS, BDS2, BDS3 and Galileo inter-system biases and their influence on RTK positioning. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2020, 31, 015009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wang, Z. Differential Inter-System Biases Estimation and Initial Assessment of Instantaneous Tightly Combined RTK with BDS-3, GPS, and Galileo. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Teunissen, P.J.G. Characterization of multi-GNSS between-receiver differential code biases using zero and short baselines. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 1840–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Teunissen, P.J.G.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, M. A modified carrier-to-code leveling method for retrieving ionospheric observables and detecting short-term temporal variability of receiver differential code biases. J. Geod. 2018, 93, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. The least-squares ambiguity decorrelation adjustment: A method for fast GPS integer ambiguity estimation. J. Geod. 1995, 70, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Teunissen, P.J.G.; El-Mowafy, A. The ADOP and PDOP: Two Complementary Diagnostics for GNSS Positioning. J. Surv. Eng. 2020, 146, 04020008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Estey, L.H.; Meertens, C.M. TEQC: The Multi-Purpose Toolkit for GPS/GLONASS Data. J. GPS Solut. 1999, 3, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, B.; Nie, L.; Wei, C.; Jia, S.; Jiang, S. Initial assessment of BeiDou-3 global navigation satellite system: Signal quality, RTK and PPP. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, W.; Li, B.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X. Combined BeiDou-2 and BeiDou-3 instantaneous RTK positioning: Stochastic modeling and positioning performance assessment. J. Spat. Sci. 2019, 65, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. A canonical theory for short GPS baselines. Part II: The ambiguity precision and correlation. J. Geod. 1997, 71, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odijk, D.; Teunissen, P.J.G. ADOP in closed form for a hierarchy of multi-frequency single-baseline GNSS models. J. Geod. 2008, 82, 473–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]









| Frequency (MHz) | Wavelength (cm) | BDS-3 | GPS | Galileo |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1575.42 | 19.03 | B1C | L1 | E1 |
| 1561.098 | 19.20 | B1I | - | - |
| 1278.75 | 23.44 | - | - | E6 |
| 1268.52 | 23.63 | B3I | - | - |
| 1227.60 | 24.42 | - | L2 | - |
| 1207.14 | 24.83 | B2b | - | E5b |
| 1191.795 | 25.15 | - | - | E5 |
| 1176.45 | 25.48 | B2a | L5 | E5a |
| Station | Location | Receiver | Antenna | Longitude | Latitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GODN 1 | America | JAVAD TRE_3 DELTA | TPSCR.G3 | ||
| GODS 1 | America | JAVAD TRE_3 DELTA | JAVRINGANT_DM | ||
| GODE 2 | America | SEPT POLARX5TR | AOAD/M_T | ||
| USN7 2 | America | SEPT POLARX5TR | TPSCR.G5 |
| System | Signal 1 1 | Signal 2 1 | Signal 3 1 | Amplification Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BDS-3 | B1C (−0.1614) | B2a (−1.2606) | B2b (1.4220) | 1.9071 |
| GPS | L1 (0.2851) | L2 (−1.5457) | L5 (1.2606) | 2.0149 |
| Galileo | E1 (−0.1614) | E5a (−1.2606) | E5b (1.4220) | 1.9071 |
| Frequency Pair | Phase ISB (Cycle) | Code ISB (m) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Expectation | STD | Expectation | STD | |
| B1C/L1 | −0.002 | 0.010 | 0.034 | 0.183 |
| B2a/L5 | −0.002 | 0.010 | −0.052 | 0.098 |
| B1C/E1 | 0.000 | 0.009 | −0.009 | 0.176 |
| B2a/E5a | 0.000 | 0.009 | −0.004 | 0.077 |
| Elevation (°) | SR (%) | Correctly Fixed Solution (cm) | Float Solution (m) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCM | TCM | Imp. 1 | LCM | TCM | Imp. | LCM | TCM | Imp. | |
| 0 | 100 | 100 | - | 2.45 | 2.37 | 3.27% | 0.27 | 0.25 | 7.41% |
| 5 | 100 | 100 | - | 2.45 | 2.37 | 3.27% | 0.27 | 0.26 | 3.70% |
| 10 | 100 | 100 | - | 2.45 | 2.37 | 3.27% | 0.28 | 0.27 | 3.57% |
| 15 | 100 | 100 | - | 2.52 | 2.46 | 2.38% | 0.32 | 0.30 | 6.25% |
| 20 | 99.89 | 100 | 0.11% | 2.57 | 2.52 | 1.95% | 0.38 | 0.35 | 7.89% |
| 25 | 99.72 | 100 | 0.28% | 2.60 | 2.58 | 7.69% | 0.46 | 0.41 | 10.87% |
| 30 | 98.71 | 100 | 1.31% | 2.68 | 2.70 | -0.77% | 0.58 | 0.50 | 13.79% |
| 35 | 96.80 | 99.13 | 2.41% | 2.89 | 2.91 | -0.69% | 0.72 | 0.59 | 18.06% |
| 40 | 90.59 | 97.47 | 7.60% | 3.54 | 3.45 | 2.5% | 0.90 | 0.78 | 13.33% |
| 45 | 75.20 | 92.16 | 22.55% | 4.36 | 4.31 | 11.47% | 1.37 | 1.15 | 16.06% |
| 50 | 53.62 | 80.20 | 49.57% | 4.66 | 4.60 | 12.87% | 1.86 | 1.49 | 19.89% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Zhu, S.; Ming, Z. Estimation of Inter-System Biases between BDS-3/GPS/Galileo and Its Application in RTK Positioning. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3507. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13173507
Li W, Zhu S, Ming Z. Estimation of Inter-System Biases between BDS-3/GPS/Galileo and Its Application in RTK Positioning. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(17):3507. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13173507
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Wei, Song Zhu, and Zutao Ming. 2021. "Estimation of Inter-System Biases between BDS-3/GPS/Galileo and Its Application in RTK Positioning" Remote Sensing 13, no. 17: 3507. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13173507
APA StyleLi, W., Zhu, S., & Ming, Z. (2021). Estimation of Inter-System Biases between BDS-3/GPS/Galileo and Its Application in RTK Positioning. Remote Sensing, 13(17), 3507. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13173507






