Abstract
This study analyzed changes in nighttime light during the 2019 Spring Festival using Luojia 1-01 nighttime images in six western cities of China (Chengdu, Panzhihua, Kunming, Yuxi, Lhasa, and Jinchang). First, the radiance of the nighttime images was calculated. Second, the light area (LA) and average light intensity (ALI) were estimated for both Spring Festival and non-festival dates. Third, the differences in LA and ALI between the Spring Festival and non-festival were analyzed for all six cities. Migration population data from Baidu Inc. were used to examine the relationship between the changes of nighttime light and the population migration. The results show that, during the non-festival to Spring Festival period, the decrease in LA values coincided with negative net immigration. During the Spring Festival to non-festival period, the LA values increased, which coincided with positive net immigration. The F-test shows that the positive linear relationship between the normalized change in LA and the normalized net immigration is significant at the 0.05 level. This strongly indicates that population migration causes changes in LA. Moreover, while the population is considerably less in these cities during the Spring Festival, the ALI is noticeably higher, which suggests that urban activities are intensified during this period. This study demonstrates the applicability of using Luojia 1-01 nighttime images to detect the nighttime light changes for the Spring Festival in western cities, China, which can then be used to evaluate population migration and urban activities in the Spring Festival. Considering the higher spatial resolution of Luojia 1-01 than NPP (National Polar-orbiting Partnership) / VIIRS (Visible infrared Imaging Radiometer), this study may inspire more applications of Luojia 1-01 to track the activities in a variety of festival-cultures and cities.
1. Introduction
The various levels of urban activity in different festivals or holidays reveal customs, traditional culture, and population mobility, providing essential information on people’s movement and travel. In China, the official holidays (i.e., legal holidays) are in the same dates for almost all the organizations, which always brings a heavy traffic in some cities and a congestion in many scenic spots. The status of urban activity in festivals has been a basis for supporting the adjustment of the policy about official holidays. The year’s most important festival in China is the Spring Festival, where the various human activities provide a glimpse of the community’s culture and the people’s vitalities. The western cities of China are less developed and receive more attention from the government than other areas of the country. The different urban activities during the Spring Festival can provide important information useful in decision-making, particularly in China’s western cities.
In determining the patterns of urban activities, ground statistical datasets have been used as the primary source for various information, such as position data from social media (e.g., Twitter, Facebook, WeChat, Weibo), urban traffic data, and ticket data of scenic spots [1,2,3,4]. However, ground statistical datasets are commonly discrete point data and feature space discontinuity. Moreover, ground statistic datasets are not always publically available. In the past few decades, remote sensing has become a popular alternative for detecting, measuring, and monitoring a variety of anthropogenic metrics. Remotely sensed nighttime imagery can provide information of artificial nighttime lights from human settlements, industrial activities, and fishing fleets, and has been used for rapid, large-scale monitoring of human activities since the 1970s [5,6,7]. In the area of urban movement monitoring, nighttime light images have been used for a number of applications, including urban area and structure extraction [8,9,10], measuring urban expansion [11,12,13], and socio-economic parameterization [14,15,16]. In terms of the response of nighttime light to holidays in cities, there are two important research works. First, the patterns for energy services during Christmas and New Year were investigated by [17]. The paper suggested that patterns for energy services were closely correlated with cultural boundaries at different levels. Second, festival patterns were explored for Carnival and a catholic event in Mexico by [18], which suggested the light change was different for different festivals. However, nighttime light images have rarely been used in detecting and analyzing patterns of urban activities during the Spring Festival.
Before 2018, there were mainly two space-borne sensors used for acquiring nighttime images. The Defense Meteorological Satellite Program/Operational Linescan System (DMSP/OLS) provided the time series of global nighttime light images from 1992–2013 with a telescope pixel (0.55 km) at high resolution (fine mode) and 2.7 km at low resolution (smooth mode) [19]. The DMSP satellite was located at a 101-minutes orbit and provided global coverage twice each day [19]. The Visible infrared Imaging Radiometer (VIIRS) Day/Night Band (DNB) onboard the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership (Suomi-NPP) was launched in October 2011 and provides nighttime light images with a spatial resolution of about 740 m [5,6,20]. Suomi-NPP/VIIRS revisits the equator every four hours. However, given the low spatial resolution of both the DMSP/OLS and the Suomi-NPP/VIIRS, the use of nighttime light images is limited when analyzing urban activities.
The Luojia 1-01 satellite was launched on June 2, 2018, and was developed by Wuhan University and Chang Guang Satellite Technology Co. LTD, China. As the first dedicated nighttime light satellite, the spatial resolution is 130 m, which is much better than that of DMSP/OLS and Suomi-NPP/VIIRS [20,21]. Hence, the Luojia 1-01 satellite significantly expands the usability of nighttime-light remote sensing, providing new nighttime light datasets with higher quality for monitoring changes of artificial nighttime lights. Since the launch of the Luojia 1-01 satellite, new applications have been performed, and the ability to monitor human activities has been verified. In particular, the current application of Luojia 1-01 nighttime images includes modeling socio-economic parameters [20], investigating artificial light pollution [22], mapping urban extent [23,24,25], low Earth orbiter (LEO)-based navigation signal augmentation [26], detecting feeble nighttime lights [27], and detecting impervious surface and artificial surface features [28,29]. In addition, some works about the design, test, calibration, and validation of Luojia 1-01 nighttime camera and image restoration have also been published [21,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37]. However, the current application of Luojia 1-01 for urban activity did not involve holidays.
In terms of the activity of China in Spring Festival, the correlation between the population movements and the urban relative humidity of Beijing was explored, which provides new evidence for this correlation [38]. In addition, the relationship between the meteorological conditions and the population movement impacts on urban heat island was investigated in Beijing [39]. However, the nighttime light image was not used in these works.
To summarize, some works has been performed on the patterns of the festivals in western society (e.g., Christmas, catholic events) using nighttime light data. However, to the best of our knowledge, there is little information available in published literatures about the analysis of urban activity in Spring Festival using nighttime images. Moreover, as a new satellite, the ability of Luojia 1-01 to detect urban activity during a holiday is still unknown.
This study attempted to apply Luojia 1-01 nighttime images to detect the nighttime light changes for the 2019 Spring Festival in China’s western cities. There were two primary goals: (1) to evaluate the ability of Luojia 1-01 to detect urban activity in holidays, specifically in the Spring Festival; (2) to know more about the patterns of activities in Spring Festival for China’s western cities.
2. Datasets
The first Spring Festival following the launch of the Luojia 1-01 occurred on 4–10 February 2019. To compare the nighttime light during the Spring Festival against non-festival, there are two important requirements for the selected city: (1) we require archived Luojia 1-01 images in both the 2019 Spring Festival and a non-festival time for the city, and the images must cover the administrative area of the city; (2) there is no cloud coverage for the images. After conducting an exhaustive search in West China, there are six cities satisfying the requirements and the corresponding Loujia 1-01 images were downloaded from the official data website (http://59.175.109.173:8888/index_en.html) (English version, accessed in November 2019). The steps on how to download Luojia 1-01 data can be found in Ref. [18]. Details of the Luojia 1-01 data used in this study are summarized in Table 1, while the locations of the research cities are shown in Figure 1. Selected portions of the study area from Luojia 1-01 nighttime images and NPP/VIIRS images are comparatively presented in Figure 2. In terms of image details (e.g., roads), the Luojia 1-01 images provide clearer and better-defined silhouettes compared with the NPP/VIIRS images, as shown in Figure 2. The lower spatial-resolution of NPP/VIIRS meant that many targets (e.g., roads) could not be unambiguously identified.

Table 1.
The Luojia 1-01 and NPP (National Polar-orbiting Partnership) / VIIRS (Visible infrared Imaging Radiometer) data used in this study.
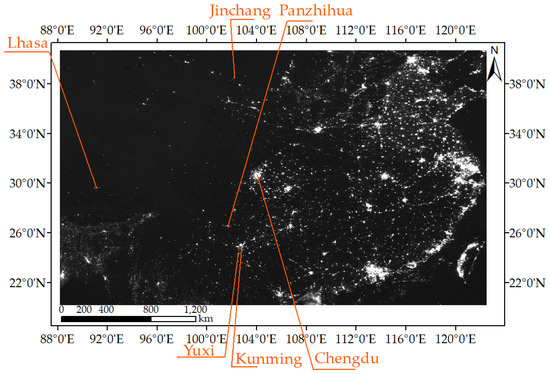
Figure 1.
The western Chinese cities investigated in this paper.

Figure 2.
Some representative parts of the radiance images: (a) Luojia 1-01 image of Kunming in Spring Festival; (b) NPP/VIIRS image of Kunming in Spring Festival; (c) Luojia 1-01 image of Lhasa in non-festival; (d) NPP/VIIRS image of Lhasa in non-festival.
Here the background information is presented for the study areas. Three of the six cities, Chengdu, Kunming, and Lhasa are the capital cities of the corresponding province, and the other three cities are prefecture-level cities. From the view of physical geography, all the cities belong to West China where the terrain mainly comprises mountains and plateaus. The inconvenient transportation to this area has hindered industrialization. Since the initiation of the Chinese government’s official strategy to develop West China, industrialization has improved rapidly. There has been more population transfer from agriculture to industry, and more people from eastern cities have chosen to work in western cities. However, compared with the eastern cities in China (e.g., Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, Hangzhou, Suzhou), these six western cities are still less developed, with a greater proportion of the population working in agriculture and less building land use.
3. Methods
The methods used in this study include data preprocessing, Light Area (LA) extraction, and the calculation of Average Light Intensity (ALI). LA and ALI were used as indicators to evaluate urban activity.
3.1. Data Preprocessing
According to the preprocessing method used by Luojia Satellite Team [20,24,25,27]) and the information on the data downloading website, the advised preprocessing of Luojia 1-01 data is the calculation of radiance. The radiance of Luojia 1-01 nighttime images after radiometric calibration was calculated using Equation (1) as follows [20].
where DN is the grey value recorded by digital numbers for each pixel in the downloaded images, and L with units in W·m−2·sr−1·μm−1 is the radiance after radiometric calibration for each pixel.
L = DN3/2 ·10−10
Actually, the downloaded Luojia 1-01 data shows a shift of several pixels in terms of georeference. For this study, the nighttime images were geometrically corrected based on control points [25] to preserve the strict consistency of covering the same research extent, which would be critical in subsequent comparative analysis.
3.2. Light Area Extraction
The pixels were divided into two classes, i.e., light pixels and non-light pixels, based on the conditions shown in Equation (2) as follows.
where L is the radiance of the pixel.
Light pixel, if L > 0
Non-light pixel, if L < or = 0
Non-light pixel, if L < or = 0
For the study area of a nighttime image, the number of light pixels was counted, and the Light Area (LA) was calculated by Equation (3) as follows.
where LA is the light area of the nighttime image in a study area; N is the number of light pixels extracted by Equation (2); and AP is the ground area (km2) per pixel that is determined by the spatial resolution of the nighttime image.
LA = N × AP
3.3. Average Light Intensity
A nighttime image comprises many pixels, and the value of a pixel after radiometric calibration is the radiance received by the sensor (W·m−2·sr−1·μm−1), which can be regarded as the Average Light Intensity (ALI) of the pixel (per square meters: m2). For the study area, the ALI of the light area was calculated by Equation (4) as follows.
where ALI (W·km−2·sr−1·μm−1) is the average light intensity of the light area. N is the number of light pixels extracted by Equation (2), and Li is the radiance (W·m−2·sr−1·μm−1) of the i-th light pixel. 106 is the factor transferring the area unit from m2 to km2.
4. Results and Discussion
The results of LA and ALI for the 2019 Spring Festival and non-festival periods are shown in Figure 3 (Chengdu), Figure 4 (Panzhihua), Figure 5 (Kunming), Figure 6 (Yuxi), Figure 7 (Lhasa), Figure 8 (Jinchang). For Chengdu, Panzhihua, Yuxi, Lhasa, and Jinchang, the images for non-festival time periods were captured prior to the Spring Festival of 2019, while for Kunming, the image used was captured after the 2019 Spring Festival. Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8 show that the LA during the Spring Festival is smaller compared to the non-festival dates for all six western cities. In contrast, the ALI values for the Spring Festival are higher in all six cities compared with the ALI values from non-festival dates.
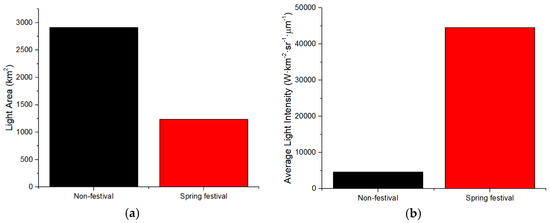
Figure 3.
The LA and ALI in the Spring Festival and non-festival in Chengdu: (a) Light Area (LA); (b) Average Light Intensity (ALI).
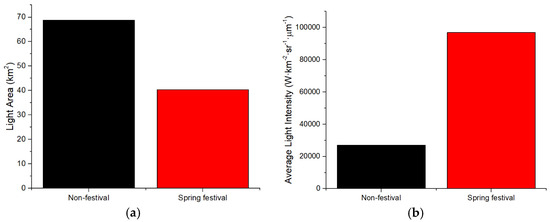
Figure 4.
The LA and ALI in the Spring Festival and non-festival in Panzhihua: (a) Light Area (LA); (b) Average Light Intensity (ALI).
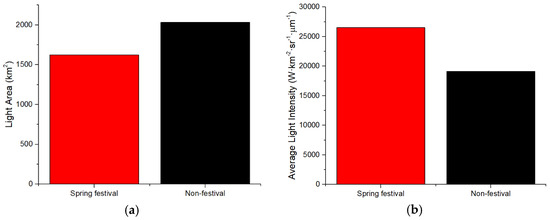
Figure 5.
The LA and ALI in Spring Festival and non-festival in Kunming: (a) Light Area (LA); (b) Average Light Intensity (ALI).
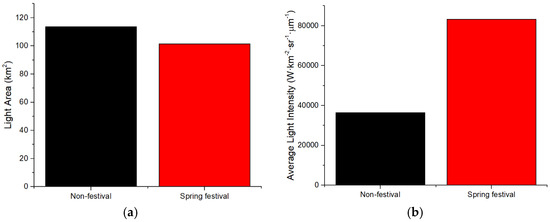
Figure 6.
The LA and ALI in Spring Festival and non-festival in Yuxi: (a) Light Area (LA); (b) Average Light Intensity (ALI).
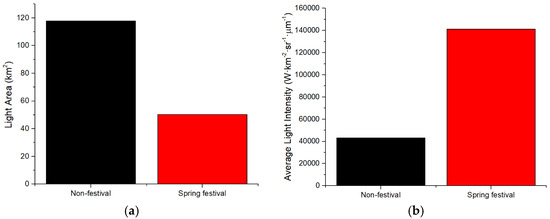
Figure 7.
The LA and ALI in Spring Festival and non-festival in Lhasa: (a) Light Area (LA); (b) Average Light Intensity (ALI).
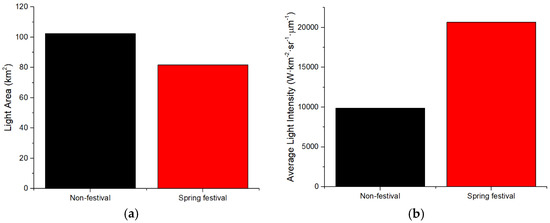
Figure 8.
The LA and ALI in the Spring Festival and non-festival in Jinchang: (a) Light Area (LA); (b) Average Light Intensity (ALI).
To further analyze the LA and ALI results shown in Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8, the migration data of the population provided by Baidu, Inc. were used in the study. The population migration data can be download from the website: “http://qianxi.baidu.com/”(accessed in February 2020). Baidu is the most widely used search-engine in China and also is the most popular Chinese-language search-engine in the world. The migration data provided by Baidu is a migration scale index, which is a relative parameter, not an absolute parameter. Baidu Inc. clearly states on the official website that the provided migration data reflect the relative migration proportion based on the total population. In particular, it also states that these migration data can be used for the comparison between different cities. In this study, the migration data refers to this index provided by Baidu, not the absolute amount of migration. For Chengdu, Panzhihua, Yuxi, Lhasa, and Jinchang, the total migration was estimated from the start of Spring Festival activities until the corresponding date of the image acquisition during the Spring Festival. The area where the total migration data was estimated coincided perfectly with the area assessed for its LA and ALI values. However, for Kunming, the area where the migration was estimated and the area covered by the image did not coincide perfectly. The former was a little bit bigger, and the very little extra area was just a group of several hilltops where there was little human activity. The error of population movement data brought by this extra area was so small that it was ignored in this study. This is clarified here for the preciseness of the study.
The changes in LA and ALI values and the total immigration and emigration data for each city were presented in Table 2. Based on the results, two main observations can be made: (1) the increase of LA and decrease of ALI trend with the positive net immigration of population from Spring Festival to non-festival (Kunming); (2) the decrease of LA and increase of ALI trend with the negative net immigration (i.e., emigration) of population from non-festival to Spring Festival (Chengdu, Panzhihua, Yuxi, Lhasa, and Jinchang). In Kunming, the date of the image in non-festival is subsequent to the date of the image in the Spring Festival, and the increase of LA, decrease of ALI, and positive net immigration were observed to be in chronological order. For the other five cities, the date of the image in non-festival is before the date of the image in Spring Festival, and the decrease of LA, increase of ALI, and negative net immigration were observed to be in chronological order. The key difference is whether the date of the image used in the non-festival data is earlier (Kunming) or later (other five cities). In fact, in terms of the change from non-festival to Spring Festival, it can be observed that the decrease of LA and increase of ALI tend to have negative net immigration (Table 2). Hence, it can be inferred that the pattern of relationship between the change of nighttime light and the population migration is coincident for all six cities.

Table 2.
The increase/decrease of LA and ALI and the corresponding net immigration data.
In order to quantitatively analyze the relationship between the changes of LA and the population migration, we normalized the change in LA and the net immigration. The normalization and results are summarized in Table 3.

Table 3.
The normalized change of LA and normalized net immigration.
We plotted the normalized change of LA (between the Spring Festival and non-festival) against the corresponding normalized net immigration (Figure 9). A positive linear relationship is observed between the normalized change of LA and the normalized net immigration, with the SSE = 0.0047 (Sum of Squares due to Error) and the RMSE = 0.0343 (Root Mean Square Error). To test the significance of the observed positive linear relationship, we conducted the F-test, which yielded an F value of 64.03. According to the F-test lookup table (LUT), it is demonstrated that the slope of the linear fitting line is significantly different from zero at the 0.05 level. In other words, the result of F-test suggests that the positive linear relationship between the normalized change of LA and the normalized net immigration is significant at the 0.05 level. This strongly indicates that the positive net migration caused an increase of LA in Kunming, while for the other five cities, the negative net immigration (i.e., emigration) resulted in the decrease of LA. In addition, a noticeable increase in ALI can be observed from the non-festival to Spring Festival dates (Table 2).
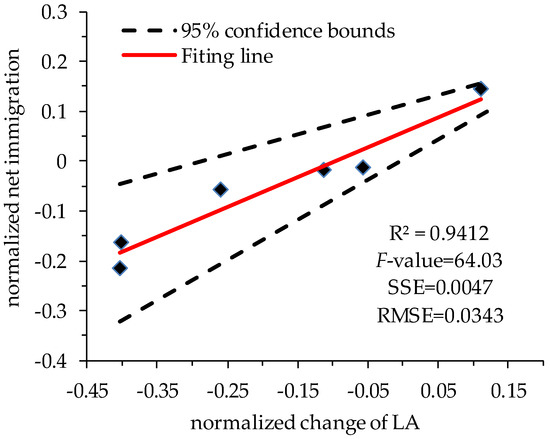
Figure 9.
The normalized change of LA between the Spring Festival and non-festival and the corresponding normalized net immigration.
The computed ALI values (Table 2) strongly suggest a substantial increase in urban activities during the Spring Festival. For example, more light-sources may be seen, including street lamps, Chinese lanterns, decorative lamps, neon lamps, and fireworks, to celebrate the most important festival in China, which are usually absent in non-festival times.
The noticeable changes of nighttime light and the population migration indicated that the six cities have vibrant and dynamic interactions with other Chinese cities. In general, the western cities of China are less developed than the main eastern cities. The results in this paper provide new knowledge about the patterns of activities in Spring Festival for China’s western cities, and are useful for evaluating the effectiveness of the Chinese government’s strategy for developing West China. The results also demonstrate that Luojia 1-01 nighttime images are able to detect the changes of nighttime light in less developed areas during the Spring Festival and indicate population migration. Considering the higher spatial resolution and more imaging details of Luojia 1-01 than NPP/VIIRS, the results in this paper may inspire future studies to use Luojia 1-01 nighttime images. For example, global human migration can be investigated using Luojia 1-01. The influences of other festivals (e.g., Christmas Day, New Year’s Day, Easter Day, and Mid-Autumn Festival) for a variety of cultures and cities around the world also deserve exploration. In terms of the above contributions, this study achieved the goals proposed in the “Introduction”. There are also limitations for this study. Luojia 1-01 was launched less than two years ago, and the archived data are still not enough to support the study in more cities for Spring Festival. In addition, if the results are used for comparison with other cities in the world, the LA and ALI can be used but should be quantitatively compared to the cities with similar industrial level (e.g., similar Gross Domestic Product) using Luojia 1-01 data. Moreover, due to the much lower spatial-resolution of DMSP/OLS and NPP/VIIRS, the comparison with other sensors should fully consider the difference in the spatial scale.
5. Conclusions
This study evaluated the changes in city nighttime light during the 2019 Spring Festival in six western cities in China using Luojia 1-01 nighttime images. Based on the results, the following conclusions were reached:
(1) For the 2019 Spring Festival, positive net immigration coincided with the increase in Light Area (LA) from Spring Festival to non-festival, while negative net immigration coincided with the decrease in LA. In addition, the Average Light Intensity (ALI) is higher during the Spring Festival than in non-festival dates.
(2) Statistically, the positive linear relationship between the normalized change of LA and the normalized net immigration is significant at the 0.05 level. This strongly suggests that population migration may cause the change in LA during the Spring Festival. Also, the increase of ALI indicates an intensification of urban activities during the Spring Festival.
(3) This study demonstrates the ability of Luojia 1-01 to detect light changes in China’s western cities during the Spring Festival. Aside from encouraging future studies in using Luojia 1-01, the approach presented in this study can be used as a reference for other studies in urban activities and festivals.
Due to limitations in the acquisition of Luojia 1-01 images, only six western cities in China were investigated in this study. In the future, more cities can be analyzed to validate the results and conclusions of this study.
Author Contributions
C.Z. proposed the idea and processed the data, and also wrote the paper. Y.P. contributed to the writing and in making the figures. J.L. and Q.Q. participated in the review and editing of the paper, and also contributed to constructing the figures. J.Y. participated in the writing of the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Open Research Fund of State Key Laboratory of Information Engineering in Surveying, Mapping and Remote Sensing, Wuhan University, grant number 18T04, Open Fund of State Key Laboratory of Coal Resources and Safe Mining, grant number SKLCRSM19KFA04, and National Facilities and Information Infrastructure for Science and Technology, grant number Y719H71006.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Hubei Data and Application Center of High Resolution Earth Observation System and the scientific research team of Luojia 1-01 satellite at Wuhan University for freely providing the Luojia 1-01 image data. The authors also thank Dr. Fu Chen (https://pan.baidu.com/s/17UqS7P66_6AMdr-a4sfUXA, accessed in June 2019) at the Aerospace Information Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Science, and thank the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) (https://ngdc.noaa.gov/eog/viirs/download_dnb_composites.html, accessed in June 2019), for freely providing NPP/VIIRS image data. The authors would like to especially thank Baidu Inc., China, for providing the migration data (http://qianxi.baidu.com/, accessed in February 2020). The authors thank to the professional English editing service from EditX.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Liu, Y.; Shi, J. How inter-city high-speed rail influences tourism arrivals: Evidence from social media check-in data. Curr. Issues Tour. 2019, 22, 1025–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Xiao, M.; Ding, X.; Tian, W.; Zhai, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, L.; Ye, X. Exploring human mobility patterns using geo-tagged social media data at the group level. J. Spat. Sci. 2019, 64, 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Hu, J.; Shi, X.; Zhao, L. Assessing disaster impacts and response using social media data in China: A case study of 2016 Wuhan rainstorm. Int. J. Disaster. Risk Reduct. 2019, 34, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Ye, X. Comparing mobility patterns between residents and visitors using geo-tagged social media data. Trans. GIS 2018, 22, 1372–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, N.; Zhang, Q. A global analysis of factors controlling VIIRS nighttime light levels from densely populated areas. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 190, 366–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, N. The impact of seasonal changes on observed nighttime brightness from 2014 to 2015 monthly VIIRS DNB composites. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 193, 150–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croft, T.A. Nighttime images of the earth from space. Sci. Am. 1978, 239, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Schaaf, C.; Seto, K.C. The Vegetation Adjusted NTL Urban Index: A new approach to reduce saturation and increase variation in nighttime luminosity. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 129, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Q.; Yu, B.L.; Song, W.; Liu, H.X.; Wu, Q.S.; Shi, K.F.; Wu, J.P. A new approach for detecting urban centers and their spatial structure with nighttime light remote sensing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 2017, 55, 6305–6319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.J.; Zhao, H.R.; Jiang, S.L. A zipf’s law-based method for mapping urban areas using NPP-VIIRS nighttime light data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wan, B.; Guo, Q.H.; Hu, M.S.; Zhou, S.P. Mapping regional urban extent using NPP-VIIRS DNB and MODIS NDVI data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.H.; Weng, Q.H.; Fu, P. Temporal variations of artificial nighttime lights and their implications for urbanization in the conterminous United States, 2013–2017. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 225, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.T.; Sun, S.K.; Zheng, S.N. Exploring urban expansion and socioeconomic vitality using NPP-VIIRS data in Xia-Zhang-Quan, China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.F.; Yu, B.L.; Huang, Y.X.; Hu, Y.J.; Yin, B.; Chen, Z.Q.; Chen, L.J.; Wu, J.P. Evaluating the ability of NPP-VIIRS nighttime light data to estimate the gross domestic product and the electric power consumption of china at multiple scales: A comparison with DMSP-OLS data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1705–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.M.; Smith, L.C. Advances in using multitemporal night-time lights satellite imagery to detect, estimate, and monitor socioeconomic dynamics. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 192, 176–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Cheng, W.M.; Zhou, C.H.; Li, M.C.; Wang, N.; Liu, Q.Y. GDP spatialization and economic differences in south china based on NPP-VIIRS nighttime light imagery. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, M.O.; Stokes, E.C. Holidays in lights: Tracking cultural patterns in demand for energy services. Earths Future 2015, 3, 182–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, X.; Levin, N.; Jendryke, M. Tracing cultural festival patterns using time-series of VIIRS monthly products. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 10, 1172–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dataset Overview|National Centers of Environment Information (NCEI). Available online: https://data.noaa.gov/metaview/page?xml=NOAA/NESDIS/NGDC/STP/DMSP/iso/xml/G01119.xml&view=getDataView&header=none (accessed on 23 June 2019).
- Zhang, G.; Guo, X.; Li, D.; Jiang, B. Evaluating the potential of LJ1-01 nighttime light data for modeling socio-economic parameters. Sensors 2019, 19, 1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Su, Z.; Zhang, G.; Chen, Z.; Meng, Y.; Li, D.; Liu, Y. Analysis and reduction of solar stray light in the nighttime imaging camera of Luojia-1 satellite. Sensors 2019, 19, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; He, G.; Long, T.; Guo, H.; Yin, R.; Leng, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, G. Potentiality of using Luojia 1-01 nighttime light imagery to investigate artificial light pollution. Sensors 2018, 18, 2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Li, D.; He, X.; Jendryke, M. A preliminary investigation of Luojia-1 night-time light imagery. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 10, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, L.; Li, D.; Xu, H. Mapping urban extent using Luojia 1-01 nighttime light imagery. Sensors 2018, 18, 3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Z.; Li, X.; Tong, F.; Li, Z.; Jendryke, M. Mapping urban expansion using night-time light images from Luojia1-01 and International Space Station. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 2603–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, R.; Li, D.; Zhang, G.; Shen, X.; Yu, B.; Wu, C.; Xie, S.; Zhang, P.; Li, M.; et al. Initial assessment of the LEO based navigation signal augmentation system from Luojia-1A satellite. Sensors 2018, 18, 3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Sun, J. Assessing the ability of luojia 1-01 imagery to detect feeble nighttime lights. Sensors 2019, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, P.; Liu, X. Evaluation of Luojia 1-01 nighttime light imagery for impervious surface detection: A comparison with NPP-VIIRS nighttime light data. Int. J. Appl. Earth. Obs. 2019, 81, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, Z.; Yang, C.; Li, Q.; Wu, Q.; Wu, J.; Zhang, G.; Yu, B. Analyzing parcel-level relationships between Luojia 1-01 nighttime light intensity and artificial surface features across Shanghai, China: A comparison with NPP-VIIRS data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2020, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, P.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, Y. On-orbit geometric calibration and validation of Luojia 1-01 night-light satellite. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, L.; Jiang, Y.; Shen, X.; Li, D. On-orbit relative radiometric calibration of the night-time sensor of the LuoJia1-01 satellite. Sensors 2018, 18, 4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Zhong, X.; Zhang, G.; Li, Y.; He, X.; Wang, Q.; Wei, Z.; He, C.; Li, D. High sensitive night-time light imaging camera design and in-orbit test of Luojia1-01 satellite. Sensors 2019, 19, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Li, Q.; Kong, L.; Gu, S.; Zhang, L. Quasi-all-passive thermal control system design and on-orbit validation of Luojia 1-01 satellite. Sensors 2019, 19, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Zhong, X.; Zhang, G.; Li, D.; Su, Z.; Meng, Y.; Jiang, Y. Thermal stability optimization of the Luojia 1-01 nighttime light remote-sensing camera’s principal distance. Sensors 2019, 19, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, L.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Z. Night-Light image restoration method based on night scattering model for luojia 1-01 satellite. Sensors 2019, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, G. Star-Based Calibration of the Installation Between the Camera and Star Sensor of the Luojia 1-01 Satellite. Remote Sens. 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhong, X.; Su, Z. On-Orbit Signal-to-Noise Ratio Test Method for Night-Light Camera in Luojia 1-01 Satellite Based on Time-Sequence Imagery. Sensors 2019, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, L. The influence of population movements on the urban relative humidity of Beijing during the Chinese Spring Festival holiday. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 170, 1508–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, J. Assessing population movement impacts on urban heat island of Beijing during the Chinese New Year holiday: Effects of meteorological conditions. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 131, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).