GB-InSAR-Based DEM Generation Method and Precision Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. GB-InSAR DEM Generation Method
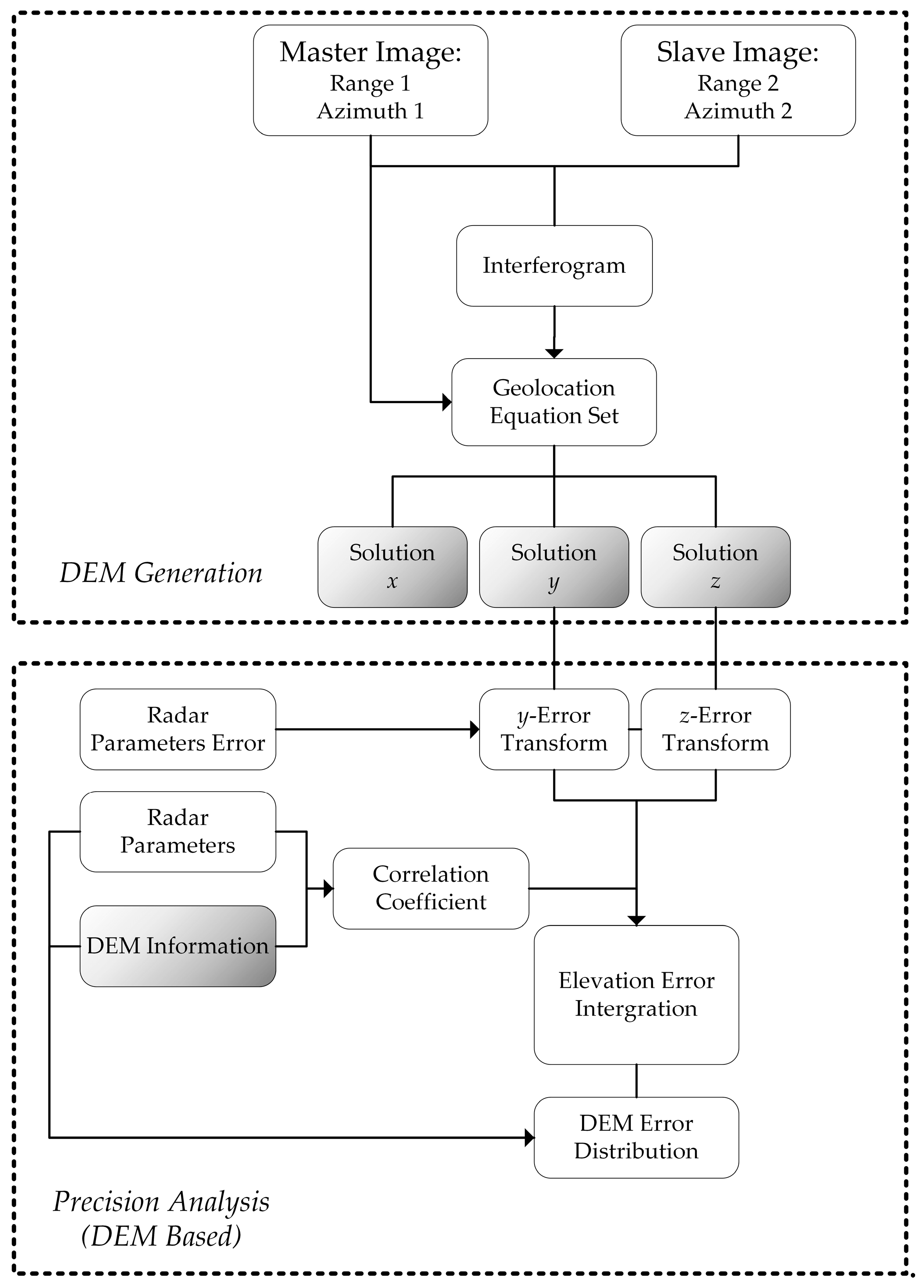
2.1. Summary of DEM Generation and Precision Analysis Method
2.2. Key Problems in GB-InSAR DEM Generation
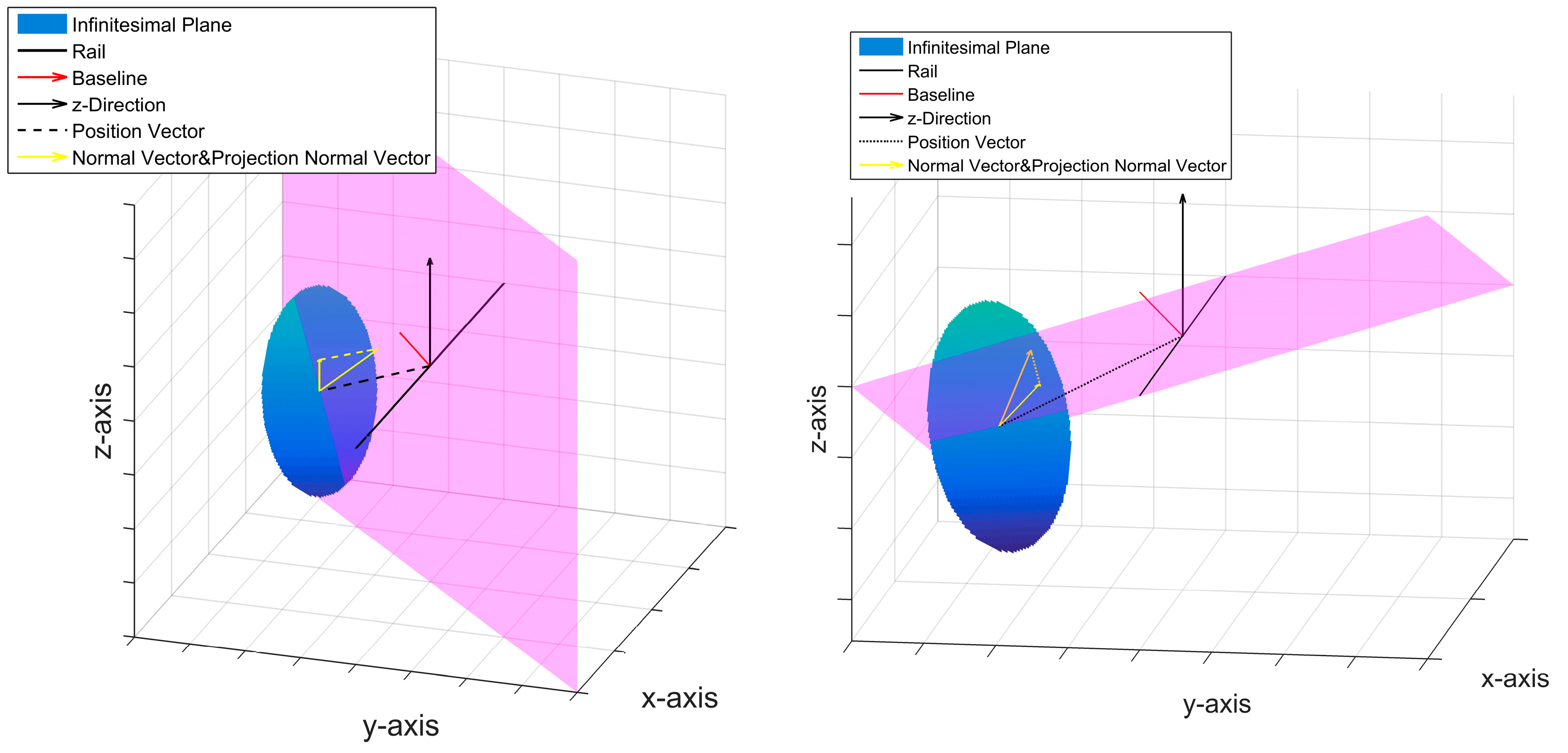
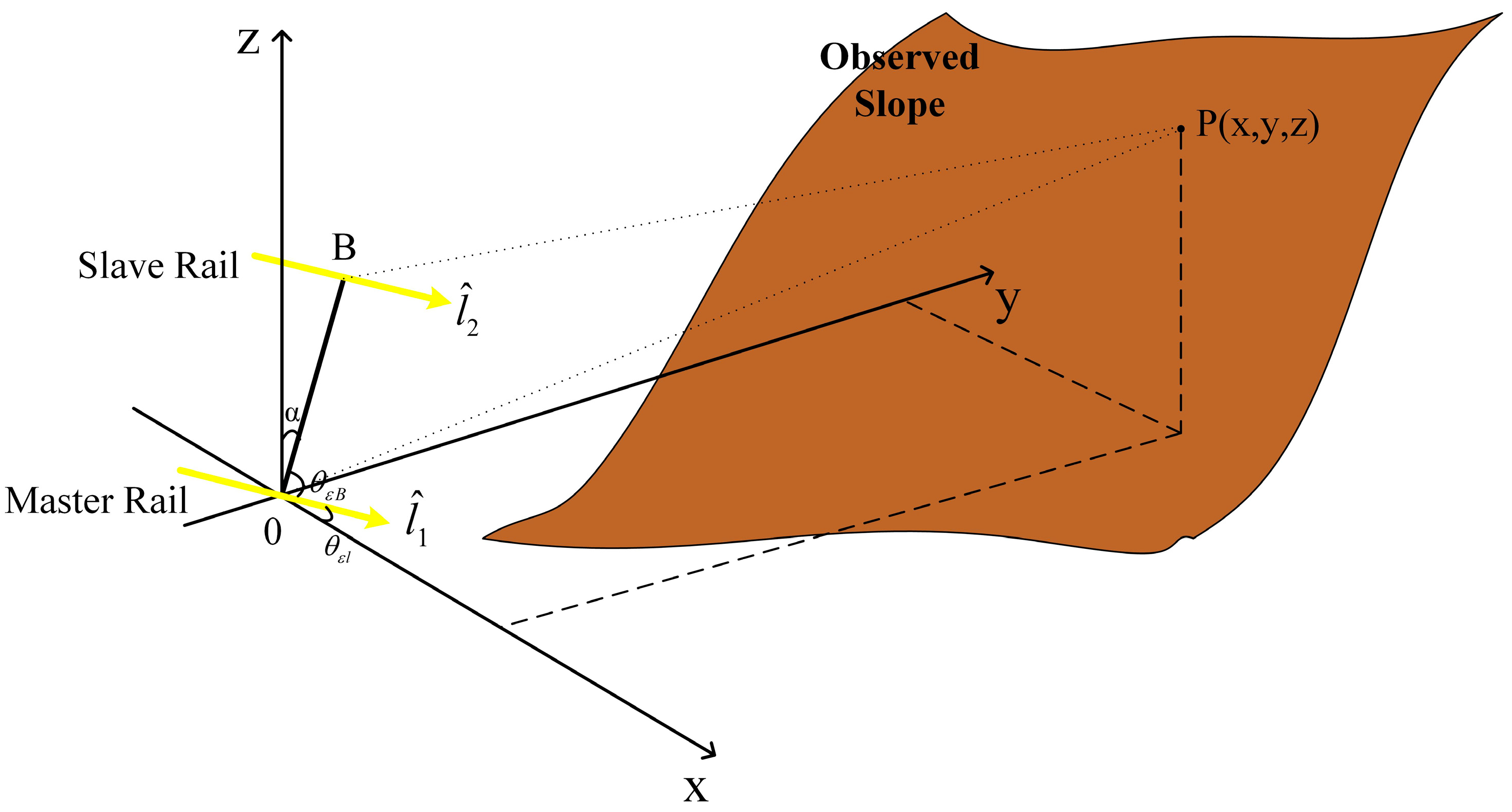
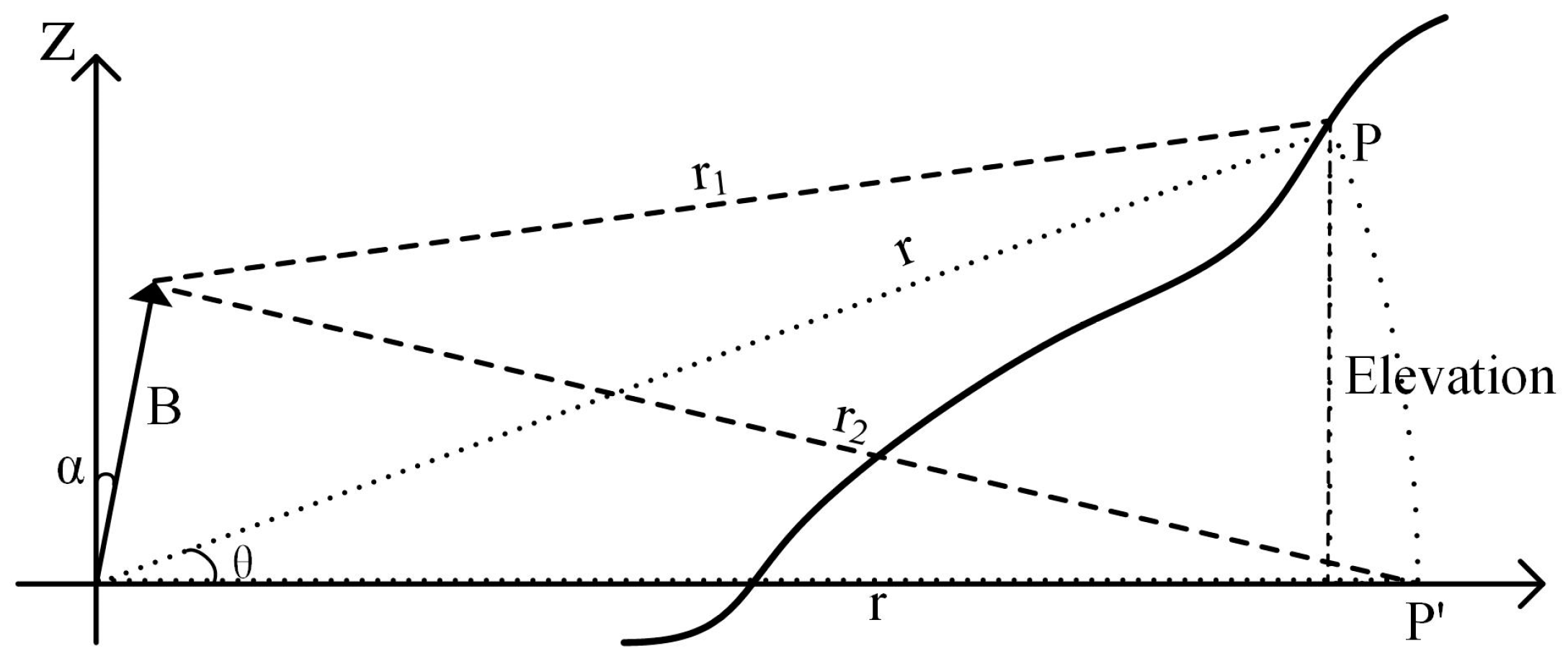
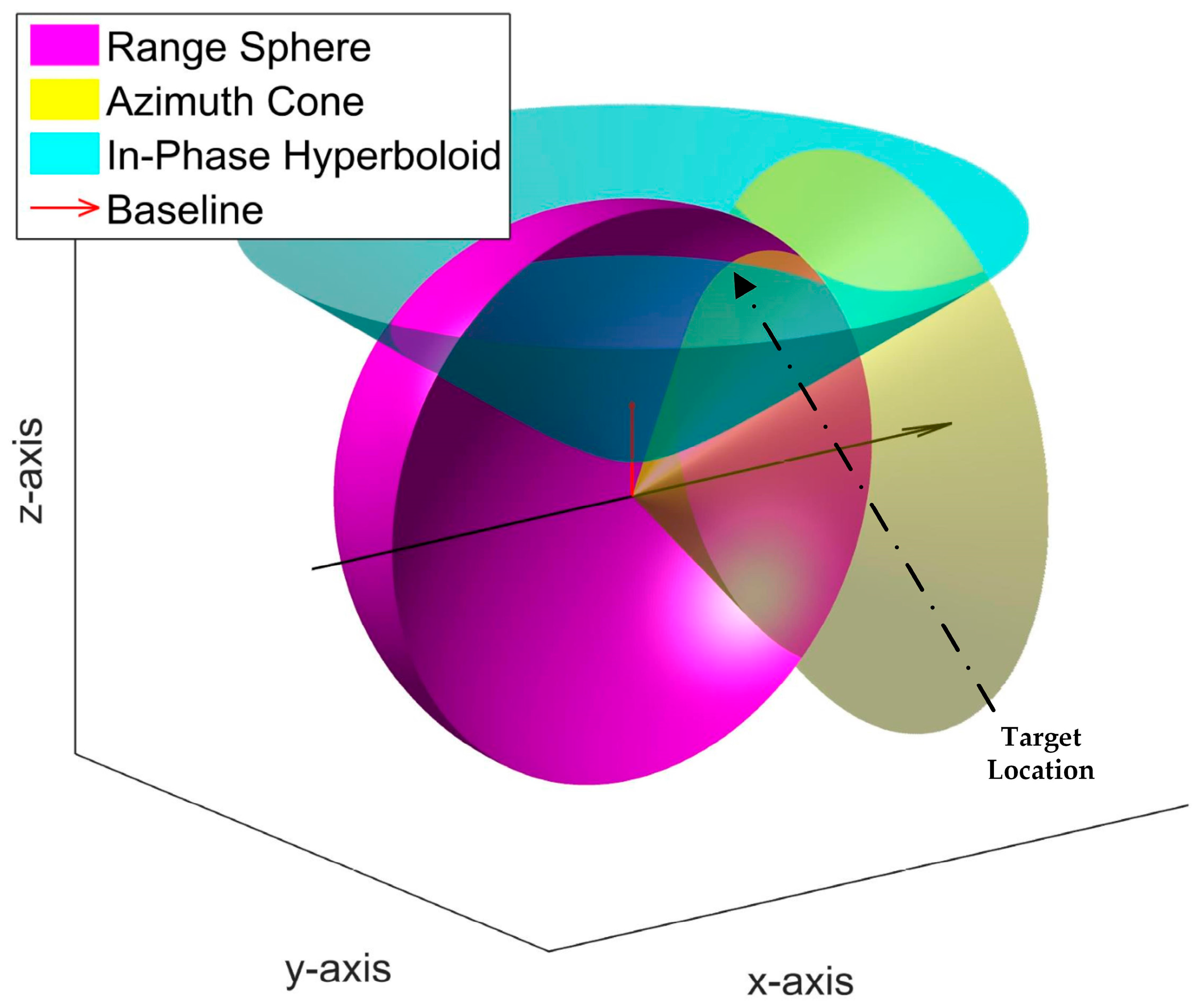
2.3. GB-InSAR Geolocation Method
3. GB-InSAR System Precision Analysis
3.1. Error Transfer in the GB-InSAR System
3.2. Coherence Analysis in the GB-InSAR System
3.2.1. GB-InSAR Decorrelation Sources
3.2.2. Theoretical Formula of the GB-InSAR Correlation Coefficient
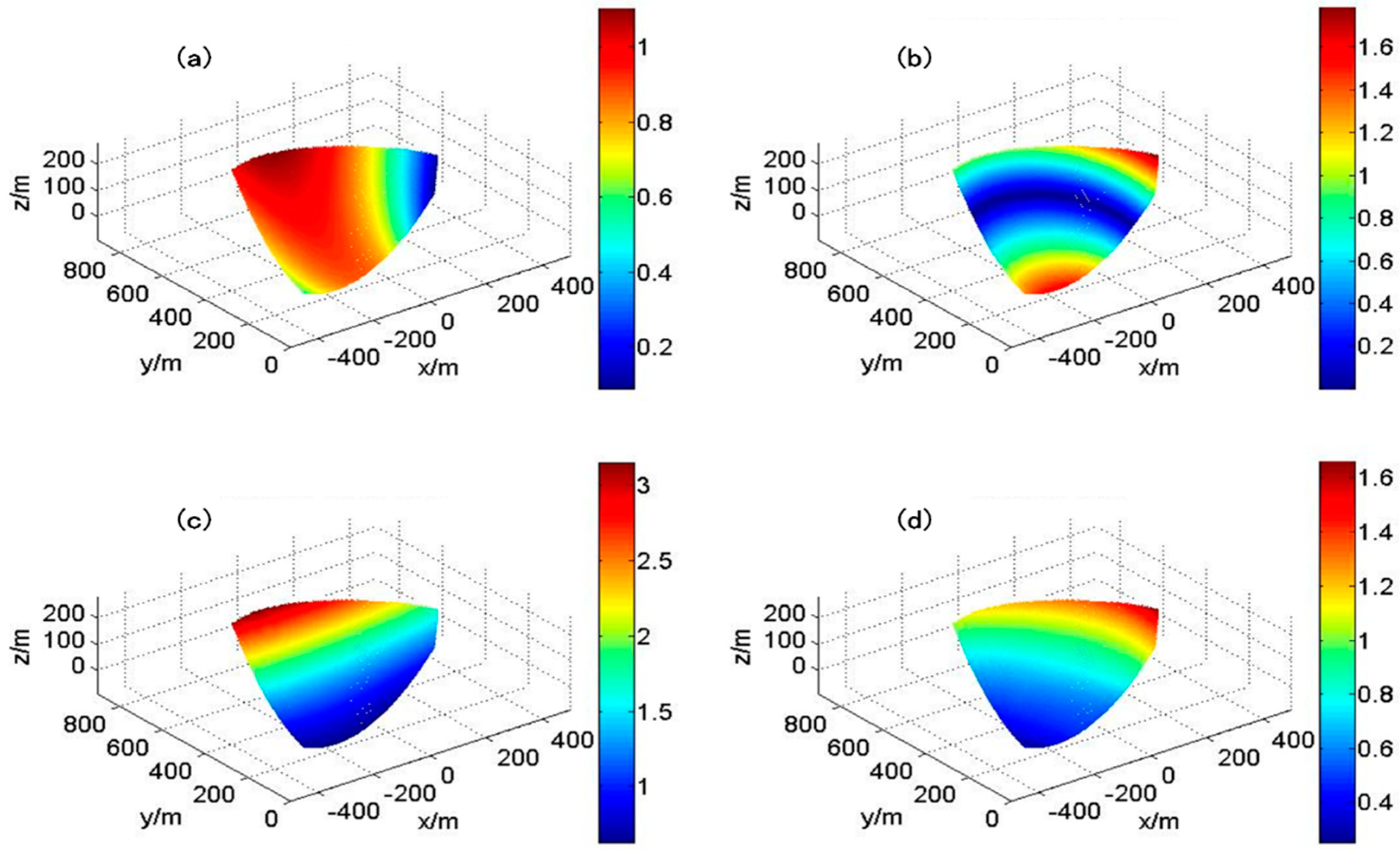
3.3. Error Spatial Distribution
4. Results
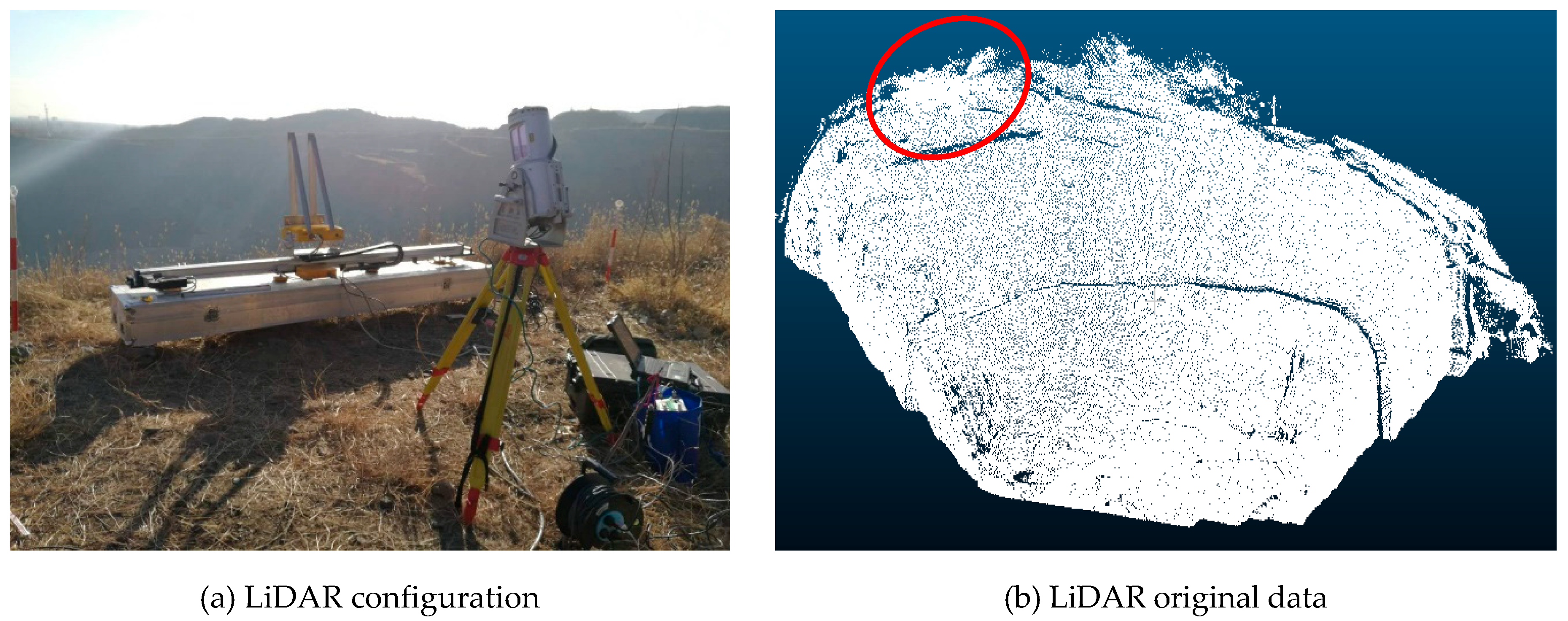
4.1. GB-InSAR System and LiDAR Data Acquisition
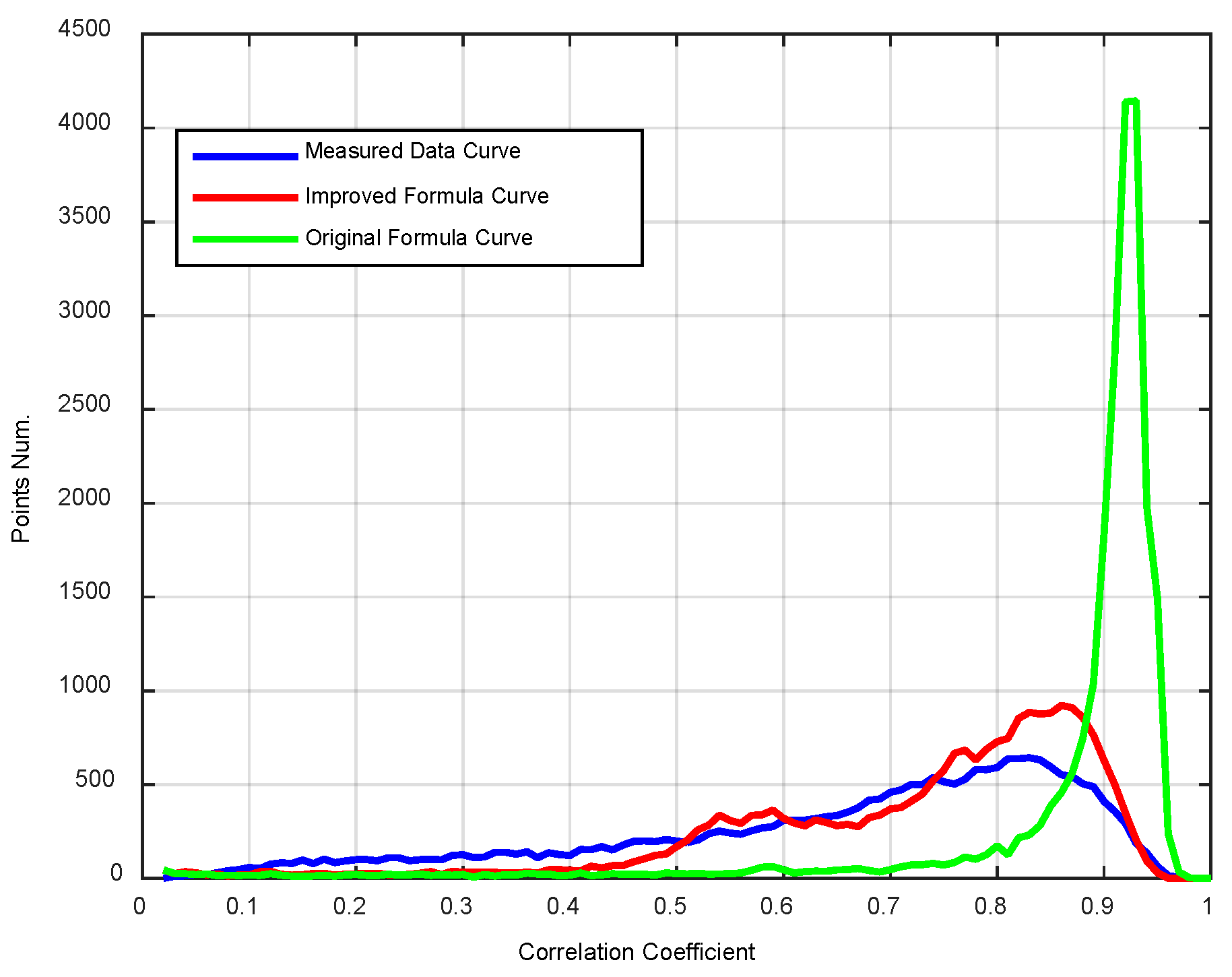
4.2. Verification of the Correlation Coefficient Calculation
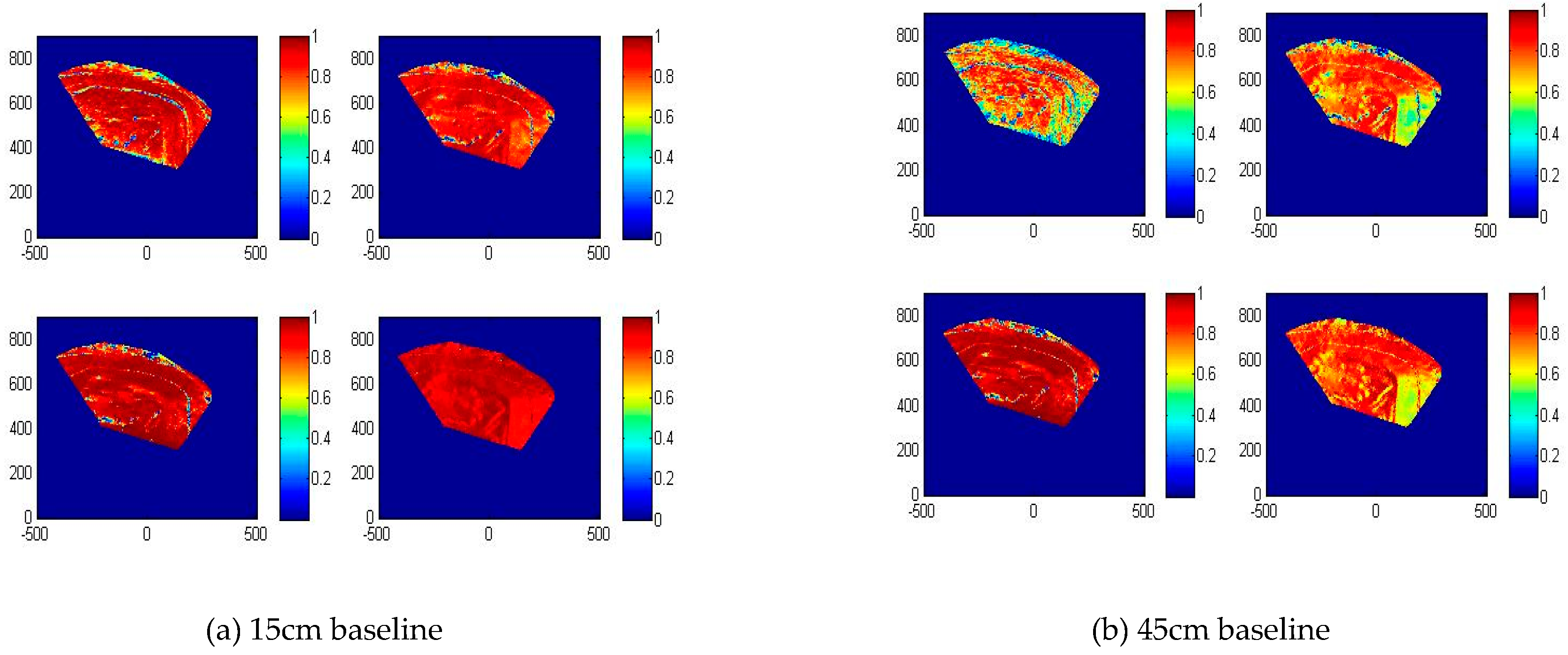
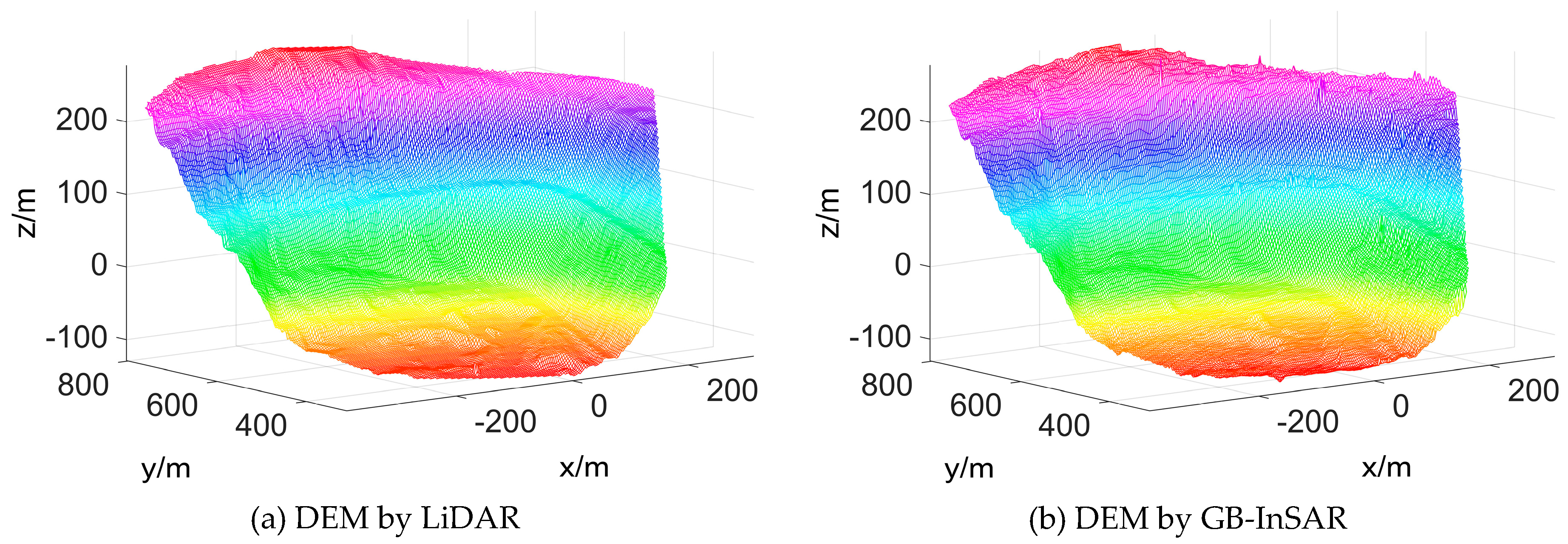
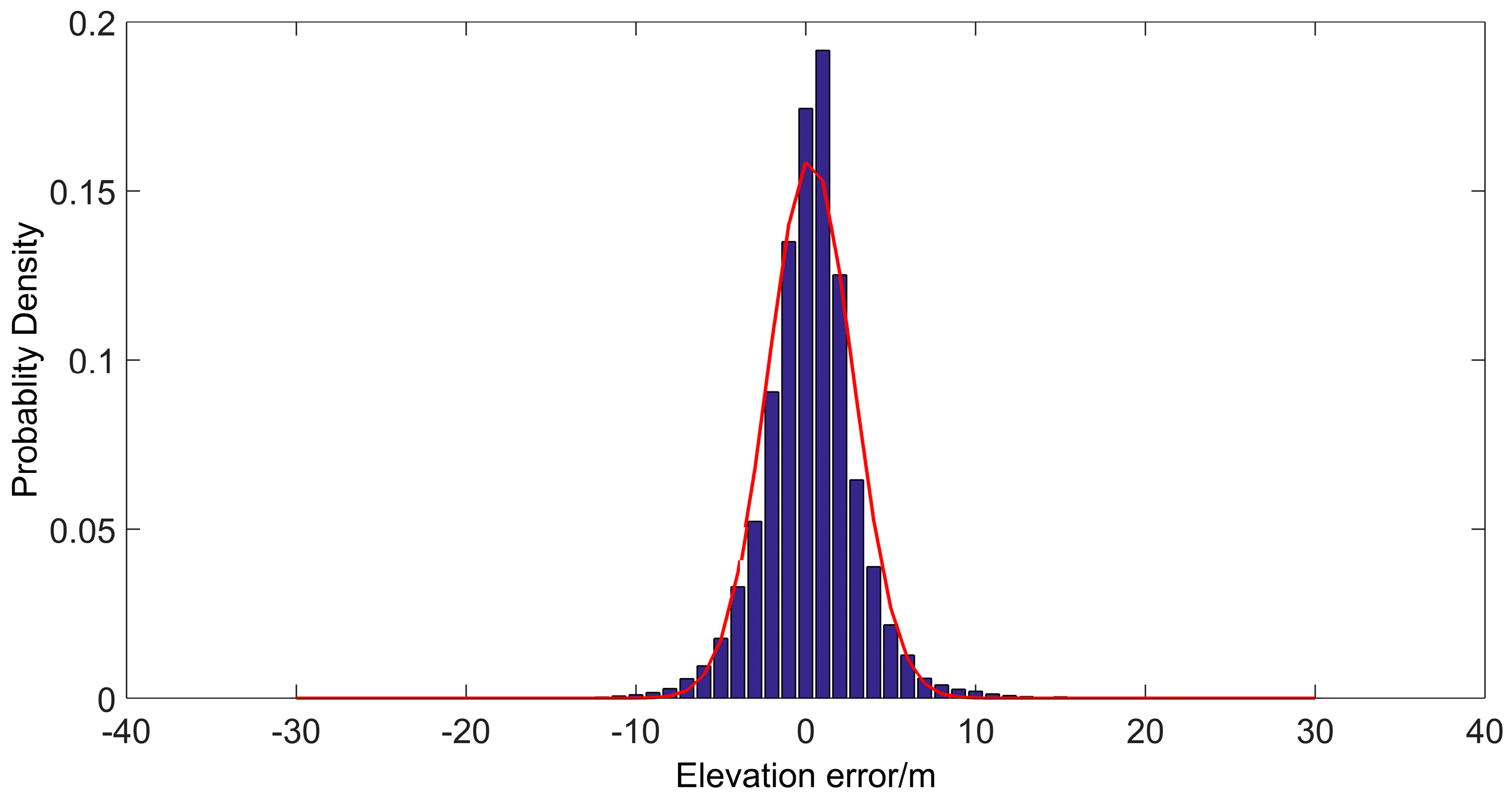
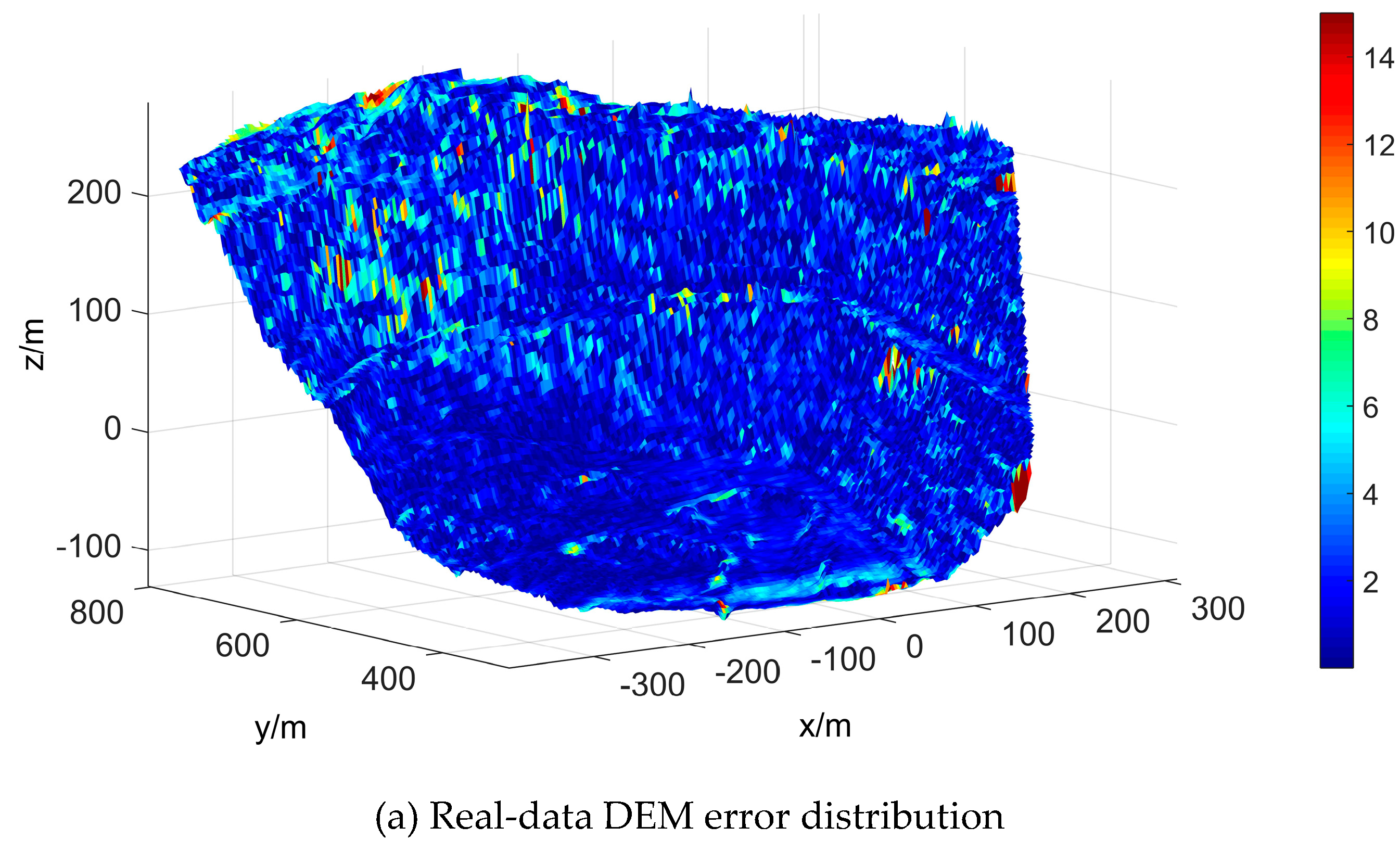
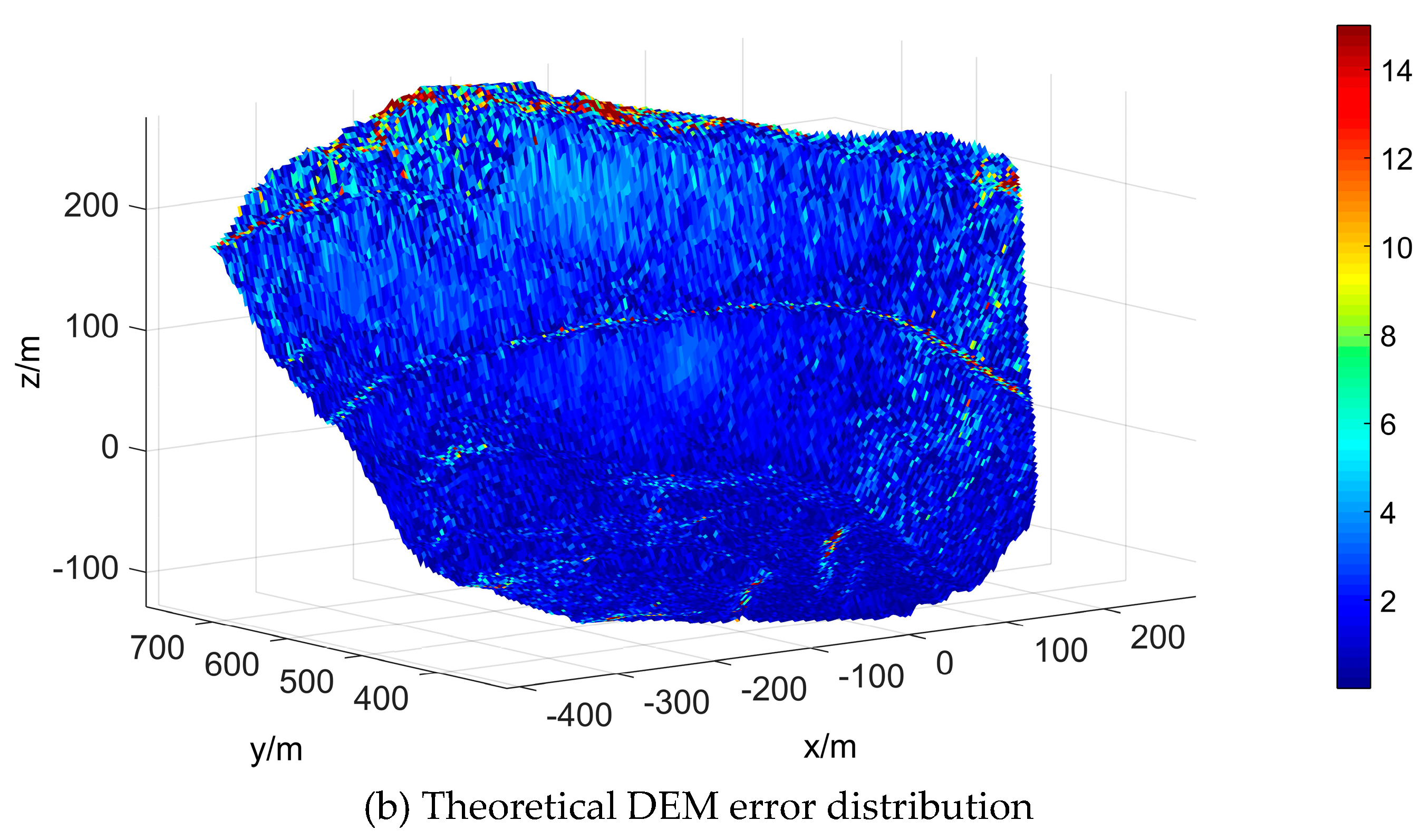
4.3. DEM Precision and Error Distribution
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Pieraccini, M.; Luzi, G.; Atzeni, C. Terrain mapping by ground-based interferometric radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Sens. 2001, 39, 2176–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casagli, N.; Farina, P.; Leva, D.; Nico, G.; Tarchi, D. Landslide monitoring on a short and long time scale by using ground-based SAR interferometry. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Remote Sensing, Baltimore, MD, USA, 6–11 October 2003; Volume 4886, pp. 322–329. [Google Scholar]
- Fuster, R.M.; Usón, M.F.; Ibars, A.B. Interferometric orbit determination for geostationary satellites. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2017, 60, 060302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanari, R.; Fornaro, G.; Riccio, D.; Migliaccio, M.; Papathanassiou, K.P.; Moreira, J.R.; Dutra, L.; Puglisi, G.; Franceschetti, G.; Coltelli, M. Genreation of digital elevation models by using SIR-C/X-SAR multi-frequency two-pass interferometry: The Etan case study. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 1097–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieraccini, M.; Casagli, N.; Luzi, G.; Tarchi, D.; Mecatti, D.; Noferini, L.; Atzeni, C. Landslide monitoring by ground-based radar interferometry: A field test in Valdarno (Italy). Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 24, 1385–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensley, S.; Rosen, P.; Joughin, I.; Li, F.; Madsen, S.; Goldstein, R.; Rodriguez, E. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry. Proc. IEEE 2000, 88, 333–382. [Google Scholar]
- Noferini, L.; Pieraccini, M.; Mecatti, D.; Macaluso, G.; Luzi, G.; Atzeni, C. DEM by Ground-Based SAR Interferometry. IEEE Geosci. Sens. Lett. 2007, 4, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Vazquez, A.; Fortuny-Guasch, J. Averaging and Formulation Impact on GB-SAR Topographic Mapping. IEEE Geosci. Sens. Lett. 2008, 5, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nico, G.; Leva, D.; Antonello, G.; Tarchi, D. Ground-based SAR interferometry for terrain mapping: Theory and sensitivity analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Sens. 2004, 42, 1344–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nico, G. Exact closed-form geolocation for SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Sens. 2002, 40, 220–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansosti, E. A simple and exact solution for the interferometric and stereo SAR geolocation problem. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Sens. 2004, 42, 1625–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Goldstein, R.M. Studies of multi-baseline spaceborne interferometric synthetic aperture radars. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1990, 28, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meta, A.; Hoogeboom, P. Development of signal processing algorithms for high resolution airborne millimeter wave FMCW SAR. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Radar Conference, Arlington, VA, USA, 9–12 May 2005; pp. 326–331. [Google Scholar]
- Just, D.; Bamler, R. Phase statistics of interferograms with applications to synthetic aperture radar. Appl. Opt. 1994, 33, 4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Hoppel, K.W.; Mango, S.A.; Miller, A.R. Intensity and Phase Statistics of Multi-look Polarimetric and Interferometric SAR Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1994, 32, 1017–1028. [Google Scholar]
- Pieraccini, M.; Mecatti, D.; Noferini, L.; Moia, F.; Atzeni, C.; Luzi, G.; Guidi, G. Ground-based radar interferometry for landslides monitoring: Atmospheric and instrumental decorrelation sources on experimental data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Sens. 2004, 42, 2454–2466. [Google Scholar]
- Iglesias, R.; Fabregas, X.; Aguasca, A.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Lopez-Martinez, C.; Gili, J.A.; Corominas, J. Atmospheric Phase Screen Compensation in Ground-Based SAR with a Multiple-Regression Model Over Mountainous Regions. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Sens. 2014, 52, 2436–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, A.K.; Goldstein, R.M.; Zebker, H.A. Mapping small elevation changes over large areas: Differential radar interferometry. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 1989, 94, 9183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Zhu, M.; Zeng, T.; Tian, W.; Mao, C. High-precision deformation monitoring algorithm for GBSAR system: Rail determination phase error compensation. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2016, 59, 082307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, B.C. The non-isotropic two-dimensional random walk. Waves Random Media 1993, 3, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.W. Radar Reflectivity of Land and Sea; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Ulaby, F.T. Microwave Remote Sensing, Vol: Microwave Remote Sensing, Fundamentals and Radiometry; Addison-Wesley Publishing Company: Boston, MA, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein, R.M.; Werner, C.L. Radar interferogram filtering for geophysical applications. Geophys. Res. Lett. Mar. 1998, 25, 4035–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bräutigam, B.; Bachmann, M.; Schulze, D.; Tridon, D.B.; Rizzoli, P.; Martone, M.; Gonzalez, C.; Zink, M.; Krieger, G. TanDEM-X Global DEM Quality Status and Acquisition Completion. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 13–18 July 2014; pp. 3390–3393. [Google Scholar]
- Mandel, L.; Wolf, E. Optical Coherence and Quantum Optics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Zebker, H.; Villasenor, J. Decorrelation in interferometric radar echoes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Sens. 1992, 30, 950–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



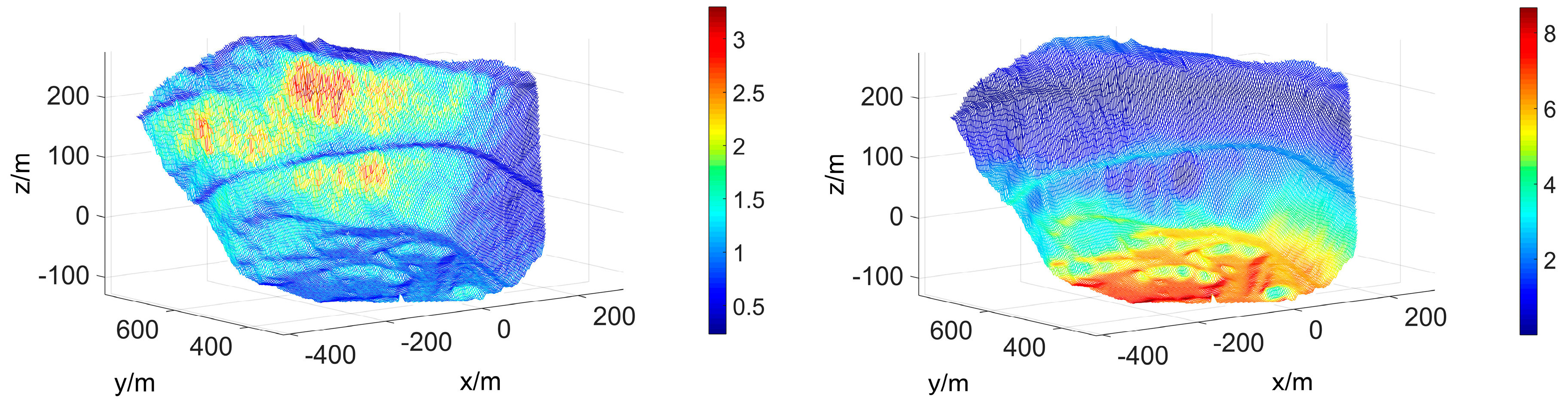
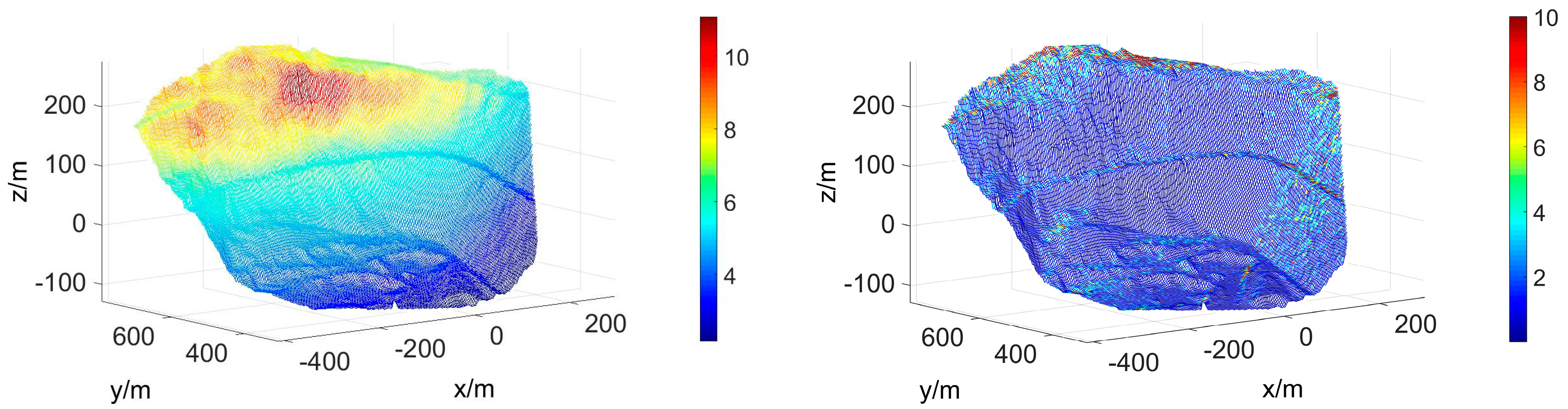

| y-Direction | z-Direction |
|---|---|
| Main Error Sources | Baseline Inclination | Baseline Length | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Upper test Set A | Theoretical/m | 8.1 | 2.9 |
| Observed/m | 8.7 | 3.1 | |
| Bottom test Set B | Theoretical/m | 2.5 | 7.2 |
| Observed/m | 3.6 | 7.9 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, W.; Zhao, Z.; Hu, C.; Wang, J.; Zeng, T. GB-InSAR-Based DEM Generation Method and Precision Analysis. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11090997
Tian W, Zhao Z, Hu C, Wang J, Zeng T. GB-InSAR-Based DEM Generation Method and Precision Analysis. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(9):997. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11090997
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Weiming, Zheng Zhao, Cheng Hu, Jingyang Wang, and Tao Zeng. 2019. "GB-InSAR-Based DEM Generation Method and Precision Analysis" Remote Sensing 11, no. 9: 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11090997
APA StyleTian, W., Zhao, Z., Hu, C., Wang, J., & Zeng, T. (2019). GB-InSAR-Based DEM Generation Method and Precision Analysis. Remote Sensing, 11(9), 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11090997





