Abstract
The aim of this paper is to evaluate the usefulness of TanDEM-X DEM (digital elevation model) for remote geomorphological analysis in Argentinian Patagonia. The use of a DEM with appropriate resolution and coverage might be very helpful and advantageous in vast and hardly accessible areas. TanDEM-X DEM could represent an unprecedented opportunity to identify geomorphological features because of its global coverage, ~12 m spatial resolution and low cost. In this regard, we assessed the vertical accuracy of TanDEM-X DEM through comparison with Differential Global Positioning System (DGPS) datasets collected in two areas of the Patagonia Region during a field survey; we then investigated different types of landforms by creating the elevation profiles. The comparison indicates a high agreement between TanDEM-X DEM and reference values, with a mean absolute vertical error (MAE) of 0.53 m, and a root mean squared error (RMSE) of 0.73 m. The results of landform analysis show an appropriate spatial resolution to detect different features such as beach ridges, which are impossible to delineate with other lower resolution DEMs. For these reasons, TanDEM-X DEM constitutes a useful tool for detailed geomorphological analyses in Argentinian Patagonia.
1. Introduction
Various scientific papers have investigated the role of digital elevation models (DEMs), spatial resolution and quality in geological studies. For example, DEMs have been used for hydrological simulation [1], geomorphological studies in glacial and periglacial environments [2], fluvial environments [3], volcanic areas [4,5,6], archeological contexts [7,8,9,10], landslide analyses [11,12] and recognition of active tectonic deformation [13].
The spatial resolution of a DEM can strongly affect the results of a specific research. Light detection and ranging (LiDAR) data have been successfully used in different geomorphological contexts thanks to their very high spatial resolution, but they are usually very expensive. LiDAR is not available everywhere and its new acquisition is expensive and time-consuming. By contrast, the free-of-charge Shuttle radar topography mission (SRTM) DEM can be used to cover very wide areas, despite the limited usefulness caused by its low spatial resolution.
The study of past sea-level changes in coastal areas based on morphological evidences can benefit from the use of DEMs. Ancient shorelines can be recognized and measured in order to achieve significant information about sea-level and climate changes. Geomorphological features such as beach ridges, littoral terraces, valley-mouth terraces, notches, shore-platforms are common features along the Argentinian Patagonia coasts [14,15,16,17,18,19]. Their elevations are the result of the interplay between tectonic uplift, glacioisostatic rebound and eustatic rise. However, an accurate measurement of the elevation of these features above sea-level by a Differential Global Positioning System (DGPS) has been rarely performed [20,21]. Most previous data sets have been referred only to the local mean high-tide e.g., [15,17,18], so as to make correlations in a global setting difficult to perform. Given their dimensions, beach ridges can be easily mapped using a digital elevation model characterized by a proper spatial resolution, but their extension (several km) along the coast requires a DEM with wide coverage. The SRTM DEM cannot be used because of its low resolution with respect to the average dimensions of these morphological features.
A correct estimation of elevation above sea-level of these deposits acquires great significance, since elevation is the basis for past sea-level reconstructions. So far, the elevation of these deposits (mainly beach ridges and marine terraces) has only been measured directly in the field because the remote-sensing data available were considered unreliable. However, some coastal areas along the Patagonian coast are hardly accessible and this makes it difficult to obtain data from part of this territory; moreover, when possible, the activity of measuring the elevation directly on the field is always time-consuming and expensive in terms of resources.
In addition to the beach ridges, which represent one of the most studied paleo sea-level indicators, a more complete framework of sea-level variation can be obtained by mapping and studying other geomorphological features such as marine terraces or other characteristic elements of this region, or hypersaline lagoon deposits locally known as “salitrales”: these are depressed areas that are remnants of old coastal lagoons formed in dry evaporative environments [22]. Other significant data related to paleo landscape changes can derive from the study of fans and fluvial terraces. The identification of salitrales, alluvial fans and fluvial and marine terraces can also benefit from a DEM characterized by an appropriate spatial resolution.
In Patagonia (Argentina, South America), most of the geomorphological features that can be used to reconstruct sea-level variation are scattered over a very wide area. The launch of the TanDEM-X DEM (TDX-DEM) product represents an unprecedented opportunity to map geomorphological features impossible to be mapped by SRTM DEM, given its higher resolution, global coverage and low cost.
The usefulness of TDX-DEM has been evaluated in different geomorphological settings. For example, Pipaud et al. [23] used TDX-DEM in mountainous areas of Tibet to detect and interpret landforms by comparing the results obtained with Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) and SRTM DEMs. The authors concluded that landforms smaller than 30 m can be detected and that TDX-DEM is widely superior to ASTER and SRTM. Erasmi et al. [24] used TDX-DEM to detect archeological features in the Seyhan river valley (Turkey), on the basis of their heights. Also in this case TDX-DEM performance is superior to that of ASTER and of SRTM DEMs, but heights measured by TDX-DEM introduce a relevant error along the coastline when compared to the Real Time Kinematic (RTK)-GPS field survey. Avtar et al [25] compared TDX-DEM with SRTM and ASTER in the urban area of Tokyo. Although their results confirm that TDX-DEM shows considerably lower root mean squared errors (RMSEs) than the existing global DEMs, TDX-DEM is characterized by a high elevation error for urban and vegetated areas. A similar problem was encountered by Rizzoli et al. [26] in highly vegetated areas affected by strong volume decorrelation phenomena. Wessel et al. [27] assessed the vertical accuracy of TDX-DEM at global scale by using three million globally distributed GPS points. This achievement confirmed the outstanding performance of TDX-DEM with an increase in RMSE in urban and highly vegetated areas. According to the literature, the performance of TDX-DEM is undoubtedly superior to that of ASTER and SRTM, despite the increased error in urban and vegetated areas.
Our study investigates the usefulness of TDX-DEM in a flat coastal area of Patagonia (Argentina), where the vegetation cover is very limited. The aim was to understand whether TDX-DEMs are able to detect peculiar geomorphological features that will be used to reconstruct past sea levels.
We compared the values inferred with the ~12 m of spatial resolution TDX-DEM with those measured by using a DGPS station along six transects perpendicular to the coasts (Figure 1) to evaluate the usefulness of the ~12 m resolution of TDX-DEM in the geomorphological analysis conducted in Patagonia. To pursue this goal, we assessed the vertical accuracy of TDX-DEM, we located areas with large discrepancies, andthen we investigated different types of landforms in the study areas or nearby regions.
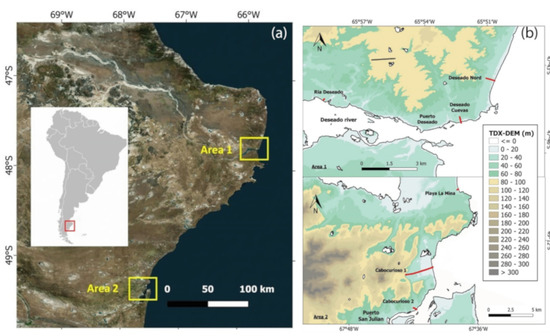
Figure 1.
(a) Location of the study areas (Sentinel 2, Google Earth); (b) classified digital elevation model (DEM) based on TDX-DEM for each area. The red lines indicate the profiles studied, while the black lines divide the land from the water bodies. The black lines also indicate the coastline.
2. Study Areas
This work is concentrated on two river mouth areas of the Patagonian region (Figure 1). The selected areas are centred in the villages of Puerto Deseado (area 1) and Puerto San Julian (area 2), located at 47°46′ S; 65°50′ W ca. and 49°16′ S; 67°40′ W ca., respectively. These areas are characterized by a similar geological and geomorphological context and have long been studied by several authors [15,28], owing to the presence of extraordinary series of Quaternary marine deposits investigated since the mid-19th century [29]. In addition to the well-known marine deposits, the areas of study included Quaternary continental deposits (e.g., alluvial fans, fluvial terraces) and transitional deposits (e.g., salitrales) [14].
Both areas are located in the geological province of the Deseado Massif [30], mainly characterized by calc-alkaline and peraluminous rhyolites, with some dacitic members [31,32]. The rocky substratum dominates the inner landscape, while the coastal landscape and the lower part of the river mouths mostly concern marine deposits of paramount importance for the study of sea-level and climate changes. The selected areas are characterized by a mixed macro-tidal regime with a tidal range of 4-6m. Exposure to oceanic waves creates a very energetic environment, triggered by a cyclonic activity mainly operating over the south [33].
3. Methodology
3.1. Elevation Dataset
3.1.1. Global Positioning System (GPS) Dataset
The GPS dataset consists of 2217 points divided into 6 topographic profiles: Cabocurioso 1 (1282 points), Cabocurioso 2 (211 points) and Playa La Mina (74 points) located in area 2 (Puerto San Julian Village); Deseado North (279 points), Deseado Cuevas (307 points) and Ria Deseado (64) located in area 1 (Puerto Deseado Village). The GPS points were collected during a field survey conducted in January/February 2016. These profiles were obtained near the shore and the end of the profile represents the sea-level at the time of measurement. GPS was used to measure ellipsoidal heights showing a difference of about 11.634m with respect to the orthometric heights in the study area. The GPS equipment was a Trimble R10 DGPS (Differential Global Position System). The data were acquired by the WGS84 Geographic Coordinate System (maximum error in the elevation of acquired points was 10 cm).
3.1.2. TanDEM-X Digital Elevation Model (DEM)
TDX-DEM is a global digital elevation model of the Earth’s land masses. TDX-DEM was generated during the TanDEM-X mission by TanDEM-X, a spaceborne radar interferometer based on two TerraSAR-X radar satellites flying in close formation [34]. The global DEM acquisition phase took four years, from December 2010 to January 2015, and the final products were the result of multiple TanDEM-X DEM acquisitions. The horizontal and vertical datum is WGS84 in its newest realization (WGS84-G1150). For the study areas, the spatial resolution is 0.4 arcseconds, which corresponds to 12.37 meters. All products are distributed in 1° × 1° tiles.
Two tiles were used for the comparison: TDM1_DEM__04_S48W066_DEM and TDM1_DEM__04_S50W068_DEM. The acquired SAR data had already been processed as described in Wessel [35]. Other DEM products were provided along with TDX-DEM, including the height error map (HEM). For each DEM pixel the HEM values represent the corresponding height error in the form of standard deviation. The value is derived from interferometric coherence and from geometrical considerations [35]. This value was taken into account for the comparisons.
Table 1 summarizes the characteristics of the elevation datasets analyzed.

Table 1.
Characteristics of the elevation datasets analyzed in this study.
3.2. Vertical Accuracy Assessment
Accuracy is the closeness of observation to a correct value or to a standard [36]. By assuming GPS measurements as reference values, absolute vertical accuracy assessment of TDX-DEM was performed comparing its elevation values with GPS elevations at each GPS point location.
Data preparation was performed through the free and open-source QGIS software. GPS and TDX-DEM datasets have the same vertical datum (WGS84), so that no reprojection was performed. TDX-DEM elevation values were extracted at the GPS measurement locations using the SAGA tool “Add raster values to point”. In order to plot the elevation with the distance, a broken line among the points was constructed and the length of each sector was calculated.
The TDX-DEM error was computed by subtracting the GPS data from TDX-DEM elevation at each GPS point location. Statistical analysis was performed in terms of mean error (ME), mean absolute error (MAE), and RMSE obtained from the Equations (1)–(3). ME tells us whether sets of measurements consistently underestimate (negative ME) or overestimate (positive ME) the true value. Both MAE and RMSE exhibit on average to what extent the observed values differ from the assumed true values [37]. The difference is that RMSE gives a relatively high weight to large errors because these are squared before they are averaged. Therefore, RMSE is useful when large errors are particularly undesirable [38], as in this case. In addition to RMSE, the linear error was also calculated with 90% confidence level (LE90). If the elevation differences between the TDX-DEM and the reference values follow a normal distribution, LE90 can be calculated directly from the RMSE by using Equation (4) [36].
The equations are as follows:
ME = 1/n ∑n i=1 (Z*i – Zi)
MAE = 1/n ∑n i=1 |Z*i – Zi|
RMSE = √ 1/n ∑n i=1 (Z*i – Zi)²
LE90 = 1.645 * RMSE
where: Z*= modeled DEM value (TanDEM-X elevations)
Z = reference height (GPS elevations)
The level of agreement between TDX-DEM elevation values and reference data is also evaluated in terms of linear regression (LR). A statistical analysis was performed without the outliers that were identified by applying a threshold. The threshold was selected as three times the mean RMSE value, derived from a preliminary calculation of profile accuracy measures [39].
The height error values obtained by HEM were used to calculate the percentage of GPS points included in the height error range and to represent the TDX-DEM profile, which is described as a strip obtained from TDX-DEM values ± height error values for each point.
3.3. Landform Analysis
Vertical accuracy assessment was designed to evaluate the usefulness of TDX-DEM in geomorphological studies carried out especially near the coast. For this reason we also identified some landforms of interest present in the study areas or nearby regions by means of optical satellite imagery (Sentinel 2, Google Earth), and we verified whether they were highlighted in the TDX-DEM by making an elevation profile. The landforms considered were: alluvial fans, fluvial terraces, marine terraces, beach ridges and salitrales.
4. Results
Figure 2a, Figure 3a, Figure 4a, Figure 5a, Figure 6a and Figure 7a shows the GPS and TDX-DEM datasets. The length of the profiles is different and varies from a minimum of 120 m (Ria Deseado) to a maximum of 4800 m (Cabocurioso 1). The TDX-DEM spatial resolution of ~12 m is highlighted in the shorter profiles. For all analyzed GPS datasets, the elevation is included in the range 10–50 m. On average, about 38% of GPS points fall within the height error range provided for TDX-DEM, indicating a good correlation between the datasets. However, some profiles (Cabocurioso 1, Deseado Cuevas and Ria Deseado) display discrepancies in the final part, very close to the shoreline. In this area the TDX-DEM has higher variability and height error than the rest of the profile.
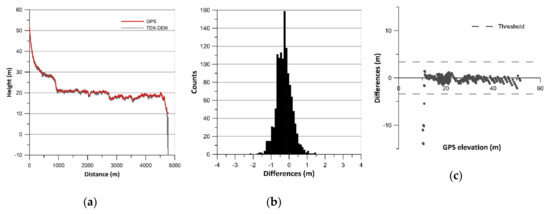
Figure 2.
Results of vertical accuracy assessment of Cabocurioso 1: (a) terrain profiles; (b) histograms of error data (TDX-DEM elevation–GPS elevation) without outliers; (c) residual plots.
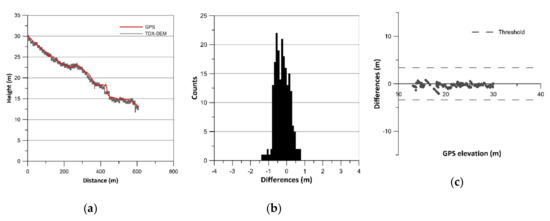
Figure 3.
Results of vertical accuracy assessment of Cabocurioso 2: (a) terrain profiles; (b) histograms of error data (TDX-DEM elevation–GPS elevation) without outliers; (c) residual plots.
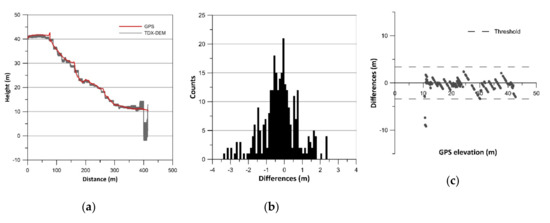
Figure 4.
Results of vertical accuracy assessment of Deseado Cuevas: (a) terrain profiles; (b) histograms of error data (TDX-DEM elevation–GPS elevation) without outliers; (c) residual plots.
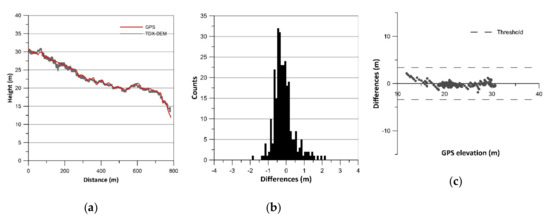
Figure 5.
Results of vertical accuracy assessment of Deseado Nord: (a) terrain profiles; (b) histograms of error data (TDX-DEM elevation–GPS elevation) without outliers; (c) residual plots.
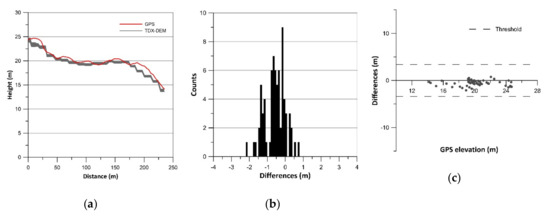
Figure 6.
Results of vertical accuracy assessment of Playa La Mina: (a) terrain profiles; (b) histograms of error data (TDX-DEM elevation–GPS elevation) without outliers; (c) residual plots.
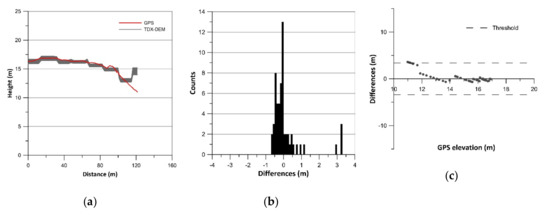
Figure 7.
Results of vertical accuracy assessment of Ria Deseado: (a) terrain profiles; (b) histograms of error data (TDX-DEM elevation–GPS elevation) without outliers; (c) residual plots.
The histograms of error data (TDX-DEM elevation–GPS elevation) are plotted in Figure 2b, Figure 3b, Figure 4b, Figure 5b, Figure 6b and Figure 7b and the statistics are reported in Table 2, which also indicates the number of outliers eliminated for each profile. The histograms show a roughly normal distribution with a mean (ME) between −0.56 and 0.12. The error dataset histograms are slightly skewed to the left, indicating that TDX-DEM mainly underestimates the true value. The MAE is rather small and varies between 0.41 m (Cabocurioso 1) and 0.78 m (Deseado Cuevas). RMSE is similar to MAE and reaches a maximum of 1.05 m in Deseado Cuevas. The total amount of outliers is 36 points out of the 2217 GPS points analyzed, which corresponds to 1.62% of the total. As expected, they are located in the profiles that show discrepancies in the final part. The outliers are displayed in Figure 2c, Figure 3c, Figure 4c, Figure 5c, Figure 6c and Figure 7c, which shows residuals plotted across the GPS elevation values and which reports the threshold used.

Table 2.
Statistics of differences between TDX-DEM elevation and GPS elevation for each profile.
LE90 is on average 1.19 m (Table 2), much lower than the value of 10 m reported in the TDX-DEM product specification (Table 1). The level of agreement between the data is also pointed out by the linear regression line equation (Equation LR) reported in Table 2. The slope of about 1 and the intercept close to zero indicate a good fit between the data.
As regards landform analysis, satellite imagery and elevation profiles are reported in Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 10, Figure 11 and Figure 12. All the variations in altitude of the landforms are detected with good precision. The larger landforms are of course detected better than others, e.g., fluvial terraces are more delineated than beach ridges, which are represented by sharp shapes due to their average size close to the resolution of TDX-DEM. Moreover, “salitral”, a depressed area characterized by marshes, is the only one that presents very noisy height values.
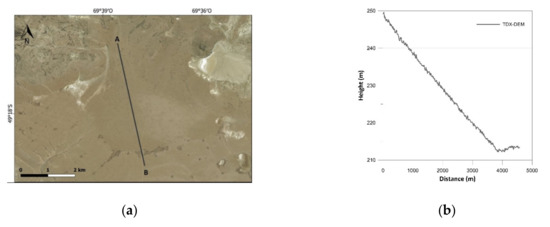
Figure 8.
Results of landform analysis of Alluvial fan: (a) satellite imagery; (b) elevation profile derived from TDX-DEM along the section line.
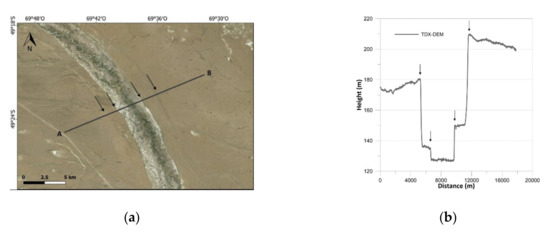
Figure 9.
Results of landform analysis of Fluvial terrace: (a) satellite imagery; (b) elevation profile derived from TDX-DEM along the section line.
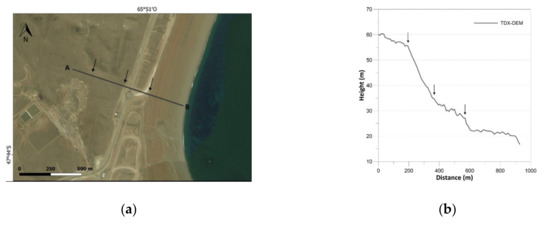
Figure 10.
Results of landform analysis of Marine terrace: (a) satellite imagery; (b) elevation profile derived from TDX-DEM along the section line.

Figure 11.
Results of landform analysis of Beach ridges: (a) satellite imagery; (b) elevation profile derived from TDX-DEM along the section line.
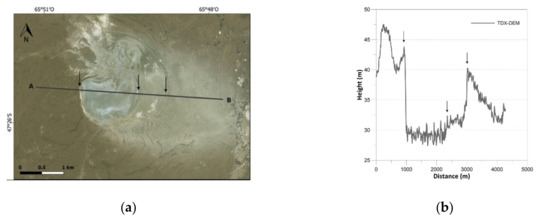
Figure 12.
Results of landform analysis of Salitral: (a) satellite imagery; (b) elevation profile derived from TDX-DEM along the section line.
5. Discussion
The results concerning vertical accuracy assessment indicate that TDX-DEM has high vertical accuracy. The analysis of the differences between the DGPS (2217 points) and the TDX-DEM elevations show a very good fit, with an MAE of 0.53 m and an RMSE of 0.73 m. The 90% LE calculated in this study is 1.19 m. These results are in agreement with those of other studies showing high accuracy of TDX-DEM and LE90 less than the value of 10m reported in the product specification [23,24,25,26,27]; they also corroborate the greater vertical accuracy of TDX-DEM compared to other currently available global elevation datasets [40,41,42,43]. RMSE and LE90 obtained in this study result in being considerably lower than the values reported in the papers cited above. The better performance of TDX-DEM in our sites probably depends on the morphological features of the analyzed profiles. Indeed, slope and land cover are some of the factors that can affect the accuracy of a DEM. Vertical errors are generally minor in areas with low slope and scarce vegetation [25,27]. The profiles analyzed in this study are characterized by a slope inferior to 10% and by rather sparse or absent vegetation. The results obtained thus agree with previous studies according to which TDX-DEM provides more accuracy in moderate and bare terrains [24,25,26,27].
The few outliers identified in the profiles are located along the shoreline. These aberrant values are due to the presence of water and of tidal oscillation that make these areas inconsistent in the DEM datasets. This is an issue of the radar-based products in which the specular reflections on flat areas such as lakes or sea surfaces result in artefacts in the unwrapping phase [44]. The inconsistency of these areas in the TDX-DEM are also highlighted in Figure 1b and in the “salitral” profile, which show very noisy height values. In this respect, we must consider that morphological analyses conducted near the shore could be affected by relevant errors.
However, in this study the extension of the area affected by aberrant values is rather small. Moreover, DEM products provided along with TDX-DEM allow us to find areas with large error and inconsistency, until they can be removed with the tools provided. In this case, some areas may not be suitable for geomorphological analysis, or greater attention should be given to the results obtained. In any case, the results of landform analyses show the usefulness of TDX-DEM, which can highlight all kinds of geomorphological features, even those with smaller average size such as beach ridges. These are in fact impossible to delineate with other DEMs with lower resolution, e.g., SRTM DEM. The high vertical accuracy of TDX-DEM demonstrates that this product can be used not only to map geomorphological features but also to infer their altitude, given the opportunity to use them in paleo-sea level variation studies.
Therefore, TDX-DEM constitutes a very good quality elevation dataset with global coverage, higher resolution and vertical accuracy than other global elevation datasets available at a low cost and therefore less expensive than LiDAR.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, we performed vertical accuracy assessment of TanDEM-X DEM in terms of absolute elevation error in two coastal areas of the Argentinian Patagonia region. Our analysis showed a very good quality DEM in strong agreement with reference values (DGPS datasets), high vertical accuracy (MAE and RMSE for LE90 of 0.53 m and 1.19 m respectively), and appropriate spatial resolution to detect landforms such as beach ridges, marine terraces, fluvial terraces, alluvial fans and “salitrals” with good precision. The high accuracy calculated in our study was probably due to the terrain features of the analyzed profiles located on low slopes and bare terrains. Less accuracy was detected in tidal areas and in the presence of water, so that greater attention must be paid to geomorphological analyses along the coast. However, the tools provided along with TanDEM-X DEM allowed us to identify and to manage areas with inconsistent elevation values. Therefore, TanDEM-X DEM is a great tool for geomorphological studies in the Argentinian Patagonia area and it constitutes an important resource for analysis and mapping in broad and hardly accessible areas. Future research will be aimed at mapping the morphology of this wide and poorly studied area through appropriate GIS tools for the study of paleo landscapes and past sea-level changes driven by paleoclimatic variations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and writing: F.P., M.B. and A.C.; Data Curation: A.C.; Formal analysis and methodology: F.P.; Supervision: A.C., M.B.; Field validation: M.B.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the DLR that provided TanDEM-X data within the framework of the project MATE (Landscape evolution of the Deseado Massif (Argentina): implication for tectonic and paleosealevel estimation in a far field area) approved for the TanDEM-X Digital Elevation Model Announcement of Opportunity. The authors are grateful to the team of the PRA project of Pisa University 2014 (leader Zanchetta G.) for the DGPS points database.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhang, W.; Montgomery, D.R. Digital elevation model grid size, landscape representation, and hydrologic simulations. Water Resour. Res. 1994, 30, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.J.; Chandler, J.; Rose, J. High spatial resolution data acquisition for the geosciences: Kite aerial photography. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2009, 34, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.L.; Ficklin, D.L.; Dixon, B.; Ibrahim, A.L.; Yusop, Z.; Chaplot, V. Impacts on DEM resolution, source, and resampling technique on SWAT-simulated streamflow. Appl. Geogr. 2015, 63, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davila, N.; Capra, L.; Gavilanes Ruiz, J.C.; Varley, N.; Norini, G.; Vazquez, A.G. Recent lahars at Volcán de Colima (Mexico): Drainage variation and spectral classification. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2007, 165, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albino, F.; Smets, B.; D’Oreye, N.; Kervyn, F. High-resolution TanDEM-X DEM: An accurate method to estimate lava flow volumes at Nyamulagira volcano (D. R. Congo). J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2015, 120, 4189–4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Traglia, F.; Bartolini, S.; Artesi, E.; Nolesini, T.; Ciampalini, A.; Lagomarsino, D.; Martí, J.; Casagli, N. Susceptibility of intrusion-related landslides at volcanic islands: The Stromboli case study. Landslides 2018, 15, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrower, M.J. Geographic information systems (GIS) hydrological modeling in archeology: An example from the origins of irrigation in Southwest Arabia (Yemen). J. Archeol. Sci. 2010, 37, 1447–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, A.F.; Chase, D.Z.; Weishampel, J.F.; Drake, J.B.; Shreshta, R.L.; Slatton, K.C.; Awe, J.J.; Carter, W.E. Airborne LiDAR, archeology, and the ancient Maya landscape at Caracol, Belize. J. Archeol. Sci. 2011, 38, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bini, M.; Rossi, V.; Amorosi, A.; Pappalardo, M.; Sarti, G.; Noti, V.; Capitani, M.; Fabiani, F.; Gualandi, M.L. Palaeoenvironments and palaeotopography of a multilayered city during the Etruscan and Roman periods: Early interaction of fluvial processes and urban growth at Pisa (Tuscany, Italy). J. Archaeol. Sci. 2015, 59, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bini, M.; Pappalardo, M.; Rossi, V.; Noti, V.; Amorosi, A.; Sarti, G. Deciphering the effects of human activity on urban areas through morphostratigraphic analysis: The case of Pisa, Northwest Italy. Geoarchaeology 2018, 33, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarolli, P. High-resolution topography for understanding Earth surface processes: Opportunities and challenges. Geomorphology 2014, 216, 295–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampalini, A.; Raspini, F.; Frodella, W.; Bardi, F.; Bianchini, S.; Moretti, S. The effectiveness of high-resolution data combined with PSInSAR data in landslide study. Landslides 2016, 13, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oskin, M.E.; Le, K.; Strane, M.D. Quantifying fault-zone activity in arid environments with high-resolution topography. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L23S05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabassa, J. The Late Cenozoic of Patagonia and Tierra del Fuego; Developments in Quaternary Science, Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; p. 513. [Google Scholar]
- Schellmann, G.; Radtke, U. Timing and magnitude of Holocene sea-level changes along the middle and south Patagonian Atlantic coast derived from beach ridge systems, littoral terraces and valley-mouth terraces. Earth-Science Rev. 2010, 103, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribolini, A.; Aguirre, M.; Baneschi, I.; Consoloni, I.; Fucks, E.; Isola, I.; Mazzarini, F.; Pappalardo, M.; Zanchetta, G.; Bini, M. Holocene beach ridges and coastal evolution in the Cabo Raso Bay (Atlantic Patagonian Coast, Argentina). J. Coast. Res. 2011, 27, 973–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanchetta, G.; Consoloni, I.; Isola, I.; Pappalardo, M.; Ribolini, A.; Aguirre, M.; Fucks, E.; Baneschi, I.; Bini, M.; Ragaini, L.; et al. New insights on the Holocene marine transgression in the Bahía Camarones (Chubut, Argentina). Ital. J. Geosci. 2012, 131, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanchetta, G.; Bini, M.; Isola, I.; Pappalardo, M.; Ribolini, A.; Consoloni, I.; Boretto, G.; Fucks, E.; Ragaini, L.; Terrasi, F. Middle- to late-Holocene relative sea-level changes at Puerto Deseado (Patagonia, Argentina). Holocene 2014, 24, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappalardo, M.; Aguirre, M.; Bini, M.; Consoloni, I.; Fucks, E.; Hellstrom, J.; Isola, I.; Ribolini, A.; Zanchetta, G. Coastal landscape evolution and sea-level change: A case study from Central Patagonia (Argentina). Z. Geomorphol. 2015, 59, 145–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bini, M.; Isola, I.; Zanchetta, G.; Pappalardo, M.; Ribolini, A.; Ragaini, L.; Baroni, C.; Boretto, G.; Fuck, E.; Morigi, C.; et al. Mid-Holocene relative sea-level changes along Atlantic Patagonia: New data from Camarones, Chubut, Argentina. Holocene 2018, 28, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bini, M.; Zanchetta, G.; Ribolini, A.; Salvatore, M.C.; Baroni, C.; Pappalardo, M.; Isola, I.; Isla, F.I.; Fucks, E.; Boretto, G.; et al. Last Interglacial Sea-level highstand deduced from notches and inner margins of marine terraces at Puerto Deseado, Santa Cruz Province, Argentina. Geogr. Fis. Din. Quat. 2017, 40, 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Isola, I.; Bini, M.; Ribolini, A.; Pappalardo, M.; Consoloni, I.; Fucks, E.; Boretto, G.; Ragaini, L.; Zanchetta, G. Geomorphologic map of northeastern sector of San Jorge gulf (Chubut, Argentina). J. Maps 2011, 7, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipaud, I.; Loibl, D.; Lehmkuhl, F. Evaluation of TanDEM-X elevation data for geomorphological mapping and interpretation in high mountain environments—A case study from SE Tibet, China. Geomorphology 2015, 246, 232–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erasmi, S.; Rosenbauer, R.; Buchbach, R.; Busche, T.; Rutishauser, S. Evaluating the Quality and Accuracy of TanDEM-X Digital Elevation Models at Archaeological Sites in the Cilician Plain, Turkey. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 9475–9493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avtar, R.; Yunus, A.P.; Kraines, S.; Yamamuro, M. Evaluation of DEM generation based on interferometric SAR using TanDEM-X data in Tokyo. Phys. Chem. Earth 2015, 83–84, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzoli, P.; Bräutigam, B.; Kraus, T.; Martone, M.; Krieger, G. Relative height error analysis of TanDEM-X elevation data. ISPRS J. Photogr. Remote Sens. 2012, 73, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessel, B.; Huber, M.; Wohlfart, C.; Marschalk, U.; Kosmann, D.; Roth, A. Accuracy assessment of the global TanDEM-X Digital Elevation Model with GPS data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 139, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bini, M.; Isola, I.; Pappalardo, M.; Ribolini, A.; Favalli, M.; Ragaini, L.; Zanchetta, G. Abrasive notches along the Atlantic patagonian coast and their potential use as sea level markers: The case of puerto deseado (Santa Cruz, Argentina). Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2014, 39, 1550–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwin, C.R. Geological Observations on South America: Being the Third Part of the Geology of the Voyage of the Beagle, under the Command of Capt. Fitzroy, R.N. during the Years 1832 to 1836; Smith Elder and Co.: London, UK, 1846. [Google Scholar]
- Guido, D.; Escayola, M.; Schalamuk, I. The basement of the Deseado Massif at Bahía Laura, Patagonia, Argentina: A proposal forits evolution. J. S. Am. Earth Sci. 2004, 16, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankhurst, R.J.; Rapela, C.R. Production of Jurassic rhyolite by anatexis of the lower crust of Patagonia. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1995, 134, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankhurst, R.J.; Leat, P.T.; Sruoga, P.; Rapela, C.W.; Márquez, M.; Storey, B.C.; Riley, T.R. The Chon Aike province of Patagonia and related rocks in West Antarctica: A silicic large igneous province. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1998, 81, 113–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronato, A.M.J.; Coronato, F.; Mazzoni, E.; Vázquez, M. The Physical Geography of Patagonia and Tierra del Fuego. Dev. Quat. Sci. 2008, 11, 13–55. [Google Scholar]
- Krieger, G.; Moreira, A.; Fiedler, H.; Hajnsek, I.; Werner, M.; Younis, M.; Zink, M. TanDEM-X: A Satellite Formation for High-Resolution SAR Interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 3317–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessel, B. TanDEM-X Ground Segment DEM Products Specification Document. EOC, DLR, Oberpfaffenhofen, Germany, 2016; Issue 3.1. Public Document TD-GSPS-0021. Available online: https://elib.dlr.de/108014/1/TD-GS-PS-0021_DEM-Product-Specification_v3.1.pdf (accessed on 11 February 2019).
- Maune, D.F.; Maitra, J.B.; McKay, E.J. Accuracy standards. In Digital Elevation Model Technologies and Applications: The DEM User Manual; Maune, D., Ed.; American Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2001; pp. 61–82. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, A.; Tate, N.J. Causes and consequences of error in digital elevation models. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2006, 30, 467–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C.J.; Matsuura, K. Advantages of the mean absolute error (MAE) over the root mean square error (RMSE) in assessing average model performance. Clim. Res. 2005, 30, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höhle, J.; Höhle, M. Accuracy assessment of digital elevation models by means of robust statistical methods. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2009, 64, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endreny, T.A.; Wood, E.F.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Satellite-derived digital elevation model accuracy: Hydrogeomorphological analysis requirements. Hydrol. Process. 2000, 14, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tighe, M.L.; Chamberlain, D. Accuracy comparison of the SRTM, ASTER, NED, NEXTMAP® USA Digital Terrain Model over several USA study sites. In Proceedings of the ASPRS/MAPPS Fall Conference, San Antonia, TX, USA, 16–19 November 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Shi, C.; Li, Z.; Muller, J.P.; Drummond, J.; Li, X.; Li, T.; Li, Y.; Liu, J. Evaluation of ASTER GDEM Ver2 Using GPS Measurements and SRTM Ver4.1 in China. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2012, I-4, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Katiyar, S.K.; Prasad, V. Performances evaluation of different open source DEM using Differential Global Positioning System (DGPS). Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2016, 19, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maire, C.; Datcu, M.; Audenino, P. SAR DEM filtering by mean of Bayesian and multi-scale, nonstationary methods. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Tolouse, France, 21–25 July 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).