A Full-Coverage Daily Average PM2.5 Retrieval Method with Two-Stage IVW Fused MODIS C6 AOD and Two-Stage GAM Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
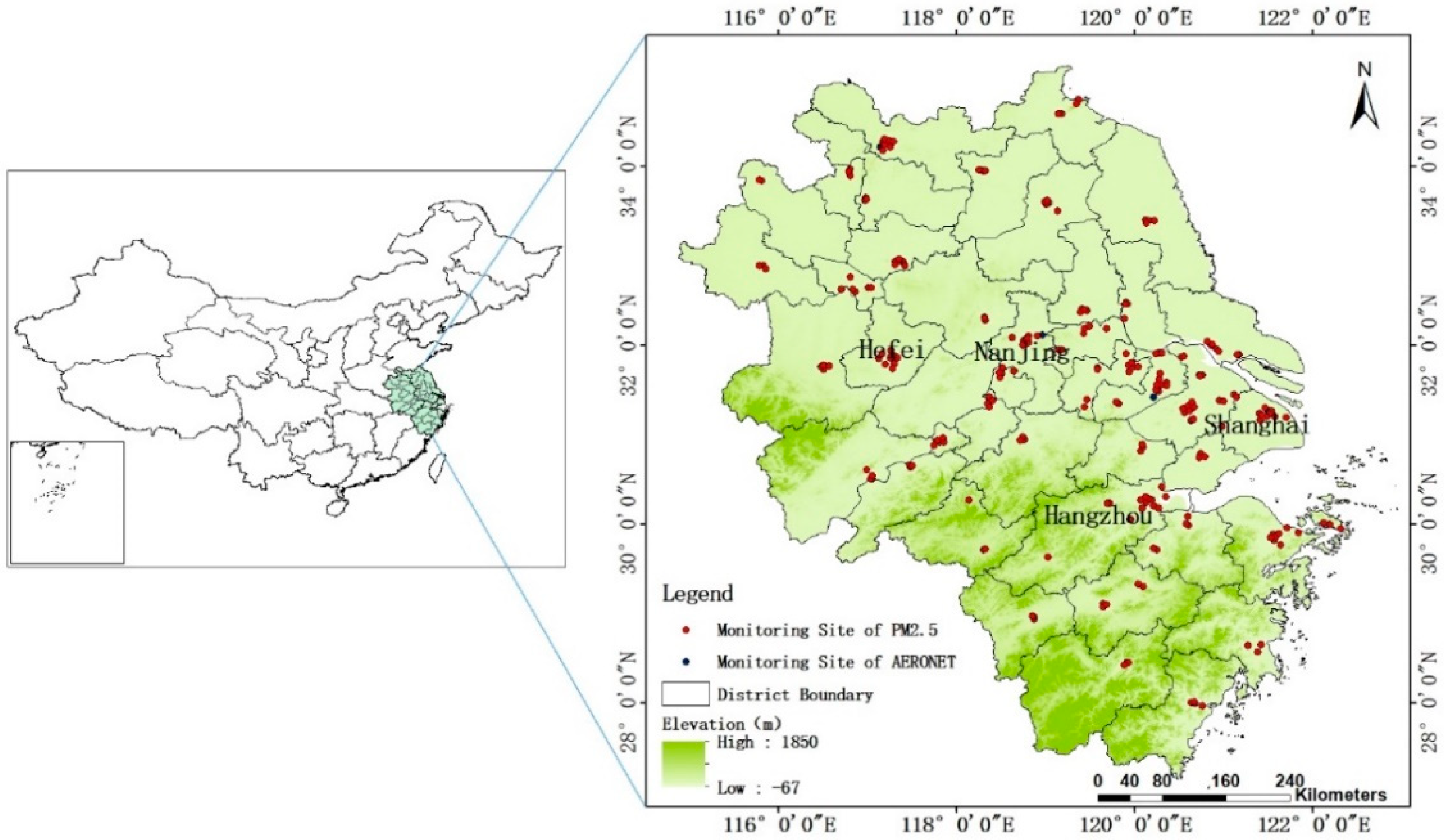
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Ground-Level PM2.5 Observations
2.2. MODIS C6 and AERONET AOD Data
2.3. Meteorological Data
2.4. Geographic Data
2.5. Data Pre-Processing and Integration
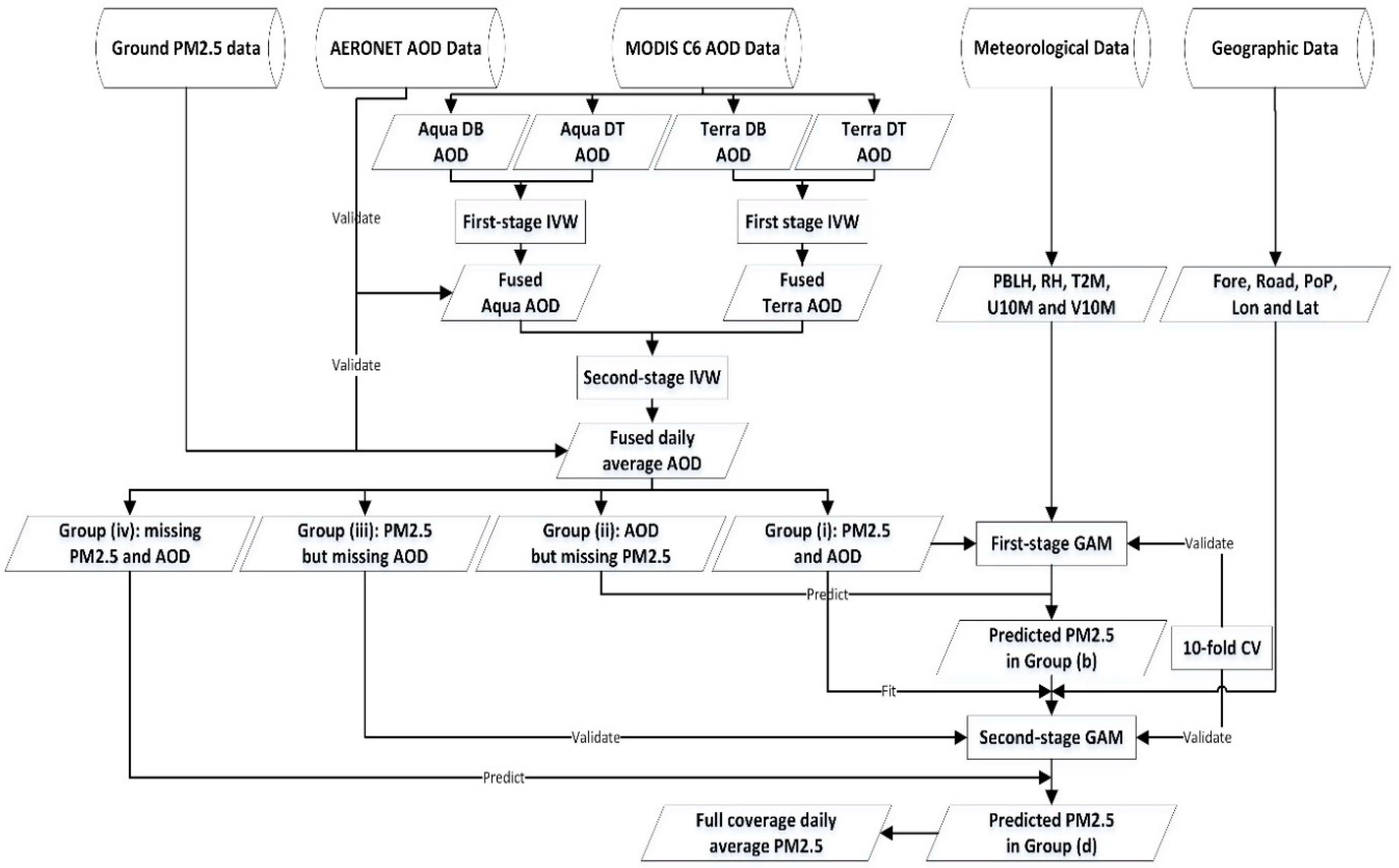
3. Methodology
3.1. Fusing MODIS Terra and Aqua AOD via Two-Stage IVW
3.2. Retrieving PM2.5 from Fused MODIS AOD and Two-Stage GAM
3.3. Model Evaluation and Validation
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Experiments on Fused Daily Average MODIS AOD
4.1.1. Accuracy Evaluation of MODIS AOD from Two-Stage IVW
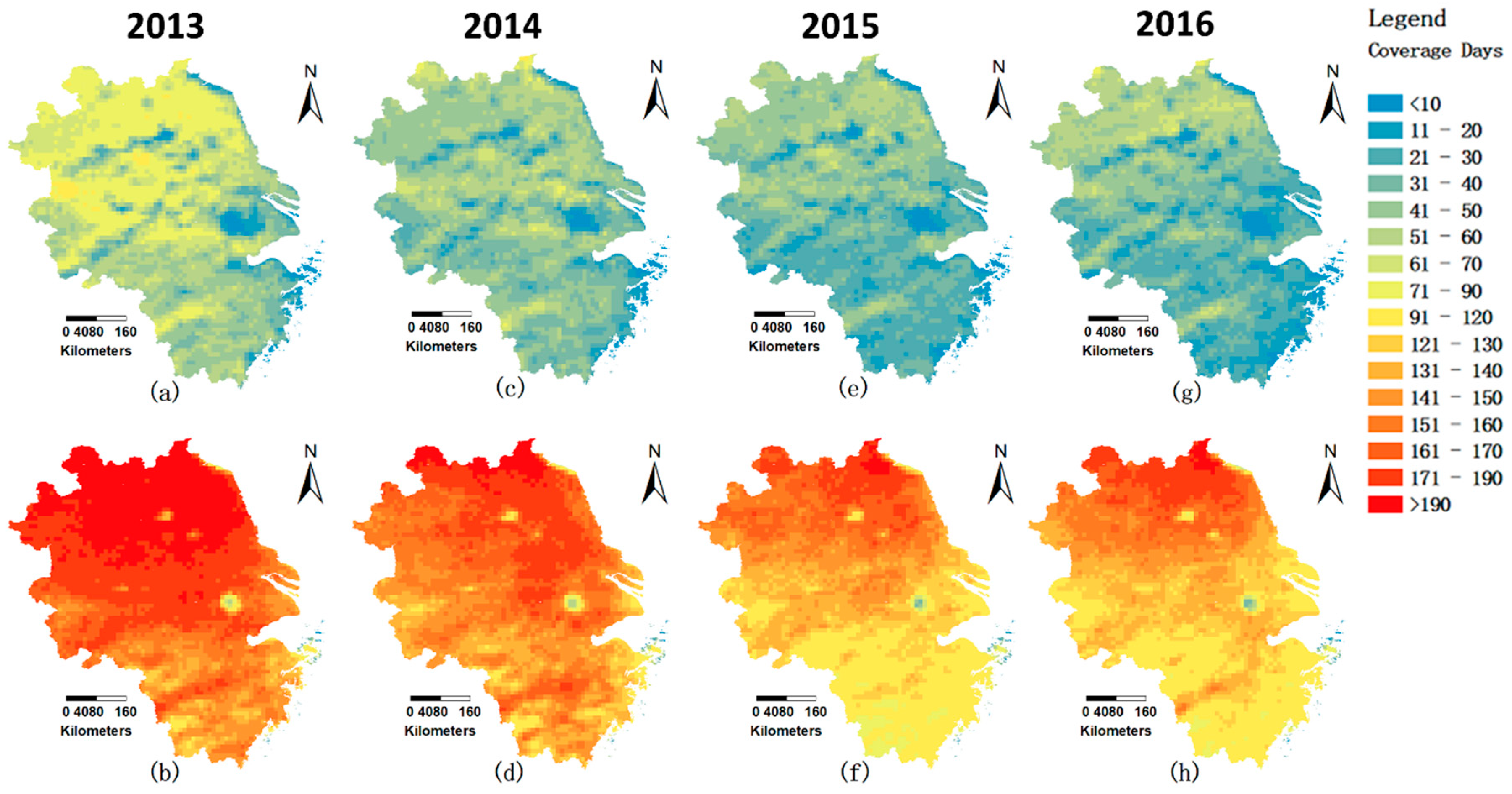
4.1.2. The SCR Evaluation of MODIS AOD from Two-Stage IVW
4.2. Experiments on PM2.5 Retrieved from Two-Stage GAM
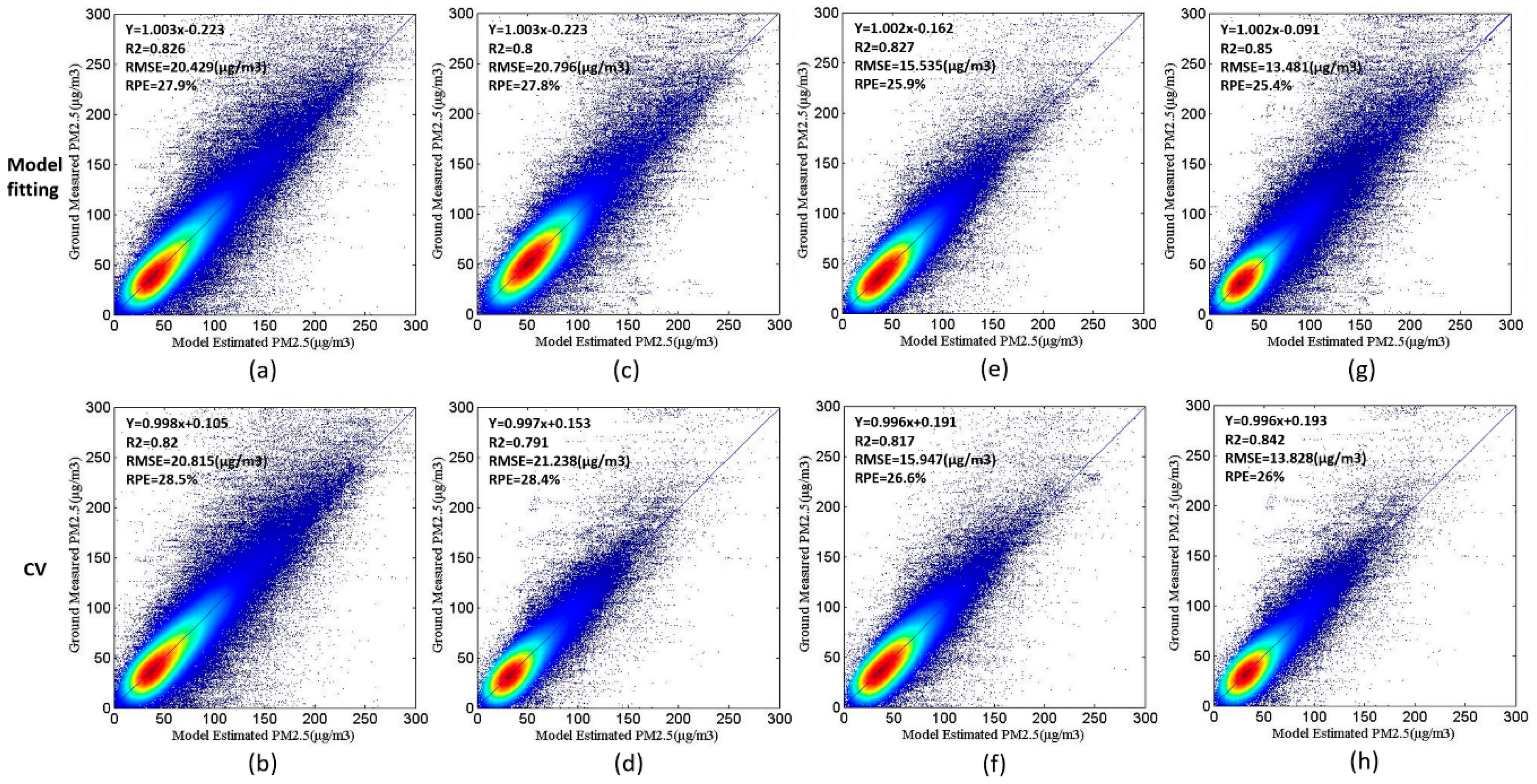
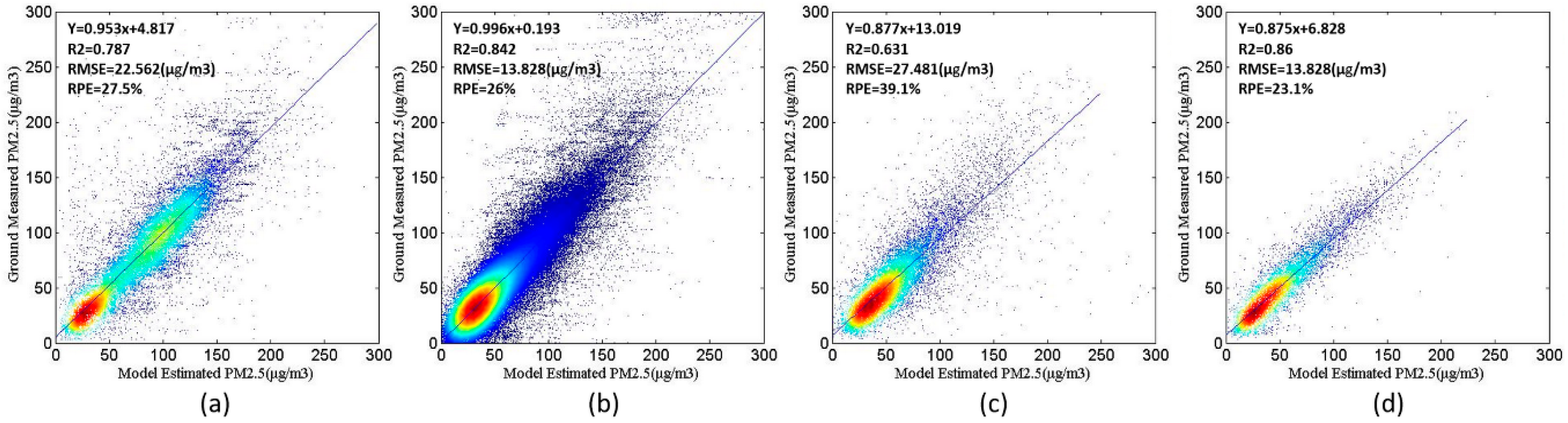
4.2.1. The Performance Verification of First-Stage GAM
4.2.2. The Performance Verification of Second-Stage GAM
4.2.3. Comparison with Other Spatial Interpolation Methods
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Q.; He, K.; Huo, H. Policy: Cleaning China’s air. Nature 2012, 484, 161–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Bozzetti, C.; Ho, K.-F.; Cao, J.-J.; Han, Y.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Slowik, J.G.; Platt, S.M.; Canonaco, F.; et al. High secondary aerosol contribution to particulate pollution during haze events in China. Nature 2014, 514, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Lu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, W.; Nielsen, C.P.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Bi, J. Trade-driven relocation of air pollution and health impacts in China. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Ding, A.; Mao, H.; Nie, W.; Zhou, D.; Liu, L.; Huang, X.; Fu, C. Impact of synoptic weather patterns and inter-decadal climate variability on air quality in the north China plain during 1980–2013. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 124, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.-M.; Ma, Z.; Lin, W.; Zhang, H.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Fuentes, J.D.; Xue, M. Impact of the loess plateau on the atmospheric boundary layer structure and air quality in the north China plain: A case study. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 499, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Jiang, F.; Deng, J.; Shen, Y.; Fu, Q.; Wang, Q.; Fu, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, D. Urban air quality and regional haze weather forecast for yangtze river delta region. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 58, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Q.; Peng, X.; Xu, Q.; Long, L.; Wei, N.; Liu, M.; Jia, W.; Zhou, T.; Han, J.; Xiang, W. Air quality and its response to satellite-derived urban form in the yangtze river delta, China. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 75, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Louie, P.K.; Zheng, J.; Yuan, Z.; Yue, D.; Ho, J.W.; Lau, A.K. Science–policy interplay: Air quality management in the pearl river delta region and Hong Kong. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 76, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Deng, T.; Li, Z.; Wang, N.; Yin, C.; Wang, S.; Fan, S. Numerical simulations for the sources apportionment and control strategies of PM2.5 over pearl river delta, China, part i: Inventory and PM2.5 sources apportionment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 1631–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.; Su, X.; Zhang, Q.; Peters, G.P.; Liu, Z.; Lei, Y.; He, K. The socioeconomic drivers of China’s primary PM2.5 emissions. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 024010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zhou, W.; Li, W.; Li, L. Impact of urbanization level on urban air quality: A case of fine particles (PM2.5) in Chinese cities. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 194, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Liu, Y.-M. The influential factors of urban PM2.5 concentrations in China: A spatial econometric analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 1443–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.-F.; Xu, Y.-H.; Shi, M.-H.; Lian, Y.-X. The impact of PM2.5 on the human respiratory system. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, E69. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Hu, X.; Sayer, A.M.; Levy, R.; Zhang, Q.; Xue, Y.; Tong, S.; Bi, J.; Huang, L.; Liu, Y. Satellite-based spatiotemporal trends in PM2.5 concentrations: China, 2004–2013. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Fu, D.; Zhang, X.; Han, X.; Song, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Xia, X. MODIS AOD sampling rate and its effect on PM2. 5 estimation in North China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 209, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Hu, X.; Huang, L.; Bi, J.; Liu, Y. Estimating ground-level PM2.5 in China using satellite remote sensing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 7436–7444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Franklin, M.; Kahn, R.; Koutrakis, P. Using aerosol optical thickness to predict ground-level PM2.5 concentrations in the st. Louis area: A comparison between misr and modis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 107, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorek-Hamer, M.; Kloog, I.; Koutrakis, P.; Strawa, A.W.; Chatfield, R.; Cohen, A.; Ridgway, W.L.; Broday, D.M. Assessment of PM2.5 concentrations over bright surfaces using modis satellite observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 163, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Dong, W.; Lv, B.; Bai, Y. Daily estimation of ground-level PM2.5 concentrations over beijing using 3 km resolution modis aod. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12280–12288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Chatfield, R.B.; Strawa, A.W. Enhancing the applicability of satellite remote sensing for PM2.5 estimation using modis deep blue aod and land use regression in California, United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 6546–6555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, D.; Kaufman, Y.; Ichoku, C.; Remer, L.; Tanré, D.; Holben, B. Validation of modis aerosol optical depth retrieval over land. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, MOD2-1–MOD2-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, A.; Hsu, N.; Bettenhausen, C.; Jeong, M.J. Validation and uncertainty estimates for modis collection 6 “deep blue” aerosol data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 7864–7872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Sun, L. Comparison and evaluation of different modis aerosol optical depth products over the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Park, R.J. Estimating ground-level PM2.5 using aerosol optical depth determined from satellite remote sensing. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, D21201–D21210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Sun, W.; Yang, G.; Zhang, D. Modelling seasonal gwr of daily PM2.5 with proper auxiliary variables for the yangtze river delta. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Park, R.J.; Jacob, D.J.; Li, Q.; Kilaru, V.; Sarnat, J.A. Mapping annual mean ground-level PM2.5 concentrations using multiangle imaging spectroradiometer aerosol optical thickness over the contiguous united states. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109, D22206–D22215. [Google Scholar]
- Boys, B.; Martin, R.; Van Donkelaar, A.; MacDonell, R.; Hsu, N.; Cooper, M.; Yantosca, R.; Lu, Z.; Streets, D.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Fifteen-year global time series of satellite-derived fine particulate matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 11109–11118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z. Remote sensing of atmospheric fine particulate matter (PM2.5) mass concentration near the ground from satellite observation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 160, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z. Study on Spatiotemporal Distribution of PM2.5 in China Using Satellite Remote Sensing. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing University, Nanjing, China, 2015; pp. 8–52. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, J.; Li, B.; Hong, J.; Liu, D.; Li, D.; Wei, P.; Li, W.; Li, L. Remote sensing of atmospheric particulate mass of dry PM2.5 near the ground: Method validation using ground-based measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 173, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Guang, J.; Xue, Y.; Li, Y.; Che, Y.; Gong, S. A physically based PM2.5 estimation method using aeronet data in beijing area. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 1957–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Lau, A.K.H.; Li, C.; Fung, J.C.H. Using satellite remote sensing data to estimate the high-resolution distribution of ground-level PM2.5. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Chen, D. A semi-empirical model for predicting hourly ground-level fine particulate matter (PM2.5) concentration in southern ontario from satellite remote sensing and ground-based meteorological measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, W.; Zang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Chen, D.; Zhang, G. Estimating ground-level PM10 concentration in northwestern China using geographically weighted regression based on satellite aod combined with calipso and modis fire count. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2015, 168, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, B.; Pu, Q.; Bilal, M.; Weng, Q.; Zhai, L.; Nichol, J.E. High-resolution satellite mapping of fine particulates based on geographically weighted regression. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, M.; Zhou, Y.; Bi, J. Satellite-derived high resolution PM2.5 concentrations in yangtze river delta region of China using improved linear mixed effects model. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 133, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Wu, L.; Qin, K.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, Y. A geographically and temporally weighted regression model for ground-level PM2.5 estimation from satellite-derived 500 m resolution aod. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Garay, M.J.; Diner, D.J.; Kalashnikova, O.V.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y. Estimating PM2.5 speciation concentrations using prototype 4.4 km-resolution misr aerosol properties over southern California. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 181, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Spurr, R.J.; Burnett, R.T. High-resolution satellite-derived PM2.5 from optimal estimation and geographically weighted regression over north America. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 10482–10491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouse, D.L.; Peters, P.A.; Hystad, P.; Brook, J.R.; van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Villeneuve, P.J.; Jerrett, M.; Goldberg, M.S.; Pope, C.A., III. Ambient PM2.5, O3, and NO2 exposures and associations with mortality over 16 years of follow-up in the Canadian census health and environment cohort (canchec). Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 1180–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Hoogh, K.; Héritier, H.; Stafoggia, M.; Künzli, N.; Kloog, I. Modelling daily PM2.5 concentrations at high spatio-temporal resolution across Switzerland. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 233, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Just, A.C.; De Carli, M.M.; Shtein, A.; Dorman, M.; Lyapustin, A.; Kloog, I. Correcting measurement error in satellite aerosol optical depth with machine learning for modeling PM2.5 in the northeastern USA. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.L.; Kolenikov, S.; Cox, L.H. Spatiotemporal modeling of PM2.5 data with missing values. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 9004–9014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Pasch, A.N.; Szykman, J.J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.X.; Chen, D. Improving the accuracy of daily satellite-derived ground-level fine aerosol concentration estimates for north America. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11971–11978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Geng, G.; He, K. Estimating ground-level PM2.5 concentrations over three megalopolises in China using satellite-derived aerosol optical depth measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 124, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Wu, X.; Agrawal, P.; Pongpaichet, S.; Jain, R. Integration of diverse data sources for spatial PM2.5 data interpolation. IEEE. Trans. Multimed. 2017, 19, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Belle, J.H.; Wang, Y.; Lyapustin, A.I.; Wildani, A.; Liu, Y. Impacts of snow and cloud covers on satellite-derived PM2.5 levels. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 221, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Hu, Z.; Zhong, K.; Xu, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, P. Satellite-based high-resolution mapping of ground-level PM2.5 concentrations over east China using a spatiotemporal regression kriging model. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 672, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Ban, J.; Chen, N.X.; Li, T. High-resolution daily aod estimated to full coverage using the random forest model approach in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 203, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, B.; Sánchez, O.; Bi, J.; Xiao, Q.; Hansel, N.; Checkley, W.; Gonzales, G.; Steenland, K.; Liu, Y. Developing an advanced PM2.5 exposure model in lima, Peru. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, T.; Zheng, Y.; Tong, D.; Zheng, B.; Li, X.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, Q. Spatiotemporal continuous estimates of PM2.5 concentrations in China, 2000–2016: A machine learning method with inputs from satellites, chemical transport model, and ground observations. Environ. Int. 2019, 123, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chang, H.H.; Meng, X.; Geng, G.; Lyapustin, A.; Liu, Y. Full-coverage high-resolution daily PM2.5 estimation using MAIAC AOD in the Yangtze river Delta of China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 199, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laden, F.; Neas, L.M.; Dockery, D.W.; Schwartz, J. Association of fine particulate matter from different sources with daily mortality in six us cities. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Paciorek, C.J.; Koutrakis, P. Estimating regional spatial and temporal variability of PM2.5 concentrations using satellite data, meteorology, and land use information. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remer, L.A.; Kaufman, Y.; Tanré, D.; Mattoo, S.; Chu, D.; Martins, J.V.; Li, R.-R.; Ichoku, C.; Levy, R.; Kleidman, R. The modis aerosol algorithm, products, and validation. J. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 62, 947–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Nichol, J.E.; Nazeer, M. Validation of aqua-modis c051 and c006 operational aerosol products using aeronet measurements over pakistan. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 2074–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hoff, R.M.; Engel-Cox, J.A. The relation between moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (modis) aerosol optical depth and PM2.5 over the united states: A geographical comparison by us environmental protection agency regions. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2009, 59, 1358–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Kloog, I.; Chudnovsky, A.; Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Melly, S.; Coull, B.; Koutrakis, P.; Schwartz, J. Spatiotemporal prediction of fine particulate matter using high-resolution satellite images in the southeastern us 2003–2011. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2016, 26, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichol, J.; Bilal, M. Validation of modis 3 km resolution aerosol optical depth retrievals over Asia. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyapustin, A.; Martonchik, J.; Wang, Y.; Laszlo, I.; Korkin, S. Multiangle implementation of atmospheric correction (MAIAC): 1. Radiative transfer basis and look-up tables. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D03210–D03218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Laszlo, I.; Kahn, R.; Korkin, S.; Remer, L.; Levy, R.; Reid, J. Multiangle implementation of atmospheric correction (MAIAC): 2. Aerosol algorithm. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D03211–D03225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloog, I.; Sorek-Hamer, M.; Lyapustin, A.; Coull, B.; Wang, Y.; Just, A.C.; Schwartz, J.; Broday, D.M. Estimating daily PM2.5 and PM10 across the complex geo-climate region of Israel using MAIAC satellite-based AOD data. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 122, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Type | Data | Units | Time Frequency | Spatial Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ground-level PM2.5 | PM2.5 | μg/m3 | Hourly | 245 stations |
| AOD Data | MODIS AOD DB/DT | N/A | Hourly | 10 km |
| AERONET AOD | N/A | Hourly | 6 stations | |
| Meteorological Data | Planetary boundary layer height (PBLH) | m | Hourly | 2/3 Lon*1/2 Lat |
| Total surface precipitation flux (PRECTOT) | kg·m−2·s−1 | Hourly | 2/3 Lon*1/2 Lat | |
| Wind speed (WS) | m·s−1 | Hourly | 2/3 Lon*1/2 Lat | |
| Time averaged surface pressure (PS) | Pa | Hourly | 2/3 Lon*1/2 Lat | |
| Temperature at 2 m above the displacement height (T2M) | K | Hourly | 2/3 Lon*1/2 Lat | |
| Eastward wind at 10 m above displacement height (U10M) | m s−1 | Hourly | 2/3 Lon*1/2 Lat | |
| Northward wind at 10 m above the displacement height (V10M) | m·s−1 | Hourly | 2/3 Lon*1/2 Lat | |
| Relative humidity (RH) | % | 3-hourly | 2/3 Lon*1/2 Lat, Level = 72 | |
| Cloud fraction (CLOUND) | % | 3-hourly | 2/3 Lon*1/2 Lat, Level = 72 | |
| Geographic Data | Population(pop) | count | year | 1 km |
| Forest coverage(fore) | % | - | 300 m | |
| Building coverage(build) | % | - | 300 m | |
| road coverage(road) | % | - | - |
| Data | R2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| MODIS Standard AOD | Fused MODIS AOD from First-Stage IVW | Fused Daily Average MODIS AOD from Two-Stage IVW | |
| Terra 2013 | 0.57 | 0.60 | 0.66 |
| Aqua 2013 | 0.44 | 0.55 | |
| Terra 2014 | 0.74 | 0.60 | 0.64 |
| Aqua 2014 | 0.66 | 0.74 | |
| Terra 2015 | 0.70 | 0.67 | 0.60 |
| Aqua 2015 | 0.64 | 0.60 | |
| Terra 2016 | 0.64 | 0.56 | 0.68 |
| Aqua 2016 | 0.64 | 0.58 | |
| Average | 0.63 | 0.60 | 0.63 |
| Dataset | SCR | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| MODIS Standard AOD | Fused MODIS AOD from First-Stage IVW | Fused Daily Average MODIS AOD from Two-Stage IVW | |
| Terra 2013 | 15.95% | 34.82% | 45.84% |
| Aqua 2013 | 15.28% | 34.81% | |
| Terra 2014 | 12.27% | 30.61% | 40.90% |
| Aqua 2014 | 11.22% | 29.77% | |
| Terra 2015 | 10.44% | 26.12% | 35.17% |
| Aqua 2015 | 9.45% | 25.86% | |
| Terra 2016 | 11.07% | 26.29% | 35.23% |
| Aqua 2016 | 9.32% | 25.27% | |
| Average | 11.88% | 29.19% | 39.29% |
| Years | Models | Quantitative Measures | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAPE | RMSE | RPE | R2 | ||
| 2013 | IDW | 35.510 | 23.210 | 34.46% | 0.697 |
| OK | 30.578 | 23.256 | 35.47% | 0.757 | |
| Ours | 15.722 | 21.419 | 28.39% | 0.806 | |
| 2014 | IDW | 37.770 | 20.910 | 31.88% | 0.658 |
| OK | 30.484 | 25.206 | 34.88% | 0.731 | |
| Ours | 20.523 | 23.212 | 31.15% | 0.742 | |
| 2015 | IDW | 37.608 | 18.170 | 32.78% | 0.654 |
| OK | 36.644 | 22.531 | 40.42% | 0.671 | |
| Ours | 21.062 | 17.513 | 29.70% | 0.778 | |
| 2016 | IDW | 38.019 | 19.265 | 40.74% | 0.673 |
| OK | 35.436 | 18.886 | 39.72% | 0.707 | |
| Ours | 19.097 | 17.416 | 32.70% | 0.733 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hua, Z.; Sun, W.; Yang, G.; Du, Q. A Full-Coverage Daily Average PM2.5 Retrieval Method with Two-Stage IVW Fused MODIS C6 AOD and Two-Stage GAM Model. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1558. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11131558
Hua Z, Sun W, Yang G, Du Q. A Full-Coverage Daily Average PM2.5 Retrieval Method with Two-Stage IVW Fused MODIS C6 AOD and Two-Stage GAM Model. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(13):1558. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11131558
Chicago/Turabian StyleHua, Zhenqun, Weiwei Sun, Gang Yang, and Qian Du. 2019. "A Full-Coverage Daily Average PM2.5 Retrieval Method with Two-Stage IVW Fused MODIS C6 AOD and Two-Stage GAM Model" Remote Sensing 11, no. 13: 1558. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11131558
APA StyleHua, Z., Sun, W., Yang, G., & Du, Q. (2019). A Full-Coverage Daily Average PM2.5 Retrieval Method with Two-Stage IVW Fused MODIS C6 AOD and Two-Stage GAM Model. Remote Sensing, 11(13), 1558. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11131558









