Raindrop Size Distributions and Rain Characteristics Observed by a PARSIVEL Disdrometer in Beijing, Northern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Dataset, Quality Control, and DSD Parameters
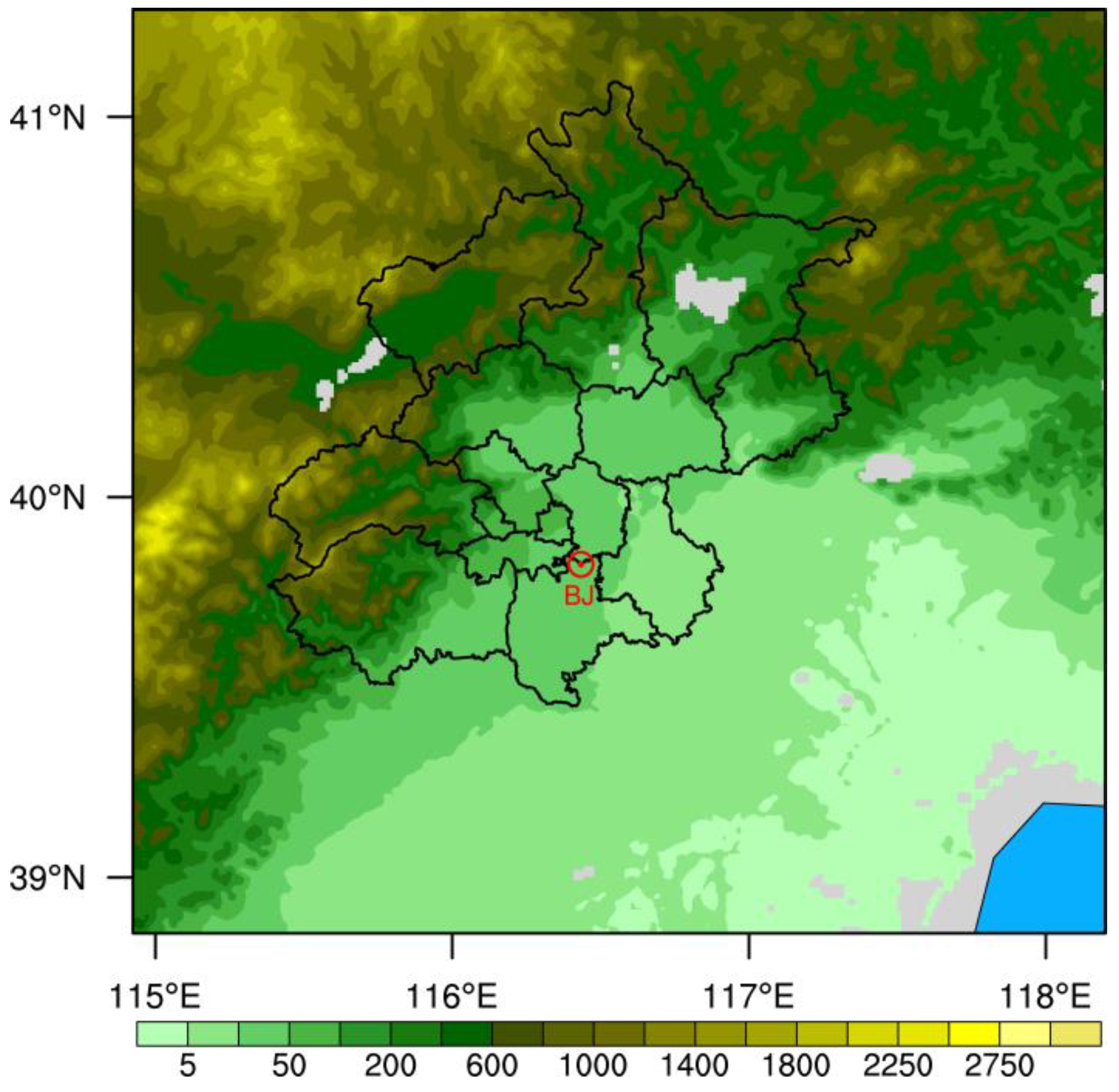
2.1. Observations
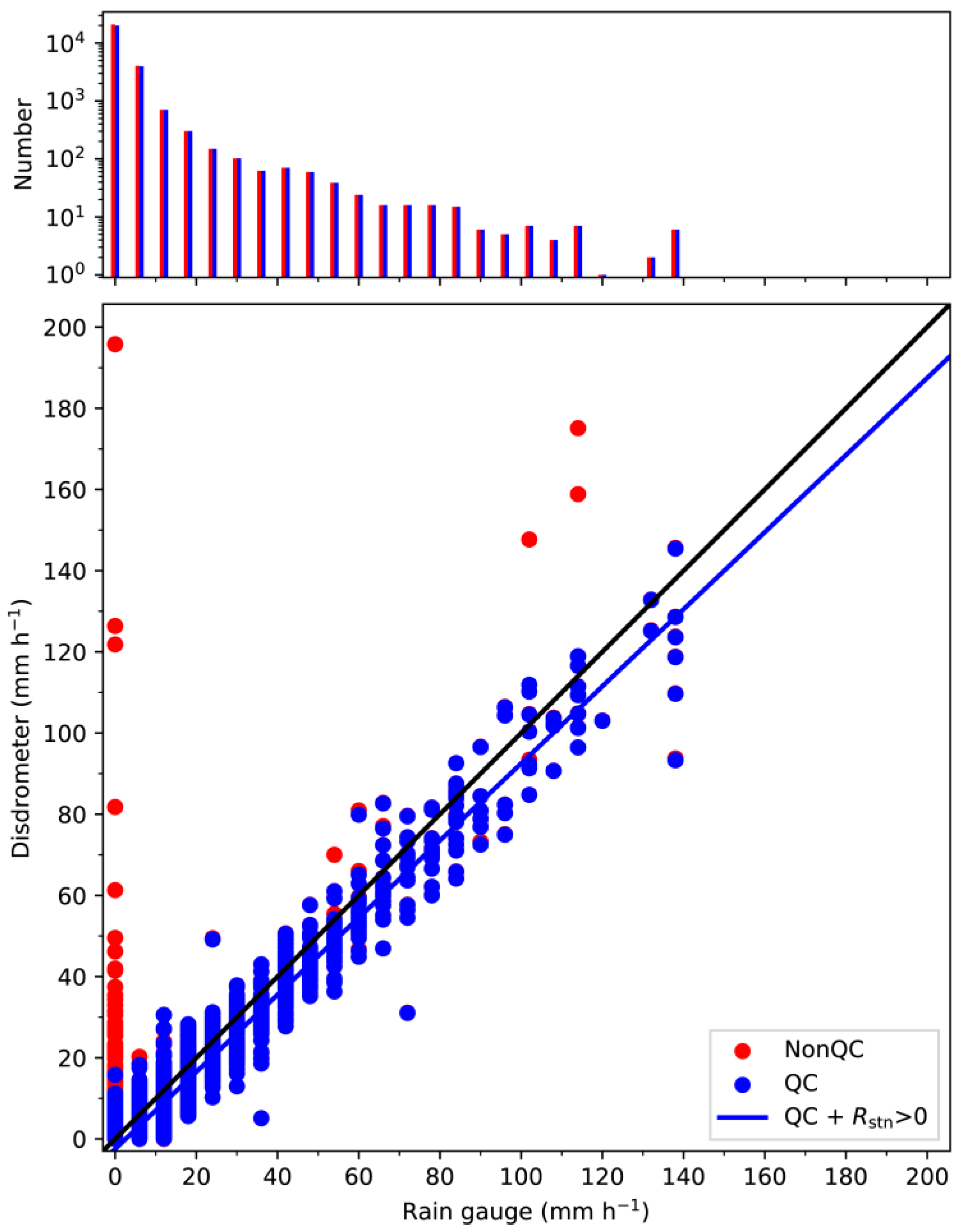
2.2. Quality Control (QC)
2.3. Integral Rainfall Parameters
3. Results
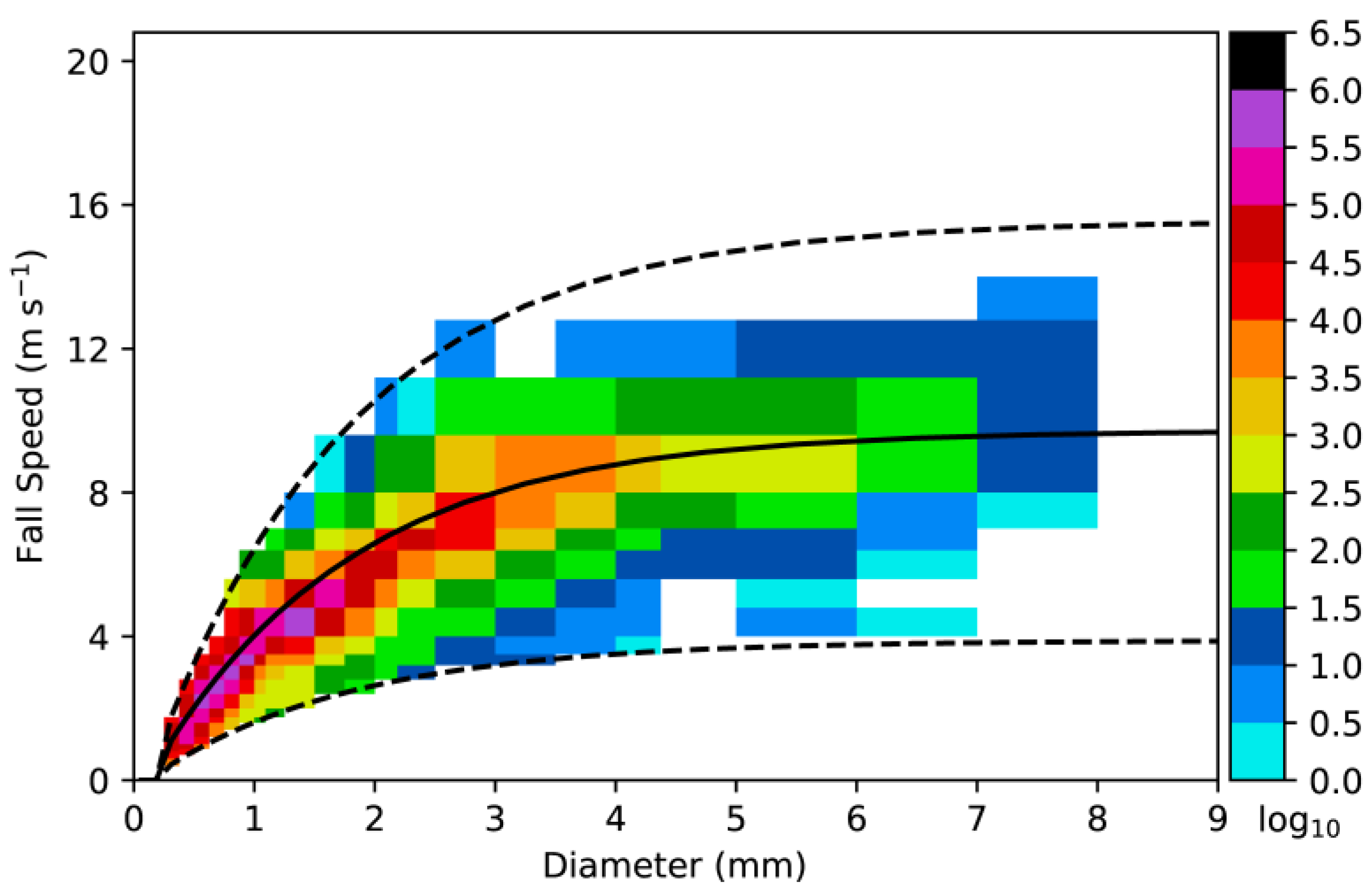
3.1. Dataset after QC
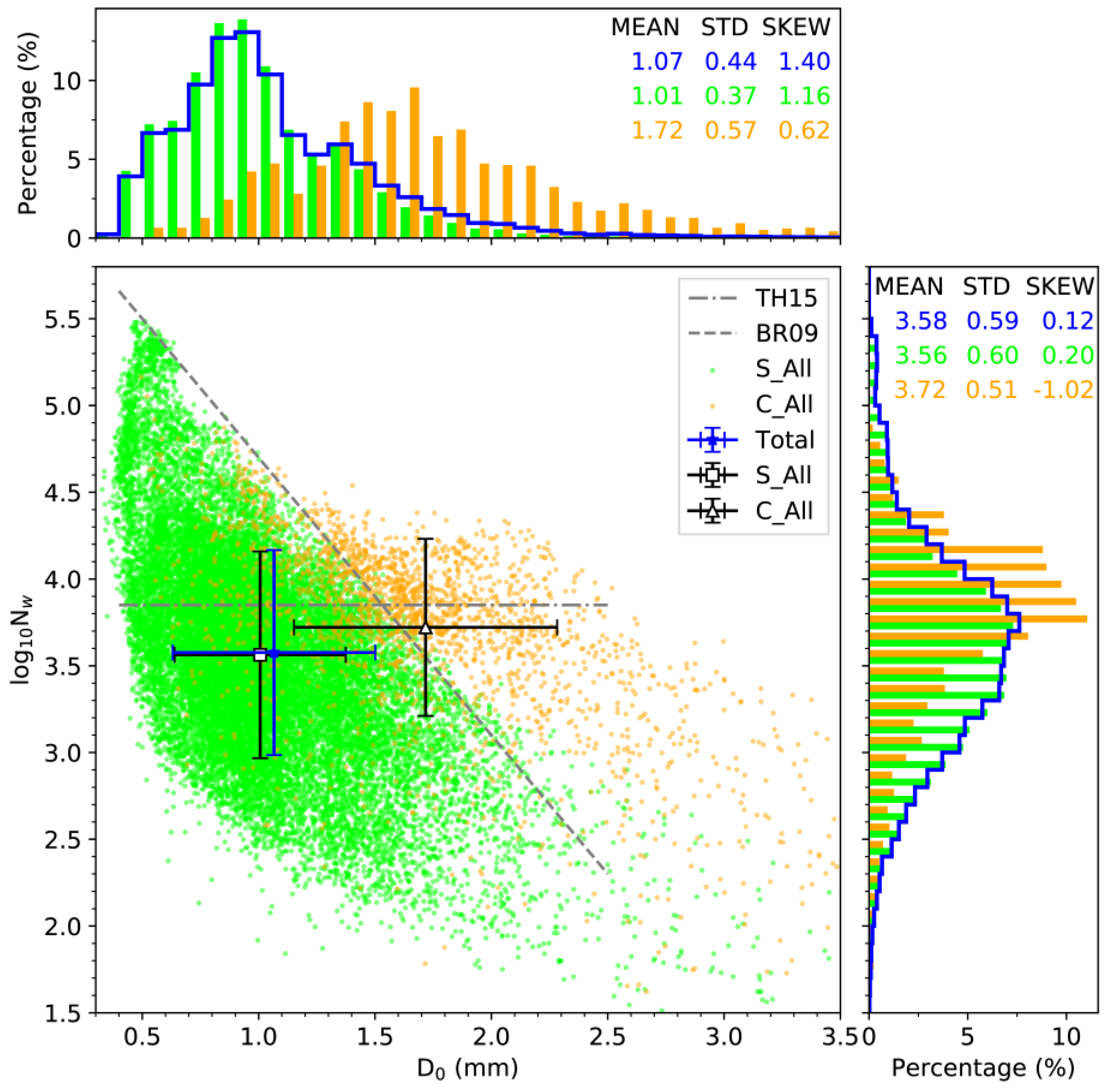
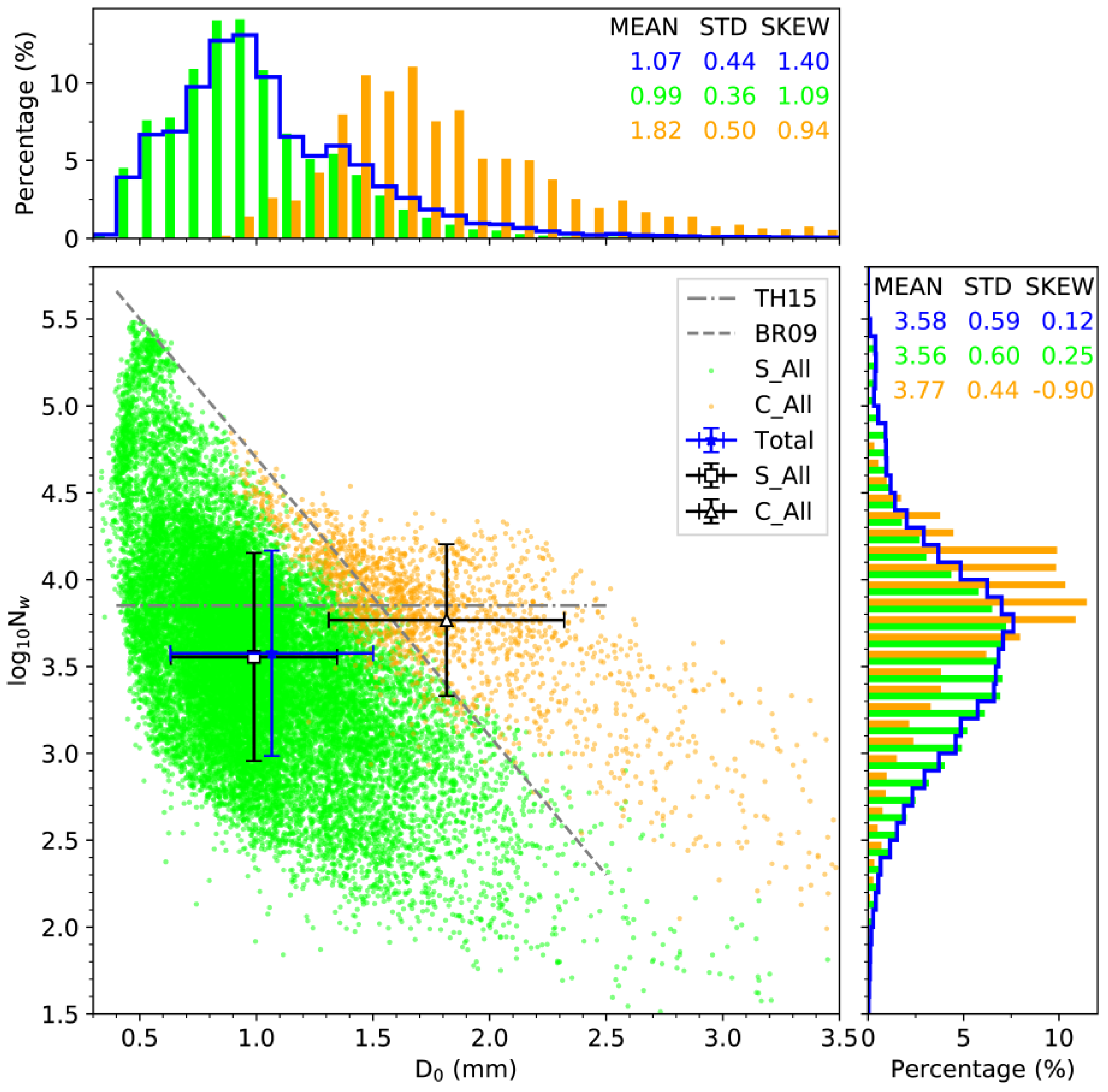
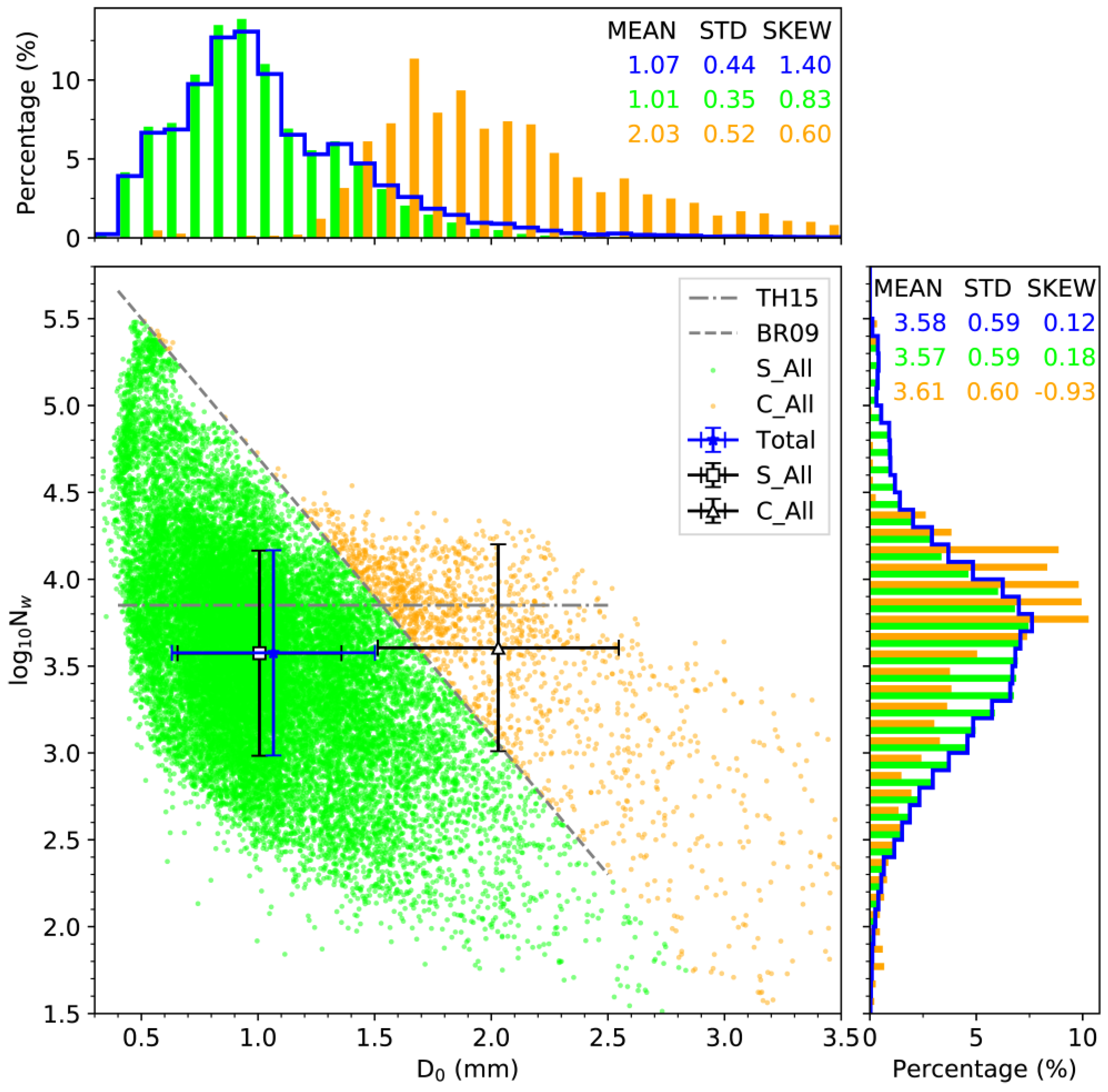
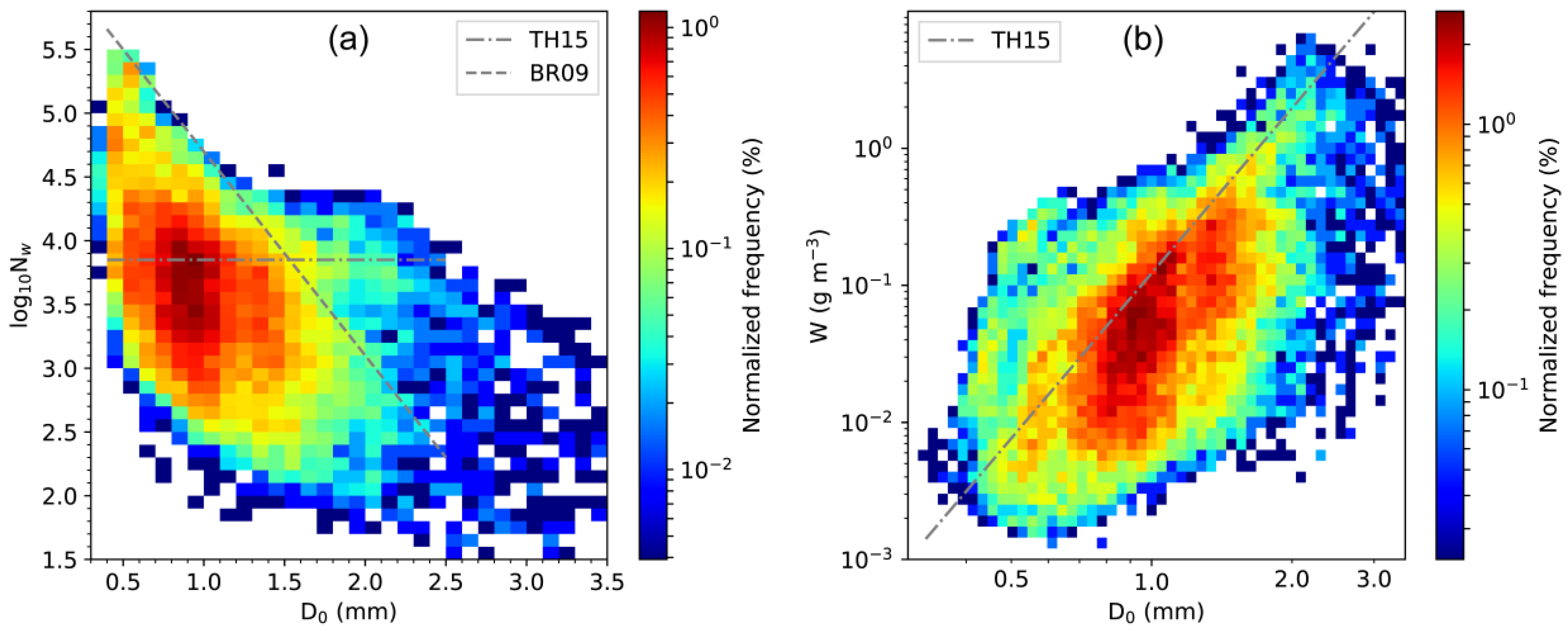
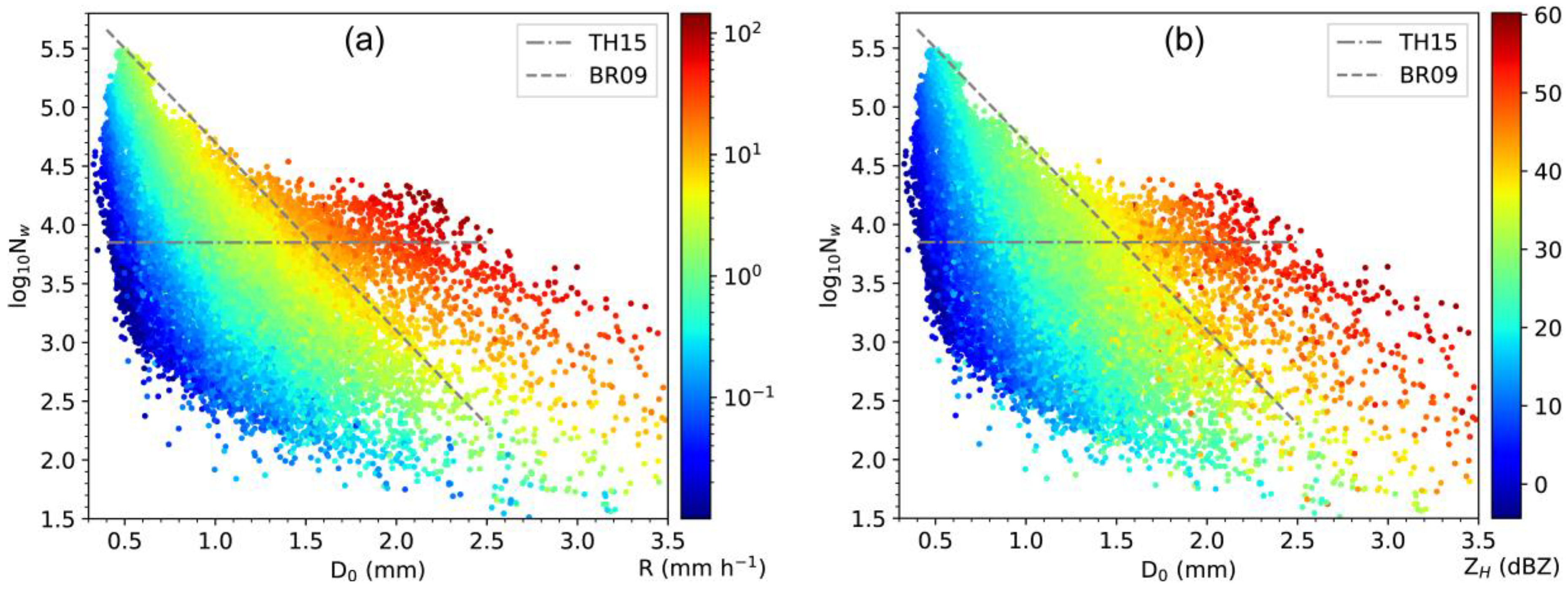
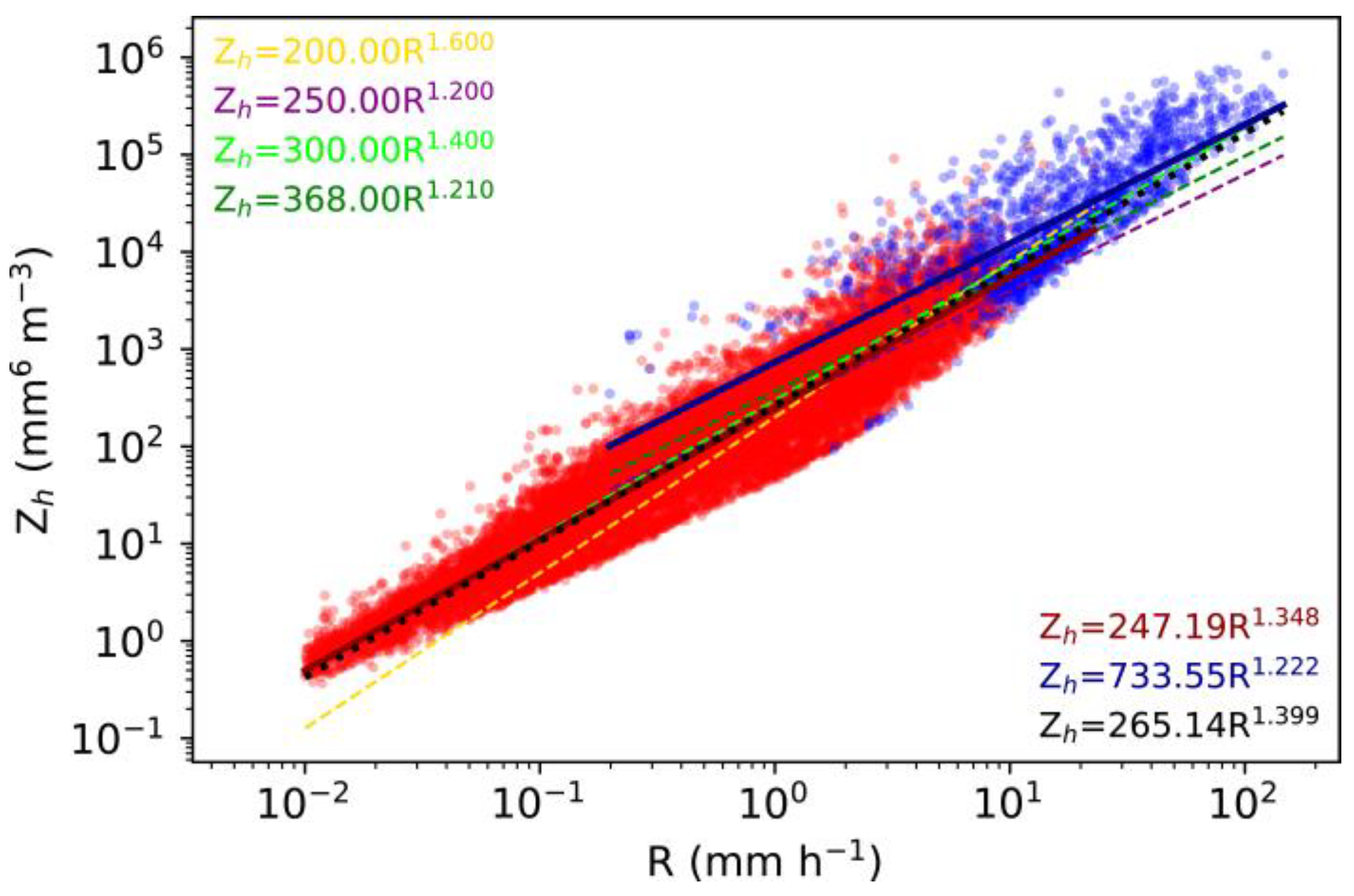
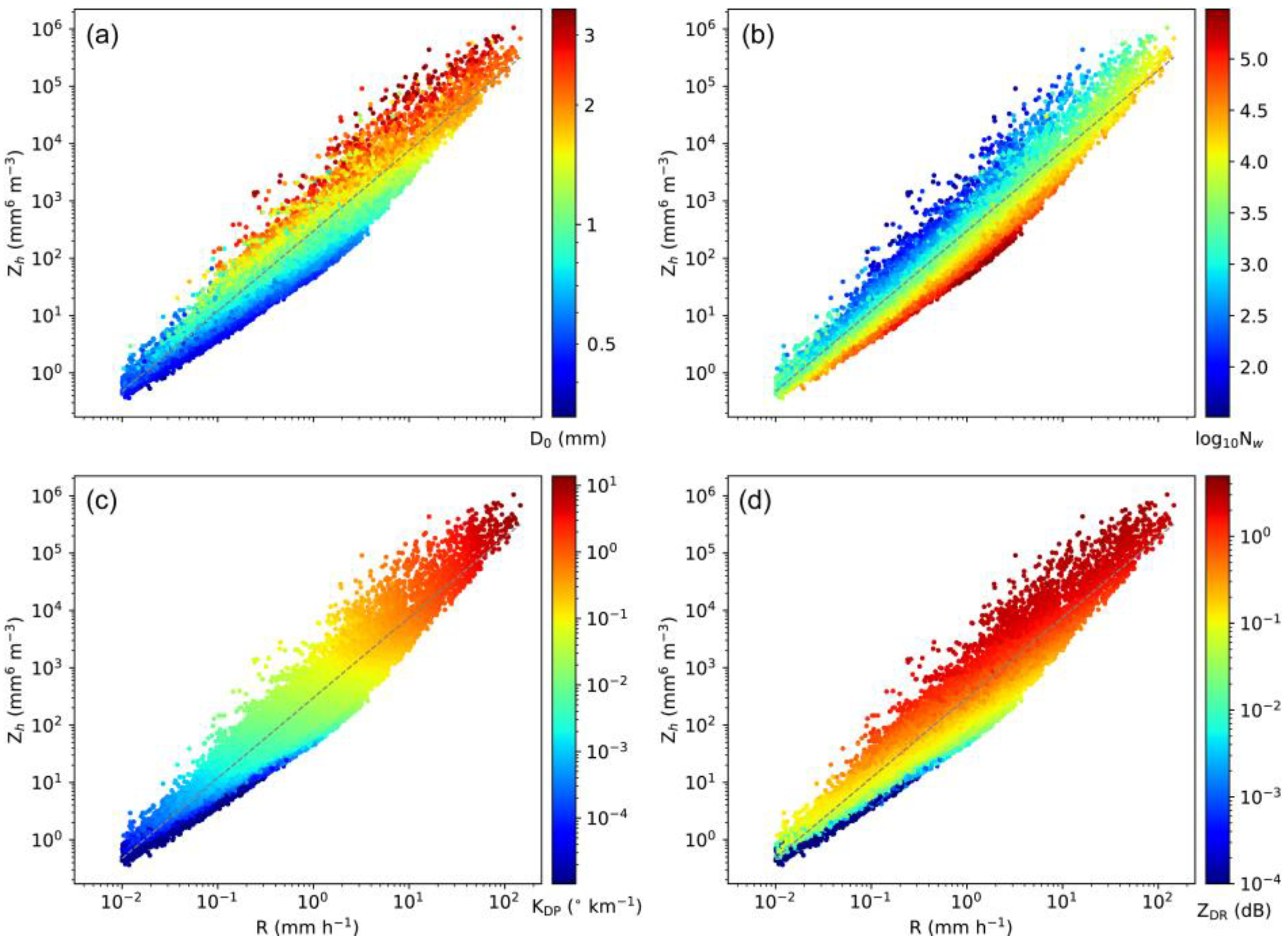
3.2. Statistical Properties of
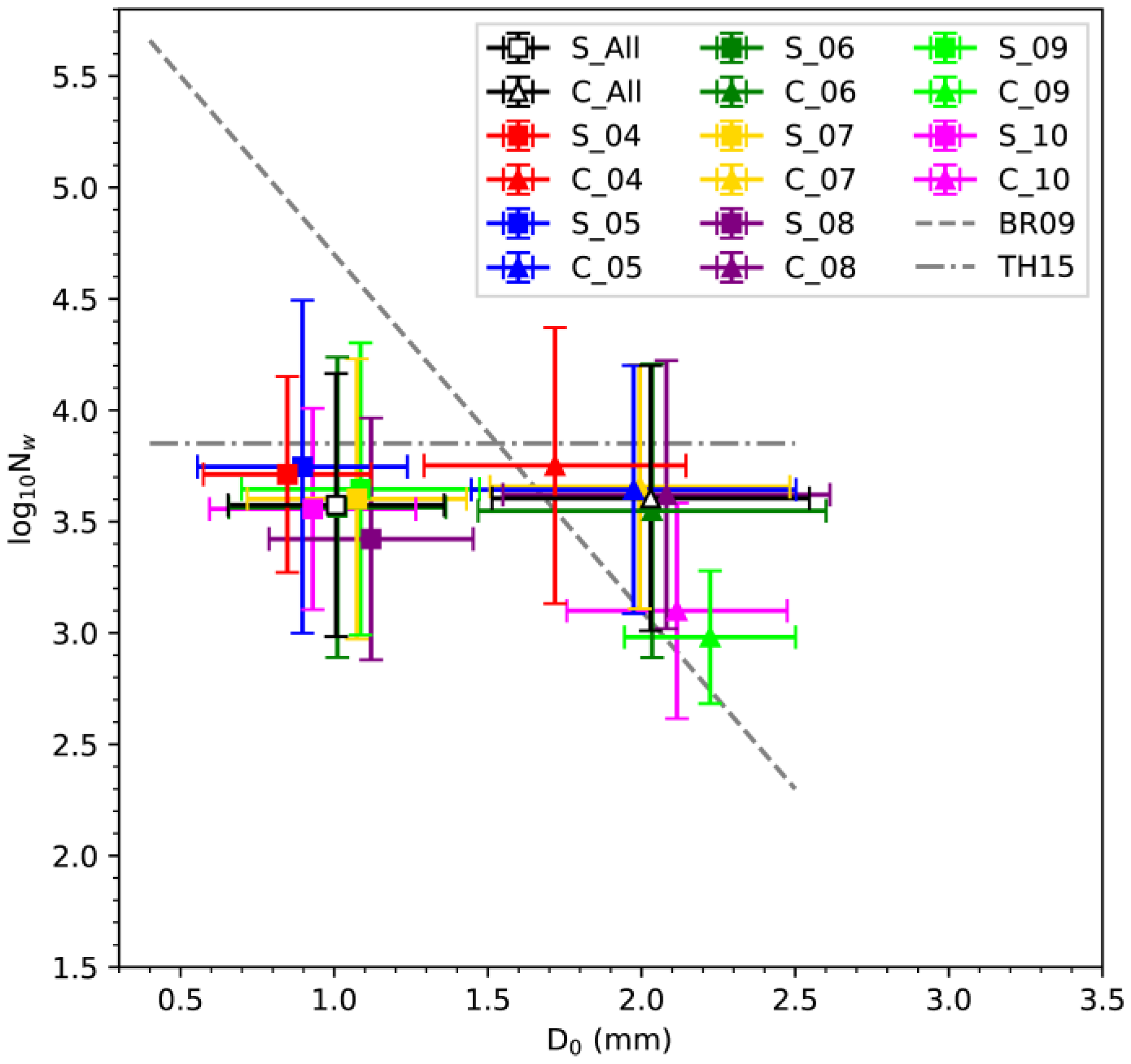
3.3. Discussion on C−S Classification Schemes
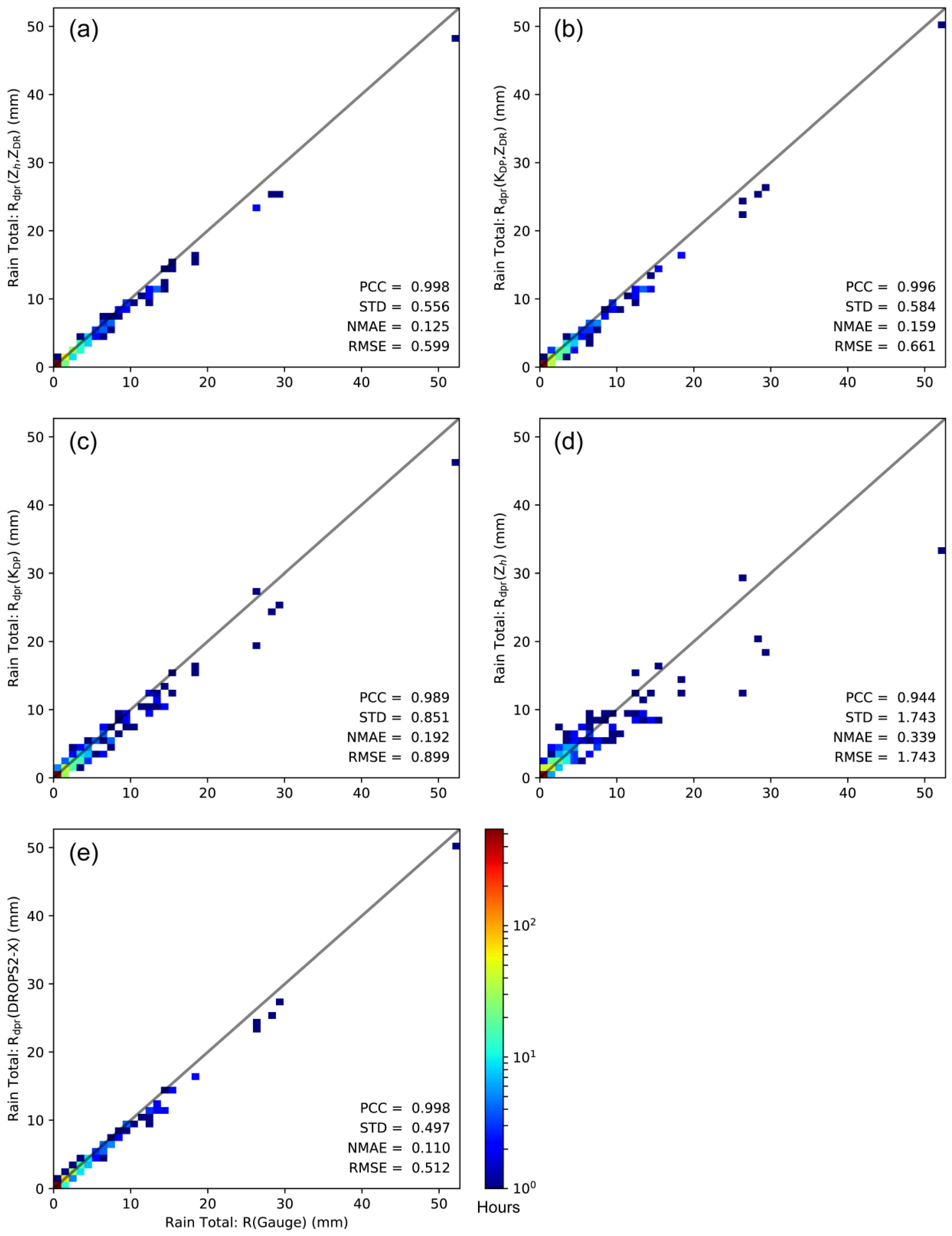
4. Radar-Based Quantitative Precipitation Estimation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Houze, R.A.J. Cloud Dynamics, 1st ed.; California Academic Press: San Jose, CA, USA, 1993; p. 573. [Google Scholar]
- Milbrandt, J.A.; Yau, M.K.; Multimoment, A. Bulk microphysics parameterization. Part i: Analysis of the role of the spectral shape parameter. J. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 62, 3051–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Sun, J.; Brandes, E. Improving parameterization of rain microphysics with disdrometer and radar observations. J. Atmos. Sci. 2006, 63, 1273–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, H.; Milbrandt, J.A. Parameterization of cloud microphysics based on the prediction of bulk ice particle properties. Part i: Scheme description and idealized tests. J. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 72, 287–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chandrasekar, V.; Bechini, R. An improved dual-polarization radar rainfall algorithm (DROPS2.0): Application in NASA ifloods field campaign. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 917–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifelli, R.; Chandrasekar, V.; Lim, S.; Kennedy, P.C.; Wang, Y.; Rutledge, S.A. A new dual-polarization radar rainfall algorithm: Application in colorado precipitation events. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2011, 28, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salles, C.; Poesen, J.; Sempere-Torres, D. Kinetic energy of rain and its functional relationship with intensity. J. Hydrol. 2002, 257, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA_Agricultural_Research_Service. Science Documentation Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation; Version 2; 2013; p. 355. Available online: https://www.ars.usda.gov/ARSUserFiles/60600505/RUSLE/RUSLE2_Science_Doc.pdf. (accessed on 7 June 2019).
- Caracciolo, C.; Prodi, F.; Battaglia, A.; Porcu, F. Analysis of the moments and parameters of a gamma DSD to infer precipitation properties: A convective stratiform discrimination algorithm. Atmos. Res. 2006, 80, 165–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Hu, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhang, G. Raindrop size distribution measurements at 4500 m on the tibetan plateau during TIPEX-III. J. Geophys. Res. 2017, 122, 11092–11106. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Yang, J.; Pu, J. Statistical characteristics of raindrop size distribution in the meiyu season observed in eastern China. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2013, 91, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzeukou, A.; Sauvageot, H.; Delfin Ochou, A.; Cheikh, M.F.K. Raindrop size distribution and radar parameters at cape verde. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2004, 43, 90–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokay, A.; Short, D.A. Evidence from tropical raindrop spectra of the origin of rain from stratiform versus convective clouds. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1996, 35, 355–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, G.; Xue, M.; Liu, B.Z.; Chen, X. Statistical characteristics of raindrop size distributions observed in east china during the asian summer monsoon season using 2-d video disdrometer and micro rain radar data. J. Geophys. Res. 2016, 121, 2265–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuter, S.E.; Kingsmill, D.E.; Nance, L.B.; Löfflermang, M. Observations of precipitation size and fall speed characteristics within coexisting rain and wet snow. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2006, 45, 1450–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Vivekanandan, J.; Brandes, E.; Meneghini, R.; Kozu, T. The shape-slope relation in observed gamma raindrop size distributions: Statistical error or useful information? J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2003, 20, 1106–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, D.; Ulbrich, C.W. Cloud Microphysical Properties, Processes, and Rainfall Estimation Opportunities. In Radar and Atmospheric Science: A collection of Essays in Honor of David Atlas, Meteorological Monographs; Wakimoto, R.M., Srivastava, R., Eds.; American Meteorological Society: Boston, MA, USA, 2003; pp. 237–258. [Google Scholar]
- Testik, F.Y.; Gebremichael, M. Rainfall: State of the Science; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; p. 287. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, S.; Jia, X.; Sang, J.; Liu, X.; Lu, C.; Liu, Y. Distributions of raindrop sizes and fall velocities in a semiarid plateau climate: Convective versus stratiform rains. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2010, 49, 632–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, K.; Higgins, S.; Masters, F.J.; Lopez, C.R. Articulating and stationary PARSIVEL disdrometer measurements in conditions with strong winds and heavy rainfall. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2013, 30, 2063–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwiebel, J.; Van Baelen, J.; Anquetin, S.; Pointin, Y.; Boudevillain, B. Impacts of orography and rain intensity on rainfall structure. The case of the HyMeX IOP7a event. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 142, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, P.T.; Bringi, V.N.; Thurai, M. Do we observe aerosol impacts on dsds in strongly forced tropical thunderstorms? J. Atmos. Sci. 2011, 68, 1902–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yu, R.C.; Wang, J.J. Diurnal variations of summer precipitation in Beijing. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2008, 53, 1933–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Guo, Y.; Hou, W.; Liu, W. Spatial and diurnal characteristics of summer rainfall over Beijing Municipality based on a high-density AWS dataset. Int. J. Climatol. 2012, 33, 2769–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wang, Y.; Gao, F.; Xiao, X. Diurnal variations in convective storm activity over contiguous North China during the warm season based on radar mosaic climatology. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D20115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wang, Y.; Gao, F.; Xiao, X. Diurnal evolution and distribution of warm-season convective storms in different prevailing wind regimes over contiguous North China. J. Geophys. Res. 2014, 119, 2742–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löfflermang, M.; Joss, J. An optical disdrometer for measuring size and velocity of hydrometeors. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2000, 17, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Xiao, H.; Guo, C.; Feng, L. Characteristics of the raindrop size distributions and their retrieved polarimetric radar parameters in northern and southern China. Atmos. Res. 2014, 135–136, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cui, X.P.; Zhang, D.L. A statistical analysis of hourly heavy rainfall events over the Beijing metropolitan region during the warm seasons of 2007–2014. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 4027–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Lin, W.L.; Zhang, Y.M.; Zhang, X.C.; Gong, S.; Zhao, P.; Yang, Y.Q.; Wang, J.Z.; Hou, Q. Changes of atmospheric composition and optical properties over beijing—2008 olympic monitoring campaign. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2009, 90, 1633–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.L.; Wang, Z.F.; Du, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q.Q.; Fu, P.Q.; Pan, X.L.; Li, J.; Jayne, J.; Worsnop, D.R. Long-term real-time measurements of aerosol particle composition in Beijing, China: Seasonal variations, meteorological effects, and source analysis. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 10149–10165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Rosenfeld, D.; Zhang, Y.; Giangrande, S.E.; Li, Z.; Machado, L.A.T.; Martin, S.T.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Artaxo, P.; et al. Substantial convection and precipitation enhancements by ultrafine aerosol particles. Science 2018, 359, 411–418. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.; Ma, X.; Bi, K.; Chen, Y.; Tian, P.; Gao, Y.; Liu, X.; He, H. Distribution of particle size and fall velocities of winter precipitation in Beijing. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2018, 76, 148–159. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Brandes, E.; Zhang, G.; Vivekanandan, J. Comparison of polarimetric radar drop size distribution retrieval algorithms. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2004, 21, 584–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekar, V.; Meneghini, R.; Zawadzki, I. Global and Local Precipitation Measurements by Radar. In Radar and Atmospheric Science: A Collection of Essays in Honor of David Atlas. Meteorological Monographs; Wakimoto, R.M., Srivastava, R., Eds.; American Meteorological Society: Boston, MA, USA, 2003; pp. 215–236. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Fan, S.; Chen, M.; Shi, J.; Zhong, J.; Zhang, X. An assessment of satellite radiance data assimilation in RMAPS. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Operating Instructions Present Weather Sensor OTT Parsivel2. Available online: https://www.ott.com/download/operating-instructions-present-weather-sensor-ott-parsivel2-without-screen-heating/ (accessed on 6 April 2019).
- Jaffrain, J.; Berne, A. Experimental quantification of the sampling uncertainty associated with measurements from PARSIVEL disdrometers. J. Hydrometeorol. 2011, 12, 352–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn, R.; Kinzer, G.D. The terminal fall velocity for water droplets in stagnant air. J. Atmos. Sci. 1949, 6, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlas, D.; Srivastava, R.C.; Sekhon, R.S. Doppler radar characteristics of precipitation at vertical incidence. Rev. Geophys. 1973, 11, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foote, G.B.; Toit, P.S.D. Terminal velocity of raindrops aloft. J. Appl. Meteor. 1969, 8, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Duan, S.; Su, D.; Lv, D. Application of X-Band dual polarization radar in precipitation estimation in summer of Beijing. Clim. Environ. Res. 2012, 17, 292–302. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Su, D.; Jin, Y.; Li, R. The impact of attenuation of X-band dual linear polarimetric radar on hail recognition. Plateau Meteorol. 2012, 31, 825–835. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Waterman, P.C. Matrix formulation of electromagnetic scattering. Proc. IEEE 1965, 53, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringi, V.N.; Chandrasekar, V. Polarimetric Doppler Weather Radar; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001; p. 664. [Google Scholar]
- Dolan, B.; Fuchs, B.; Rutledge, S.A.; Barnes, E.A.; Thompson, E.J. Primary modes of global drop size distributions. J. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 75, 1453–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, P.T. Functional fits to some observed drop size distributions and parameterization of rain. J. Atmos. Sci. 1984, 41, 1648–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, A.Y.; Kakar, R.K.; Neeck, S.; Azarbarzin, A.A.; Kummerow, C.D.; Kojima, M.; Oki, R.; Nakamura, K.; Iguchi, T. The global precipitation measurement mission. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skofronick-Jackson, G.; Petersen, W.A.; Berg, W.; Kidd, C.; Stocker, E.F.; Kirschbaum, D.B.; Kakar, R.; Braun, S.A.; Huffman, G.J.; Iguchi, T.; et al. The Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission for science and society. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 98, 1679–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringi, V.N.; Williams, C.R.; Thurai, M.; May, P.T. Using dual-polarized radar and dual-frequency profiler for DSD characterization: A case study from Darwin, Australia. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 2107–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringi, V.N.; Chandrasekar, V.; Hubbert, J.; Gorgucci, E.; Randeu, W.L.; Schoenhuber, M. Raindrop size distribution in different climatic regimes from disdrometer and dual-polarized radar analysis. J. Atmos. Sci. 2003, 60, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testud, J.; Oury, S.; Black, R.A.; Amayenc, P.; Dou, X. The concept of ‘normalized’ distribution to describe raindrop spectra: A tool for cloud physics and cloud remote sensing. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2001, 40, 1118–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, E.J.; Rutledge, S.A.; Dolan, B.; Thurai, M. Drop size distributions and radar observations of convective and stratiform rain over the equatorial indian and west pacific oceans. J. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 72, 4091–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Hu, J.; Chen, S.; Hu, D.; Liang, Z.; Huang, C.; Xiao, L.; Min, C.; Li, H. Statistical characteristics of raindrop size distribution in the monsoon season observed in southern china. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurai, M.; Bringi, V.N.; May, P.T. CPOL radar-derived drop size distribution statistics of stratiform and convective rain for two regimes in Darwin, Australia. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2010, 27, 932–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurai, M.; Gatlin, P.N.; Bringi, V.N. Separating stratiform and convective rain types based on the drop size distribution characteristics using 2D video disdrometer data. Atmos. Res. 2016, 169, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, M.; Smith, J.A.; Uijlenhoet, R. A Microphysical interpretation of radar reflectivity–rain rate relationships. J. Atmos. Sci. 2004, 61, 1114–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.S.; Palmer, W.M.K. The distribution of raindrops with size. J. Meteorol. 1948, 5, 165–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, D.; Wolff, D.B.; Atlas, D. General probability-matched relations between radar reflectivity and rain rate. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1993, 32, 50–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, R.A.; Breidenbach, J.P.; Seo, D.J.; Miller, D.A.; O’Bannon, T. The WSR-88D rainfall algorithm. Weather Forecast. 1998, 13, 377–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G. Weather Radar Polarimetry, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; p. 304. [Google Scholar]

| Type | April | May | June | July | August | September | October | 2017 | 2018 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2599 | 1910 | 4374 | 5373 | 5396 | 1036 | 4811 | 14319 | 11180 | |
| (mm h−1) | 0.85 | 1.33 | 2.14 | 4.00 | 3.47 | 1.64 | 1.00 | 2.23 | 2.58 |
| (mm h−1) | 26.46 | 45.72 | 84.92 | 145.43 | 123.61 | 10.02 | 12.17 | 118.92 | 145.43 |
| Amount (mm) | 36.63 | 42.48 | 155.88 | 358.28 | 312.44 | 28.26 | 79.80 | 532.78 | 481.00 |
| Type | C_BR09 | C_BR03 | C_TE01 | S_BR09 | S_BR03 | S_TE01 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spectra (min/%) | 1488/5.8 | 1858/7.3 | 2134/8.4 | 24011/94.2 | 22094/86.6 | 23365/91.6 |
| Amount (mm/%) | 555.22/54.8 | 605.23/59.7 | 596.33/58.8 | 458.55/45.2 | 347.43/34.3 | 417.45/41.2 |
| (mm h−1) | 22.39 | 19.54 | 16.77 | 1.15 | 0.94 | 1.07 |
| 1%/99% (mm h−1) | 1.03/104.55 | 5.10/102.63 | 0.16/100.96 | 0.02/7.23 | 0.01/6.13 | 0.01/6.79 |
| (g m−3) | 1.08 | 0.97 | 0.83 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.08 |
| (m−3) | 1179.96 | 1132.05 | 1017.30 | 318.09 | 299.14 | 309.12 |
| (dBZ) | 43.24 | 41.40 | 38.58 | 19.62 | 18.82 | 19.39 |
| (dB) | 1.75 | 1.48 | 1.34 | 0.38 | 0.36 | 0.38 |
| (° km−1) | 1.71 | 1.43 | 1.23 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.04 |
| 3.61 | 3.77 | 3.72 | 3.57 | 3.56 | 3.56 | |
| (mm) | 2.03 | 1.82 | 1.72 | 1.01 | 0.99 | 1.01 |
| (mm) | 2.05 | 1.86 | 1.76 | 1.03 | 1.01 | 1.03 |
| (mm) | 0.78 | 0.70 | 0.66 | 0.32 | 0.31 | 0.32 |
| min | 5% | 25% | median | 75% | 95% | max | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (dBZ) | −4.37 | 4.59 | 13.88 | 20.35 | 27.58 | 38.93 | 60.21 |
| (dB) | 1.00 × 10−4 | 1.95 × 10−2 | 0.12 | 0.25 | 0.57 | 1.71 | 4.95 |
| (° km−1) | 1.03 × 10−5 | 1.42 × 10−4 | 2.85 × 10−3 | 1.24 × 10−2 | 5.82 × 10−2 | 0.48 | 13.82 |
| Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.696 × 10−3 | 23.045 | 15.375 | 6.986 × 10−2 | |
| 0.986 | 0.947 | 0.836 | 0.540 | |
| −0.464 | −0.101 | ---- | ---- |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, L.; Chen, H.; Li, L.; Chen, B.; Xiao, X.; Chen, M.; Zhang, G. Raindrop Size Distributions and Rain Characteristics Observed by a PARSIVEL Disdrometer in Beijing, Northern China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1479. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121479
Ji L, Chen H, Li L, Chen B, Xiao X, Chen M, Zhang G. Raindrop Size Distributions and Rain Characteristics Observed by a PARSIVEL Disdrometer in Beijing, Northern China. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(12):1479. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121479
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Lei, Haonan Chen, Lin Li, Baojun Chen, Xian Xiao, Min Chen, and Guifu Zhang. 2019. "Raindrop Size Distributions and Rain Characteristics Observed by a PARSIVEL Disdrometer in Beijing, Northern China" Remote Sensing 11, no. 12: 1479. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121479
APA StyleJi, L., Chen, H., Li, L., Chen, B., Xiao, X., Chen, M., & Zhang, G. (2019). Raindrop Size Distributions and Rain Characteristics Observed by a PARSIVEL Disdrometer in Beijing, Northern China. Remote Sensing, 11(12), 1479. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121479






