Cubesats Allow High Spatiotemporal Estimates of Satellite-Derived Bathymetry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Insitu Data
2.2. Satellite Remote Sensing Data
2.3. Empirical Satellite-Derived Bathymetry (SDB)
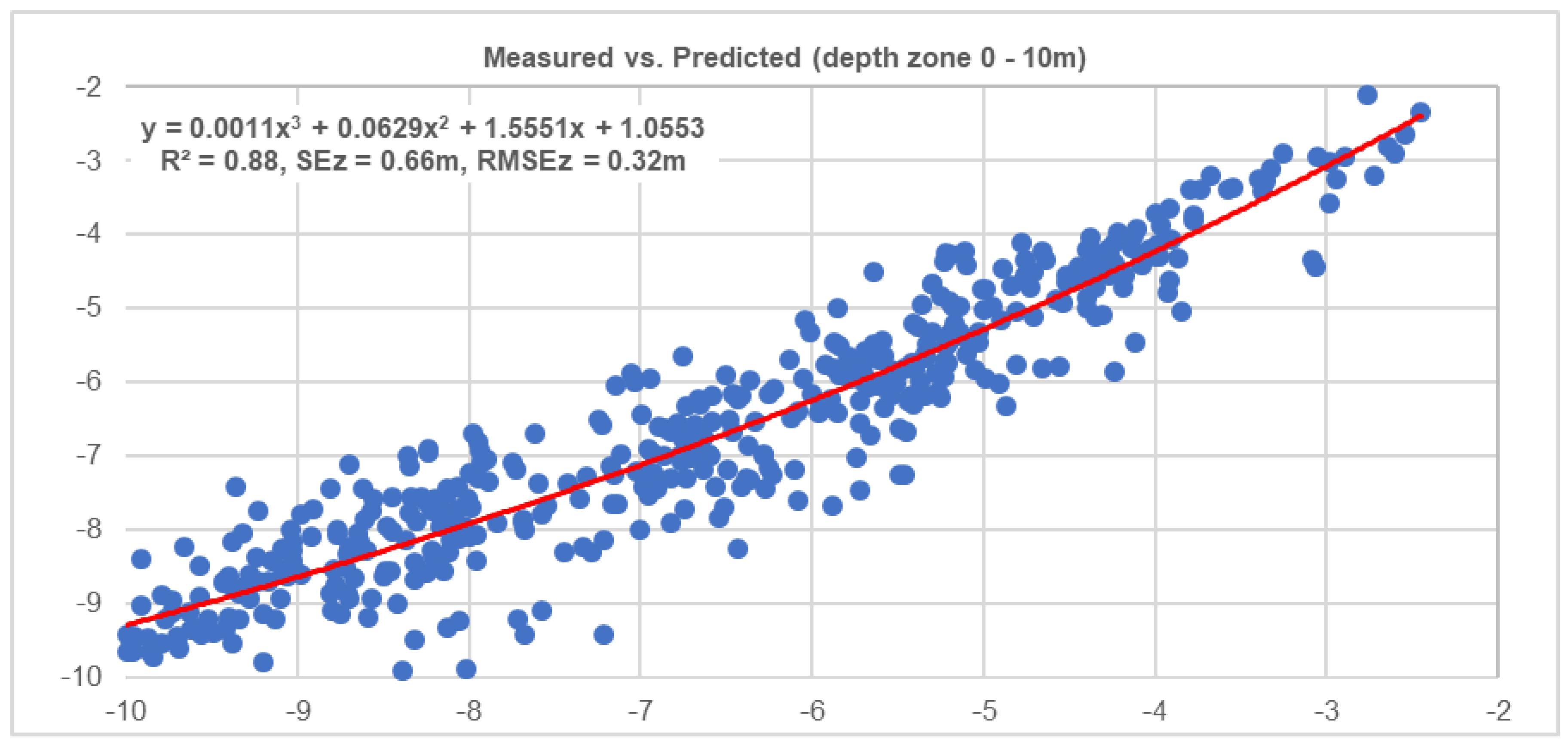
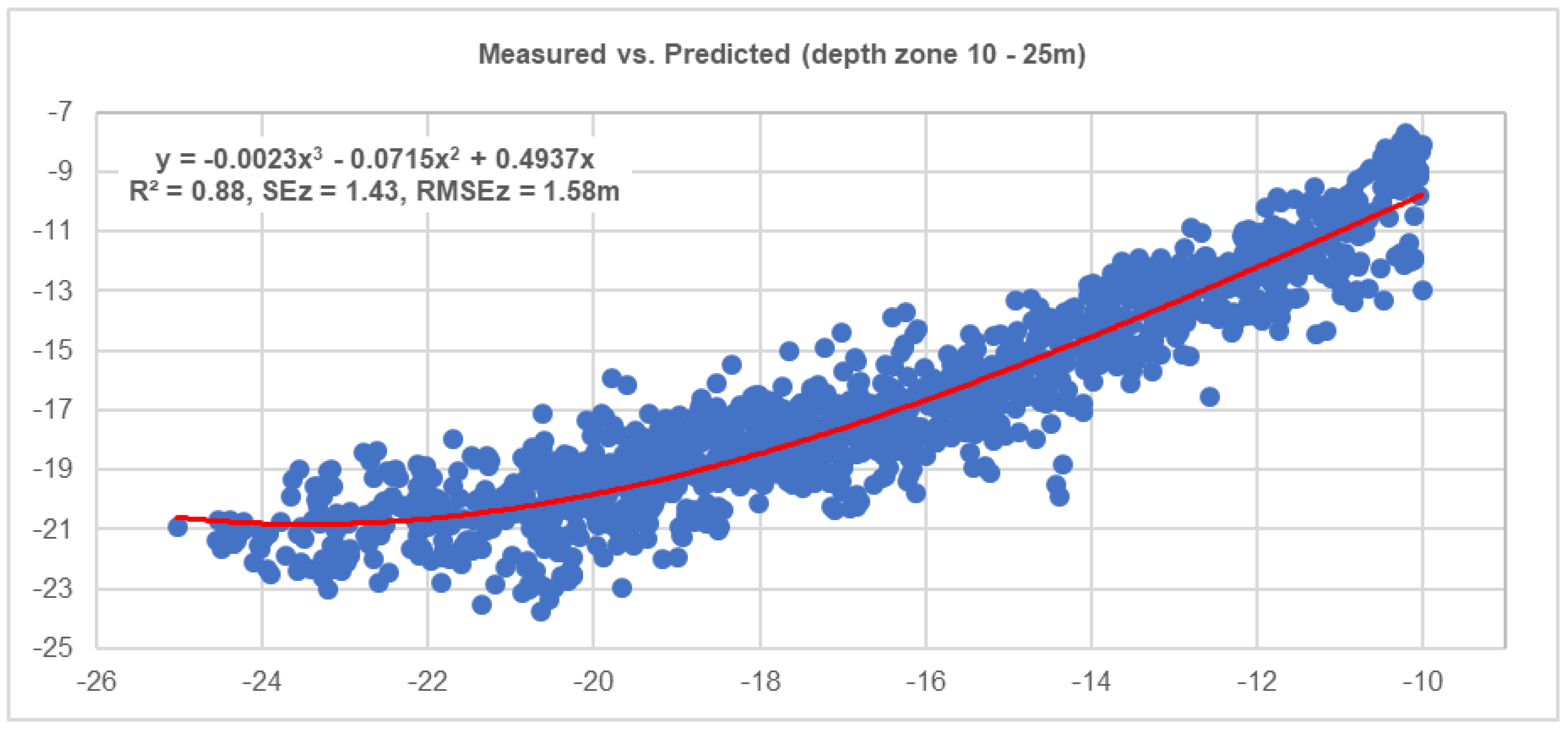
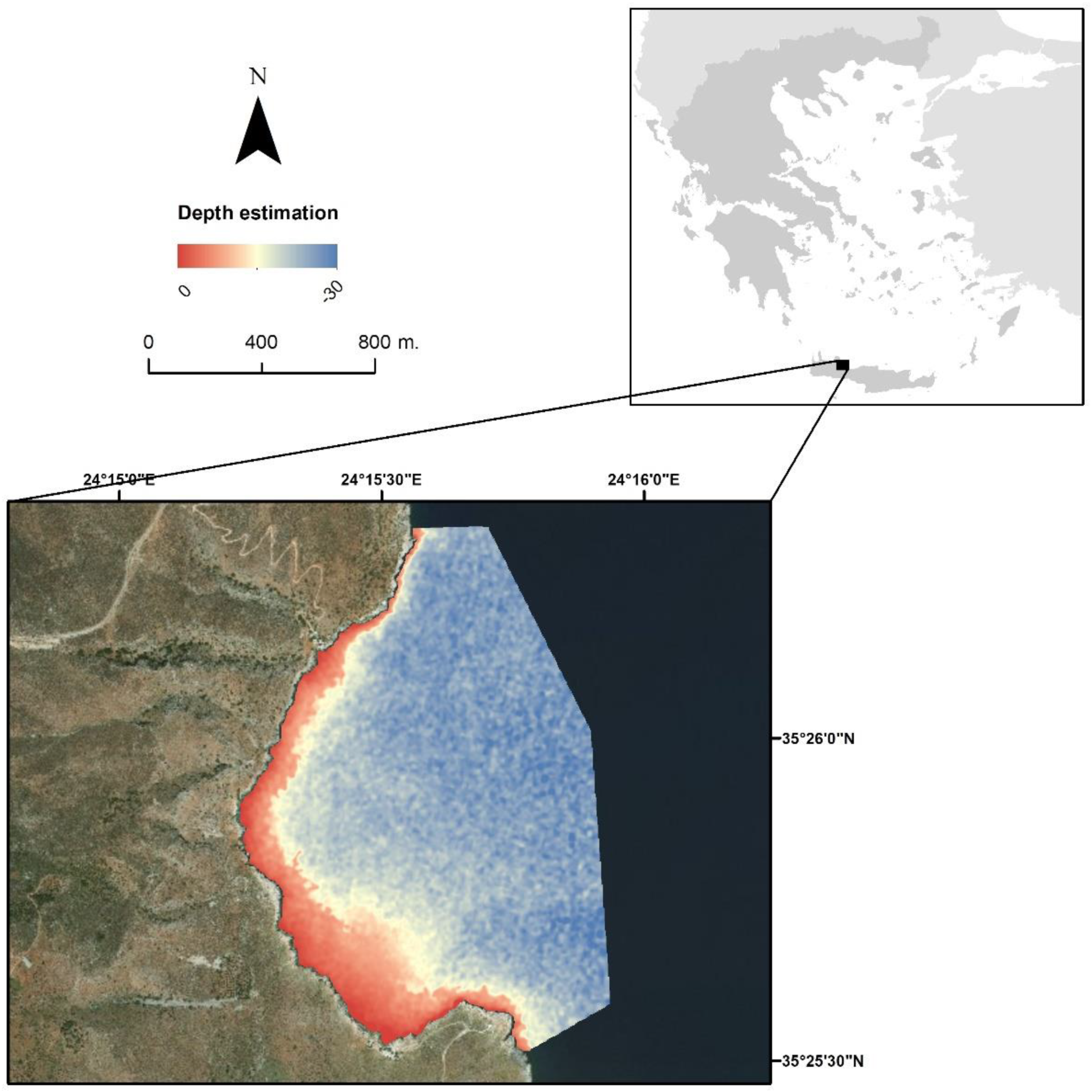
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. The CubeSats and the Performance of the Models
4.2. Are PlanetScope Suitable for Data Inclusion in Navigation Maps?
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hamylton, S.M.; Hedley, J.D.; Beaman, R.J. Derivation of High-Resolution Bathymetry from Multispectral Satellite Imagery: A Comparison of Empirical and Optimisation Methods through Geographical Error Analysis. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 16257–16273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walbridge, S.; Slocum, N.; Pobuda, M.; Wright, D.J. Unified Geomorphological Analysis Workflows with Benthic Terrain Modeler. Geosciences 2018, 8, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Hydrographic Organization (IHO). S-57 Supplement No. 3—Supplementary Information for the Encoding of S-57 Edition 3.1 ENC Data. International Hydrographic Organization: Monaco, 2014. Available online: https://www.iho.int/iho_pubs/standard/S-57Ed3.1/S-57_e3.1_Supp3_Jun14_EN.pdf (accessed on 5 January 2019).
- Saylam, K.; Hupp, J.R.; Averett, A.R.; Gutelius, F.W.; Gelhar, B.W. Airborne lidar bathymetry: Assessing quality assurance and qualitycontrol methods with Leica Chiroptera examples. Inter. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 2518–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Carnero, N.; Aceña, S.; Rodríguez-Pérez, D.; Couñago, E.; Fraile-Jurado, P.; Freire, J. Fast and low-cost method for VBES bathymetry generation in coastal areas. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 114, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyzenga, D. Passive remote sensing techniques for mapping water depth and bottom features. Appl. Opt. 1978, 17, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyzenga, D. Remote sensing of bottom reflectance and Water attenuation parameters in shallow water using aircraft and Landsat data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1981, 2, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, T.H.; Naraghi, M.; McNutt, M.K.; Smith, S.M. Bathymetric prediction from SEASAT altimeter data. J. Geophys. Res. 1983, 88, 1563–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandwell, D.T.; Smith, W.H. Marine gravity anomaly from Geosat and ERS 1 satellite altimetry. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1997, 102, 10039–10054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olson, C.J.; Becker, J.J.; Sandwell, D.T. A new global bathymetry map at 15 arcsecond resolution for resolving seafloor fabric: SRTM15_PLUS. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, San Francisco, CA, USA, 15–19 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Conger, C.L.; Hochberg, E.J.; Fletcher, C.H.; Atkinson, M.J. Decorrelating remote sensing color bands from bathymetry in optically shallow waters. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 1655–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyzenga, D.R. Shallow-water bathymetry using combined lidar and passive multispectral scanner data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1985, 6, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyzenga, D.R.; Malinas, N.P.; Tanis, F.J. Multispectral bathymetry using a simple physically based algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2251–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philpot, W.D. Bathymetric mapping with passive multispectral imagery. Appl. Opt. 1989, 28, 1569–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanno, A.; Tanaka, Y.; Kurosawa, A.; Sekine, M. Generalized Lyzenga’s Predictor of Shallow Water Depth for Multispectral Satellite Imagery. Mar. Geod. 2013, 36, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houborg, R.; McCabe, M.F. High-Resolution NDVI from Planet’s constellation of earth observing nano-satellites: A new data source for precision agriculture. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traganos, D.; Cerra, D.; Reinartz, P. Cubesat-Derived Detection of Seagrasses Using Planet Imagery Following Unmixing-Based Denoising: Is Small the Next Big? Available online: https://doi.org/10.5194/isprs-archives-XLII-1-W1-283-2017 (accessed on 20 April 2019).
- Wicaksono, P.; Lazuardi, W. Assessment of PlanetScope images for benthic habitat and seagrass species mapping in a complex optically shallow water environment. Inter. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 5739–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traganos, D.; Poursanidis, D.; Aggarwal, B.; Chrysoulakis, N.; Reinartz, P. Estimating Satellite-Derived Bathymetry (SDB) with the Google Earth Engine and Sentinel-2. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planet. Planet Education and Research Program. Available online: https://www.planet.com/markets/education-and-research/ (accessed on 10 March 2019).
- Planet. Planet Imagery Product Specification. 2018. Available online: https://assets.planet.com/docs/Combined-Imagery-Product-Spec-Dec-2018.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2019).
- Fox, J.; Weisberg, S. An {R} Companion to Applied Regression, Second Edition; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2011; Available online: http://socserv.socsci.mcmaster.ca/jfox/Books/Companion (accessed on 10 March 2019).
- Akaike, H. Information Theory and an Extension of the Maximum Likelihood Principle. In Selected Papers of Hirotugu Akaike; Parzen, E., Tanabe, K., Kitagawa, G., Eds.; Springer Series in Statistics (Perspectives in, Statistics); Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Burnham, K.; Anderson, D. Model Selection and Multimodal Inference; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Mazerolle, M.J. AICcmodavg: Model Selection and Multimodel Inference Based on (Q)AIC(c). R Package Version 2.2-1. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=AICcmodavg (accessed on 20 April 2019).
- Chénier, R.; Faucher, M.-A.; Ahola, R. Satellite-Derived Bathymetry for Improving Canadian Hydrographic Service Charts. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooley, S.W.; Smith, L.C.; Stepan, L.; Mascaro, J. Tracking Dynamic Northern Surface Water Changes with High-Frequency Planet CubeSat Imagery. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghuffar, S. DEM Generation from Multi Satellite PlanetScope Imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asner, G.P.; Martin, R.E.; Mascaro, J. Coral reef atoll assessment in the South China Sea using Planet Dove satellites. Remote Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 2017, 3, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen Coral Atlas. 2019. Available online: http://www.allencoralatlas.com/ (accessed on 5 January 2019).
- Lemajic, S.; Vajsová, B.; Aastrand, P. New Sensors Benchmark Report on PlanetScope: Geometric Benchmarking Test for Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) Purposes. Available online: http://publications.jrc.ec.europa.eu/repository/bitstream/JRC111221/jrc_technical_report_planetscope-final_2.pdf (accessed on 29 May 2019).

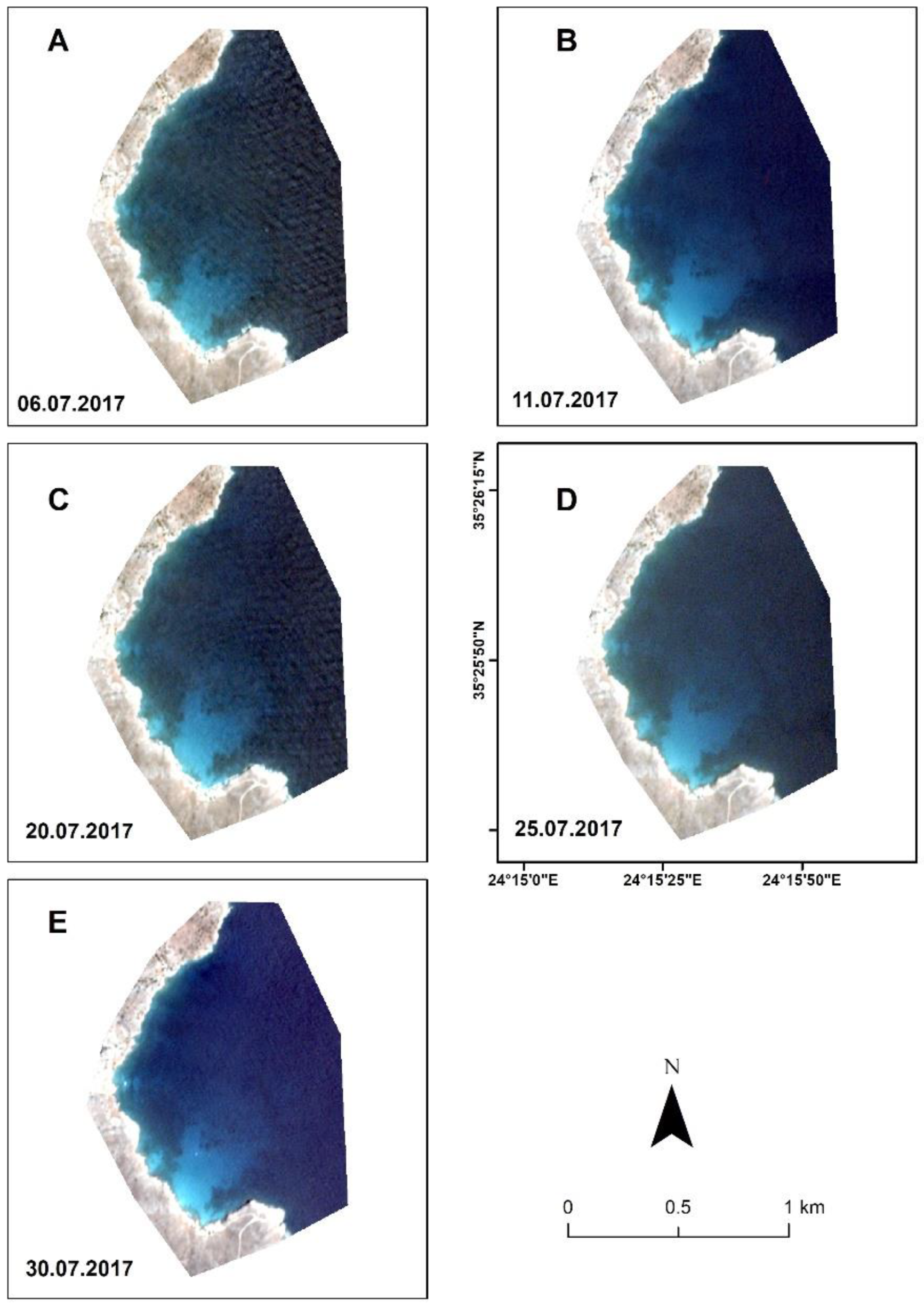

| Scene ID | Date | Time (UTC) | Sun Azimuth | Sun Elevation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20170706_082033_103e_3B_AnalyticMS_SR | 6 July 2017 | 8:20 | 106.24 | 59.69 |
| 20170711_082041_1012_3B_AnalyticMS_SR | 11 July 2017 | 8:20 | 107.14 | 59.27 |
| 20170720_082118_101d_3B_AnalyticMS_SR | 20 July 2017 | 8:21 | 109.4 | 58.37 |
| 20170725_082251_1011_3B_AnalyticMS_SR | 25 July 2017 | 8:22 | 111.02 | 57.78 |
| 20170730_082318_102e_3B_AnalyticMS_SR | 30 July 2017 | 8:23 | 112.69 | 57.17 |
| ID | Modnames | AICc | Delta_AICc | AICcWt | LL | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | sdb.glm0706 | 12497.5 | 1128.5 | 8.584 × 10−246 | −6243.7 | 0.84 |
| 2 | sdb.glm0711 | 11368.9 | 0 | 1 | −5679.4 | 0.89 |
| 4 | sdb.glm0720 | 12143.5 | 774.6 | 6.203 × 10−169 | −6066.7 | 0.86 |
| 5 | sdb.glm0725 | 12989.2 | 1620.3 | 0 | −6489.6 | 0.81 |
| 6 | sdb.glm0730 | 12583.9 | 1214.9 | 1.51 × 10−264 | −6286.9 | 0.84 |
| Regression Statistics | RAW (0–10 m) | 3 × 3 (0–10 m) | RAW (10–24 m) | 3 × 3 (10–24 m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multiple R | 0.93 | 0.94 | 0.9 | 0.92 |
| R Square | 0.86 | 0.88 | 0.81 | 0.84 |
| Adjusted R Square | 0.86 | 0.88 | 0.81 | 0.84 |
| Standard Error | 0.72 | 0.66 | 1.63 | 1.48 |
| Observations | 702 | 702 | 2152 | 2152 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Poursanidis, D.; Traganos, D.; Chrysoulakis, N.; Reinartz, P. Cubesats Allow High Spatiotemporal Estimates of Satellite-Derived Bathymetry. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11111299
Poursanidis D, Traganos D, Chrysoulakis N, Reinartz P. Cubesats Allow High Spatiotemporal Estimates of Satellite-Derived Bathymetry. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(11):1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11111299
Chicago/Turabian StylePoursanidis, Dimitris, Dimosthenis Traganos, Nektarios Chrysoulakis, and Peter Reinartz. 2019. "Cubesats Allow High Spatiotemporal Estimates of Satellite-Derived Bathymetry" Remote Sensing 11, no. 11: 1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11111299
APA StylePoursanidis, D., Traganos, D., Chrysoulakis, N., & Reinartz, P. (2019). Cubesats Allow High Spatiotemporal Estimates of Satellite-Derived Bathymetry. Remote Sensing, 11(11), 1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11111299








