Abstract
The Geostationary Environment Monitoring Spectrometer (GEMS) is scheduled to be in orbit in 2019 onboard the GEO-KOMPSAT 2B satellite and will continuously monitor air quality over Asia. The GEMS will make measurements in the UV spectrum (300–500 nm) with 0.6 nm resolution. In this study, an algorithm is developed to retrieve aerosol optical properties from UV-visible measurements for the future satellite instrument and is tested using 3 years of existing OMI L1B data. This algorithm provides aerosol optical depth (AOD), single scattering albedo (SSA) and aerosol layer height (ALH) using an optimized estimation method. The retrieved AOD shows good correlation with Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) AOD with correlation coefficients of 0.83, 0.73 and 0.80 for heavy-absorbing fine (HAF) particles, dust and non-absorbing (NA) particles, respectively. However, regression tests indicate underestimation and overestimation of HAF and NA AOD, respectively. In comparison with AOD from the OMI/Aura Near-UV Aerosol Optical Depth and Single Scattering Albedo 1-orbit L2 Swath 13 km × 24 km V003 (OMAERUV) algorithm, the retrieved AOD has a correlation coefficient of 0.86 and linear regression equation, AODGEMS = 1.18AODOMAERUV + 0.09. An uncertainty test based on a reference method, which estimates retrieval error by applying the algorithm to simulated radiance data, revealed that assumptions in the spectral dependency of aerosol absorptivity in the UV cause significant errors in aerosol property retrieval, particularly the SSA retrieval. Consequently, retrieved SSAs did not show good correlation with AERONET values. The ALH results were qualitatively compared with the Cloud-Aerosol Lidar with Orthogonal Polarization (CALIOP) products and were found to be well correlated for highly absorbing aerosols. The difference between the attenuated-backscatter-weighted height from CALIOP and retrieved ALH were mostly closed to zero when the retrieved AOD is higher than 0.8 and SSA is lower than 0.93. Although retrieval accuracy was not significantly improved, the simultaneous consistent retrieval of AOD, SSA and ALH alone demonstrates the value of this stand-alone algorithm, given their nature for error using other methods. The use of these properties as input parameters for the air mass factor calculation is expected to improve the retrieval of other trace gases over Asia.
1. Introduction
Rapid industrialization and urbanization in Asia has raised serious concerns related to air quality and climate change. Persistent emissions of pollutants affect air quality and the regional climate not only for Asia but also for the North Pacific because of long-range transport by westerly wind [1]. Consequently, understanding aerosol optical properties (AOPs) over Asia becomes important to estimate radiative forcing and its effects on human activity.
Advances in measurement technology have improved our understanding of the chemical and physical properties of aerosols. Aerosol properties can be measured by ground-based instruments locally and their regional-scale variations can be observed using satellite remote sensing. Geostationary satellite measurements in particular have been widely adopted to monitor the continuous variation of aerosols with high temporal resolution. Over Asia, serial geostationary satellite projects, such as the Geostationary Korea Multi-Purpose Satellite (Geo-KOMPSAT), the Feng-Yun (FY) and the Himawari have been operated by the Korean, Chinese and Japanese governments, respectively and several algorithms to retrieve aerosol information have been developed optimized to each instrument. Since the Geo-KOMPSAT-1 was launched in 2010, its Meteorological Imager (MI) and Geostationary Ocean Color Imager (GOCI) have been used to monitor aerosol properties over northeast Asia. The MI provides a single visible measurement of AOD with 4 km × 4 km resolution on a 15 min interval [2] and a multi-visible/near-IR GOCI algorithm retrieves AOD, fine-mode fraction (FMF) and aerosol type with 6 km × 6 km resolution on a 1 h interval [3,4,5]. The Advanced Himawari Imager (AHI) was launched in 2013 and provides AOD and the Ångström exponent from multi-visible and near-IR measurements [6].
As part of the Geo-KOMPSAT project, the Geo-KOMPSAT 2A and 2B twin-satellites are planned to be launched in 2018 and 2019, respectively. While the Geo-KOMPSAT1 mission focused solely on the measurement of atmosphere and ocean properties, the Geo-KOMPSAT2 mission is also tasked with understanding the wide variations in air quality over Asia. Towards this goal, a scanning spectrometer, the Geostationary Environmental Monitoring Spectrometer (GEMS), will be launched onboard the GEO-KOMPSAT 2B satellite with GOCI-II. The GEMS will measure the UV-visible spectrum (300–500 nm) with 0.6 nm resolution to retrieve total column ozone (O3), aerosol loading and key gas-phase species (NO2, SO2, HCHO) concentrations over Asia (5°S–45°N, 75°E–145°E) with high temporal resolution (1 h). The GEMS will be the first mission to monitor air pollutants over Asia from geostationary orbit. The coverage area of the GEMS instrument includes regions with air pollution from industrial activities and biomass burning as well as from natural sources, such as desert dust. The nominal spatial resolution is 7 km (NS) × 8 km (EW) at Seoul (128°20′E, 37°24′N) and 4.9 km (NS) × 8 km (EW) near the equator (128°20′E, 5°00′S) but that for aerosol properties will be enhanced to 3.5 km (NS) × 8 km (EW) at Seoul without pixel binning to avoid possible noise due to subpixel cloud on a pixel. Table 1 lists major specifications of the GEMS. To achieve 0.6 nm spectral resolution, the spectral sampling by one pixel of the focal plane is 0.2 nm. In comparison with low-earth orbit (LEO) environmental satellites, such as OMI (13 km × 24 km) and SCHIAMACHY (30 km × 60 km), the GEMS has significantly improved spatial and temporal resolution.

Table 1.
GEMS specifications.
Measurements in the UV range can be used to estimate the radiative absorptivity of aerosols [7], while those in the visible range provide optical depth and particle size information. The large contribution of Rayleigh scattering in the UV range increases sensitivity to aerosol absorptivity and the spectral features of backward radiance mainly vary with the amount, size and scattering properties of aerosols. Additionally, the surface tends to be darker in the UV range than in the visible over land pixels [8]. Based on these sensitivities, this study develops a UV-visible algorithm to retrieve aerosol optical depth (AOD), single scattering albedo (SSA) and aerosol layer height (ALH) from GEMS measurements.
As aerosol extinction varies considerably with the chemical composition and physical properties of particles, an understanding of SSA, which represents the radiative absorptivity of particles, is required to evaluate aerosol effects on climate change. Additionally, estimations of ALH are important to estimating PM concentrations [9] and to retrieving gas concentrations for species such as NO2 and HCHO. Kwon et al. [10] suggested that temporal variations of aerosols cannot be neglected for geostationary HCHO measurements, because the aerosol height in the boundary layer and scattering properties change the air mass factor (AMF). Hong et al. [11] investigated effects of aerosol properties on NO2 retrieval and found that the aerosol height relative to the NO2 profile is the most significant factor in calculating AMF. They found that a 2 km error in aerosol height under high solar zenith angle (SZA) conditions leads to over 60% error in AMF and thus NO2 vertical column density. The estimation of ALH is particularly important to AOD and SSA retrieval using UV-visible measurements because aerosol contributions to backward radiance in the shortwave region depend on the aerosol height, AOD and SSA, simultaneously. Accordingly, the Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) near-UV aerosol algorithm [12,13,14] applied the backscatter coefficient of an active sensor, the Cloud-Aerosol Lidar with Orthogonal Polarization (CALIOP; Winker et al. [15]), to the retrieval of AOD and SSA from OMI measurements. Torres et al. [14] reported that the use of the CALIOP climatology value as an input to the OMI near-UV algorithm improved the agreement between OMI and Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) AOD [16] at five AERONET sites as indicated by an increased correlation coefficient and decreased y-intercept. As an example, at the Banizombou site (13.5°N, 2.7°E), the correlation coefficient, y-intercept and root-mean square (RMS) error improved from 0.71, 0.21 and 0.19 to 0.75, 0.17 and 0.16, respectively. Their study mainly discussed the effects of the combined use of OMI, the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) and CALIOP on aerosol type classification and aerosol layer assumptions.
With regard to AOP retrieval, the aerosol height has been estimated by adopting the multi-sensor measurements of the A-Train (Afternoon satellite constellation; NASA [17]). Jeong and Hsu [18] retrieved SSA and aerosol height for biomass-burning smoke using the MODerate resolution Imaging Spectrophotometer (MODIS) and the OMI and Lee et al. [19] expanded the algorithm to retrieve smoke and dust aerosol height by synergistic use of the CALIOP, the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) and the Ozone Mapping and Profiler Suite (OMPS). They obtained AOD and the Ångström exponent from the VIIRS, UV aerosol index (UVAI) from the OMPS and the backscatter coefficient from the CALIOP measurement and retrieved aerosol height with SSA based on a look-up table (LUT) approach. For passive remote sensing, the OMI measurement of the 477 nm O2–O2 spectral band has been widely used to retrieve aerosol height information. Park et al. [20] and Chimot et al. [21] applied the differential optical absorption spectroscopy technique and the multilayer perceptron neural network approach to the OMI O2–O2 band measurement over northeast Asia, collocated with the MODIS aerosol product and obtained ALH.
Previous studies achieved good performance for aerosol height derivation or AOD and SSA retrieval through multi-sensor measurements but there has been limited work on the stand-alone retrieval of AOD, SSA and aerosol height. With regard to the GEMS operation, differences in spatial coverage, temporal and spatial resolution and the lifetime of multiple sensors can cause problems in operation efficiency and stability. Thus, the GEMS aerosol retrieval algorithm uses the optimal estimation (OE) method [22]. The OE method finds the best solution to minimize differences between measured and simulated spectral intensity and has traditionally been used to retrieve vertical profiles of the atmosphere from sounding observations [23]. It has also been used for the retrieval of aerosol vertical profiles [24] and the joint retrieval of surface reflectance and AOD [25,26]. In this study, the OE method is applied to find optimized values for AOD, SSA and ALH to fit the simulated radiance to observations.
To describe the vertical profile of aerosols, Torres et al. [27] used the Gaussian function characterized by a peak height (in km) and a half-width. The peak height and half-width were defined as the ALH and geometrical thickness, respectively. Then, the concept of ALH was introduced to the Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer (TOMS) and OMI aerosol algorithms [14,27]. Using the CALIOP-measured attenuated backscatter profiles at 1064 nm, the ALH can be estimated by the attenuated-backscatter-weighted height (Zaer) according to the expression
where Bsc(i) is the attenuated backscatter at height H(i) and n is the number of altitude bins. The assumption of a Gaussian aerosol vertical distribution is adopted in this study.
To apply the OE method, a two-channel method [28] is adopted first to estimate an a priori state for AOD and SSA. Wagner et al. [26] showed that updating the a priori state clearly improved the performance of the OE to retrieve AOD and surface reflectance. Because of the importance of the a priori state, the GEMS aerosol algorithm retrieves a priori states for AOD and SSA prior to applying the OE method based on the two-channel approach, which has been used in the OMI UV algorithm, instead of using the climatological state.
Because the sensitivity of backscattering in the UV-visible spectrum to AOD and SSA varies with aerosol type, three types of aerosol (dust (absorbing coarse particles), highly absorbing fine (HAF) and non-absorbing (NA)) were defined for a radiative transfer model (RTM) simulation using the Vector Linearized Discrete Ordinate Radiative Transfer code (VLIDORT; Spurr [29]). The optical characteristics for each type were calculated from the AERONET inversion product over Asia using the classification method suggested by Lee et al. [30]. Then, the aerosol type was distinguished using the aerosol index (AI) calculated from two pairs of wavelengths in the UV (354 nm and 388 nm) and the blue range (477 nm and 490 nm) before the OE retrieval. The algorithm was tested using OMI measurements, which has specifications similar to those of the GEMS and its retrieval uncertainties were estimated using a synthetic spectrum.
The simultaneous retrieval of AOD and SSA with high temporal resolution is expected to improve the accuracy of aerosol products, the understanding of the radiometric effects of aerosols and the estimation of trends in aerosol distributions over Asia. Thus, by using these products, further investigations of the role of aerosols in Asia on climate and air quality change can be performed.
A general description of the validation and ancillary dataset is given in Section 2. In Section 3, the general design of the algorithm is presented and details of each process are described in subsections. Results obtained from the developed algorithm are compared with AERONET, CALIOP and OMI products and are presented in Section 4. In Section 5, a reference test is performed to estimate retrieval uncertainty. Further development of the algorithm based on the uncertainty analysis is discussed in Section 6. The final section provides a summary of the results.
2. Validation and Ancillary Dataset
2.1. OMI L1B and OMI Surface LER Product (OMLER)
Because GEMS is not scheduled to be in orbit until 2019, the hyper-spectral UV-visible measurements of OMI, which has specifications similar to those of the GEMS, are used here as a proxy to test the retrieval over Asia. The OMI instrument [31] is a nadir-viewing imaging spectrometer that measures the solar radiation backscattered by the Earth’s atmosphere and surface over the entire wavelength range from 270 to 500 nm with a spectral resolution of about 0.5 nm. The 114° viewing angle of the telescope corresponds to a 2600-km-wide swath on the surface, which enables measurements with daily global coverage. The 740 wavelength bands along the satellite track provide global coverage in one day. The spatial resolution is 13 km × 24 km (along track × across track) at nadir in the nominal operation mode and the pixel size can be resolved to 13 km × 13 km for detecting urban-scale pollution events. The instrument was launched in July 2004 onboard NASA’s Earth Observing System (EOS) Aura platform as a follow-up to the TOMS.
The hyper-spectral capabilities of the OMI instruments enable the measurement of key air-quality components such as tropospheric ozone (O3), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), sulphur dioxide (SO2) and aerosols. In the present study, the hyper-spectral radiances ranging from 350 nm to 500 nm were used to retrieve AOD, SSA and ALH over Asia. Because of a row anomaly, the OMI Lv1B datasets from 2005 to 2007 were used for the algorithm test.
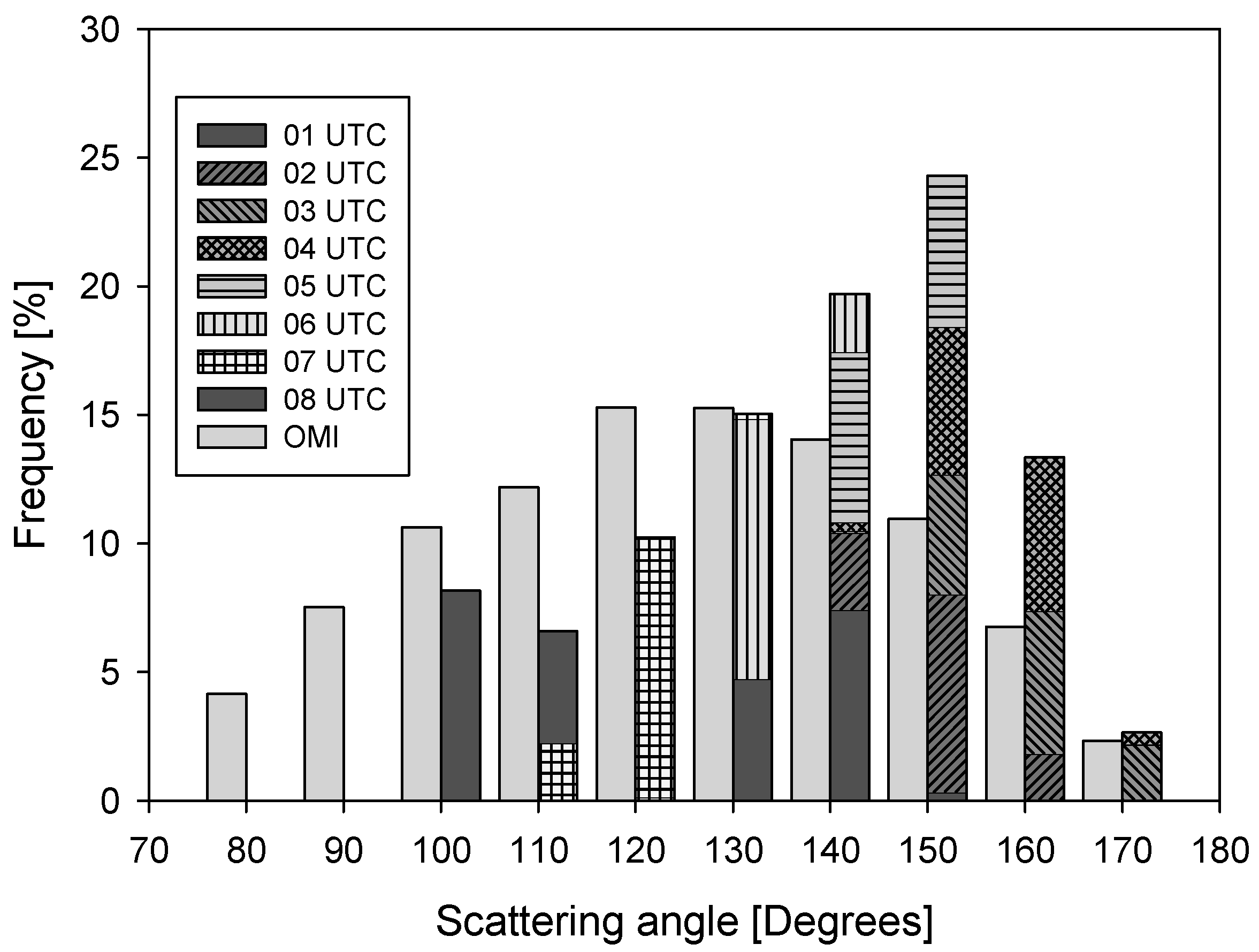
Figure 1 shows the frequency distribution of the scattering angle in the viewing geometry of GEMS and OMI. Compared with OMI, the scattering angle of GEMS has a narrower distribution that shifts towards the backscattered direction over time. However, the cross-track measurements of OMI cover a wider scattering-angle range than do GEMS measurements. This comparison indicates that, in regard to angular coverage, LEO measurements can be used as a proxy for GEO measurements.
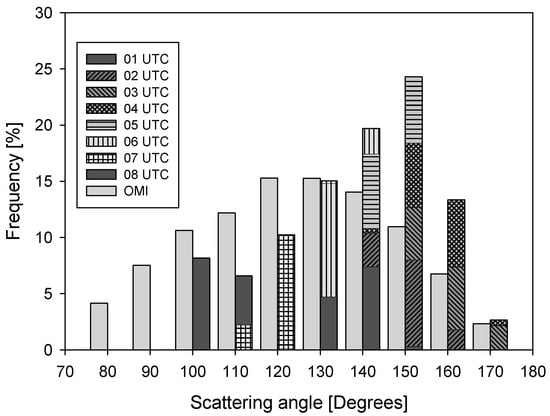
Figure 1.
Frequency distribution of the scattering angle of GEMS and OMI over the GEMS coverage range. The frequency is calculated using the actual sun- and satellite-geometry of OMI measurements and numerical calculations of the expected GEMS ground pixel per day for each month during 2006. Patterns indicate the frequency at each observation time of the GEMS. Tick values on the x-axis are the minimum value of each bin.
The OMI surface reflectance climatology data product OMLER (v003; Kleipool et al. [8]) was adopted to correct for the surface contribution to the atmospheric signal. The level-3 global gridded product provides the monthly climatology of OMI Lambert Equivalent spectral surface Reflectance (LER) for 23 wavelengths between 307 and 500 nm with a spatial resolution of 0.5° × 0.5°. The LER products are obtained by finding the minimum value of Rayleigh-corrected reflectance within a temporal window under the assumption that aerosol scattering increases upwelling radiance. The 5-year temporal window from 2005 to 2009 was applied to the LER-v003 product.
2.2. AERONET Sun-Photometer
The AERONET, a network of globally distributed ground-based sun-photometers, has been widely used to measure global AOPs. The AERONET sun-photometer measurement of direct solar radiation provides cloud-free AOD from 340 to 1020 nm with a high retrieval accuracy of about 0.01 in the visible and near infrared and about 0.02 in the UV range [16,32,33]. Measurements under the almucantar scenario can be inverted to produce AOPs such as the size distribution, single scattering albedo at 440, 675, 870 and 1020 nm, phase functions and the complex index of refraction [34,35,36]. Because total column aerosol properties provided by AERONET sun-photometer measurements are comparable to passive satellite measurements, the data have also been used extensively to validate satellite-based aerosol products.
In this study, all quality-assured AERONET inversion data (version 2.0 level 2 all-point products) from 1992 to 2016 were adopted to obtain optimized AOPs, the volume size distribution and refractive indices. These values were categorized according to three aerosol types following an aerosol type classification method [30] and were then applied to look-up table (LUT) calculations. In addition, level 2.0 AOD and SSA datasets at 26 AERONET sites in Asia (20°N–50°N, 100°E–145°E) that include measurements during 2005–2007 were selected to validate retrieval results. The site name, location and number of AOD data points are listed in Table 2. The initial and final days and number of data points in Table 2 summarize the AOD data used for the validation. SSA data at the same AEORNET sites as listed in Table 2 were used to validate retrieved SSA.

Table 2.
List of AERONET sites from which the four level 2.0 products were used to validate retrieval results. The number of data points denotes the number of AOD measurements from 2005 to 2007. The initial and final days indicate the measurement period.
2.3. CALIOP
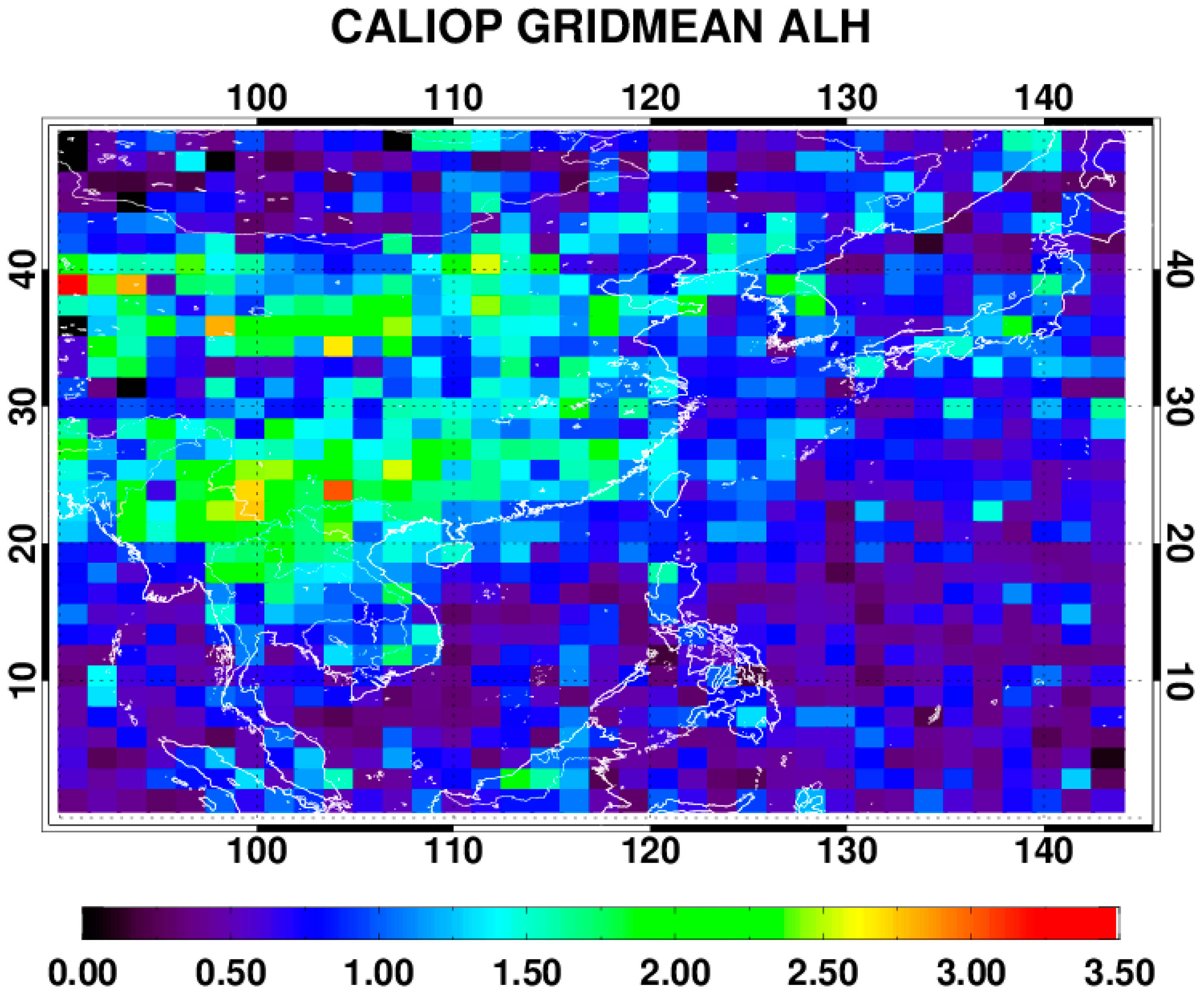
CALIOP is one of the payloads onboard the CALIPSO (Cloud-Aerosol Lidar and Infrared Pathfinder Satellite Observation) satellite, launched in April 2006. The instrument was the first polarization-sensitive lidar in space [15] and provides high-resolution vertical profiles of aerosols and clouds with footprints of 70 m along the ground. CALIOP utilizes three receiver channels, two of which measure the parallel- and perpendicular-polarized components of the backscattered signal from linearly polarized pulses at 532 nm and the third detects backscatter intensity at 1064 nm. Using the three-channel signal, layer and vertical profile information of aerosols and clouds along with their microphysical and optical properties are obtained from CALIOP measurements. The ratio of the perpendicular and parallel backscatter allows one to classify spherical and non-spherical particles of aerosols and clouds and the ratio between the signals at both wavelengths provides qualitative information of aerosol characteristics such as shape and the size distribution. In the present study, using the CALIPSO Lidar Level 2 aerosol profile data, the Zaer was calculated from the backscattering extinction coefficient for 2007, coincident with the test period of the current algorithm. Figure 2 shows the grid-averaged Zaer value with 1.5° × 1.5° resolution, which was used as the a priori state of ALH in the developed algorithm. The pixel Zaer was temporally and spatially collocated with OMI measurements and used to validate ALH results from the developed algorithm.
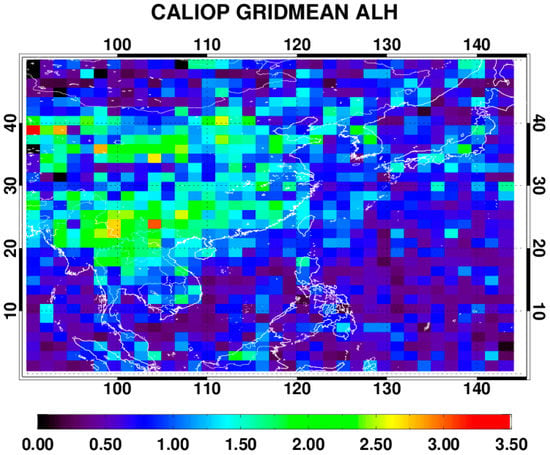
Figure 2.
Annual average value of the aerosol layer height (ALH) (km) for 2007 from CALIOP-measured attenuated backscatter profiles at 1064 nm (1.5° × 1.5° resolution). By definition, the ALH is equal to the attenuated-backscatter-weighted height.
3. Algorithm Description
In this section, the current algorithm is described in the order of LUT construction with aerosol model and retrieval process based on OE with a priori. The aim of this algorithm is the retrieval of AOD and SSA. To improve retrieval accuracy and to make the algorithm standalone, ALH is simultaneously retrieved with the AOD and SSA by fitting the reflectance spectrum from simulations and observations.
The basic assumption of this algorithm is that the measured spectrum consists of wavelength-dependent Rayleigh scattering and aerosol effects and therefore the aerosol information can be retrieved by fitting the spectrum. Thus, the OE method, which optimizes state variables to represent the measured radiance spectrum, is adopted here.
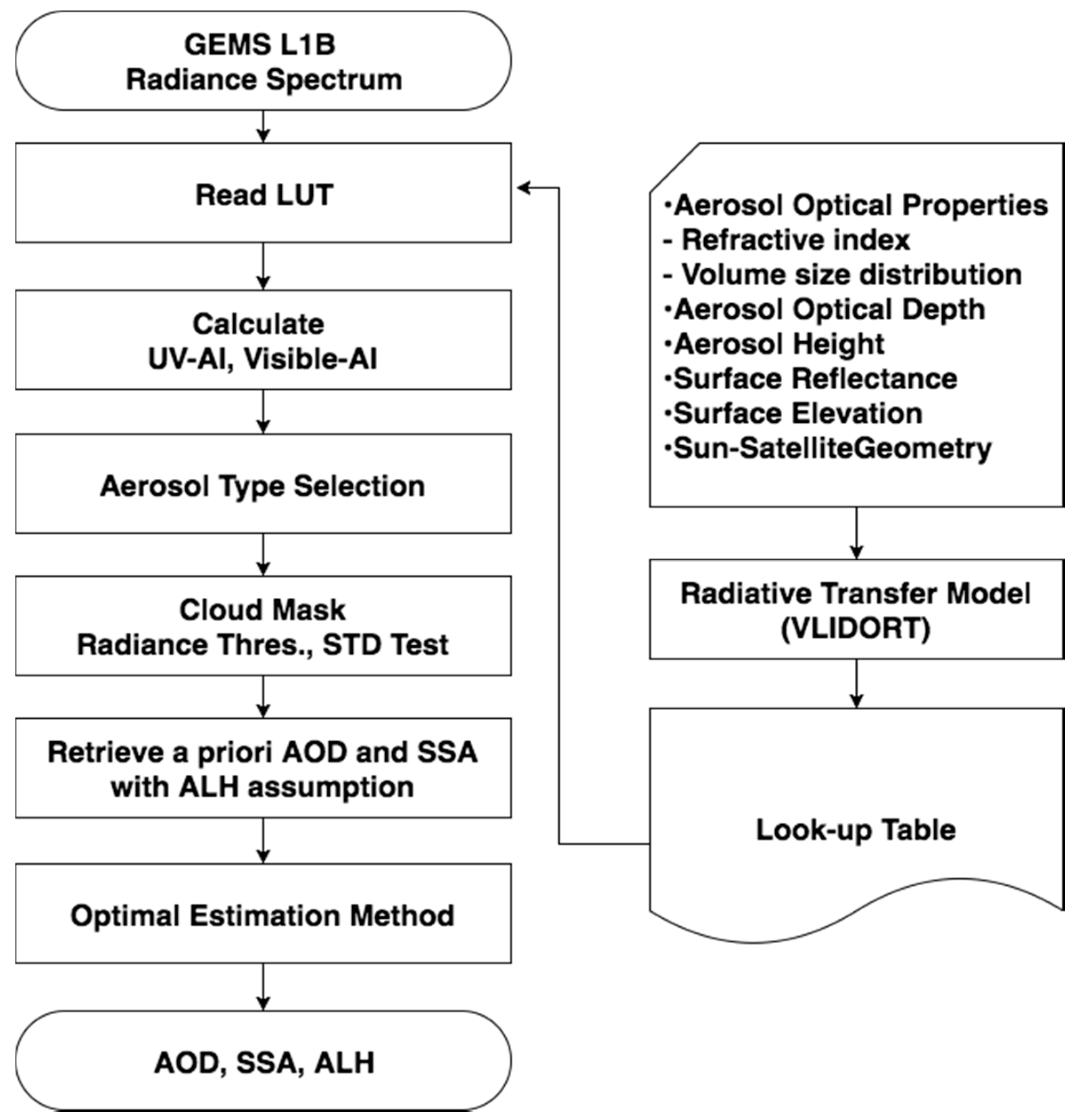
Figure 3 presents a schematic of the UV-visible aerosol algorithm. LUTs for the three aerosol types are calculated using VLIDORT (see Section 3.1 and Section 3.2). One value from the LUTs is selected according to the aerosol type and geometry for each pixel (see Section 3.3). Before the retrieval, cloud pixels are removed using a reflectance threshold and standard deviation of reflectance within a 3 pixel × 3 pixel window. The thresholds for the cloud mask and surface reflectance dataset will be optimized after the launch of GEMS. After the aerosol type selection and cloud masking, a priori values of AOD and SSA are estimated based on the two-channel method; a priori ALH are assumed to be the grid-averaged Zaer shown in Figure 2 (see Section 3.4). Those a priori states are applied to solve the Levenberg Marquardt equation and are optimized to fit the measured spectrum (see Section 3.5).
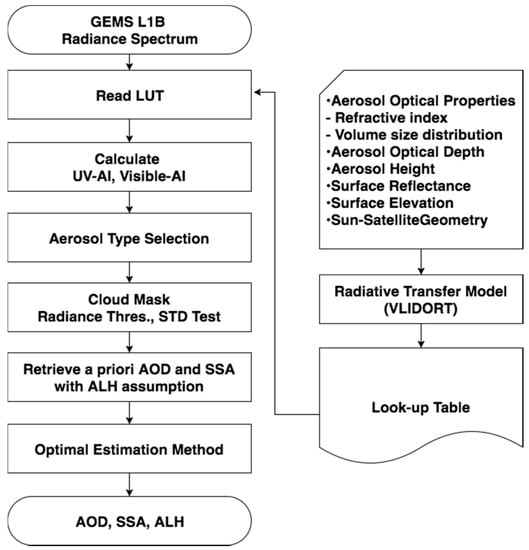
Figure 3.
Flowchart of the UV-visible algorithm used to retrieve AOD, SSA and ALH.
3.1. Aerosol Model Assumptions
To improve computational efficiency, the algorithm takes the LUT approach. AOPs for three aerosol types are integrated from AERONET inversion data and used in the LUT calculation.
Physically, aerosol types can be generally categorized into highly absorbing coarse (e.g., dust), highly absorbing fine (HAF; e.g., carbonaceous), non-absorbing (NA) coarse (sea-salt) and non-absorbing fine (sulfate) particles [30,37,38]. Because of the high sensitivity of near-UV radiance to aerosol absorptivity, three aerosol types (HAF, dust and NA) were used in this study to classify particles based on AERONET inversion products using the aerosol type classification method suggested by Lee et al. [30]. The size of NA particles was not considered here because radiance in the UV range is not sensitive to particle size [7]. The categorized aerosol types of dust, HAF and NA accounted for 33.98%, 15.73% and 16.19% of the entire AERONET inversion product, respectively. The remaining 44.00% of particles can be classified as polluted dust (12.22%) and moderately absorbing fine particles (21.87%), which represent mixtures of particle size and absorptivity, respectively, in accordance with Lee et al. [30]. These mixture conditions are not considered here. The developed algorithm is designed to retrieve AOPs over Asia but the AOPs of the aerosol model were estimated from a global dataset to ensure sufficient data for each aerosol type.
The optical properties for each aerosol type, which were obtained by averaging the integrated AERONET inversion dataset, are summarized in Table 3. In terms of the volume size distribution, the coarse mode of the bimodal size distribution is clearly dominant for dust, whereas the fine mode is dominant for HAF and NA. The Absorbing Ångström Exponent (AAE), which represents the wavelength dependence of particle absorption, differs significantly between dust and the other two types in the 440–675 nm wavelength range. At shorter wavelengths, spectral variations of the imaginary part of the refractive index for the HAF and dust types are assumed based on Kirchstetter et al. [39] and Lee et al. [40], respectively. Kirchstetter et al. [39] showed that the imaginary index for brown carbon varies following a power law in the UV range. The exponent (ω) in the power formula was obtained as 3.9 and adopted for the HAF properties in this study. Lee et al. [40] obtained the spectral variation from 0.2 to 1.0 μm by assuming transported Asian dust consists of internally mixed mineral components and showed that the imaginary index varies more slowly between 350 and 500 nm than indicated by the Optical Properties of Aerosols and Clouds (OPAC) ‘mineral-transported’ dataset [41]. Using the results of Lee et al. [40], the ω for dust was obtained as 1.835. This ω value is generally lower than the values of the Saharan dust sample described by Wagner et al. [42]. The ω value for NA particles is assumed to be 0, following the optical properties of water-soluble particles in the OPAC dataset.

Table 3.
Integrated optical properties for HAF, dust and NA aerosol types. Optical properties were obtained by averaging inversion data categorized for the three aerosol types. The entire global AERONET inversion dataset was used for the calculation. The mean radius (r) and standard deviation of r (σ) represent a bimodal number size distribution and the M1 fraction indicates the fraction of the total number concentration corresponding to fine particles (mode 1). Re(RI) is the real part of the refractive index; this value is fixed in LUT simulations for each aerosol type. The imaginary part of the refractive index is adjusted to account for SSA variations in the LUT simulations. The single scattering albedo (SSA), absorbing Ångström exponent (AAE) and Ångström exponent (AE) are the nominal value for each aerosol type obtained from the AERONET inversion dataset.
3.2. LUT Calculation
To account for the sensitivity of UV-visible measurements to aerosol properties, the dimensions of the LUT are constructed as listed in Table 4. The entries for each variable are selected assuming a linear variation in reflectance. Because aerosol extinction changes slowly with wavelength, five wavelengths (354, 388, 443, 477 and 490 nm) are selected here. These channels are selected to avoid absorption by gases other than O2–O2, which has a high sensitivity to ALH. The LUTs were calculated assuming a fixed vertical distribution of ozone and O2–O2.

Table 4.
Dimensions of the LUT for the UV-visible algorithm (SZA: solar zenith angle; VZA: viewing zenith angle; RAA: relative azimuth angle; and SUR: surface reflectance).
The AOD and SSA are based on values at 443 nm. In the RTM simulation, the SSA is obtained based on the refractive index and volume size distribution using Mie theory [43]. The ranges of AOD and SSA were chosen to cover the range of variation. An analysis using the integrated AERONET inversion dataset shows that 99.9% of AOD at 440 nm is lower than 3.0 and that most SSA values are higher than 0.84. The real part of the refractive index for each aerosol type is assumed to be 1.46, 1.48 and 1.41 for HAF, dust and NA, respectively, as shown in Table 3. Seven values for the imaginary part of the refractive index are used to account for the SSA variation from 0.82 to 1.0 at 443 nm. To investigate the wavelength dependence of particle absorptivity, the imaginary indices at 354, 388, 477 and 490 nm were estimated from the value at 443 nm using the power formula with the values for ω mentioned in the previous section.
The LUT is used to retrieve the a priori state of AOD and SSA using an inversion method with assumed ALH. The Jacobian and forward model spectrum used for the OE method are also estimated from the LUT to reduce the run time of the algorithm.
3.3. Aerosol Type Selection
The aerosol type is selected using the UV and visible AI, which indicate aerosol absorptivity and particle size, respectively [28]. The following equation defines the AI [7]:
where and are the radiance normalized to solar irradiance at two wavelengths (λ2 > λ1) and the subscripts ‘meas’ and ‘calc’ denote measured and calculated values, respectively. The LER is the surface reflectance estimated by correcting for Rayleigh scattering in the measured top-of-atmosphere (TOA) signal under the assumption of aerosol-free conditions. Here, two wavelength pairs (354 and 388.0 nm; and 477 and 490 nm) are used to calculate the UV and visible AI, respectively. LER is evaluated at the shorter wavelength in each pair [7]. Recently, the AI in OMAERUV (v1.8.9.1) has been updated to account for the angular dependence of clouds and the wavelength dependence of surface albedo but the updated equation was not adopted in this study.
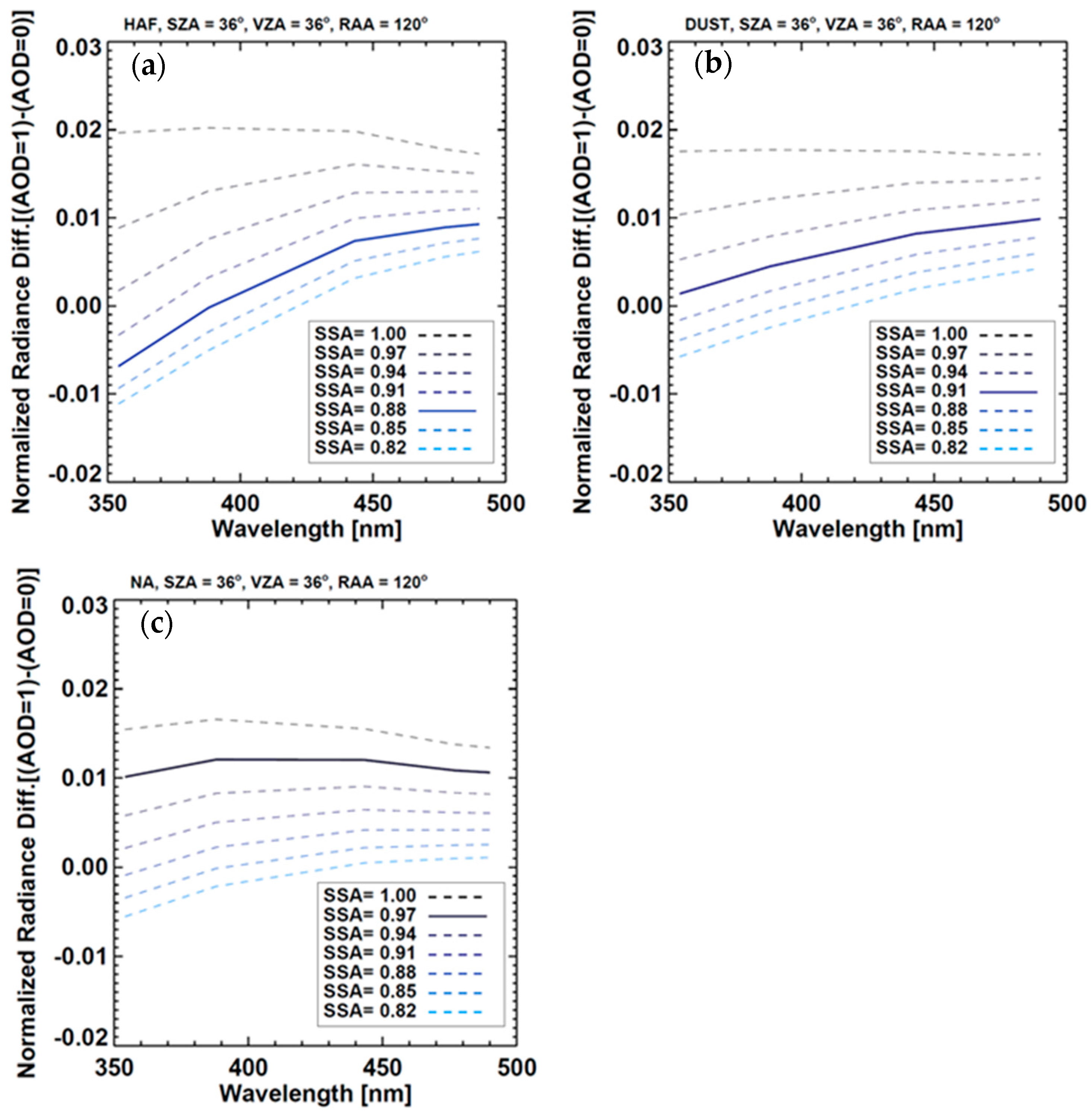
While the spectral variation of visible radiance is sensitive to particle size, the spectral variation in the UV range depends on aerosol absorptivity. Figure 4 shows the difference of normalized radiance as the AOD varies from 0 to 1 with respect to aerosol type and seven conditions of SSA (0.82, 0.85, 0.88, 0.91, 0.94, 0.97 and 1.0). For SSA higher than 0.91, upward radiance increases with AOD, regardless of aerosol type and wavelength. Under low SSA conditions, aerosols absorb upward radiation from the surface and from molecular scattering below the aerosol layer, causing upward radiation to decrease with increasing AOD for wavelengths shorter than about 400 nm. Assuming typical SSA values of 0.88, 0.91 and 0.97 for HAF, dust and NA, respectively, as shown in Table 3, spectral variations can be separated into absorbing (Figure 4a,b) and NA (Figure 4c) types. The increasing value of N, normalized radiance, with UV wavelength leads to positive values for AI and increases AI with increasing particle absorptivity, by definition. Torres et al. [7] showed that UVAI was positive for absorbing aerosols and negative for non-absorbing small particles using RTM simulations. de Vries et al. [44] introduced a scattering index based on the negative UVAI but Torres et al. [45] noted that negative UVAI values could generally be attributed to measurement noise. Therefore, the UVAI is useful for identifying absorbing particles with positive UVAI value, rather than categorizing particle absorptivity. At longer wavelengths, the spectral variation depends primarily on particle size. Radiance increases continuously with wavelength only for dust particles (Figure 4b) and thus the visible AI can be used to indicate the presence of dust particles. Accordingly, dust aerosol was detected by positive values of UVAI and visible AI and HAF and NA particles were identified by UVAI. If both of the AIs were negative, the aerosol was identified as NA.
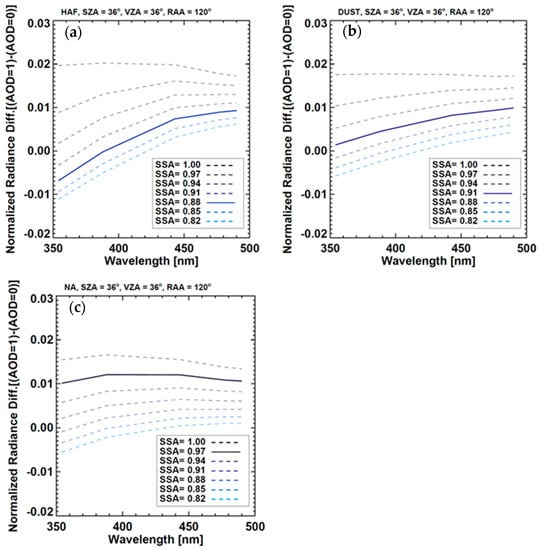
Figure 4.
Spectral difference in normalized radiance (N) for pristine (AOD = 0) and polluted (AOD = 1) conditions with respect to aerosol type: (a) HAF, (b) dust and (c) NA. Colors indicate SSA and solid lines show the average SSA obtained from integrated AERONET inversion data for each type.
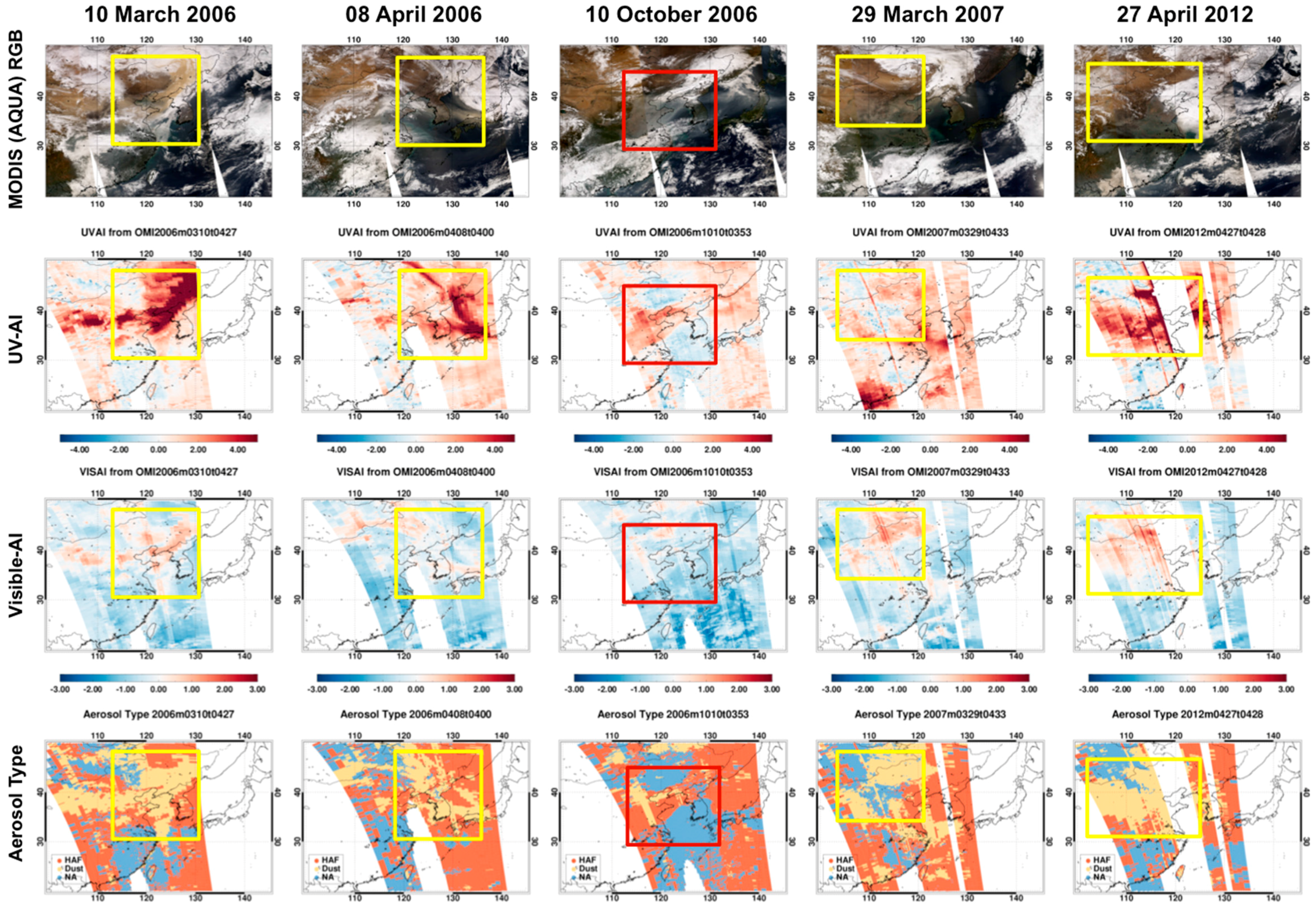
Figure 5 shows five RGB images obtained from MODIS (Aqua) measurements on 10 March 2006, 8 April 2006, 10 October 2006, 29 March 2007 and 27 April 2012 and shows UV and visible AI and aerosol type determined from OMI L1B radiance. Each RGB image shows the aerosol plume within the boxed region. Here, the aerosol plume can be identified by particle color, which is indicated by the box color in the figure as follows: red boxes denote white particles (10 October 2006) and yellow boxes denote yellow particles. Most aerosol pixels have positive UVAI but the white aerosol plume that passed through the southern part of the Korean peninsula had a negative UVAI. Because the pixels with negative UVAI also had a negative visible AI, they were classified as fine NA aerosol. The region with positive UVAI and negative visible AI enclosed by the red box is identified as fine absorbing HAF particles. Most other aerosol plumes (yellow boxes) have positive UVAI and visible AI and thus were identified as dust particles in this study. In cloud pixels, both UV and visible AI were negative. To avoid cloud contamination in the retrieval, a cloud mask is applied based on radiance and its spatial standard deviation. Additionally, most pixels with weak aerosol signal have positive UVAI and negative visible AI and thus HAF aerosols were frequently detected in this study.
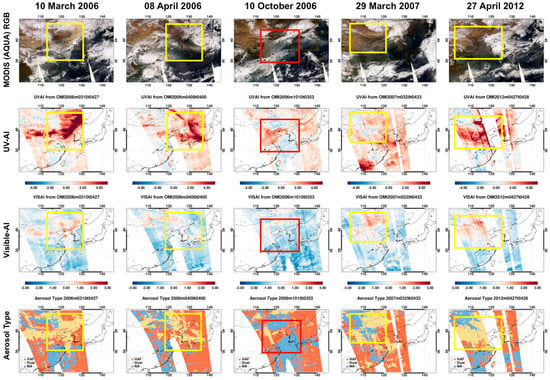
Figure 5.
RGB images observed from MODIS (Aqua), UVAI, visible AI and aerosol type calculated from OMI measurement on 10 March 2006, 8 April 2006, 10 October 2006, 29 March 2007 and 27 April 2012. Yellow and red boxes indicate dust and HAF scenarios, respectively.
However, visible range measurements are strongly dependent on the land surface type, which can introduce noise into the visible AI calculation. Furthermore, detection of absorbing aerosol near the surface is difficult because the UVAI is sensitive to elevated aerosol [14]. Based on the positive relationship between concentrations of CO and carbonaceous aerosol, Torres et al. [14] introduced the CO index (COI) using AIRS CO products to distinguish smoke and dust particles, to avoid errors induced by visible-AI noise. The COI was used to detect high concentrations of smoke particles in the boundary layer, which otherwise could have been mistaken as cloud contamination. However, the combined use of observations from various satellite instruments is possible when the measurements are performed within a specified time window. The OMI algorithm also takes advantage of A-train observations. In this study, the visible AI is used instead of the COI to identify dust layers in high-UVAI pixels.
3.4. Estimation of a Priori Quantity
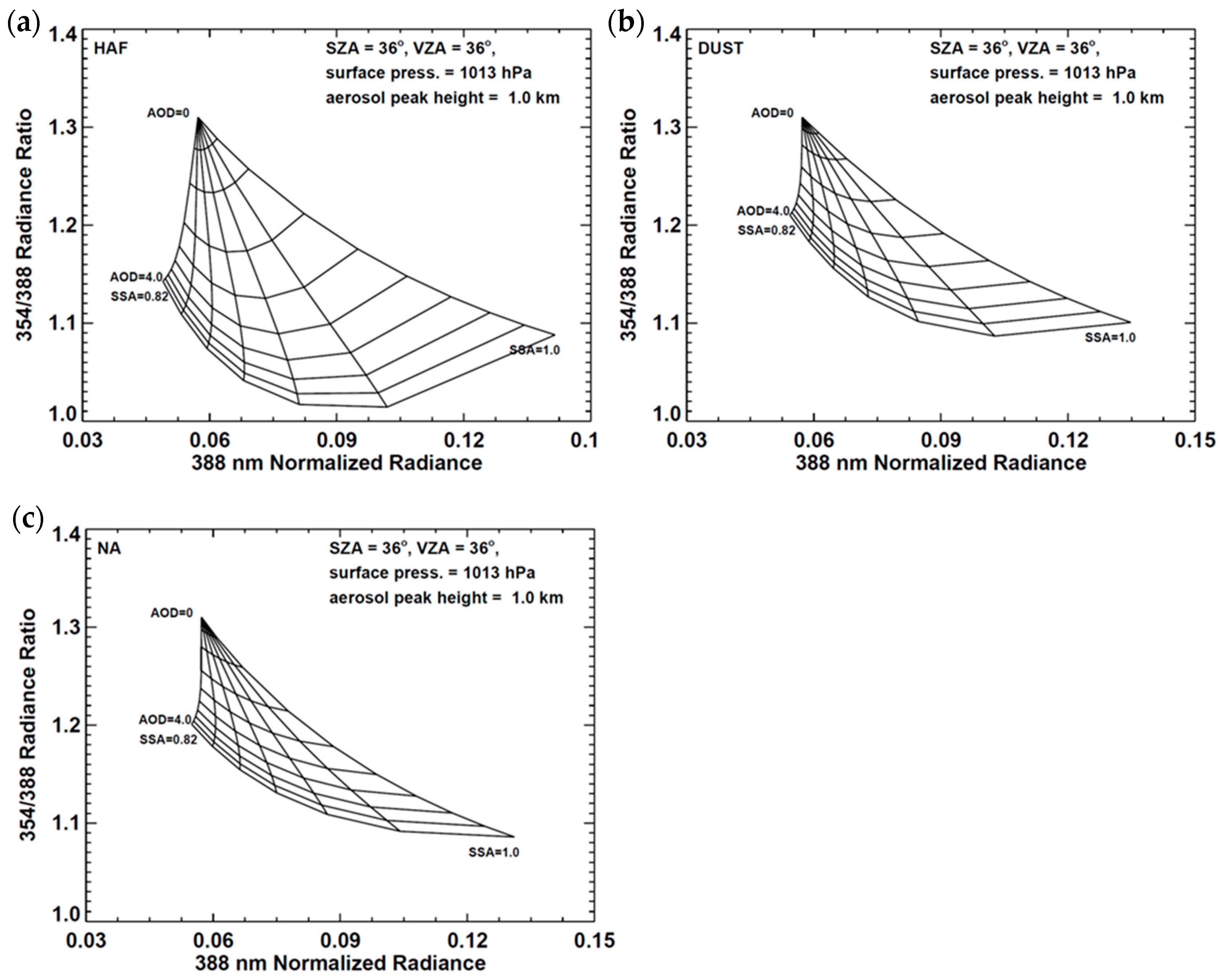
The OE performance depends on an accurate estimation of a priori quantities and their errors, as well as observed quantities [9]. Because of the large spatiotemporal variations of aerosol properties, assuming constant a priori aerosol states may result in large uncertainties in the OE. Therefore, a priori states for AOD and SSA are retrieved from measured reflectance using the two-channel inversion method used in the OMI UV algorithm. Figure 6 shows the sensitivity of normalized radiance to AOD and SSA, which is the theoretical basis of the two-channel method. Changes in AOD and SSA lead to changes in the ratio between radiances at neighboring UV wavelengths (e.g., 354 nm and 388 nm, as shown in Figure 6) and this relationship changes with aerosol type significantly. Thus, the aerosol type is selected first and a priori states of AOD and SSA are obtained from the two-channel method by assuming the a priori ALH to be the gridded Zaer value shown in Figure 2.
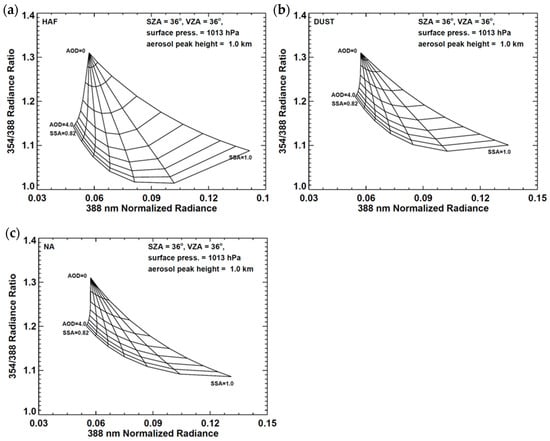
Figure 6.
Example of LUT used to estimate a priori AOD and SSA for three different aerosol types: (a) HAF, (b) Dust and (c) NA. The x-axis represents the normalized radiance at 388 nm and the y-axis represents the ratio between the radiances at 354 nm and 388 nm.
3.5. Optimal Estimation
Based on the theoretical relationship between measured values (y), retrieval variables (x) and the uncertainties of the observations and the estimation of a priori values (xa), the optimal solution, x, can be described as follows:
where K is the Jacobian and represents the sensitivity of measured values to the state vector as dy/dx. G is the gain matrix, which is defined as
and indicates the sensitivity of the retrieval variable to observations taking into account the errors in a priori state () and observations () [22].
To find the optimal solution, Rodgers [22] proposed OE theory, which provides a solution that optimizes the balance between the measured spectrum and one that is derived from a priori states by minimizing the following cost function (c):
On each iteration i, c is recalculated by updating xi using the Levenberg Marquardt equation,
where is the radiance simulated from a priori values and represents the change of the state vectors between iteration steps (i.e., ). To control the width of , the Levenberg parameter () is applied as a damping factor, which is adjusted at each iteration. In this study, is adjusted from 1.0. K and F(xi) are calculated using VLIDORT.
After solving for dxi+1, a conversion test is conducted to assess the reduction of the cost function by calculating the following quantity:
where ci and ci+1 are the cost functions calculated from Equation (5) for each iteration i and i+1 and ci+1,FC is calculated assuming that F(x + dxi+1) = F(x) + Kdxi+1. When R is lower than 0.25, the case is considered convergent and γ is increased by a factor of 10 for the next iteration. In cases with 0.25 < R < 0.75, the γ is left as-is. When R is higher than 0.75, γ is reduced by a factor of 2 and dxi+1 is recalculated as described by Boesch et al. [46].
In Equation (6), y is the normalized radiance in the UV-visible range measured from OMI and is assumed to be 1%, as suggested by Dobber et al. [47] and Levelt and Noordhoek [48]. AOD, SSA and ALH are the retrieval variables and a priori values are obtained using the OMI near-UV algorithm (OMAERUV). The error covariances () of AOD and SSA are assumed to be 30% of the retrieved a priori state and 0.05 [49], based on the expected error of OMAERUV, respectively. For the error covariance of ALH, 100% of the a priori value is used to allow the state variable to vary widely from the a priori value.
4. Results and Validation
4.1. Comparison with OMI AOD and SSA
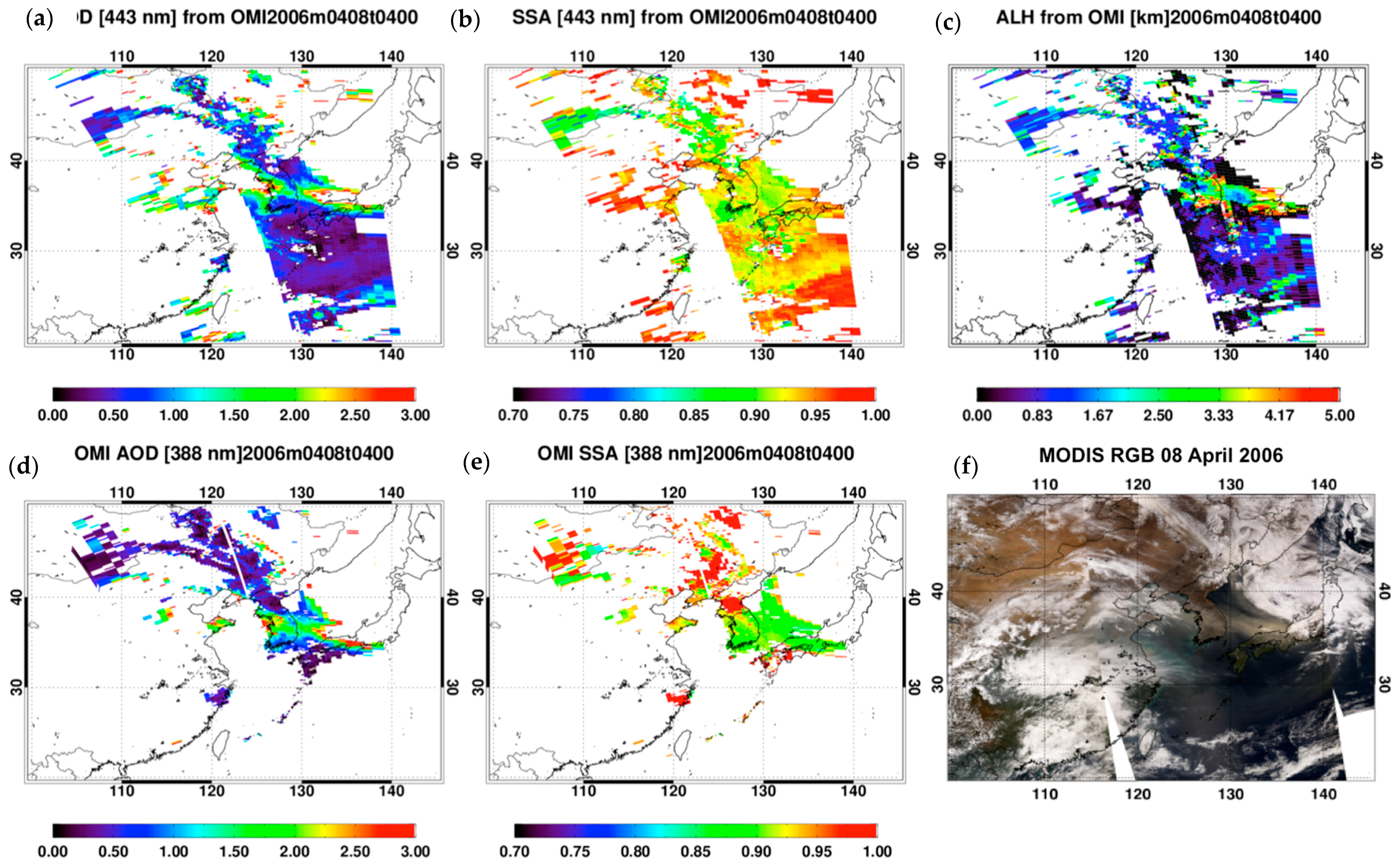
An example of the output of the developed UV-visible algorithm is shown in Figure 7. For comparison, the operational products of the OMI UV algorithm and MODIS RGB image are also shown in the figure. A dust flow was observed across the East Sea between the Korean Peninsula and Japan on 8 April 2006. Over the dust region, both AOD products from OMI measurements show high AOD above 1.0 and the SSA ranges from 0.90 to 0.95. The spatial distribution of calculated AOD and SSA follow the operational products of OMI, in general. The major difference between the operational products and results from the developed algorithm occurs in pixels where NA aerosols are detected. The operational algorithm applies a single-channel method to retrieve land AOD in this case and the SSA is assumed to be 1 [14]. Because of retrieval noise associated with ocean color effects, the operational retrieval over the ocean is performed only when absorbing aerosols are detected [14]. Consequently, the data coverage of the operational product is significantly lower than that of the developed product. When compared with the operational SSA, the retrieved values are relatively high over dust regions.
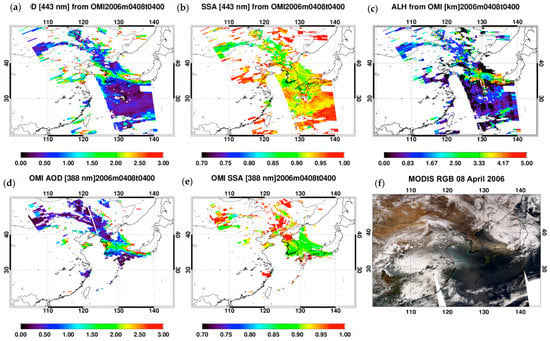
Figure 7.
Example of retrieved (a) AOD, (b) SSA and (c) ALH. The upper panels show the products of the proposed algorithm and the lower panels show the (d) AOD and (e) SSA of the OMI near-UV algorithm and an (f) RGB image from MODIS on 8 April 2006.
4.2. Comparison with CALIOP ALH
The median value of the retrieved ALH in Figure 7c is located at 0.889 km and 45.36% of the data points are lower than 1.0 km. The ALH in high AOD regions is generally higher than other regions. However, similarly high values are found over the ocean in the southern part of the Korean Peninsula and Japan, because weak aerosol attenuation increases the uncertainty in SSA and thus ALH retrieval. As the ALH of the operational OMI near-UV algorithm is defined according to aerosol type and location, the results are not compared quantitatively. Instead, the results are compared with the heights (Zaer) derived from CALIOP measurements.
Figure 8 shows the difference between retrieved ALH from the current algorithm using OMI and the estimated Zaer from CALIOP (retrieved ALH − Zaer) from March to May 2007. In this comparison, the ALH products were collocated within a 0.5° × 0.5° range around a CALIOP pixel when the temporal difference between the two measurements was shorter than 30 min. Then, the average value of the collocated dataset was compared with the Zaer value from the CALIOP lv2 backscatter coefficient if the standard deviation of the dataset was lower than 50% of the average value.
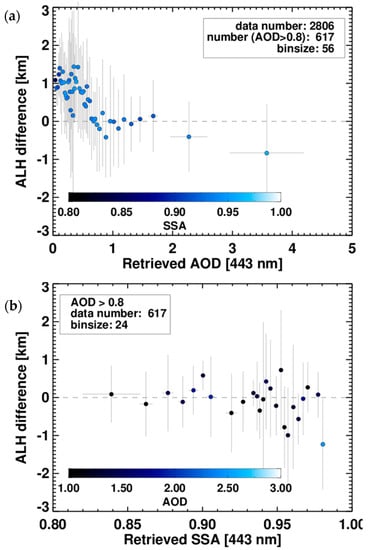
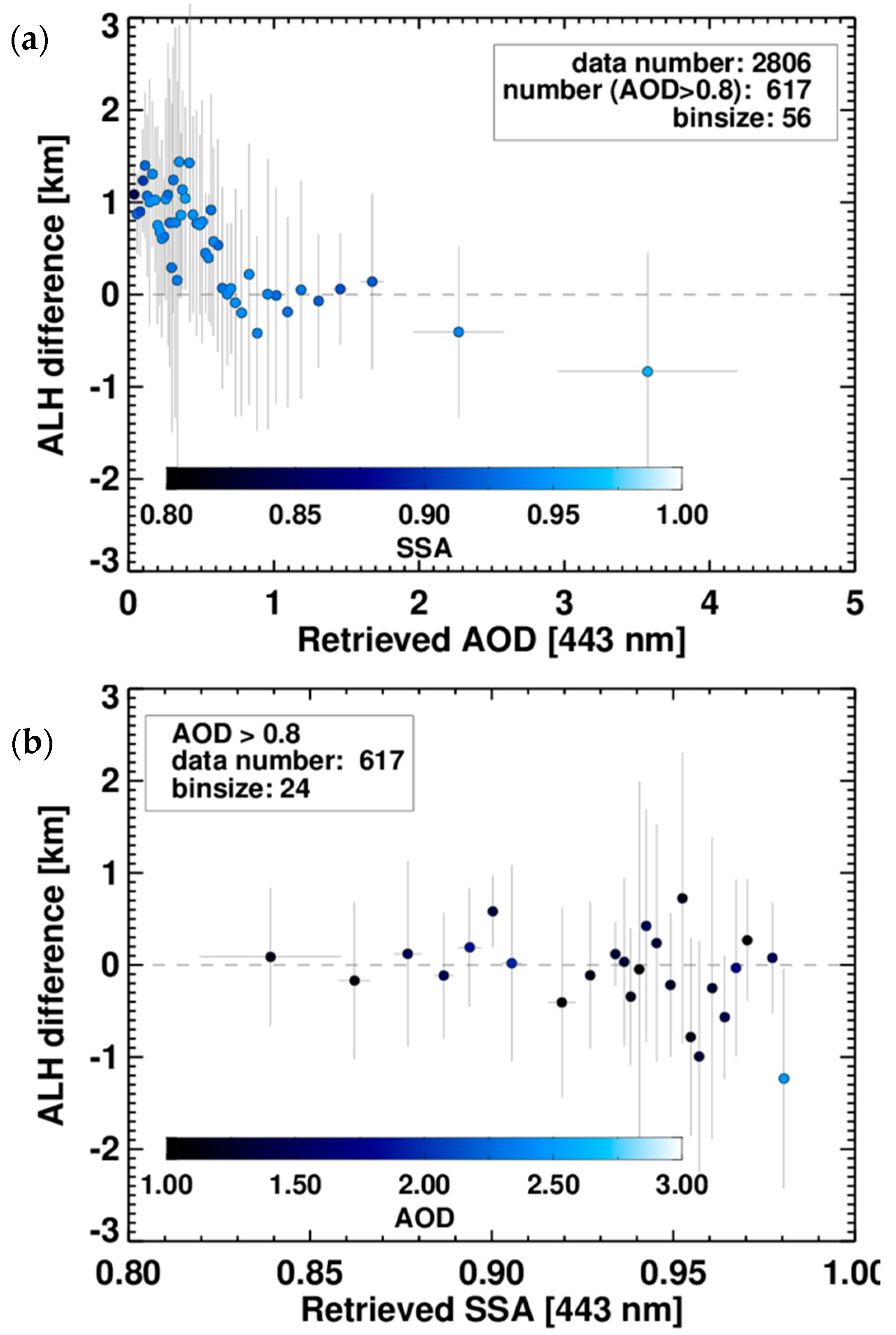
Figure 8.
Difference between ALH retrieved from the developed algorithm and the attenuated-backscatter-weighted height estimated from the CALIOP 1064 nm product for the period from March to May 2007. The difference values are sorted by (a) AOD and (b) SSA and the bottom panel only includes values for AOD > 0.8. Standard deviations of the values sorted by each bin are shown by vertical and horizontal bars. Colors indicate mean (a) SSA and (b) AOD for each bin.
In Figure 8a, the differences and retrieved SSA are sorted according to retrieved AOD and divided so as to have the same number of data points in each bin. While mean ALH difference and its standard deviation are represented by symbols and error bars, respectively, the mean SSA is shown by color. The horizontal error bar represents standard deviation of AOD for each bin. The ‘binsize’ in Figure 8 shows the number of data points in each bin. As shown in Figure 8a, the retrieval error in ALH decreased as the AOD increased from 0.0 to about 0.8, because the contribution of ALH to the normalized radiance increases with aerosol extinction. When the AOD is between 0.8 and 2.0, the mean difference between the ALH and CALIOP Zaer is close to 0.0 km with a standard deviation of about 1.0 km. However, the ALH error increases negatively with increasing AOD in the high-AOD range. It should be noted that data points in the high-AOD bin may be affected by cloud contamination, contributing to the high mean value. In this case, Zaer would be overestimated due to the increase in the backscatter coefficient from high cloud layers and ALH would be underestimated because of the underestimated radiative absorption of aerosols. The high SSA of 0.96 for the highest AOD bin suggests frequent cloud contamination.
Based on results shown in Figure 8a, the dependence of ALH error on SSA was analyzed for conditions with AOD higher than 0.8 to investigate the sensitivity of ALH retrieval errors to SSA without interference from other retrieval uncertainties. The SSA dependence results are shown in Figure 8b. In this figure, color represents the mean AOD for each bin sorted according to the retrieved SSA. Because of the AOD threshold, the number of data points was reduced from 2806 to 615 and thus the bin size was decreased to 24. Although ALH retrieval error increased with decreasing AOD, the error decreased with decreasing SSA. The maximum error was found for the highest AOD (2.48).
4.3. Comparison with AERONET AOD and SSA
Following Ahn et al. [12], the AOD and SSA products are quantitatively compared with AERONET values and their accuracy is assessed using statistics of linear regression such as correlation coefficient (R), root-mean-square error (RMSE), slope (a), y-offset (b) and the Q value, which shows data points within a 30% error range.
For the validation, the algorithm is used on data for the three years from 2005 to 2007 while accounting for the row anomalies of OMI. The 26 AERONET sites that have measurements in the test window are selected as shown in Table 2. The retrieved AODs within a 0.4° × 0.4° area from the AERONET site are averaged and compared with AERONET values within the overpass time of 10 min from OMI observations. The retrieved SSAs are collocated when they are within a 0.4° × 0.4° area regardless of observation time during the day because of the large time difference between OMI measurements and the AERONET inversion product. The AERONET SSA is valid for SZA higher than 50° [36] but the OMI has a local equator crossing time of about 13:45.
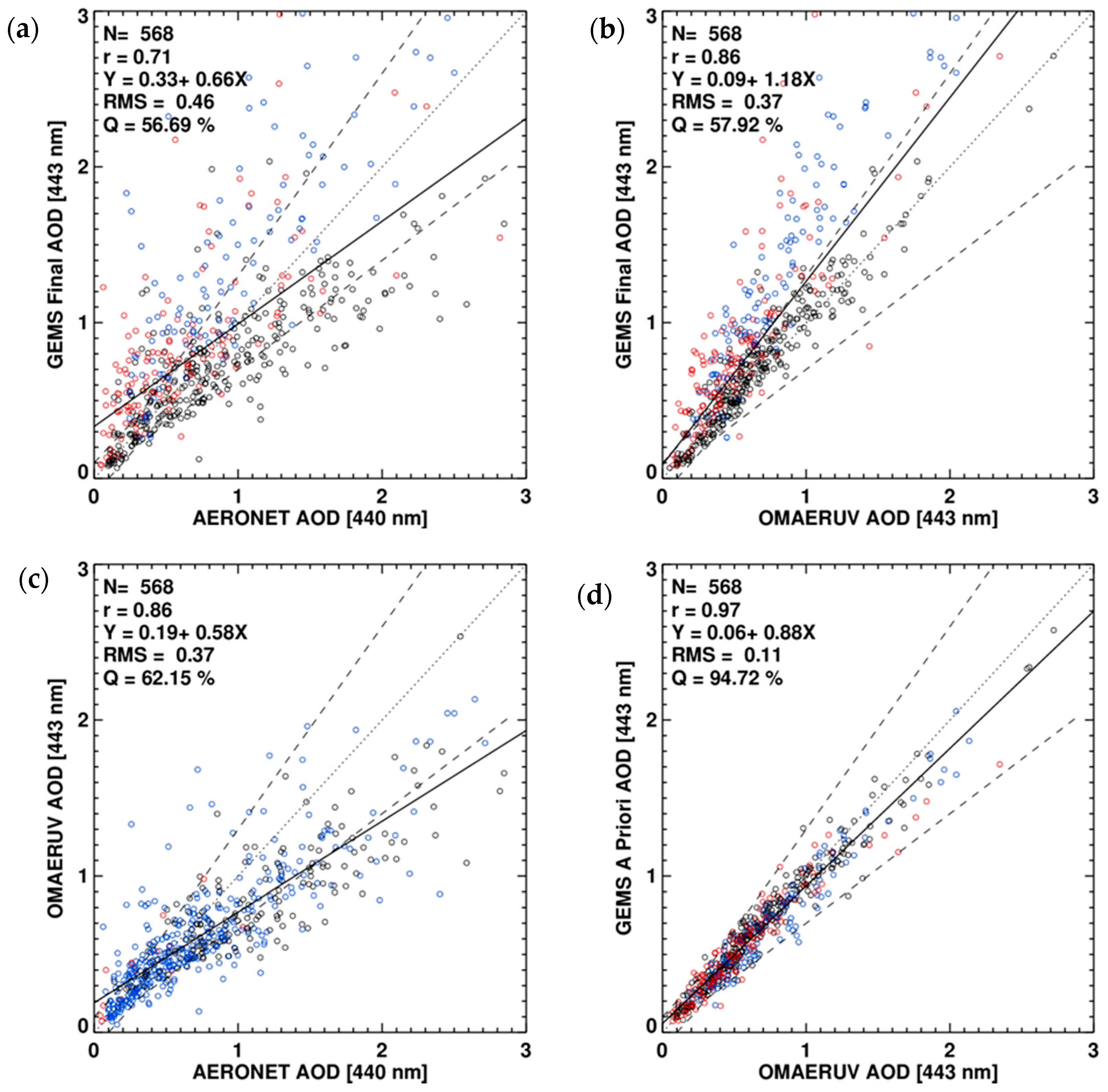
Figure 9 compares AOD and SSA. The AODs retrieved from the developed algorithm are compared with those from AERONET observations (Figure 9a) and the OMAERUV algorithm (Figure 9b). The comparison between AODs from OMAERUV and AERONET is shown in Figure 9c and the a priori AOD, which are retrieved based on the same two-channel approach of the OMAERUV algorithm, are also compared to the OMI products (Figure 9d). The retrieved AOD shows a good correlation with the AEORNET AOD with a correlation coefficient (R) of 0.71 and a Q value of 57% (Figure 9a), although the correlation is weaker than that shown in Figure 9c. Compared with the OMI AOD, retrieved AODs from the developed algorithm are mostly overestimated with a regression slope of 1.18 (Figure 9b), while the a priori AODs are highly correlated (R = 0.97). As shown in Figure 9a, the R values for HAF, dust and NA are 0.83, 0.73 and 0.80, respectively. The variation in regression line slopes from 0.56 (HAF) to 0.98 (NA) indicates uncertainties in model parameter assumptions. In the algorithm, a LUT for each aerosol type was calculated assuming a wavelength dependence of aerosol absorptivity based on the literature. Kirchstetter et al. [39] obtained the spectral variation of the imaginary refractive index for biomass smoke samples and Mok et al. [50] measured the spectral dependence of brown carbon absorptivity in the Amazon. However, the database cannot accurately represent the AOPs of anthropogenic aerosol over Asia. Therefore, measuring accurate AOPs over Asia in the shortwave region is essential for future work. Though the developed algorithm does not perform better than the OMI OMAERUV algorithm, it lays the foundation for improved retrieval in the future as the characterization of the optical properties of Asian aerosols improves. With the improved spatial resolution of GEMS over that of OMI, the cloud contamination can be reduced significantly.
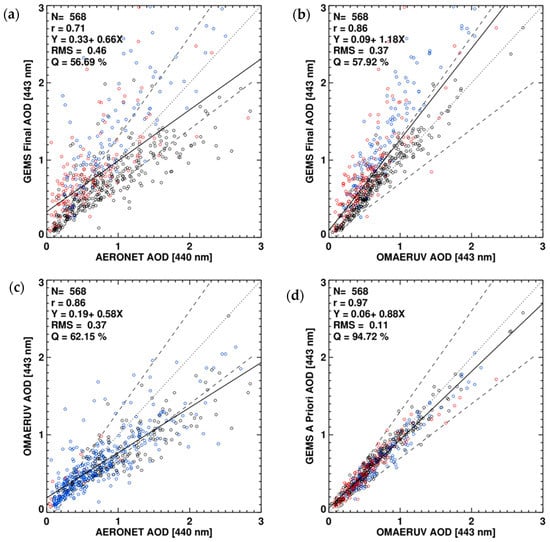
Figure 9.
Comparison of (a) GEMS and AERONET AOD, (b) GEMS and OMAERUV AOD, (c) OMAERUV and AERONET AOD and (d) GEMS a priori and OMAERUV AOD (443 nm). Colors indicate the aerosol type distinguished by the satellite algorithm shown on the y-axis. Black: HAF (smoke for OMAERUV), red: dust and blue: NA. Dashed lines indicate an uncertainty envelope of ±30% in AOD and dotted lines are 1:1 lines. Black solid lines are linear regression lines for which the equations are shown in the upper left of each panel.
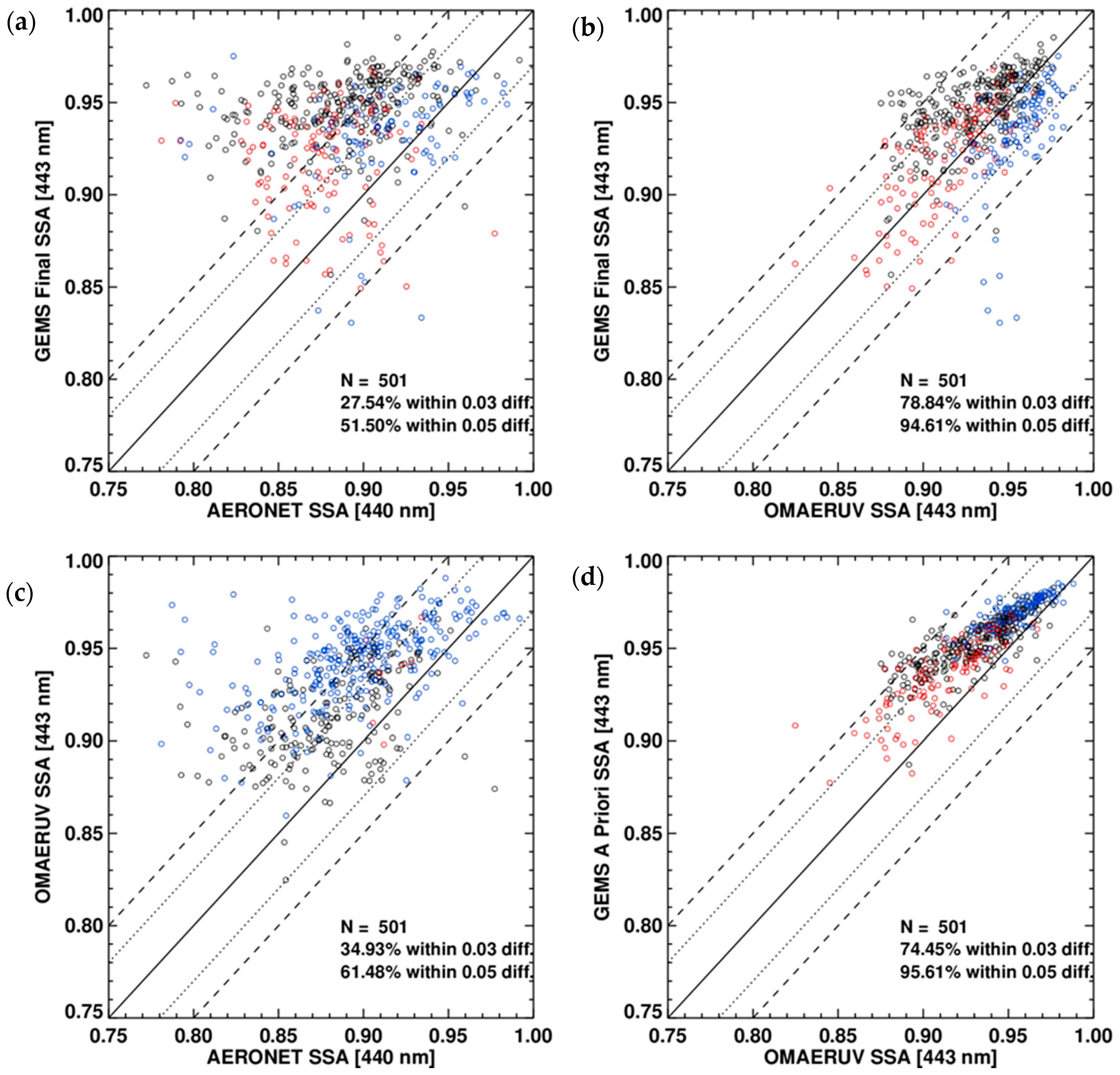
This uncertainty has a greater impact on the accuracy of SSA retrieval. Figure 10 compares the retrieved SSA with AERONET values (Figure 10a) and OMI SSA (Figure 10b). Jethva et al. [13] showed that 70% of OMI SSA differed by less than 0.05 from AERONET values over northeast Asia. Similarly, Figure 10c shows that 61% of OMI SSAs are within the same 0.05 difference. The Q value for the data shown in Figure 10a is generally lower than that for OMI SSA, while 95% of the retrieved SSAs differed by less than 0.05 from the OMI SSA (Figure 10b). Unlike the AOD comparison shown in Figure 9d, a priori SSAs are higher than OMI values and this difference increases with decreasing OMI SSA because of differing aerosol model assumptions. The large error in SSA retrieval could be caused by errors in classifying aerosols by type and in surface reflectance estimations. Section 5 includes a detailed discussion of retrieval uncertainties.
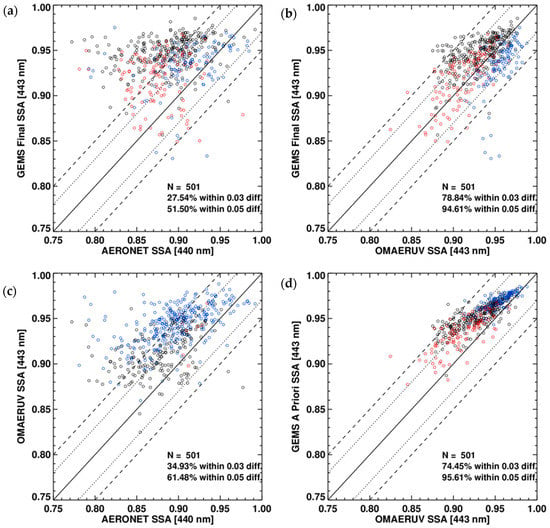
Figure 10.
Comparison of (a) GEMS and AERONET SSA, (b) GEMS and OMAERUV SSA, (c) OMAERUV and AERONET SSA and (d) GEMS a priori and OMAERUV SSA (443 nm). Colors indicate the aerosol type distinguished by the satellite algorithm shown on the y-axis. Black: HAF (smoke for OMAERUV), red: dust and blue: NA. Dashed and dotted lines indicate an uncertainty envelope of ±0.05 and ±0.03 in SSA, respectively. Black solid lines are 1:1 lines.
5. Uncertainty Estimation
Retrieval uncertainties of the developed UV-visible algorithm are estimated using a reference test. In the test, the inversion (i.e., the retrieval algorithm) is applied to simulated UV-visible radiances by the forward model under known reference conditions. Then, retrieval uncertainties are analyzed by comparing the results with the reference conditions.
In the simulation, VZA, RAA and surface reflectance are fixed at 12°, 33° and 0.06, respectively and other measurement geometry and aerosol conditions were assumed to be as follows:
- -
- SZA: 0°–56° in 7° intervals,
- -
- AOD at 443 nm: 0.3, 0.8 and 1.5,
- -
- SSA at 443 nm: 0.89, 0.92 and 0.97,
- -
- ALH: 1.0, 2.5, 4.0 and 5.5 km, and
- -
- Surface elevation: 0 km.
5.1. Inversion Error
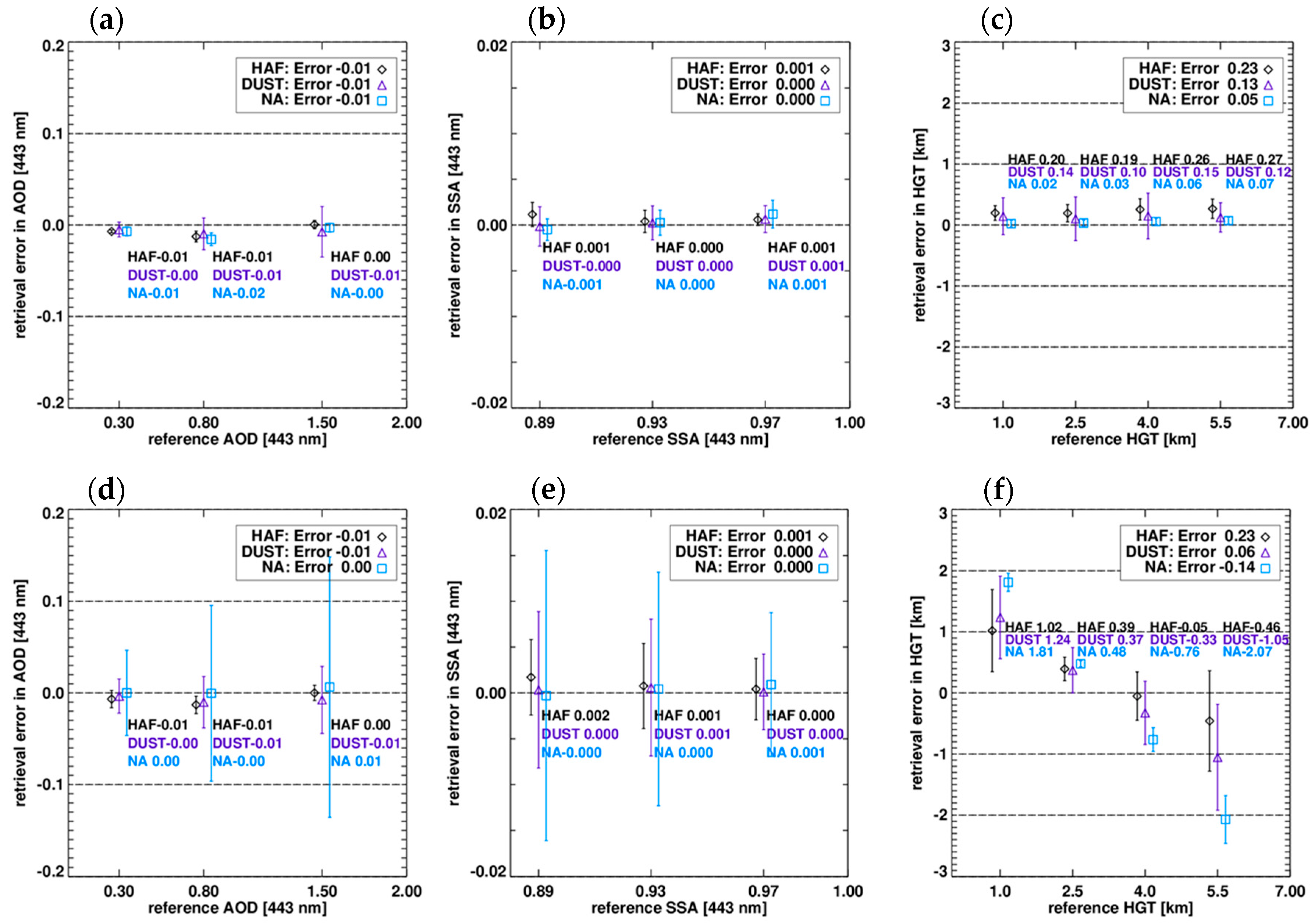
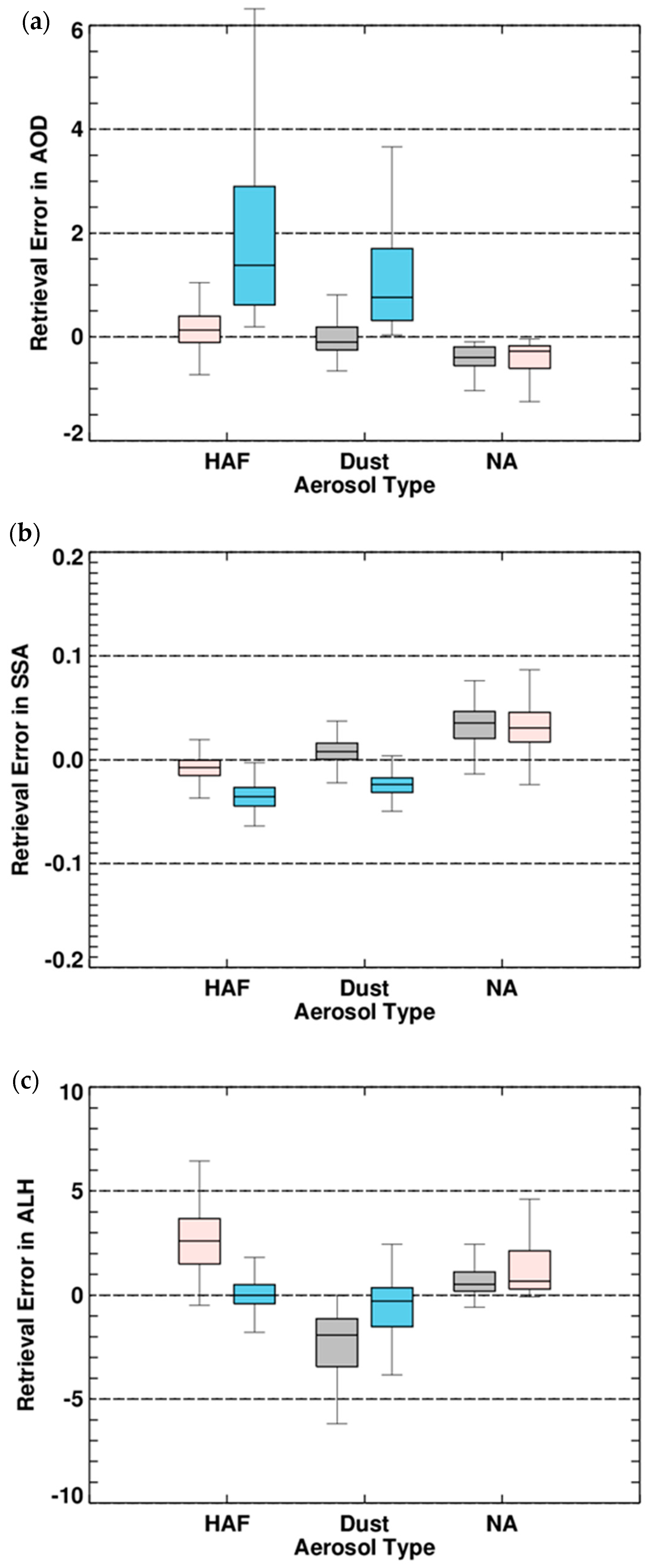
The LUT approach reduces the computational burden but can lead to errors during the inversion process because of a limited set of entries. Figure 11 shows the inversion error as a function of the reference value. The retrieval error is defined as the difference between the retrieved value and the reference condition and is shown as symbols with error bars in Figure 11. The error bar indicates the 1-σ range of retrieval results together with mean values (symbols) for each aerosol type. Depending on SZA, AOD, SSA and ALH dimensions of simulation, the average and standard deviation were obtained from 108 retrievals for each set of AOD and SSA conditions and 81 retrievals for each ALH condition. The inversion error investigation starts from an a priori state retrieval with the assumption that all measurement conditions and model parameters are exactly estimated. Because the a priori states of AOD and SSA are estimated using the two-channel method in which ALH is assumed, the inversion error test is performed in two ways by changing the ALH assumption from the reference condition to an arbitrary value of 3 km. The results of the two simulations are shown in the upper and lower panels of the Figure 11.
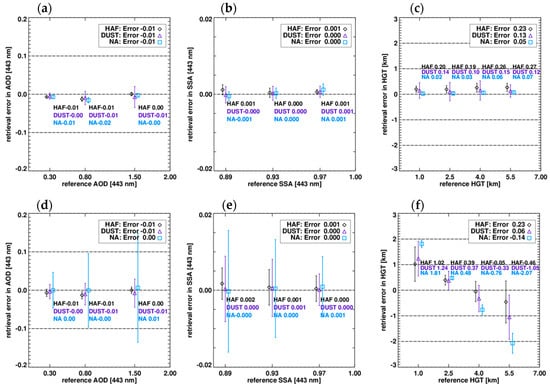
Figure 11.
Inversion error of the OE method for (a,d) AOD, (b,e) SSA and (c,f) ALH retrieval, without errors in model parameters. The a priori ALH is based on actual conditions in the upper panels but an a priori ALH of 3 km is assumed in the lower panels. The retrieval errors are estimated from 108-member ensembles of AOD and SSA retrieval and 81-member ensembles for ALH retrieval for a given set of reference conditions. Symbols indicate the aerosol type (diamonds: HAF, triangles: dust, squares: NA) and error bars represent the standard deviation of the smoothing error for the reference test dimension.
In general, the fitting errors in AOD and SSA are not significant. When the a priori ALH is assumed as the reference condition (Figure 11a), the average errors in AOD are −0.01, −0.01 and −0.01 for HAF, dust and NA aerosols, respectively and a maximum error of −0.02 is found for the NA type. While the average error for NA aerosols is relatively higher than the error for absorbing aerosols, the standard deviation for dust is generally higher than that for the other types. The inversion errors in SSA (Figure 11b) are below 0.001 on average and the deviation in SSA for each aerosol type is almost negligible. Although the magnitude of the error is smaller than that of AOD, it is not negligible due to the narrow range of SSA values, approximately 0.7 to 1.0. In comparison with AOD and SSA, ALH shows a wider range of retrieval errors from 0.19 to 0.27, 0.10 to 0.15 and 0.02 to 0.07 for HAF, dust and NA aerosols, respectively, because the sensitivity of the backscattered radiance to the ALH is relatively lower than the contribution of AOD and SSA.
Figure 11d–f shows that changing the a priori ALH state increases the inversion error in the order ALH > SSA > AOD. Although changes in the average errors for AOD and SSA are insignificant, an increasing 1-σ range indicates that the error can increase depending on the measurement geometry. The large variation (1-σ range) for NA aerosols indicates that the retrieval accuracy increases with increasing absorption. Moreover, the ALH inversion error for NA aerosols is relatively higher compared with other types because high aerosol absorptivity increases the sensitivity to ALH. Figure 11f also shows that the retrieval error in ALH significantly increases with an increase of the difference between the reference ALH condition and the assumed a priori value. The algorithm uses the grid-averaged Zaer value as the a priori state for ALH to take account of the spatial variation of ALH but temporal variations cannot be applied in real time. The uncertainty of the a priori state assumption is likely a major cause of the ALH retrieval uncertainty.
5.2. Estimation of Model Parameters
While the inversion error is related to uncertainty caused by the non-linearity of radiation between LUT entries, the model parameter error is related to the accuracy of input parameters, which affect the simulated spectrum. In the UV-visible algorithm, the model parameters include surface reflectance and aerosol properties, which are defined by the size distribution and refractive index. Because results are obtained after solving the Levenberg Marquardt equation, the inversion error is also included in the estimated uncertainty but the sensitivity to the a priori ALH assumption is removed by assuming the reference ALH condition. The errors were estimated using the developed algorithm with assumptions of surface reflectance or aerosol type that differed from the conditions used to calculate the synthetic radiation. Sensitivity to surface reflectance errors was estimated for four error conditions with surface reflectance deviations of −40%, −20%, 20% and 40% from 0.06, which was assumed for the radiance simulation. The sensitivity to aerosol type was tested by selecting the wrong aerosol type during the retrieval process. For each set of error conditions, 108 retrievals for each set of AOD and SSA conditions and 81 retrievals for each ALH were applied, as described above.
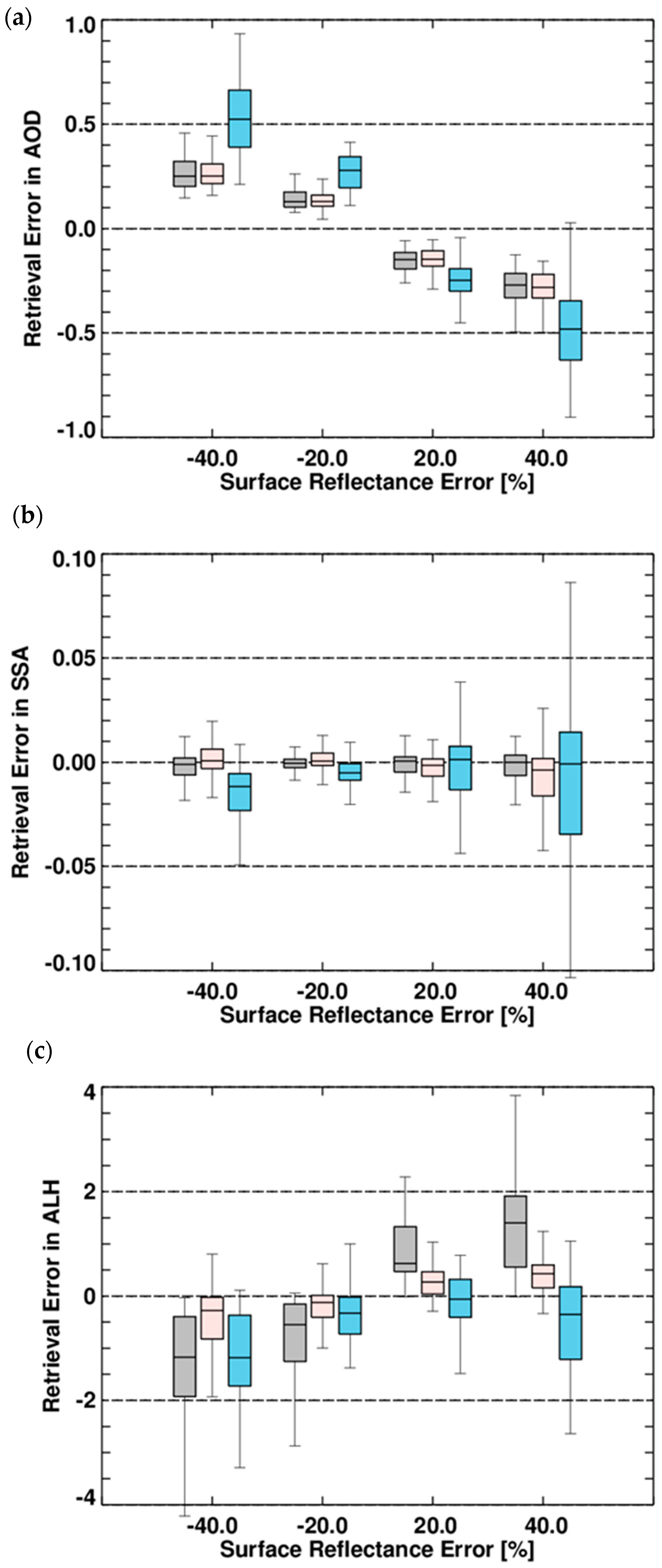
The sensitivity to surface reflectance error is first analyzed by applying systematic errors within ±40% and the results are shown in Figure 12 and listed in Table 5. The error range is defined based on the error range of the OMLER product reported by Kleipool et al. [8]. Their study revealed that an overall 2% error in the TOA reflectance causes 40% errors in LER at 320 nm and 5% errors at 500 nm. Assumptions related to surface pressure, total ozone concentration and the bidirectional reflectance distribution function effect can also increase the LER error.
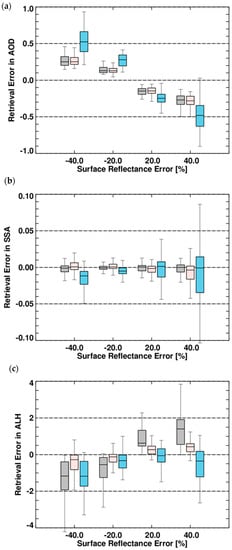
Figure 12.
Retrieval error in (a) AOD, (b) SSA and (c) ALH (km) due to errors in surface reflectance for each aerosol type. Gray: HAF, pink: Dust and blue: NA. Errors are obtained by testing the algorithm with four LERs that are −40%, −20%, 20% and 40% from the true condition of 0.06. Each box-and-whisker plot for a given LER error condition shows the retrieval error distribution derived from the 108-member ensemble for AOD and SSA and 81-member ensemble for ALH.

Table 5.
Median values of the data plotted in Figure 12. Errors are the median retrieval error obtained by comparing retrieved values from the developed algorithm with the reference condition, assuming biased LER.
Figure 12 shows the distribution of retrieval errors in retrieval products as a box-and-whisker plot and the median values are summarized for each reference condition in Table 5. While the inversion error in AOD is less than −0.01 for dust (see previous section), the median value of retrieval errors increases to 0.25 when a −40% error is applied (Figure 12a). In general, underestimation of surface reflectance results in an overestimation of aerosol extinction along the optical path and thus leads to an overestimation of AOD. This effect is most significant when the AOD is 0.3 and decreases with increasing AOD (Table 5). The error is most significant for NA aerosols (light blue colored box in Figure 12a), because of different sensitivities of the normalized radiance to changes in AOD for the various aerosol types. In the aerosol model used in this study, the radiance change related to the increase of NA AOD is lower than that of the absorbing AODs. Therefore, a higher AOD is required to offset the underestimation of surface contributions to radiance under NA aerosol conditions.
Similarly, an underestimation of surface reflectance is expected to lead to an overestimation of SSA. However, because the OE finds the best solution to fit the measured spectra by updating state vectors simultaneously, the results of a reference test cannot be simply interpreted. Figure 12b shows that the retrieval errors in SSA due to surface reflectance errors are not much higher than the effects of inversion errors for absorbing particles. The SSA errors under NA conditions are significantly higher than those for other types and have a wider range. Because the contribution of aerosol particles to upward radiance depends on AOD rather than SSA, the effects of surface reflectance uncertainty are mostly offset by AOD. The overestimation of surface reflectance results in a larger error in SSA than the underestimation in general, because the sensitivity to aerosol extinction decreases as the surface reflectance approaches the critical reflectance [51]. When the SSA is 0.89 under NA conditions, an overestimation of surface reflectance of 40% results in an SSA error of −0.033, while a −40% underestimation causes and SSA error of −0.005.
An underestimation of surface reflectance results in an overestimation of atmospheric scattering and thus leads to an underestimation of the shielding effect of aerosols. Therefore, an underestimation (overestimation) of surface reflectance results in an underestimation (overestimation) of ALH. However, under NA conditions the underestimation of molecular scattering due to an overestimation of surface reflectance results in an underestimation of ALH. The absolute ALH error caused by errors in surface reflectance ranges between −1.18 and 1.40 km and the highest error was found for HAF aerosols.
After correcting for measurement geometry in the measured spectrum, the most important parameter for simulating the TOA spectrum is the aerosol model chosen for the RTM simulation, which consists of the volume size distribution and indices of refraction. With respect to spectral variations in the simulated TOA reflectance, assumptions related to the wavelength dependence of the imaginary component of the refractive index play a crucial role [52]. This dependence leads to spectral variations in the Aerosol Absorbing Optical Depth (AAOD). A parameter which represents the slope of the AAOD-wavelength relationship in log space is commonly used to describe this spectral dependence [52] and is known as AAE. Numerous studies have investigated the AAE in the UV range for various aerosol types and the values 3.9 [39], 1.8 [40] and 0.0 [41] were adopted for HAF, dust and NA aerosols, respectively, in this study. The AAE affects simulations of the spectral variation of the backscattered radiance and the accuracy of the OE method by affecting a priori retrieval and spectral fitting. Errors in classifying aerosols by type lead to errors in AAE. For example, the classification of dust as HAF (NA) results in an overestimation (underestimation) of AAE.
Figure 13 and Table 6 show the retrieval errors caused by incorrect aerosol classification. For this error analysis, the algorithm is forced to use an incorrect aerosol type by deactivating the aerosol type selection process. The effect of classification errors is more dramatic than that of surface reflectance errors. The median error in AOD for the reference condition of 1.5 reaches 5.51 when HAF aerosol is incorrectly classified as NA and the SSA error ranges from −0.040 to 0.048 under various reference conditions. In terms of ALH, an overestimation of 3.9 km occurs at a reference condition of 1 km. As shown in Figure 3, the ratio between radiances at 354 and 388 nm decreases with increasing AOD and this decrease accelerates as AAE increases. Thus, the higher the AAE, the lower the AOD for a given radiance spectrum; i.e., AODNA > AODdust > AODHAF. The radiance increases in the UV region due to increasing SSA becomes more dramatic as the AAE increases. This means that the SSA retrieved under the assumption of high AAE is larger than that for low AAE. Therefore, overestimations of AAE—e.g., classifying dust as HAF aerosols (gray box in the dust case in Figure 13a,b) or classifying NA aerosols as HAF or dust aerosols (gray or pink box in the NA case in Figure 13a,b)—result in an underestimation of AOD and an overestimation of SSA. In general, the retrieval error in AOD and SSA is high when NA particles are mistakenly classified as an absorbing type (blue box in Figure 13a,b) because of large differences in AAE. Misclassifying NA particles as absorbing results in an underestimation of AOD, as expected but the error does not vary significantly between a misclassification as dust or HAF. However, this misclassification results in a severe overestimation of SSA under low SSA conditions.
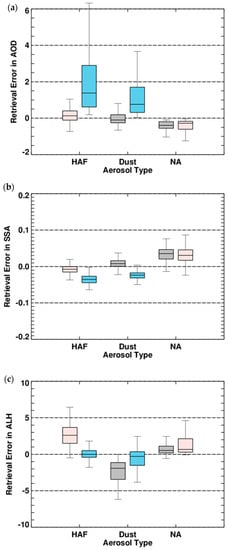
Figure 13.
Retrieval error in (a) AOD, (b) SSA and (c) ALH (km) due to aerosol misclassification for each aerosol type. Box colors denote misclassified aerosol type under the conditions shown on the x-axis. Gray: HAF, pink: Dust and blue: NA Errors are obtained by testing the algorithm with an aerosol type that is different from the true condition. Each box-and-whisker plot for a true condition shows the retrieval error distribution derived from the 108-member ensemble for AOD and SSA and 81-member ensemble for ALH.

Table 6.
Median values of the data plotted in Figure 13. Errors are the median retrieval error obtained by comparing retrieved values from the developed algorithm with the reference condition, assuming a different aerosol type than that used in the radiance simulation.
Because absorbing aerosols absorb the upward Rayleigh scattering below the aerosol layer, an increase in ALH decreases the radiance at TOA and reduces spectral variations. The spectral dependence is also decreased with the decreasing AAE. Thus, it can be expected that an overestimation of the AAE results in an overestimation of the ALH, as shown by the gray and pink boxes for NA conditions in Figure 13c. However, the radiance decrease and change in spectral variation resulting from an ALH increase is smaller than the effects of AOD and SSA variation and thus the change in radiance from an incorrect AAE assumption can be offset by adjusting the AOD and SSA, rather than the ALH. Because of this, the general trend of retrieval error with varying ALH under different misclassification scenarios cannot be easily explained.
6. Discussion
The strength of the proposed algorithm lies in its ability to retrieve horizontal distributions of AOD and SSA with an estimation of vertical location of aerosol layer, as shown in Figure 7. This retrieval will be valuable for gas concentrations from GEMS measurements with its contribution to the improved accuracy of AMF calculations. Because the GEMS is the only payload onboard a geostationary satellite covering Asia with hyperspectral UV measurements, the stand-alone operation of the developed algorithm is useful to assure stability. The validation results, however, indicate that the correlation with AERONET products was not improved relative to that of the OMAERUV algorithm. An approach to improve the performance of the algorithm was revealed by a reference test. Results from the reference test can be summarized as follows. (1) The OE algorithm products are most robust for AOD, followed by SSA and ALH. The large uncertainty in ALH retrieval may be caused by insufficient degrees of freedom (DOF), although the O4 absorption band (477 nm) is used in this study. (2) Uncertainty in AAE caused by the misclassification of aerosols or aerosol model assumptions is the most important issue in the developed algorithm. Results from the reference test of aerosol misclassification ultimately reflect the effects of uncertainty in AAE, as explained above. Therefore, optimization of AAE for each aerosol type in Asia should be the subject of future work. Recently, an intensive field campaign, the Korea U.S.-Air Quality (KORUS-AQ) campaign, was carried out over South Korea from May to June 2016. During and after the KORUS-AQ campaign, Mok et al. [53] measured aerosol absorptivity using UV- and visible-MFRSF at Seoul and retrieved spectral SSA variation from 305 to 870 nm. The quantification of the aerosol absorption properties at UV wavelengths may improve assumptions in the aerosol model and thus improve the accuracy of the algorithm.
In addition, Figure 13 suggests that errors in particle size increase the error in ALH significantly, unlike what is seen for AOD and SSA retrieval. This is an important issue for the algorithm because the low sensitivity of UV radiance to particle size complicates the distinction of HAF and dust particles. Therefore, updating the GEMS AOP retrieval algorithm with improved aerosol model assumptions and an advanced method for aerosol type selection will be the focus of future work.
7. Conclusions
In this study, an UV-visible algorithm to provide AOD and SSA simultaneously was developed using the OE method. The AOD and SSA were estimated based on an ALH optimized to fit the calculated spectrum to observations. Because of the large spatial and temporal variations of aerosol properties, a priori states for AOD and SSA were retrieved for six heights by using a two-channel inversion method. Then, these a priori states were used to solve the Levenberg Marquardt equation.
To analyze the performance of the algorithm, retrieved AOD and SSA were compared with AERONET values for 3 years from 2005 to 2007. The retrieved AOD showed reasonable agreement with observations, with a correlation coefficient of 0.71. However, a regression slope of 0.56 with y-intercept of 0.24 and a general overestimation of SSA for HAF aerosols indicate that the AAE is typically overestimated. In addition, the ALH showed good agreement with the CALIOP Zaer when the AOD (at 443 nm) is higher than 0.8 and the SSA (at 443 nm) is lower than 0.93.
The reference test (see Section 5) revealed that the inversion errors in AOD and SSA are negligible, regardless of errors in a priori assumptions for ALH but the error in ALH due to errors in a priori assumptions increased from 0.02 to 1.81 km when the reference ALH was 1.0 km, under NA-aerosol conditions. To reduce this uncertainty, a yearly-averaged ALH from CALIOP level 2 products was adopted as an a priori ALH.
Uncertainties in model parameters such as aerosol type and surface reflectance caused significant errors in AOD, SSA and ALH. The underestimation of surface reflectance resulted in an overestimation of AOD, an overestimation of SSA and an underestimation of ALH. When the surface reflectance error was −40%, the median error reached 0.52 for AOD, −0.012 for SSA and −1.18 km for ALH. The error caused by the misclassification of aerosols was more significant than that of surface reflectance. Uncertainty in AAE affected the estimated spectral distribution of radiance, which led to spectral fitting errors. In general, the overestimation of AAE resulted in an underestimation of AOD, overestimation of SSA and overestimation of ALH. It should be noted that conditions exist that do not follow the general relationship between retrieval error and uncertainty in model parameters. The relationship is not linear because each state vector simultaneously contributes to the radiance spectrum and retrieval errors from other sources can cancel out the effects of errors in model parameters. Cloud contamination error is another contributor to retrieval errors and climatological surface reflectance may contain uncertainties that result in the underestimation of AOD.
Despite these uncertainties, the UV algorithm has demonstrated the ability to retrieve aerosol absorptivity, which plays a crucial role in the radiative forcing of aerosols and thus climate change. The estimation of AOPs over Asia can contribute to an understanding of the role of Asian aerosols in climate change, as well as direct effects on public health. Results will contribute to the estimate of aerosol effects on regional climate change and improve air quality forecasting via a data assimilation system. An improvement in results from the UV algorithm is expected once GEMS measurements are available, as these will have a finer spatial resolution (3.5 km (NS) × 8 km (EW) at Seoul). Furthermore, continuous monitoring of aerosol properties together with their precursor measurements can be expanded to the global scale by combining the measurements of the NASA TEMPO and the ESA Sentinel-4, which have specifications similar to those of GEMS. The GEO constellation of GEMS, TEMPO and Sentinel-4 will significantly improve the understanding of air quality over the Northern Hemisphere.
Acknowledgments
This subject is supported by Korea Ministry of Environment (MOE) as Public Technology Program based on Environmental Policy (2017000160001) and the Korea Meteorological Administration Research and Development Program under Grant KMIPA 2015-5010.
Author Contributions
Mijin Kim developed the algorithm under the guidance of Jhoon Kim, Omar Torres, and Changwoo Ahn. Woogyung Kim and Ukkyo Jeong, and Sujung Go contributed the error analysis. Xiong Liu guided the optimal estimation method. Kyung Jung Moon and Deok-Rae Kim participated in algorithm operation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Yu, H.; Remer, L.A.; Chin, M.; Bian, H.; Tan, Q.; Yuan, T.; Zhang, Y. Aerosols from overseas rival domestic emissions over North America. Science 2012, 337, 566–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Kim, J.; Jeong, U.; Kim, W.; Hong, H.; Holben, B.; Eck, T.F.; Lim, J.H.; Song, C.K.; Lee, S.; et al. Aerosol optical properties derived from the DRAGON-NE Asia campaign, and implications for a single-channel algorithm to retrieve aerosol optical depth in spring from Meteorological Imager (MI) on-board the Communication, Ocean, and Meteorological Satellite (COMS). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 1789–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, M.; Park, Y.J.; Jeong, U.; Kim, W.; Hong, H.; Holben, B.; Eck, T.F.; et al. GOCI Yonsei Aerosol Retrieval (YAER) algorithm and validation during the DRAGON-NE Asia 2012 campaign. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 1377–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Song, C.H.; Ryu, J.H.; Ahn, Y.H.; Song, C.K. Algorithm for retrieval of aerosol optical properties over the ocean from the Geostationary Ocean Color Imager. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 1077–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, M.; Park, Y.-J.; Holben, B.; Eck, T.F.; Li, Z.; Song, C.H. GOCI Yonsei aerosol retrieval version 2 aerosol products: Improved algorithm description and error analysis with uncertainty estimation from 5-year validation over East Asia. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessho, K.; Date, K.; Hayashi, M.; Ikeda, A.; Imai, T.; Inoue, H.; Kumagai, Y.; Miyakawa, T.; Murata, H.; Ohno, T.; et al. An Introduction to Himawari-8/9-Japan’s New-Generation Geostationary Meteorological Satellites. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2016, 94, 151–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, O.; Bhartia, P.K.; Herman, J.R.; Ahmad, Z.; Gleason, J. Derivation of aerosol properties from satellite measurements of backscattered ultraviolet radiation: Theoretical basis. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 17099–17110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleipool, Q.L.; Dobber, M.R.; de Haan, J.F.; Levelt, P.F. Earth surface reflectance climatology from 3 years of OMI data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Spurr, R.J.D.; Drury, E.; Remer, L.A.; Levy, R.C.; Wang, J. Optimal estimation for global ground-level fine particulate matter concentrations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 5621–5636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.A.; Park, R.J.; Jeong, J.I.; Lee, S.; González Abad, G.; Kurosu, T.P.; Palmer, P.I.; Chance, K. Sensitivity of formaldehyde (HCHO) column measurements from a geostationary satellite to temporal variation of the air mass factor in East Asia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 4673–4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Lee, H.; Kim, J.; Jeong, U.; Ryu, J.; Lee, D. Investigation of Simultaneous Effects of Aerosol Properties and Aerosol Peak Height on the Air Mass Factors for Space-Borne NO2 Retrievals. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, C.; Torres, O.; Jethva, H. Assessment of OMI near-UV aerosol optical depth over land. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 2457–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jethva, H.; Torres, O.; Ahn, C. Global assessment of OMI aerosol single-scattering albedo using ground-based AERONET inversion. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 9020–9040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, O.; Ahn, C.; Chen, Z. Improvements to the OMI near-UV aerosol algorithm using A-train CALIOP and AIRS observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 3257–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, D.M.; Vaughan, M.A.; Omar, A.; Hu, Y.X.; Powell, K.A.; Liu, Z.Y.; Hunt, W.H.; Young, S.A. Overview of the CALIPSO Mission and CALIOP Data Processing Algorithms. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 2310–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanre, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Nakajima, T.; et al. AERONET—A federated instrument network and data archive for aerosol characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). Formation Flying: The Afternoon “A-Train” Satellite Constellation; NASA Fact Sheet 2003, FS-2003-1-053-GSFC; Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2003.
- Jeong, M.J.; Hsu, N.C. Retrievals of aerosol single-scattering albedo and effective aerosol layer height for biomass-burning smoke: Synergy derived from “A-Train” sensors. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Hsu, N.C.; Bettenhausen, C.; Sayer, A.M.; Seftor, C.J.; Jeong, M.J. Retrieving the height of smoke and dust aerosols by synergistic use of VIIRS, OMPS, and CALIOP observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 8372–8388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.S.; Kim, J.; Lee, H.; Torres, O.; Lee, K.M.; Lee, S.D. Utilization of O-4 slant column density to derive aerosol layer height from a space-borne UV-visible hyperspectral sensor: Sensitivity and case study. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 1987–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimot, J.; Veefkind, J.P.; Vlemmix, T.; de Haan, J.F.; Amiridis, V.; Proestakis, E.; Marinou, E.; Levelt, P.F. An exploratory study on the aerosol height retrieval from OMI measurements of the 477 nm O-2-O-2 spectral band using a neural network approach. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 783–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, C.D. Inverse Methods for Atmospheric Sounding: Theory and Practice; World Scientific: Singapore, 2000; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers, C.D. Retrieval of atmospheric temperature and composition from remote measurements of thermal radiation. Rev. Geophys. 1976, 14, 609–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huneeus, N.; Boucher, O. One-dimensional variational retrieval of aerosol extinction coefficient from synthetic LIDAR and radiometric measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govaerts, Y.M.; Wagner, S.; Lattanzio, A.; Watts, P. Joint retrieval of surface reflectance and aerosol optical depth from MSG/SEVIRI observations with an optimal estimation approach: 1. Theory. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.C.; Govaerts, Y.M.; Lattanzio, A. Joint retrieval of surface reflectance and aerosol optical depth from MSG/SEVIRI observations with an optimal estimation approach: 2. Implementation and evaluation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, O.; Bhartia, P.K.; Sinyuk, A.; Welton, E.J.; Holben, B. Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer measurements of aerosol absorption from space: Comparison to SAFARI 2000 ground-based observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, O.; Bhartia, P.K.; Herman, J.R.; Sinyuk, A.; Ginoux, P.; Holben, B. A long-term record of aerosol optical depth from TOMS observations and comparison to AERONET measurements. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 398–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurr, R.J. VLIDORT: A linearized pseudo-spherical vector discrete ordinate radiative transfer code for forward model and retrieval studies in multilayer multiple scattering media. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2006, 102, 316–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Song, C.H.; Kim, S.B.; Chun, Y.; Sohn, B.J.; Holben, B.N. Characteristics of aerosol types from AERONET sunphotometer measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 3110–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levelt, P.F.; Van den Oord, G.H.J.; Dobber, M.R.; Malkki, A.; Visser, H.; de Vries, J.; Stammes, P.; Lundell, J.O.V.; Saari, H. The Ozone Monitoring Instrument. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Reid, J.S.; Dubovik, O.; Smirnov, A.; O’Neill, N.T.; Slutsker, I.; Kinne, S. Wavelength dependence of the optical depth of biomass burning, urban, and desert dust aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 31333–31349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Tanre, D.; Smirnov, A.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Abuhassan, N.; Newcomb, W.W.; Schafer, J.S.; Chatenet, B.; Lavenu, F.; et al. An emerging ground-based aerosol climatology: Aerosol optical depth from AERONET. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 12067–12097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.; Eck, T.F.; Smirnov, A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; King, M.D.; Tanre, D.; Slutsker, I. Variability of absorption and optical properties of key aerosol types observed in worldwide locations. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 590–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; King, M.D. A flexible inversion algorithm for retrieval of aerosol optical properties from Sun and sky radiance measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 20673–20696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.N.; King, M.D.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I. Accuracy assessments of aerosol optical properties retrieved from Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) Sun and sky radiance measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 9791–9806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higurashi, A.; Nakajima, T. Detection of aerosol types over the East China Sea near Japan from four-channel satellite data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.C.; Higurashi, A.; Takemura, T.; Song, C.H. Consistency of the aerosol type classification from satellite remote sensing during the Atmospheric Brown Cloud-East Asia Regional Experiment campaign. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchstetter, T.W.; Novakov, T.; Hobbs, P.V. Evidence that the spectral dependence of light absorption by aerosols is affected by organic carbon. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Choi, H.; Kim, J. Optical Constants for Asian Dust in UV-VIS Region and OMI Observations. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, San Francisco, CA, USA, 12–16 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hess, M.; Koepke, P.; Schult, I. Optical properties of aerosols and clouds: The software package OPAC. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, R.; Ajtai, T.; Kandler, K.; Lieke, K.; Linke, C.; Muller, T.; Schnaiter, M.; Vragel, M. Complex refractive indices of Saharan dust samples at visible and near UV wavelengths: A laboratory study. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 2491–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grainger, R.G.; Lucas, J.; Thomas, G.E.; Ewen, G.B. Calculation of Mie derivatives. Appl. Opt. 2004, 43, 5386–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vries, M.J.M.P.; Beirle, S.; Wagner, T. UV Aerosol Indices from SCIAMACHY: Introducing the SCattering Index (SCI). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 9555–9567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, O.; Tanskanen, A.; Veihelmann, B.; Ahn, C.; Braak, R.; Bhartia, P.K.; Veefkind, P.; Levelt, P. Aerosols and surface UV products from Ozone Monitoring Instrument observations: An overview. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boesch, H.; Brown, L.; Castano, R.; Christi, M.; Crisp, D.; Eldering, A.; Fisher, B.; Frankenberg, C.; Gunson, M.; Granat, R. Orbiting Carbon Observatory (OCO)-2. Available online: https://docserver.gesdisc.eosdis.nasa.gov/public/project/OCO/OCO2_L2_ATBD.V6.pdf (accessed on 21 January 2018).
- Dobber, M.R.; Dirksen, R.J.; Levelt, P.F.; Van den Oord, G.H.J.; Voors, R.H.M.; Kleipool, Q.; Jaross, G.; Kowalewski, M.; Hilsenrath, E.; Leppelmeier, G.W.; et al. Ozone-Monitoring Instrument calibration. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 1209–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levelt, P.; Noordhoek, R. OMI Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document Volume I: OMI Instrument, Level 0-1b Processor, Calibration & Operations, Technology Report ATBD-OMI-01, Version 1.1; 2002. Available online: https://projects.knmi.nl/omi/documents/data/OMI_ATBD_Volume_1_V1d1.pdf (accessed on 21 January. 2018).
- Stammes, P.; Noordhoek, R. OMI Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document Volume III: Clouds, Aerosols, and Surface UV Irradiance, Technology Report ATBD-OMI-03, Version 2; 2002. Available online: https://projects.knmi.nl/omi/documents/data/OMI_ATBD_Volume_3_V2.pdf (accessed on 21 January 2018).
- Mok, J.; Krotkov, N.A.; Arola, A.; Torres, O.; Jethva, H.; Andrade, M.; Labow, G.; Eck, T.F.; Li, Z.; Dickerson, R.R.; et al. Impacts of brown carbon from biomass burning on surface UV and ozone photochemistry in the Amazon Basin. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, R.S.; Kaufman, Y.J. The Relative Importance of Aerosol Scattering and Absorption in Remote-Sensing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1985, 23, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jethva, H.; Torres, O. Satellite-based evidence of wavelength-dependent aerosol absorption in biomass burning smoke inferred from Ozone Monitoring Instrument. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 10541–10551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, J.; Krotkov, N.A.; Torres, O.; Jethva, H.; Li, Z.; Kim, J.; Koo, J.H.; Go, S.; Irie, H.; Labow, G.; et al. Comparisons of spectral aerosol absorption in Seoul, South Korea. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).