Green, Green, It’s Green: A Triad Model of Technology, Culture, and Innovation for Corporate Sustainability
Abstract
1. Introduction
“Green, green, it’s green, they say on the far side of the hill. Green, green, I’m going away to where the grass is greener still.”—Johnny Rivers
2. Key Components of Green Endeavor
2.1. Green Innovation
2.2. Green Culture
2.3. Green IS Infrastructure
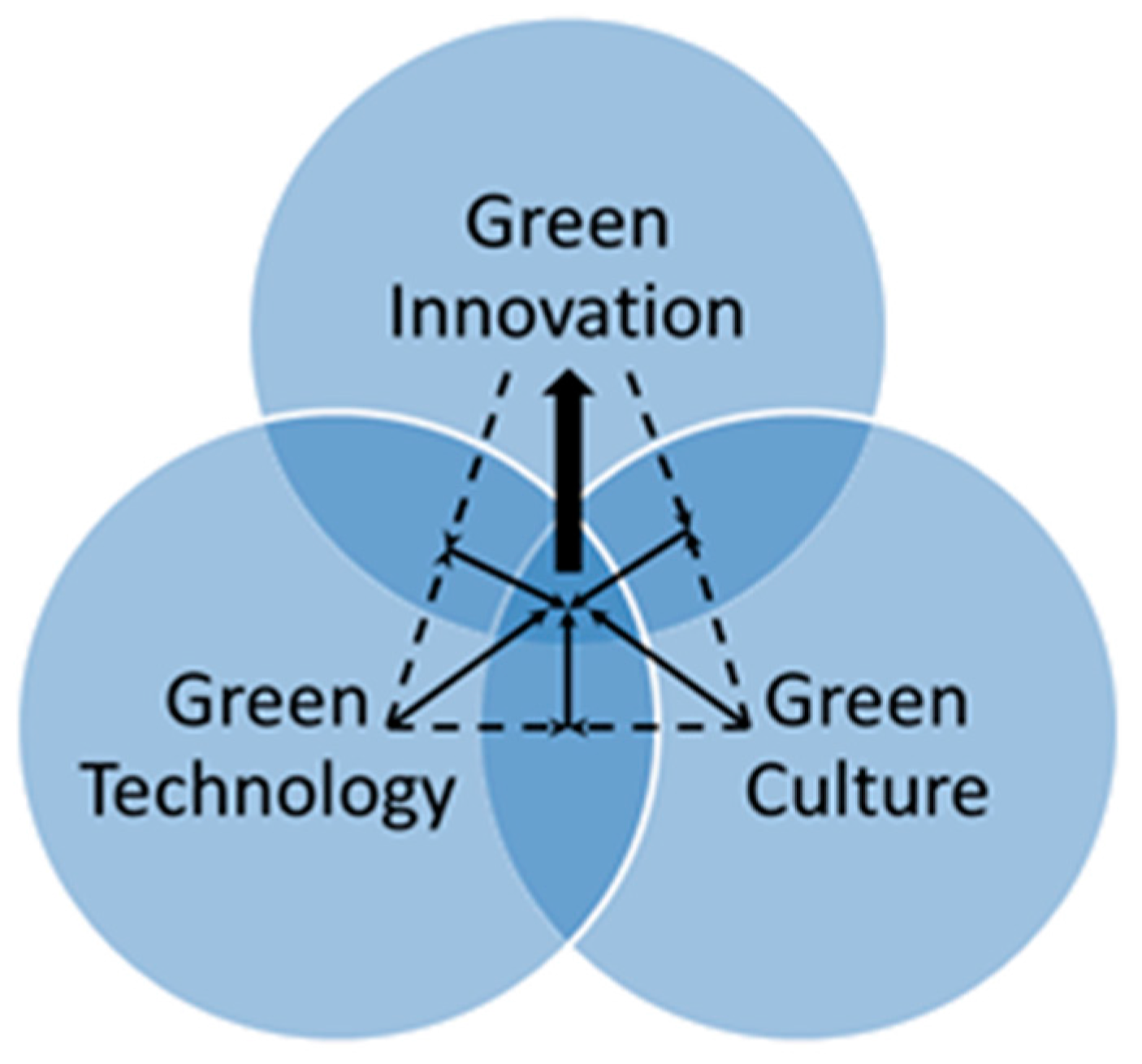
3. Mutuality among Key Components
3.1. Organizational Innovation and IS Infrastructure
3.2. Organizational Innovation and Organizational Culture
3.3. IS Infrastructure and Organizational Culture
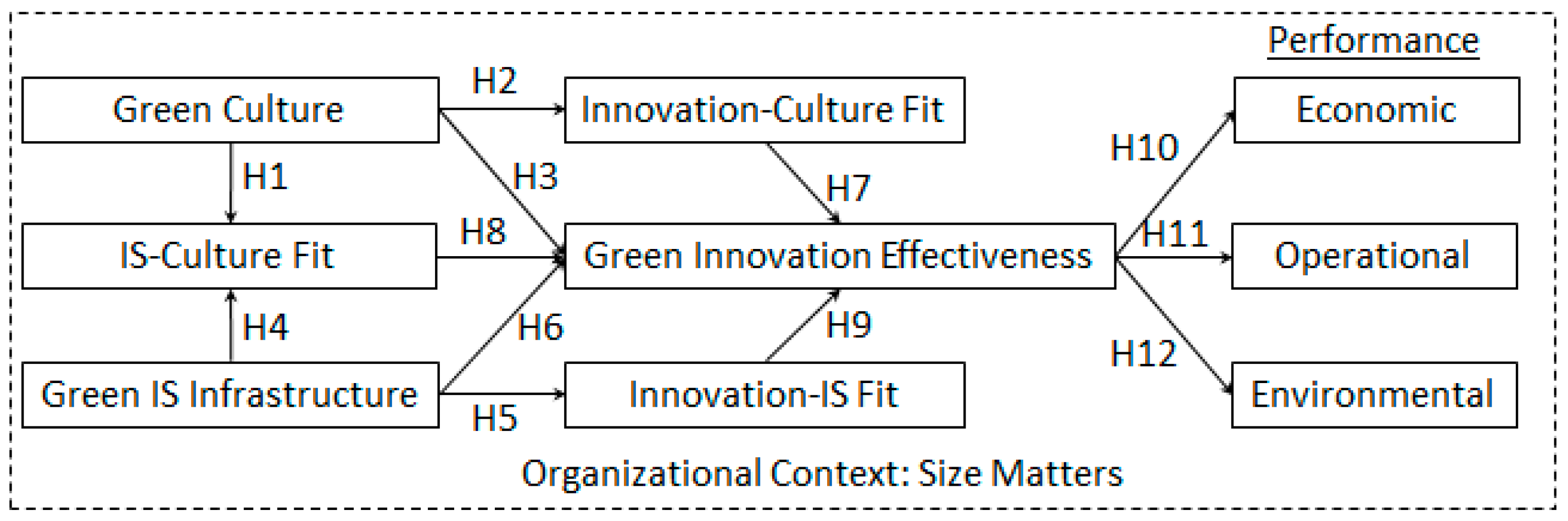
4. Research Model and Hypotheses
4.1. Green Culture-Related Hypotheses
4.2. Green IS-Related Hypotheses
4.3. Alignment-Related Hypotheses
4.4. Performance-Related Hypotheses
5. Methodology
5.1. Measurement
5.2. Survey Method and Sample
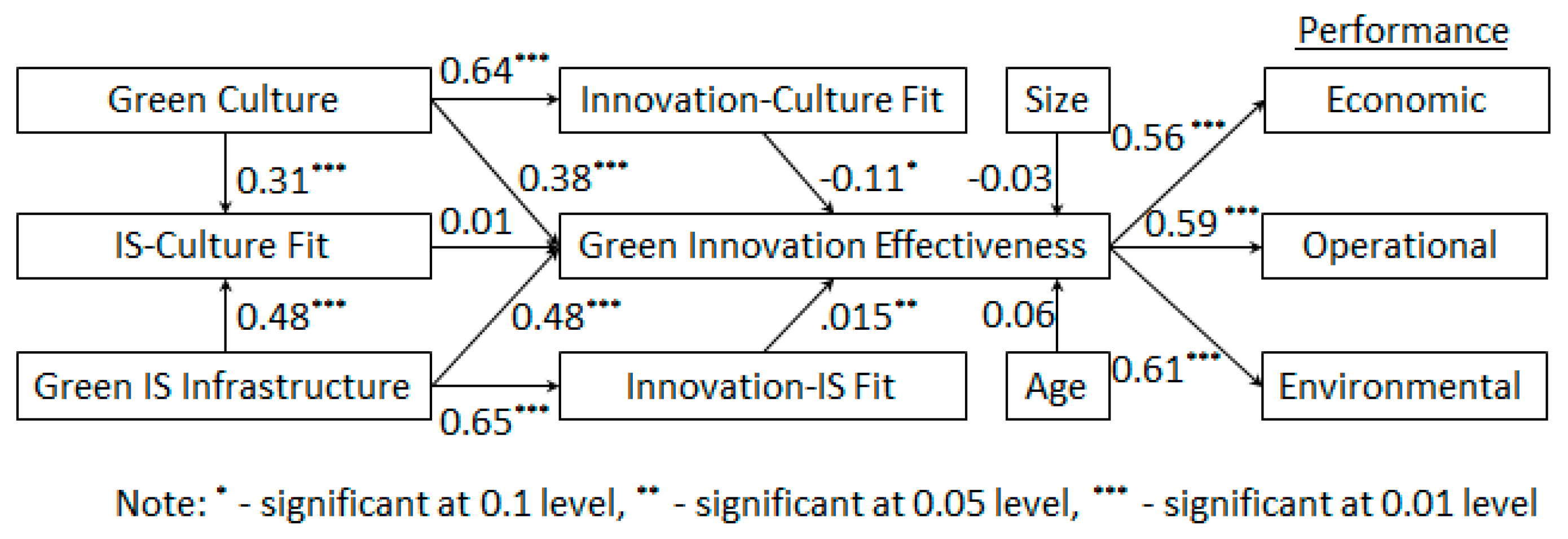
6. Results
7. Conclusions and Implications
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Measurement Items
- ☐
- Energy saving
- ☐
- Paperless office (e.g., email, workflow, ERP)
- ☐
- Online collaboration
- ☐
- Remote meetings
- ☐
- Pollution control
- ☐
- Environmental monitoring
- ☐
- Emissions audit
- ☐
- Green procurement and logistics
- ☐
- Green manufacturing and packaging
- ☐
- Others (please specify): _________________
- …
- reduce overall consumption and emissions.
- …
- reduce overall waste.
- …
- reduce overall use of hazardous and toxic materials.
- …
- make material sourcing and acquisition more environmentally friendly.
- …
- make product distribution and delivery more environmentally friendly.
- …
- make product disassembly and remanufacturing routings more environmentally friendly.
- …
- facilitate online collaboration (e.g., teleconferencing, electronic workflow) among employees.
- …
- facilitate green operations across all the departments.
- …
- facilitate management support and control for sustainable development.
- …
- facilitate environmental compliance and auditing.
- …
- most people in our organization have input into the decisions that affect them.
- …
- collaboration across functional roles is actively encouraged.
- …
- there is continuous investment in the skills of employees.
- …
- there is a high level of agreement about the way that we do things in our organization.
- …
- our approach of doing business is very consistent and predictable.
- …
- there is a clear and consistent set of values that governs the way we do business.
- …
- customers’ comments and recommendations often lead to changes in our organization.
- …
- our organization is very responsive and changes easily.
- …
- learning is viewed critical for organizational improvement.
- …
- our organization has a long-term purpose and direction.
- …
- there is a shared vision of what our organization will be like in the future.
- …
- we understand what needs to be done for us to succeed in the long run.
- …
- using less or non-polluting/toxic materials.
- …
- environment-friendly packaging for products.
- …
- recovering and recycling end-of-life products.
- …
- eco-labelling of products (green stickers like “Energy Star”).
- …
- consuming less resource (e.g., water, electricity, fuel) during production/use/disposal.
- …
- reducing the emission of hazardous substances or waste during the manufacturing process.
- …
- recycling, reusing and remanufacturing materials or parts.
- …
- using cleaner or renewable technology to make savings (e.g., energy, water).
- …
- reducing the use of raw materials during the manufacturing process.
- …
- redesigning production and operation processes to enhance environmental efficiency
- …
- improving products/services to meet new environmental criteria or directives
- …
- encouraging IT usage (e.g., paperless office) to reach ecological objectives
- …
- establishing green strategy and ecological initiative
- …
- adapting organizational structure to the needs of sustainable development
- …
- enhancing managerial procedures (e.g., carbon footprint tracking) to support ecological decisions.
- …
- adequate
- …
- appropriate
- …
- compatible
- …
- helpful
- …
- valuable
- …
- adequate
- …
- appropriate
- …
- compatible
- …
- helpful
- …
- valuable
- …
- adequate
- …
- appropriate
- …
- compatible
- …
- helpful
- …
- valuable
- …
- investment recovery
- …
- cost containment
- …
- profitability
- …
- labour productivity
- …
- inventory reduction
- …
- product delivery
- …
- product quality
- …
- capacity utilization
- …
- cycle time reduction
- …
- customer service
- …
- material reuse
- …
- environmental compliance
- …
- environment preservation
- …
- reduction of hazardous wastes and emissions
- …
- reduction of resource consumptions (e.g., energy, water, electricity, fuel)
References
- Fankhauser, S.; Bowen, A.; Calel, R.; Dechezleprêtre, A.; Grover, D.; Rydge, J.; Sato, M. Who will win the green race? In search of environmental competitiveness and innovation. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2013, 23, 902–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillestad, T.; Xie, C.; Abimbola, T.; Haugland, S.A. Innovative corporate social responsibility: The founder’s role in creating a trustworthy corporate brand through “green innovation”. J. Prod. Brand Manag. 2010, 19, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhl, A.; Blazejewski, S.; Dittmer, F. The more, the merrier: Why and how employee-driven eco-innovation enhances environmental and competitive advantage. Sustainability 2016, 8, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-H. The influence of corporate environmental ethics on competitive advantage: The mediation role of green innovation. J. Bus. Ethics 2011, 104, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.J.; Boudreau, M.-C.; Watson, R.T. Information systems and ecological sustainability. J. Syst. Inf. Technol. 2008, 10, 186–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkin, T.A.; Webster, J.; McShane, L. An agenda for ‘green’ information technology and systems research. Inf. Organ. 2011, 21, 17–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ar, I.M. The impact of green product innovation on firm performance and competitive capability: The moderating role of managerial environmental concern. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 62, 854–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-S. The positive effect of green intellectual capital on competitive advantages of firms. J. Bus. Ethics 2007, 77, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, T.-Y.; Chan, H.K.; Lettice, F.; Chung, S.H. The influence of greening the suppliers and green innovation on environmental performance and competitive advantage in Taiwan. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2011, 47, 822–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, M.-L.; Wang, R.; Chiu, A.S.; Geng, Y.; Lin, Y.H. Improving performance of green innovation practices under uncertainty. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 40, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernauer, T.; Engel, S.; Kammerer, D.; Sejas Nogareda, J. Determinants of green innovation—Ten years after porter’s win-win proposition: How to study the effects of environmental regulation? Polit. Vierteljahresschr. 2007, 39, 323–341. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, G.; Shen, L.; Zeng, S.; Jorge, O.J. The drivers for contractors’ green innovation: An industry perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2010, 18, 1358–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, M.-H.; Lin, C.-Y. Determinants of green innovation adoption for small and medium-size enterprises (SMEs). Afr. J. Bus. Manag. 2011, 5, 9154–9163. [Google Scholar]
- Gluch, P.; Gustafsson, M.; Thuvander, L. An absorptive capacity model for green innovation and performance in the construction industry. Constr. Manag. Econ. 2009, 27, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.; Zeng, S.; Tam, C.; Yin, H.; Zou, H. Stakeholders’ influences on corporate green innovation strategy: A case study of manufacturing firms in china. CSR. Environ. Manag. 2013, 20, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.-H.; Chen, Y.-S. Green organizational identity and green innovation. Manag. Decis. 2013, 51, 1056–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, F.; Ågerfalk, P.J. Information technology as a change actant in sustainability innovation: Insights from Uppsala. J. Strateg. Inf. Syst. 2011, 20, 96–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faucheux, S.; Nicolaï, I. It for green and green it: A proposed typology of eco-innovation. Ecol. Econ. 2011, 70, 2020–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melville, N.P. Information systems innovation for environmental sustainability. MIS Q. 2010, 34, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Cabrera, Á.; Cabrera, E.F.; Barajas, S. The key role of organizational culture in a multi-system view of technology-driven change. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2001, 21, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, M.V.; Fouts, P.A. A resource-based perspective on corporate environmental performance and profitability. Acad. Manag. J. 1997, 40, 534–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collis, D.J.; Montgomery, C.A. Competing on resources: Strategy in the 1990s. Harv. Bus. Rev. 1995, 73, 118–129. [Google Scholar]
- Büschgens, T.; Bausch, A.; Balkin, D.B. Organizational culture and innovation: A Metas-Strategy Review. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2013, 30, 763–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claver, E.; Llopis, J.; Garcia, D.; Molina, H. Organizational culture for innovation and new technological behavior. J. High Technol. Manag. Res. 1998, 9, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazanchi, S.; Lewis, M.W.; Boyer, K.K. Innovation-supportive culture: The impact of organizational values on process innovation. J. Oper. Manag. 2007, 25, 871–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naranjo-Valencia, J.C.; Jiménez-Jiménez, D.; Sanz-Valle, R. Innovation or imitation? The role of organizational culture. Manag. Decis. 2011, 49, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter-O’Grady, T.; Malloch, K. Innovation: Driving the green culture in healthcare. Nurs. Adm. Q 2010, 34, E1–E5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirtenberg, J. Building a Culture for Sustainability: People, Planet, and Profits in a New Green Economy; ABC-CLIO: Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fussler, C.; James, P. A Breakthrough Discipline for Innovation and Sustainability; Pitman Publishing: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Brunnermeier, S.B.; Cohen, M.A. Determinants of environmental innovation in us manufacturing industries. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2003, 45, 278–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geffen, C.A.; Rothenberg, S. Suppliers and environmental innovation: The automotive paint process. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2000, 20, 166–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrión-Flores, C.E.; Innes, R. Environmental innovation and environmental performance. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2010, 59, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verghese, K.; Lewis, H. Environmental innovation in industrial packaging: A supply chain approach. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2007, 45, 4381–4401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oltra, V.; Saint Jean, M. Sectoral systems of environmental innovation: An application to the French automotive industry. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2009, 76, 567–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theyel, G. Management practices for environmental innovation and performance. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2000, 20, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horbach, J. Determinants of environmental innovation—New evidence from German panel data sources. Res. Policy 2008, 37, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foxon, T.; Pearson, P. Overcoming barriers to innovation and diffusion of cleaner technologies: Some features of a sustainable innovation policy regime. J. Clean. Prod. 2008, 16, S148–S161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiederig, T.; Tietze, F.; Herstatt, C. Green innovation in technology and innovation management—An exploratory literature review. R&D Manag. 2012, 42, 180–192. [Google Scholar]
- Rennings, K. Redefining innovation—Eco-innovation research and the contribution from ecological economics. Ecol. Econ. 2000, 32, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellström, T. Dimensions of environmentally sustainable innovation: The structure of eco-innovation concepts. Development 2007, 15, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, D.; Trifilova, A. Green technology and eco-innovation: Seven case-studies from a russian manufacturing context. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2010, 21, 910–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, V.-H.; Ooi, K.-B.; Chong, A.Y.-L.; Seow, C. Creating technological innovation via green supply chain management: An empirical analysis. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 6983–6994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amores-Salvadó, J.; Martín-de Castro, G.; Navas-López, J.E. Green corporate image: Moderating the connection between environmental product innovation and firm performance. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 83, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arundel, A.; Kemp, R. Measuring Eco-Innovation. Available online: http://econpapers.repec.org/paper/taswpaper/10062.htm (accessed on 2 August 2017).
- Carrillo-Hermosilla, J.; del Río, P.; Könnölä, T. Diversity of eco-innovations: Reflections from selected case studies. J. Clean. Prod. 2010, 18, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zailani, S.; Govindan, K.; Iranmanesh, M.; Shaharudin, M.R.; Chong, Y.S. Green innovation adoption in automotive supply chain: The Malaysian case. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 108, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, S.; Clausen, T. Comparing the innovation process in environmental and non-environmental firms: A look at barriers to innovation. In Proceedings of the DRUID Society Conference, Copenhagen, Denmark, 16–18 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cuerva, M.C.; Triguero-Cano, Á.; Córcoles, D. Drivers of green and non-green innovation: Empirical evidence in low-tech smes. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 68, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, S.; Clausen, T.H. Innovating for a greener future: The direct and indirect effects of firms’ environmental objectives on the innovation process. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 128, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fok, L.Y.; Zee, S.M.; Hartman, S.J. Relationships among individual green orientation, employee perceptions of organizational commitment to the green movement, and organizational culture: A comparative study of Jamaica and the United States. J. Organ. Cutl. Commun. Confl. 2012, 16, 125–144. [Google Scholar]
- Fraj, E.; Martínez, E.; Matute, J. Green marketing strategy and the firm's performance: The moderating role of environmental culture. J. Strateg. Mark. 2011, 19, 339–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreton, K.; Williamson, D.; Lynch-Wood, G. An emergent typology of strategy, innovation and culture as determinants of business performance in small and medium-sized environmental enterprises. In Proceeding of the 11th Annual International Sustainable Development Research Conference, Helsinki, Finland, 6–8 June 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sugita, M.; Takahashi, T. Influence of corporate culture on environmental management performance: An empirical study of Japanese firms. CSR Environ. Manag. 2015, 22, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, L.D. Organizational culture’s influence on creativity and innovation: A review of the literature and implications for human resource development. ADHR 2005, 7, 226–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.; Zhao, D.; Yao, L. Enterprise culture and technological innovation capability from the perspective of resources. Cross Cult. Comm. 2013, 9, 92. [Google Scholar]
- Steiber, A.; Alänge, S. A corporate system for continuous innovation: The case of Google Inc. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2013, 16, 243–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-S.; Chang, C.-H.; Wu, F.-S. Origins of green innovations: The differences between proactive and reactive green innovations. Manag. Decis. 2012, 50, 368–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkis, J.; Koo, C.; Watson, R.T. Green information systems & technologies-this generation and beyond: Introduction to the special issue. Inf. Syst. Front. 2013, 15, 695–704. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, R.T.; Boudreau, M.-C.; Chen, A.J. Information systems and environmentally sustainable development: Energy informatics and new directions for the IS community. MIS Q. 2010, 34, 23–38. [Google Scholar]
- Tarafdar, M.; Gordon, S.R. Understanding the influence of information systems competencies on process innovation: A resource-based view. J. Strateg. Inf. Syst. 2007, 16, 353–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anaya, L.; Dulaimi, M.; Abdallah, S. An investigation into the role of enterprise information systems in enabling business innovation. Bus. Process Manag. J. 2015, 21, 771–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganotakis, P.; Hsieh, W.-L.; Love, J.H. Information systems, inter-functional collaboration and innovation in taiwanese high-tech manufacturing firms. Prod. Plan. Contr. 2013, 24, 837–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaparro-Peláez, J.; Pereira-Rama, A.; Pascual-Miguel, F.J. Inter-organizational information systems adoption for service innovation in building sector. J. Bus. Res. 2014, 67, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallivan, M.; Srite, M. Information technology and culture: Identifying fragmentary and holistic perspectives of culture. Inf. Organ. 2005, 15, 295–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.; Ye, H.J.; Teo, H.H.; Li, J. Information technology and open innovation: A strategic alignment perspective. Inf. Manag. 2015, 52, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatraman, N. The concept of fit in strategy research: Toward verbal and statistical correspondence. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1989, 14, 423–444. [Google Scholar]
- Ashurst, C.; Freer, A.; Ekdahl, J.; Gibbons, C. Exploring it-enabled innovation: A new paradigm? Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2012, 32, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A. Researching MIS-in Rethinking Management Information Systems; Currie, W., Galliers, B., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Pellissier, R. A conceptual framework for the alignment of innovation and technology. J. Technol. Manag. Innov. 2008, 3, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carcary, M.; Doherty, E.; Thornley, C. Business innovation and differentiation: Maturing the IT capability. IT Prof. 2015, 17, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mashari, M. Innovation through information technology (IT) enabled business process management (BPM): A review of key issues. Int. J. Innov. Learn. 2006, 3, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, S.; Møller, E.; Nygaard, T. IT-enabled process innovation: A literature review. In Proceedings of the 18th AMCIS, Washington, DC, USA, 9–11 August 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chae, B.K. A complexity theory approach to IT-enabled services (IESs) and service innovation: Business analytics as an illustration of IES. Decis. Support Syst. 2014, 57, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-C.; Liu, J.-C. Exploration for the relationship between innovation, it and performance. J. Intellect. Cap. 2000, 6, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, P.K. Culture and climate for innovation. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 1998, 1, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaruzelski, B.; Loehr, J.; Holman, R. Why culture is key. Strateg. Bus. 2011, 65, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Harrington, S.J.; Guimaraes, T. Corporate culture, absorptive capacity and IT success. Inf. Organ. 2005, 15, 39–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denison, D.R.; Mishra, A.K. Toward a theory of organizational culture and effectiveness. Organ. Sci. 1995, 6, 204–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schein, E.H. Organizational culture. Am. Psychol. 1990, 45, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.L.; Rafiq, M. Ambidextrous organizational culture, contextual ambidexterity and new product innovation: A comparative study of UK and Chinese high-tech firms. Br. J. Manag. 2014, 25, 58–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S. Organizational culture and information systems adoption: A three-perspective approach. Inf. Organ. 2011, 21, 57–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leidner, D.E.; Kayworth, T. A review of culture in information systems research: Toward a theory of information technology culture conflict. MIS Q. 2006, 30, 357–399. [Google Scholar]
- Bajwa, D.S.; Lewis, L.F. Does size matter? An investigation of collaborative information technology adoption by us firms. J. Inf. Technol. Theory Appl. 2003, 5, 29–46. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, J.E.; Xu, X.; Liu, C.; Lu, J. Organizational size: A significant predictor of it innovation adoption. J. Comput. Inf. Syst. 2003, 43, 76–82. [Google Scholar]
- Chuang, T.-T.; Rutherford, M.W.; Lin, B. Owner/manager characteristics, organisational characteristics and it adoption in small and medium enterprises. Int. J. Manag. Enterp. Dev. 2007, 4, 619–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, K.S.; Quinn, R.E. Diagnosing and Changing Organizational Culture: Based on the Competing Values Framework; Jossey-Bass: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Choo, C.W.; Bergeron, P.; Detlor, B.; Heaton, L. Information culture and information use: An exploratory study of three organizations. J. Assoc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2008, 59, 792–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-C.; Hsu, J.-M. Organizational process alignment, culture and innovation. Afr. J. Bus. Manag. 2010, 4, 2231–2240. [Google Scholar]
- Denison, D.R.; Haaland, S.; Goelzer, P. Corporate culture and organizational effectiveness: Is there a similar pattern around the world? Organ. Dyn. 2003, 3, 205–227. [Google Scholar]
- Southern, G.; Murray, A.U. Quality information management: The way to a better company culture. Inf. Manag. Comput. Secur. 1994, 2, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvius, A.G.; Smit, J.; Driessen, H. The relationship between organizational culture and the alignment of business and it. In Proceedings of the AMCIS, Lima, Peru, 12–15 August 2010; p. 186. [Google Scholar]
- Claver, E.; Llopis, J.; Reyes González, M.; Gascó, J.L. The performance of information systems through organizational culture. Inf. Technol. People 2001, 14, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-W.; Li, Y.-H. A Study of Environmental Innovation Strategy, Resource Alignment, and Green Innovation Performance, Academy of Management Proceedings. 2014. Available online: http://proceedings.aom.org/content/2014/1/13674.short (accessed on 2 August 2017).
- Chen, Y.-S.; Lai, S.-B.; Wen, C.-T. The influence of green innovation performance on corporate advantage in Taiwan. J. Bus. Ethics 2006, 67, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damanpour, F.; Aravind, D. Managerial innovation: Conceptions, processes, and antecedents. Manag. Organ. Rev. 2012, 8, 423–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-S.; Lin, Y.-H.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chang, C.-W. Enhancing green absorptive capacity, green dynamic capacities and green service innovation to improve firm performance: An analysis of structural equation modeling (SEM). Sustainability 2015, 7, 15674–15692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojnik, J.; Ruzzier, M. The driving forces of process eco-innovation and its impact on performance: Insights from slovenia. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 133, 812–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryszko, A. Proactive environmental strategy, technological eco-innovation and firm performance—Case of poland. Sustainability 2016, 8, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, H.R.; Chen, J.; Chen, P. Effects of green innovation on environmental and corporate performance: A stakeholder perspective. Sustainability 2015, 4997–5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, R.; Sulaiman, A.B.; Ramayah, T.; Molla, A. Senior managers’ perception on green information systems (IS) adoption and environmental performance: Results from a field survey. Inf. Manag. 2013, 50, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-C.; Huang, C.-C. Understanding knowledge management system usage antecedents: An integration of social cognitive theory and task technology fit. Inf. Manag. 2008, 45, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, K.W., Jr.; Zelbst, P.J.; Meacham, J.; Bhadauria, V.S. Green supply chain management practices: Impact on performance. Supply Chain Manag. 2012, 17, 290–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Tae Kim, S.; Choi, D. Green supply chain management and organizational performance. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2012, 112, 1148–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daugherty, P.J.; Richey, R.G.; Genchev, S.E.; Chen, H. Reverse logistics: Superior performance through focused resource commitments to information technology. Transp. Res. Part E 2005, 41, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, J.S.; Overton, T.S. Estimating nonresponse bias in mail surveys. J. Market. Res. 1977, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; MacKenzie, S.B.; Lee, J.-Y.; Podsakoff, N.P. Common method biases in behavioral research: A critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. J. Appl. Psychol. 2003, 88, 879–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; MacKenzie, S.B.; Podsakoff, N.P. Sources of method bias in social science research and recommendations on how to control it. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2012, 63, 539–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, H.A.; Simmering, M.J.; Sturman, M.C. A tale of three perspectives: Examining post hoc statistical techniques for detection and correction of common method variance. Organ. Res. Methods 2009, 12, 762–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzels, M.; Odekerken-Schröder, G.; van Oppen, C. Using pls path modeling for assessing hierarchical construct models: Guidelines and empirical illustration. MIS Q. 2009, 177–195. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F., Jr.; Hult, G.T.M. A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM); Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hemmert, M.; Bstieler, L.; Okamuro, H. Bridging the cultural divide: Trust formation in university–industry research collaborations in the US, Japan, and South Korea. Technovation 2014, 34, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, J.D.; Gromb, D. Cultural inertia and uniformity in organizations. J. Law Econ. Organ. 2006, 23, 743–771. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, R.B. The inertial impact of culture on it implementation. Inf. Manag. 1994, 27, 17–31. [Google Scholar]
- Byrd, T.A.; Turner, D.E. An exploratory examination of the relationship between flexible it infrastructure and competitive advantage. Inf. Manag. 2001, 39, 41–52. [Google Scholar]
- Dooley, R.S.; Fryxell, G.E. Are conglomerates less environmentally responsible? An empirical examination of diversification strategy and subsidiary pollution in the U.S. Chemical industry. J. Bus. Ethics 1999, 21, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.Y. Drivers for the participation of small and medium-sized suppliers in green supply chain initiatives. SCM 2013, 13, 185–198. [Google Scholar]
| Characteristics | Frequency | % (N = 368) |
|---|---|---|
| Organization Type | ||
| - Manufacturing | 65 | 17.7 |
| - Energy | 30 | 8.2 |
| - Real Estate | 58 | 15.8 |
| - Logistics | 8 | 2.2 |
| - IT | 69 | 18.8 |
| - Service | 45 | 12.2 |
| - Other | 93 | 25.3 |
| Size (Number of Employees) | ||
| - Small and Medium (<1000) | 193 | 52.4 |
| - Large (≥1000) | 175 | 47.6 |
| Respondent Gender | ||
| - Male | 254 | 69 |
| - Female | 113 | 30.7 |
| - Not Reported | 1 | 0.3 |
| Managerial Level | ||
| - Senior | 24 | 6.5 |
| - Middle | 117 | 31.8 |
| - Operational | 226 | 61.4 |
| - Not Reported | 1 | 0.3 |
| Home Department | ||
| - Administration | 164 | 44.6 |
| - Research and Development | 84 | 22.8 |
| - Production | 63 | 17.1 |
| - Marketing | 57 | 15.5 |
| Model | χ2 | df | χ2/df | RMSEA | CFI | NFI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method-Only (1-Factor) | 8870.004 | 2153 | 4.12 | 0.092 | 0.625 | 0.56 |
| Trait-Only (16-Factor) | 3981.704 | 2037 | 1.955 | 0.051 | 0.891 | 0.803 |
| Trait/Method (17-Factor) | 4370.532 | 2072 | 2.109 | 0.055 | 0.872 | 0.783 |
| Concept_Variable | Mean (SD) | α | V1 | V2 | V3 | V4 | V5 | V6 | V7 | V8 | V9 | V10 | V11 | V12 | V13 | V14 | V15 | V16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V1: Culture_Involvement | 3.63 (0.82) | 0.79 | 0.84 | |||||||||||||||
| V2: Culture_Consistency | 3.65 (0.77) | 0.81 | 0.67 | 0.85 | ||||||||||||||
| V3: Culture_Adaptivity | 3.79 (0.69) | 0.73 | 0.67 | 0.65 | 0.81 | |||||||||||||
| V4: Culture_Mission | 3.72 (0.75) | 0.83 | 0.55 | 0.65 | 0.71 | 0.87 | ||||||||||||
| V5: IS_Pollution Prevention | 3.77 (0.80) | 0.88 | 0.47 | 0.49 | 0.48 | 0.45 | 0.90 | |||||||||||
| V6: IS_Product Stewardship | 3.77 (0.78) | 0.86 | 0.51 | 0.49 | 0.54 | 0.51 | 0.78 | 0.88 | ||||||||||
| V7: IS_SustainableDevelopment | 3.84 (0.74) | 0.86 | 0.49 | 0.51 | 0.51 | 0.50 | 0.70 | 0.77 | 0.84 | |||||||||
| V8: Innovation_Product | 3.68 (0.72) | 0.85 | 0.50 | 0.56 | 0.53 | 0.53 | 0.57 | 0.60 | 0.60 | 0.80 | ||||||||
| V9: Innovation_Process | 3.80 (0.66) | 0.85 | 0.51 | 0.52 | 0.57 | 0.55 | 0.56 | 0.60 | 0.62 | 0.71 | 0.79 | |||||||
| V10: Innovation_Management | 3.72 (0.70) | 0.88 | 0.52 | 0.56 | 0.57 | 0.63 | 0.62 | 0.64 | 0.69 | 0.66 | 0.78 | 0.79 | ||||||
| V11: Fit_Innovation-Culture | 3.76 (0.69) | 0.91 | 0.54 | 0.53 | 0.55 | 0.56 | 0.53 | 0.53 | 0.62 | 0.48 | 0.46 | 0.54 | 0.86 | |||||
| V12: Fit_IS-Culture | 3.75 (0.68) | 0.90 | 0.54 | 0.52 | 0.51 | 0.53 | 0.58 | 0.58 | 0.66 | 0.52 | 0.48 | 0.60 | 0.80 | 0.84 | ||||
| V13: Fit_Innovation-IS | 3.72 (0.68) | 0.91 | 0.49 | 0.51 | 0.51 | 0.5 | 0.56 | 0.58 | 0.62 | 0.53 | 0.51 | 0.59 | 0.71 | 0.77 | 0.85 | |||
| V14: PerformanceEconomic | 3.76 (0.67) | 0.88 | 0.43 | 0.39 | 0.43 | 0.39 | 0.42 | 0.48 | 0.47 | 0.49 | 0.52 | 0.52 | 0.55 | 0.51 | 0.54 | 0.83 | ||
| V15: PerformanceOperational | 3.77 (0.67) | 0.89 | 0.44 | 0.41 | 0.53 | 0.53 | 0.44 | 0.47 | 0.49 | 0.47 | 0.53 | 0.58 | 0.62 | 0.61 | 0.55 | 0.77 | 0.83 | |
| V16: PerformanceEnvironmental | 3.85 (0.62) | 0.87 | 0.43 | 0.41 | 0.45 | 0.44 | 0.40 | 0.42 | 0.51 | 0.49 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.62 | 0.60 | 0.57 | 0.66 | 0.67 | 0.81 |
| Formative Indicator | Tolerance | VIF |
|---|---|---|
| Green Culture | ||
| - Involvement | 0.467 | 2.142 |
| - Consistency | 0.426 | 2.345 |
| - Adaptability | 0.351 | 2.850 |
| - Mission | 0.400 | 2.499 |
| Green IS | ||
| - Pollution Prevention | 0.367 | 2.722 |
| - Product Stewardship | 0.293 | 3.414 |
| - Sustainable Development | 0.388 | 2.580 |
| Green Innovation | ||
| - Product | 0.452 | 2.212 |
| - Process | 0.324 | 3.084 |
| - Management | 0.356 | 2.813 |
| Path | All | Big | S&M | Diff |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control: Size→Innovation Effectiveness | −0.025 | - | - | - |
| Control: Age→Innovation Effectiveness | 0.056 | 0.050 | 0.008 | 0.042 |
| H1: Green Culture→IS-Culture Fit | 0.313 *** | 0.316 *** | 0.299 ** | 0.017 |
| H2: Green Culture→Innovation-Culture Fit | 0.637 *** | 0.633 *** | 0.659 *** | 0.026 |
| H3: Green Culture→Innovation Effectiveness | 0.380 *** | 0.350 *** | 0.362 *** | 0.012 |
| H4: Green IS Infrastructure→IS-Culture Fit | 0.481 *** | 0.542 *** | 0.436 *** | 0.106 |
| H5: Green IS Infrastructure→Innovation-IS Fit | 0.648 *** | 0.680 *** | 0.619 *** | 0.061 |
| H6: Green IS Infrastructure→Innovation Effectiveness | 0.481 *** | 0.399 *** | 0.535 *** | 0.136 |
| H7: Innovation-Culture Fit→Innovation Effectiveness | −0.113 * | 0.027 | −0.202 ** | 0.229 ** |
| H8: IS-Culture Fit→Innovation Effectiveness | 0.008 | 0.146 | −0.052 | 0.198 * |
| H9: Innovation-IS Fit→Innovation Effectiveness | 0.152 ** | 0.023 | 0.208 *** | 0.185 * |
| H10: Innovation Effectiveness→Economic Performance | 0.563 *** | 0.610 *** | 0.532 *** | 0.078 |
| H11: Innovation Effectiveness→Operational Performance | 0.592 *** | 0.660 *** | 0.544 *** | 0.116 |
| H12: Innovation Effectiveness→Environmental Performance | 0.607 *** | 0.697 *** | 0.536 *** | 0.161 ** |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Z.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. Green, Green, It’s Green: A Triad Model of Technology, Culture, and Innovation for Corporate Sustainability. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1369. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9081369
Yang Z, Sun J, Zhang Y, Wang Y. Green, Green, It’s Green: A Triad Model of Technology, Culture, and Innovation for Corporate Sustainability. Sustainability. 2017; 9(8):1369. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9081369
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Zhaojun, Jun Sun, Yali Zhang, and Ying Wang. 2017. "Green, Green, It’s Green: A Triad Model of Technology, Culture, and Innovation for Corporate Sustainability" Sustainability 9, no. 8: 1369. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9081369
APA StyleYang, Z., Sun, J., Zhang, Y., & Wang, Y. (2017). Green, Green, It’s Green: A Triad Model of Technology, Culture, and Innovation for Corporate Sustainability. Sustainability, 9(8), 1369. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9081369





