Adsorption of Arsenate by Nano Scaled Activated Carbon Modified by Iron and Manganese Oxides
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Reagents
2.2. Carbon Impregnation
2.3. Characterization—Instrumentation
2.4. Adsorption Experiments
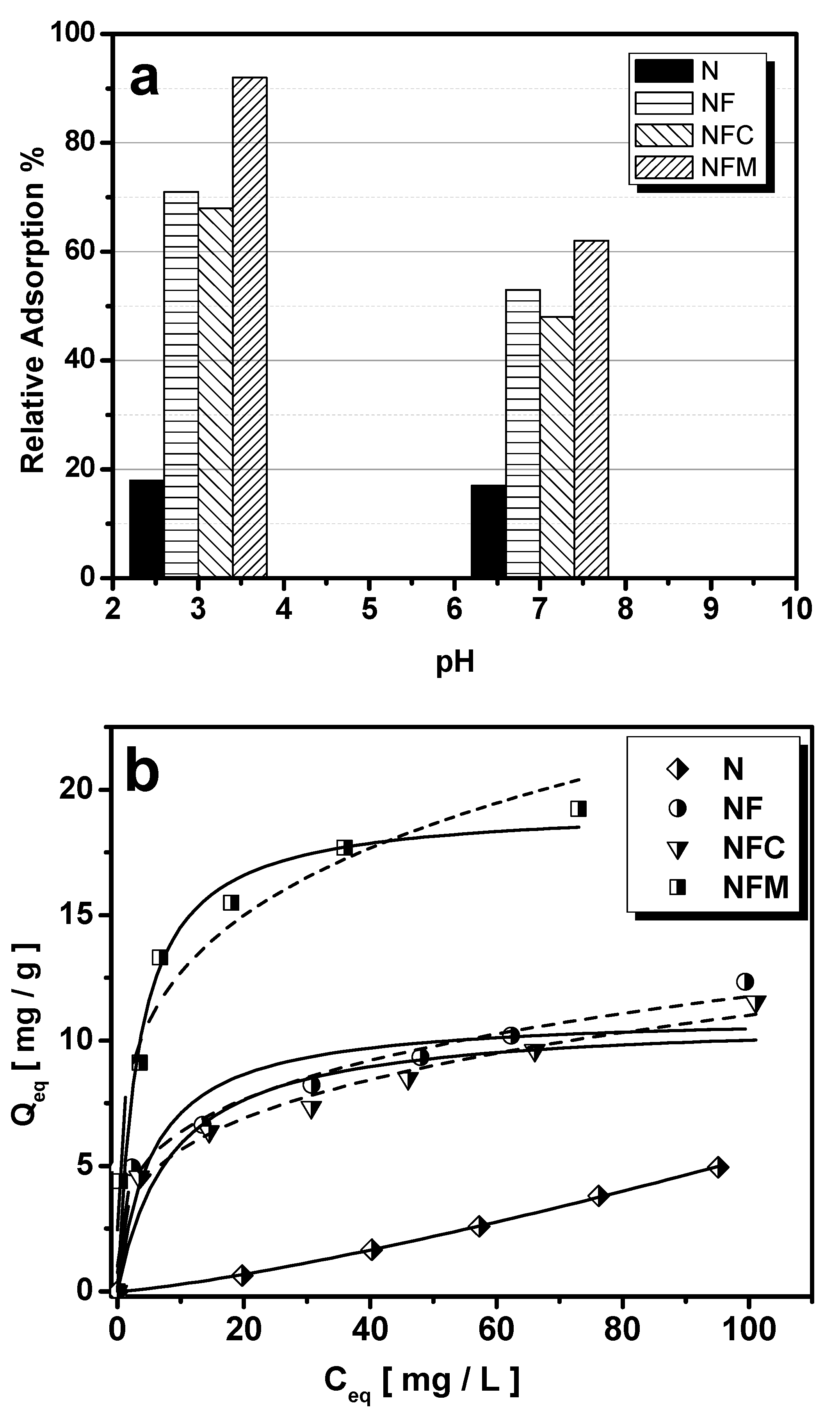
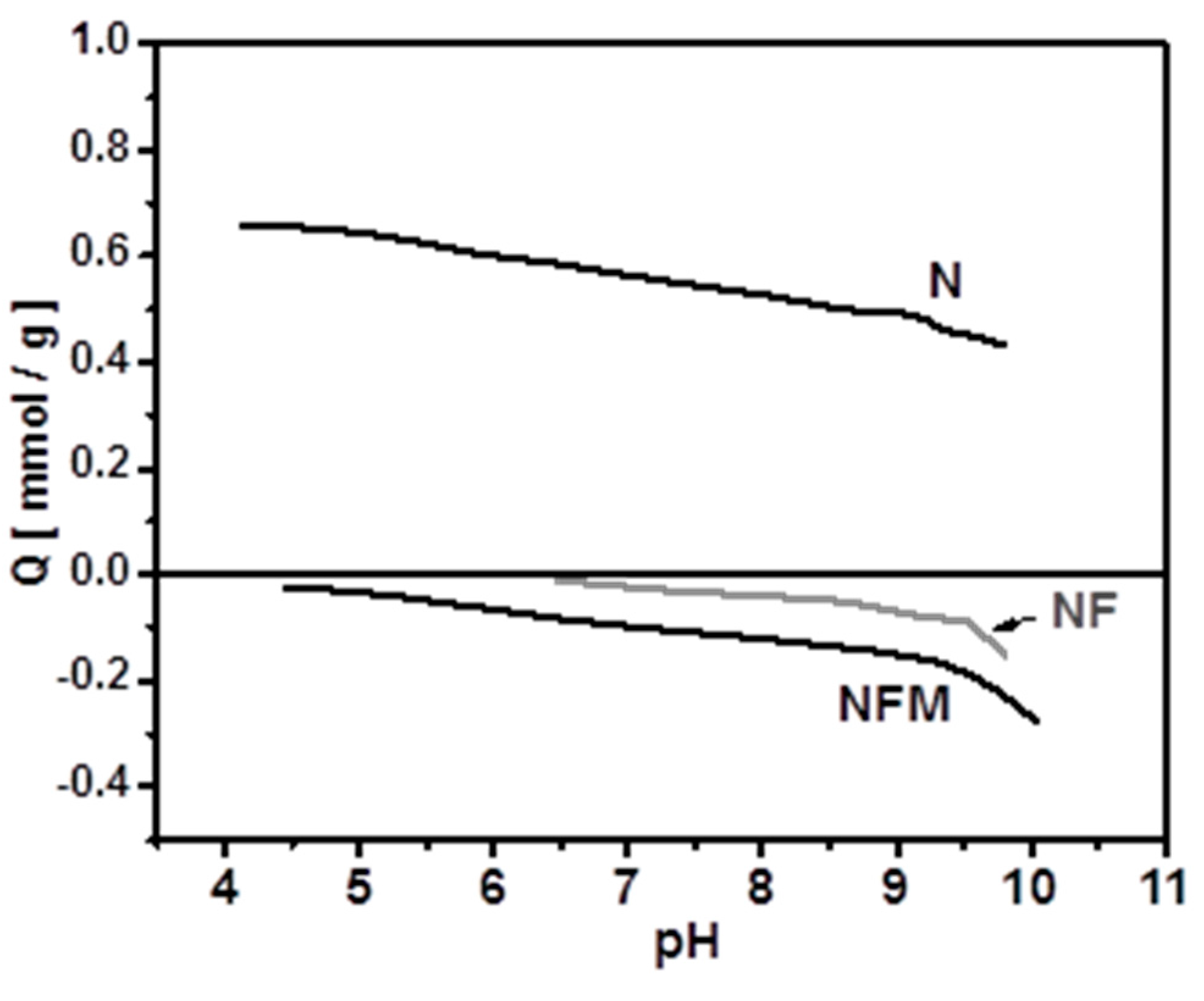
2.4.1. Effect of pH
2.4.2. Effect of Initial As(V) Concentration—Isotherms
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Adsorption Performance
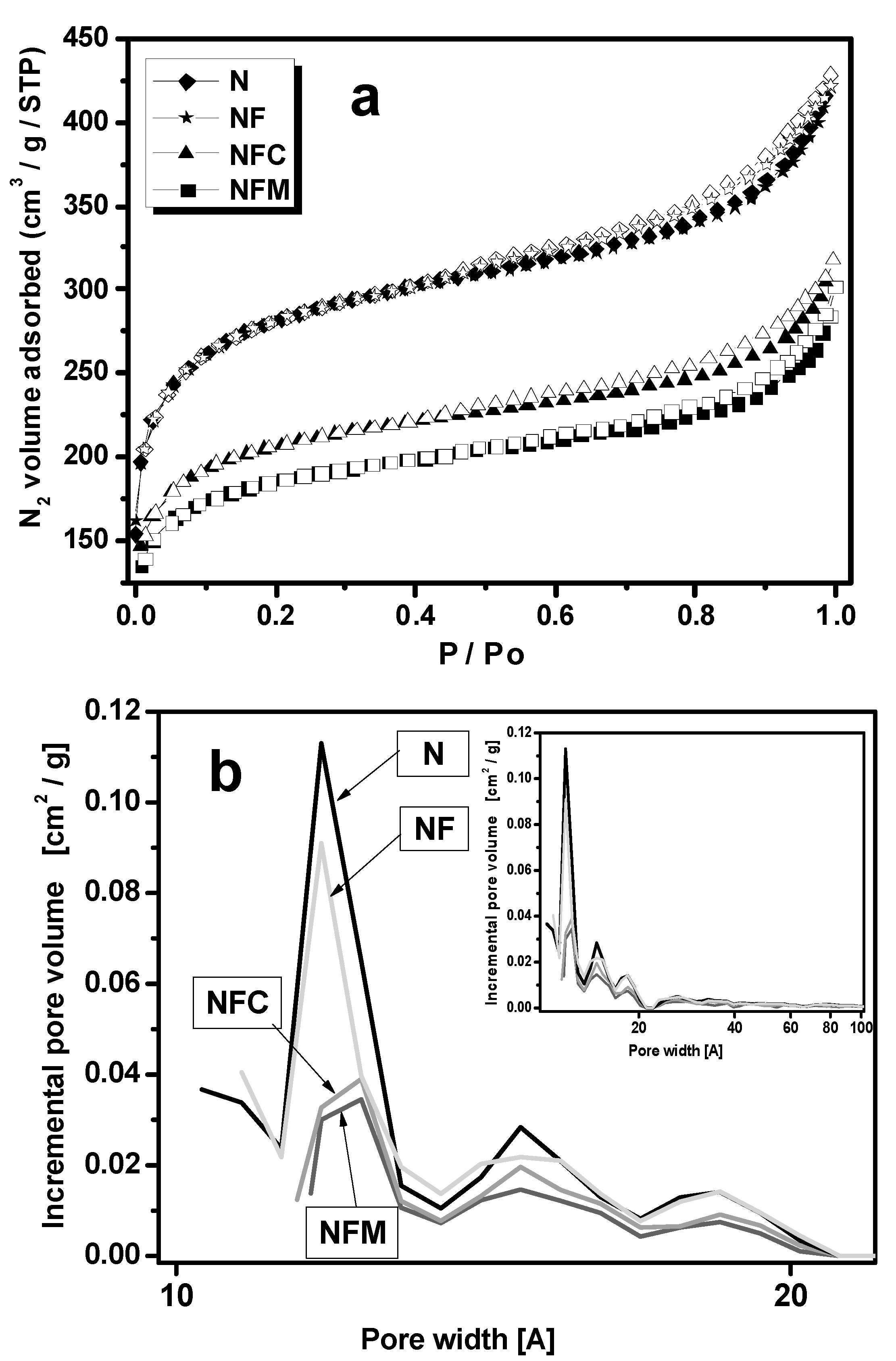
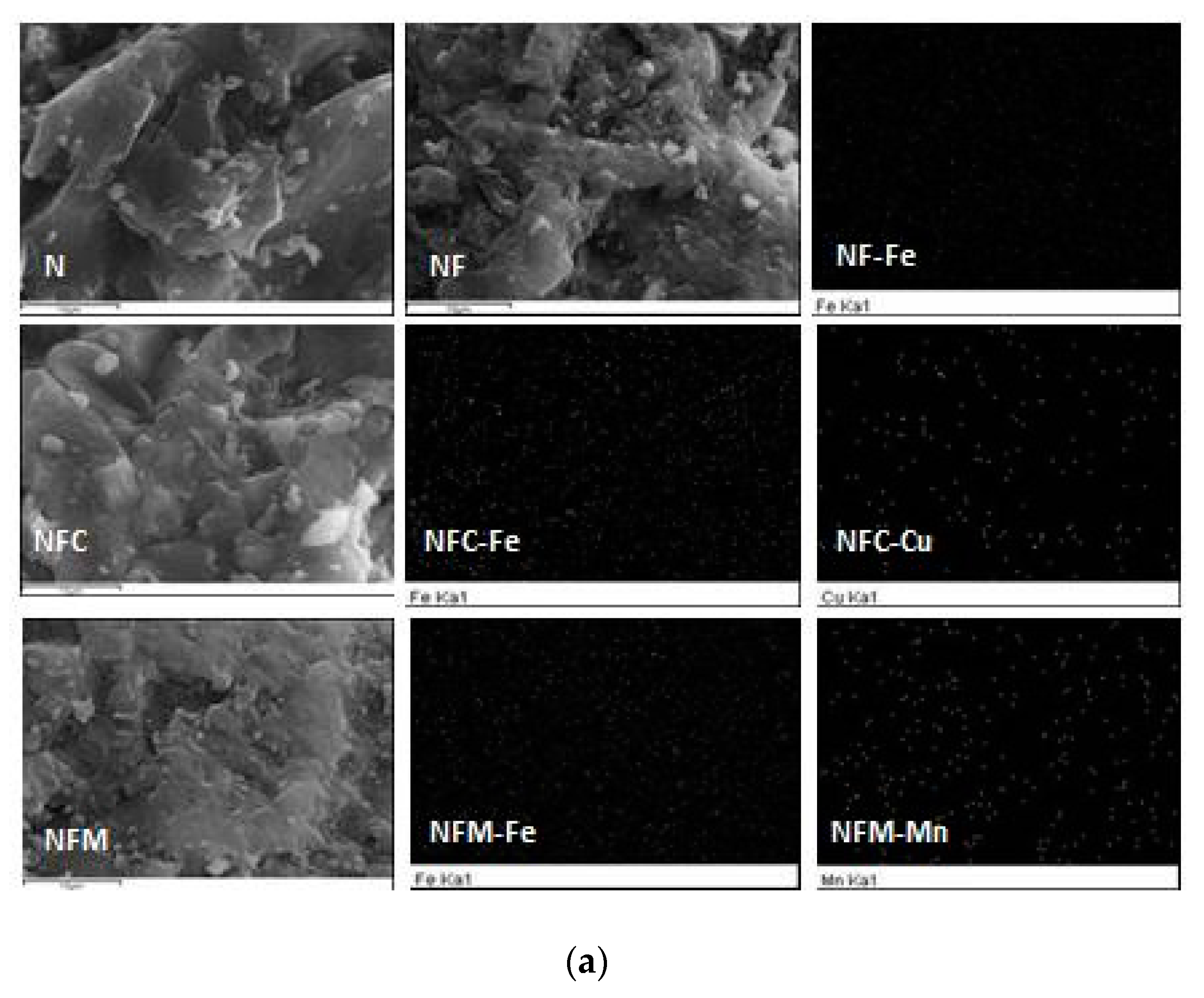
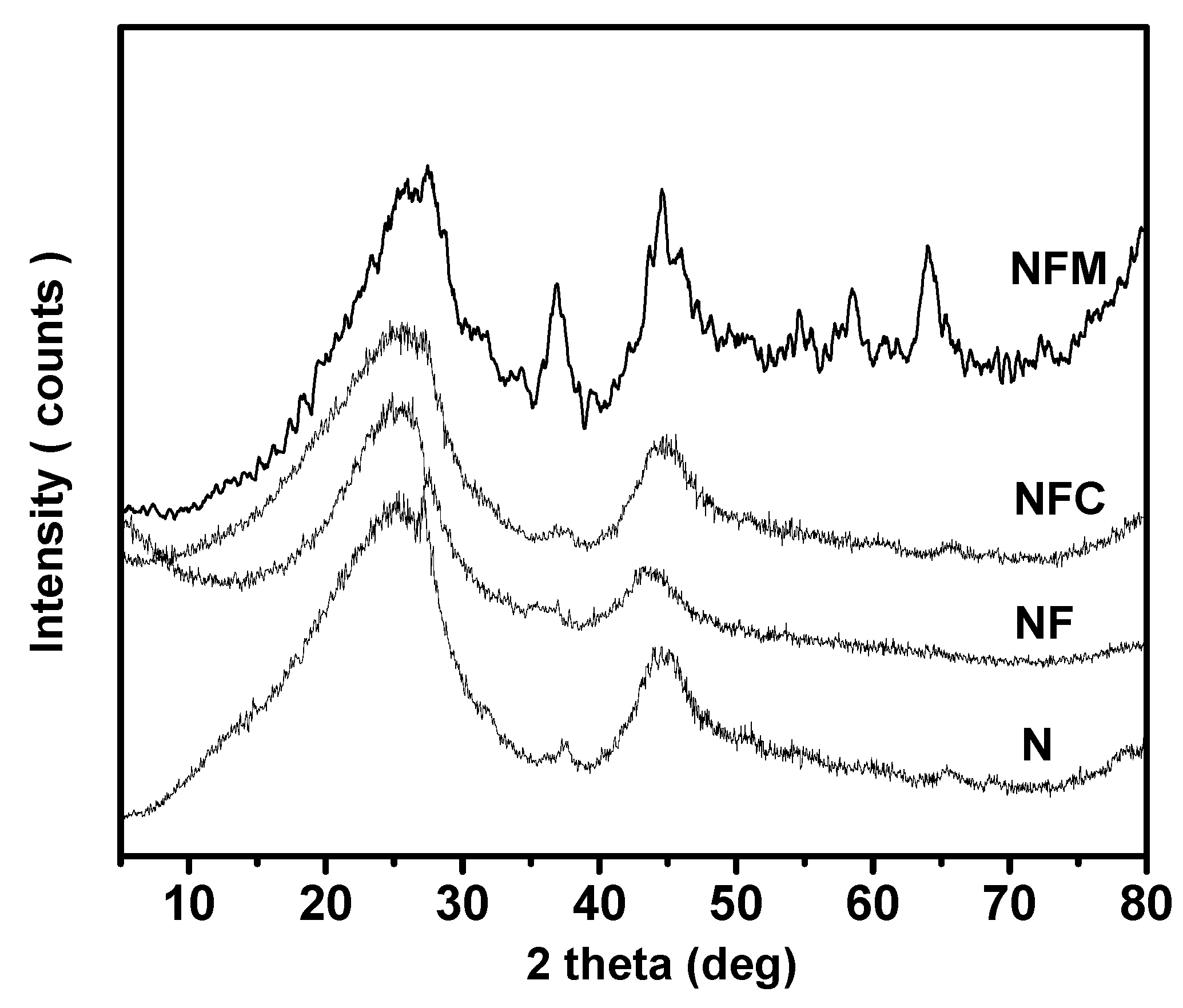
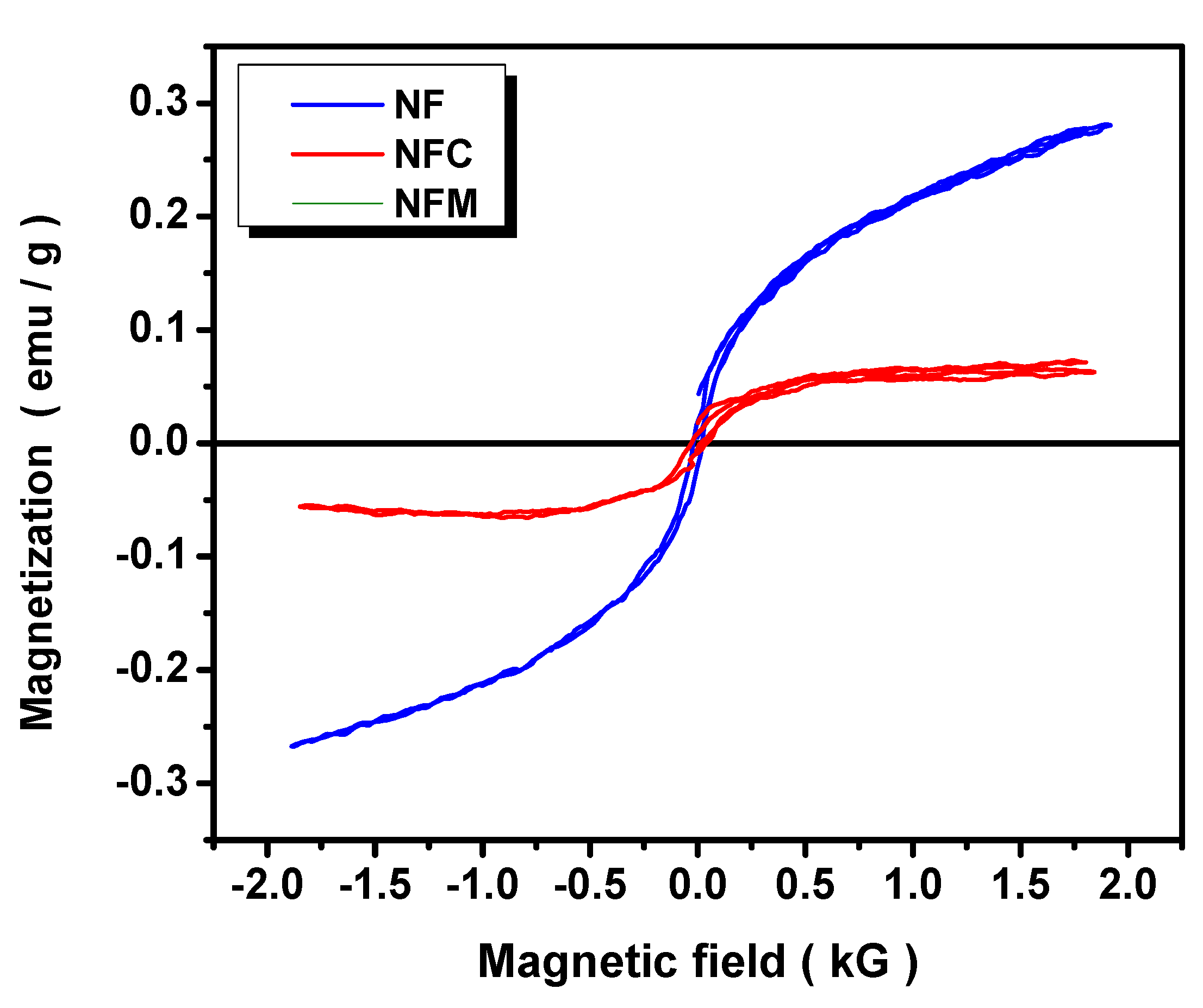
3.2. Materials Characterization
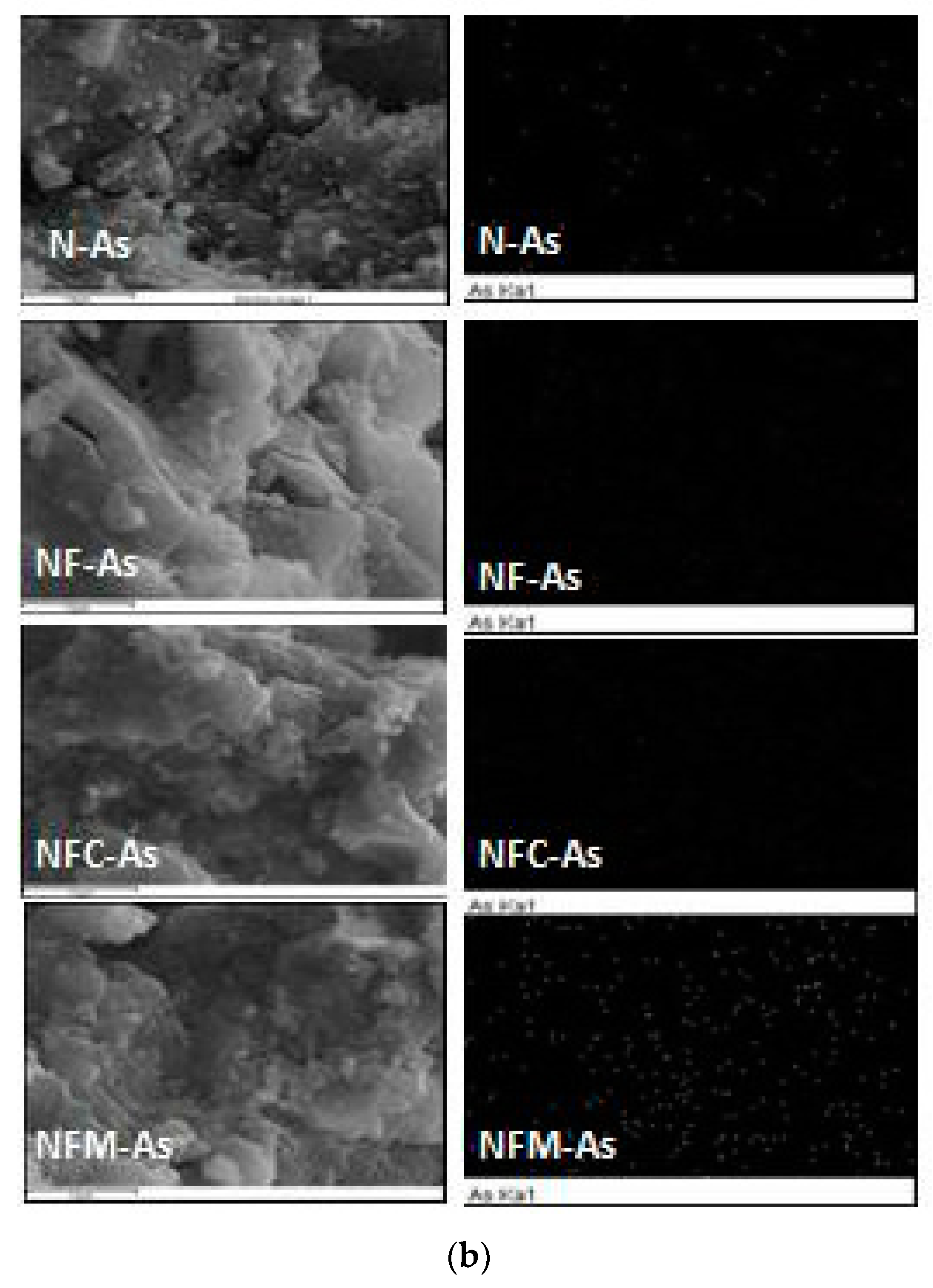
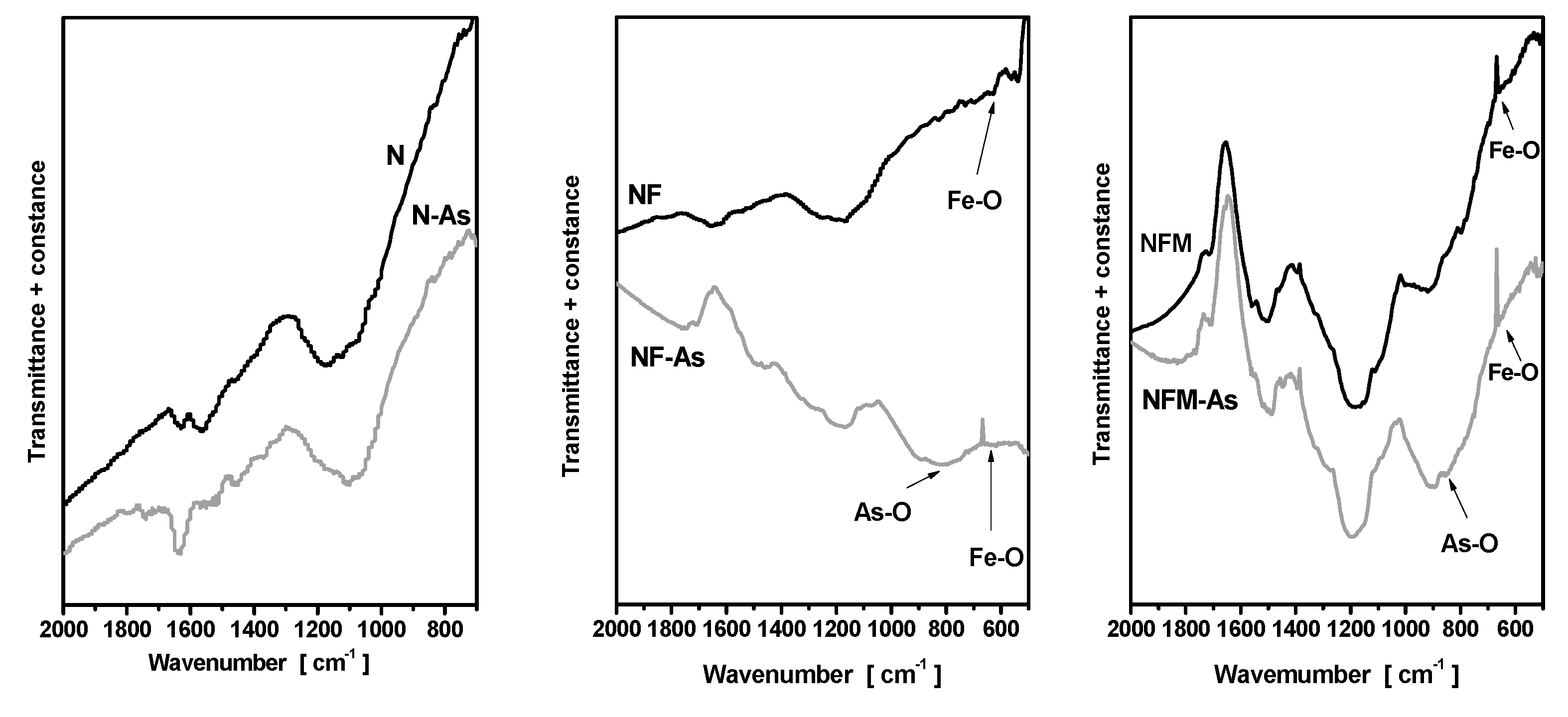
3.3. Adsorption Mechanism
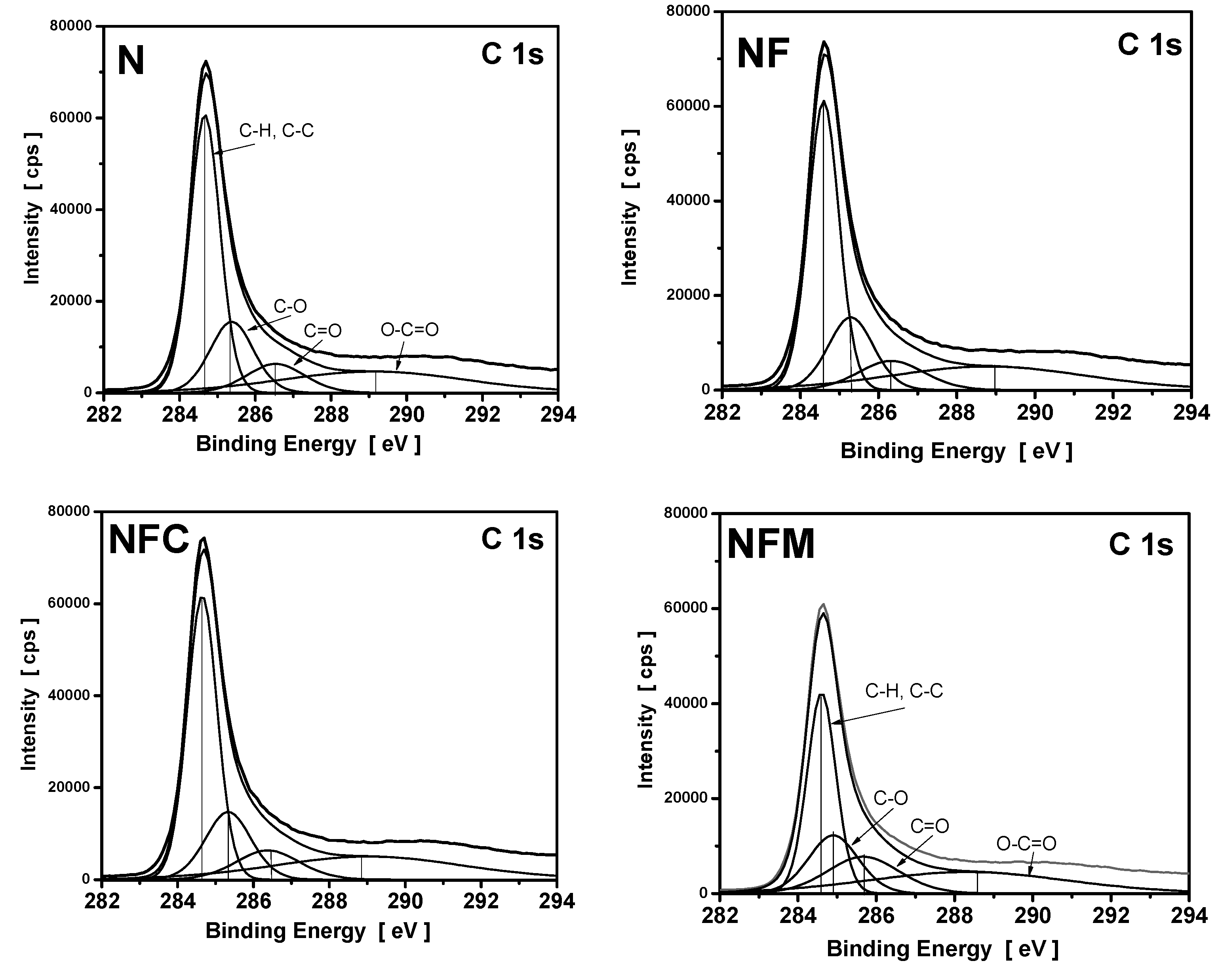
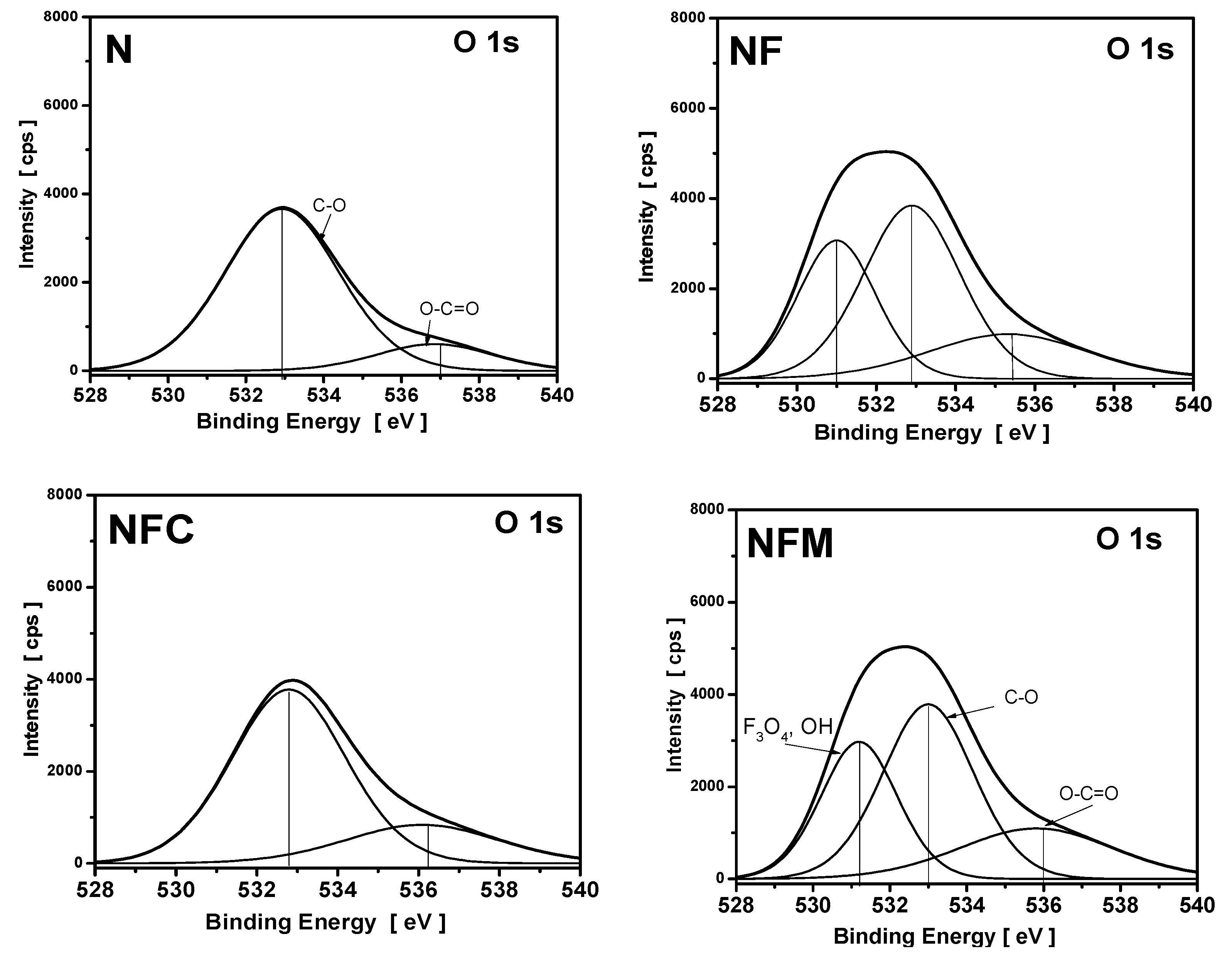
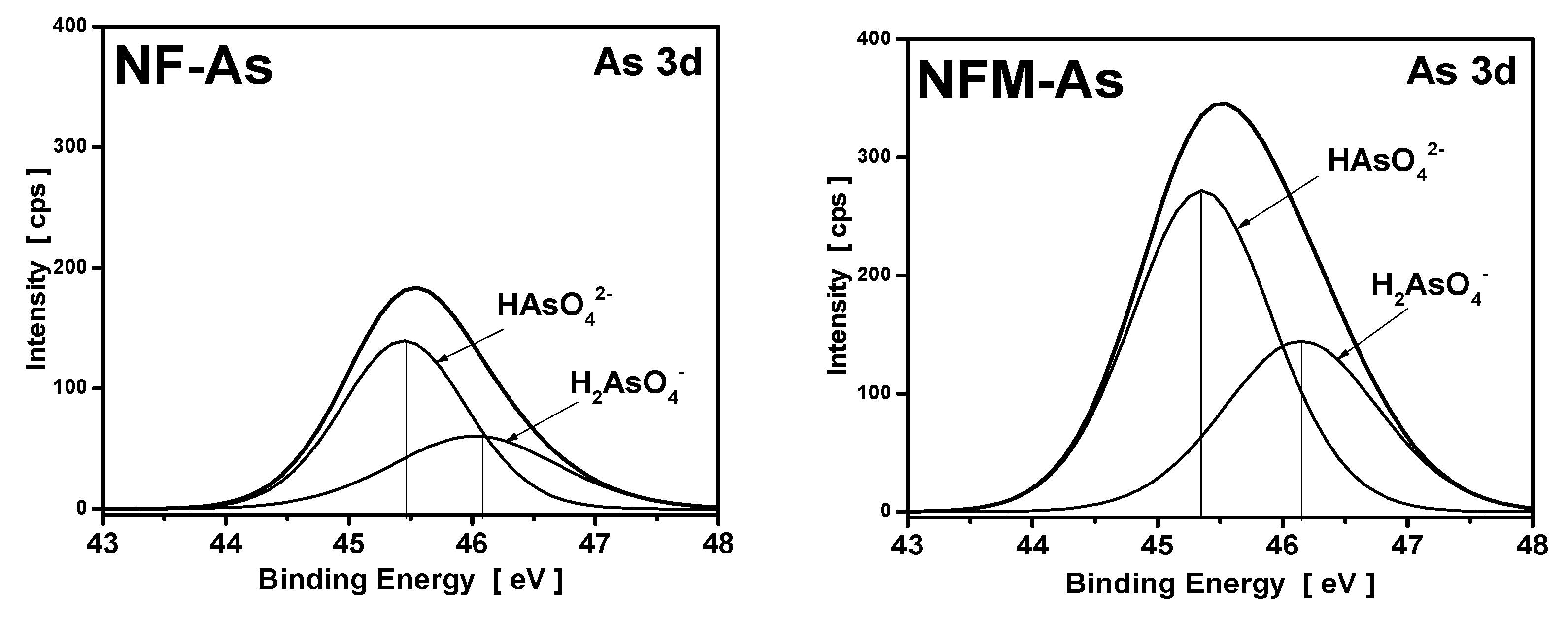
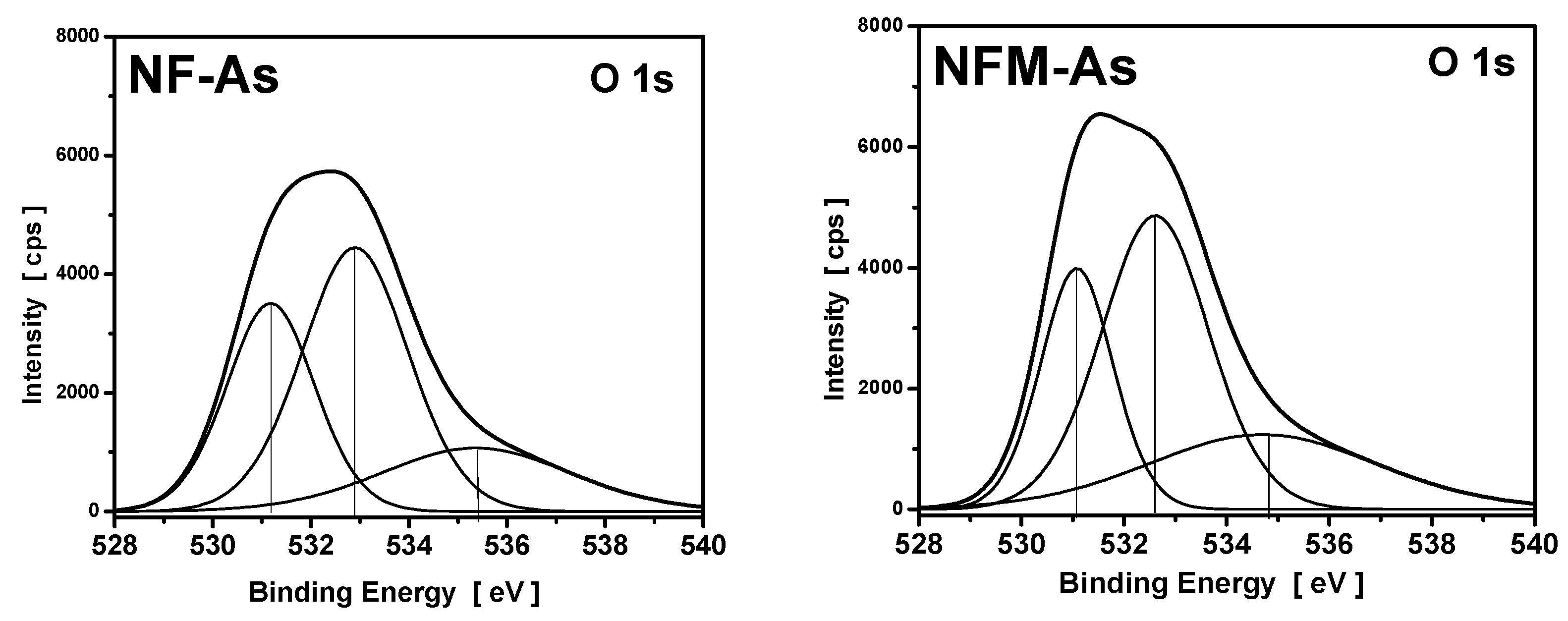
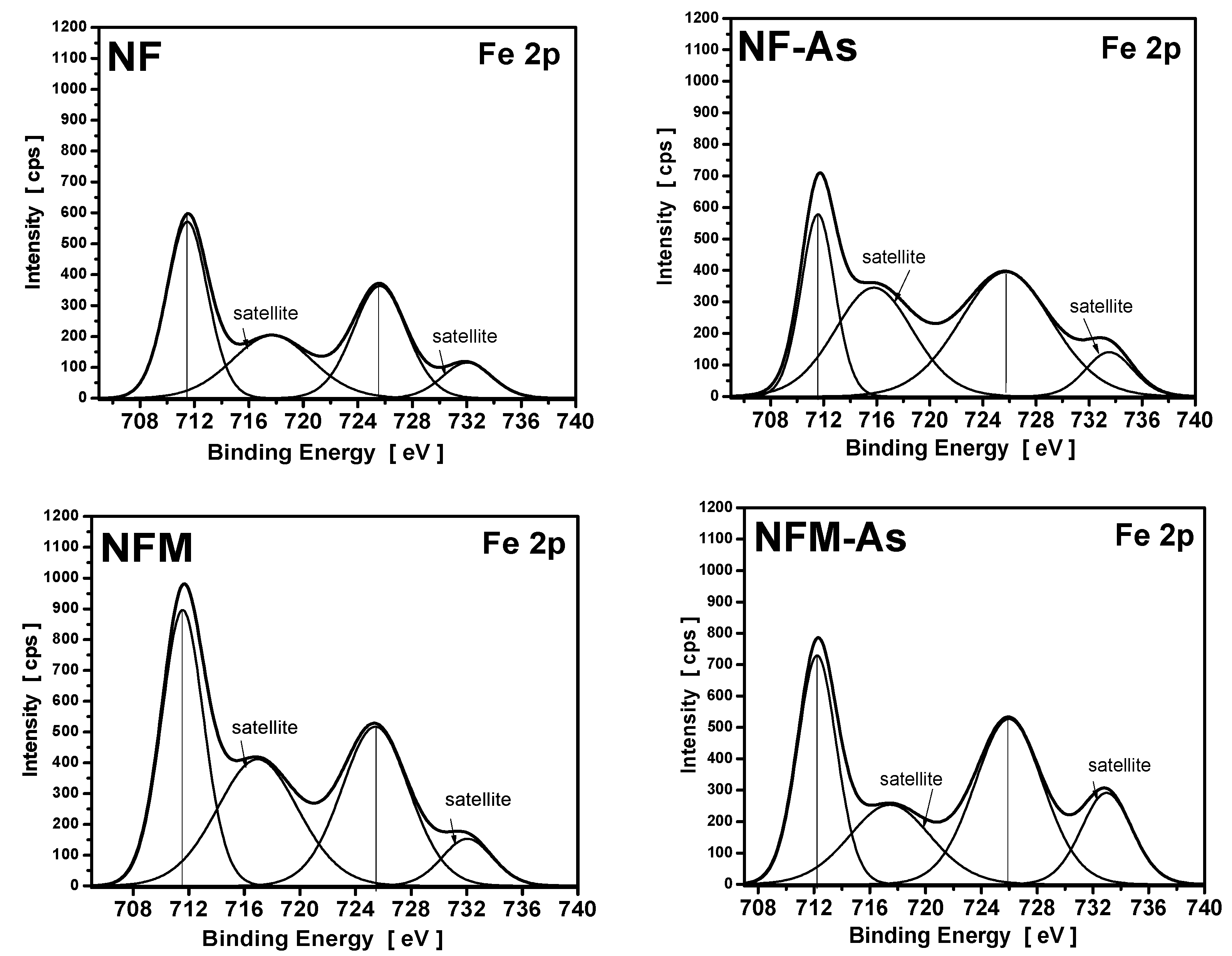
3.4. XPS Measurements
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Preventing Disease through Healthy Environments. 2010. Available online: http://www.who.int/ipcs/features/arsenic.pdf?ua=1 (accessed on 4 December 2014).
- Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Hug, S.J.; Ammann, A.; Zikoudi, A.; Hatziliontos, C. Arsenic speciation and uranium concentrations in drinking water supply wells in Northern Greece: Correlations with redox indicative parameters and implications for groundwater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 383, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Zouboulis, A.I. Comparative evaluation of conventional and alternative methods for the removal of arsenic from contaminated groundwaters. Rev. Environ. Health 2006, 21, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Mitrakas, M.; Zouboulis, A.I. Arsenic occurrence in Europe: Emphasis in Greece and description of the applied full-scale treatment plants. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 54, 2100–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, M.C.; Vu, N.D.; Ammann, A.; Le, V.C.; Kissner, R.; Pham, H.V.; Cao, T.H.; Berg, M.; Von Gunten, U. Kinetics and mechanistic aspects of As(III) oxidation by aqueous chlorine, chloramines, and ozone: Relevance to drinking water treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 3285–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Zouboulis, A.I.; Mitrakas, M.; Althoff, H.W.; Bartel, H. A hybrid system incorporating a pipe reactor and microfiltration for biological iron, manganese and arsenic removal from anaerobic groundwater. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2013, 22, 3848–3853. [Google Scholar]
- Hering, J.G.; Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Theoduloz, G.A.; Berg, M.; Hug, S.J. Arsenic removal from drinking water: Experiences with technologies and constraints in practice. J. Environ. Eng. 2017, 143, 03117002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deliyanni, E.A.; Bakoyannakis, D.N.; Zouboulis, A.I.; Matis, K.A. Sorption of As(V) ions by akaganeite-type nanocrystals. Chemosphere 2003, 50, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaclavikova, Μ.; Gallios, G.P.; Misaelides, P.; Hredzak, S.; Matik, M.; Gesperova, D. The treatment of Waste Waters Containing Heavy Metals by Magnetic Nanoparticles. Acta Montan. Slovaca 2004, 9, 414–417. [Google Scholar]
- Vaclavikova, M.; Gallios, G.; Matik, M.; Jakabsky, S.; Hredzak, S. The Synthesis and Characterization of Fe Nanostructures inside Porous Zeolites and Their Applications in Water Treatment Technologies. In NATO ASI on Carbon Nanotubes; NATO Science Series II: Mathematics, Physics and Chemistry; Popov, V., Lambin, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2005; Volume 222, pp. 239–240. [Google Scholar]
- Ricci Nicomel, N.; Leus, K.; Folens, K.; Van Der Voort, P.; Du Laing, G. Technologies for Arsenic Removal from Water: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Voegelin, A.; Zouboulis, A.I.; Hug, S.J. Enhanced As(III) oxidation and removal by combined use of zero valent iron and hydrogen peroxide in aerated waters at neutral pH values. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 297, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitela-Rodriguez, A.V.; Rangel-Mendez, J.R. Arsenic removal by modified activated carbons with iron hydro (oxide) nanoparticles. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 114, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mũniz, G.; Fierro, V.; Celzard, A.; Furdin, G.; Gonzalez-Sαnchez, G.; Ballinas, M.L. Synthesis, characterization and performance in arsenic removal of iron-doped activated carbons prepared by impregnation with Fe(III) and Fe(II). J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.L.; Lin, Y.C.; Chen, X.; Gao, N.Y. A method for preparing ferric activated carbon composites adsorbents to remove arsenic from drinking water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 148, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Q.; Lin, W.; Ying, W. Preparation of iron-impregnated granular activated carbon for arsenic removal from drinking water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 184, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto-Delgado, C.; Rangel-Mendez, J.R. Anchorage of iron hydro (oxide) nanoparticles onto activated carbon to remove As(V) from water. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2973–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, A.M.; Hristovski, K.D.; Möller, T.; Westerhoff, P.; Sylvester, P. The effect of carbon type on arsenic and trichloroethylene removal capabilities of iron (hydr)oxide nanoparticle-impregnated granulated activated carbons. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 183, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seung, H.H. Thermal reduction of graphene oxide. In Physics and Applications of Graphene—Experiments; Mikhailov, S., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; pp. 73–90. [Google Scholar]
- Triantafyllidis, K.S.; Deliyanni, E.A. Desulfurization of diesel fuels: Adsorption of 4,6-DMDBT on different origin and surface chemistry nanoporous activated carbons. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 236, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM). Standard Practice for Checking the Operating characteristics of X-Ray Photoelectron Spectrometers (ASTM E902-88). In Annual Book of ASTM Standards; American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM). Chemical Analysis of Metals and Metal Bearing Ores; Des. E87-58, Reappr. 1978; American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1982; Part 12. [Google Scholar]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surface of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H. Uber Dye Adsorption in hosungen. Z. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 387–470. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Li, X.-Y.; Chen, J.P. An XPS study for mechanisms of arsenate adsorption onto a magnetite-doped activated carbon fiber. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 343, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deliyanni, E.; Bandosz, T.J. Importance of carbon surface chemistry in development of iron–carbon composite adsorbents for arsenate removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, M.; Kaddour, S.; Trari, M. Kinetic and equilibrium studies of cobalt adsorption on apricot stone activated carbon. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Castilla, C.; Álvarez-Merino, M.A.; Pastrana-Martínez, L.M.; López-Ramón, M.V. Adsorption mechanisms of metal cations from water on an oxidized carbon surface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 345, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Nasser, A.; El-Hendawy, A.; Alexander, J.; Andrews, R.J.; Forrest, G. Effects of activation schemes on porous, surface and thermal properties of activated carbons prepared from cotton stalks. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2008, 82, 272–278. [Google Scholar]
- Liou, T.H. Development of mesoporous structure and high adsorption capacity of biomass-based activated carbon by phosphoric acid and zinc chloride activation. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 158, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, K.S. IUPAC Recommendations, Reporting physisorption data for gas s-1olid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity. Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girgis, B.S.; Temerk, Y.M.; Gadelra, M.M.; Abdullah, I.D. X-ray Diffraction Patterns of Activated Carbons Prepared under Various Conditions. Carbon Sci. 2007, 8, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakintuna, B.; Yurum, Y. Evolution of Carbon Microstructures during the Pyrolysis of Turkish Elbistan Lignite in the Temperature Range 700–1000 °C. Energy Fuels 2004, 18, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Fan, Y.; Huang, Y. Facile Low Temperature Hydrothermal Synthesis of Magnetic Mesoporous Carbon Nanocomposite for Adsorption Removal of Ciprofloxacin Antibiotics. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 2604–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Deliyanni, E.A.; Lazaridis, N.K. Magnetic modification of microporous carbon for dye adsorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 430, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varshney, D.; Yogi, A. Structural and transport properties of stoichiometric Mn2+-doped magnetite: Fe3−xMnxO4. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 128, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, H.W.P.; Hammer, P.; Pulcinelli, S.H.; Santilli, C.V.; Molina, E.F. Improvement of the photocatalytic activity of magnetite by Mn-incorporation. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2014, 181, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Phan, N.H.; Do, M.H.; Ngo, K.T. Magnetic Fe2MO4 (M:Fe, Mn) activated carbons: Fabrication, characterization and heterogeneous Fenton oxidation of methyl orange. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Shen, C.H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, C.; Chen, S.H.; Xu, Z.H.; Shi, D.; Li, J.; Gao, H. Highly ordered self-assembly with large area of Fe3O4 nanoparticles and the magnetic properties. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 23233–23236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masala, O.; Seshadri, R. Magnetic properties of capped, soluble MnFe2O4 nanoparticles. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2005, 402, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, D.; Gupta, K.; Ghosh, A.Κ.; De, A.; Banerjee, S.; Ghosh, U.C. Manganese-incorporated iron(III) oxide–graphene magnetic nanocomposite: Synthesis, characterization, and application for the arsenic(III)-sorption from aqueous solution. J. Nanopart. Res. 2012, 14, 1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.R.; Yanful, E.K.; Pratt, A.R. Arsenic removal from aqueous solutions by mixed magnetite–maghemite nanoparticles. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 64, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco, J.A.; Josue, D.B.; Rios-Hurtado, J.C.; Rangel-Mendez, J.R. Influence of iron content, surface area and charge distribution in the arsenic removal by activated carbons. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 249, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Qu, J.; Liu, H.; Cooper, A.T.; Wu, R. CuFe2O4/activated carbon composite: A novel magnetic adsorbent for the removal of acid orange II and catalytic regeneration. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayo, J.T.; Yavuz, C.; Yean, S.; Cong, L.; Shipley, H.; Yu, W.; Falkner, J.; Kan, A.; Tomson, M.; Colvin, V.L. The effect of nanocrystalline magnetite size on arsenic removal. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2007, 8, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Freundlich | Langmuir | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KF | 1/n | R2 | Qmax | KL | R2 | |
| N | 0.015 | 1.2778 | 0.9995 | - | - | - |
| NF | 3.437 | 0.2671 | 0.9691 | 11.05 | 0.1797 | 0.7299 |
| NFC | 2.881 | 0.2908 | 0.9748 | 10.87 | 0.1175 | 0.7879 |
| NFM | 7.344 | 0.238 | 0.9471 | 19.35 | 0.3000 | 0.9523 |
| Carbon Samples | Iron Content (m %) | SBET (m2 g−1) | Vtot (cm3 g−1) | Vmeso (cm3 g−1) | Vmicro (cm3 g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 0 | 980.4 | 0.67 | 0.16 | 0.33 |
| NF | 14, σ = 0.05 | 973.4 | 0.65 | 0.16 | 0.33 |
| NFC | 8.4, σ = 10−6 | 670.3 | 0.49 | 0.11 | 0.25 |
| NFM | 6.4, σ = 10−6 | 649.4 | 0.47 | 0.11 | 0.22 |
| Carbons | Binding Energy (eV) | Calculated Charge (Q*, esu) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1s | Fe2p | O1s | Fe2p | |
| NF | 532.3 | 711.5 | −0.7348 | 1.5179 |
| NF-As | 532.1 | 711.8 | −0.7471 | 1.6149 |
| NFM | 532.5 | 711.8 | −0.7226 | 1.6149 |
| NFM-As | 531.5 | 712.2 | −0.7841 | 1.7604 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gallios, G.P.; Tolkou, A.K.; Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Stefusova, K.; Vaclavikova, M.; Deliyanni, E.A. Adsorption of Arsenate by Nano Scaled Activated Carbon Modified by Iron and Manganese Oxides. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9101684
Gallios GP, Tolkou AK, Katsoyiannis IA, Stefusova K, Vaclavikova M, Deliyanni EA. Adsorption of Arsenate by Nano Scaled Activated Carbon Modified by Iron and Manganese Oxides. Sustainability. 2017; 9(10):1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9101684
Chicago/Turabian StyleGallios, George P., Athanasia K. Tolkou, Ioannis A. Katsoyiannis, Katarina Stefusova, Miroslava Vaclavikova, and Eleni A. Deliyanni. 2017. "Adsorption of Arsenate by Nano Scaled Activated Carbon Modified by Iron and Manganese Oxides" Sustainability 9, no. 10: 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9101684
APA StyleGallios, G. P., Tolkou, A. K., Katsoyiannis, I. A., Stefusova, K., Vaclavikova, M., & Deliyanni, E. A. (2017). Adsorption of Arsenate by Nano Scaled Activated Carbon Modified by Iron and Manganese Oxides. Sustainability, 9(10), 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9101684








