Novel and Conventional Technologies for Landfill Leachates Treatment: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Leachate Characteristics and Main Issues
- Step 1: aerobic phase;
- Step 2: anaerobic and acidogenic phase;
- Step 3: methanogenic phase (unstable);
- Step 4: stable methanogenic phase.
- L = volume of leachate;
- P = rainfall;
- R = surface runoff;
- R* = surface runoff from external areas;
- ET = evapotranspiration;
- J = irrigation and/or recirculation of leachate;
- IS = infiltration water from surface water bodies;
- IG = infiltration water from groundwater;
- ΔUS = variations of water content in the capping material;
- ΔUW = variation of water content in the amount of disposed waste;
- b = production or consumption of water associated with the different aerobic and anaerobic biochemical degradation reactions of organic substances.
- leachate is formed mainly in wet and rainy areas;
- leachate is extremely variable and follows the precipitation trends;
- leachate amounts are a function of the efficiency of the coverage of capping and continue to be generated for long periods.
3. Review of the Main Landfill Leachate Treatment Technologies
- (a)
- biological processes (aerobic or anaerobic);
- (b)
- chemical and physical processes;
- (c)
- a combination of physical-chemical and biological processes.
3.1. Biological Treatment
- Aerobic treatment allows reducing organic pollutants and is able to accomplish nitrification processes. It exhibits rapid removal kinetics, low sensitivity for the presence of toxic substances and considerable efficiency in ammonia stripping. As disadvantages, there is a remarkable production of excess sludge and great energy costs due to the high amount of oxygen required.
- Anaerobic and anoxic processes are based on the activity of microorganisms able to break down organic matter within the environment with no dissolved oxygen. Notwithstanding the several benefits of the anaerobic treatment, the application processes are limited, mainly due to the low growth rate of anaerobic microorganisms, ineffective NH4-N removal and poor retention of biomass [19]. These processes do not require aeration systems, and thus treatment costs are contained, also allowing energy recovery by biogas collection and exploitation. They are characterized by low reaction kinetics and low biomass growth as compared to aerobic systems.
3.1.1. Aerobic Treatments
Aerated Lagoons
Constructed Wetlands (CW)
Aerated Reactors
- high sludge production, which involves considerable costs for disposal;
- significant energy demand;
- the presence of inhibitor microorganisms due to the high concentrations of NH4-N.
Rotating Biological Contactors (RBCs)
Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR)
Trickling Filters (TFs)
Moving Bed Bioreactor (MBBR)
Fluidized Bed Bioreactors (FBBR)
Membrane Biological Reactor (MBR)
Membrane-Aerated Biofilm Reactor (MABR)
Single Reactor High Activity Ammonium Removal Over Nitrite (SHARON)
3.1.2. Anaerobic and Anoxic Treatment
Up-Flow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB)
Submerged Anaerobic MBR (SAMBR)
Anaerobic Filter (AF)
Anaerobic Ammonium Oxidation (Anammox)
3.2. Physical-Chemical Treatment
3.2.1. Flocculation-Coagulation
- FeCl3 (3000 mg/L): it removes 67.3% of COD and 87% of turbidity;
- FeCl3 (3000 mg/L) added with polyelectrolyte in variable quantities: it removes 64% of COD and 100% of turbidity.
3.2.2. Separation Treatments with Membrane Filtration
- High transmembrane pressure: 50–60 bar required to win the osmosis pressure; it means that high energy amounts are necessary;
- The fouling phenomenon which entails frequent surface cleaning processes.
3.2.3. Air Stripping
3.2.4. Adsorption by Activated Carbon (AC)
3.2.5. Chemical Precipitation
3.2.6. Ion Exchange
3.2.7. Chemical Oxidation and Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOP)
Fenton Process
Photocatalysis
- post-separation methods of titanium after water treatment;
- depth of light penetration into the aqueous titanium suspension;
- low quantum efficiencies of the degradation process on the irradiated catalyst;
- the catalyst turnover number and catalyst poisoning also need to be further investigated.
3.2.8. Electrochemical Processes
Electro-Coagulation
- i)
- formation of the coagulating electrode through the sacrificial electrolytic oxidation;
- ii)
- pollutants and suspended particles being destabilized and emulsions breaking;
- iii)
- aggregation of destabilized phases and the formation of flakes.
Electro-Oxidation
- Direct oxidation allows the polluting particles to exchange electrons directly with the anode surface. This method does not appear to be effective in the degradation of organic material; despite that, it promotes the formation of very powerful oxidizing agents that are used for indirect oxidation;
- Indirect EO takes place when high chlorine compounds are concentrated within the leachate. The active chlorine is oxidized by the anode producing hypochlorite, which has a strong oxidation effect with respect to the organic compounds [145]. This reaction is particularly suitable for saline leachates, where many pollutants are removed, such as ammonium, and with the presence of metal ions (Ag+, Fe3+, Co3+, Ni2+).
- i)
- implement this technology combining other techniques, either as a pre-treatment or as a finishing step;
- ii)
- introduce renewable energy within the system.
3.3. Combination of Physical-Chemical and Biological Processes
3.3.1. Combined Treatments Introduced in 2016
SAMBR–MBR (Synthetic Leachate, London)
SBBGR–EO (Italy)
SBR–Fenton-Like–SBR Post-Oxidation (Estonia)
Aerobic Lagoon–Activated Sludge Biological Pre-Oxidation–Coagulation–Photo-Fenton (Portugal)
Photo-Electro-Fenton Process–Membrane Bio Reactor (India)
Trickling Filters—Electro-Coagulation (Magnesium-Based Anode) (Canada)
Fenton Process–Passive Aerated Immobilized Biomass (PAB) (Egypt)
Aerobic SBR–Zeolite Adsorption (Malaysia)
Co-Treatment Constructed Wetland–Adsorption by ZELIAC/Zeolite (Iran)
MBR–UF–EO (Québec, Canada)
MBR-PAC to Activated Sludge–NF (Iran)
4. Discussion
5. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vaccari, M.; Torretta, V.; Collivignarelli, C. Effect of improving environmental sustainability in developing countries by upgrading solid waste management techniques: A case study. Sustainability 2012, 4, 2852–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guerrero, L.A.; Maas, G.; Hogland, W. Solid waste management challenges for cities in developing countries. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatham-Stephens, K.; Caravanos, J.; Ericson, B.; Landrigan, P.; Fuller, R. The pediatric burden of disease from lead exposure at toxic waste sites in low and middle income countries. Environ. Res. 2014, 132, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raboni, M.; Torretta, V.; Urbini, G.; Viotti, P. Automotive shredder residue: A survey of the hazardous organic micro-pollutants spectrum in landfill biogas. Waste Manag. Res. 2015, 33, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, R.; Chowdhury, M.A.I.; Hasan, G.M.J.; Karanjit, B.; Shrestha, L.R. Generation, storage, collection and transportation of municipal solid waste–A case study in the city of Kathmandu, capital of Nepal. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 1088–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Sabbagh, M.K.; Velis, C.A.; Wilson, D.C.; Cheeseman, C.R. Resource management performance in Bahrain: A systematic analysis of municipal waste management, secondary material flows and organizational aspects. Waste Manag. Res. 2012, 30, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Oloibiri, V.; Chys, M.; Audenaert, W.; Decostere, B.; He, Y.; Van Langenhove, H.; Demeestere, K.; Van Hulle, S.W. The present status of landfill leachate treatment and its development trend from a technological point of view. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2015, 14, 93–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilić, M.; Nikolić, M. Drivers for development of circular economy–A case study of Serbia. Habitat Int. 2016, 56, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, A.U.; Lehmann, S. Urban growth and waste management optimization towards ‘zero waste city’. City Cult. Soc. 2011, 2, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EEA (European Environment Agency). Managing Municipal Solid Waste. A Review of Achievements in 32 European Countries. EEA Report. 2013. Available online: http://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/managing-municipal-solid-waste (accessed on 25 October 2016).
- Kjeldsen, P.; Barlaz, M.A.; Rooker, A.P.; Baun, A.; Ledin, A.; Christensen, T.H. Present and long-term composition of MSW landfill leachate: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 32, 297–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, T.H.; Kjeldsen, P.; Bjerg, P.L.; Jensen, D.L.; Christensen, J.B.; Baun, A.; Albrechtsen, H.J.; Heron, G. Biogeochemistry of landfill leachate plumes. Appl. Geochem. 2001, 16, 659–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaruddin, M.A.; Yusoff, M.S.; Aziz, H.A.; Hung, Y.T. Sustainable treatment of landfill leachate. Appl. Water Sci. 2015, 5, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bove, D.; Merello, S.; Frumento, D.; Arni, S.A.; Aliakbarian, B.; Converti, A. A Critical Review of Biological Processes and Technologies for Landfill Leachate Treatment. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2015, 38, 2115–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renou, S.; Givaudan, J.G.; Poulain, S.; Dirassouyan, F.; Moulin, P. Landfill leachate treatment: Review and opportunity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 150, 468–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Qian, G.; Liu, J.; Xu, Z.P. Anaerobic methanogenesis of fresh leachate from municipal solid waste: A brief review on current progress. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 49, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collivignarelli, C. II Trattamento del Percolato da Discarica RSU Situazioni e Prospettive; CIPA: Brescia, Italy, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Wiszniowski, J.; Robert, D.; Surmacz-Gorska, J.; Miksch, K.; Weber, J.V. Landfill Leachate Treatment Methods: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2006, 4, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, Z.; Zou, X.; Feng, J.; Wu, Z. Microbial communities in an anaerobic dynamic membrane bioreactor (AnDMBR) for municipal wastewater treatment: Comparison of bulk sludge and cake layer. Process Biochem. 2013, 48, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalini, S.S.; Joseph, K. Nitrogen management in landfill leachate: Application of SHARON, ANAMMOX and combined SHARON–ANAMMOX process. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 2385–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Gohary, F.A.; Kamel, G. Characterization and biological treatment of pre-treated landfill leachate. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 94, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frascari, D.; Bronzini, F.; Giordano, G.; Tedioli, G.; Nocentini, M. Long-term characterization, lagoon treatment and migration potential of landfill leachate: a case study in an active Italian landfill. Chemosphere 2004, 54, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulc, T.G. Long term performance of a constructed wetland for landfill leachate treatment. Ecol. Eng. 2006, 26, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spengel, D.B.; Dzombak, D.A. Treatment of landfill leachate with rotating biological contactors: bench-scale experiments. Res. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1991, 63, 971–981. [Google Scholar]
- Neczaj, E.; Okoniewska, E.; Kacprazak, M. Treatment of landfill leachate by sequencing batch reactor. Desalination 2005, 185, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluko, O.O.; Sridhar, M.K.C. Evaluation of leachate treatment by trickling filter and sequencing batch reactor processes in Ibadan, Nigeria. Waste Manag. Res. 2013, 31, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loukidou, M.X.; Zouboulis, A.I. Comparison of two biological treatment process using attached-growth biomass for sanitary landfill leachate treatment. Environ. Pollut. 2001, 111, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldyasti, A.; Chowdhury, N.; Nakhla, G.; Zhu, J. Biological nutrient removal from leachate using a pilot liquid–solid circulating fluidized bed bioreactor (LSCFB). J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashisho, J.; El-Fadel, M.; Al-Hindi, M.; Salam, D.; Alameddine, I. Hollow fiber vs. flat sheet MBR for the treatment of high strength stabilized landfill leachate. Waste Manag. 2016, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visvanathan, C.; Choudhary, M.K.; Montalboa, M.T.; Jegatheesan, V. Landfill leachate treatment using thermophilic membrane Bioreactor. Desalination 2007, 204, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khin, T.; Annachhatre, A.P. Novel microbial nitrogen removal processes. Biotechnol. Adv. 2004, 22, 519–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.Y.; Chang, F.Y.; Chang, C.H. Co-digestion of leachate with septage using a UASB reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2000, 73, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettunen, R.H.; Rintala, J.A. Performance of an on-site UASB reactor treating leachate at low temperature. Water Resour. 1998, 32, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddoud, A.; Ellouze, M.; Dhouib, A.; Sayadi, S. Anaerobic membrane bioreactor treatment of domestic wastewater in Tunisia. Desalination 2007, 207, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.A.; Jingsong, G.; Ping, L.Z.; Ya, P. Y.; Al-Rekabi, W.S. Review on Landfill Leachate Treatments. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2009, 5, 534–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Banks, C.J. Treatment of a high-strength sulphate-rich alkaline leachate using an anaerobic filter. Waste Manag. 2007, 27, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Miao, L.; Cao, T.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S.; Han, J. Continuous-flow combined process of nitritation and ANAMMOX for treatment of landfill leachate. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 214, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nhat, P.T.; Biec, H.N.; Mai, N.T.T.; Thanh, B.X.; Dan, N.P. Application of a partial nitritation and anammox system for the old landfill leachate treatment. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 95, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, M.K.; Adetutu, E.; Nedwell, D.B.; Ball, A.S. In situ microbial treatment of landfill leachate using aerated lagoons. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 2741–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kivaisi, A.K. The potential for constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment and reuse in developing countries: A review. Ecol. Eng. 2001, 16, 545–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.L.; Williamson, K.L.; Owen, A.G. Phytoremediation of landfill leachate. Waste Manag. 2006, 26, 825–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinbile, C.O.; Yusoff, M.S.; Zuki, A.A. Landfill leachate treatment using sub-surface flow constructed wetland by Cyperus haspan. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 1387–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foladori, P.; Ruaben, J.; Ortigara, A.R. Recirculation or artificial aeration in vertical flow constructed wetlands: a comparative study for treating high load wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 149, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dan, A.; Fujii, D.; Soda, S.; Machimura, T.; Ike, M. Removal of phenol, bisphenol A, and 4-tert-butylphenol from synthetic landfill leachate by vertical flow constructed wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Ranieri, E.; Fratino, U.; Petrella, A.; Torretta, V.; Rada, E.C. Ailanthus Altissima and Phragmites Australis for chromium removal from a contaminated soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, Y.; Ishigaki, T.; Ebie, Y.; Sutthasil, N.; Chiemchaisri, C.; Yamada, M. Water reduction by constructed wetlands treating waste landfill leachate in a tropical region. Waste Manag. 2015, 44, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortez, S.; Teixeira, P.; Oliveira, R.; Mota, M. Rotating biological contactors: A review on main factors affecting performance. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2008, 7, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castillo, E.; Vergara, M.; Moreno, Y. Landfill leachate treatment using a rotating biological contactor and an upward-flow anaerobic sludge bed reactor. Waste Manag. 2007, 27, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.W.; Tay, J.H. A unified theory for upscaling aerobic granular sludge sequencing batch reactors. Biotechnol. Adv. 2005, 23, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Ji, M.; Li, R.; Qin, F. Organic and nitrogen removal from landfill leachate in aerobic granular sludge sequencing batch reactors. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, L.; Wang, S.; Li, B.; Cao, T.; Xue, T.; Peng, Y. Advanced nitrogen removal via nitrite using stored polymers in a modified sequencing batch reactor treating landfill leachate. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 192, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, B.; Warith, M.A.; Burns, S.D. Comparison of Shredded Tire Chips and Tire Crumbs as Packing Media in Trickling Filters. Water Qual. Res. J. Can. 2007, 42, 319–326. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, A.; Warith, M.; Liu, J.; Mondal, B. Determination of the Suitable Size of Tire Chips for Landfill Leachate Treatment. Available online: http://geoserver.ing.puc.cl/info/conferences/PanAm2011/panam2011/pdfs/GEO11Paper1073.pdf (accessed on 25 October 2016).
- Jokela, J.P.Y.; Kettunen, R.H.; Sormunen, K.M.; Rintala, J.A. Biological nitrogen removal from municipal landfill leachate: Low-cost nitrification in biofilters and laboratory scale in-situ denitrification. Water Resour. 2002, 36, 4079–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hem, L.J.; Rusten, B.; Ødegaard, H. Nitrification in a moving bed biofilm reactor. Water Res. 1994, 28, 1425–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welander, U.; Henrysson, T.; Welander, T. Biological nitrogen removal from municipal landfill leachate in a pilot scale suspended carrier biofilm process. Water Resour. 1998, 4, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Sun, D.; Chung, J.S. Simultaneous removal of COD and ammonium from landfill leachate using an anaerobic–aerobic moving-bed biofilm reactor system. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werther, J.; Hartge, E.U.; Heinrich, S. Fluidized-Bed Reactors–Status and Some Development Perspectives. Chemie Ingenieur Technik 2014, 86, 2022–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Zhu, J.; Nakhla, G. Simultaneous carbon, nitrogen and phosphorous removal from municipal wastewater in a circulating fluidized bed bioreactor. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christianson, L.; Lepine, C.; Tsukuda, S.; Saito, K.; Summerfelt, S. Nitrate removal effectiveness of fluidized sulfur-based autotrophic denitrification biofilters for recirculating aquaculture systems. Aquacult. Eng. 2015, 68, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerfelt, S.T. Design and management of conventional fluidized-sand biofilters. Aquacult. Eng. 2006, 34, 275–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, N.; Nakhla, G.; Zhu, J.; Islam, M. Pilot-scale experience with biological nutrient removal and biomass yield reduction in a liquid-solid circulating fluidized bed bioreactor. Water Environ. Res. 2010, 82, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Zhao, H.; Ge, L.; Chen, Z.; Dang, Y.; Sun, D. Comparison of the performance of waste leachate treatment in submerged and recirculated membrane bioreactors. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 102, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkotsis, P.K.; Batsari, E.L.; Peleka, E.N.; Tolkou, A.K.; Zouboulis, A.I. Fouling control in a lab-scale MBR system: Comparison of several commercially applied coagulants. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.; Ma, W.; Judd, S.J. Membrane bioreactors: two decades of research and implementation. Desalination 2011, 273, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Zhang, H.F.; Yang, F.; Liu, L. Characterization of cake layer in submerged membrane bioreactor. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 4065–4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Kitade, T.; Chong, T.H.; Uemura, T.; Fane, A.G. Role of initially formed cake layers on limiting membrane fouling in membrane bioreactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 118, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanguanpak, S.; Chiemchaisri, C.; Chiemchaisri, W.; Yamamoto, K. Influence of operating pH on biodegradation performance and fouling propensity in membrane bioreactors for landfill leachate treatment. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 102, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.N.; Lan, C.Q. Treatment of landfill leachate using membrane bioreactors: A review. Desalination 2012, 287, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, S.; Terada, A.; Tsuneda, S. Modeling of membrane-aerated biofilm: effects of C/N ratio, biofilm thickness and surface loading of oxygen on feasibility of simultaneous nitrification and denitrification. Biochem. Eng. J. 2007, 37, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankhania, M.; Stephenson, T.; Semmens, M.J. Hollow-fiber bioreactor for waste-water treatment using bubbleless membrane aeration. Water Resour. 1994, 28, 2233–2236. [Google Scholar]
- Semmens, M.J.; Dahm KShanahan, J.; Christianson, A. COD and nitrogen removal by biofilms growing on gas permeable membranes. Water Resour. 2003, 37, 4343–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syron, E.; Semmens, M.J.; Casey, E. Performance analysis of a pilot-scale membrane aerated biofilm reactor for the treatment of landfill leachate. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 273, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zhang, P.; Li, G.; Yin, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, X. Effect of COD/N ratio on nitrogen removal in a membrane-aerated biofilm reactor. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 113, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claros, J.; Serralta, J.; Seco, A.; Ferrer, J.; Aguado, D. Real-time control strategy for nitrogen removal via nitrite in a SHARON reactor using pH and ORP sensors. Process Biochem. 2012, 47, 1510–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, K.J.; Lentz, E.M. Treatment of landfill leachate using sequencing batch and continuous flow upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactors. Water Res. 2000, 34, 3640–3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seghezzo, L.; Zeeman, G.; van Lier, J.B.; Hamelers, H.V.M.; Lettinga, G. A review: the anaerobic treatment of sewage in UASB and EGSB reactors. Bioresour. Technol. 1998, 65, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Yang, Q.; Peng, Y.; Shi, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, S. Advanced landfill leachate treatment using a two-stage UASB-SBR system at low temperature. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.L.; Stadler, L.B.; Love, N.G.; Skerlos, S.J.; Raskin, L. Perspectives on anaerobic membrane bioreactor treatment of domestic wastewater: a critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 122, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohdziewicz, J.; Neczaj, E.; Kwarciak, A. Landfill leachate treatment by means of anaerobic membrane bioreactor. Desalination 2008, 221, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunacheva, C.; Soh, Y.N.A.; Trzcinski, A.P.; Stuckey, D.C. Soluble Microbial Products (SMPs) in the Effluent from a Submerged Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor (SAMBR) under Different HRTs and Transient Loading Conditions. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umaiyakunjaram, R.; Shanmugam, P. Study on submerged anaerobic membrane bioreactor (SAMBR) treating high suspended solids raw tannery wastewater for biogas production. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 216, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Show, K.Y.; Tay, J.H. Influence of support media on biomass growth and retention in anaerobic filters. Water Res. 1999, 33, 1471–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourari, S.; Achkari-Begdouri, A. Use of baked clay media as biomass supports for anaerobic filters. Appl. Clay Sci. 1997, 12, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, J.G.; Prasad, D.; Young, H. Removal of organics from leachates by anaerobic filter. Water Res. 1987, 21, 1395–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartal, B.; Kuenen, J.G.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Sewage treatment with anammox. Science 2010, 328, 702–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, L.; Wang, S.; Cao, T.; Peng, Y. Optimization of three-stage Anammox system removing nitrogen from landfill leachate. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 185, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Lo, W.H.; Chan, G.Y. Physico-chemical treatments for removal of recalcitrant contaminants from landfill leachate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 129, 80–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, F.; Wang, Q. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assou, M.; Madinzi, A.; Anouzla, A.; Aboulhassan, M.A.; Souabi, S.; Hafidi, M. Reducing pollution of stabilized landfill leachate by mixing of coagulants and flocculants: A comparative study. Int. J. Eng. Innov. Technol. 2014, 4, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Ameen, E.S.; Muyibi, S.A.; Abdulkarim, M.I. Microfiltration of pretreated sanitary landfill leachate. Environmentalist 2011, 31, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linde, K.; Jönsson, A.S. Nanofiltration of salt solutions and landfill leachate. Desalination 1995, 103, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, T.A. Purification of landfill leachate with reverse osmosis and nanofiltration. Desalination 1998, 119, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chianese, A.; Ranauro, R.; Verdone, N. Treatment of landfill leachate by reverse osmosis. Water Res. 1999, 33, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marttinen, S.K.; Kettunen, R.H.; Sormunen, K.M.; Soimasuo, R.M.; Rintala, J.A. Screening of physical–chemical methods for removal of organic material, nitrogen and toxicity from low strength landfill leachates. Chemosphere 2002, 46, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, I.; Altinbas, M.; Koyuncu, I.; Arikan, O.; Gomec-Yangin, C. Advanced physico-chemical treatment experiences on young municipal landfill leachates. Waste Manag. 2003, 23, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.C.; Dezotti, M.; Sant’Anna, G.L. Treatment and detoxication of a sanitary landfill leachate. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ching, S.L.; Yusoff, M.S.; Aziz, H.A.; Umar, M. Influence of impregnation ratio on coffee ground activated carbon as landfill leachate adsorbent for removal of total iron and orthophosphate. Desalination 2011, 279, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, M.J.; Aziz, H.A.; Yusoff, M.S.; Adlan, M.N. Application of response surface methodology (RSM) for optimization of ammoniacal nitrogen removal from semi-aerobic landfill leachate using ion exchange resin. Desalination 2010, 254, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haapea, P.; Korhonen, S.; Tuhkanen, T. Treatment of industrial landfill leachates by chemical and biological methods: ozonation, ozonation + hydrogen peroxide, hydrogen peroxyde and biological posttreatment for ozonated water. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2002, 24, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigot, V.; Luck, F.; Paillard, H.; Wagner, A. Landfill leachate treatment: comparison of three oxidation processes using ozone. In Proceedings of the International Ozone Association Regional Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, August 1994.
- Hilles, A.H.; Amr, S.S.A.; Hussein, R.A.; El-Sebaie, O.D.; Arafa, A.I. Performance of combined sodium persulfate/H2O2 based advanced oxidation process in stabilized landfill leachate treatment. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 166, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, A.; Pagano, M.; Volpe, A.; Di Pinto, A. Fenton’s pre-treatment of mature landfill leachate. Chemosphere 2004, 54, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.W.; Hwang, K.Y. Effects of reaction conditions on the oxidation efficiency in the Fenton process. Water Resour. 2000, 34, 2786–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Englehardt, J.D. Treatment of landfill leachate by the Fenton process. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3683–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.P.; Hong, S.C.; Hong, S.I. Study of the end point of photocatalytic degradation of landfill leachate containing refractory matter. Chem. Eng. J. 2004, 98, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Qin, Q. UV-TiO2 photocatalytic degradation of landfill leachate. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 217, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.; Pacheco, M.J.; Cirìaco, L.; Lopes, A. Review on the electrochemical processes for the treatment of sanitary landfill leachates: Present and future. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 176, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rada, E.C.; Istrate, I.A.; Ragazzi, M.; Andreottola, G.; Torretta, V. Analysis of electro-oxidation suitability for landfill leachate treatment through an experimental study. Sustainability 2013, 5, 3960–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verma, M.; Kumar, R.N. Can coagulation–flocculation be an effective pre-treatment option for landfill leachate and municipal wastewater co-treatment? Perspect. Sci. 2016, 8, 492–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marañón, E.; Castrillón, L.; Fernández-Nava, Y.; Fernández-Méndez, A.; Fernández-Sánchez, A. Coagulation–flocculation as a pretreatment process at a landfill leachate nitrification–denitrification plant. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 156, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amokrane, A.; Comel, C.; Veron, J. Landfill leachates pretreatment by coagulation–flocculation. Water Resour. 1997, 31, 2775–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolkou, A.; Zouboulis, A. Review of Recent Patents on Coagulation/Flocculation (C/F) Process: Methods and Applications with Emphasis on Phosphates Removal. Recent Pat. Mater. Sci. 2014, 7, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolkou, A.; Zouboulis, A. Synthesis and coagulation performance of composite poly-aluminum-ferric-silicate-chloride coagulants in water and wastewater. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 53, 3309–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsi, A.A.; Zouboulis, A.I.; Matis, K.A.; Samaras, P. Coagulation–flocculation pretreatment of sanitary landfill leachates. Chemosphere 2003, 53, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, H.A.; Alias, S.; Adlan, M.N.; Asaari, A.H.; Zahari, M.S. Colour removal from landfill leachate by coagulation and flocculation processes. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 218–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atab, M.S.; Smallbone, A.J.; Roskilly, A.P. An operational and economic study of a reverse osmosis desalination system for potable water and land irrigation. Desalination 2016, 397, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insel, G.; Dagdar, M.; Dogruel, S.; Dizge, N.; Cokgor, E.U.; Keskinler, B. Biodegradation characteristics and size fractionation of landfill leachate for integrated membrane treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 260, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, M.H.; Chen, Y.H.; Tsai, J.Y.; Chang, C.Y. Ammonia removal from ammonia-rich wastewater by air stripping using a rotating packed bed. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2016, 102, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, K.C.; Chu, L.M.; Wong, M.H. Ammonia stripping as a pretreatment for landfill leachate. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1997, 94, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B.H. An overview of landfill leachate treatment via activated carbon adsorption process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dąbrowski, A. Adsorption—From theory to practice. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 93, 135–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, L.B.; Peng, J.H.; Li, N.; Zhu, X.Y. Preparation of high surface area activated carbons from tobacco stems with K2CO3 activation using microwave radiation. Ind. Crops Prod. 2008, 27, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehzad, A.; Bashir, M.J.; Sethupathi, S.; Lim, J.W. An overview of heavily polluted landfill leachate treatment using food waste as an alternative and renewable source of activated carbon. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2015, 98, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Hur, J. Heterogeneous adsorption behavior of landfill leachate on granular activated carbon revealed by fluorescence excitation emission matrix (EEM)-parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC). Chemosphere 2016, 149, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, J.; Castrillón, L.; Marañón, E.; Sastre, H.; Fernández, E. Removal of non-biodegradable organic matter from landfill leachates by adsorption. Water Resour. 2004, 38, 297–303. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.K.; Townsend, T.G.; Mazyck, D.; Boyer, T.H. Equilibrium and intra-particle diffusion of stabilized landfill leachate onto micro-and meso-porous activated carbon. Water Res. 2012, 46, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Z.; Zhao, Q.L.; Hao, X.D. Ammonium removal from landfill leachate by chemical precipitation. Waste Manag. 1999, 19, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collivignarelli, C.; Sorlini, S. Potabilizzazione Delle Acque; Dario Flaccovio Editore: Palermo, Italy, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Janin, A.; Blais, J.F.; Mercier, G.; Drogui, P. Selective recovery of Cr and Cu in leachate from chromated copper arsenate treated wood using chelating and acidic ion exchange resins. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, Y.; Maranon, E.; Castrillón, L.; Vázquez, I. Removal of Cd and Zn from inorganic industrial waste leachate by ion exchange. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 126, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreozzi, R.; Caprio, V.; Insola, A.; Marotta, R. Advanced oxidation processes (AOP) for water purification and recovery. Catal. Today 1999, 53, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wable, O.; Jousset, M.; Courant, P.; Duguet, J.P. Oxidation of landfill leachates by ozone and hydrogen peroxide: A French example. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Ozone-Oxidation Methods for Water and Wastewater treatment, Berlin, Germany, 26–28 April 1993.
- Schulte, P.; Bayer, A.; Kuhn, F.; Luy, T.; Volkmer, M. H2O2/O3, H2O2/UV and H2O2/Fe2+ processes for the oxidation of hazardous wastes. Ozone Sci. Eng. 1995, 17, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Morais, J.L.; Zamora, P.P. Use of advanced oxidation processes to improve the biodegradability of mature landfill leachates. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 123, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oller, I.; Malato, S.; Sánchez-Pérez, J. Combination of advanced oxidation processes and biological treatments for wastewater decontamination—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 4141–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbusiński, K. The modified Fenton process for decolorization of dye wastewater. Polish J. Environ. Stud. 2005, 14, 281–285. [Google Scholar]
- Benatti, C.T.; Tavares, C.R.G. Fentons Process for the Treatment of Mixed Waste Chemicals, Faculdade Ingá–UNINGÁ, Universidade Estadual de Maringá–UEM: Vila Esperanca, Brazil, 2012; unpublished work.
- Silva, T.F.C.V.; Fonseca, A.; Saraiva, I.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Vilar, V.J.P. Scale-up and cost analysis of a photo-Fenton system for sanitary landfill leachate treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 283, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotvajn, A.Ž.; Zagorc-Končan, J.; Cotman, M. Fenton’s oxidative treatment of municipal landfill leachate as an alternative to biological process. Desalination 2011, 275, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Torres-Socías, E.; Prieto-Rodríguez, L.; Zapata, A.; Fernández-Calderero, I.; Oller, I.; Malato, S. Detailed treatment line for a specific landfill leachate remediation. Brief economic assessment. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 261, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Zhao, Y.; Xie, B. Employing TiO2 photocatalysis to deal with landfill leachate: Current status and development. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 285, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhezila, F.; Hariti, M.; Lounici, H.; Mameri, N. Treatment of the OUED SMAR town landfill leachate by an electrochemical reactor. Desalination 2011, 280, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orkun, M.O.; Kuleyin, A. Treatment performance evaluation of chemical oxygen demand from landfill leachate by electro-coagulation and electro-fenton technique. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2012, 31, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, L.; Chang, J.; Wen, T. Indirect oxidation effect in electrochemical oxidation treatment of landfill leachate. Water Resour. 1995, 29, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Yu, Z.; Wei, Q.; Long, H.Y.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Y. Electrochemical oxidation of biological pretreated and membrane separated landfill leachate concentrates on boron doped diamond anode. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 377, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panizza, M.; Martinez-Huitle, C.A. Role of electrode materials for the anodic oxidation of a real landfill leachate—Comparison between Ti–Ru–Sn ternary oxide, PbO2 and boron-doped diamond anode. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 1455–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moraes, P.B.; Bertazzoli, R. Electro-degradation of landfill leachate in a flow electrochemical reactor. Chemosphere 2005, 58, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, A.H. Landfill leachate treatment. Membr. Technol. 2005, 2005, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, J.P.; Beslec, D.A.; Atwater, J.A.; Mavinic, D.S. Treatment of methanegenic landfill leachate to remove ammonia using a rotating biological contactor. Environ. Technol. 1997, l8, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słomczyńska, B.; Słomczyński, T. Physic-Chemical and Toxicological Characteristics of Leachates from MSW Landfills. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2004, 13, 627–637. [Google Scholar]
- Kargi, F.; Pamukoglu, M. Repeated fed-batch biological treatment of pretreated landfill leachate by powdered actived carbon addition. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2004, 34, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heavey, M. Low-cost treatment of landfill leachate using peat. Waste Manag. 2003, 23, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Liu, J.X. Landfill leachate treatment with a novel process: Anaerobic ammonium oxidation (Anammox) combined with soil infiltration system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 151, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasar, H.; Unsal, S.A.; Ipek, U.; Karatas, S.; Cınar, O.; Yaman, C.; Kınacı, C. Stripping/flocculation/membrane bioreactor/reverse osmosis treatment of municipal landfill leachate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Iaconi, C.; De Sanctis, M.; Rossetti, S.; Mancini, A. Bio-chemical treatment of medium-age sanitary landfill leachates in a high synergy system. Process Biochem. 2011, 46, 2322–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Iaconi, C.; Di Rossetti, S.; Lopez, A.; Ried, A. Effective treatment of stabilized municipal landfill leachates. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 168, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar]
- Tugtas, A.E.; Cavdar, P.; Calli, B. Bio-electrochemical post-treatment of anaerobically treated landfill leachate. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 128, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, C.; Wu, Z. An anaerobic dynamic membrane bioreactor (AnDMBR) for landfill leachate treatment: Performance and microbial community identification. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 161, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Wu, W.; Shi, P.; Guo, J.; Cheng, J. Characterization of dissolved organic matter in landfill leachate during the combined treatment process of air stripping, Fenton, SBR and coagulation. Waste Manag. 2015, 41, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, M.C.S.; Moravia, W.G.; Lange, L.C.; Roberto, M.M.Z.; Magalhães, N.C.; dos Santos, T.L. Nanofiltration as post-treatment of MBR treating landfill leachate. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 53, 1482–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.L.; Oloibiri, V.; Chys, M.; De Wandel, S.; Decostere, B.; Audenaert, W.; He, Y.L.; Van Hulle, S.W.H. Integration of autotrophic nitrogen removal, ozonation and activated carbon filtration for treatment of landfill leachate. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 275, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, W.; Feng, D.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Z. Self-powered denitration of landfill leachate through ammonia/nitrate coupled redox fuel cell reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 203, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trzcinski, A.P.; Stuckey, D.C. Inorganic fouling of an anaerobic membrane bioreactor treating leachate from the organic fraction of municipal solid waste (OFMSW) and a polishing aerobic membrane bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 204, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Moro, G.; Prieto-Rodríguez, L.; De Sanctis, M.; Di Iaconi, C.; Malato, S.; Mascolo, G. Landfill leachate treatment: Comparison of standalone electrochemical degradation and combined with a novel biofilter. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 288, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, K.; Kivi, A.; Dulova, N.; Zekker, I.; Mölder, E.; Tenno, T.; Trapido, M.; Tenno, T. A pilot study of three-stage biological–chemical treatment of landfill leachate applying continuous ferric sludge reuse in Fenton-like process. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.F.; Soares, P.A.; Manenti, D.R.; Fonseca, A.; Saraiva, I.; Boaventura, R.A.; Vilar, V.J. An innovative multistage treatment system for sanitary landfill leachate depuration: Studies at pilot-scale. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 576, 99–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nivya, T.K.; Pieus, T.M. Comparison of Photo ElectroFenton Process (PEF) and combination of PEF Process and Membrane Bioreactor in the treatment of Landfill Leachate. Procedia Technol. 2016, 24, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oumar, D.; Patrick, D.; Gerardo, B.; Rino, D.; Ihsen, B.S. Coupling biofiltration process and electrocoagulation using magnesium-based anode for the treatment of landfill leachate. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 181, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, S.; Tawfik, A. Performance of passive aerated immobilized biomass reactor coupled with Fenton process for treatment of landfill leachate. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 111, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.K.; Seow, T.W.; Neoh, C.H.; Nor, M.H.M.; Ibrahim, Z.; Ware, I.; Sarip, S.H.M. Treatment of landfill leachate using ASBR combined with zeolite adsorption technology. 3 Biotech 2016, 6, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojiri, A.; Ziyang, L.; Tajuddin, R.M.; Farraji, H.; Alifar, N. Co-treatment of landfill leachate and municipal wastewater using the ZELIAC/zeolite constructed wetland system. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 166, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zolfaghari, M.; Jardak, K.; Drogui, P.; Brar, S.K.; Buelna, G.; Dubé, R. Landfill leachate treatment by sequential membrane bioreactor and electro-oxidation processes. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 184, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyravi, M.; Jahanshahi, M.; Alimoradi, M.; Ganjian, E. Old landfill leachate treatment through multistage process: Membrane adsorption bioreactor and nanofitration. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 39, 1803–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keenan, J.D.; Steiner, R.L.; Fungaroli, A.A. Landfill leachate treatment. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1984, 56, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Oakley, S.M.; Jimenez, R. Sustainable sanitary landfills for neglected small cities in developing countries: The semi-mechanized trench method from Villanueva, Honduras. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 2535–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Ye, X.; Chen, D.; Zheng, K.; Qin, F. Transformation of pollutants in landfill leachate treated by a combined sequence batch reactor, coagulation, Fenton oxidation and biological aerated filter technology. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2011, 89, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moravia, W.G.; Amaral, M.C.; Lange, L.C. Evaluation of landfill leachate treatment by advanced oxidative process by Fenton’s reagent combined with membrane separation system. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassano, D.; Zapata, A.; Brunetti, G.; Del Moro, G.; Di Iaconi, C.; Oller, I.; Malato, S.; Mascolo, G. Comparison of several combined/integrated biological-AOPs setups for the treatment of municipal landfill leachate: Minimization of operating costs and effluent toxicity. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 172, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, K.; Hossain, M.D.; Shams, S. Different treatment strategies for highly polluted landfill leachate in developing countries. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 2096–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
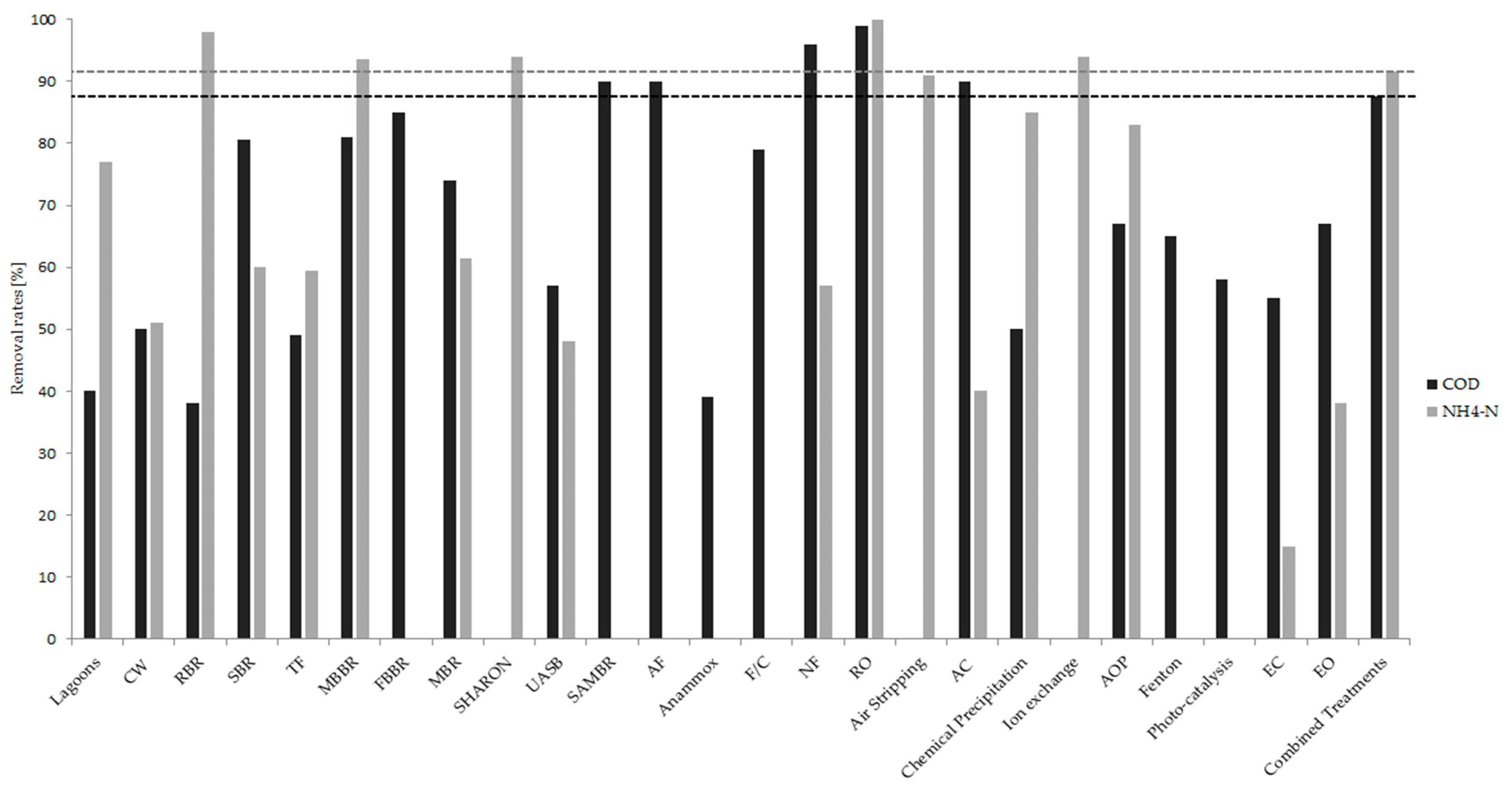
| Technology | References | Pollutant Removal Rates (%) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COD | BOD | NH4-N | TN | PO43− | Cl− | Heavy Metals | Fe | SS | SO42− | Turbidity | ||
| Aerobic Methods | ||||||||||||
| Lagoons | [22] | 40 | 64 | 77 | 42 | 27 | 30 | 44 | ||||
| Constructed Wetlands | [23] | 50 | 59 | 51 | 53 | 35 | 84 | 49 | ||||
| Rotating Biological Contactors | [24] | 38 | 80 | 98 | ||||||||
| Sequencing Batch Reactor | [25,26] | 76, 85 | 84, / | 65, 55 | 23, / | 26, / | 62, / | |||||
| Trickling Filters | [26] | 49 | 77 | 59.5 | 56 | 73 | 72 | |||||
| MBBR | [27] | 60–81 | 92–95 | |||||||||
| FBBR | [28] | 85 | 80 | 70 | ||||||||
| MBR | [29,30] | 71, 79 | 93, 99 | 63, 60 | 87, / | |||||||
| SHARON | [31] | 90–98 | ||||||||||
| Anaerobic and Anoxic Methods | ||||||||||||
| UASB | [32,33] | 42, 55–75 | /, 72–95 | 48, / | 45, 45 | |||||||
| SAMBR | [34] | 90 | 88 | 100 | ||||||||
| AF | [35,36] | 90, 90 | ||||||||||
| Anammox | [37,38] | 62, 14–16 | 94, 80–94 | |||||||||
| Technology | References | Pollutant Removal Rates (%) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COD | BOD | NH4-N | TN | PO43− | Cl− | Heavy Metals | Fe | SS | SO42− | Turbidity | ||
| Flocculation/Coagulation | [90] | 79 | 90 | 93 | ||||||||
| Membrane Process | ||||||||||||
| MF | [91] | 99.6 | 98.3 | |||||||||
| NF | [92,93] | /, 96 | /, 42 | /, 57 | 70, / | /, 92 | ||||||
| RO | [93,94] | 99, / | 99.9, / | 98, 97 | ||||||||
| Air Stripping | [95,96,97] | 89, 85, 99.5 | ||||||||||
| Adsorption | [88,98] | /, 90 | /, 40 | 84,/ | /, 80–96 | 77, / | ||||||
| Chemical Precipitation | [89,96] | 50, / | 85, / | /, 92–100 | ||||||||
| Ion Exchange | [89,99] | /, 94 | 55–100, / | |||||||||
| AOP | [100,101,102] | 50, 70, 81 | /, /, 83 | |||||||||
| Fenton | [103,104,105] | 60, 45, 85 | ||||||||||
| Photo-catalysis | [106,107] | 56, 60 | ||||||||||
| Electrochemical Processes | ||||||||||||
| EC | [108] | 40–70 | 10–25 | |||||||||
| EO | [109] | 64–70 | 15–61 | |||||||||
| Technologies | Reference | Combined Treatments | BOD/COD | Pollutant Removal Rates (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COD | NH4-N | Total N | BOD | PO43− | SS | Heavy Metals | ||||
| SAMBR, BR | [164] | A, An | >0.5 | 96.1 | ||||||
| SBR, EO | [165] | A, P/C | 0.2 | 98 | 99 | 83.5 | 55.2 | |||
| SBR, Fenton-like, SBR | [166] | A, P/C, A | 0.17–0.57 | 95 | 95 | 95 | ||||
| Activated Sludge, Coagulation, PhotoFenton | [167] | A, P/C, P/C | 0.07–0.13 | 96 | 62–99 | 88 | ||||
| PhotoFenton, MBR | [168] | P/C, A | 0.18 | 96 | 88 | 90.2 | 100 | 95.5 | ||
| Trickling filters, EC | [169] | A, P/C | 0.09 | 80 | 94 | 94 | 98 | |||
| Fenton, Aereted Biomass | [170] | P/C, A | 0.16–0.27 | 83 | 95 | 46 | ||||
| Aerobic SBR, Adsorption | [171] | A, P/C | <0.1 | 43 | 96 | 24–100 | ||||
| CW, Adsorption | [172] | A, P/C | 0.2 | 86.7 | 99.2 | 87–89 | ||||
| MBR, UF, EO | [173] | A, P/C | 0.14–0.3 | 94 | 77 | 97 | 53 | |||
| MBR, PAC to activated sludge, NF | [174] | A, P/C, P | 0.3 | 94 | 97 | 99 | 99 | |||
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Torretta, V.; Ferronato, N.; Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Tolkou, A.K.; Airoldi, M. Novel and Conventional Technologies for Landfill Leachates Treatment: A Review. Sustainability 2017, 9, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9010009
Torretta V, Ferronato N, Katsoyiannis IA, Tolkou AK, Airoldi M. Novel and Conventional Technologies for Landfill Leachates Treatment: A Review. Sustainability. 2017; 9(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleTorretta, Vincenzo, Navarro Ferronato, Ioannis A. Katsoyiannis, Athanasia K. Tolkou, and Michela Airoldi. 2017. "Novel and Conventional Technologies for Landfill Leachates Treatment: A Review" Sustainability 9, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9010009
APA StyleTorretta, V., Ferronato, N., Katsoyiannis, I. A., Tolkou, A. K., & Airoldi, M. (2017). Novel and Conventional Technologies for Landfill Leachates Treatment: A Review. Sustainability, 9(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9010009










