Understanding Grassland Degradation and Restoration from the Perspective of Ecosystem Services: A Case Study of the Xilin River Basin in Inner Mongolia, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
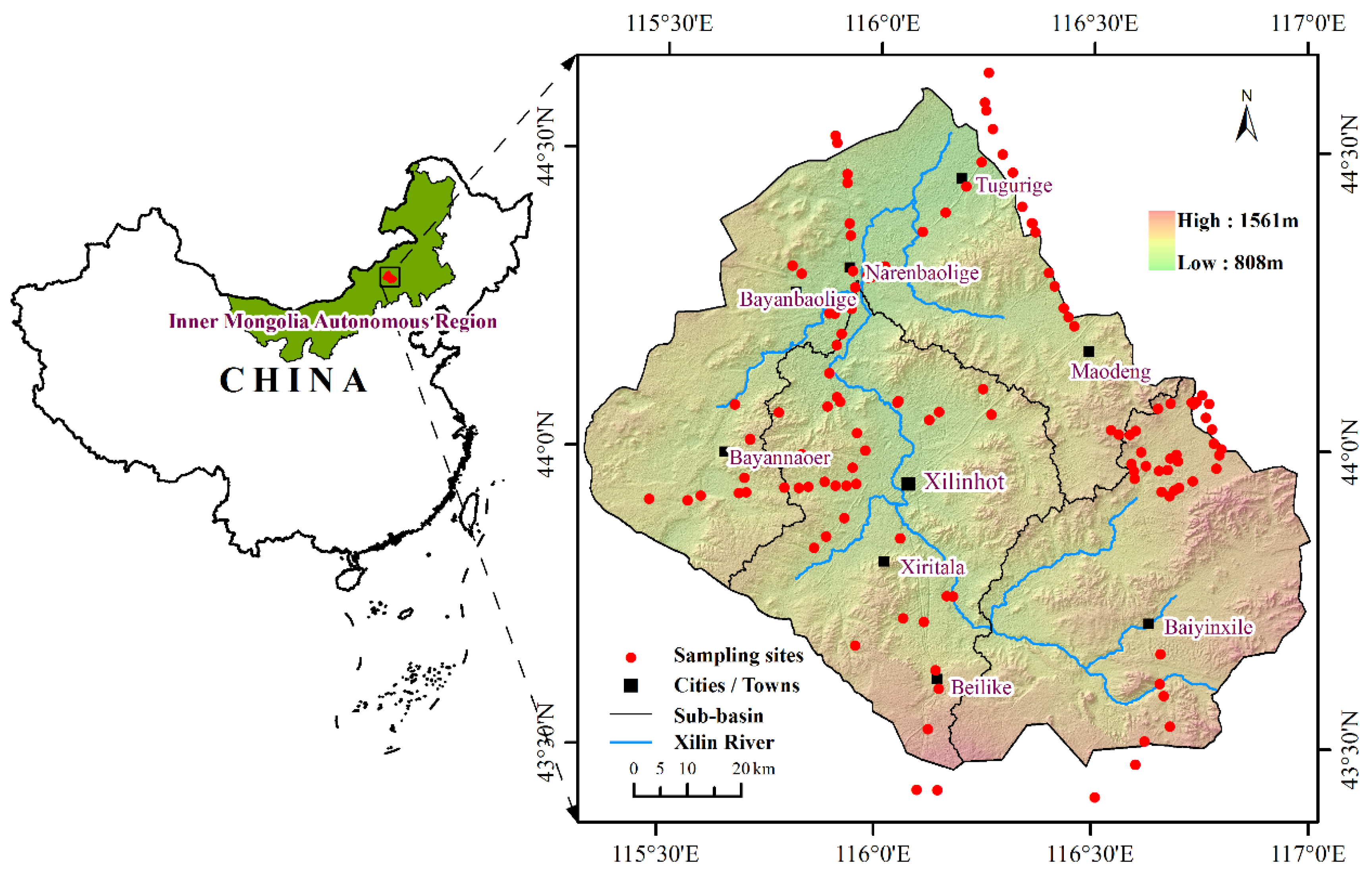
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection and Processing
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Grassland Degradation Index (GDI)
2.3.2. Quantification of Grassland Ecosystem Services (ESs)
Aboveground Biomass (AGB)
Soil Conservation (SC)
Water Retention (WR)
2.3.3. Correlations and Trade-offs Analysis
3. Results
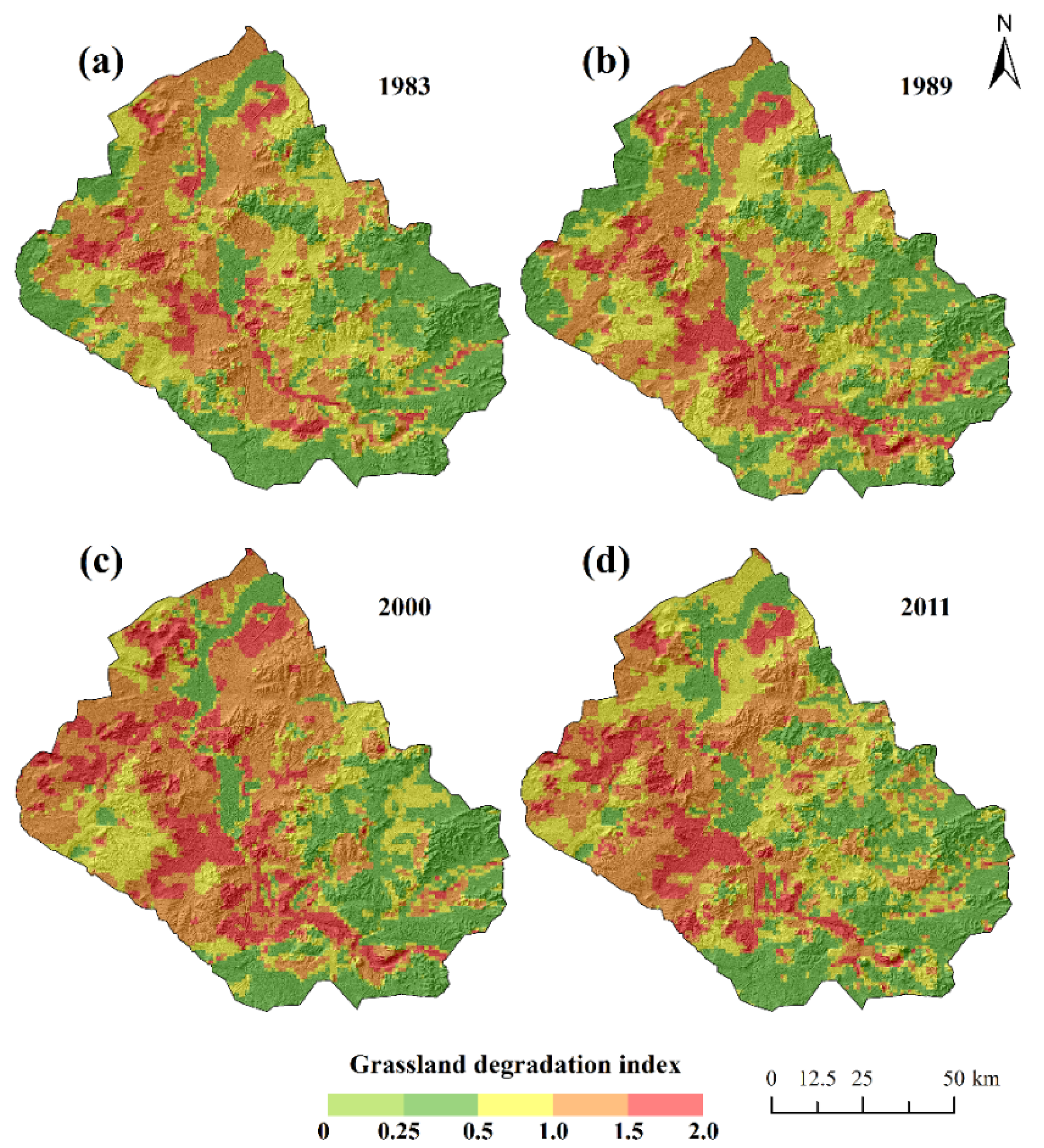
3.1. Spatiotemporal Patterns of GDI
3.2. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Grassland ESs
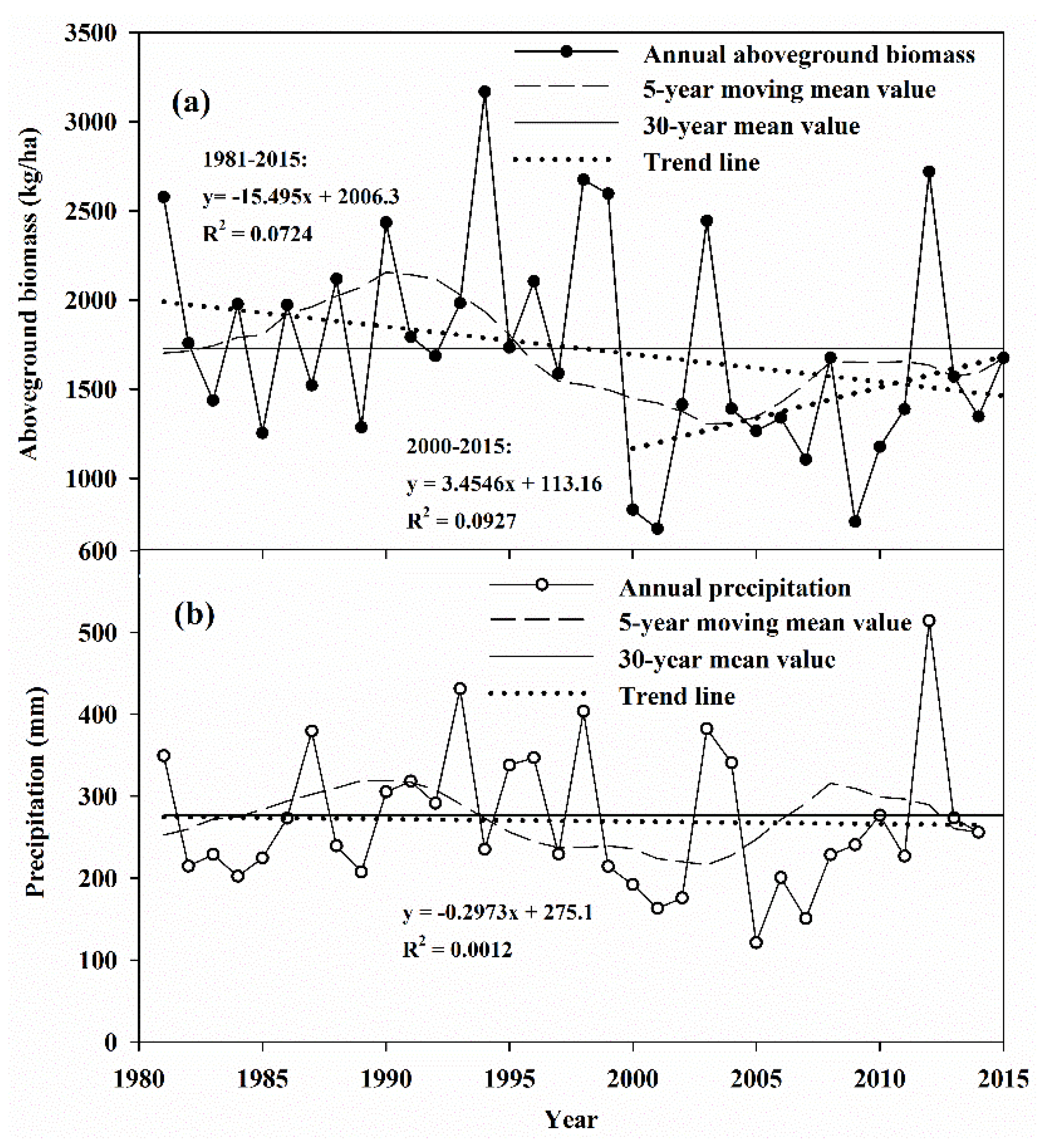
3.2.1. Aboveground Biomass (AGB)
3.2.2. Soil Conservation (SC)
3.2.3. Water Retention (WR)
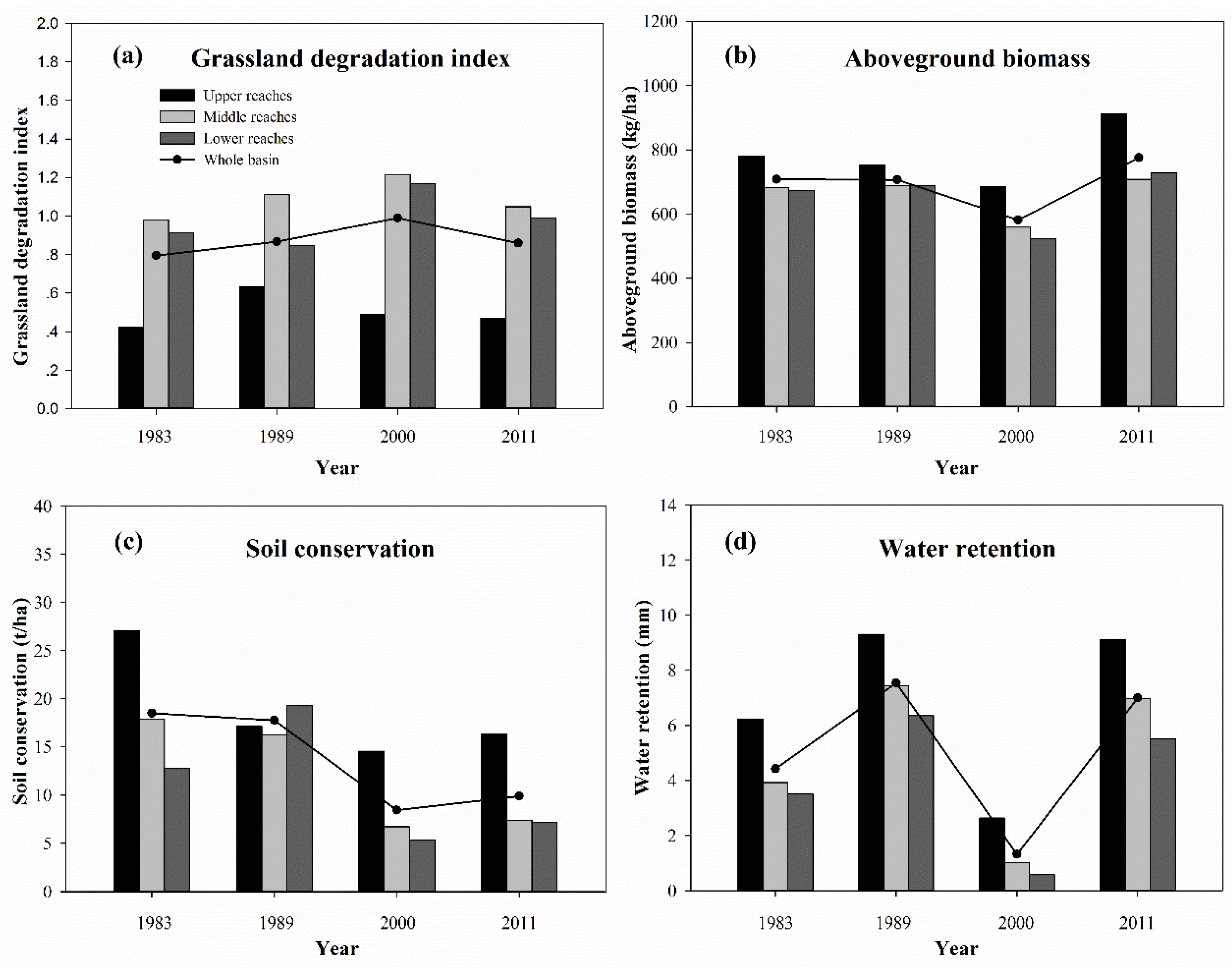
3.3. Grassland Degradation and Changes in ESs at the Sub-basin Level
3.4. Relationships Between Grassland Degradation and ESs
4. Discussion
4.1. Impacts of Grassland Degradation and Restoration on ESs
4.2. Relationships between Grassland ESs
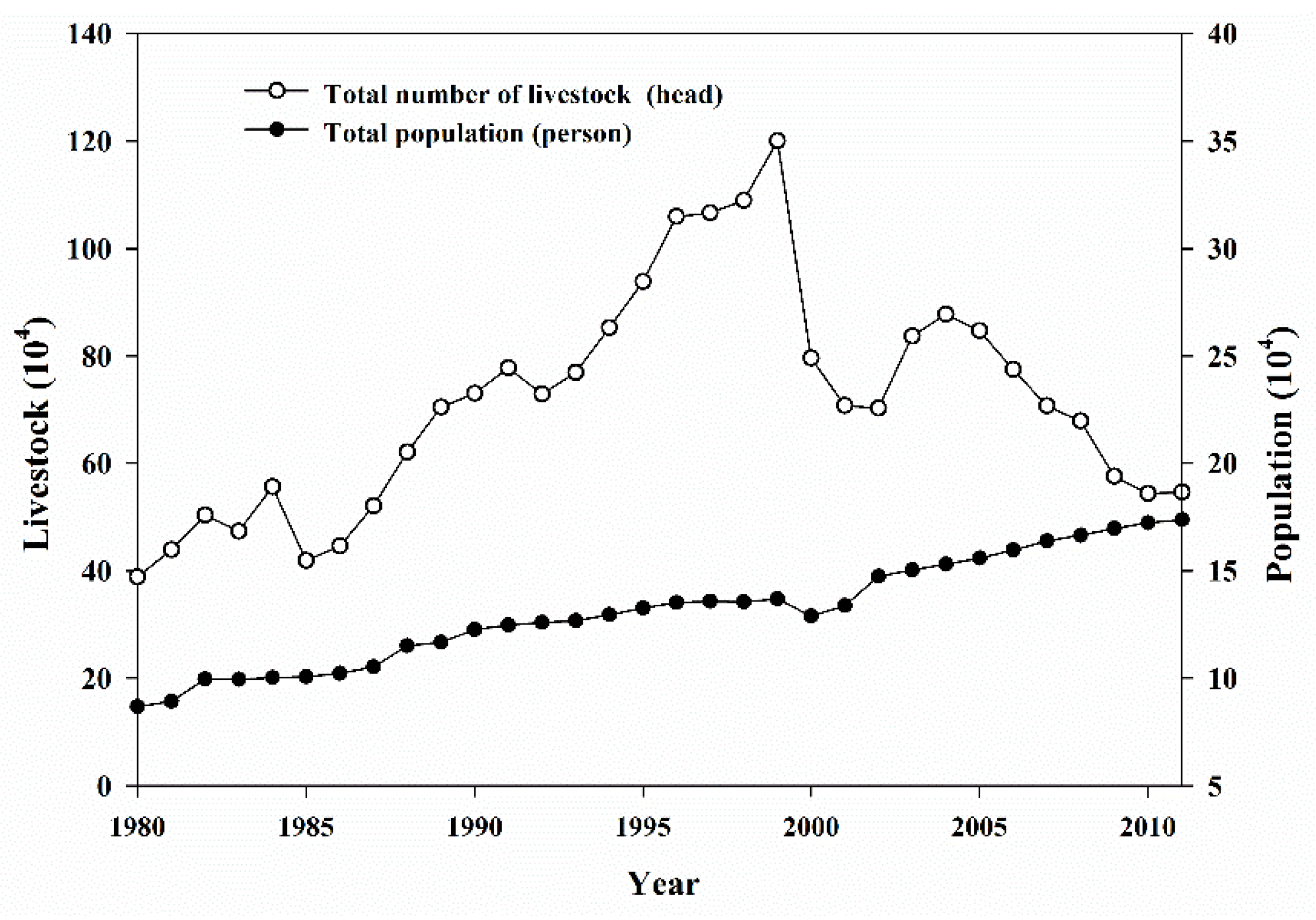
4.3. Drivers of Grassland Degradation
4.4. Uncertainties in Mapping and Modeling Grassland ESs
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Millennium Ecosystem Assessment. Ecosystems and Human Well-being: Synthesis; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sala, O.E.; Paruelo, J.M. Ecosystem services in grasslands. In Nature’s Services: Societal Dependence on Natural Ecosystems; Daily, G., Ed.; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; pp. 237–251. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J. Landscape sustainability science: Ecosystem services and human well-being in changing landscapes. Landsc. Ecol. 2013, 28, 999–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.Z.; Hu, Z.Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, D.G.; Hou, F.J.; Lin, H.L.; Mu, X.D. A grassland classification system and its application in China. Rangeland J. 2008, 30, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook 2008; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2008.
- Li, B. The rangeland degradation in North China and its preventive strategy. Sci. Agric. Sin. 1997, 30, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama, T.; Kawamura, K. Grassland degradation in China: Methods of monitoring, management and restoration. Grassl. Sci. 2007, 53, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.; Wu, J.; Yong, S.; Yang, J.; Yong, W. A landscape-scale assessment of steppe degradation in the Xilin River Basin, Inner Mongolia, China. J. Arid Environ. 2004, 59, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Verburg, P.H.; Lv, S.; Wu, J.; Li, X. Spatial analysis of the driving factors of grassland degradation under conditions of climate change and intensive use in Inner Mongolia, China. Reg. Environ. Change 2012, 12, 461–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liang, C.; Liu, Z. Basic characteristics of recovery succession of degraded steppes. Acta Phytoecol. Sin. 1996, 24, 449–459. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, Y.; Chen, M. Plant community succession after shallow plowing in a degraded Leymus chinensis grassland. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Grassland Resources, Huhehot, China, 16–18 August 1993; China Agriculture Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, W.; Liang, C.; Hao, D. The regressive succession pattern and its diagnostic of Inner Mongolia steppe in sustained and superstrong grazing. Acta Agrestia Sin. 1998, 6, 244–251. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, W.; Hao, D.; Liang, C. Probes on the degeneration and recovery succession mechanisms of Inner Mongolia steppe. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2002, 16, 84–91. [Google Scholar]
- Geerken, R.; Ilaiwi, M. Assessment of rangeland degradation and development of a strategy for rehabilitation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 90, 490–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanser, F.C.; Palmer, A.R. The application of a remotely-sensed diversity index to monitor degradation patterns in a semi-arid, heterogeneous, South African landscape. J. Arid Environ. 1999, 43, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, H.; Karnieli, A. Remote sensing of the seasonal variability of vegetation in a semi-arid environment. J. Arid Environ. 2000, 45, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, X.; Shao, Q. Grassland degradation in the “three-river headwaters” region, Qinghai province. J. Geogr. Sci. 2008, 18, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, K.; Akiyama, T.; Yokota, H.; Tsutsumi, M.; Yasuda, T.; Watanabe, O.; Wang, G.; Wang, S. Monitoring of forage conditions with MODIS imagery in the Xilingol steppe, Inner Mongolia. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 1423–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Gu, Z.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Shi, P. Analysis of human-induced steppe degradation based on remote sensing in Xilin Gole, Inner Mongolia, China. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2005, 30, 268–277. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Q.; Li, Y.; Wan, Y.; Lin, E.; Xiong, W.; Jiangcun, W.; Wang, B.; Li, W. Grassland degradation in Northern Tibet based on remote sensing data. J. Geogr. Sci. 2006, 16, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, B.O.; Koch, C.; Boldrini, I.I.; Vélez-Martin, E.; Hasenack, H.; Hermann, J.M.; Kollmann, J.; Pillar, V.D.; Overbeck, G.E. Grassland degradation and restoration: A conceptual framework of stages and thresholds illustrated by southern Brazilian grasslands. Nat. Conservaçao 2015, 13, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, R.S.; Wilson, M.A.; Boumans, R.M.J. A typology for the classification, description and valuation of ecosystem functions, goods and services. Ecol. Econ. 2002, 41, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; de Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daily, G. Nature’s Services: Societal Dependence on Natural Ecosystems; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, F.; de Groot, R.; Willemen, L. Ecosystem services at the landscape scale: The need for integrative approaches. Landsc. online 2010, 23, 1–11. Available online: http://www.landscapeonline.de/103097lo201023 (accessed on 21 June 2016). [Google Scholar]
- Ayanu, Y.Z.; Conrad, C.; Nauss, T.; Wegmann, M.; Koellner, T. Quantifying and mapping ecosystem services supplies and demands: A review of remote sensing applications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 8529–8541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Harms, M.J.; Balvanera, P. Methods for mapping ecosystem service supply: A review. Int. J. Biodiversity Sci. Ecosystem Ser. Manag. 2012, 8, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J.P.; Beard, J.T.D.; Bennett, E.M.; Cumming, G.S.; Cork, S.J.; Agard, J.; Dobson, A.P.; Peterson, G.D. Trade-offs across space, time, and ecosystem services. Ecol. Soc. 2006, 11, 28. [Google Scholar]
- Kragt, M.E.; Robertson, M.J. Quantifying ecosystem services trade-offs from agricultural practices. Ecol. Econ. 2014, 102, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Turner, M.G. Spatial interactions among ecosystem services in an urbanizing agricultural watershed. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12149–12154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egoh, B.; Rouget, M.; Reyers, B.; Knight, A.T.; Cowling, R.M.; van Jaarsveld, A.S.; Welz, A. Integrating ecosystem services into conservation assessments: A review. Ecol. Econ. 2007, 63, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabucchi, M.; Ntshotsho, P.; O'Farrell, P.; Comín, F.A. Ecosystem service trends in basin-scale restoration initiatives: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 111, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonagh, J.; Stocking, M.; Lu, Y. Global Impacts of Land Degradation; Overseas Development Group, University of East Anglia Norwich, for the Scientific and Technical Panel of the Global Environment Facility: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Huang, J.; Zheng, S.; Pan, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, H.; Xu, H.; Li, Y.; Ma, J. Drivers and regulating mechanisms of grassland and desert ecosystem services. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2014, 38, 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Yong, S.; Li, Z. The vegetation of the Xilin River Basin and its utilization. In Research on Grassland Ecosystem; Inner Mongolia Grassland Ecosystem Research Station; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1988; Volume 3, pp. 84–183. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Q.; Liu, X.; Li, Y. Changes in soil carbon storage due to over-grazing in Leymus chinensis steppe in the Xilin River Basin of Inner Mongolia. J. Environ. Sci. 1997, 9, 104–108. [Google Scholar]
- The United States Geological Survey. Available online: http://glovis.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 21 April 2015).
- ENVI, version 4.7; Exelis Visual Information Solutions: Boulder, CO, USA, 2009.
- TWINSPAN for Windows, version 2.3; Centre for Ecology and Hydrology and University of South Bohemia: Huntingdon, UK; Ceske Budejovice, Czech Republic, 2005.
- eCongnition Developer, version 8.0; Definiens: Munich, Germany, 2010.
- ArcGIS Desktop, version 10.0; Environmental Systems Research Institute: Redlands, CA, USA, 2011.
- Han, Y.; Niu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Dong, J.; Zhang, X.; Kang, S. The changing of vegetation pattern and its driven forces of grassland in Xilin River Basin in thirty years. Chin. J. Grassl. 2014, 36, 70–77. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Niu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Dong, J.; Zhang, J. Soil conservation function and its spatial distribution of grassland ecosystems in Xilin River Basin, Inner Mongolia. Acta Pratac. Sin. 2015, 24, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- The Cold and Arid Regions Sciences Data Center. Available online: http://westdc.westgis.ac.cn (accessed on 5 January 2016).
- The MODIS Level 1 and Atmosphere Archive and Distribution System in NASA. Available online: https://ladsweb.nascom.nasa.gov/ (accessed on 5 January 2016).
- Japan Space Systems. Available online: http://www.jspacesystems.or.jp/en_/ (accessed on 1 June 2014).
- Kumar, P. The Economics of Ecosystems and Biodiversity: Ecological and Economic Foundations; Earthscan: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J. Estimation of Primary Productivity of Typical Grasslands based on Multi-source Satellite Data. Master’s Thesis, Inner Mongolia University, Hohhot, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; McCool, D.; Yoder, D. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); United States Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1997.
- Kareiva, P.; Tallis, H.; Ricketts, T.H.; Daily, G.C.; Polasky, S. Natural Capital: Theory and Practice of Mapping Ecosystem Services; Oxford University Press: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Zhou, B.; Lü, X.; Yang, Z. Evaluation of water conservation function in mountain forest areas of Beijing based on InVEST model. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2012, 48, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sharp, R.; Tallis, H.; Ricketts, T.; Guerry, A.; Nelson, E.; Ennaanay, D.; Wolny, S.; Olwero, N.; Vigerstol, K.; Pennington, D.; et al. InVEST User’s Guide; The Natural Capital Project: Stanford, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Budyko, M.I. Climate and Life; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Hickel, K.; Dawes, W.R.; Chiew, F.H.S.; Western, A.W.; Briggs, P.R. A rational function approach for estimating mean annual evapotranspiration. Water Resour. Res. 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Liu, G.; Pan, J.; Feng, X. Distribution of available soil water capacity in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2005, 15, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, version 19; IBM Corp: Armonk, NY, USA, 2010.
- Bennett, E.M.; Peterson, G.D.; Gordon, L.J. Understanding relationships among multiple ecosystem services. Ecol. Lett. 2009, 12, 1394–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.; Fu, B.; He, C.; Lü, Y. Variation of ecosystem services and human activities: A case study in the Yanhe watershed of China. Acta Oecol. 2012, 44, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wu, J.; Xu, Z. Analysis of the tradeoffs between provisioning and regulating services from the perspective of varied share of net primary production in an alpine grassland ecosystem. Ecol. Complex. 2014, 17, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Han, X.; Wu, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, L. Ecosystem stability and compensatory effects in the Inner Mongolia grassland. Nature 2004, 431, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Piao, S.; Zhou, L.; He, J.; Wei, F.; Myneni, R.B.; Tucker, C.J.; Tan, K. Precipitation patterns alter growth of temperate vegetation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Yang, Y.; He, J.; Zeng, H.; Fang, J. Above-and belowground biomass in relation to environmental factors in temperate grasslands, Inner Mongolia. Sci. China Life Sci. 2008, 51, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Liu, P.; Li, P. The dynamic state of the NDVI index in Xilingol grassland during 1981–2010. Chin. J. Grassl. 2014, 36, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Feng, X.; Wu, L. The evaluation of ecological service value in a typical grassland nature reserve under the context of global climate changes. J. Desert Res. 2015, 35, 1700–1707. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, E.; Ouyang, Z.; Yu, X.; Xiao, Y. Spatial patterns and impacts of soil conservation service in China. Geomorphology 2014, 207, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, D.H.; Bardgett, R.D.; Behan-Pelletier, V.; Herrick, J.E.; Jones, T.H.; Six, J.; Strong, D.R. Soil Ecology and Ecosystem Services; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, M.; Hao, R.; Hou, Q.; Di, R.; Yang, J. Impact of climatic vacillation on potential evaporation on typical grassland. T. Atmos. Sci. 2011, 34, 351–355. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, X.; Wang, X.; Yan, H.; Zhang, Q.; Jin, G. Land use/land cover change induced impacts on water supply service in the upper reach of Heihe River Basin. Sustainability 2014, 7, 366–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, J.; Zhuang, D.; Xiao, X.; Steve, B. Quantifying land use and land cover change in Xilin river basin using multi-temporal Landsat TM/ETM sensor data. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2003, 58, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Alatengtuya; Hu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yu, G. The tendency and its spatial pattern of grassland changes in the east Xilin Gol from 1975 to 2009. J. Geo-Inform. Sci. 2011, 13, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raudsepp-Hearne, C.; Peterson, G.D.; Bennett, E.M. Ecosystem service bundles for analyzing tradeoffs in diverse landscapes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 5242–5247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Fu, B.; Hu, H.; Sun, G. A method to identify the variable ecosystem services relationship across time: A case study on Yanhe Basin, China. Landsc. Ecol. 2014, 29, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millennium Ecosystem Assessment. Ecosystems and Human Well-being: Current State and Trends; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Loucks, O. The Xilingol grassland. In Grasslands and Grassland Sciences in Northern China; US National Research Council, Ed.; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1992; pp. 67–84. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, B. Steppe ecosystem degradation and management in the Xilingol Biosphere Reserve. In Management of the Degraded Ecosystem in Xilingol Biosphere Reserve; Han, N., Jiang, G., Li, W., Eds.; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2002; pp. 117–132. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Bi, X.; Huang, J.; Bai, Y. Patterns and drivers of vegetation degradation in Xilin River Basin, Inner Mongolia, China. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2010, 34, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar]
- Xilinhot Statistic Bureau. Statistic Yearbook of Xilinhot; Xilinhot Statistic Bureau: Xilinhot, China, 1980–2012.
- Chen, S.; Liu, J.; Zhuang, D.; Xiao, X. Characterization of land cover types in Xilin River Basin using multi-temporal Landsat images. J. Geogr. Sci. 2003, 13, 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.J.; Ali, S.H.; Zhang, Q. Property rights and grassland degradation: A study of the Xilingol Pasture, Inner Mongolia, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2007, 85, 461–470. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, G.; Han, X.; Wu, J. Restoration and management of the Inner Mongolia grassland require a sustainable strategy. AMBIO 2006, 35, 269–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). FAOSTAT. Available online: http://faostat.fao.org/site/291/default.aspx (accessed on 31 August 2015).


| Vegetation Subtypes | Formation Types | Association | Degradation Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|
| Meadow steppe | Mesophyious forbs meadow steppe | L. chinensis + forbs | Undegraded |
| Typical steppe | Leymus chinensis steppe | L. chinensis + Stipa. spp. | Undegraded |
| L. chinensis + Artemisia frigida | Moderately degraded | ||
| Stipa grandis steppe | S. grandis | Undegraded | |
| S. grandis + L. chinensis | Undegraded | ||
| S. grandis + Cleistogenes squarrosa | Slightly degraded | ||
| Stipa krylovii steppe | S. krylovii + S. gobica | Undegraded | |
| S. krylovii + L. chinensis | Slightly degraded | ||
| S. krylovii + C. squarrosa | Moderately degraded | ||
| Cleistogenes squarrosa steppe | C. squarrosa + A. frigida | Heavily degraded | |
| Caragana microphylla thicketization of steppe | Caragana microphylla – grass + forbs | Heavily degraded | |
| Sand vegetation | Pioneer plants in sand dunes | Agriophyllum pungens + Corispermum spp. | Heavily degraded |
| Artemisia intramongolica formation | A. intramongolica | Undegraded | |
| C. microphylla scrub | C. microphylla – A. intramongolica | Undegraded | |
| Meadow | Carex korshinskyi meadow | Carex spp. + forbs | Heavily degraded |
| Achnatherum splendens meadow | A. splendens | Undegraded | |
| Others | Others | Farmland, Waters, Saline and alkali land, Bare land, Urban or residential area, Industry and mining land | Undegraded |
| Sub-Basins | Change Rate (%) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1983–1989 | 1989–2000 | 2000–2011 | ||||||||||
| GDI | AGB | SC | WR | GDI | AGB | SC | WR | GDI | AGB | SC | WR | |
| Upper reaches | 49.15 | −3.45 | −36.68 | 49.25 | −22.36 | −9.02 | −15.07 | −71.64 | −4.05 | 32.89 | 12.49 | 245.34 |
| Middle reaches | 13.24 | 1.12 | −9.23 | 89.63 | 9.40 | −18.99 | −58.58 | −86.19 | −13.72 | 26.74 | 9.89 | 577.33 |
| Lower reaches | −7.42 | 2.42 | 51.41 | 81.25 | 38.13 | −23.97 | −72.20 | −90.86 | −15.42 | 39.02 | 33.90 | 848.12 |
| Whole basin | 9.09 | −0.17 | −3.93 | 70.45 | 14.13 | −17.76 | −52.49 | −82.58 | −13.16 | 33.32 | 17.30 | 432.63 |
| Year/Period | GDI vs. AGB | GDI vs. SC | GDI vs. WR | AGB vs. SC | AGB vs. WR | SC vs. WR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1983 | −0.488** | −0.354** | −0.312** | 0.679** | 0.492** | 0.393** |
| 1989 | −0.307** | −0.339** | −0.205** | 0.732** | 0.120* | 0.209** |
| 2000 | −0.706** | −0.592** | −0.389** | 0.768** | 0.543** | 0.510** |
| 2011 | −0.652** | −0.451** | −0.228** | 0.762** | 0.247** | 0.306** |
| 1983–1989 | −0.421** | −0.414** | 0.075 | 0.848** | −0.051 | −0.015 |
| 1989–2000 | −0.582** | −0.539** | 0.016 | 0.565** | 0.027 | 0.196** |
| 2000–2011 | −0.374** | −0.198** | 0.049 | 0.733** | −0.144** | −0.051 |
| 1983–2011 | −0.153** | −0.143** | 0.031 | 0.143** | −0.116* | −0.479** |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Niu, J.; Buyantuev, A.; Zhang, Q.; Dong, J.; Kang, S.; Zhang, J. Understanding Grassland Degradation and Restoration from the Perspective of Ecosystem Services: A Case Study of the Xilin River Basin in Inner Mongolia, China. Sustainability 2016, 8, 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8070594
Zhang X, Niu J, Buyantuev A, Zhang Q, Dong J, Kang S, Zhang J. Understanding Grassland Degradation and Restoration from the Perspective of Ecosystem Services: A Case Study of the Xilin River Basin in Inner Mongolia, China. Sustainability. 2016; 8(7):594. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8070594
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xuefeng, Jianming Niu, Alexander Buyantuev, Qing Zhang, Jianjun Dong, Sarula Kang, and Jing Zhang. 2016. "Understanding Grassland Degradation and Restoration from the Perspective of Ecosystem Services: A Case Study of the Xilin River Basin in Inner Mongolia, China" Sustainability 8, no. 7: 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8070594
APA StyleZhang, X., Niu, J., Buyantuev, A., Zhang, Q., Dong, J., Kang, S., & Zhang, J. (2016). Understanding Grassland Degradation and Restoration from the Perspective of Ecosystem Services: A Case Study of the Xilin River Basin in Inner Mongolia, China. Sustainability, 8(7), 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8070594






