Environmental Regulation, Economic Network and Sustainable Growth of Urban Agglomerations in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Environmental Regulation, Economic Growth and Spillover Effects
3. Theoretical Background and the Model
3.1. Theoretical Assumptions and Background
3.2. The Impact of Environmental Regulation on Urban Economic Growth: a Micro View from Firms’ Location Choices
3.2.1. A Location Choice Model: The Same Stringent Environmental Regulations
3.2.2. A Location Choice Model: The Discriminatory Environmental Regulations
3.3. Firm’s Relocation Choice, Spillover Effects and Economic Growth
4. Methodology
4.1. Empirical Models
4.2. Data Description
4.3. Study Area and Data Description
5. Results
5.1. Dynamics of Environmental Regulation and Economic Growth
5.2. Empirical Results
5.2.1. The Results of the Benchmark Model
5.2.2. The Long-Term Effects of Environmental Regulation on Economic Growth
5.2.3. Channels for the Spillover in the Urban Agglomeration
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. List of cities
| City | Urban Agglomeration | ER Index | Growth Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bei Jing | Jing-Jin-Ji | 73.09 | 7.12 |
| Tian Jin | Jing-Jin-Ji | 22.98 | 11.66 |
| Shi Jia zhuang | Jing-Jin-Ji | 10.35 | 11.12 |
| Tang Shan | Jing-Jin-Ji | 6.09 | 11.96 |
| Qin Huang dao | Jing-Jin-Ji | 8.17 | 10.48 |
| Bao Ding | Jing-Jin-Ji | 18.67 | 11.01 |
| Zhang Jia kou | Jing-Jin-Ji | 5.10 | 11.32 |
| Cheng De | Jing-Jin-Ji | 6.13 | 12.58 |
| Cang Zhou | Jing-Jin-Ji | 32.00 | 12.57 |
| Lang Fang | Jing-Jin-Ji | 18.79 | 10.72 |
| Shang Hai | Yangtze River Delta | 34.46 | 8.38 |
| Nan Jing | Yangtze River Delta | 13.52 | 11.07 |
| Wu Xi | Yangtze River Delta | 20.25 | 11.46 |
| Chang Zhou | Yangtze River Delta | 15.75 | 11.68 |
| Su Zhou | Yangtze River Delta | 19.35 | 10.12 |
| Nan Tong | Yangtze River Delta | 15.43 | 14.12 |
| Yang Zhou | Yangtze River Delta | 17.07 | 13.87 |
| Zhen Jiang | Yangtze River Delta | 15.12 | 12.90 |
| Tai Zhou | Yangtze River Delta | 15.11 | 14.09 |
| Hang Zhou | Yangtze River Delta | 16.34 | 10.79 |
| Ning Bo | Yangtze River Delta | 24.33 | 10.55 |
| Jia Xing | Yangtze River Delta | 14.45 | 11.54 |
| Hu Zhou | Yangtze River Delta | 12.73 | 12.42 |
| Shao Xing | Yangtze River Delta | 18.48 | 11.33 |
| Zhou Shan | Yangtze River Delta | 9.03 | 15.01 |
| Taii Zhou | Yangtze River Delta | 33.34 | 10.63 |
| Guang Zhou | Pearl River Delta | 24.91 | 10.64 |
| Shen Zhen | Pearl River Delta | 87.22 | 9.94 |
| Zhu Hai | Pearl River Delta | 12.83 | 10.74 |
| Fo Shan | Pearl River Delta | 11.64 | 12.44 |
| Jiang Men | Pearl River Delta | 5.68 | 11.38 |
| Zhao Qing | Pearl River Delta | 3.95 | 13.39 |
| Hui Zhou | Pearl River Delta | 23.39 | 11.96 |
| Dong Guan | Pearl River Delta | 8.69 | 11.69 |
| Zhong Shan | Pearl River Delta | 13.46 | 12.54 |
Appendix B. Data Summary
| Dataset of Jing-Jin-Ji | |||||
| Variable | Obs | Mean | Std. Dev. | Min | Max |
| lndpgdp | 110 | 2.369032 | 0.2797751 | 1.308333 | 2.879198 |
| lner | 110 | 2.611696 | 0.854208 | 1.280318 | 4.755158 |
| lnpop | 110 | 6.526294 | 0.5722113 | 5.61057 | 7.656715 |
| lnexpen | 110 | 8.041019 | 0.8960005 | 6.315459 | 10.25969 |
| lnk | 110 | 9.554422 | 0.7842207 | 7.665441 | 11.13821 |
| Dataset of the Yangtze River Delta | |||||
| Variable | Obs | Mean | Std. Dev. | Min | Max |
| lndpgdp | 176 | 2.433569 | 0.2920543 | 1.526056 | 3.437208 |
| lner | 176 | 2.842103 | 0.3744399 | 1.786678 | 3.867998 |
| lnpop | 176 | 6.153497 | 0.6269467 | 4.572647 | 7.789516 |
| lnexpen | 176 | 7.25558 | 1.801288 | 1.158025 | 9.74724 |
| lnk | 176 | 10.03026 | 0.6178513 | 8.301827 | 11.30529 |
| Dataset of the Pearl River Delta | |||||
| Variable | Obs | Mean | Std. Dev. | Min | Max |
| lndpgdp | 99 | 2.371605 | 0.473177 | −0.693147 | 3.127383 |
| lner | 99 | 2.582349 | 0.9350277 | 0.7626465 | 5.006705 |
| lnpop | 99 | 6.18255 | 0.6150132 | 4.904163 | 7.764538 |
| lnexpen | 99 | 8.247163 | 0.7055152 | 6.794734 | 9.674568 |
| lnk | 99 | 9.599427 | 0.5590546 | 8.074893 | 11.00911 |
References
- World Bank. China Water Quality Management: Policy and Institutional Considerations; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- World Bank. Cost of Pollution in China: Economic Estimates of Physical Damages; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- China Daily. Promise of Iron Fist against Pollution. Available online: http://www.chinadaily.com.cn/china/2013npc/2013–03/18/content_16314997.htm (accessed on 6 November 2015).
- Kostka, G.; Moslener, U.; Andreas, J. Barriers to increasing energy efficiency: Evidence from small-and medium-sized enterprises in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 57, 59–68. [Google Scholar]
- Porter, M.E.; van der Linde, C. Green and competitive: Ending the stalemate. Harv. Bus. Rev. 1995, 73, 120–134. [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, F. Confessions of an Eco-Sinner: Tracking down the Sources of My Stuff; Beacon Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Jorgenson, D.W.; Wilcoxen, P.J. Environmental regulation and US economic growth. Rand J. Econ. 1990, 21, 314–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostka, G. Barriers to the Implementation of Environmental Policies at the Local Level in China. Available online: http://ssrn.com/abstract=2487614 (accessed on 1 August 2015).
- Sigman, H. Transboundary spillovers and decentralization of environmental policies. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2005, 50, 82–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernauer, T.; Kuhn, P.M. Is there an environmental version of the Kantian peace? Insights from water pollution in Europe. Eur. J. Int. Relat. 2010, 16, 77–102. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, H.; Chen, Y.; Gong, Q. Polluting thy neighbor: Unintended consequences of China’s pollution reduction mandates. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2015. [CrossRef]
- Batten, D.F. Network cities: Creative urban agglomerations for the 21st century. Urban Stud. 1995, 32, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Goei, B.; Burger, M.J.; van Oort, F.G.; Kitson, M. Functional polycentrism and urban network development in the Greater South East, United Kingdom: Evidence from commuting patterns, 1981–2001. Reg. Stud. 2010, 44, 1149–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.P. Economies of network, urban agglomeration, and regional development: A theoretical model and empirical evidence. Reg. Stud. 2007, 41, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggins, R.; Thompson, P. A Network-based view of regional growth. J. Econ. Geogr. 2014, 14, 511–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, W.B.; Shadbegian, R.J. The Environmental Performance of Polluting Plants: A Spatial Analysis. J. Reg. Sci. 2007, 47, 63–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Zhang, W.; Chen, L.; Deng, F. Sustainable Urban Development Capacity Measure—A Case Study in Jiangsu Province, China. Sustainability 2016, 8, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashford, N.A.; Hall, R.P. The importance of regulation-induced innovation for sustainable development. Sustainability 2011, 3, 270–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popp, D. ENTICE: Endogenous Technological Change in the DICE model of global warming. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2004, 48, 742–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dernbach, J.C.; Mintz, J.A. Environmental laws and sustainability: An introduction. Sustainability 2011, 3, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, S.; Morley, B. Environmental taxes and economic growth: Evidence from panel causality tests. Energ. Econ. 2014, 42, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGowan, F. Regulating innovation: European responses to shale gas development. Environ. Polit. 2014, 23, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Zheng, M.; Chen, J. The effects of environmental regulation and technical progress on CO2 Kuznets curve: An evidence from China. Energy Policy 2015, 77, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, A.B.; Palmer, K. Environmental regulation and innovation: A panel data study. Rev. Econ. Stat. 1997, 79, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunnermeier, S.B.; Cohen, M.A. Determinants of environmental innovation in US manufacturing industries. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2003, 45, 278–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, N.; Labonne, J.; Thevenot, C. Environmental policy and economies of scope in facility-level environmental practices. Environ. Econ. Policy Stud. 2008, 9, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, N. Environmental Policy and Corporate Behaviour; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lanoie, P.; Laurent-Lucchetti, J.; Johnstone, N.; Stefan, A. Environmental policy, innovation and performance: New insights on the Porter hypothesis. J. Econ. Manag. Strat. 2011, 20, 803–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, W.; Levinson, A. Pollution abatement costs and foreign direct investment inflows to US states. Rev. Econ. Stat. 2002, 84, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raspiller, S.; Riedinger, N. Do Environmental Regulations Influence the Location Behavior of French Firms? Land Econ. 2008, 84, 382–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheder, S.B.; Zugravu, N. Environmental regulation and French firms location abroad: An economic geography model in an international comparative study. Ecol. Econ. 2012, 77, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, J.B.; Pauly, L.W. The obsolescence of capital controls?: Economic management in an age of global markets. World Polit. 1993, 46, 50–82. [Google Scholar]
- Holzinger, K.; Knill, C. Competition and cooperation in environmental policy: Individual and interaction effects. J. Public Policy 2004, 24, 25–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drezner, D.W. Globalization and policy convergence. Int. Stud. Rev. 2001, 3, 53–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioppolo, G.; Cucurachi, S.; Salomone, R.; Saija, G.; Shi, L. Sustainable Local Development and Environmental Governance: A Strategic Planning Experience. Sustainability 2016, 8, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, R.; Henderson, V. Effects of air quality regulations on polluting industries. J. Polit. Econ. 2000, 108, 379–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, M.E.; Mansur, E.T. Do local energy prices and regulation affect the geographic concentration of employment? J. Public Econ. 2013, 101, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovenberg, A.L.; de Mooij, R.A. Environmental levies and distortionary taxation. Am. Econ. Rev. 1994, 84, 1085–1089. [Google Scholar]
- Ricci, F. Channels of transmission of environmental policy to economic growth: A survey of the theory. Ecol. Econ. 2007, 60, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloi, M.; Tournemaine, F. Inequality, growth, and environmental quality trade-offs in a model with human capital accumulation. Can. J. Econ. 2013, 46, 1123–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smulders, S.; Toman, M.; Withagen, C. Growth theory and ‘green growth’. Oxf. Rev. Econ. Policy 2014, 30, 423–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkansson, H. Technological collaboration in industrial networks. Eur. Manag. J. 1990, 8, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, D.; Kick, E.L. Structural position in the world system and economic growth, 1955–1970: A multiple-network analysis of transnational interactions. Am. J. Sociol. 1979, 84, 1096–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oerlemans, L.A.G.; Meeus, M.T.H.; Boekema, F.W.M. Do networks matter for innovation? The usefulness of the economic network approach in analysing innovation. Tijdschr. Econ. Soc. Geogr. 1998, 89, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantarat, S.; Barrett, C.B. Social network capital, economic mobility and poverty traps. J. Econ. Inequal. 2012, 10, 299–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Ren, S.; Cai, H. The state’s role and position in international trade: A complex network perspective. Econ. Model 2014, 39, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.R. Do local policy networks deter the race to the bottom in environmental regulation? The case of South Korea. Environ. Plan. C 2011, 29, 1037–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acemoglu, D.; García-Jimeno, C.; Robinson, J.A. State Capacity and Economic Development: A Network Approach. Am. Econ. Rev. 2015, 105, 2364–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topa, G.; Zenou, Y. Neighborhood versus Network Effects. In Handbook of Regional and Urban Economics; Duranton, G., Henderson, V., Strange, W., Eds.; Elsevier Publisher: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, C.E.; Ma, H.; Pan, W. Spatial spillover and regional economic growth in China. China Econ. Rev. 2012, 23, 982–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrado, L.; Fingleton, B. Where is the economics in spatial econometrics? J. Reg. Sci. 2012, 52, 210–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Head, K.; Mayer, T. Market potential and the location of Japanese investment in the European Union. Rev. Econ. Stat. 2004, 86, 959–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Checherita-Westphal, C.; Rother, P. The impact of high government debt on economic growth and its channels: An empirical investigation for the euro area. Eur. Econ. Rev. 2012, 56, 1392–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhorst, J.P. Applied spatial econometrics: Raising the bar. Spat. Econ. Anal. 2010, 5, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L. Spatial Econometrics: Methods and Models; Springer Science & Business Media: Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bavaud, F. Spatial Weights: Constructing Weight-Compatible Exchange Matrices from Proximity Matrices; Springer International Publishing: Berlin, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Greenhut, M.L.; Norman, G.; Hung, C.S. The Economics of Imperfect Competition: A Spatial Approach; Cambridge University Press: London, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Fingleton, B.; Le Gallo, J. Estimating spatial models with endogenous variables, a spatial lag and spatially dependent disturbances: Finite sample properties. Pap. Reg. Sci. 2008, 87, 319–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Vargas, A.; Mansilla-Sanchez, R.; Aguilar-Ibarra, A. An empirical analysis of the nonlinear relationship between environmental regulation and manufacturing productivity. J. Appl.Econ. 2013, 16, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinson, A. Environmental regulatory competition: A status report and some new evidence. Natl. Tax J. 2003, 56, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China City Statistical Yearbook, 2004–2014; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2004–2014. (In Chinese)
- HeBei Statistical Bureau. HeBei Economic Yearbook, 2004–2014; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2004–2014. (In Chinese)
- JiangSu Statistical Bureau. JiangSu Statistical Yearbook, 2004–2014; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2004–2014. (In Chinese)
- ZheJiang Statistical Bureau. ZheJiang Statistical Yearbook, 2004–2014; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2004–2014. (In Chinese)
- Guangdong Statistical Bureau. GuangDong Statistical Yearbook, 2004–2014; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2004–2014. (In Chinese)
- Oud, J.H.L.; Folmer, H.A. Structural equation approach to models with Spatial Dependence. Geogr. Anal. 2008, 40, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.; Moffat, J.; Kravtsova, V. In Search of ‘W’. Spat. Econ. Anal. 2011, 6, 249–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
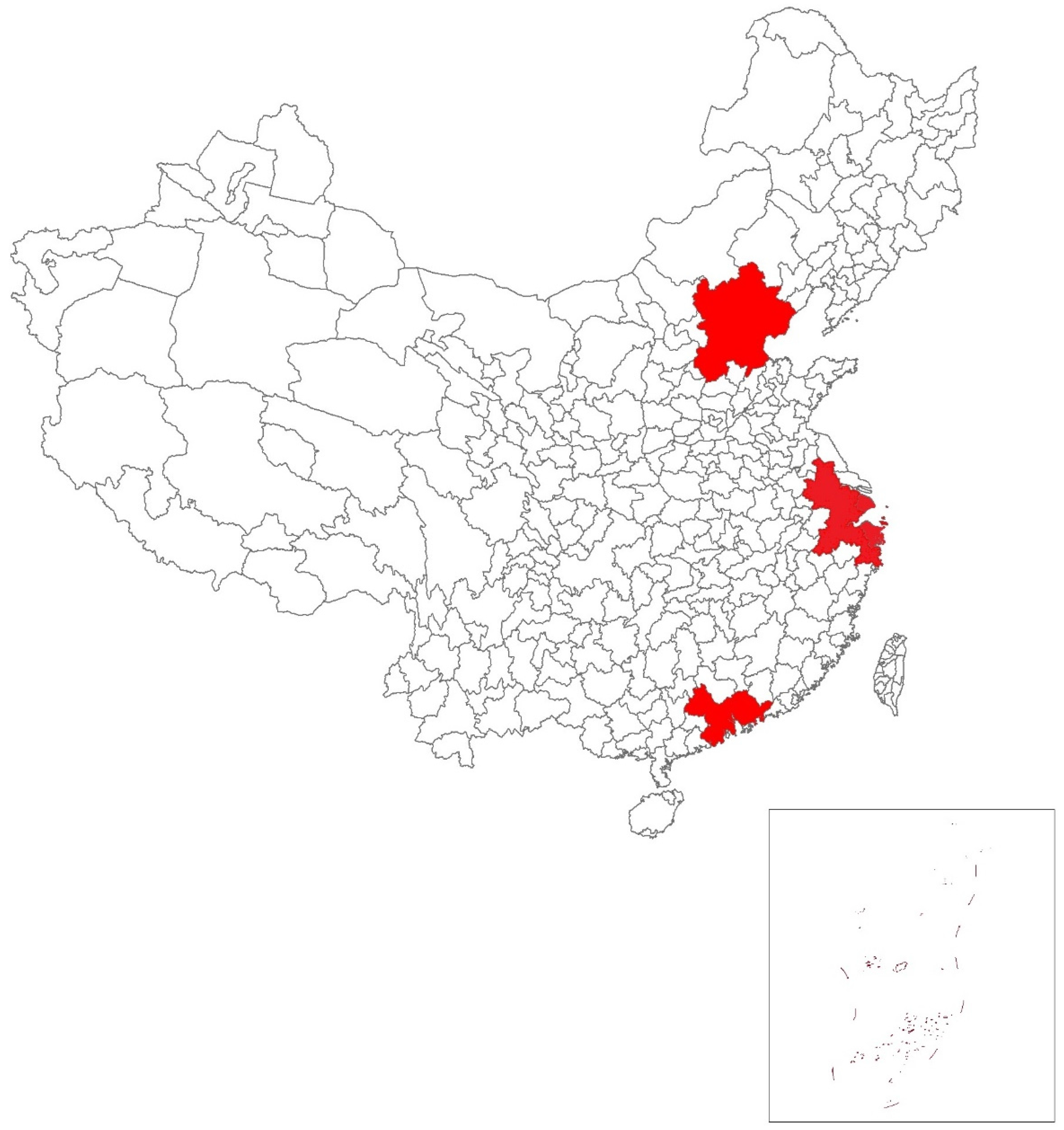
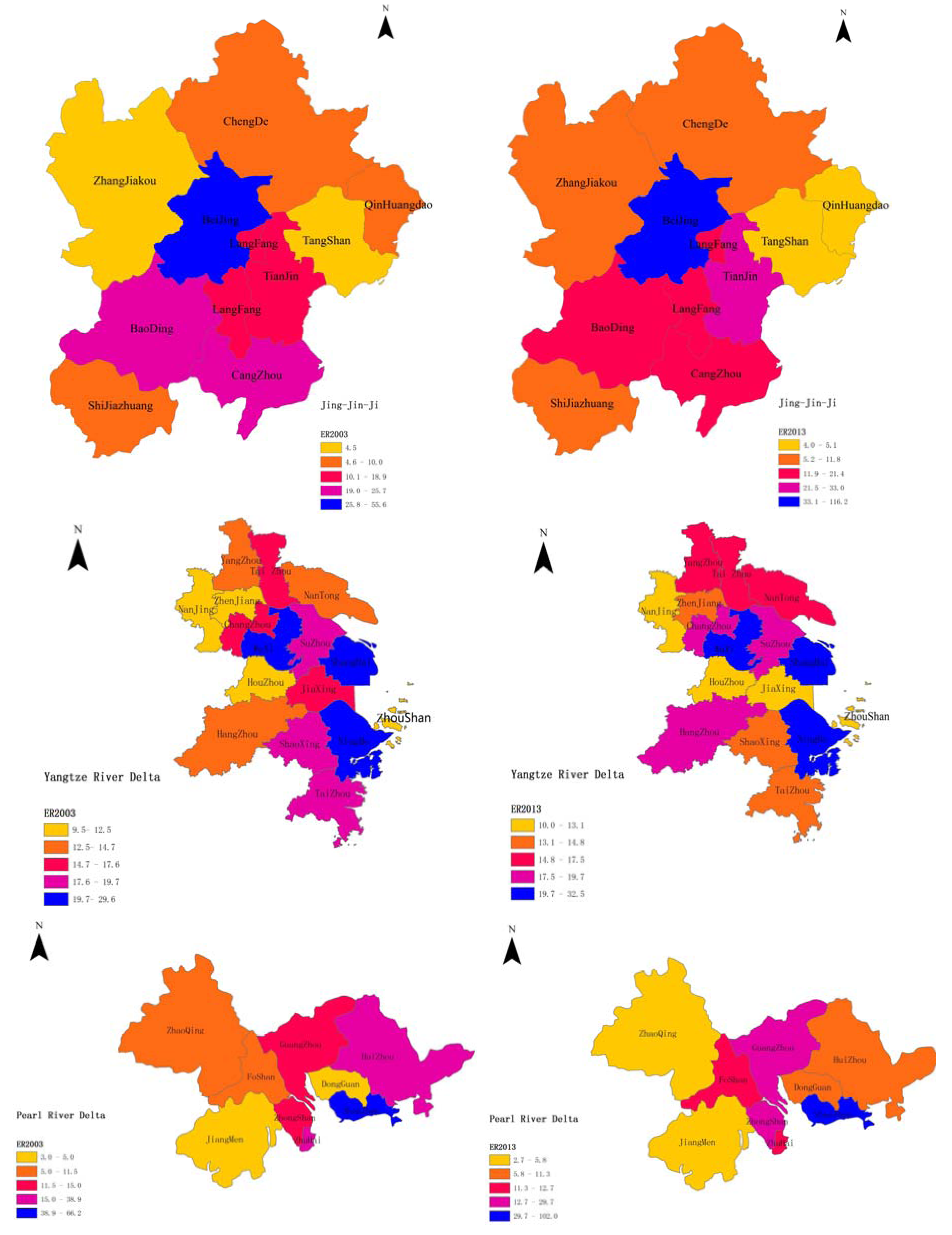
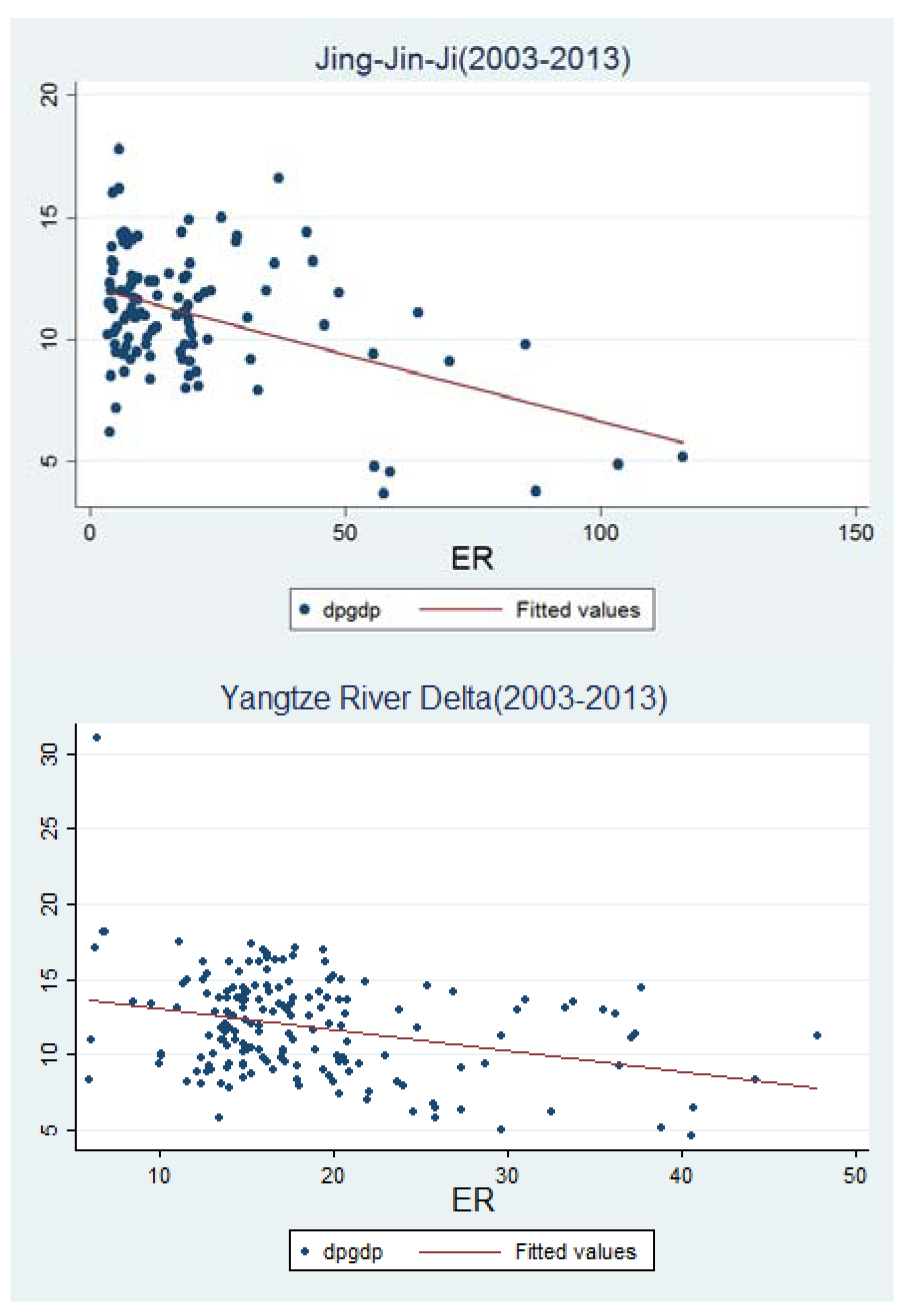
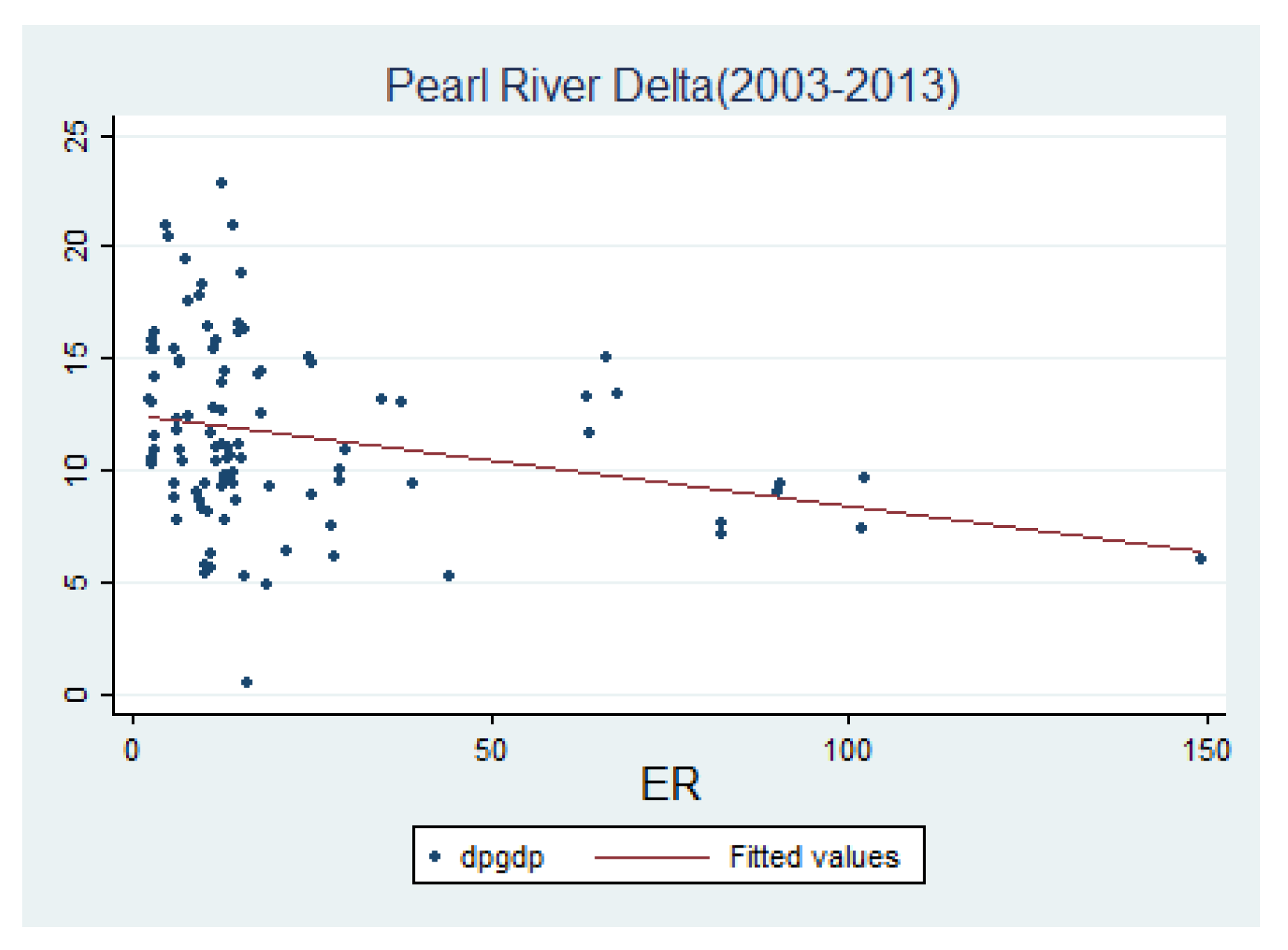
| Year | JJJ | YRD | PRD | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | Max | C.V | Average | Max | C.V | Average | Max | C.V | |
| 2003 | 17.6 | 55.6 | 0.87 | 18.1 | 37.7 | 0.41 | 19.6 | 66.3 | 1.04 |
| 2006 | 21.4 | 85.4 | 1.18 | 18.4 | 37.3 | 0.41 | 17.8 | 67.5 | 1.10 |
| 2009 | 20.1 | 58.9 | 0.91 | 19.7 | 44.2 | 0.51 | 31.7 | 149.4 | 1.44 |
| 2013 | 24.4 | 116.2 | 1.37 | 17.3 | 32.5 | 0.32 | 22.3 | 102.1 | 1.38 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnERt−1 | −0.054 * | 0.164 | −0.055 ** | −0.052 ** | −0.053 ** | −0.043 |
| (−1.94) | (1.07) | (−2.04) | (−2.11) | (−2.01) | (−1.50) | |
| lnPop | −0.044 | −0.037 | −0.0424 | −0.073 * | −0.057 | −0.039 |
| (−1.06) | (−0.91) | (−1.06) | (−1.93) | (−1.43) | (−0.98) | |
| lnExpen | −0.253 *** | −0.200 *** | −0.254 *** | −0.289 *** | −0.262 *** | −0.242 *** |
| (−6.34) | (−3.69) | (−6.56) | (−7.86) | (−6.82) | (−6.08) | |
| lnk | 0.209 *** | 0.160 ** | 0.210 *** | 0.233 *** | 0.219 *** | 0.194 *** |
| (4.10) | (2.63) | (4.25) | (5.06) | (4.48) | (3.81) | |
| recession | −0.268 *** | −0.267 *** | −0.249 *** | −0.277 *** | −0.178 ** | −0.350 *** |
| (−5.11) | (−5.12) | (−4.07) | (−5.87) | (−2.49) | (−3.87) | |
| lnERt−12 | −0.041 | |||||
| (−1.44) | ||||||
| cons | 2.981 *** | 2.717 *** | 2.825 *** | 3.429 *** | 2.418 *** | 3.423 *** |
| (8.96) | (7.19) | (6.54) | (10.85) | (5.36) | (6.64) | |
| Rho | 0.059 | −4.6e-04 *** | 0.247 * | −0.182 | ||
| (0.54) | (−4.33) | (1.75) | (−1.10) | |||
| Prob > Chi2(1) | 0.5873 | 0.0000 | 0.0797 | 0.2724 | ||
| Likelihood Ratio Test | 0.2946 | 18.7204 | 3.0717 | 1.2044 | ||
| Log AIC | −3.8168 | −3.8439 | −3.8314 | −3.8083 | ||
| Log SC | −3.6695 | −3.6966 | −3.6841 | −3.6610 | ||
| R2 | 0.6163 | 0.6239 | 0.7457 | 0.7525 | 0.7494 | 0.7435 |
| N. of obs. | 111 | 111 | 111 | 111 | 111 | 111 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnERt−1 | −0.147 *** | 0.394 | −0.127 *** | −0.143 *** | −0.137 *** | −0.087 * |
| (−2.77) | (1.07) | (−2.68) | (−2.71) | (−2.70) | (−1.62) | |
| lnPop | −0.115 *** | −0.124 *** | −0.129 *** | −0.121 *** | −0.104 *** | −0.121 *** |
| (−3.66) | (−3.88) | (−4.58) | (−3.32) | (−3.43) | (−4.04) | |
| lnExpen | −0.012 | −0.010 | −0.012 | −0.012 | −0.010 | −0.012 |
| (−1.53) | (−1.22) | (−1.62) | (−1.59) | (−1.27) | (−1.58) | |
| lnk | −0.088 *** | −0.099 *** | −0.091 *** | −0.091 *** | −0.081 ** | −0.111 *** |
| (−2.68) | (−2.96) | (−3.11) | (−2.68) | (−2.55) | (−3.48) | |
| recession | −0.294 *** | −0.283 *** | −0.135 *** | −0.292 *** | −0.451 *** | −0.488 *** |
| (−7.32) | (−6.94) | (−2.94) | (−7.38) | (−6.13) | (−6.77) | |
| lnERt−12 | −0.093 | |||||
| (−1.48) | ||||||
| cons | 4.693 *** | 4.067 *** | 3.643 *** | 4.771 *** | 5.559 *** | 5.966 *** |
| (12.88) | (7.29) | (9.65) | (10.87) | (11.30) | (11.25) | |
| Rho | 0.419 *** | −7.11e–06 | −0.397 ** | −0.454 *** | ||
| (5.48) | (−0.31) | (−2.50) | (−3.17) | |||
| Prob > Chi2(1) | 0.0000 | 0.7574 | 0.0123 | 0.0015 | ||
| Likelihood Ratio Test | 30.0194 | 0.0954 | 6.2733 | 10.0359 | ||
| Log AIC | −3.4808 | −3.5256 | −3.5303 | −3.4986 | ||
| Log SC | −3.3727 | −3.4175 | −3.4222 | −3.3905 | ||
| R2 | 0.5822 | 0.5876 | 0.6609 | 0.6758 | 0.6773 | 0.6670 |
| N. of obs. | 176 | 176 | 176 | 176 | 176 | 176 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnERt−1 | −0.494 *** | −0.413 | −0.478 *** | −0.470 *** | −0.493 *** | −0.469 *** |
| (−4.21) | (−1.23) | (−4.01) | (−4.22) | (−4.19) | (−4.02) | |
| lnPop | 0.353 | 0.361 | 0.321 | 0.278 | 0.349 | 0.277 |
| (0.80) | (0.81) | (0.72) | (0.66) | (0.78) | (0.63) | |
| lnExpen | 0.0190 | 0.016 | −0.011 | −0.080 | 0.016 | −0.072 |
| (0.07) | (0.05) | (−0.04) | (−0.30) | (0.05) | (−0.25) | |
| lnk | 0.104 | 0.102 | 0.123 | 0.168 | 0.106 | 0.151 |
| (0.39) | (0.38) | (0.45) | (0.65) | (0.39) | (0.56) | |
| recession | −0.675 *** | −0.670 *** | −0.591 *** | −0.455 *** | −0.668 *** | −0.408 * |
| (−4.62) | (−4.52) | (−3.13) | (−2.93) | (−3.18) | (−1.93) | |
| lnERt−12 | −0.0167 | |||||
| (−0.25) | ||||||
| cons | 0.674 | 0.584 | 0.590 | 0.533 | 0.671 | 0.241 *** |
| (0.23) | (0.20) | (0.20) | (0.19) | (0.23) | (0.08) | |
| Rho | 0.110 | 0.001 *** | 0.011 | 0.431 * | ||
| (0.70) | (3.15) | (0.05) | (1.73) | |||
| Prob > Chi2(1) | 0.4877 | 0.0023 | 0.9635 | 0.0870 | ||
| Likelihood Ratio Test | 0.4860 | 9.9040 | 0.0021 | 2.9983 | ||
| Log AIC | −2.0771 | −2.1828 | −2.0714 | −2.1064 | ||
| Log SC | −1.8150 | −1.9207 | −1.8093 | −1.8443 | ||
| R2 | 0.4984 | 0.4988 | 0.5381 | 0.5844 | 0.5355 | 0.5515 |
| N. of obs. | 99 | 99 | 99 | 99 | 99 | 99 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chong, Z.; Qin, C.; Ye, X. Environmental Regulation, Economic Network and Sustainable Growth of Urban Agglomerations in China. Sustainability 2016, 8, 467. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8050467
Chong Z, Qin C, Ye X. Environmental Regulation, Economic Network and Sustainable Growth of Urban Agglomerations in China. Sustainability. 2016; 8(5):467. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8050467
Chicago/Turabian StyleChong, Zhaohui, Chenglin Qin, and Xinyue Ye. 2016. "Environmental Regulation, Economic Network and Sustainable Growth of Urban Agglomerations in China" Sustainability 8, no. 5: 467. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8050467
APA StyleChong, Z., Qin, C., & Ye, X. (2016). Environmental Regulation, Economic Network and Sustainable Growth of Urban Agglomerations in China. Sustainability, 8(5), 467. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8050467






