Landsat Imagery-Based Above Ground Biomass Estimation and Change Investigation Related to Human Activities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
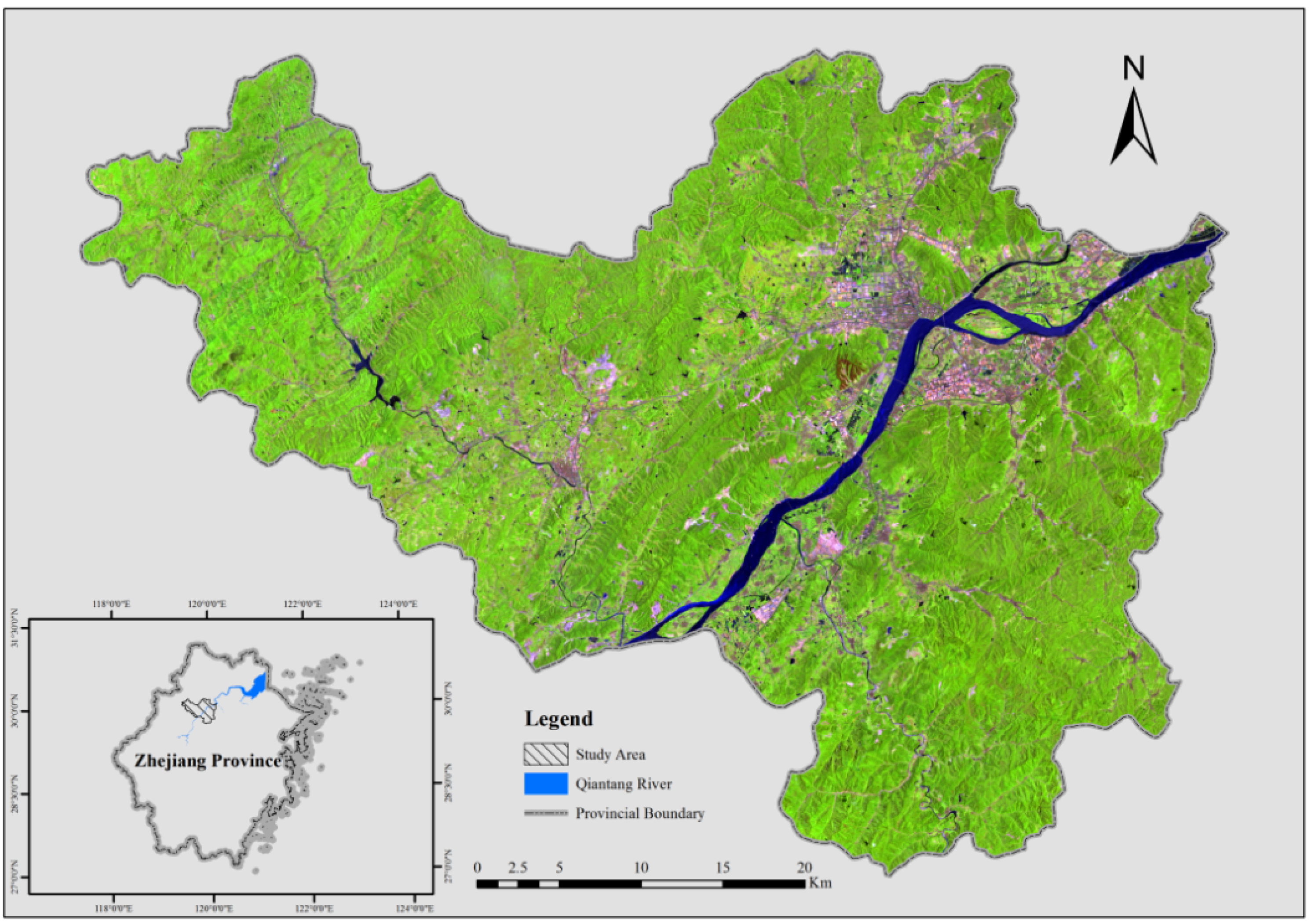
2.2. Field Measurement
| Years | # Plots | Min AGB (ton/ha) | Max AGB (ton/ha) | Mean AGB (ton/ha) | Std.Dev.AGB (ton/ha) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2008 | 87 | 8.05291 | 193.2647 | 86.1533 | 40.76886446 |
| 2013 | 80 | 14.70901 | 219.692 | 98.7338 | 47.8469626 |
2.3. Remote Sensing Data Pre-Processing
2.4. Variables Derivation
2.5. Modeling Methods and Precision Assessment
3. Results
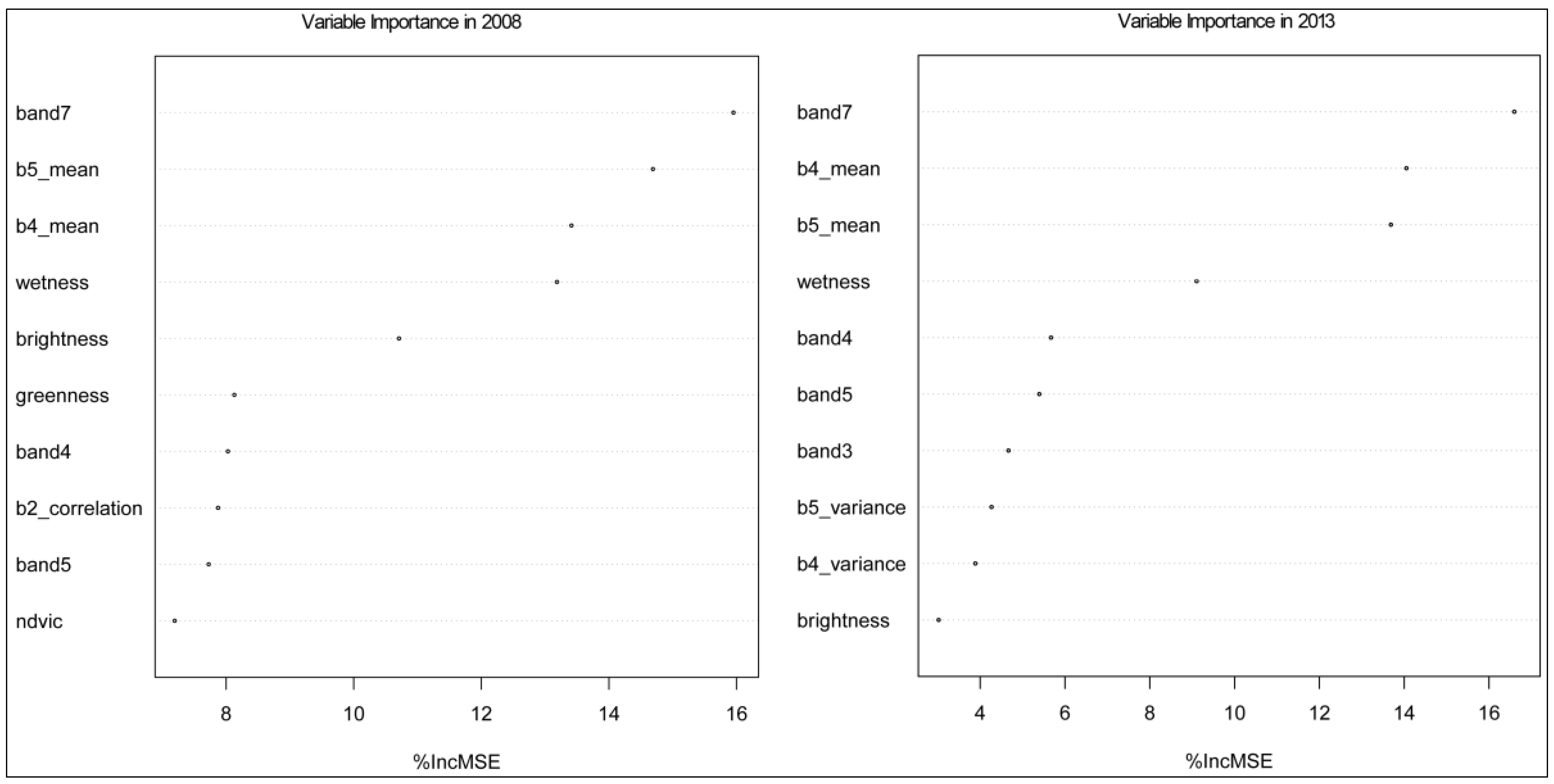
3.1. Variable Importance for Modeling
| CorrelativeVariables in 2008 | CorrelativeVariables in 2013 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| band7 | −0.514 ** | band7 | −0.566 ** |
| b5_mean | −0.499 ** | b5_mean | −0.539 ** |
| wetness | 0.483 ** | b4_mean | −0.539 ** |
| band5 | −0.480 ** | wetness | 0.509 ** |
| brightness | −0.460 ** | band5 | −0.493 ** |
| b4_mean | −0.439 ** | band2 | −0.386 ** |
| band4 | −0.413 ** | brightness | −0.376 ** |
| ndvic | 0.397 ** | b2_mean | −0.369 ** |
| greenness | −0.396 ** | band3 | −0.363 ** |
| band2 | −0.372 ** | band4 | −0.262 * |
| b4_contrast | −0.285 ** | band1 | −0.240 * |
| band3 | −0.284 ** | b2_second moment | 0.235 * |
| b2_mean | −0.278 ** | b2_entropy | −0.228 * |
| b4_dissimilarity | −0.248 * | ||
| b3_mean | −0.232 * | ||
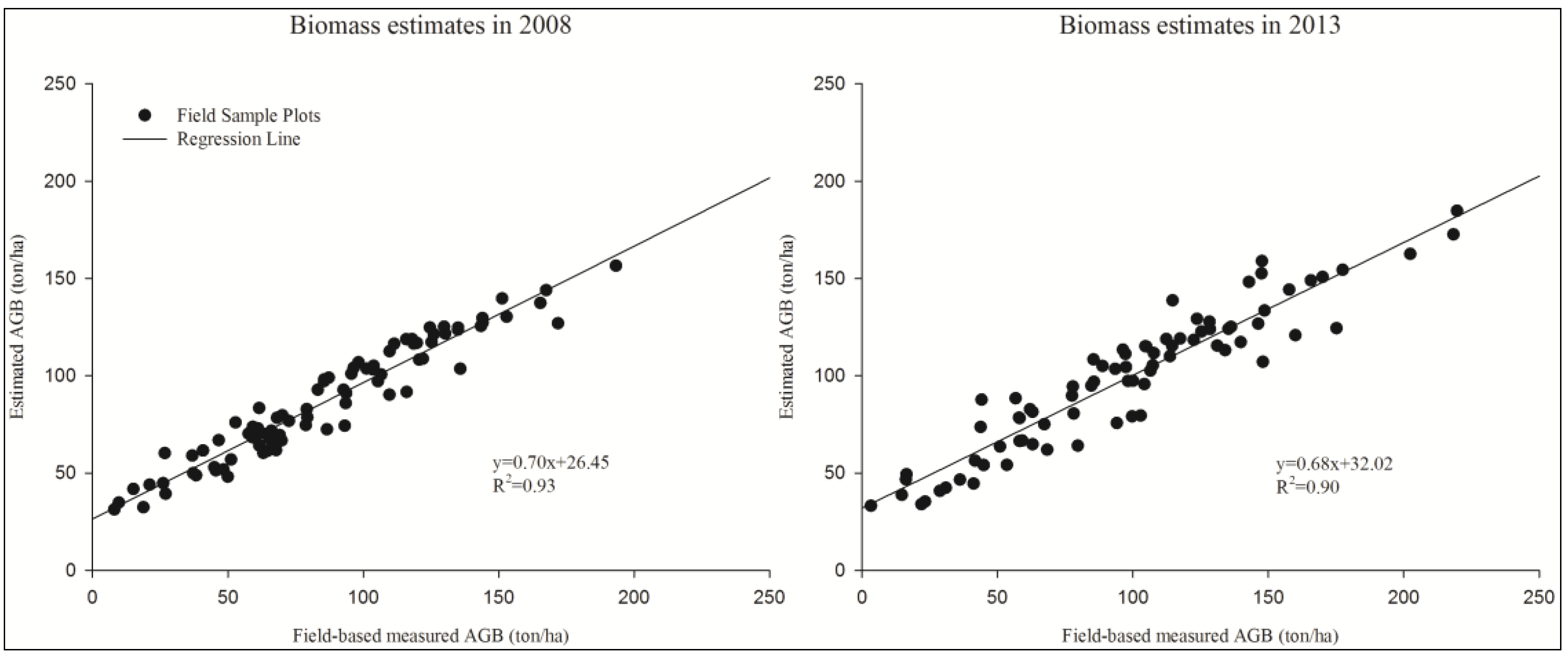
3.2. Accuracy Assessment
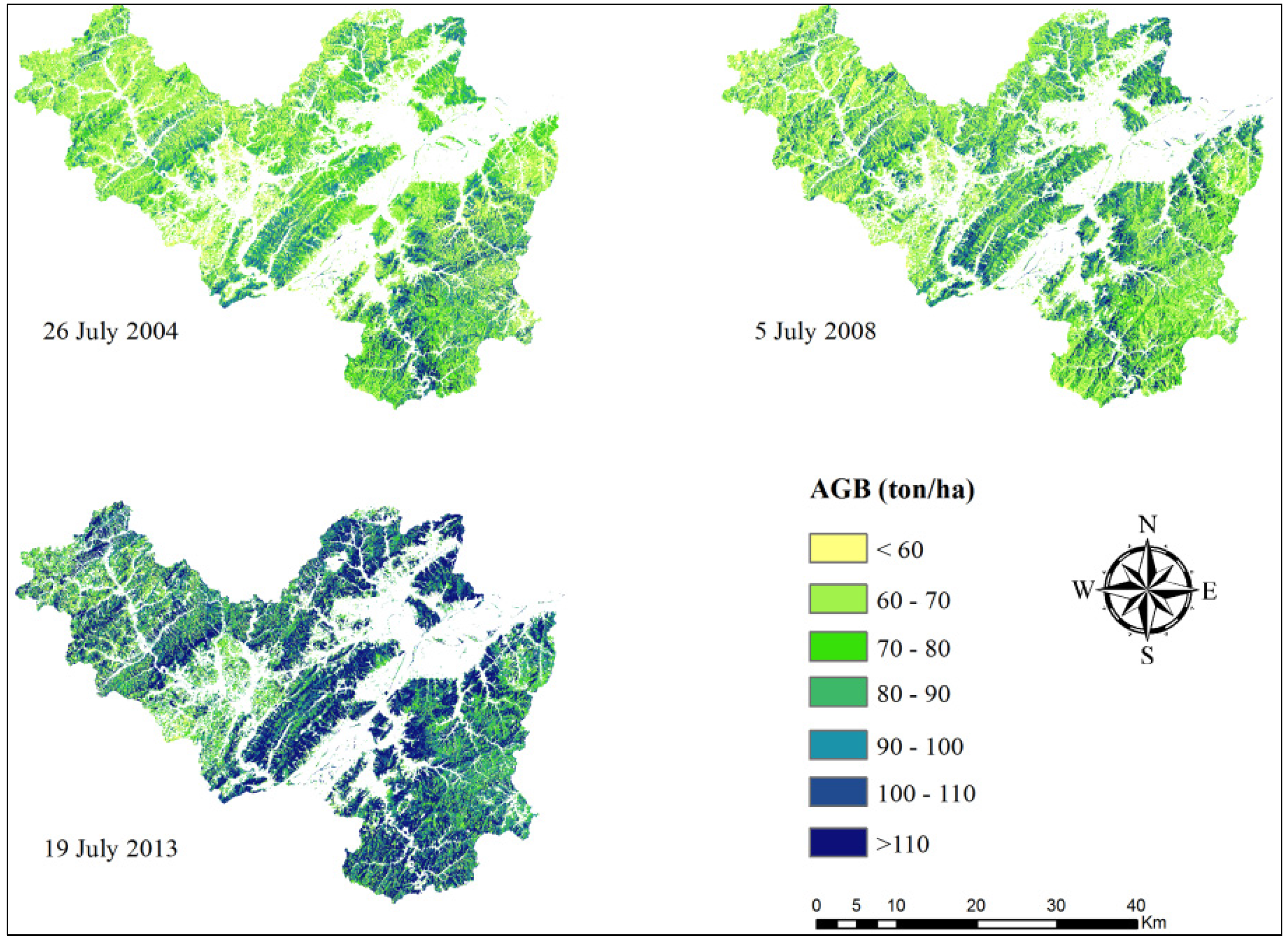
3.3. Aboveground Biomass Estimates
3.3.1. AGB Distribution Characteristic
3.3.2. AGB Changes with Terrain

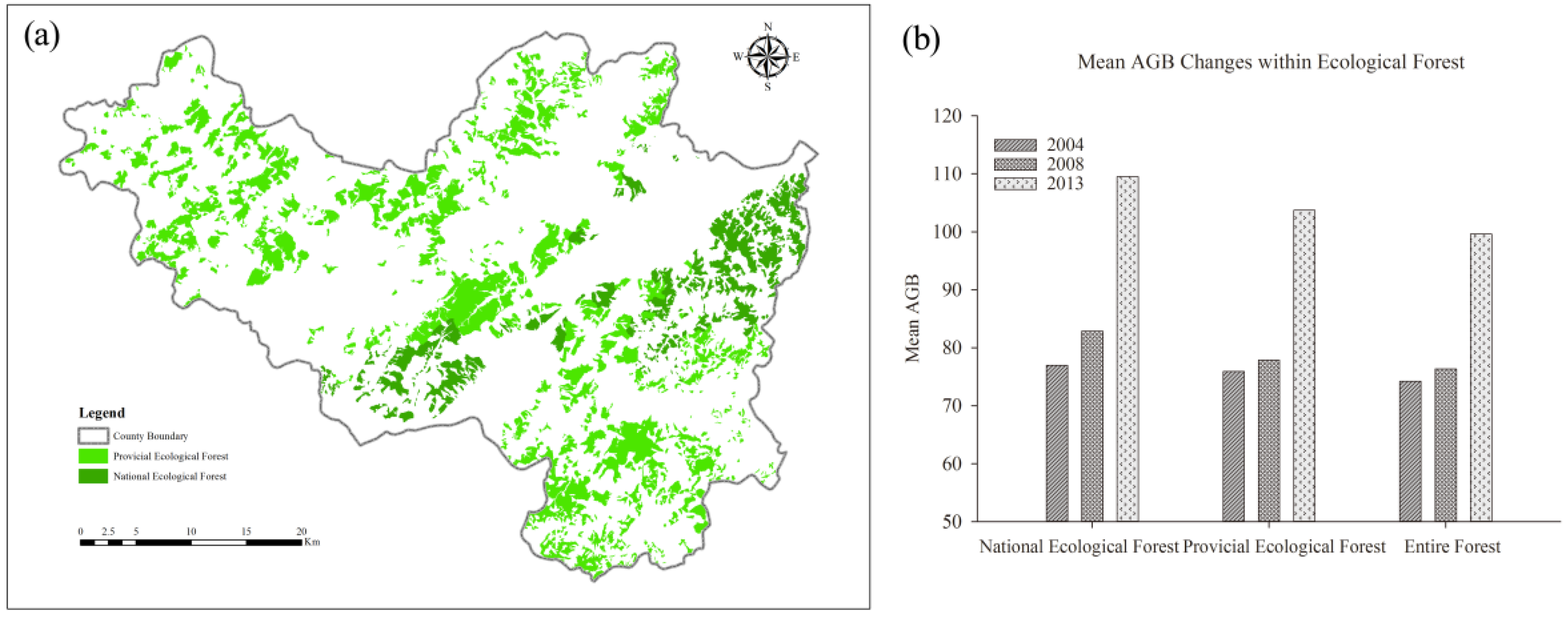
3.3.3. AGB Change within Ecological Forest
4. Discussion
4.1. Reasons for AGB Changes
4.2. Uncertainty Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGB | Above Ground Biomass |
| REDD | Reducing carbon Emissions associated with Deforestation and forest Degradation |
| DBH | Diameter at Breast Height |
| TM | Thematic Mapper |
| OLI | Operational Land Imager |
| DEM | Digital elevation model |
| RF | Random Forest |
| RMSE | Root Mean Squared Error |
References
- Costanza, R.; D’Arge, R.; de Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Ecol. Econ. 1998, 25, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Dietz, T.; Carpenter, S.R.; Alberti, M.; Folke, C.; Moran, E.; Pell, A.N.; Deadman, P.; Kratz, T.; Lubchenco, J.; et al. Complexity of coupled human and natural systems. Science 2007, 317, 1513–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olander, L.P.; Gibbs, H.K.; Steininger, M.; Swenson, J.J.; Murray, B.C. Reference scenarios for deforestation and forest degradation in support of REDD: A review of data and methods. Environ. Res. Lett. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Ganguly, S.; Nemani, R.R.; White, M.A.; Milesi, C.; Hashimoto, H.; Wang, W.; Saatchi, S.; Yu, Y.; Myneni, R.B. Estimation of forest aboveground biomass in California using canopy height and leaf area index estimated from satellite data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 151, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Cao, C.; Dang, Y.; Xiang, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, H. Retrieval of forest growing stock volume by two different methods using Landsat TM images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shao, G.; Chen, H.; Lewis, B.J.; Qi, G.; Yu, D.; Zhou, L.; Dai, L. An Application of Remote Sensing Data in Mapping Landscape-Level Forest Biomass for Monitoring the Effectiveness of Forest Policies in Northeastern China. Environ. Manag. 2013, 52, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.; Chen, Q.; Wang, G.; Liu, L.; Li, G.; Moran, E. A survey of remote sensing-based aboveground biomass estimation methods in forest ecosystems. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Zhou, T.; Zou, Z.; Zhao, X.; Huang, K.; Wu, H. Mapping Forest Biomass Using Remote Sensing and National Forest Inventory in China. Forests 2014, 5, 1267–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.P.; Wulder, M.A.; Loveland, T.R.; Woodcock, C.E.; Allen, R.G.; Anderson, M.C.; Helder, D.; Irons, J.R.; Johnson, D.M.; Kennedy, R.; et al. Landsat-8: Science and product vision for terrestrial global change research. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 145, 154–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D. The potential and challenge of remote sensing-based biomass estimation. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 1297–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, T.; Mutanga, O. Evaluating the utility of the medium-spatial resolution Landsat 8 multispectral sensor in quantifying aboveground biomass in Mgeni catchment, South Africa. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 101, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, D. Improving forest aboveground biomass estimation using seasonal Landsat NDVI time-series. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 102, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pflugmacher, D.; Cohen, W.B.; Kennedy, R.E.; Yang, Z. Using Landsat-derived disturbance and recovery history and lidar to map forest biomass dynamics. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 151, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yang, L.; Liu, Q.; Li, J. Review of forest above ground biomass inversion methods based on remote sensing technology. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 19, 62–74. [Google Scholar]
- Latifi, H.; Nothdurft, A.; Koch, B. Non-parametric prediction and mapping of standing timber volume and biomass in a temperate forest: Application of multiple optical/LiDAR-derived predictors. Forestry 2010, 83, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güneralp, İ.; Filippi, A.M.; Randall, J. Estimation of floodplain aboveground biomass using multispectral remote sensing and nonparametric modeling. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinform. 2014, 33, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Fu, Z.; Ge, H.; Ji, B.; Jiang, P.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhao, K. Spatial Variation of Biomass Carbon Density in a Subtropical Region of Southeastern China. Forests 2015, 6, 1966–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Peng, D.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Y. Improving artificial forest biomass estimates using afforestation age information from time series Landsat stacks. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 7293–7306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, F.; Jin, X. Spatial modeling of the carbon stock of forest trees in Heilongjiang Province, China. J. For. Res. 2014, 25, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Zhu, J.; Wang, K.; Hu, W. Land Use Changes Induced County-Scale Carbon Consequences in Southeast China 1979–2020, Evidence from Fuyang, Zhejiang Province. Sustainability 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Jiang, B.; Ge, Y.; Zhu, J.; Shen, A. Study on Biomass Model of Key Ecological Forest in Zhejiang Province. J. Zhejiang For. Sci. Technol. 2009, 29, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Gao, H.; Ying, B.; Wang, J.; Yuan, W.; Zhu, J.; Yi, L.; Jiang, B. The biomass dynamic analysis of public walfare forest in Xianju county of Zhejiang province. J. Nanjing For. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2011, 35, 147–150. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Q.; Xu, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Ji, B. Correlation between forest carbon distribution and terrain elements of altitude and slope. J. Zhejiang AF. Univ. 2013, 30, 330–335. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Y.; Yilita; Dou, P.; Zhu, G.; Ying, B.; Yu, S. Biomass and carbon fixation with oxygen release benefits in an ecological service forest of Jinyun County, China. J. Zhejiang AF. Univ. 2012, 29, 257–264. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Geological Survey. Available online: http://glovis.usgs.gov (accessed on 20 July 2015).
- Cooley, T.; Anderson, G.P.; Felde, G.W.; Hoke, M.L.; Ratkowski, A.J.; Chetwynd, J.H.; Gardner, J.A.; Adler-Golden, S.M.; Matthew, M.W.; Berk, A.; et al. FLAASH, a MODTRAN4-based atmospheric correction algorithm, its application and validation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Geoscience and Remote Sensing (IGARSS), Munich, Germany, 24–28 June 2002; pp. 1414–1418.
- Myeong, S.; Nowak, D.J.; Duggin, M.J. A temporal analysis of urban forest carbon storage using remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 101, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soenen, S.A.; Peddle, D.R.; Coburn, C.A. SCS+C: A modified Sun-canopy-sensor topographic correction in forested terrain. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 2148–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemani, R.; Pierce, L.; Running, S.; Band, L. Forest ecosystem processes at the watershed scale—Sensitivity to remotely-sensed leaf-area index estimates. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1993, 14, 2519–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crist, E.P.; Cicone, R.C. A physically-based transformation of Thematic Mapper data—The TM Tasseled Cap. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1984, 22, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, T.; Mutanga, O. Investigating the robustness of the new Landsat-8 Operational Land Imager derived texture metrics in estimating plantation forest aboveground biomass in resource constrained areas. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 108, 12–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, S.; Hogg, E.H.; Lieffers, V.; Qin, Y.; He, F. Estimating spatial variation in Alberta forest biomass from a combination of forest inventory and remote sensing data. Bio. Geosci. 2014, 11, 2793–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.; Li, F.; Chung, N.; Bae, M.; Hwang, S.; Byoen, M.; Park, S.; Park, Y. Response of Fish Communities to Various Environmental Variables across Multiple Spatial Scales. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 3629–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Available online: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 20 September 2015).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Baccini, A.; Laporte, N.; Goetz, S.J.; Sun, M.; Dong, H. A first map of tropical Africa’s above-ground biomass derived from satellite imagery. Environ. Res. Lett. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Batistella, M. Exploring TM image texture and its relationships with biomass estimation in Rondônia, Brazilian Amazon. Acta Amazon. 2005, 35, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clipp, H.; Anderson, J. Environmental and Anthropogenic Factors Influencing Salamanders in Riparian Forests: A Review. Forests 2014, 5, 2679–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Yi, L.; Zhang, C.; Yu, S.; Shen, L.; Peng, D.; Zheng, C. Biomass and Carbon Storage of Public Service Forests in the Central Area of Zhejiang Province. Sci. Silvae. Sin. 2013, 49, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Yan-fen, C. Dynamic analysis of Vegetation Biomass and Carbon Storage of Public Welfare Forests in Liandu District. J. Sichuan For. Sci. Technol. 2014, 35, 66–69. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, D.; Chen, Q.; Wang, G.; Moran, E.; Batistella, M.; Zhang, M.; Vaglio Laurin, G.; Saah, D. Aboveground Forest Biomass Estimation with Landsat and LiDAR Data and Uncertainty Analysis of the Estimates. Int. J. For. Res. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Wylie, B.K.; Brown, D.R.N.; Peterson, B.; Alexander, H.D.; Mack, M.C.; Rover, J.; Waldrop, M.P.; McFarland, J.W.; Chen, X.; et al. Spatially explicit estimation of aboveground boreal forest biomass in the Yukon River Basin, Alaska. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, C.; Shen, H.; Wang, K.; Shen, A.; Deng, J.; Gan, M. Landsat Imagery-Based Above Ground Biomass Estimation and Change Investigation Related to Human Activities. Sustainability 2016, 8, 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8020159
Wu C, Shen H, Wang K, Shen A, Deng J, Gan M. Landsat Imagery-Based Above Ground Biomass Estimation and Change Investigation Related to Human Activities. Sustainability. 2016; 8(2):159. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8020159
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Chaofan, Huanhuan Shen, Ke Wang, Aihua Shen, Jinsong Deng, and Muye Gan. 2016. "Landsat Imagery-Based Above Ground Biomass Estimation and Change Investigation Related to Human Activities" Sustainability 8, no. 2: 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8020159
APA StyleWu, C., Shen, H., Wang, K., Shen, A., Deng, J., & Gan, M. (2016). Landsat Imagery-Based Above Ground Biomass Estimation and Change Investigation Related to Human Activities. Sustainability, 8(2), 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8020159






