New Insights into the Geography and Modelling of Wind Erosion in the European Agricultural Land. Application of a Spatially Explicit Indicator of Land Susceptibility to Wind Erosion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. The Index of Land Susceptibility to Wind Erosion—ILSWE
3. Results and Discussion
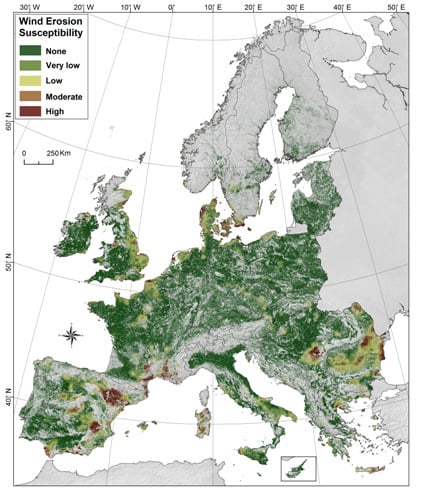
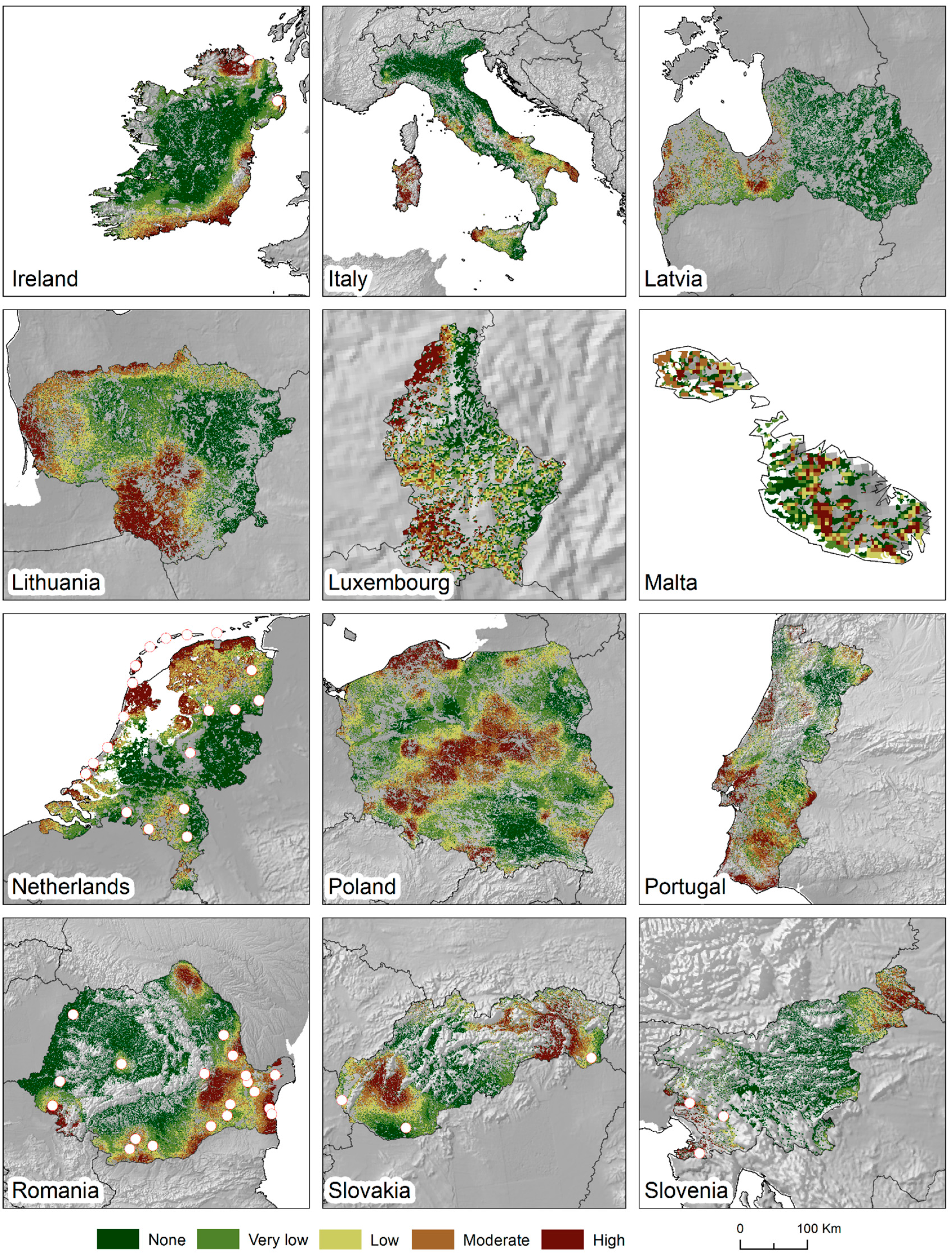
3.1. Agricultural Land Susceptibility to Wind Erosion
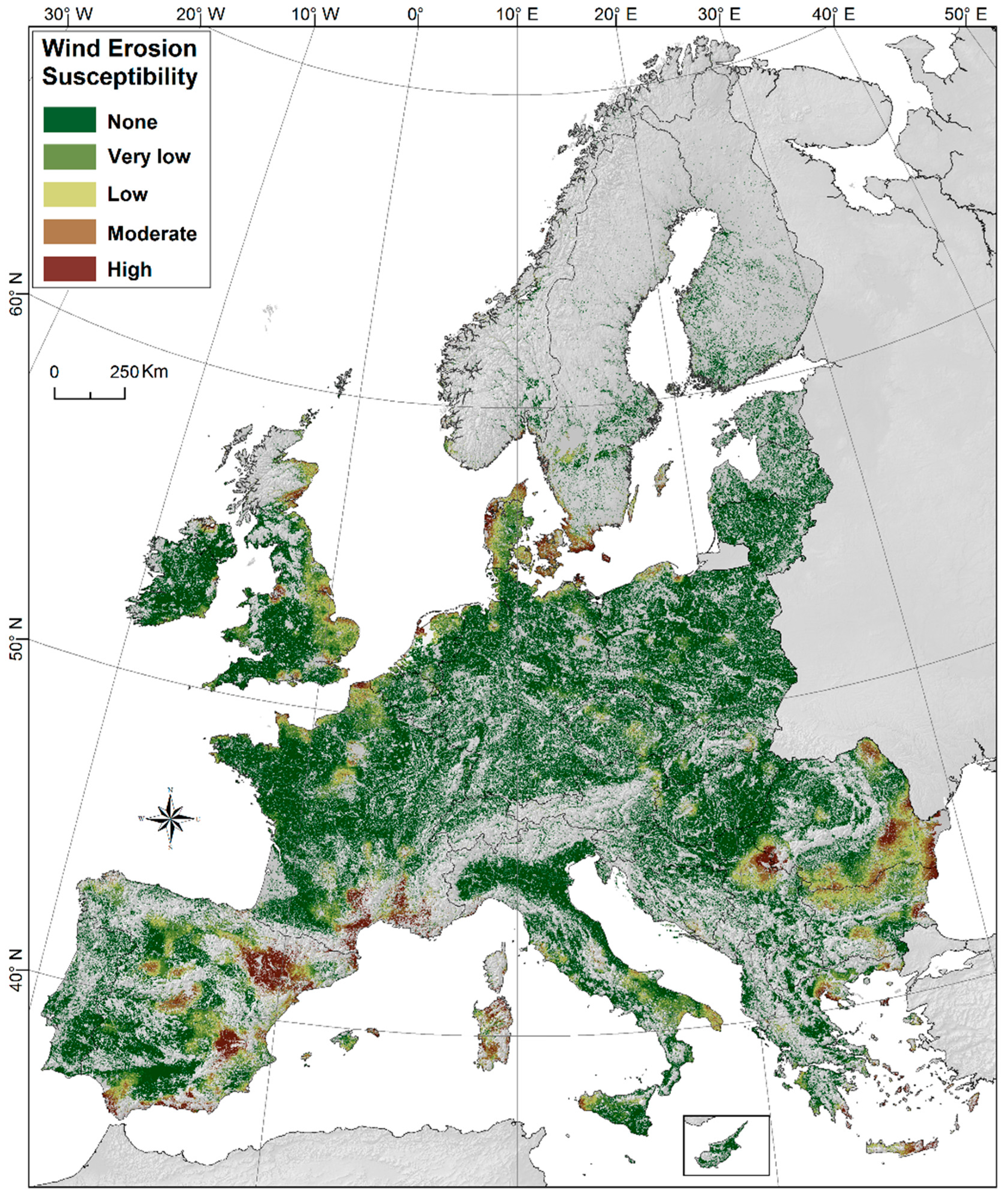
| Bio-Geographical Region | Land Susceptibility to Wind Erosion | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Surface (%) | None | Very Low | Low | Moderate | High |
| (%) | ||||||
| Alpine | 3.3 | 88.7 | 5.2 | 3.8 | 1.6 | 0.7 |
| Arctic | 0.04 | 72.4 | 3.3 | 8.9 | 9.9 | 5.5 |
| Black Sea | 0.2 | 9.1 | 0.7 | 5.5 | 16.2 | 68.5 |
| Continental | 38.5 | 77.6 | 7.2 | 7.2 | 6.2 | 1.7 |
| Mediterranean | 21.3 | 47.4 | 12.5 | 16.4 | 12.4 | 11.3 |
| Pannonian | 5.2 | 80.4 | 7.4 | 5.2 | 4.1 | 2.8 |
| Steppic | 1.4 | 5.7 | 2.7 | 19.6 | 52.3 | 19.7 |
| Atlantic | 23.2 | 64.5 | 11.6 | 14.4 | 7.8 | 1.6 |
| Boreal | 7.0 | 91.5 | 3.3 | 2.7 | 2.1 | 0.4 |
| Country | Land Susceptibility to Wind Erosion | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| None | Very Low | Low | Moderate | High | |
| (%) | |||||
| Albania | 96.8 | 2.1 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.0 |
| Austria | 82.5 | 7.0 | 7.8 | 2.7 | 0.0 |
| Belgium | 78.2 | 7.4 | 10.8 | 3.6 | 0.0 |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina | 93.4 | 2.1 | 1.7 | 2.8 | 0.0 |
| Bulgaria | 29.8 | 11.1 | 26.8 | 27.0 | 5.3 |
| Cyprus | 100 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Croatia | 95.5 | 2.8 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 0.0 |
| Czech Republic | 67.6 | 18.6 | 11.2 | 2.5 | 0.0 |
| Denmark | 6.1 | 7.6 | 30.1 | 37.8 | 18.3 |
| Estonia | 98.2 | 1.7 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Finland | 91.8 | 4.4 | 3.0 | 0.8 | 0.0 |
| Former Yugoslav Rep. Macedonia | 84.7 | 11.9 | 3.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| France | 71.0 | 10.6 | 9.1 | 5.2 | 4.0 |
| Germany | 88.7 | 5.8 | 3.7 | 1.5 | 0.2 |
| Greece | 53.2 | 10.4 | 15.1 | 12.2 | 9.2 |
| Hungary | 87.8 | 7.4 | 3.7 | 1.1 | 0.0 |
| Ireland | 85.2 | 7.3 | 4.6 | 2.2 | 0.6 |
| Italy | 65.1 | 11.6 | 12.6 | 7.7 | 3.0 |
| Latvia | 98.4 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.0 |
| Liechtenstein | 100 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Lithuania | 100 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Luxembourg | 100 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Malta | 100 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Montenegro | 86.5 | 9.2 | 4.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Netherlands | 48.3 | 14.6 | 24.3 | 9.4 | 3.4 |
| Norway | 64.9 | 7.7 | 11.9 | 11.0 | 4.5 |
| Poland | 89.6 | 7.0 | 2.3 | 0.9 | 0.1 |
| Portugal | 97.3 | 2.3 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Romania | 47.4 | 7.4 | 15.0 | 21.7 | 8.4 |
| Serbia and Kosovo | 64.1 | 6.6 | 9.3 | 13.8 | 6.1 |
| Slovakia | 78.5 | 11.1 | 7.4 | 2.9 | 0.1 |
| Slovenia | 99.8 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Spain | 39.7 | 13.9 | 19.5 | 14.0 | 13.0 |
| Sweden | 59.5 | 7.8 | 8.9 | 14.6 | 9.2 |
| Switzerland | 98.5 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.0 |
| United Kingdom | 53.2 | 11.7 | 20.1 | 12.5 | 2.4 |
3.2. Model Evaluation
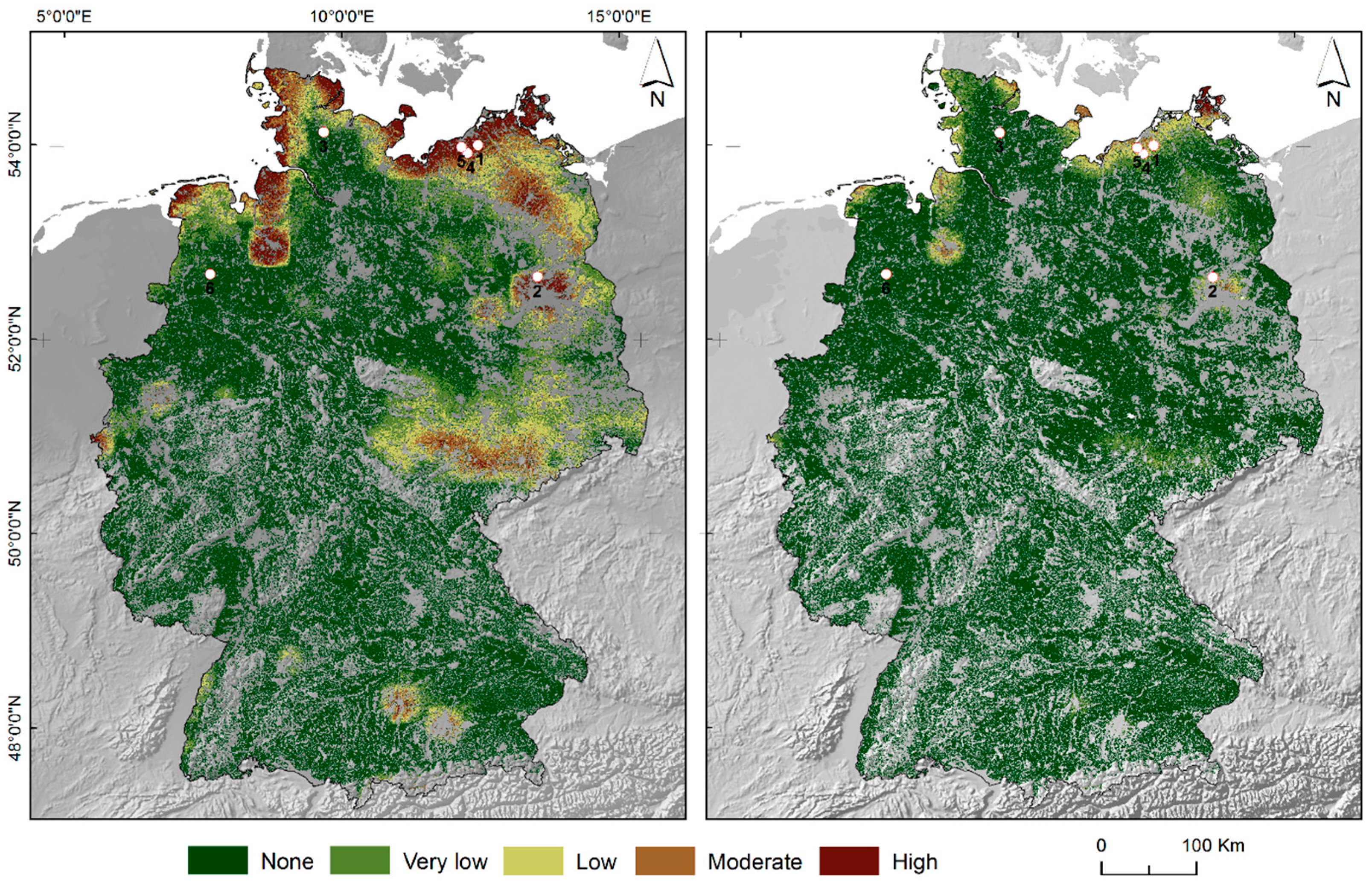
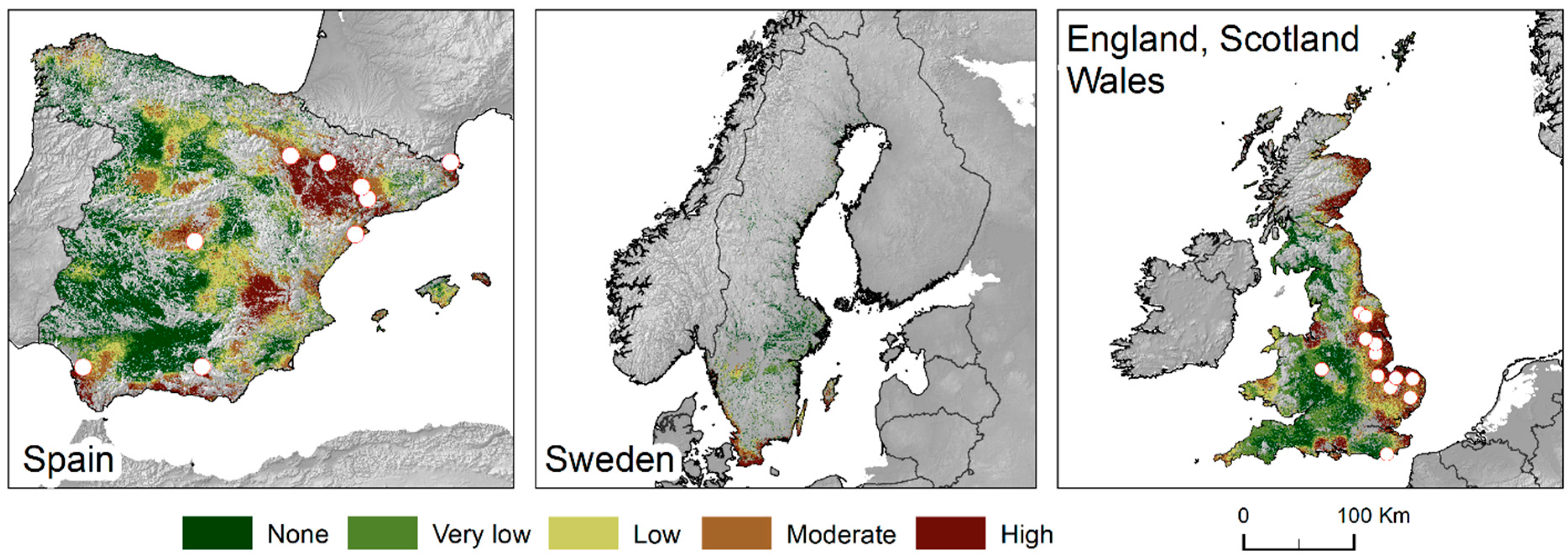

3.3. Data Availability
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lal, R. Soil erosion by wind and water: Problems and prospects. Soil Eros. Res. Methods 1994, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff, N.P.; Siddoway, F.H. A wind erosion equation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1965, 29, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalma, J.D.; Speight, J.G.; Wasson, R.J. Potential wind erosion in Australia: A continental perspective. J. Climatol. 1988, 8, 411–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, R.; Reuter, H.I. Wind erosion. In Soil Erosion in Europe; Boardman, J., Poesen, J., Eds.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2006; pp. 563–582. [Google Scholar]
- Bagnold, R.A. The Physics of Blown Sand and Desert Dunes; Methuen and Company: London, UK, 1941. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Y. Physics and Modelling of Wind Erosion; Springer: Cologne, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Funk, R.; Skidmore, E.L.; Hagen, L.J. Comparsion of wind erosion measurements in Germany with simulated soil losses by WEPS. In Proceedings of the ICAR5/GCTE-SEN Joint Conference, Lubbock, TA, USA, 22–25 July 2002; pp. 235–238.
- Eppink, L.A.A.J.; Spaan, W.P. Agricultural wind erosion control measures in The Netherlands. Soil Technol. Ser. 1989, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- López, M.V.; Sabre, M.; Gracia, R.; Arrue, J.L.; Gomes, L. Tillage effects on soil surface conditions and dust emission by wind erosion in semiarid Aragon (NE Spain). Soil Tillage Res. 1998, 45, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bärring, L.; Jönsson, P.; Mattsson, J.O.; Åhman, R. Wind erosion on arable land in Scania, Sweden and the relation to the wind climate—A review. Catena 2003, 52, 173–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, A. Wind Erosion on Agricultural Land in Europe: Research Results for Land Managers; Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Bruxelles, Belgium, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Graña, A.M.; Goy, J.L.; Zazo, C. Water and Wind Erosion Risk in Natural Parks—A Case Study in “Las Batuecas-Sierra de Francia” and “Quilamas” Protected Parks (Central System, Spain). Int. J. Environ. Res. 2014, 8, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Graña, A.M.; Goy, J.L.; Zazo, C. Cartographic procedure for the analysis of aeolian erosion hazard in natural parks (Central System, Spain). Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 26, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Environment Agency (EEA). Europe’s Environment: The Second Assessment; Elsevier: London, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- European Environment Agency (EEA). The Third Assessment. Environmental Assessment; Report No 10; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Chappell, A.; Warren, A. Spatial scales of 137Cs-derived soil flux by wind in a 25 km2 arable area of eastern England. Catena 2003, 52, 209–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhner, J.; Schäfer, W.; Conrad, O.; Gross, J.; Ringeler, A. The WEELS model: Methods, results and limitations. Catena 2003, 52, 289–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, L.; Arrue, J.L.; Lopez, M.V.; Sterk, G.; Richard, D.; Gracia, R.; Frangi, J.P. Wind erosion in a semiarid agricultural area of Spain: The WELSONS project. Catena 2003, 52, 235–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, P.; Ballabio, C.; Panagos, P.; Montanarella, L. Wind erosion susceptibility of European soils. Geoderma 2014, 232, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, P.; Panagos, P.; Ballabio, C.; Lugato, E.; Weynants, M.; Montanarella, L. Towards a pan-European assessment of land susceptibility to wind erosion. Land Degrad. Dev. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leys, J.F. Wind Erosion on Agricultural Land. In Aeolian Environments, Sediments and Landforms; Goudie, A.S., Livingstone, I., Eds.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1999; pp. 143–166. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, L.E. An overview of the wind erosion prediction system. Available online: https://webdisk.ucalgary.ca/~walkerd/public_html/Wind%20Erosion%20Prediction/WEPS_Overview.pdf (accessed on 30 June 2015).
- European Environment Agency (EEA). Assessment and Reporting on Soil Erosion; Technical Report 94; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zobeck, T.M.; Parker, N.C.; Haskell, S.; Guoding, K. Scaling up from field to region for wind erosion prediction using a field-scale wind erosion model and GIS. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2000, 82, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Leslie, L.M. Wind erosion prediction over the Australian continent. J. Geophys. Res. Atmospheres 1997, 102, 30091–30105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryrear, D.W.; Bilbro, J.D.; Saleh, A.; Schomberg, H.; Stout, J.E.; Zobeck, T.M. RWEQ: Improved wind erosion technology. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2000, 55, 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Poilve, H. BioPar Product User Manual: MERIS FR Biophysical Products. Available online: http://web.vgt.vito.be/documents/BioPar/g2-BP-RP-BP053-ProductUserManual-MERISFR-I1.50.pdf (accessed on 30 June 2015).
- TA-Luft. Erste Allgemeine Verwaltungsvorschrift zum Bundes-Immissionsschutzgesetz. Available online: https://recht.nrw.de/lmi/owa/br_bes_text?anw_nr=1&gld_nr=7&ugl_nr=7129&bes_id=994&val=994&ver=7&sg=0&aufgehoben=N&menu=1 (accessed on 30 June 2015).
- Klir, G.J.; Yuan, B. Fuzzy Sets and Fuzzy Logic; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Mezõsi, G.; Blanka, V.; Bata, T.; Kovács, F.; Meyer, B. Estimation of regional differences in wind erosion sensitivity in Hungary. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2013, 1, 4713–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veihe, A.; Hasholt, B.; Schiøtz, I.G. Soil erosion in Denmark: Processes and politics. Environ. Sci. Policy 2003, 6, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, R. Quantifizierung der Winderosion auf einem Sandstandort Brandenburgs unter besonderer Beruecksichtigung der Vegetationswirkung; ZALF-Berichte: Ems, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Funk, R.; Voelker, L. Einschätzung der potentiellen Winderosionsgefährdungin Mecklenburg-Vorpommern im Landesmaßstab mit der Revised WindErosion Equation. In Mitteilungen der Deutschen Bodenkundlichen Gesellschaft; Deutsche Bodenkundliche Gesellschaft: Göttingen, Germany, 1998; pp. 557–560. [Google Scholar]
- Goossens, D. Wind erosion and tillage as a dust production mechanism on North European farmland. In Wind Erosion and Dust Dynamics: Observations, Simulations, Modelling; Goossens, D., Riksen, M., Eds.; ESW Publications: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 15–40. [Google Scholar]
- BGR (Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources) Winderosion. Available online: http://www.bgr.bund.de/DE/Themen/Boden/Ressourcenbewertung-management/Bodenerosion/Wind/BodenerosionWind_node.html (accessed on 1 December 2013).
- Panagos, P.; Van Liedekerke, M.; Jones, A.; Montanarella, L. European Soil Data Centre: Response to European policy support and public data requirements. Land Use Policy 2012, 29, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Soil Data Centre (ESDAC). Available online: http://esdac.jrc.ec.europa.eu/ (accessed on 30 June 2015).
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borrelli, P.; Panagos, P.; Montanarella, L. New Insights into the Geography and Modelling of Wind Erosion in the European Agricultural Land. Application of a Spatially Explicit Indicator of Land Susceptibility to Wind Erosion. Sustainability 2015, 7, 8823-8836. https://doi.org/10.3390/su7078823
Borrelli P, Panagos P, Montanarella L. New Insights into the Geography and Modelling of Wind Erosion in the European Agricultural Land. Application of a Spatially Explicit Indicator of Land Susceptibility to Wind Erosion. Sustainability. 2015; 7(7):8823-8836. https://doi.org/10.3390/su7078823
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorrelli, Pasquale, Panos Panagos, and Luca Montanarella. 2015. "New Insights into the Geography and Modelling of Wind Erosion in the European Agricultural Land. Application of a Spatially Explicit Indicator of Land Susceptibility to Wind Erosion" Sustainability 7, no. 7: 8823-8836. https://doi.org/10.3390/su7078823
APA StyleBorrelli, P., Panagos, P., & Montanarella, L. (2015). New Insights into the Geography and Modelling of Wind Erosion in the European Agricultural Land. Application of a Spatially Explicit Indicator of Land Susceptibility to Wind Erosion. Sustainability, 7(7), 8823-8836. https://doi.org/10.3390/su7078823