Abstract
Nowadays, an increasing shortage of water resources intensifies the contradiction among different water-using sectors in the social-economic-ecological complex system. To adjust water used configuration in a holistic framework, a water use system (WUS) model was constructed with inclusive five water-using sectors including aquatic systems, primary industry, secondary industry, tertiary industry and resident consumption. The Baiyangdian Basin in Northern China was used as a case area. Six years data from 2008 to 2013 were used to quantify the model. By introducing the ecological network analysis (EAN), we holistically assessed the WUS under different water use configuration. System organization, activities and development degree, etc. were used to character the prosperities of the water use system. Results indicate that the WUS encountered a lasting degradation in system organization (AMI index decreased in an annual rate of 0.6%) and development degree though with an ascending system activities in the studies periods (with an annual growth rate of 11.3%). Scenario analysis results suggest several potential ways to achieve a better water use configuration in this basin, such as environmental and ecological restoration, water-saving technology and water recycling rate, etc. The current study may provide ways to optimize water use structure to balance the interests of different sectors both ecologically and economically.
1. Introduction
Nowadays, increasing shortage of water resources intensifies the contradiction among different water-using sectors in the social-economic-ecological complex system in China [1,2]. Water stress within basins has intensified water use conflicts between upstream and downstream areas and also between aquatic ecosystems and social-economic ecosystem (e.g., agriculture, the municipal and industrial sectors). Function deterioration of aquatic ecosystems has been widely appeared in China, which resulted in many ecological and environmental issues in both quantity (aquifer over-exploitation and dry rivers, etc.) and quality (eutrophication, organic matter pollution, saline intrusion, etc.) [3,4,5].
Increasingly researchers have realized the importance of integrated water resources allocations in river basin scale [6,7,8,9,10]. The interdisciplinary nature of water resources problems requires the integration several aspects including economic, environmental, social, and legal aspects into a coherent analytical framework [11,12,13]. Some basin-scale water use frameworks were constructed to search the balance points among different sectors [14,15]. For example, socio-economic water sectors were included in the framework to detect the interactions among various sectors. The ascendency value 0.459 is chosen as the optimal network structure balance point for sustainability of the ecosystem. Basin-scale holistic assessment on water use framework is the first step to optimize the water allocations.
Without the contents of holistic assessment, one has no idea of the system functioning under different water allocation schemes. An example can be seen in the Baiyangdian Basin in Northern China. To alleviate the water stress among different water use sectors, integrated water resources allocation plan has been operated in the basin for many years. For example, basin-scale virtual water strategy was also considered in solving the water crisis in some water scarce regions to balance the water resources among different sectors [16,17,18]. Partial ecological, social and economic effects have been achieved in this basin, however, it is hard to know the holistic status of the large water use system and thus the holistic effects are also hard to assess. Without the above information, further measures and goals are difficult to operate and achieve for the whole basin. Understanding the integrity and organization of a water use system (WUS) is the first step to achieve system-based basin water resources management and ecological restoration.
Derived from the economic input-output analysis, ecological network analysis (ENA) is further developed to depict mutual relationships and holistic attributes of complex ecosystems as well as other systems [19,20]. ENA allows researchers to study complex ecosystems from the perspective of the overall system. By ENA one can identify many indices of ecosystem functioning and relate them to environmental or ecological phenomena (e.g., eutrophication, succession and functional degradation), which provide important information for ecosystems management. Since the first application of ENA on hydrological system in 1982 [21], the ENA has also been widely applied in water resources system [22,23,24,25].
To realize a holistic assessment to the water allocations system in the Baiyangdian Basin, ENA is introduced in the current study. The present work may explore the use of ENA to provide meaningful reference information for integrated water resource management in basin-scale. Specific objectives addressed here were as follows: First, to holistically assess the WUS under different water use configurations of the Baingyangdian Basin. Second, to provide some suggested water use strategies for integrated water resources allocation for the Baingyangdian Basin.
2. Methodology
2.1. Study Area
The Baiyangdian Basin is located in the middle of the North China Plain with an area of 31,199 km2 (39.4°N–40.4°N, 113.39°E–116.11°E). Its climate is characterized by continental monsoons and the average annual rainfall is 556 mm. The name of the basin comes from the largest Baiyangdian Lake of the northern China. Due to its important ecological and environmental role in the region, the lake was described as the “kidney” of the northern China. There are in total 3 municipalities (Baoding, Gaobeidian and Dingzhou) and 20 countries (Fuping, Quyang, Anguo, Boye, Tang, Wangdou, Shunping, Mancheng, Qingyuan, Li, Gaoyang, Anxin, Xiong, Rongcheng, Xushui, Laiyuan, Yi, Laishui, Dingxian and Zhuozhou) in the basin (Figure 1).
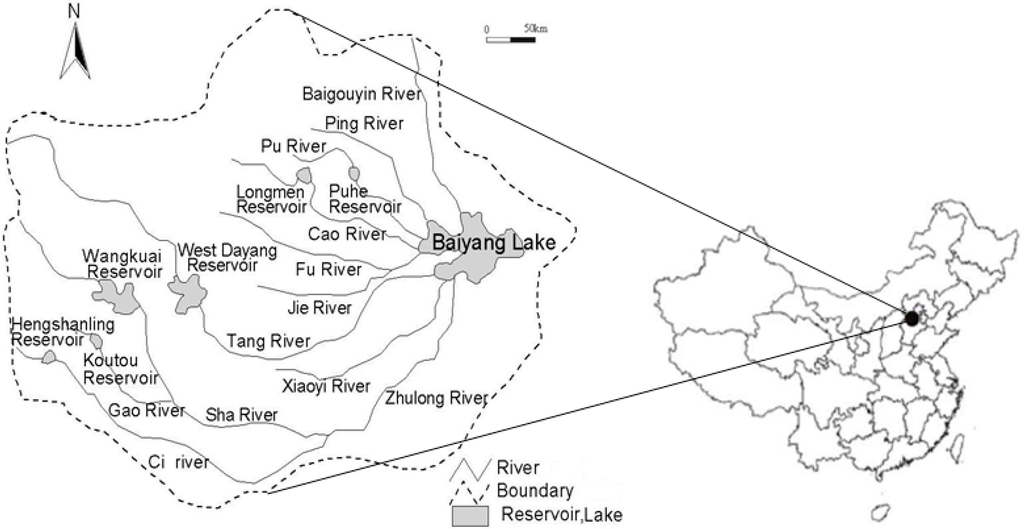
Figure 1.
The location of the Baiyangidan Basin.
Water pollution and ecosystem degradation in the Baiyangdian Basin have been accelerated in the last two decades due to continued water pressures from rapid economic growth, industrialization, and urbanization in this basin [26]. In addition to the fragmental water resources management model, the phenomena of “low” or “no” inflows from upstream rivers into the lake becomes more and more frequent, which resulted in the shrinkage of the Baiyangdian Lake [27]. An innovative integrated water resources management and assessment approach is needed to alleviate the contradiction among different water-using sectors in the Baiyangdian Basin.
2.2. Network Analysis for the Water Use System
2.2.1. Network Model Description
To holistic assess the WUS of the Baiyangdian Basin, a five-water-using-sectors model including aquatic systems, primary industry, secondary industry, tertiary industry and resident consumption was constructed in the current study (Figure 2).
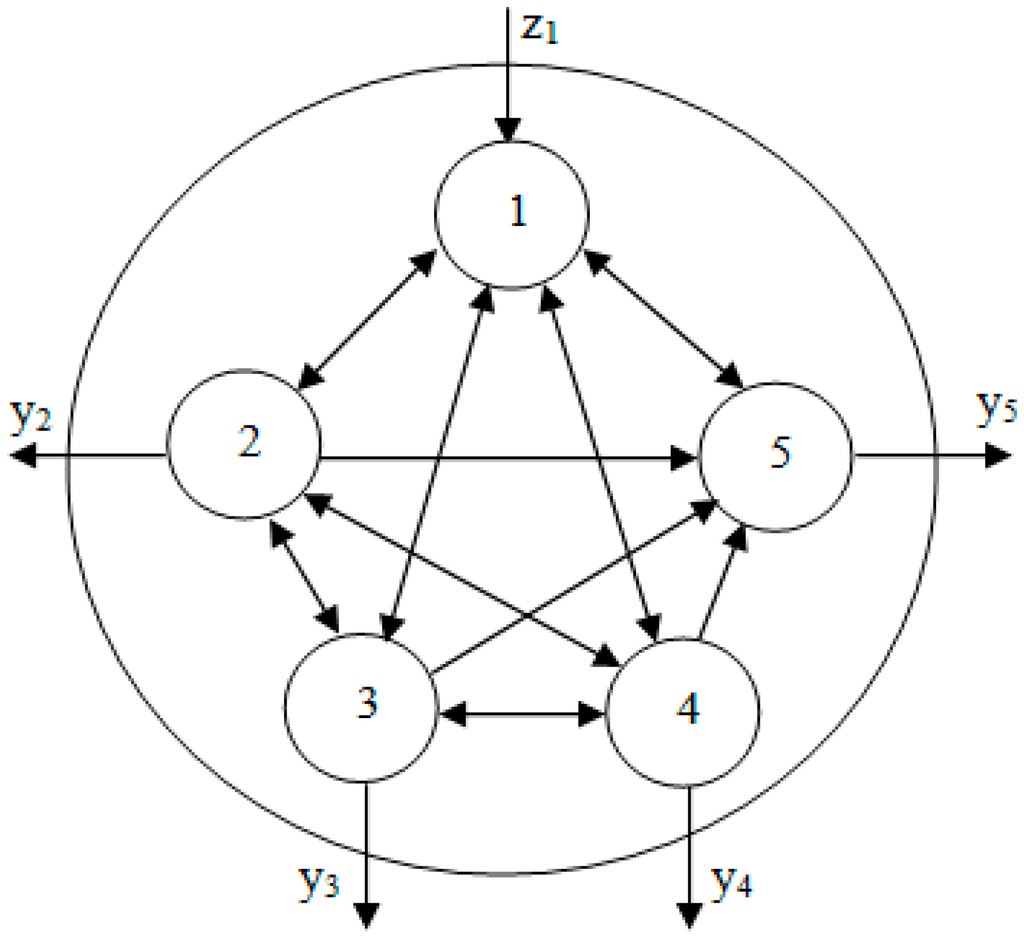
Figure 2.
The water use system (WUS) network model (1-Aquatic systems; 2-Primary industry; 3-Secondary industry; 4-Tertiary industry; 5-Resident consumption).
In the Figure 1, zk and yk represent boundary inputs (m3·year−1) and boundary output (m3·year−1) of the kth compartment, respectively. It is assumed that each component withdraws water from aquatic systems for consumption or production, and water will transfer between different sectors due to physical and virtual water trade transactions. The network model incorporates social-economic-ecological sectors into a whole system. The function of the system can be evaluated with ENA with a holistic perspective.
2.2.2. Network Analysis Methods
The ascendency analysis of ENA was utilized to assess the function of the current WUS. Ulanowicz (1980, 1986) founded an ascendency theory on the basis of information theory, which founded by Shannon (1948) and further developed by Rutledge et al. (1976) [28,29,30,31]. Ascendency is developed to quantify organization and system size, which seeks to explain mathematically much of the phenomena in developing ecosystems [32]. System size is quantified by total system throughput (TSTP) is the sum of the total link flows in the system and the system development is measured by the average mutual information (AMI).
Since water is the only currency used to quantify the WUS, the characteristics of WUS under different water allocation regimes can be depicted through various network indicators. Indicator TSTP can be used to reflect the magnitude of system activity that is affected by system characteristics such as size of the basin water consumption. The organization by which the water use processes are linked can be detected by AMI. Ascendency that combines TSTP and AMI can be used to gauge how well the WUS performs in terms of processing the given water flows. Moreover, various indicators can be used to depict holistic and partial properties of the system. Here, we focused on eight network indicators in Table 1.

Table 1.
Network analysis indicator name, symbol and algorithms.
| No. | Name | Symbol | Algorithms |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Total System Throughput | TSTP | |
| 2 | Average Mutual Information | AMI | |
| 3 | Ascendency | A | |
| 4 | Import Ascendency | A0 | |
| 5 | Internal Ascendency | Ai | |
| 6 | Export Ascendency | Ae | |
| 7 | Development Capacity | C | |
| 8 | Ratio ascendency | A/C, A0/A, Ai/A, Ae/A | |
is the TSTP; (n+1) are import value; (n+2) are export value; Tij means total amount of flow from compartment j to compartment i.
These indicators are divided into three categories: whole-system indicators (TSTP, AMI, A and C), component system indicators (A0, Ai and Ae) and ratio-based indicators (A/C, A0/A, Ai/A and Ae/A). Whole system indicators were used to describe the whole attribute of the WUS. TSTP reflects the system activity of the WUS and AMI represents the organization inherent in the WUS. Ascendency is the production of TSTP and AMI that quantifies both the level of system activity and the degree of the organization of the WUS. Capacity is functions as a mathematical upper bound on the ascendency. It represents the scope of the system for further development. A/C represents realized Ascendency under specific system structure. Component system indicators exhibit the characteristics of boundary input, output and interflows. For instance, A0 may be used to describe the water withdrawal of each sector, and Ae is associated with boundary output caused by each sector. The internal measures (Ai) are generated by interflows, which affected mostly by water transfers among different sectors.
2.3. Scenarios Analysis
Eight scenarios were designed to represent realistic changes but in their limited scope are only interpreted as semi quantitative-see the discussion below (Table 2). Each scenario is specially designed to represent changes caused by realistic situations, such as precipitation fluctuation, water abstraction changes, cycle of water use and so on. We detect the variations of different indicators to understand the WUS. The indicator changes between the baseline model and modified models was calculated by percent differences: (WUSi − WUS0)/WUS0 × 100%.

Table 2.
Network modifications to the baseline model.
| No. | WS | Modification | Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | WS1 | Increasing boundary input by 10% | Precipitation increase |
| 2 | WS2 | Decreasing boundary input by 10% | Precipitation decrease |
| 3 | WS3 | Increasing boundary output by 10% | Lower water use efficient |
| 4 | WS4 | Decreasing boundary output by 10% | Higher water use efficient |
| 5 | WS5 | Increasing interflows among component 2–5 by 10% | More water exchanges |
| 6 | WS6 | Decreasing interflows among component 2–5 by 10% | Less water exchanges |
| 7 | WS7 | Adding new pathways from 5–2, 5–3 and 5–4 | New water exchange mode |
| 8 | WS8 | Reducing pathways among component 2, 3 and 4 | Less water exchanges |
2.4. Data Sources
To demonstrate the water footprint structure of the whole basin, all the municipalities and countries with the basin are included in our research. A total of 3 municipalities and 20 countries were covered in the calculation. The primary data comes from Hebei Statistical Yearbook, Hebei Economy Yearbook, Baoding Statistical Yearbook and Baoding Economy Yearbook from 2008–2013. Virtual water data was calculated by Equation (1).
where VWC denotes the virtual water content (m3·ton−1) of the commodity, P represents the sum of the volume of a single products’ production (ton) and VW is the virtual water quantity. The VWC of a specific crop or animal is taken as the raw material of the processed product [33]. Footprints of industrial sector were calculated with an average VWC per dollar added value in the industrial sector for simplicity [34]. Footprints of services sector were acquired by multiplying the VWC with the services output of 2008–2013 and the VWC of tertiary industry was provided by Zhao et al. (2009) [35].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fluctuations of Network Indicators from 2008–2013
Variations of various network indicators were illustrated in Figure 3(1)–(6), which reflects the variations of functional condition of the WUS. Three types of indicators are included in various network indicators, including whole-system indicators (TSTP, AMI, A and C), component system indicators (A0, Ai and Ae) and ratio-based indicators (A/C, A0/A, Ai/A and Ae/A).
Ulanowicz (1986, 1997) has proposed that stressed ecosystems would decrease their ascendency [29,32]. It seemed that the WUS functioning well in the studied periods if we focused only on the increasing Ascendency index. Annual growth rate of system Ascendency reached about 10.1% in the studies periods. Similarly, the TSTP also has an upward tendency in six periods with an annual growth rate of 11.3%. However, one may notice that the AMI index decreased in an annual rate of 0.6%. The AMI index coincide is well with the productivity of fish and Phragmites australis, which can be employed to represent the ecological conditions of the Baiyangdian Basin [36]. It is considered that the AMI is more suitable to represent the system function state. A similar variation tendency can be observed in the fluctuation of index A/C. The WUS in 2008 has the highest A/C index, and then continued to decrease to 0.289 of 2013.
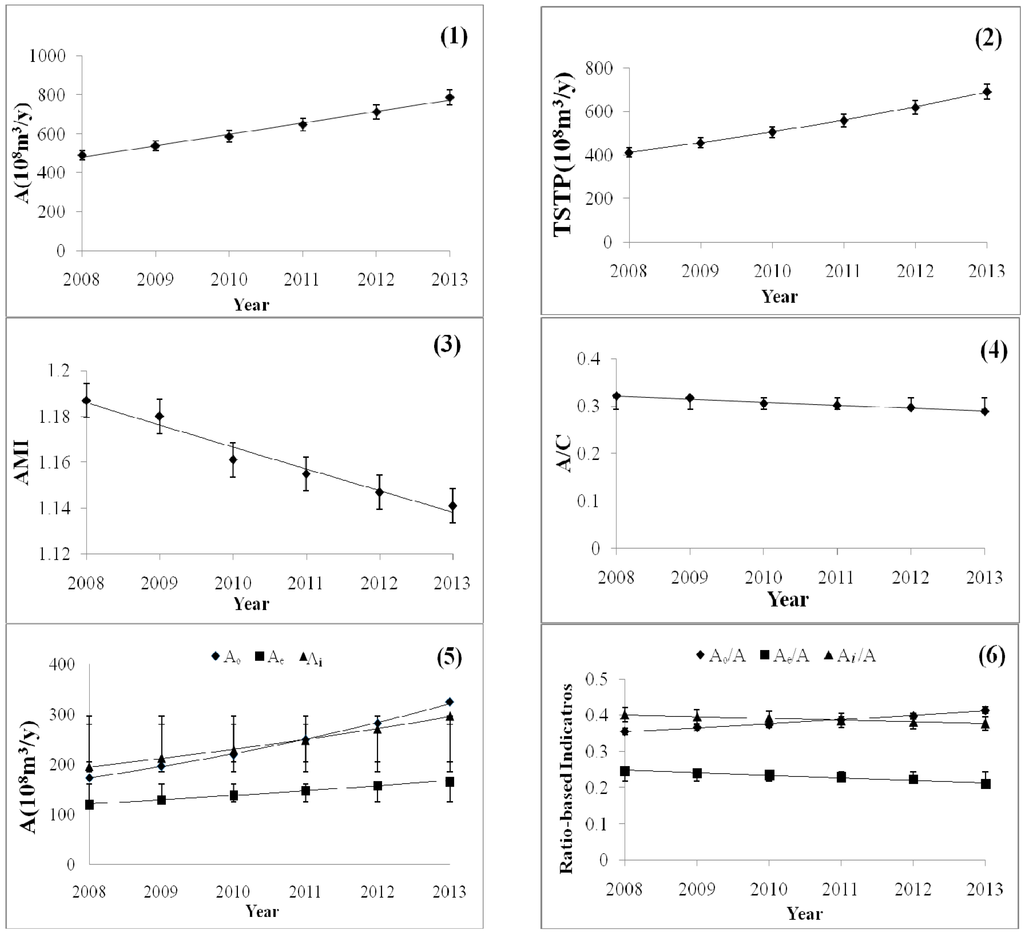
Figure 3.
Variation of network indicators of the WUS during 2008–2013.
Compared to whole-system indicators, component indicators provide more detailed information of dynamic system functional variations. Results indicate each component indicators increased in different scopes in six consequential periods. Index A0 shares the largest growth with an annual growth rate of 14.6% and Ae gets the least growth with an annual growth rate of 6.3%. The above results indicate that boundary outputs contribute more to the increases of system ascendency, which is corresponding to the increasing water withdrawals from aquatic systems. The above fact can be testified by the ratio-based indicators A0/A, Ai/A and Ae/A. The annual decrease rate of Ai/A and Ae/A are 0.9% and 2.3%, respectively, while the annual growth rate of A0/A reaches 2.7%.
3.2. Results of Scenario Analysis
Results of different modified scenarios are presented in Figure 4. Increased boundary input indicates more water inflows of aquatic systems. As a result, it gives increase to all indicators yet in different extents. Indicator A shares the largest increase ratio (24%) while index AMI gets the lowest increase ratio (1.9%) of all indicators. More boundary input will lead to the increases of system activities, which brings with increases of system Ascendency. However, the higher A is not match with a better WUS since the AMI index is almost unchanged. Decreased boundary input indicates lower water flow loss from each component, which gives decreases to all indicators.
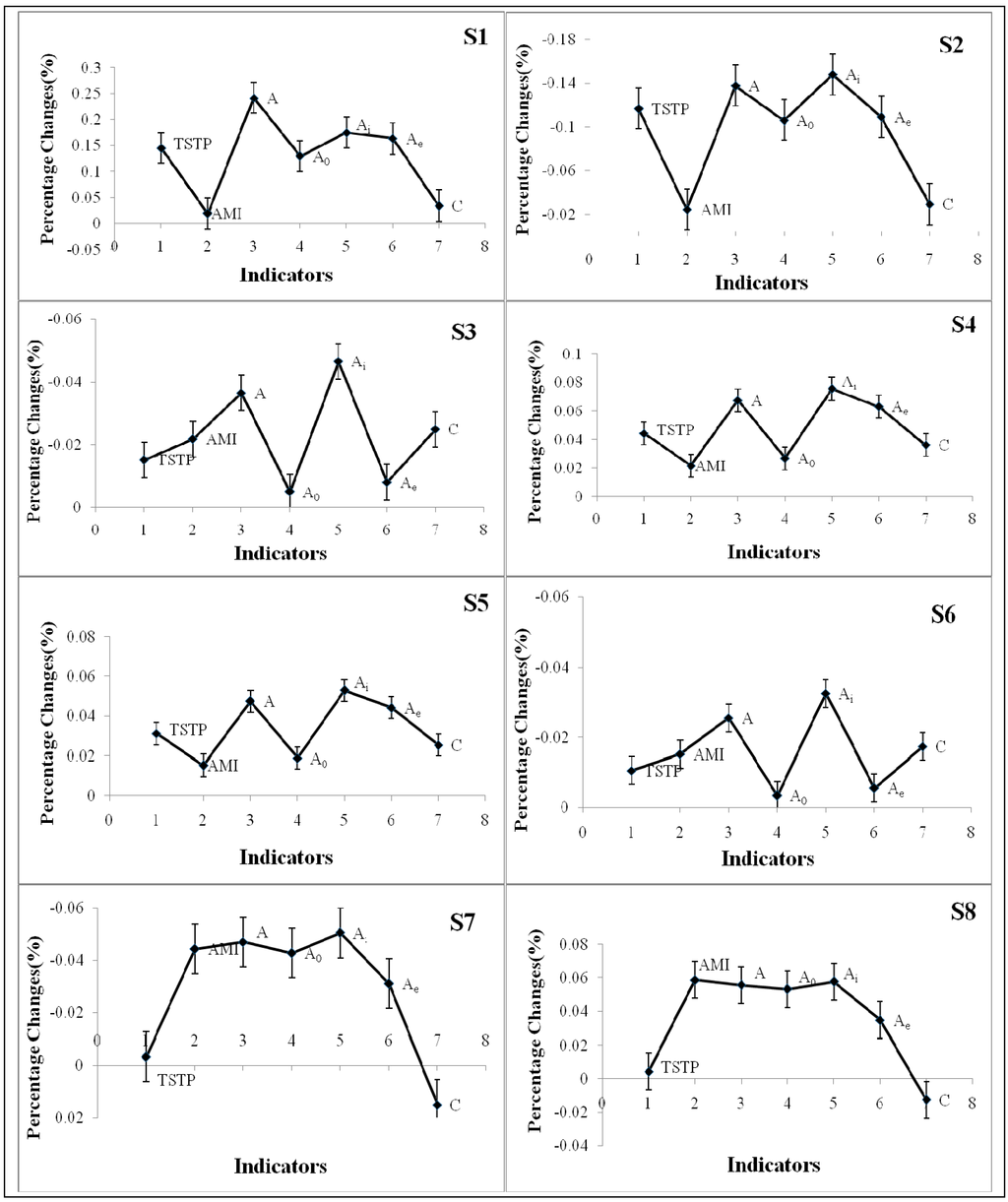
Figure 4.
Results of scenario analysis (S1–S8).
Increased boundary outputs will result in less interflow among system components, which give rise to decrease of all the indicators. Indicator Ai decreased most (4.6%) in all detected indicators. Decreased boundary output releases more interflows among different sectors of the WUS, resulting in a sharply decreased Ai (7.5%) under scenario IV. Overall, indicator Ai is robust most to the fluctuation of boundary outputs. In the same vein, increasing or decreasing the interflows will directly impacts the values of Ai, and in a fierier way compared with that of scenario III and IV. An interesting phenomenon is the system organization measured by A and AMI became worse after adding additional links. For example, the percent change of TSTP is about −0.3% while A and AMI reduced more than 4.5%. Additions of new pathways may increase the ambiguity to the network. Oppositely, reducing inter-component-link will give rise to increases to all indicators except for index C.
3.3. Suggested Water Use Strategies for the WUS
Ascendency is said to be dominated by TSTP. The above results suggest that AMI and A/C are more suitable to represent the system function state. Increased internal flows are equivalent to increases of the AMI, which result in an overall increase in A/C. AMI-generated increases of Ascendency are recommended for the current WUS. Both inner-sector-water cycles and inter-sector-water cycles will lead to increases of AMI and A/C. For each sector, we give some suggestion for a better water use configuration with respect to the results of holistic assessment on the WUS (Table 3).

Table 3.
Suggested water use strategies for the WUS.
| Industry | Measures | Goal Function |
|---|---|---|
| Aquatic systems | Environmental and ecological restoration | Higher TSTP, less damage to Aquatic systems |
| Primary Industry | Using water-saving technology, reducing evapotranspiration and infiltration, planting low-water-consumption crop | Lower Ae and higher Ai |
| Secondary Industry | Increasing water recycling rate both inside and outside the industry | Lower Ae and higher Ai and A/C |
| Tertiary Industry | Water Saving and reclaimed water using | Lower A0 and Ae |
3.4. Discussion
The WUS is a large coordinated dissipative and self-organized system. Ascendency reflects the general properties of the system, which linked to specific water use configuration. The WUS can be interpreted as the results of information transmission between different system components by units of water flows. Holistic assessment may provide useful information of the functioning operation of the WUS.
Network indicators are not just the sum of different water flows within network; it was calculated through an information-based calculated method that delves deeply into the inner operation mechanism of WUS. TSTP captures the system activity of the WS and AMI captures topographical constraint based upon the pattern of flow in the network. Ascendency is actually the network efficiency of a specific network structure [30,37]. Both inner-sector-water cycles and inter-sector-water cycles are encouraged to a better system organization of the WUS.
In sustainability quantification of ecosystem, the ascendency value 0.45 is considered as the optimal network structure balance point for sustainability of the ecosystems [38]. The corresponding value of the current WUS is only 0.32, indicating great spaces for higher water use efficient. Network indicator, in a holistic way, provides more potential measures and direction for future improvements.
4. Conclusions
In the current paper, a static water-use-network model was developed to evaluate the WUS functioning of the Baiyangdian Basin. ENA was introduced as a useful method in the investigation of system evolution during 2008–2013. Results indicate network-based assessment method can well capture the system attributes and fluctuation, which gives accurate and objective evaluation to the WUS. Different types of indicators may depict different parts of the system. Indicator AMI and A/C are more suitable to represent the holistic function state of the system.
The findings of the study call for a greater emphasis on integrated water resources study to improve the water security and environmental sustainability of basins. The value of the approach presented in this paper is to inform policy decision of water resources, which may serve to optimize across aggregations of socia-economic and environmental considerations. The current study is an interesting starting point as we continue to progress towards more applications of ENA for basin-scale water resources management.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51409144, 51209003 & 51478026), the National Water Pollution Control and Management Technology Major Project (No. 2010ZX07320-002 & 2011ZX07301-004), key projects in the National Science & Technology Pillar Program (No. 2012BAJ21B08), and Special Fund for Basic Scientific Research Business of Central Public Research Institutes (No. CAFINT2012C9).
Author Contributions
Xufeng Mao made substantial contributions to the acquisition of data, calculation and results interpretation. Donghai Yuan made substantial contributions to the logical structure of the manuscript. Xiaoyan Wei contributed to data collection and the manuscript revisions. Qiong Chen, Chenling Yan, and Liansheng He provides useful advices for the structure and grammar revision the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cai, X.M. Water stress, water transfer and social equity in Northern China—Implications for policy reforms. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 87, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B. Integration of Energy, Ecology and Environment. Front. Earth Sci. 2014, 8, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.A.; Yang, Z.F. Development of a coupled reservoir operation and water diversion model: Balancing human and environmental flow requirements. Ecol. Model. 2011, 222, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Zhao, J.; Chen, B.; Ji, P.; Wu, Y.H.; Feng, L. Longitudinal spread of bicomponent contaminant in wetland flow dominated by bank-wall effect. J. Hydrol. 2014, 509, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Wu, H.; Ji, P.; Chen, B.; Zhao, Y.J.; Chen, Q.; Wu, Z. Effect of wind on contaminant dispersion in a wetland flow dominated by free-surface effect. Ecol. Model. 2014, 237–238, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Radif, A.A. Integrated water resources management (IWRM): An approach to face the challenges of the next century and to avert future crises. Desalination 1999, 124, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.J.; Brown, M.T. A model examining hierarchical wetland networks for watershed storm water management. Ecol. Model. 1997, 201, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medema, W.; McIntosh, B.S.; Jeffrey, P.J. From premise to practice: A critical assessment of integrated water resources management and adaptive management approaches in the water sector. Ecol. Soc. 2008, 13, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolic, V.V.; Simonovic, S.P.; Milicevic, D.B. Analytical Support for Integrated Water Resources Management: A New Method for Addressing Spatial and Temporal Variability. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 401–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, A.; Pahl-Wostl, C. The global policy network behind integrated water resources management: Is it an effective norm diffusor? Ecol. Soc. 2014, 19, 11–24. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B. Ecosystem metabolism framework, metrics and indicators towards sustainable society design and management. Ecol. Inform. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Q.; Chen, B. Urban Metabolism and Nexus. Ecol. Inform. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serageldin, I. Water resources management: A new policy for a sustainable future. Water Int. 1995, 20, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Fath, B.D.; Chen, B.; Ursula, S. Network Environ Analysis for a socio-economic water system. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 47, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, B. Study on sustainable water use of the Haihe River Basin using ecological network analysis. Front. Earth Sci. China 2009, 3, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.F.; Yang, Z.F. Ecological network analysis for virtual water trade systems: A case study for the Baiyangdian Basin in Northern China. Ecol. Inform. 2012, 10, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.F.; Chen, B. Driving force analysis of the agricultural water footprint in China based on the LMDI method. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 12723–12731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Chen, B.; Hayat, T.; Alsaedi, A.; Ahmad, B. Driving force analysis of water footprint change based on extended STIRPAT model: Evidence from the Chinese agricultural sector. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 47, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fath, B.D.; Patten, B.C. Review of the foundations of network environ analysis. Ecosystems 1999, 2, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulanowicz, R.E.; Tuttle, J.H. The trophic consequences of oyster stock rehabilitation in Chesapeake Bay. Estuar 1992, 15, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patten, B.C.; Matis, J.H. The water envions of Okefenokee Swamp: Applications of static liner environ analysis. Ecol. Model. 1982, 16, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodini, A.; Bondavalli, C. Towards a sustainable use of water resources. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2002, 18, 463–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, B.; Yang, Z.F. Ecological network analysis for water use systems—A case study of the Yellow River Basin. Ecol. Model. 2009, 220, 3167–3173. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.F.; Fath, B.D. Ecological network analysis of an urban water metabolic system: Model development, and a case study for Beijing. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 4702–4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.F.; Cui, L.J.; Wang, C.H. Exploring the hydrologic relationships in a swamp-dominated watershed—A network-environ-analysis based approach. Ecol. Model. 2013, 252, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Cui, B.S.; Yang, Z.F. Influence of hydrological characteristic change of Baiyangdian on the ecological environment in wetland. J. Nat. Sci. 2004, 19, 63–69. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, P.; Yang, Z.F.; Cui, B.S.; Liu, J.L. Eco-environmental water demands for the Baiyangdian Wetland. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. China 2008, 2, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulanowicz, R.E. A hypothesis on the development of natural communities. J. Theor. Biol. 1980, 85, 223–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulanowicz, R.E. Growth and Development: Ecosystems Phenomenology; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 1986; p. 203. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutledge, R.W.; Basore, B.L.; Mulholland, R.J. Ecological stability: An information theory viewpoint. J. Theor. Biol. 1976, 57, 223–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulanowicz, R.E. Ecology, the Ascendency Perspective; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997; p. 201. [Google Scholar]
- Chapagain, A.K.; Hoekstra, A.Y. Virtual Water Flows between Nations in Relation to Trade in Livestock and Livestock Products; Value of Water Research Report Series No. 13; UNESCO-IHE: Delft, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Chapagain, A.K.; Hoekstra, A.Y. Water Footprints of Nations; Value of Water Research Report Series No. 16; UNESCO-IHE: Delft, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Yang, H.; Yang, Z.F.; Chen, B.; Qin, Y. Applying the input-output method to account for water footprint and virtual water trade in the Haihe River basin in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 9150–9156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.F.; Mao, X.F. Wetland system network analysis for environmental flow allocations in the Baiyangdian Basin, China. Ecol. Model. 2011, 222, 3785–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, Z.F. Quantifying the sustainability of water use systems: Calculating the balance between network efficiency and resilience. Ecol. Model. 2011, 222, 1771–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorach, A.C.; Ulanowicz, R.E. Quantifying the complexity of flow networks: How many roles are there? Complexity 2003, 8, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).