Factors Influencing the Conversion of Arable Land to Urban Use and Policy Implications in Beijing, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Methods
2.1. Study Area
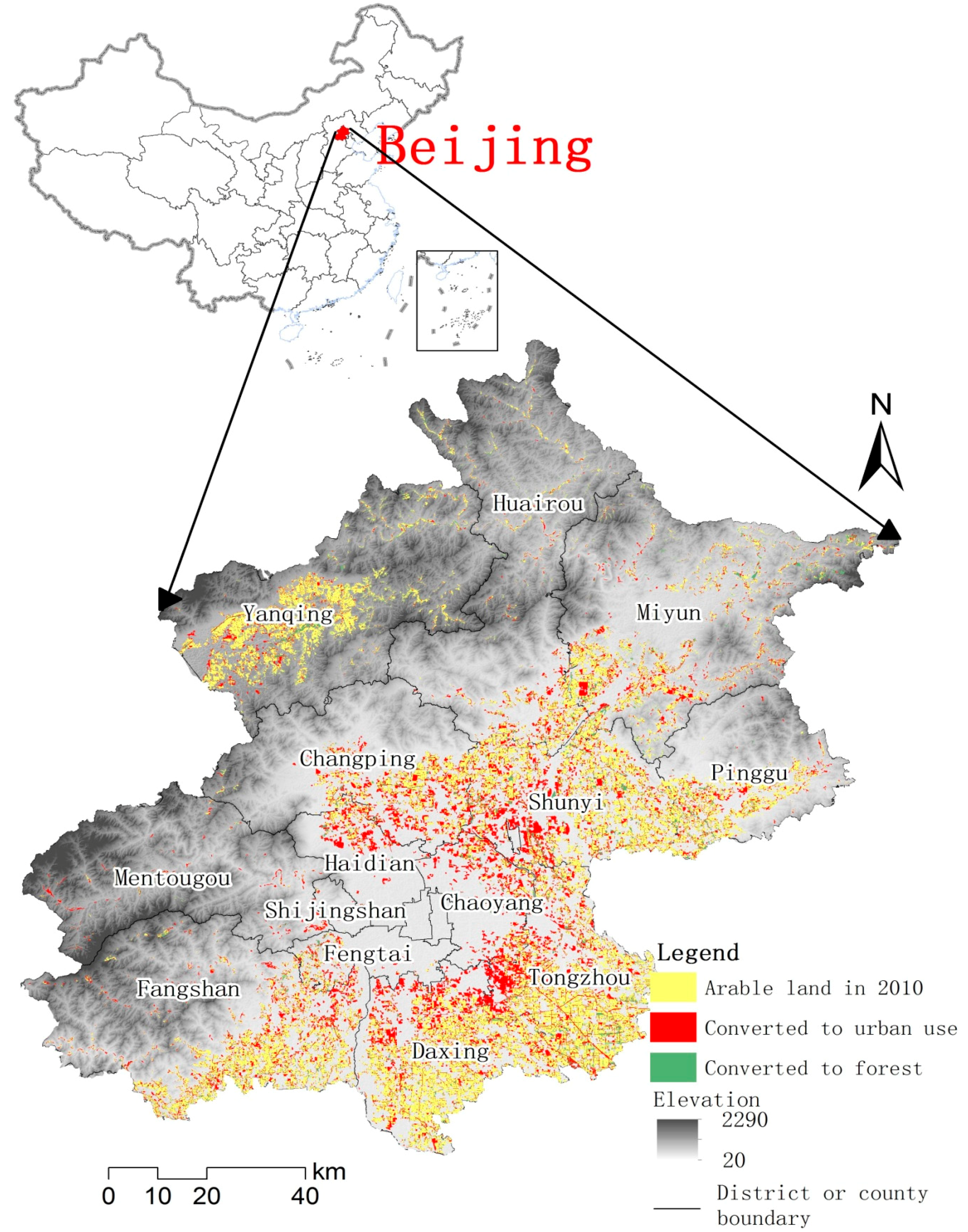
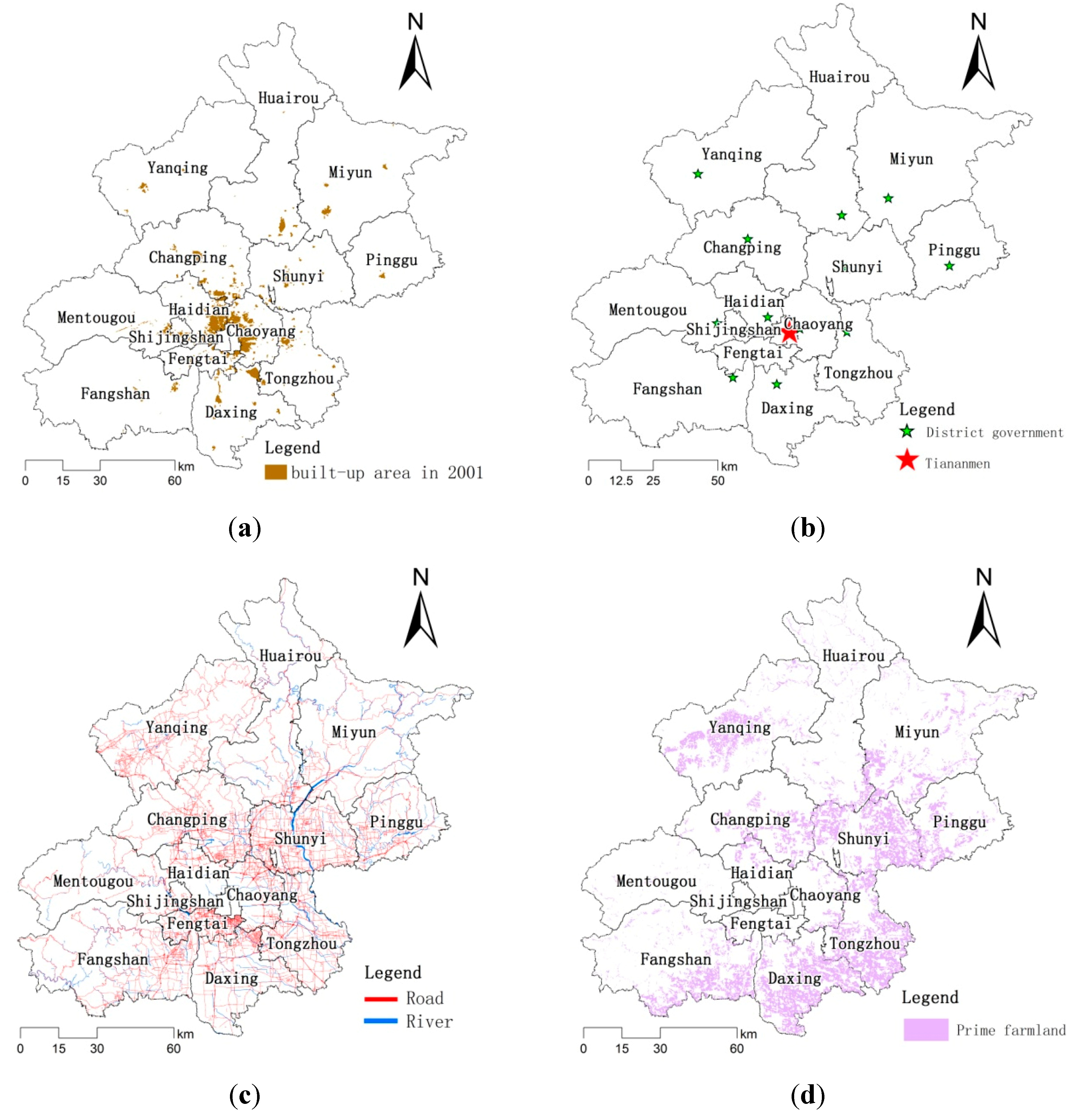
2.2. Data Sources and Processing
2.3. Method
2.3.1. Logistic Regression Model
2.3.2. Variable
| Variable Name | Variable | Interpretation | Unit | Expected Signs | Mean | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent Variable | ||||||||
| Conversion of arable land | Y | If the grid is converted to urban use from arable land, assign it 1, if not, assign it 0 | − | 0.31 | 0.45 | 0.00 | 1.00 | |
| Independent Variable | ||||||||
| BA | X1 | Distance from nearest built-up area | km | − | 0.89 | 1.66 | 0.00 | 23.07 |
| DG | X2 | Distance from district governments | km | − | 16.13 | 9.75 | 0.05 | 72.41 |
| CG | X3 | Distance from Tiananmen | km | − | 44.72 | 20.05 | 5.29 | 123.37 |
| IC | X4 | Distance from irrigation canals | km | + | 0.82 | 2.79 | 0.00 | 34.00 |
| River | X5 | Distance from river | km | + | 1.61 | 1.46 | 0.00 | 17.11 |
| RR | X6 | Distance from rural road | km | + | 0.95 | 3.66 | 0.00 | 42.84 |
| Road | X7 | Shortest distance from highway | km | − | 0.50 | 0.56 | 0.00 | 9.62 |
| PFP | X8 | If parcel is in prime farmland protection zone, assign “1”; “0” otherwise | − | − | 0.59 | 0.49 | 0.00 | 1.00 |
| Area | X9 | Area of parcels | km2 | − | 301.66 | 351.40 | 0.04 | 850 |
| Shape Index | X10 | The ratio between area and perimeter of parcels, from which the grids are created | − | − | 0.22 | 0.25 | 0.04 | 1.00 |
| Pop | X11 | Population (streets as a unit) | 10000 people | + | 5.99 | 7.33 | 0.25 | 47.47 |
| Elevation | X12 | Perpendicular distance from sea level | km | − | 0.10 | 0.18 | 0.02 | 1.18 |
| Slope | X13 | Degree of steepness | ° | − | 3.24 | 3.33 | 0.00 | 61.00 |
| Aspect | X14 | Aspect of earth surface | ° | + | 166.41 | 106.04 | −1.00 | 359.46 |
3. Results and Discussion
| β | Coefficient (e^β) | Standard Error | Significance Level | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Location and Accessibility | ||||
| BA | −0.132 | 0.876 | 0.010 | 0.000 |
| DG | −0.002 | 0.998 | 0.001 | 0.124 |
| CG | −0.025 | 0.975 | 0.001 | 0.000 |
| IC | 0.054 | 1.056 | 0.007 | 0.000 |
| River | 0.002 | 1.002 | 0.007 | 0.777 |
| RR | 0.057 | 1.059 | 0.005 | 0.000 |
| Road | −0.265 | 0.767 | 0.019 | 0.000 |
| Policy | ||||
| PFP | −1.018 | 0.361 | 0.018 | 0.000 |
| Parcel Characteristics | ||||
| Area | −0.015 | 0.985 | 0.001 | 0.000 |
| Shape Index | −0.113 | 0.893 | 0.021 | 0.000 |
| Socioeconomic Condition | ||||
| Pop | 0.011 | 1.011 | 0.001 | 0.000 |
| Terrain | ||||
| Elevation | −0.067 | 0.935 | 0.089 | 0.454 |
| Slope | −0.017 | 0.983 | 0.003 | 0.000 |
| Aspect | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.295 |
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Foley, J.A.; Ramankutty, N.; Brauman, K.A.; Cassidy, E.S.; Gerber, J.S.; Johnston, M.; Mueller, N.D.; O’Connell, C.; Ray, D.K.; West, P.C.; et al. Solutions for a cultivated planet. Nature 2011, 478, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, J.A.; DeFries, R.; Asner, G.P.; Barford, C.; Bonan, G.; Carpenter, S.R.; Chapin, F.S.; Coe, M.T.; Daily, G.C.; Gibbs, H.K.; et al. Global consequences of land use. Science 2005, 309, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, S.L.; Jiang, Z.L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.A. Transformation of agricultural landscapes under rapid urbanization: A threat to sustainability in Hang-Jia-Hu region, China. Appl. Geogr. 2011, 31, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.L.; Li, Y.R.; Liu, Y.S.; Woods, M.; Zou, J. Accelerated restructuring in rural China fueled by ‘increasing vs. decreasing balance’ land-use policy for dealing with hollowed villages. Land Use Policy 2012, 29, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.L.; Zou, J.L.; Jiang, H.L.; Zhang, N.; Choi, Y. Spatiotemporal pattern and driving forces of arable land-use intensity in China: Toward sustainable land management using emergy analysis. Sustainability 2014, 6, 3504–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. Rapid urbanization in china: A real challenge to soil protection and food security. Catena 2007, 69, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.C.S.; Ho, S.P.S. China’s land resources and land-use change: Insights from the 1996 land survey. Land Use Policy 2003, 20, 87–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, T.Y.; Huang, X.J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Scott, S.; Wang, K. The effects of basic arable land protection planning in Fuyang County, Zhejiang Province, China. Appl. Geogr. 2012, 35, 422–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, M.; Kuemmerle, T.; Elbakidze, M.; Ozdogan, M.; Radeloff, V.C.; Keuler, N.S.; Prishchepov, A.V.; Kruhlov, I.; Hostert, P. Patterns and drivers of post-socialist farmland abandonment in Western Ukraine. Land Use Policy 2011, 28, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flinn, K.M.; Vellend, M.; Marks, P.L. Environmental causes and consequences of forest clearance and agricultural abandonment in central New York, USA. J. Biogeogr. 2005, 32, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, E.F.; Turner, B.L.; Geist, H.J.; Agbola, S.B.; Angelsen, A.; Bruce, J.W.; Coomes, O.T.; Dirzo, R.; Fischer, G.; Folke, C.; et al. The causes of land-use and land-cover change: Moving beyond the myths. Glob. Environ. Chang. Hum. Policy Dimens. 2001, 11, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prishchepov, A.V.; Muller, D.; Dubinin, M.; Baumann, M.; Radeloff, V.C. Determinants of agricultural land abandonment in post-Soviet European Russia. Land Use Policy 2013, 30, 873–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, M.K.; York, A.M.; Boone, C.G.; Zhang, S. Land fragmentation due to rapid urbanization in the Phoenix Metropolitan Area: Analyzing the spatiotemporal patterns and drivers. Appl. Geogr. 2012, 32, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doos, B.R. Population growth and loss of arable land. Glob. Environ. Chang. Hum. Policy Dimens. 2002, 12, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firman, T. Rural to urban land conversion in Indonesia during boom and bust periods. Land Use Policy 2000, 17, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S.; Wang, L.J.; Long, H.L. Spatio-temporal analysis of land-use conversion in the eastern coastal China during 1996–2005. J. Geogr. Sci. 2008, 18, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Li, H.Q.; Wang, R.S.; Paulussen, J.; He, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, B.H.; Wang, Z. Monitoring and predicting land use change in Beijing using remote sensing and GIS. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2006, 78, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P. Assessment of economic drivers of land use change in urban ecosystems of Delhi, India. Ambio 2009, 38, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, J.K.; McChesney, R.; Munroe, D.K.; Irwin, E.G. Spatial characteristics of exurban settlement pattern in the United States. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 90, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deininger, K.; Savastano, S.; Carletto, C. Land fragmentation, cropland abandonment, and land market operation in Albania. World Dev. 2012, 40, 2108–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, D.; Munroe, D.K. Changing rural landscapes in Albania: Cropland abandonment and forest clearing in the postsocialist transition. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2008, 98, 855–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, V.; Walls, M. US experience with transferable development rights. Rev. Environ. Econ. Policy 2009, 3, 288–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S.; Wang, J.Y.; Long, H.L. Analysis of arable land loss and its impact on rural sustainability in Southern Jiangsu Province of China. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, T.Y.; Huang, X.J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, K. Temporal and spatial variability of agricultural land loss in relation to policy and accessibility in a low hilly region of southeast China. Land Use Policy 2011, 28, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verburg, P.H.; van de Steeg, J.; Veldkamp, A.; Willemen, L. From land cover change to land function dynamics: A major challenge to improve land characterization. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 1327–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tscharntke, T.; Clough, Y.; Wanger, T.C.; Jackson, L.; Motzke, I.; Perfecto, I.; Vandermeer, J.; Whitbread, A. Global food security, biodiversity conservation and the future of agricultural intensification. Biol. Conserv. 2012, 151, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramb, R.A.; Colfer, C.J.P.; Dressler, W.; Laungaramsri, P.; Le, Q.T.; Mulyoutami, E.; Peluso, N.L.; Wadley, R.L. Swidden transformations and rural livelihoods in Southeast Asia. Hum. Ecol. 2009, 37, 323–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leichenko, R.M.; Solecki, W.D. Exporting the American dream: The globalization of suburban consumption landscapes. Reg. Stud. 2005, 39, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, K.C.; Reenberg, A.; Boone, C.G.; Fragkias, M.; Haase, D.; Langanke, T.; Marcotullio, P.; Munroe, D.K.; Olah, B.; Simon, D. Urban land teleconnections and sustainability. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 2012, 109, 7687–7692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.Y.; Okada, N.; Zhang, Q.F.; Shi, P.J.; Zhang, J.S. Modeling urban expansion scenarios by coupling cellular automata model and system dynamic model in Beijing, China. Appl. Geogr. 2006, 26, 323–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Data from National Bureau of Statistics of the People’s Republic of China. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/zxfb/201311/t20131129_475486.html (accessed on 18 December 2014).
- Liu, R.; Wong, T.C.; Liu, S.H. Peasants’ counterplots against the state monopoly of the rural urbanization process: Urban villages and ‘small property housing’ in Beijing, China. Environ. Plan. A 2012, 44, 1219–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.Y.; Tian, J.; Shi, P.J.; Hu, D. Simulation of the spatial stress due to urban expansion on the wetlands in Beijing, China using a GIS-based assessment model. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 101, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geospatial Data Cloud of Chinese Academy of Sciences. Available online: http://www.gscloud.cn (accessed on 18 December 2014).
- Aguiar, A.P.D.; Camara, G.; Escada, M.I.S. Spatial statistical analysis of land-use determinants in the Brazilian Amazonia: Exploring intra-regional heterogeneity. Ecol. Model. 2007, 209, 169–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gellrich, M.; Zimmermann, N.E. Investigating the regional-scale pattern of agricultural land abandonment in the Swiss mountains: A spatial statistical modelling approach. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2007, 79, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsuda, Y.; Ito, S. A review of spatial-explicit factors determining spatial distribution of land use/land-use change. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 7, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domon, G.; Bouchard, A. The landscape history of Godmanchester (Quebec, Canada): Two centuries of shifting relationships between anthropic and biophysical factors. Landsc. Ecol. 2007, 22, 1201–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikor, T.; Muller, D.; Stahl, J. Land fragmentation and cropland abandonment in Albania: Implications for the roles of state and community in post-socialist land consolidation. World Dev. 2009, 37, 1411–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Land and Resources of the People’s Republic of China. Technical specification for the second national land survey. In Land Management Industry Standard of the People’s Republic of China (TD/T 1014-2007); Ministry of Land and Resources of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ewing, R.; Schmid, T.; Killingsworth, R.; Zlot, A.; Raudenbush, S. Relationship between urban sprawl and physical activity, obesity, and morbidity. Am. J. Health Promot. 2003, 18, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talen, E.; Knaap, G. Legalizing smart growth—An empirical study of land use regulation in Illinois. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 2003, 22, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaap, G.; Talen, E. New urbanism and smart growth: A few words from the academy. Int. Reg. Sci. Rev. 2005, 28, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, D.; Jin, H.; Zhao, X.; Liu, S. Factors Influencing the Conversion of Arable Land to Urban Use and Policy Implications in Beijing, China. Sustainability 2015, 7, 180-194. https://doi.org/10.3390/su7010180
Huang D, Jin H, Zhao X, Liu S. Factors Influencing the Conversion of Arable Land to Urban Use and Policy Implications in Beijing, China. Sustainability. 2015; 7(1):180-194. https://doi.org/10.3390/su7010180
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Daquan, Haoran Jin, Xingshuo Zhao, and Shenghe Liu. 2015. "Factors Influencing the Conversion of Arable Land to Urban Use and Policy Implications in Beijing, China" Sustainability 7, no. 1: 180-194. https://doi.org/10.3390/su7010180
APA StyleHuang, D., Jin, H., Zhao, X., & Liu, S. (2015). Factors Influencing the Conversion of Arable Land to Urban Use and Policy Implications in Beijing, China. Sustainability, 7(1), 180-194. https://doi.org/10.3390/su7010180





