The Contribution of Forests and Trees to Sustainable Diets
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Forest Ecosystems and Agroforestry
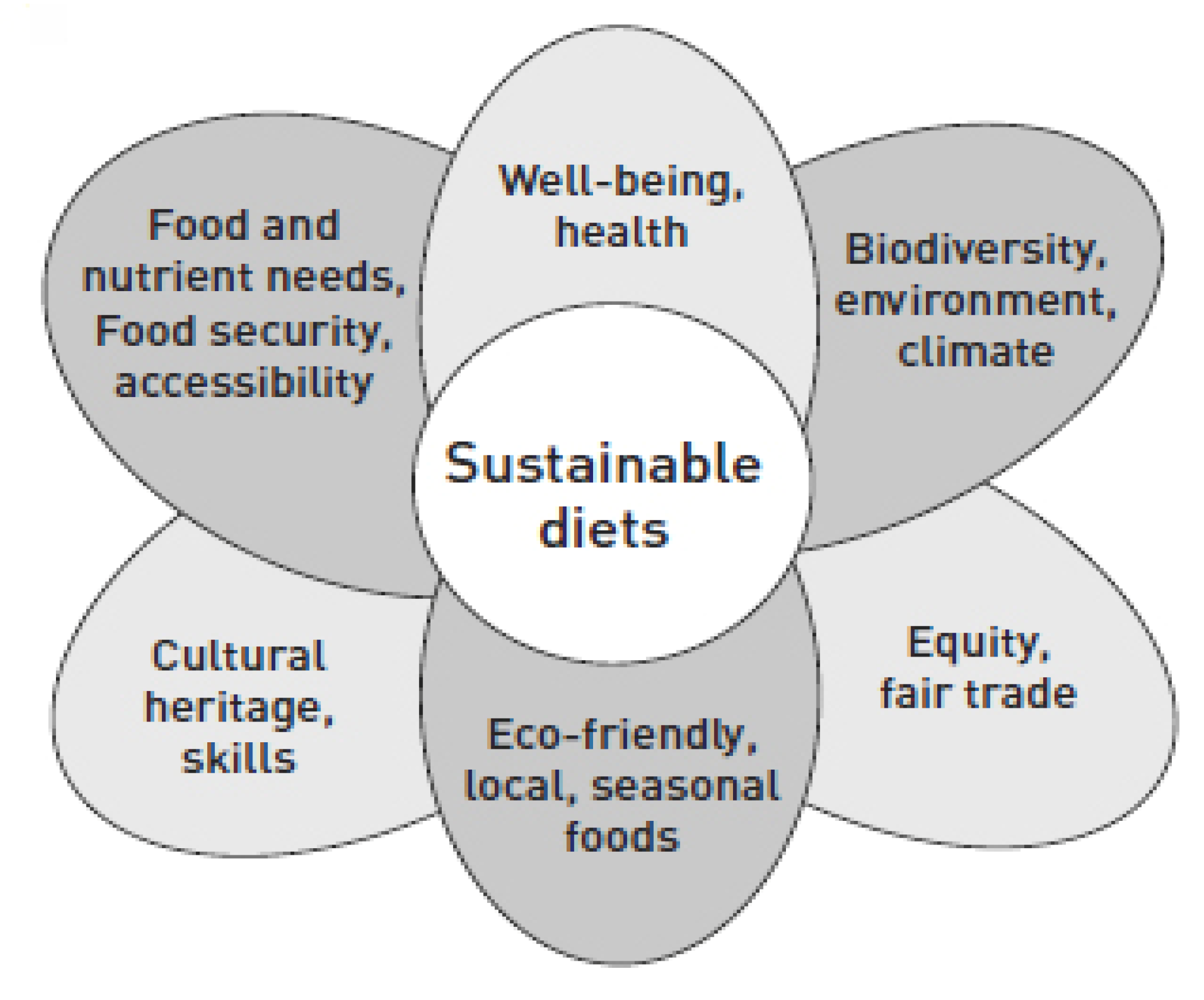
1.2. Sustainable Diets
Those diets with low environmental impacts which contribute to food and nutrition security and to healthy life for present and future generations. Sustainable diets are protective and respectful of biodiversity and ecosystems, culturally acceptable, accessible, economically fair and affordable; nutritionally adequate, safe and healthy; while optimizing natural and human resources [15].
2. Forest Foods and Sustainable Diets
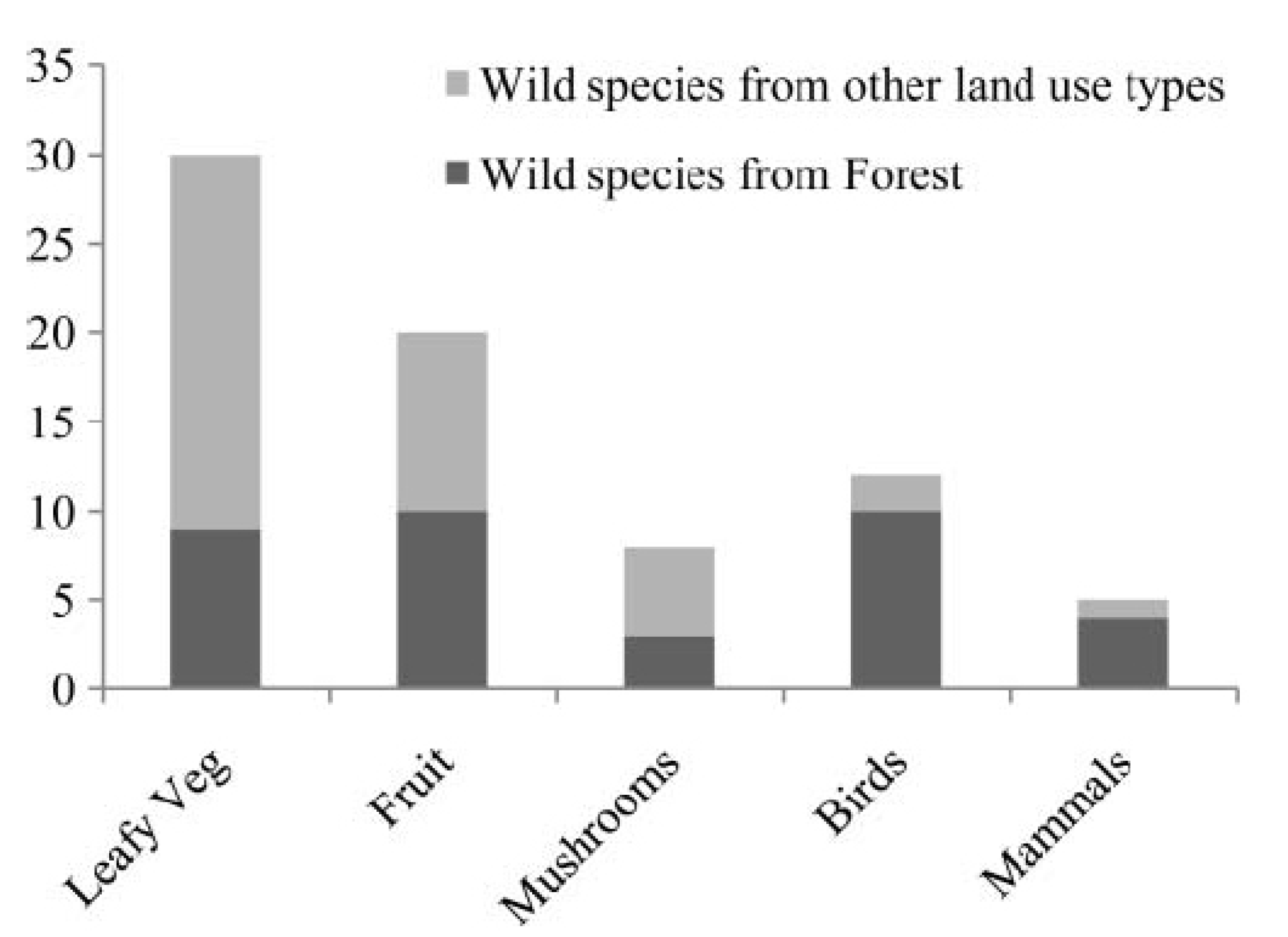
2.1. Availability and Accessibility of Local, Affordable Forest Foods
| Tree Species | Months | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | |
| Uapaca kirkiana | ||||||||||||
| Azanza garckeana | ||||||||||||
| Flacourtia indica | ||||||||||||
| Vangueria infausta | ||||||||||||
| Vitex doniana | ||||||||||||
| Adansonia digitata | ||||||||||||
| Ziziphus mauritiana | ||||||||||||
| Parinari curatellifolia | ||||||||||||
| Strychnos cocculoides | ||||||||||||
2.2. Nutritional Quality of Forest Foods
| Species | Energy (Kcal) | Protein (g) | Vit C (mg) | Vit A (RE) (µg) | Iron (mg) | Calcium (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indigenous fruits: | ||||||
| Adansonia digitata L. | 327 | 2.5 | 126–509 | 0.03–0.06 | 6.2 | 275 |
| Grewia tenax (Forrsk.) Fiori | N.A. | 3.6 | N.A. | N.A. | 7.4–20.8 | 610 |
| Sclerocarya birrea Hochst. | 225 | 0.7 | 85–319 | 0.035 | 3.4 | 35 |
| Tamarindus indica L. | 275 | 3.6 | 11–20 | 0.01–0.06 | 3.1 | 192 |
| Ziziphus mauritiana Lam. | 184 | 0.4 | 3–14 | 0.07 | 0.8 | 23 |
| Exotic fruits: | ||||||
| Guava (Psidium guajava L.) | 68 | 2.6 | 228.3 | 0.031 | 0.3 | 18 |
| Mango (Mangifera indica L.) | 65 | 0.5 | 27.7 | 0.038 | 0.1 | 10 |
| Orange (Citrus sinensis L. Osbeck) | 47 | 0.9 | 53.0 | 0.008 | 0.1 | 40 |
| Pawpaw (Carica papaya L.) | 39 | 0.6 | 62.0 | 0.135 | 0.1 | 24 |
2.3. Cultural Importance of Forest Foods
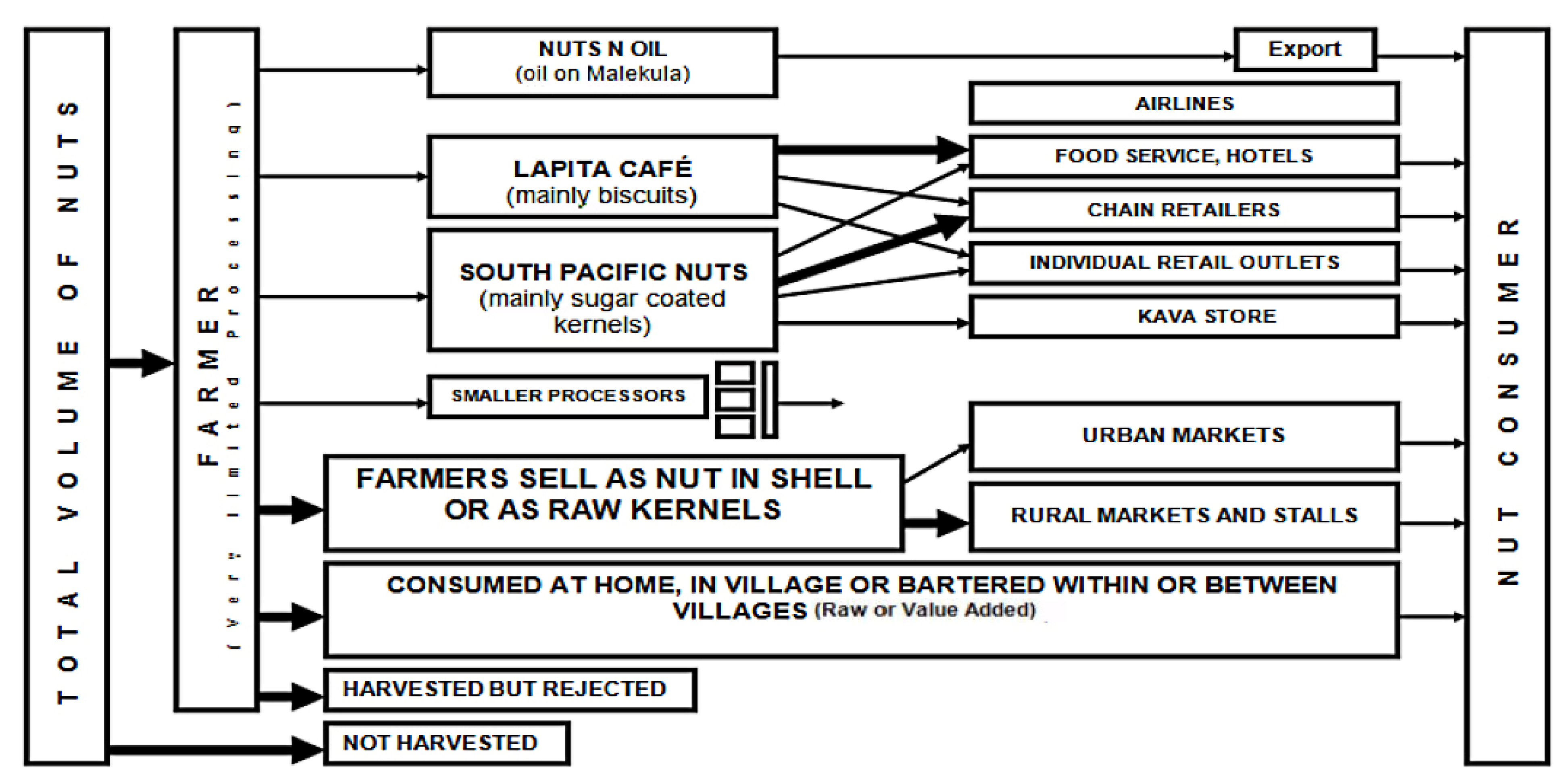
2.4. Marketing and Value Chains Integrating Forest Foods
| Nutrient | Content | Nutrient | Content | Nutrient | Content | Nutrient | Content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water (g) | 35.4 | Protein (g) | 8.2 | Fat (g) | 45.9 | Sugar (g) | 0.2 |
| Starch (g) | 0.3 | Ash (g) | 2.6 | Fiber | 10.6 | β-car. Eq. (μg) | 165 |
| Vit. C (mg) | 8 | Thiamin (mg) | 0.13 | Riboflavin | 0.06 | Niacin (mg) | 1.7 |
| Fe (mg) | 3.5 | Na (mg) | 18 | K (mg) | 627 | Ca (mg) | 44 |
| Mn (mg) | 1.1 | Mg (mg) | 284 | Zn (mg) | 2.4 | Cu (mg) | 1.6 |
| Edible portion (*) | 13% | Energy | 439 kcal/1838 kJ |
2.5. Environmental Aspects of Forest Food Systems
3. Challenges and Opportunities to Strengthen the Role of Forest Foods in Sustainable Diets
3.1. Cultural Challenges
3.2. Sustainable Use of NWFPs and Threats to the Resource Base
3.3. Challenges in Organizing Forest Food Provisioning
3.4. Relying More on Food-Based Approaches
3.5. Increasing Knowledge on Forest Foods
3.6. Adapting Management of Forests and Trees to Account for Forest Foods
3.7. Access Rights to Forest Foods
3.8. Integrating Forest Biodiversity into Complex Landscapes Managed for Multiple Benefits
4. General Recommendations
- Prioritize research that examines the relative contribution of forest foods to local diets and nutrition, including analysis and documentation of their nutritional composition, digestibility and bioavailability, the effect of storage and processing on the nutritional value of specific forest foods, and the potential for domestication and integration of important tree species into value chains.
- Describe and measure the sustainability of diets reliant on forest foods in relation to indigenous peoples’ food systems, and compare these systems in terms of resilience, health, cost-effectiveness and sustainability with other diets and food systems across countries and regions.
- Support research on governance and access issues and on the development of nutrition-sensitive value chains involving forest foods, with a particular focus on improving understanding of the risks associated with potential overharvesting and changes to access, as targeted NWFPs become more valuable.
- Ensure extension services, NGOs, schools, hospitals and health centers are aware of the benefits and promote the consumption of nutritious forest foods within their programs and interventions, including efforts to counter negative perceptions and attitudes to local, traditional foods.
- Promote a better integration of information and knowledge on nutritious forest foods and their conservation into national nutrition strategies and programs by establishing cross-sectoral policy platforms that bring together environment, health, development, agriculture and other sectors. These platforms would enable to better mainstream the use of tree biodiversity with high nutritional value into strategies addressing food security, nutrition, conservation, and land use planning and policy.
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of interest
References
- Hunter, D.; Fanzo, J. Agricultural Biodiversity, Diverse Diets and Improving Nutrition. In Diversifying Food and Diets: Using Agricultural Biodiversity to Improve Nutrition and Health; Fanzo, J., Hunter, D., Borelli, T., Mattei, F., Eds.; Earthscan: London, UK, 2013; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson, K.; Amthor, R.; Mallowa, S.; Nungo, R.; Maziya-Dixon, B.; Gichuki, S.; Mbanaso, A.; Manary, M. Consuming cassava as a staple food places children 2–5 years old at risk for inadequate protein intake, an observational study in Kenya and Nigeria. Nutr. J. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tontisirin, K.; Nantel, G.; Bhattacharjee, L. Food-based strategies to meet the challenges of micronutrient malnutrition in the developing world. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2002, 61, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, T.; Sthapit, B.R. Biocultural diversity in the sustainability of developing-country food systems. Food Nutr. Bull. 2004, 25, 143–155. [Google Scholar]
- Johns, T.; Powell, B.; Maundu, P.; Eyzaguirre, P.B. Agricultural biodiversity as a link between traditional food systems and contemporary development, social integrity and ecological health. J. Sci. Food Agr. 2013, 93, 3433–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunderland, T.C.H. Food security: why is biodiversity important? Int. For. Rev. 2011, 13, 265–274. [Google Scholar]
- Jamnadass, R.H.; Dawson, I.K.; Franzel, S.; Leakey, R.R.B.; Mithöfer, D.; Akinnifesi, F.K.; Tchoundjeu, Z. Improving livelihoods and nutrition in sub-Saharan Africa through the promotion of indigenous and exotic fruit production in smallholders’ agroforestry systems: A review. Int. For. Rev. 2011, 13, 338–354. [Google Scholar]
- Vinceti, B.; Eyzaguirre, P.; Johns, T. The Nutritional Role of Forest Plant Foods for Rural Communities. In Human Health and Forests: A Global Overview of Issues, Practice and Policy; Colfer, C.J.P., Ed.; Earthscan: London, UK, 2008; Volume 12, pp. 63–96. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, M.; Powell, B.; Shanley, P.; Sunderland, T.C.H. Forests, biodiversity and food security. Int. For. Rev. 2011, 13, 259–264. [Google Scholar]
- Hladik, C.M.; Hladik, A.; Linares, O.; Oagezy, H.; Semple, A.; Hadley, M. (Eds.) Tropical Forests, People and Food: Biocultural Interactions and Applications to Development; UNESCO/Parthenon Publishing Group: Carnforth, UK, 1993.
- Millennium Ecosystem Assessment. Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Health Synthesis and Biodiversity Synthesis; World Health Organization (WHO), World Research Institute: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). Global Forest Resources Assessment 2010: Progress towards Sustainable Forest Management; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). Global Forest Resources Assessment 2000; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Mery, G.; Katila, P.; Galloway, G.; Alfaro, R.I.; Kanninen, M.; Lobovikov, M.; Vario, J. Changes in Global Markets for Forest Products and Timberlands. In Forests and Society—Responding to Global Drivers of Change; IUFRO: Vienna, Austria, 2010; pp. 137–156. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization, Bioversity International. Sustainable Diets and Biodiversity; Burlingame, B., Dernini, S., Eds.; Food and Agriculture Organization and Bioversity International: Rome, Italy, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Fanzo, J.; Cogill, B.; Mattei, F. Metrics of Sustainable Diets and Food Systems; Bioversity International: Rome, Italy, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Dansi, A.; Adjatin, A.; Adoukonou-Sagbadja, H.; Faladé, V.; Yedomonhan, H.; Odou, D.; Dossou, B. Traditional leafy vegetables and their use in the Benin Republic. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2008, 55, 1239–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, B.; Hall, J.; Johns, T. Forest cover, use and dietary intake in the East Usambara Mountains, Tanzania. Int. For. Rev. 2011, 13, 305–324. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, R.C.; Head, G.; Jenike, M.; Owen, B.; Rechtman, R.; Zechenter, E. Hunting and gathering in tropical rain forest: Is it possible? Am. Anthropol. 1989, 91, 59–82. [Google Scholar]
- Colfer, C.J.P. Human Health and Forests: Global Overview of Issues, Practice and Policy; Earthscan: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Humphry, C.M.; Clegg, M.S.; Keen, C.L.; Grivetti, L.E. Food diversity and drought survival: The Hausa example. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 1993, 44, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Black, G.; Somnasang, P. In times of plenty and times of scarcity: nondomesticated food in north-eastern Thailand. Ecol. Food Nutr. 2000, 38, 563–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faye, M.; Weber, J.; Mounkoro, B.; Dakouo, J.M. Contribution of parkland trees to farmers’ livelihoods: a case study from Mali. Dev. Pract. 2010, 20, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J. Managing ecosystems to enhance the food security of the rural poor: A situation analysis prepared for IUCN. Available online: http://intranet.iucn.org/webfiles/ftp/public/ForumEvents/E1533/Final%20Document/Situation%20Analysis%20Forests%20and%20Food%20Security%20by%20M%20Arnold%20FINAL%20DRAFT%2030.05.08.pdf (accessed on 18 October 2013).
- Food and Agriculture Organization. Non-wood forest products in nutrition. Paper prepared for the FAO/GOI Expert Consultation on Non-Wood Forest Products, Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 17–27 January 1995. Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 1995. Available online: http://www.fao.org/docrep/v7540e/V7540e15.htm (accessed on 15 October 2013).
- Scoones, I.; Melnyk, M.; Pretty, J. The Hidden Harvest. Wild Foods and Agricultural Systems: A Literature Review and Annotated Bibliography; International Institute for Environment and Development (IIED)/SIDA and WWF International: London, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Heywood, V. Overview of agricultural biodiversity and its contribution to nutrition and health. In Diversifying Food and Diets: Using Agricultural Biodiversity to Improve Nutrition and Health; Fanzo, J., Hunter, D., Borelli, T., Mattei, F., Eds.; Earthscan: London, UK, 2013; pp. 35–67. [Google Scholar]
- Penafiel, D.; Lachat, C.; Espinel, R.; van Damme, P.; Kolsteren, P. A systematic review on the contributions of edible plant and animal biodiversity to human diets. EcoHealth 2011, 8, 381–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Standing Committee on Nutrition. 5th Report on the World Nutrition Situation; Standing Committee on Nutrition and International Food Policy Research Institute: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Black, R.E.; Morris, S.S.; Bryce, J. Where and why are 10 million children dying every year? Lancet 2003, 361, 2226–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, G.; Nantel, G.; Shetty, P. The scourge of “hidden hunger”: Global dimensions of micronutrient deficiencies. Food Nutr. Agric. 2003, 32, 8–16. [Google Scholar]
- Underwood, B.A. Vitamin A deficiency disorders: international efforts to control a preventable “pox”. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 231S–236S. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, I.F.; Eyzaguirre, P.B. African leafy vegetables: their role in the world health organization’s global fruit and vegetables initiative. Afr. J. Food Agric. Nutr. Dev. 2007, 7, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Van Rensburg, W.J.; Venter, S.L.; Netshiluvhi, T.R.; van den Heever, E.; Vorster, H.J.; de Ronde, J.A. Role of indigenous leafy vegetables in combating hunger and malnutrition. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2004, 70, 52–59. [Google Scholar]
- Misra, S.; Maikhuri, R.; Kala, C.; Rao, K.; Saxena, K. Wild leafy vegetables: A study of their subsistence dietetic support to the inhabitants of Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve, India. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belem, B.; Sane, B.; Ouattara, E.; Sama, P.; Boussim, J. Wild leafy vegetables in the community of Séguénéga, northern Burkina Faso and their contribution to food security and income generation. Acta Hortic. (ISHS) 2009, 806, 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Nasi, R.; Brown, D.; Wilkie, D.; Bennett, E.; Tutin, C.; van Tol, G.; Christophersen, T. Conservation and Use of Wildlife-Based Resources: The Bushmeat Crisis; Technical Series No. 33; Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity, Montreal, and Center for International Forestry Research (CIFOR): Bogor, Indonesia, 2008; p. 50. [Google Scholar]
- Biesalski, H.-K. Meat as a component of a healthy diet—are there any risks or benefits if meat is avoided in the diet? Meat Sci. 2005, 70, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, L. To what extent can food-based approaches improve micronutrient status? Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 17, 103–105. [Google Scholar]
- Golden, C.D.; Fernald, L.C.H.; Brashares, J.S.; Rasolofoniaina, B.J.R.; Kremen, C. Benefits of wildlife consumption to child nutrition in a biodiversity hotspot. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 19653–19656. [Google Scholar]
- Toledo, Á.; Burlingame, B. Biodiversity and nutrition: A common path toward global food security and sustainable development. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2006, 19, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutaladio, N.; Burlingame, B.; Crews, J. Horticulture, biodiversity and nutrition. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2010, 23, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bélanger, J.; Johns, T. Biological diversity, dietary diversity, and eye health in developing country populations: establishing the evidence-base. EcoHealth 2008, 5, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, T.; Eyzaguirre, P.B. Linking biodiversity, diet and health in policy and practice. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2006, 65, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HarvestPlus Nutrients. Available online: www.harvestplus.org/content/nutrients (accessed on 17 June 2013).
- Ruel, M.; Minot, N.; Smith, L. Patterns and Determinants of Fruit and Vegetable Consumption in Sub-Saharan Africa; WHO: Kobe, Japan, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kehlenbeck, K.; Asaah, E.; Jamnadass, R.H. Diversity of indigenous fruit trees and their contribution to nutrition and livelihoods in sub-Saharan Africa: Examples from Kenya and Cameroon. In Diversifying Food and Diets: Using Agricultural Biodiversity to Improve Nutrition and Health; Fanzo, J., Hunter, D., Borelli, T., Mattei, F., Eds.; Earthscan: London, UK, 2013; pp. 257–269. [Google Scholar]
- Leakey, R.R.B. Potential for novel food products from agroforestry trees: A review. Food Chem. 1999, 66, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadlmayr, B.; Charrondiere, U.R.; Enujiugha, V.N.; Bayili, R.G.; Fagbohoun, E.G.; Samb, B.; Addy, P.; Barikmo, I.; Ouattara, F.; Oshaug, A.; et al. West African Food Composition Table; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2012; p. 173. [Google Scholar]
- Stadlmayr, B.; Charrondiere, R.; Eisenwagen, S.; Jamnadass, R.H.; Kehlenbeck, K. Nutrient composition of selected indigenous fruits from sub-Saharan Africa. J. Sci. Food Agr. 2013, 93, 2627–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colfer, C.J.P.; Sheil, D.; Kishi, M. Forests and Human Health Assessing the Evidence; CIFOR Occasional Paper No. 45; CIFOR: Bogor, Indonesia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Leakey, R.; Fuller, S.; Treloar, T.; Stevenson, L.; Hunter, D.; Nevenimo, T.; Binifa, J.; Moxon, J. Characterization of tree-to-tree variation in morphological, nutritional and medicinal properties of Canarium indicum nuts. Agroforest. Syst. 2007, 73, 77–87. [Google Scholar]
- Graefe, S.; Dufour, D.; Zonneveld, M.; Rodriguez, F.; Gonzalez, A. Peach palm (Bactris gasipaes) in tropical Latin America: implications for biodiversity conservation, natural resource management and human nutrition. Biodivers. Conserv. 2012, 22, 269–300. [Google Scholar]
- Leakey, R. Domestication potential of Marula (Sclerocarya birrea subsp. caffra) in South Africa and Namibia: 3. Multiple trait selection. Agroforest. Syst. 2005, 64, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leakey, R.; Schreckenberg, K.; Tchoundjeu, Z. The participatory domestication of West African indigenous fruits 1. Int. For. Rev. 2003, 5, 338–347. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization. Convention for the Safeguarding of the Intangible Cultural Heritage; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Chweya, J.A.; Eyzaguirre, P.B. (Eds.) The Biodiversity of Traditional Leafy Vegetables; International Plant Genetic Resources Institute: Rome, Italy, 1999; p. 182.
- Macia, M.J. Multiplicity in palm uses by the Huaorani of Amazonian Ecuador. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2004, 144, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndam, N.; Nkefor, P.; Blackmore, P. Domestication of Gnetum africanum and G. buchholzianum (Gnetaceae), over-exploited wild forest vegetables of the Central African Region. Syst. Geogr. Plants 2001, 71, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slikkerveer, L. Indigenous Agricultural Knowledge Systems in Developing Countries: A Bibliography; Leiden Ethnosystems and Development Programme (LEAD): Leiden, The Netherlands, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Shackleton, S.; Shanley, P.; Ndoye, O. Invisible but viable: recognising local markets for non- timber forest products. Int. For. Rev. 2007, 9, 697–712. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhnlein, H.V.; Erasmus, B.; Spigelski, D. Indigenous Peoples’ Food Systems: The Many Dimensions Of Culture, Diversity And Environment For Nutrition And Health; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2009; p. 339. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhnlein, H.V.; Erasmus, B.; Spigelski, D.; Burlingame, B. Indigenous Peoples’ Food Systems and Well-Being: Interventions and Policies for Healthy Communities; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2013; p. 398. [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd, A. The implications of supermarket development for horticultural farmers and traditional marketing systems in Asia. In Paper presented to the FAO/AFMA/fama regional workshop on the growth of supermarkets as retailers of fresh produce, Kuala, Lumpur, Malaysia, 4–7 October 2004.
- Wong, W.W.W. Good Practices of On-Farm Conservation of Tropical Fruit Tree Diversity in Malaysia. Paper Presented at International Good Practices Workshop, Bangkok, Thailand, 4–5 April 2005; Available online: http://www.sabah.gov.my/tani/pdf/penyelidikan/Publication%20List%20Research%20Branch.pdf (accessed on 18 October 2013).
- Kalitu, N.; Wong, W.W.W.; Chong, T.C. Indigenous fruits with potential for use as food crop. In Indigenous Fruits with Potential for Use as Food Crop, Seminar on Food Crop Production in Sabah, Kota Kinabalu, Sabah, 8–9 October 2002.
- Sthapit, B.; Sajise, P.; Rao, R.; Queck, P.; de Cruz, F.; Bellon, M. Selection of Good Practices of In Situ Conservation of Tropical Fruit Tree Species Diversity: Methodology and Key Practices; Appendix K of the GEF UNEP Bioversity Project “Conservation and Sustainable Use of Cultivated and Wild Tropical Fruit Diversity”; Bioversity: Rome, Italy, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Belcher, B.; Ruizperez, M.; Achdiawan, R. Global patterns and trends in the use and management of commercial NTFPs: Implications for livelihoods and conservation. World Dev. 2005, 33, 1435–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelsen, A.; Wunder, S.; Babigumira, R.; Belcher, B.; Börner, J.; Smith-Hall, C. Environmental Incomes and Rural Livelihoods: A Global-Comparative Assessment; Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics/Food and Agricultural Organization: Paper presented at the 4th Wye Global Conference, Rio de Janeiro, country, 9–11 November 2011; Available online: http://www.fao.org/fileadmin/templates/ess/pages/rural/wye_city_group/2011/documents/session4/Angelsen_Wunder_Babigumira_Belcher_Birner__Smith-Hall-Paper.pdf (accessed on 18 October 2013).
- Ruiz-Pérez, M.; Belcher, B.; Achdiawan, R.; Alexiades, M.; Aubertin, C.; Campbell, B.; Clement, C.; Cunningham, T.; Fantini, A.; Foresta, H.D.; et al. Markets drive the specialization strategies of forest peoples. Available online: http://www.ecologyandsociety.org/vol9/iss2/art4/ (accessed on 18 October 2013).
- Marshall, D.; Schreckenberg, K.; Newton, A.C. (Eds.) Commercialization of Non-Timber Forest Produts: Factors Influencing Success. Lessons from Mexico and Bolivia and Policy Implications for Decision-Makers; UNEP World Monitoring Centre: Cambridge, UK, 2006.
- Pimentel, D.; McNair, M.; Buck, L.; Pimentel, M.; Kamil, J. The value of forests to world food security. Hum. Ecol. 1997, 25, 91–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanley, P.; Luz, L.; Swingland, I.R. The faint promise of a distant market: a survey of Belém’s trade in non-timber forest products. Biodivers. Conserv. 2002, 11, 615–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belcher, B.; Schreckenberg, K. Commercialisation of non-timber forest products: A reality check. Dev. Policy Rev. 2007, 25, 355–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackleton, C.; Shackleton, S. The importance of non-timber forest products in rural livelihood security and as safety nets: a review of evidence from South Africa. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2004, 100, 658–664. [Google Scholar]
- Delang, C.O. The role of wild food plants in poverty alleviation and biodiversity conservation in tropical countries. Prog. Dev. Stud. 2006, 6, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoian, D. Making the Best of Two Worlds: Rural and Peri-Urban Livelihood Options Sustained by Nontimber Forest Products from the Bolivian Amazon. World Dev. 2005, 33, 1473–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaimovitz, D. Not by bread alone... forests and rural livelihoods in sub-Saharan Africa. In Forestry in Poverty Reduction Strategies: Capturing the Potential; Oksanen, T., Pajari, B., Tuomasjukka, T., Eds.; European Forest Institute: Joensuu, Finland, 2003; pp. 45–64. [Google Scholar]
- Termote, C.; Everaert, G.; Bwama Meyi, M.; Dhed’a Djailo, B.; Damme, P. Wild edible plant markets in Kisangani, Democratic Republic of Congo. Hum. Ecol. 2012, 40, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndoye, O.; Ruiz Perez, M.; Eyebe, A. The markets of non-timber forest products in the humid forest zone of Cameroon. Available online: http://www.odi.org.uk/sites/odi.org.uk/files/odi-assets/publications-opinion-files/1168.pdf (accessed on 18 October 2013).
- Hawkes, C.; Ruel, M. Agriculture and nutrition linkages: Old lessons and new paradigms. In Reshaping Agriculture for Nutrition and Health; Fan, S., Pandya-Lorch, R., Eds.; IFPRI: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; pp. 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Von Braun, J.; Diaz-Bonilla, E. Globalization of agriculture and food: Causes, consequences and policy implications. In Globalization of Food and Agriculture and the Poor; von Braun, J., Diaz-Bonilla, E., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New Delhi, India, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes, C.; Ruel, M. Value chains for nutrition. In Reshaping Agriculture for Nutrition and Health; Fan, S., Pandya-Lorch, R., Eds.; IFPRI: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; pp. 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, B.R. Overview of Resource Potential for Indigenous Nut Production in the South Pacific; Stevens, M.L., Bourke, R.M., Evans, B.R., Eds.; Austrialian Centre for International Agricultural Research (ACIAR): Canberra, Australia, 1996; pp. 10–35. [Google Scholar]
- English, R.M.; Aalbersberg, W.G.L.; Scheelings, P. Pacific Islands Foods—Description and Nutrient Composition of 78 Local Food Samples; IAS Technical Report No. 96/02; University of the South Pacific: Suva, Fiji, 1996; p. 94. [Google Scholar]
- Pacific Agribusiness Research & Development Initiative (PARDI). AIARC Canarium Nut Value Chain Review. Available online: https://www.spc.int/lrd/index.php?option=com_docman&task=doc_download&gid=1627&Itemid=575 (accessed on 15 October 2013).
- Thomson, L.A.J.; Evans, B. Canarium indicum var. indicum and C. harveyi (canarium nut) ver 2.1. In Species Profiles for Pacific Island Agroforestry; Permanent Agriculture Resources (PAR): Holualoa, HI, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- McMichael, A.J. Integrating nutrition with ecology: balancing the health of humans and biosphere. Publ. Health Nutr. 2005, 8, 706–715. [Google Scholar]
- Montagnini, F.; Nair, P.K.R. Carbon sequestration: An underexploited environmental benefit of agroforestry systems. Agroforest. Syst. 2004, 61, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.T.; Akinnifesi, F.K. Agroforestry as alternative land-use production systems for the tropics. Nat. Resourc. Forum 2000, 24, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, S. Agroforestry for ecosystem services and environmental benefits: An overview. Agroforest. Syst. 2009, 76, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Caluwe, E.; De Smedt, S.; Assogbadjo, A.E.; Samson, R.; Sinsin, B.; van Damme, P. Ethnic differences in use value and use patterns of baobab (Adansonia digitata L.) in northern Benin. Afr. J. Ecol. 2009, 433–440. [Google Scholar]
- Termote, C.; Damme, P.; Dhed’a Djailo, B. Eating from the wild: Turumbu, Mbole and Bali traditional knowledge on non-cultivated edible plants, District Tshopo, DRCongo. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2011, 58, 585–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhnlein, H.V.; Receveur, O. Dietary change and traditional food systems of indigenous peoples. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1996, 16, 417–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lykke, A.M.; Mertz, O.L.E.; Ganaba, S. Food comsumption in rural Burkina Faso. Ecol. Food Nutr. 2002, 41, 119–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, G.B.; Mndiga, H.; Maass, B.L. Diversity and genetic erosion of traditional vegetables in Tanzania from the farmer’s point of view. Plant Gen. Resour. Char. Utili. 2005, 3, 400–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falconer, J. The Major Significance of “Minor” Forest Products: The Local Use and Value of Forests in the West African Humid Forest Zone; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1990; FAO Community Forestry Note 6. [Google Scholar]
- Bharucha, Z.; Pretty, J. The roles and values of wild foods in agricultural systems. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2010, 365, 2913–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Popkin, B.M. The nutrition transition: an overview of world patterns of change. Nutr. Rev. 2004, 62, S140–S143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ticktin, T. The ecological implications of harvesting non-timber forest products. J. Appl. Ecol. 2004, 41, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasquez, R.; Gentry, A.H. Use and Misuse of Forest-harvested Fruits in the Iquitos Area. Conserv. Biol. 1989, 3, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delvaux, C.; Sinsin, B.; van Damme, P. Impact of season, stem diameter and intensity of debarking on survival and bark re-growth pattern of medicinal tree species, Benin, West Africa. Biol. Conserv. 2010, 143, 2664–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundriyal, M.; Sundriyal, R.C. Wild Edible Plants of the Sikkim Himalaya: Marketing, Value Addition and Implications for Management. Econ. Bot. 2004, 58, 300–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rist, L.; Shanley, P.; Sunderland, T.; Sheil, D.; Ndoye, O.; Liswanti, N.; Tieguhong, J. The impacts of selective logging on non-timber forest products of livelihood importance. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2012, 268, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndoye, O.; Tieguhong, J.C. Forest Resources and Rural Livelihoods: The Conflict Between Timber and Non-timber Forest Products in the Congo Basin. Scand. J. For. Res. 2004, 19, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limberg, G.R.; Iwan, M.; Moeliono, M.; Sudana, I.M.; Wollenberg, E. Community-based forestry and management planning. In Managing forest resources in a decentralized environment: lessons learnt from the Malinau Research Forest, East Kalimantan; Gunarso, P., Setyawati, T., Sunderland, T., Shackleton, C., Eds.; CIFOR (Center for International Forestry Research): Bogor, Indonesia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Guariguata, M.R.; García-Fernández, C.; Sheil, D.; Nasi, R.; Herrero-Jáuregui, C.; Cronkleton, P.; Ingram, V. Compatibility of timber and non-timber forest product management in natural tropical forests: Perspectives, challenges, and opportunities. For. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 259, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndoye, O.; Awono, A. Case Study B: policies for Gnetum spp. trade in Cameroon: overcoming constraints that reduce benefits and discourage sustainability. In Wild Governance: Finding Policies that Work for Non-Timber Forest Products; Laird, S.A., McLain, R.J., Wynberg, R.P., Eds.; Earthscan: London, UK, 2010; pp. 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Ingram, V.J.; Ndumbe, L.N.; Ewane, M.E. Small scale, high value: Gnetum africanum and Gnetum buchholzianum value chains in Cameroon. Small Scale For. 2012, 11, 539–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faye, M.D.; Weber, J.C.; Abasse, T.A.; Boureima, M.; Larwanou, M.; Bationo, A.B.; Diallo, B.O.; Sigué, H.; Dakouo, J.M.; Samaké, O.; Diaité, D.S. Farmers’ preferences for tree functions and species in the West African Sahel. For. Trees Livelihoods 2011, 20, 113–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gijsbers, H.J.M.; Kessler, J.J.; Knevel, M.K. Dynamics and natural regeneration of woody species in farmed parklands in the Sahel region (province of Passore, Burkina-Faso). For. Ecol. Manag. 1994, 64, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiema, A. Agroforestry Parkland Species Diversity: Uses and Management in Semi-Arid West Africa (Burkina Faso). PhD Thesis, University of Wageningen, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Maranz, S. Tree mortality in the African Sahel indicates an anthropogenic ecosystem displaced by climate change. J. Biogeogr. 2009, 36, 1181–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasi, R.; Taber, A.; van Vliet, N. Empty forests, empty stomachs? Bushmeat and livelihoods in the Congo and Amazon Basins. Int. For. Rev. 2011, 13, 355–368. [Google Scholar]
- Akinnifesi, F.K.; Kwesiga, F.; Mhango, J.; Chilanga, T.; Mkonda, A.; Kadzere, I.; Mithofer, D.; Sileshi, G.; Ramadhani, T.; Dhliwayo, P. Towards the development of Miombo fruit trees as commercial tree crops in Southern Africa. For. Trees Livelihoods 2006, 16, 103–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppell, C. Marketing Information Systems for Non-Timber Forest Products; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1995; Community Forestry Field Manual 6; p. 115. [Google Scholar]
- Bamoninga, B. Analyse de L’état de Lieux du Secteur des Produits Forestiers non Ligneux et Evaluation de Leur Contribution à la Sécurité Alimentaire en RDC; (in French). FAO project GCP/RAF/398/GER; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Tabuna, H. Evaluation des Échanges des Produits Forestiers non Ligneux Entre l'Afrique Subsaharienne et l'Europe; (in French). FAO: Rome, Italy, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lombard, C.; Leakey, R.R.B. Protecting the rights of farmers and communities while securing long term market access for producers of non-timber forest products: Experience in Southern Africa. For. Trees Livelihoods 2010, 19, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leakey, R.R.B.; Izac, A.M.N. Linkages between domestication and commercialization of non-timber forest products: Implications for agroforestry. In Domestication and Commercialization of Non-Timber Forest Products; Leakey, R., Temu, A., Melnyk, M., Eds.; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1996; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Tchoundjeu, Z.; Degrande, A.; Leakey, R.R.B.; Nimino, G.; Kemajou, E.; Asaah, E.; Facheux, C.; Mbile, P.; Mbosso, C.; Sado, T.; et al. Impacts of participatory tree domestication on farmer livelihoods in west and central Africa. For. Trees Livelihoods 2010, 19, 217–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, D.; Franzel, S. Trees of prosperity: Agroforestry, markets and the African smallholder. Agroforest. Syst. 2004, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherr, S.J.; White, A.; Kaimowitz, D. Making markets work for forest communities. Int. For. Rev. 2003, 5, 67–73. [Google Scholar]
- Gruère, G.; Giuliani, A.; Smale, M. Marketing Underutilized Plant Species for the Benefit of the Poor : A Conceptual Framework; Environment and Production Technology Discussion Paper 154; IFPRI: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Frison, E.; Smith, I.F.; Johns, T.; Cherfas, J.; Eyzaguirre, P. Agricultural biodiversity, nutrition, and health: Making a difference to hunger and nutrition in the developing world. Food Nutr. Bull. 2006, 27, 167–179. [Google Scholar]
- Remans, R.; Flynn, D.F.B.; de Clerck, F.; Diru, W.; Fanzo, J.; Gaynor, K.; Lambrecht, I.; Mudiope, J.; Mutuo, P.K.; Nkhoma, P.; et al. Assessing nutritional diversity of cropping systems in African villages. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torheim, L.E.; Ferguson, E.L.; Penrose, K.; Arimond, M. Women in resource-poor settings are at risk of inadequate intakes of multiple micronutrients. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 2051S–2058S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanzo, J.; Hunter, D.; Borelli, T.; Mattei, F. (Eds.) Diversifying Food and Diets: Using Agricultural Biodiversity to Improve Nutrition and Health; Earthscan: London, UK, 2013.
- Hoddinott, J.; Yohannes, Y. Dietary Diversity as a Food Security Indicator. Dietary Diversity as a Household Food Security Indicator: Food and Nutrition Technical Assistance; Academy for Educational Development: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Arimond, M.; Wiesmann, D.; Becquey, E.; Carriquiry, A.; Daniels, M.C.; Deitchler, M.; Fanou-Fogny, N.; Joseph, M.L.; Kennedy, G.; Martin-Prevel, Y.; et al. Simple food group diversity indicators predict micronutrient adequacy of women’s diets in 5 diverse, resource-poor settings. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 2059S–2069S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruel, M.T. Is dietary diversity an indicator of food security or dietary quality? A review of measurement issues and research needs. Food Nutr. Bull. 2003, 24, 231–232. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, G.; Fanou-Fogny, N.; Seghieri, C.; Arimond, M.; Koreissi, Y.; Dossa, R.; Kok, F.J.; Brouwer, I.D. Food groups associated with a composite measure of probability of adequate intake of 11 micronutrients in the diets of women in urban Mali. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 2070S–2078S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruel, M.T. Operationalizing dietary diversity: A review of measurement issues and research priorities. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 3911S–3926S. [Google Scholar]
- Savy, M.; Martin-Prével, Y.; Sawadogo, P.; Kameli, Y.; Delpeuch, F. Use of variety/diversity scores for diet quality measurement: Relation with nutritional status of women in a rural area in Burkina Faso. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 59, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torheim, L.E.; Ouattara, F.; Diarra, M.M.; Thiam, F.D.; Barikmo, I.; Hatløy, A.; Oshaug, A. Nutrient adequacy and dietary diversity in rural Mali: Association and determinants. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr 2004, 58, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuyper, E.; Vitta, B.; Dewey, K. Novel and underused food sources of key nutrients for complementary feeding. Available online: http://aliveandthrive.org/sites/default/files/Issue%206%20Novel%20and%20underused%20food%20sournces%20of%20key%20nutrients%20for%20complementary%20feeding_0.pdf (accessed on 14 June 2013).
- Ouédraogo, H.Z.; Traoré, T.; Zèba, A.N.; Dramaix-Wilmet, M.; Hennart, P.; Donnen, P. Effect of an improved local ingredient-based complementary food fortified or not with iron and selected multiple micronutrients on Hb concentration. Publ. Health Nutr. 2010, 13, 1923–1930. [Google Scholar]
- Savadogo, A.; Ilboudo, A.J.; Gnankiné, O.; Traoré, A. Numeration and Identification of thermotolerant endospore-forming Bacillus from two fermented condiments Bikalga and Soumbala. Adv. Environ. Biol. 2011, 5, 2960–2966. [Google Scholar]
- Parada, J.; Aguilera, J.M. Food microstructure affects the bioavailability of several nutrients. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisseleua, H.B.D.; Niang, A.I. Lessons from Sub-Saharan Africa: Delivery Mechanisms for Mobilizing Agricultural Biodiversity for Improved Food and Nutrition Security; Fanzo, J., Hunter, D., Borelli, T., Mattei, F., Eds.; Earthscan: London, UK, 2013; pp. 111–121. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, I.F. Sustained and integrated promotion of local, traditional food systems for nutrition security. In Diversifying Food and Diets: Using Agricultural Biodiversity to Improve Nutrition and Health; Fanzo, J., Hunter, D., Borelli, T., Mattei, F., Eds.; Earthscan: London, UK, 2013; pp. 122–139. [Google Scholar]
- De Foliart, G.R. Insects as food: Why the western attitude is important. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1999, 44, 21–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Huis, A. Edible Insects: Future Prospects For Food And Feed Security; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Burlingame, B.; Charrondiere, R.; Mouille, B. Food composition is fundamental to the cross-cutting initiative on biodiversity for food and nutrition. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2009, 22, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, M.; McBurney, R.P.H.; Broin, M.; Beentje, H.J. Linking biodiversity, food and nutrition: The importance of plant identification and nomenclature. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2010, 23, 486–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudasaini, R.; Sthapit, S.; Suwal, R.; Sthapit, B.R. The role of integrated home gardens and local, neglected and underutilized plant species in food security in Nepal and meeting the Millennium Development Goal 1 (MDG). In Diversifying Food and Diets: Using Agricultural Biodiversity to Improve Nutrition and Health; Fanzo, J., Hunter, D., Borelli, T., Mattei, F., Eds.; Earthscan: London, UK, 2013; pp. 242–256. [Google Scholar]
- Low, J.W.; Arimond, M.; Osman, N.; Cunguara, B.; Zano, F.; Tschirley, D. A food-based approach introducing orange-fleshed sweet potatoes increased vitamin A intake and serum retinol concentrations in young children in rural Mozambique. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 1320–1327. [Google Scholar]
- Masset, E.; Haddad, L.; Cornelius, A.; Isaza-Castro, J. Effectiveness of agricultural interventions that aim to improve nutritional status of children: Systematic review. BMJ. 2012. [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, R.A. Shady Practice: Gender and the Political Ecology of Resource Stabilization in Gambian Garden/Orchards. Econ. Geogr. 1993, 69, 349–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, L. Women in the garden and kitchen: the role of cuisine in the conservation of traditional house lot crops among the Yucatec Mayan immigrants. In Women and Plants: Gender Relations in Biodiversity Management and Conservation; Howard, P.L., Ed.; Zed Books Ltd.: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, K. Tending the Wild: Native American Knowledge and the Management of California’s Natural Resources; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Garrity, D.P.; Akinnifesi, F.K.; Ajayi, O.C.; Weldesemayat, S.G.; Mowo, J.G.; Kalinganire, A.; Larwanou, M.; Bayala, J. Evergreen Agriculture: A robust approach to sustainable food security in Africa. Food Secur. 2010, 2, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehlenbeck, K.; Arifin, H.; Maass, B. Plant diversity in homegardens in a socio-economic and agro-ecological context. In The Stability of Tropical Rainforest Margins: Linking Ecological, Economic and Social Constraints of Land Use and Conservation; Tscharntke, T., Leuschner, C., Zeller, M., Guhardja, E., Bidin, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007; pp. 297–319. [Google Scholar]
- Berti, P.R.; Krasevec, J.; FitzGerald, S. A review of the effectiveness of agriculture interventions in improving nutrition outcomes. Publ. Health Nutr. 2004, 7, 599–609. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, K.M.; Specio, S.E.; Shrestha, P.; Brown, K.H.; Allen, L.H. Nutrition knowledge and practices, and consumption of vitamin A-rich plants by rural Nepali participants and nonparticipants in a kitchen-garden program. Food Nutr. Bull. 2005, 26, 198–208. [Google Scholar]
- Kitinoja, L.; Kader, A. Small-Scale Postharvest Practices A Manual for Horticultural Crops—Postharvest Technology Center; University of California Davis: Davis, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ogunsina, B.S.; Koya, O.A.; Adeosun, O.O. A Table Mounted Device for Cracking Dika Nut (Irvingia gabonensis). Available online: http://www.cigrjournal.org/index.php/Ejounral/article/viewFile/1096/1039 (accessed on 17 September 2013).
- Ibnouf, F.O. The role of women in providing and improving household food security in sudan: Implications for reducing hunger and malnutrition. J. Int. Womens Stud. 2009, 10, 144–167. [Google Scholar]
- De Schutter, O. Report submitted by the UN Special Rapporteur on the right to food to the UN General Assembly Human Rights Council. Available online: http://www.srfood.org/images/stories/pdf/officialreports/20110308_a-hrc-16-49_agroecology_en.pdf (accessed on 12 October 2013).
- Hoddinott, J. Operationalizing Household Food Security in Development Projects: An Introduction; IFPRI (International Food Policy Research Institute): Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Teklehaimanot, Z. Exploiting the potential of indigenous agroforestry trees: Parkia biglobosa and Vitellaria paradoxa in sub-Saharan Africa. Agroforest. Syst. 2004, 61–62, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ræbild, A.; Hansen, U.B.; Kambou, S. Regeneration of Vitellaria paradoxa and Parkia biglobosa in a parkland in Southern Burkina Faso. Agroforest. Syst. 2011, 85, 443–453. [Google Scholar]
- Larson, A.M.; Ribot, J.C. The poverty of forestry policy: double standards on an uneven playing field. Sustain. Sci. 2007, 2, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boef, W.S.; Subedi, A.; Peroni, N.; Thijssen, M. Community Biodiversity Management: Promoting Resilience and the Conservation of Plant Genetic Resources; Earthscan: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- High, C.; Shackleton, C.M. The comparative value of wild and domestic plants in home gardens of a south African rural village. Agroforest. Syst. 2000, 48, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padoch, C.; Pinedo-Vasquez, M. Saving Slash-and-Burn to Save Biodiversity. Biotropica 2010, 42, 550–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, A.G.; Richards, P. Rain Forest in Mende Life: Resources and Subsistence Strategies in Rural Communities around the Gola North Forest Reserve (Sierra Leone); A Report to ESCOR; Overseas Development Administration: London; UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- May, P.H.; Anderson, A.B.; Frazão, J.M.F.; Balick, M.J. Babassu palm in the agroforestry systems in Brazil’s mid-north region. Agroforest. Syst. 1985, 3, 275–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.E.M.; Dewees, P.A. Farms, Trees and Farmers: Responses to Agricultural Intensification; Earthscan: London, UK, 1997; Volume 20, pp. 328–329. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Vinceti, B.; Termote, C.; Ickowitz, A.; Powell, B.; Kehlenbeck, K.; Hunter, D. The Contribution of Forests and Trees to Sustainable Diets. Sustainability 2013, 5, 4797-4824. https://doi.org/10.3390/su5114797
Vinceti B, Termote C, Ickowitz A, Powell B, Kehlenbeck K, Hunter D. The Contribution of Forests and Trees to Sustainable Diets. Sustainability. 2013; 5(11):4797-4824. https://doi.org/10.3390/su5114797
Chicago/Turabian StyleVinceti, Barbara, Céline Termote, Amy Ickowitz, Bronwen Powell, Katja Kehlenbeck, and Danny Hunter. 2013. "The Contribution of Forests and Trees to Sustainable Diets" Sustainability 5, no. 11: 4797-4824. https://doi.org/10.3390/su5114797