Estimation of Lithium-Ion Battery State of Health-Based Multi-Feature Analysis and Convolutional Neural Network–Long Short-Term Memory
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- To address the dual challenge of balancing local feature extraction and time-dependent modeling in battery SOH estimation, the CNN-LSTM model is introduced. The structural design of the model plays a key role in achieving efficient SOH estimation. The CNN part enhances the sensitivity of the model to the change in the battery state by extracting the local features of the battery charge and discharge curve. The LSTM part improves the model’s ability to predict long-term trends by capturing the time series dependencies in the battery degradation process.
- (2)
- To capture the changes in battery state comprehensively, multi-dimensional feature information, time features on the basis of battery voltage, and current traditional features are introduced. Six health features—the lowest point in time-of-discharge voltage H1, average discharge time H2, average discharge voltage H3, constant voltage charging time H4, average discharge current H5, and lowest point in voltage H6—are extracted, and then Pearson correlation is used to analyze them. Three features, H1, H2, and H3, most relevant to battery SOH are selected.
- (3)
- To ensure the high quality of data and the stability of the model, this paper uses the K-means clustering method to detect and process outliers in the CALCE data. Considering the possibility for noise and outliers in experimental data to interfere with model training, this paper introduces the K-means unsupervised clustering method to detect outliers in charge and discharge data, and combines the Elbow method and contour coefficient to automatically determine the optimal number of clusters, thereby effectively improving data quality and model stability.
2. Experimental Data and Feature Analysis
2.1. Dataset
2.1.1. CALCE Dataset Information
2.1.2. NASA Dataset Information
2.1.3. Data Outlier Detection
2.2. Feature Extraction
2.3. Pearson Correlation Analysis
3. Model Building
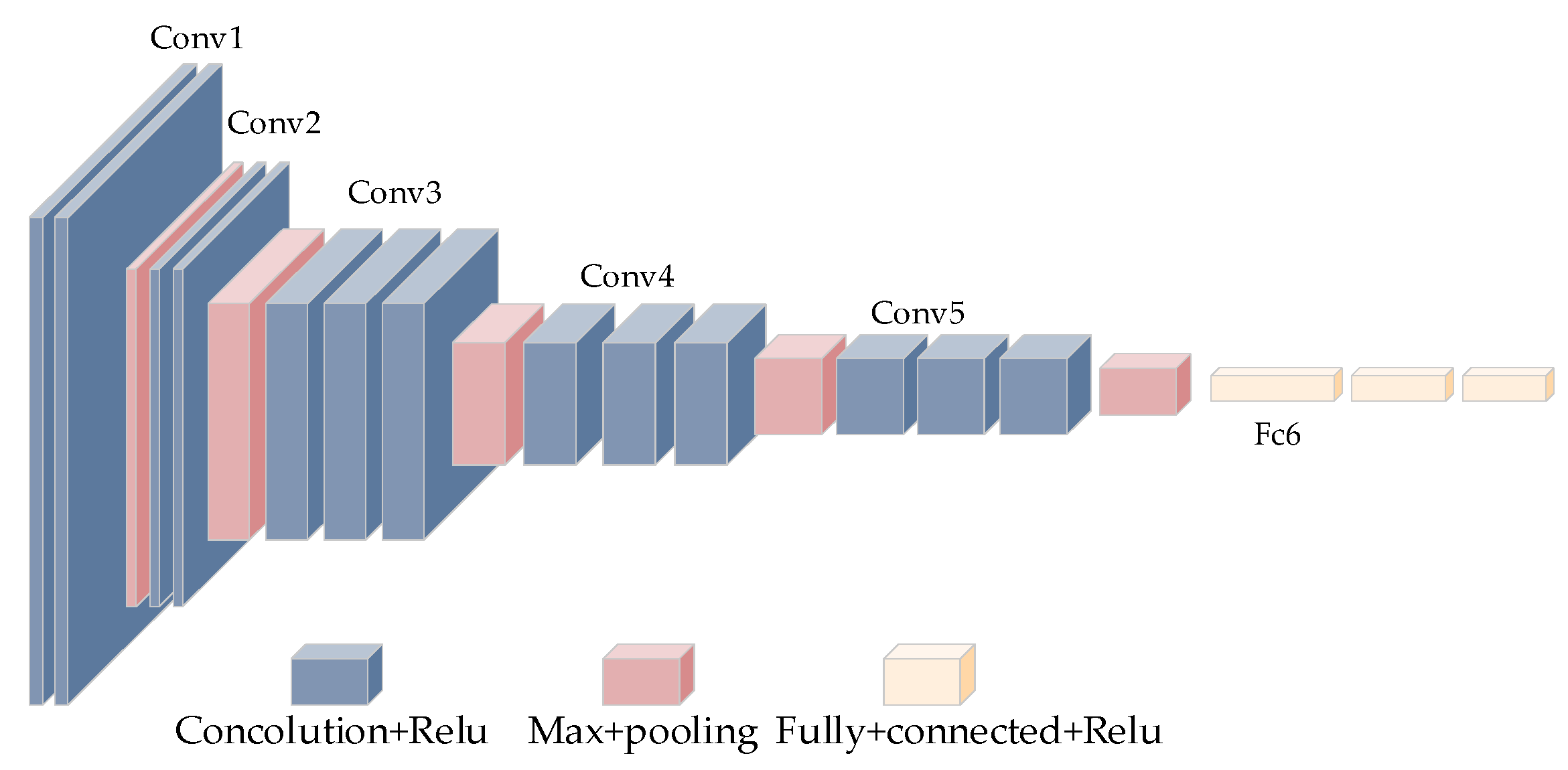
3.1. Convolutional Neural Networks
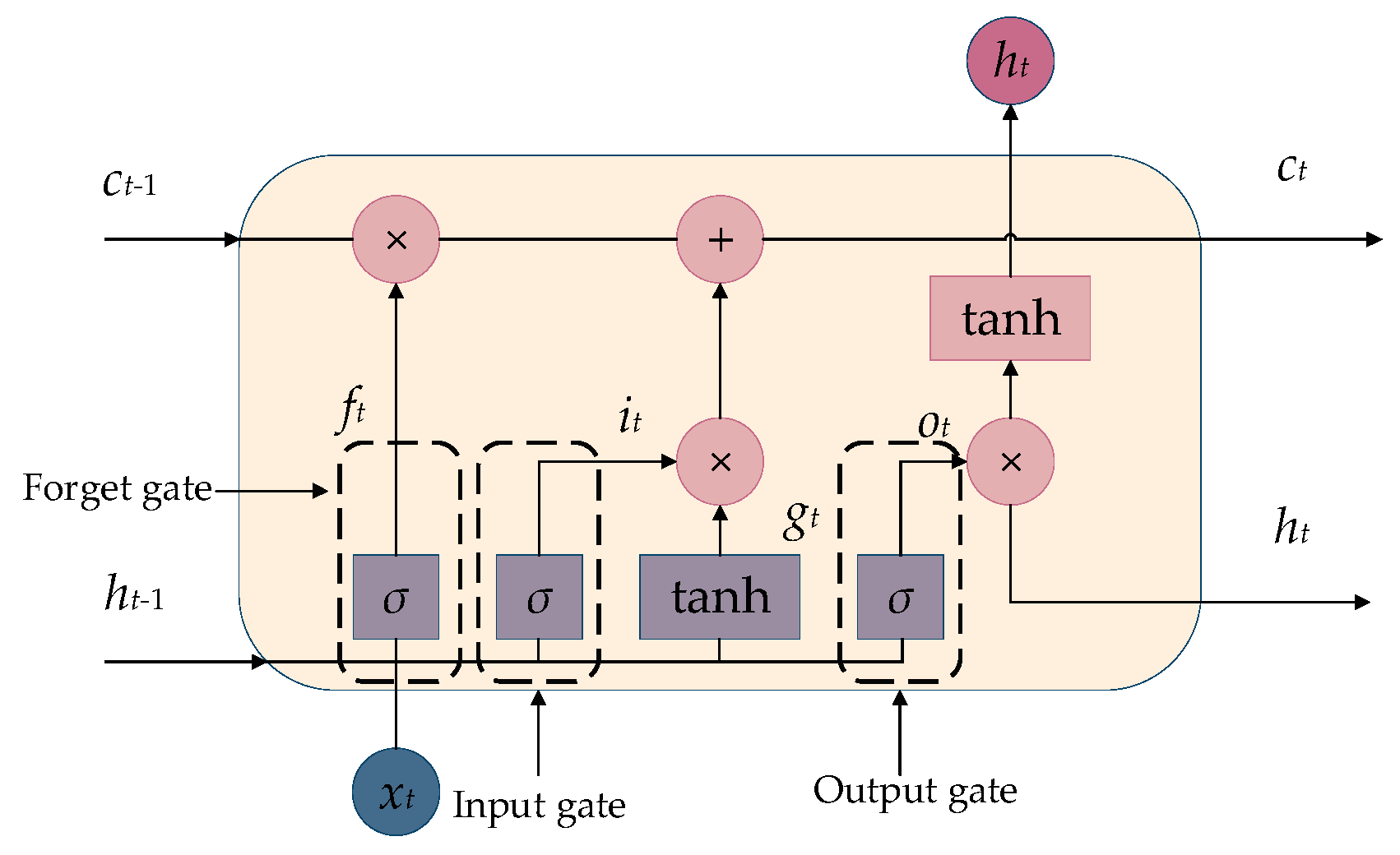
3.2. Long Short-Term Memory Neural Networks
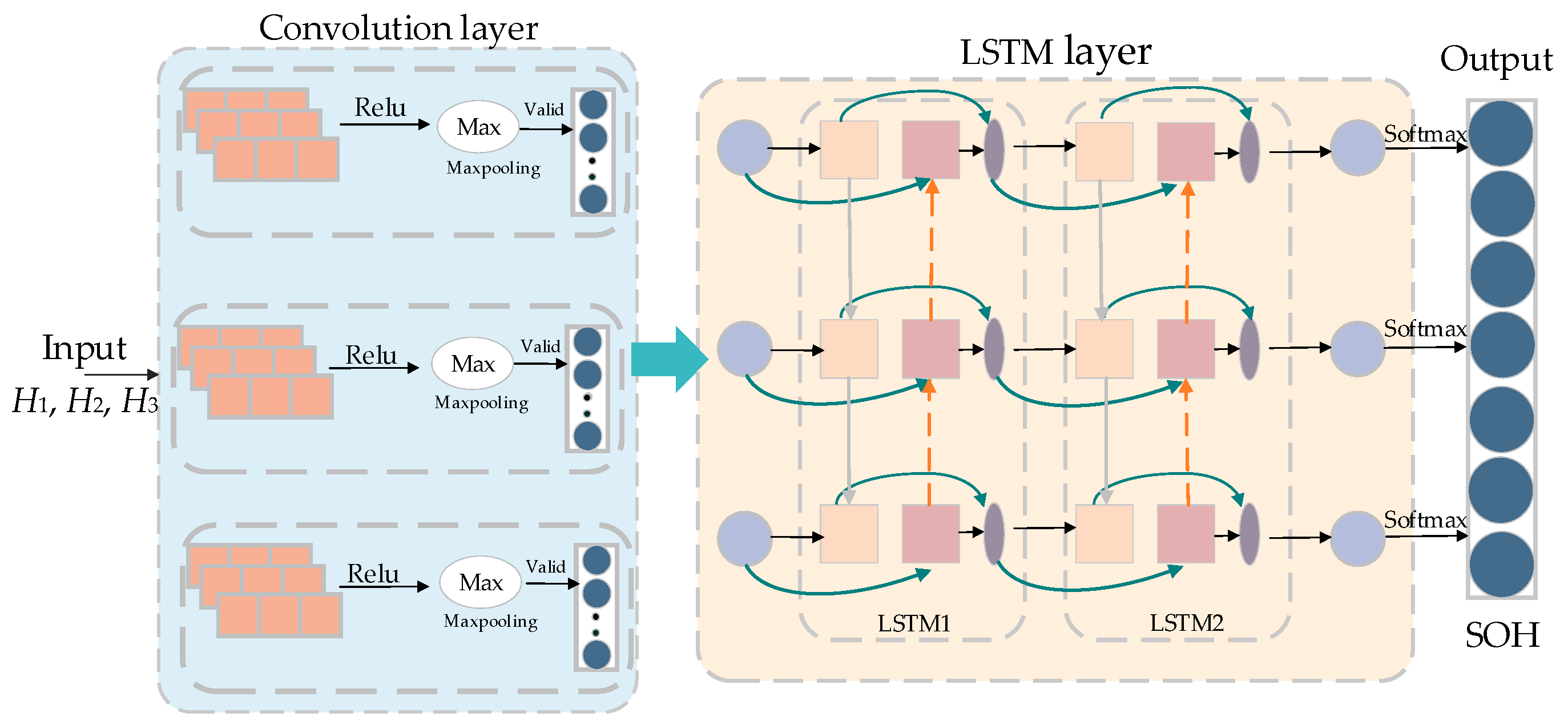
3.3. CNN-LSTM Model
4. Experimental Results and Analysis
4.1. Evaluation Indicators
4.1.1. R-Square
4.1.2. Mean Absolute Error
4.1.3. Mean Bias Error
4.1.4. Root Mean Square Error
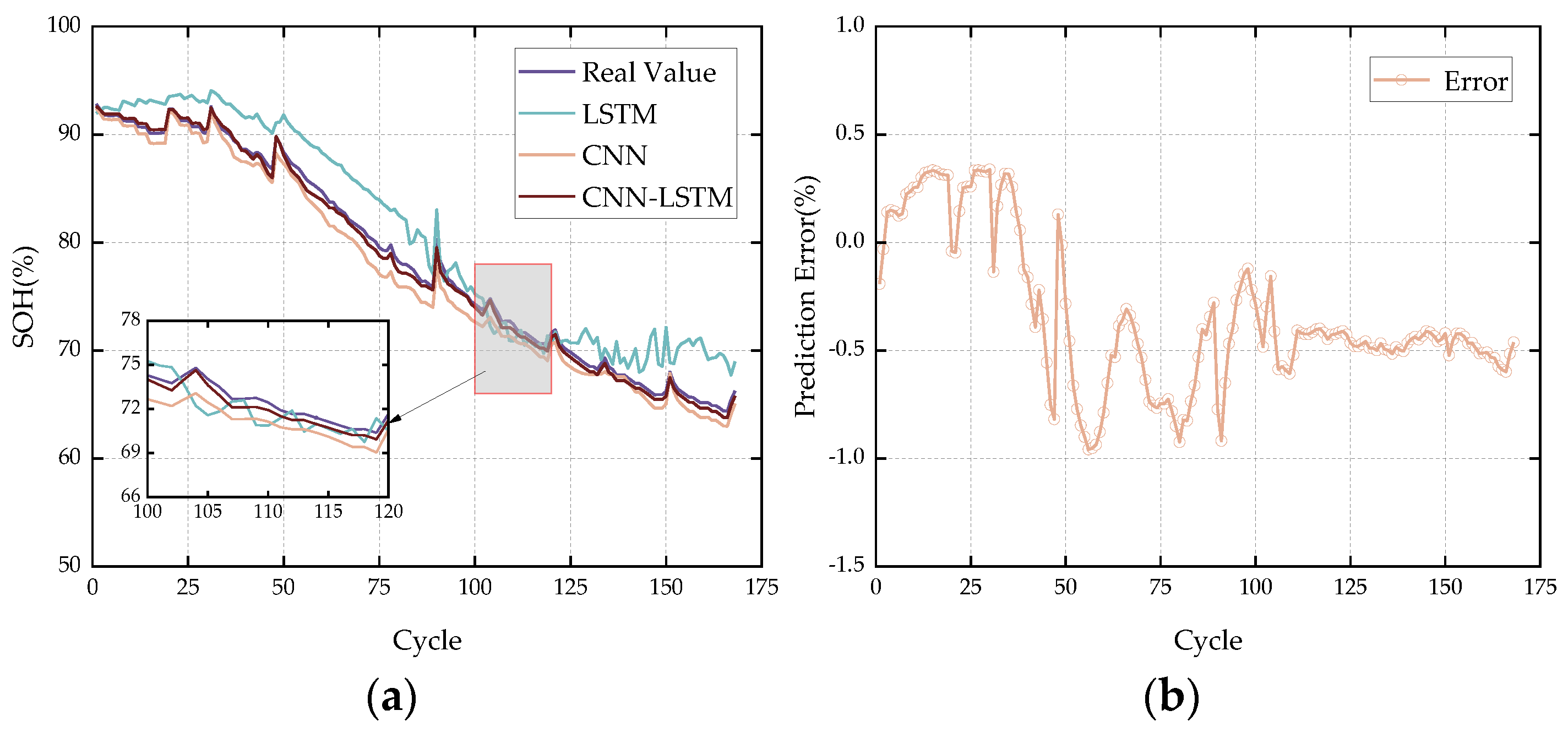
4.2. SOH Prediction Results of the CNN-LSTM Model
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Li, L.; Hao, Y. Economic effects of sustainable energy technology progress under carbon reduction targets: An analysis based on a dynamic multi-regional CGE model. Appl. Energy 2024, 363, 123071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.M.; Rasul, M.G.; Sayem, A.S.M.; Mandal, N.K. Design and optimization of lithium-ion battery as an efficient energy storage device for electric vehicles: A comprehensive review. J. Energy Storage 2023, 71, 108033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.P.; Lv, H.P.; Ping, P.; Wang, G.Q. A review of early warning methods of thermal runaway of lithium ion batteries. J. Energy Storage 2023, 64, 107073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yang, D.F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.C.; Wang, K. Online estimation of SOH for lithium-ion battery based on SSA-Elman neural network. Prot. Control Mod. Power Syst. 2022, 7, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, H.K.; He, H.W.; Wei, Z.B.; Quan, Z.Y.; Li, Y.W. State of Health Estimation of Lithium-Ion Battery Based on Constant-Voltage Charging Reconstruction. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2023, 11, 4393–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, M.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y. Method of Predicting SOH and RUL of Lithium-Ion Battery Based on the Combination of LSTM and GPR. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.J.; Zhang, C.P.; Jiang, J.C.; Zhang, W.G.; Zhang, L.J.; Wang, Y.B. Review on state-of-health of lithium-ion batteries: Characterizations, estimations and applications. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 314, 128015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, D.B.; Li, M.L.; Lam, V.N.; Braatz, R.D.; Chueh, W.C.; Bazant, M.Z. Physics-Informed Design of Hybrid Pulse Power Characterization Tests for Rechargeable Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2024, 171, 050510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruj, O.; Calborean, A. Lifecycle Evaluation of Lithium-Ion Batteries Under Fast Charging and Discharging Conditions. Batteries 2025, 11, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hou, J.W.; Wang, Z.K.; Jiang, Y.Q. Joint SOH-SOC Estimation Model for Lithium-Ion Batteries Based on GWO-BP Neural Network. Energies 2023, 16, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Yang, F.; Ma, L.; Wang, Y. Joint Estimation Method with Multi-Innovation Unscented Kalman Filter Based on Fractional-Order Model for State of Charge and State of Health Estimation. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Gu, P.; Kang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, B.; Zhang, C. The state of health estimation of lithium-ion batteries based on data-driven and model fusion method. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 366, 132742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obregon, J.; Han, Y.R.; Ho, C.W.; Mouraliraman, D.; Lee, C.W.; Jung, J.Y. Convolutional autoencoder-based SOH estimation of lithium-ion batteries using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. J. Energy Storage 2023, 60, 106680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.F.; Yang, L.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Q.S.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Meng, Y.Z.; Zhao, X.W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, S.M.; Li, Y.; et al. SOH estimation method for lithium-ion batteries based on an improved equivalent circuit model via electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. J. Energy Storage 2024, 86, 111167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.C.; Wang, J.; Lund, P.D.; Zhang, Y.M. Co-estimating the state of charge and health of lithium batteries through combining a minimalist electrochemical model and an equivalent circuit model. Energy 2022, 240, 122815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseininasab, S.; Lin, C.W.; Pischinger, S.; Stapelbroek, M.; Vagnoni, G. State-of-health estimation of lithium-ion batteries for electrified vehicles using a reduced-order electrochemical model. J. Energy Storage 2022, 52, 104684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.P.; Xiong, R.; Yu, Q.Q. Fractional-Order Model-Based Incremental Capacity Analysis for Degradation State Recognition of Lithium-Ion Batteries. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 1576–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.S.; Li, W.; Mou, J.H.; Garg, A.; Gao, L.; Liu, J. A Hybrid Battery Equivalent Circuit Model, Deep Learning, and Transfer Learning for Battery State Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2023, 9, 1113–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.P.; Chen, X.; Li, X.H.; Li, Y.K. SOH prediction of lithium battery based on IC curve feature and BP neural network. Energy 2022, 261, 125234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.M.; Zhu, J.C.; Wu, T.Z.; Tang, A.H.; Kan, J.R.; Pecht, M. SOH early prediction of lithium-ion batteries based on voltage interval selection and features fusion. Energy 2024, 308, 132993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.T.; Liu, F.; Ma, Y.X.; Fan, J.M. A Neural-Network-Based Method for RUL Prediction and SOH Monitoring of Lithium-Ion Battery. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 87178–87191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Tang, T.; Jiang, F.S.; Xia, Q.; Zhu, X.Y.; Sun, B.; Yang, D.Z.; Feng, Q.; Qian, C. A novel state of health estimation method for lithium-ion battery pack based on cross generative adversarial networks. Appl. Energy 2025, 377, 124385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Cui, X.C.; Meng, J.H.; Peng, J.C.; Lin, M.Q. Data-Driven Transfer-Stacking-Based State of Health Estimation for Lithium-Ion Batteries. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 71, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.J.; Zhai, Z.; Zhao, Z.B.; Di, Y.; Chen, X.F. Physics-informed neural network for lithium-ion battery degradation stable modeling and prognosis. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.X.; Liu, Z.T.; Xu, Y.; Chen, G.W.; Su, H.Y. An Electrochemical Aging-Informed Data-Driven Approach for Health Estimation of Lithium-Ion Batteries with Parameter Inconsistency. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2025, 40, 7354–7369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.X.; Hu, J.X.; Chen, J.J.; Deng, H.W.; Hu, W.H. State of health estimation for lithium battery random charging process based on CNN-GRU method. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.K.; Song, Z.Y.; Hofmann, H.; Sun, J. Robust State of Health estimation of lithium-ion batteries using convolutional neural network and random forest. J. Energy Storage 2022, 48, 103857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, C.N.; Quang, D.T. Estimation of SoH and internal resistances of Lithium ion battery based on LSTM network. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2023, 18, 100166. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, H.L.; Kang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.C.; Wang, K. Prediction of Health Level of Multiform Lithium Sulfur Batteries Based on Incremental Capacity Analysis and an Improved LSTM. Prot. Control Mod. Power Syst. 2024, 9, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradyumna, T.K.; Cho, K.; Kim, M.; Choi, W. Capacity estimation of lithium-ion batteries using convolutional neural network and impedance spectra. J. Power Electron. 2022, 22, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.S.; Lee, J.K.; Kim, B.W. SOH Estimation of Li-Ion Battery Using Discrete Wavelet Transform and Long Short-Term Memory Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; He, T.; Zhu, W.L.; Liao, Y.X.; Zeng, J.H.; Xu, Q.; Niu, Y.C. A lithium-ion battery SOH estimation method based on temporal pattern attention mechanism and CNN-LSTM model. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2025, 122, 109930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.F.; Zhou, G.D.; Lai, C.S.; Dong, Z.K. Time-Frequency Hybrid Neuromorphic Computing Architecture Development for Battery State-of-Health Estimation. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 39941–39957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Bai, W.Y.; Wang, L.L.; Wu, H.B.; Ding, M. SOH estimation for lithium-ion batteries: An improved GPR optimization method based on the developed feature extraction. J. Energy Storage 2024, 83, 110678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laszlo, M.; Mukherjee, S. A genetic algorithm that exchanges neighboring centers for k-means clustering. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2007, 28, 2359–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.L.; Shan, Q.Y.; Zhang, Z.M.; Qu, Z.Y. Visual Extraction of Refined Operation Mode of New Power System Based on IPSO-Kmeans. Electronics 2023, 12, 2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbalakshmi, C.; Krishna, G.R.; Rao, S.K.M.; Rao, P.V. A Method to Find Optimum Number of Clusters Based on Fuzzy Silhouette on Dynamic Data Set. Proc. Int. Congr. Inf. Commun. Technol. 2015, 46, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neunzling, J.; Hainke, P.; Winter, H.; Henriques, D.; Fleckenstein, M.; Markus, T. Investigation of the Suitability of the DTV Method for the Online SoH Estimation of NMC Lithium-Ion Cells in Battery Management Systems. Batteries 2025, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Wang, K.A.; Chen, J.J. State of health and remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion batteries based on a disturbance-free incremental capacity and differential voltage analysis method. J. Energy Storage 2023, 64, 107161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.Y.; See, K.W.; Li, P.H.; Shan, K.H.; Wang, Y.P.; Zhao, L.; Lim, K.C.; Zhang, N. A novel state-of-health estimation for the lithium-ion battery using a convolutional neural network and transformer model. Energy 2023, 262, 125501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.L.; Li, D.Z.; Zhao, K.; Wang, L.C.; Wang, K. State of health estimation of lithium-ion battery based on improved ant lion optimization and support vector regression. J. Energy Storage 2022, 50, 104215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, B.; Xu, Y.; Feng, X. State-of-Health Estimation and Remaining-Useful-Life Prediction for Lithium-Ion Battery Using a Hybrid Data-Driven Method. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 10854–10867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.W.; Wu, L.F.; Xiong, S.Z.; Li, W.; Garg, A.; Gao, L. An improved CNN-LSTM model-based state-of-health estimation approach for lithium-ion batteries. Energy 2023, 276, 127585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.H.; Jiang, Y.H.; Yu, Q.Q.; Zhang, Z.G. A hybrid neural network model with attention mechanism for state of health estimation of lithium-ion batteries. J. Energy Storage 2023, 68, 107734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonthalia, A.; Josephin, J.S.F.; Varuvel, E.G.; Chinnathambi, A.; Subramanian, T.; Kiani, F. A deep learning multi-feature based fusion model for predicting the state of health of lithium-ion batteries. Energy 2025, 317, 134569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Zhang, X.D.; Zou, Y.; He, J.T. Multitimescale Feature Extraction From Multisensor Data Using Deep Neural Network for Battery State-of-Charge and State-of-Health Co-Estimation. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2024, 10, 5689–5702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elachhab, A.; Laadissi, E.; Tabine, A.; Hajjaji, A. Deep learning and data augmentation for robust battery state of charge estimation in electric vehicles. In Electrical Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Bamati, S.; Chaoui, H.; Gualous, H. Enhancing Battery Thermal Management With Virtual Temperature Sensor Using Hybrid CNN-LSTM. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2024, 10, 10272–10287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zuo, W.; Zhou, K.; Li, Q.Q.; Huang, Y.H. State of charge estimation of lithium-ion batteries based on PSO-TCN-Attention neural network. J. Energy Storage 2024, 84, 110806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Shan, C.; Gao, J.W.; Chen, H. A novel method for state of health estimation of lithium-ion batteries based on improved LSTM and health indicators extraction. Energy 2022, 251, 123973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.; Kim, J.; Byun, Y.C. Integrating ensemble learning and meta bagging techniques for temperature-specific State of Health prediction in Lithium-ion Batteries. Energy Rep. 2024, 12, 2388–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.K.; Sun, X.W.; Fu, Y.P.; Wang, K. Lithium-ion battery health estimate based on electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and CNN-BiLSTM-Attention. Ionics 2025, 31, 1389–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

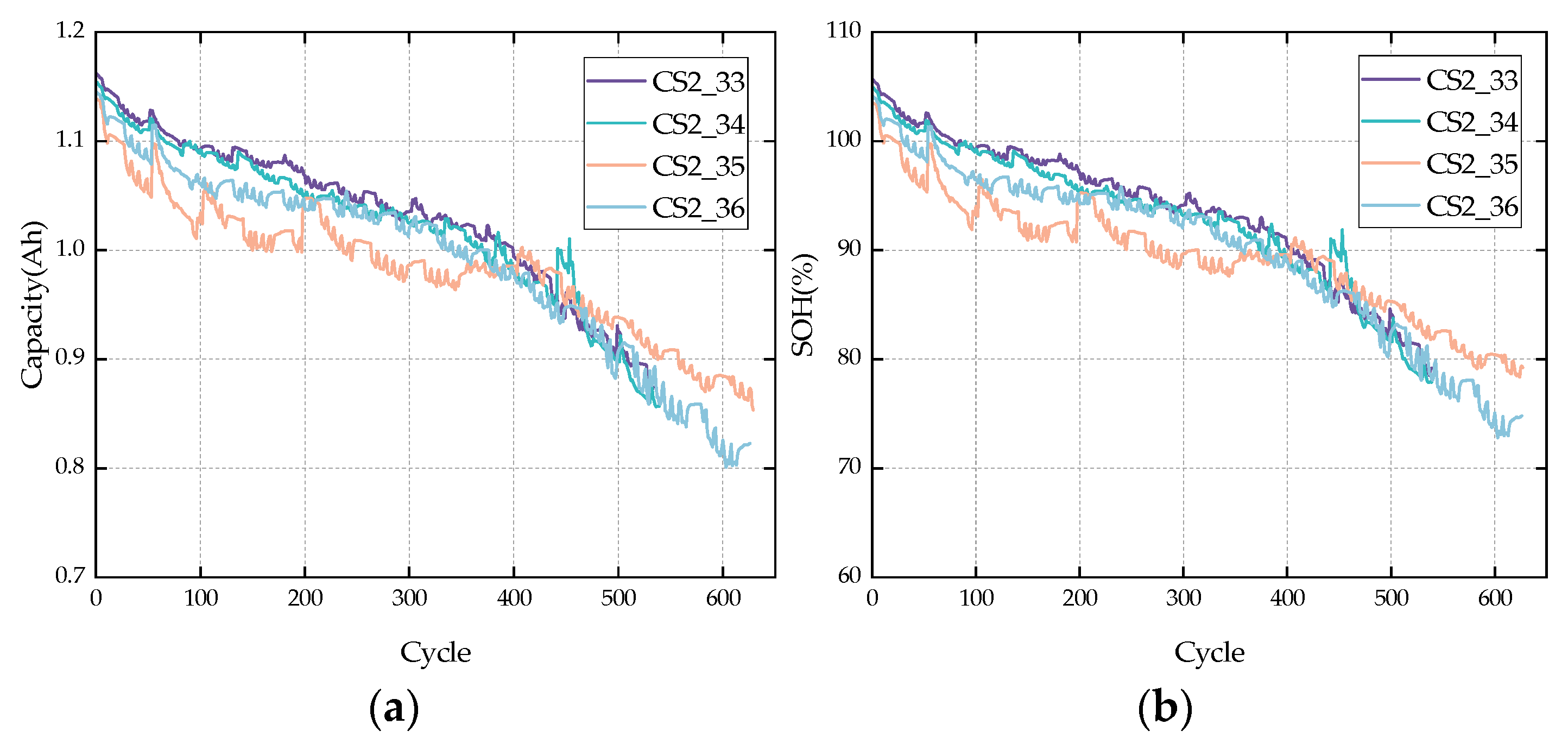
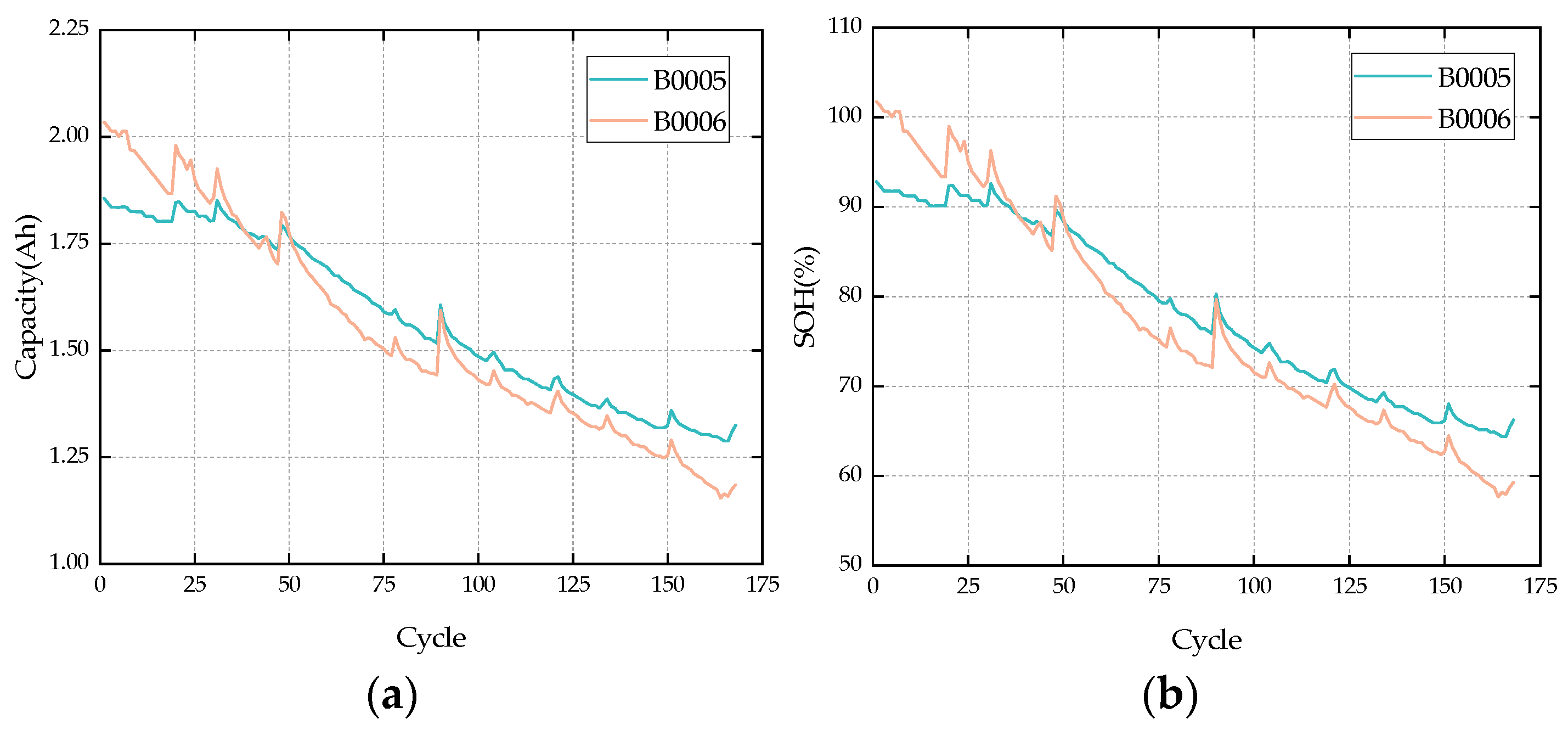

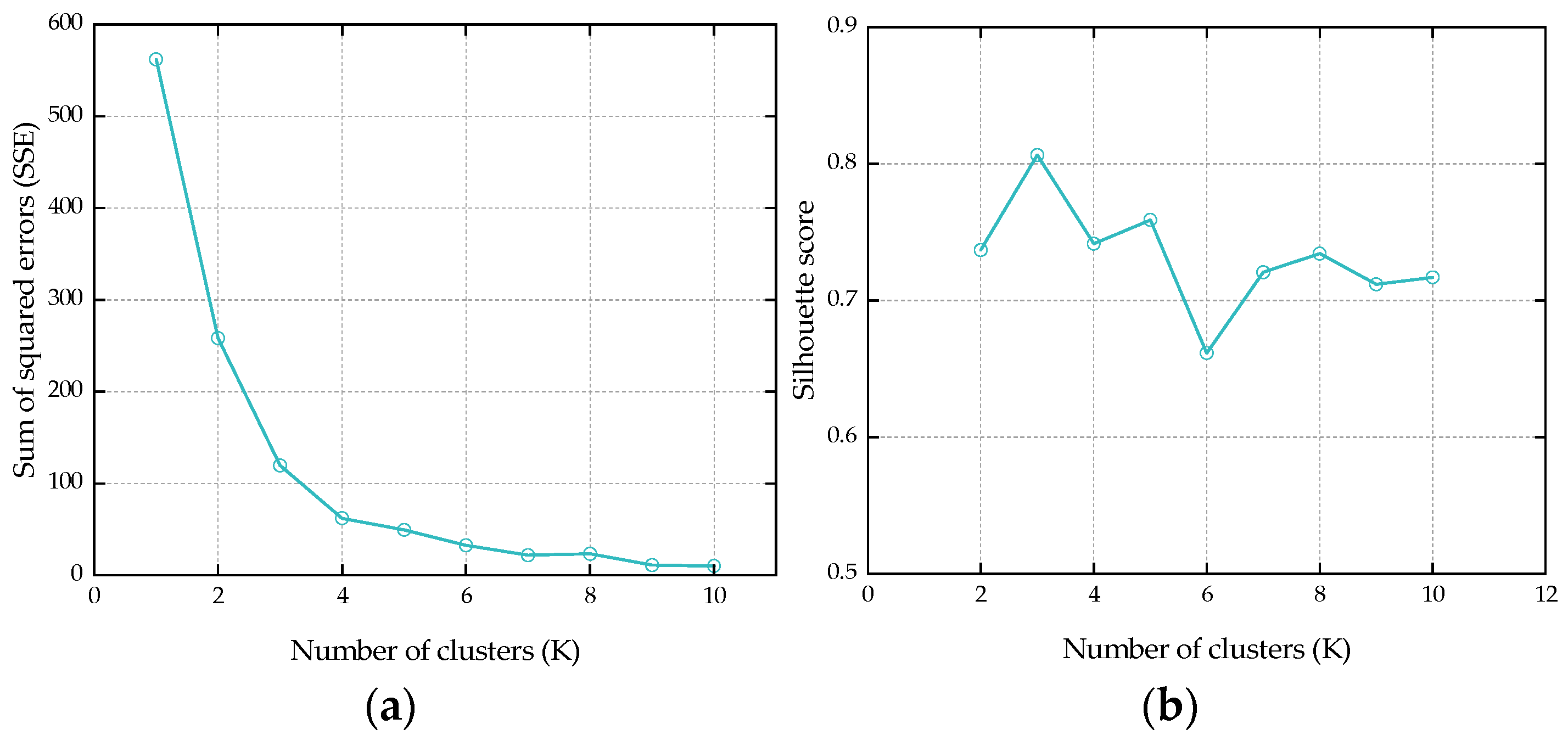

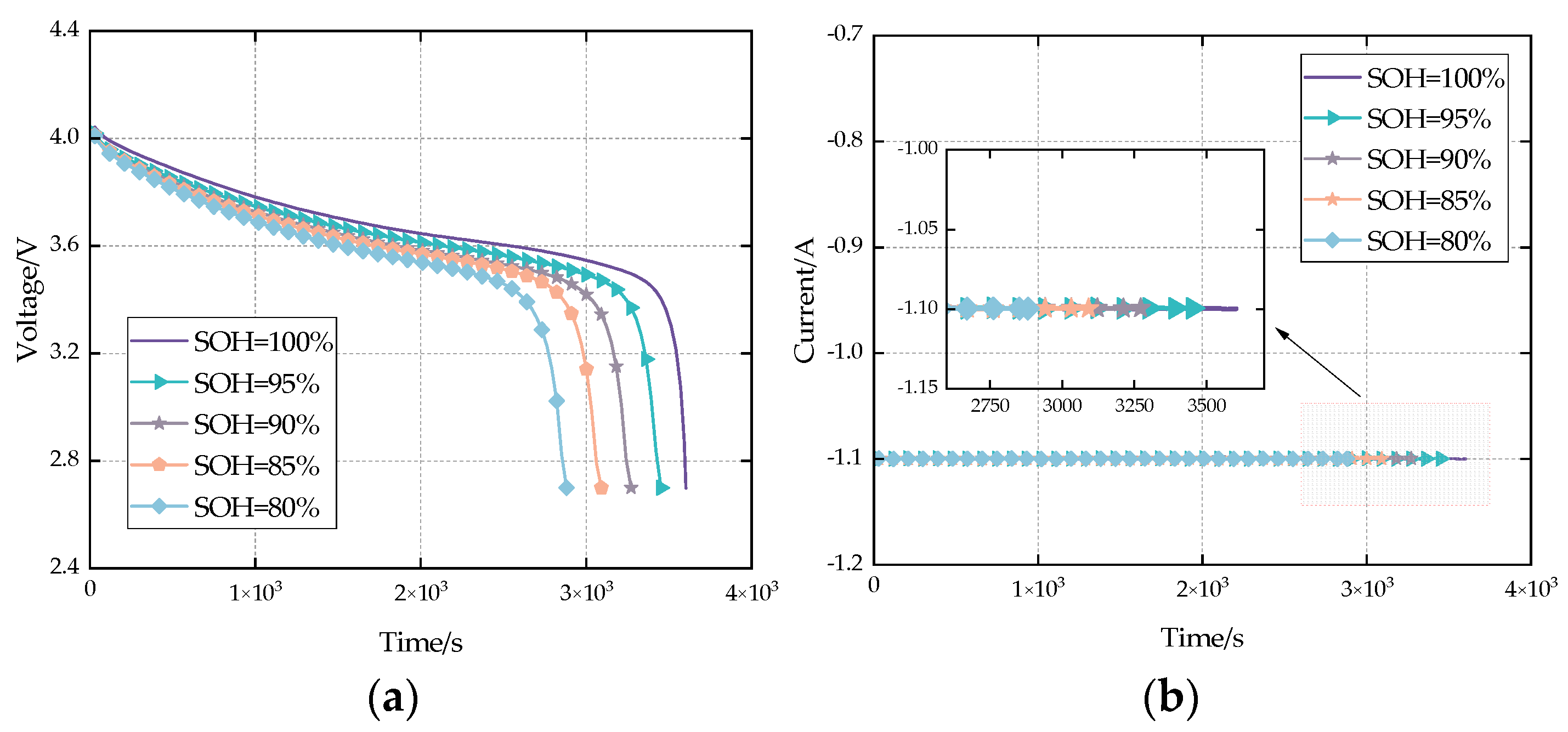


| CS2_33 | CS2_34 | CS2_35 | CS2_36 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capacity (mAh) | 1100 | 1100 | 1100 | 1100 |
| Charge rate (C) | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 |
| Discharge rate (C) | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 |
| Charge cut-off voltage (V) | 4.2 | 4.2 | 4.2 | 4.2 |
| Discharge cut-off voltage (V) | 2.7 | 2.7 | 2.7 | 2.7 |
| Cycle number | 540 | 540 | 628 | 627 |
| B0005 | B0006 | |
|---|---|---|
| Capacity (mAh) | 2000 | 2000 |
| Charge rate (C) | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| Discharge rate (C) | 2 | 2 |
| Charge cut-off voltage (V) | 4.2 | 4.2 |
| Discharge cut-off voltage (V) | 2.7 | 2.5 |
| Cycle number | 168 | 168 |
| Health Factor | CS2_33 | CS2_35 |
|---|---|---|
| H1 | 1.0000 | 0.9778 |
| H2 | 0.9998 | 0.9990 |
| H3 | 0.8290 | 0.8702 |
| H4 | −0.7659 | −0.8691 |
| H5 | 0.0454 | −0.1425 |
| H6 | −0.2669 | −0.2278 |
| Algorithm | R2 | MAE (%) | MBE (%) | RMSE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSTM | 0.974 | 0.993 | 0.992 | 1.023 |
| CNN | 0.987 | 0.459 | −0.393 | 0.719 |
| CNN-LSTM | 0.997 | 0.297 | −0.004 | 0.339 |
| Algorithm | R2 | MAE (%) | MBE (%) | RMSE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSTM | 0.971 | 0.683 | −0.674 | 0.916 |
| CNN | 0.958 | 0.684 | 0.405 | 1.102 |
| CNN-LSTM | 0.998 | 0.184 | −0.111 | 0.239 |
| Algorithm | R2 | MAE (%) | MBE (%) | RMSE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSTM | 0.905 | 2.541 | 2.310 | 2.930 |
| CNN | 0.979 | 1.254 | −1.254 | 1.390 |
| CNN-LSTM | 0.99735 | 0.442 | −0.341 | 0.488 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, X.; Ding, X.; Tian, C.; Tian, C.; Zhu, R. Estimation of Lithium-Ion Battery State of Health-Based Multi-Feature Analysis and Convolutional Neural Network–Long Short-Term Memory. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4014. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094014
Ma X, Ding X, Tian C, Tian C, Zhu R. Estimation of Lithium-Ion Battery State of Health-Based Multi-Feature Analysis and Convolutional Neural Network–Long Short-Term Memory. Sustainability. 2025; 17(9):4014. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094014
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Xin, Xingke Ding, Chongyi Tian, Changbin Tian, and Rui Zhu. 2025. "Estimation of Lithium-Ion Battery State of Health-Based Multi-Feature Analysis and Convolutional Neural Network–Long Short-Term Memory" Sustainability 17, no. 9: 4014. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094014
APA StyleMa, X., Ding, X., Tian, C., Tian, C., & Zhu, R. (2025). Estimation of Lithium-Ion Battery State of Health-Based Multi-Feature Analysis and Convolutional Neural Network–Long Short-Term Memory. Sustainability, 17(9), 4014. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094014






