Soil Heavy Metal Pollution and Health Risk Assessment Based on Monte Carlo Simulation: Case Study of Xicheng Lead-Zinc Mining Area
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sampling Site
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Geo-Accumulation Index
2.3.2. Comprehensive Pollution Index
2.3.3. Pollution Risk Assessment
- (1)
- Potential Ecological Risk Index
- (2)
- Ecological Risk Early Warning Index
2.3.4. Human Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals
| Parameter | Meaning | Unit | Probability Distribution | Adult | Child | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dust intake | mg·d−1 | Triangular | 4, 30, and 52 | 66, 103, and 161 | [38] | |
| Exposure frequency | d·a−1 | Triangular | 180, 345, and 365 | [38] | ||
| Exposure period | a | Point | 24 | 6 | [35] | |
| Exposed skin area | cm2 | Point | 0.54 | 0.23 | [35] | |
| skin adhesion coefficient | mg·cm−2 | Logarithmic | 0.49 and 0.54 | 0.65 and 1.2 | [38] | |
| Inhalation factor | — | Point | 0.001 (non-carcinogenic risk) | [35] | ||
| 0.01 (carcinogenic risk) | ||||||
| Air intake | m3·a−1 | Point | 19 | 8.6 | [39] | |
| Average body mass | kg | Logarithmic | 57.03 and 1.18 | 16.68 and 1.48 | [40] | |
| Action time | d | Point | 365 × ED (non-carcinogenic risk) | [40] | ||
| 365 × 70 (carcinogenic risk) | ||||||
| Particulate emission factor | m3·kg−1 | Point | 1.36 × 109 | 1.36 × 109 | [40] | |
| Elements | Reference Dose (RfD)/mg·(kg·d)−1 | Slope Factor (SF)/(kg·d)·mg−1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Digestive System | Respiratory System | Skin Contact | Digestive System | Respiratory System | Skin Contact | |
| As | 3.00 × 10−4 | 1.23 × 10−4 | 1.23 × 10−4 | 1.50 | 1.51 | 3.66 |
| Ni | 2.00 × 10−2 | 2.06 × 10−2 | 5.40 × 10−3 | — | 8.40 × 10−1 | — |
| Cu | 4.00 × 10−2 | 4.02 × 10−2 | 1.20 × 10−2 | — | — | — |
| Zn | 3.00 × 10−1 | 3.00 × 10−1 | 6.00 × 10−2 | — | — | — |
| Cd | 1.00 × 10−3 | 1.00 × 10−5 | 1.00 × 10−5 | 6.10 | 6.30 | — |
| Pb | 3.50 × 10−3 | 3.52 × 10−3 | 5.25 × 10−4 | 8.50 × 10−3 | — | — |
| Hg | 3.00 × 10−4 | 8.57 × 10−5 | 2.10 × 10−5 | — | — | — |
| Cr | 3.00 × 10−3 | 2.86 × 10−2 | 6.00 × 10−5 | 8.50 × 10−3 | 4.20 | |
2.3.5. Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistical Analysis of Heavy Metal Contents and Soil pH Values
3.2. Evaluation of Heavy Metal Pollution
3.2.1. Evaluation of the Geo-Accumulation Index
3.2.2. Evaluation of the Single-Factor Pollution Index and Comprehensive Pollution Index
3.3. Assessment of Ecological Risks Posed by Heavy Metals
3.3.1. Potential Ecological Risk Assessment
3.3.2. Ecological Risk Early Warning Evaluation
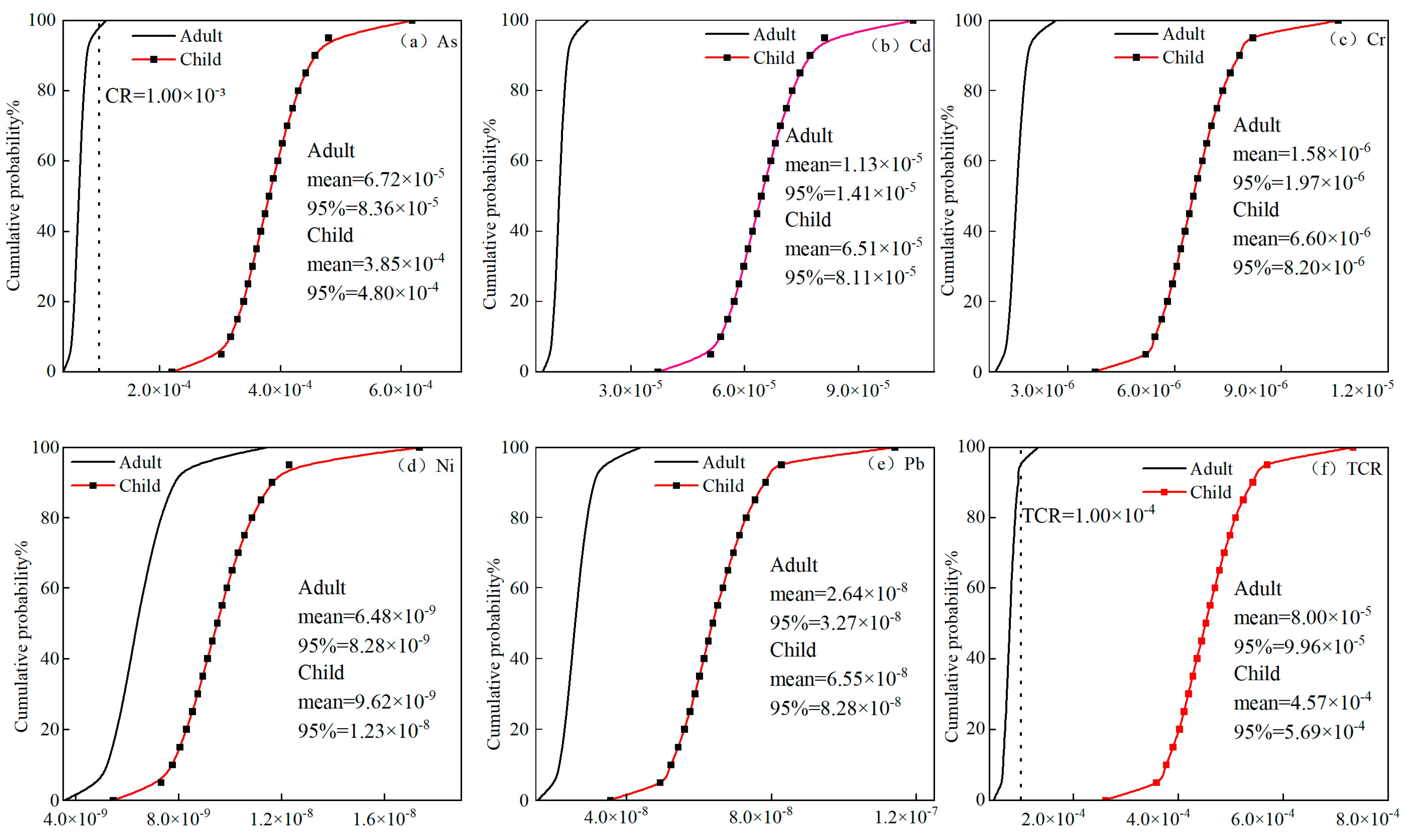
3.4. Human Health Risk Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fei, X.; Lou, Z.; Xiao, R.; Ren, Z.; Lv, X. Contamination assessment and source apportionment of heavy metals in agricultural soil through the synthesis of PMF and GeogDetector models. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 747, 141293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Wei, J.; Hou, Z.; Chen, R.; Zhang, X. Evaluation and sources of heavy metal pollution in soils of cultivated land around a lead-zinc mine area in Hebei province. J. Arid Land Res. Environ. 2023, 37, 136–142. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Jin, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, X. Evaluation of Heavy Metal Pollution in the Soil Around A Typical Tailing Reservoir in Irtysh River Basin. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2022, 31, 1015–1023. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, S.; Yang, K.; Liu, F.; Peng, M.; Li, K.; Yang, Z.; Liu, X.; Guo, F.; Ma, H. Overview of heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment of urban soils in Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 44, 4455–4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Chen, Y.; Ma, J.; Cao, J.; Jiang, Y. Sustainable Strategies for the Agricultural Development of Shaanxi Province Based on the Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution. Foods 2022, 11, 1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, D.; Kumar, A.; Maiti, S.K. Evaluation of toxic metal(loid)s concentration in soils around an open-cast coal mine (Eastern India). Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Xu, S.; Yang, B.; Zeng, G.; Qian, L.; Huang, H.; Ren, S. Contamination, Source Apportionment, and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Farmland Soils Surrounding a Typical Copper Tailings Pond. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Ding, K.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, M.; Baker, A.J.M.; Yang, W.; et al. Factors influencing heavy metal availability and risk assessment of soils at typical metal mines in Eastern China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gope, M.; Masto, R.E.; George, J.; Hoque, R.R.; Balachandran, S. Bioavailability and health risk of some potentially toxic elements (Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn) in street dust of Asansol, India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 138, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Gao, Y.; Yang, Y. Leaching of heavy metals from lead-zinc mine tailings and the subsequent migration and transformation characteristics in paddy soil. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Guo, Z.; Peng, C.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Xiao, X. Heavy metals in soils around non-ferrous smelteries in China: Status, health risks and control measures. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 282, 117038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, B.; Zhou, Z. Pollution assessment and source apportionment of heavy metals in soil from lead-Zinc mining areas of south China. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Z.; Yang, W.; Pan, L.; Gu, M.; Lee, D. Assessment of Metals Pollution on Agricultural Soil Surrounding a Lead-Zinc Mining Area in the Karst Region of Guangxi, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2013, 90, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Yao, X.; Wang, J.; Duan, H.; Hu, J.; Wu, T. Characteristics and Sources of Heavy Metal Pollution in Cropland near a Typical Lead-Zinc Processing Plant in Xieping Village, Hui County, China. Land 2023, 12, 1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Li, H.; Lu, L.; Liang, G.; Wu, T.; Zhu, J. Distributions and risk assessment of heavy metals in solid waste in lead-zinc mining areas and across the soil, water body, sediment and agricultural product ecosystem in their surrounding areas. China Geol. 2025, 8, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Xie, C.; Hou, Z. Ecological evaluation of heavy metal pollution in the soil of Pb-Zn mines. Ecotoxicology 2022, 31, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, H.; Yang, X. Quantifying ecological and human health risks of heavy metals from different sources in farmland soils within a typical mining and smelting industrial area. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 5669–5683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Cao, L.; Liang, Y. Spatial distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals inside and outside a typical lead-zinc mine in southeastern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 26265–26275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Xie, C.; Hou, Z. Spatiotemporal distribution patterns and risk characteristics of heavy metal pollutants in the soil of lead-zinc mines. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2022, 34, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Tian, K.; Liu, B.; Zhang, X.; Bian, Z.; Huang, B.; Yuan, X.; Wu, L.; Luo, D. Ecological risks of heavy metals and the relationship between sources and sinks in an abandoned mining area of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2021, 40, 987–998. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, H.; Cui, Z. Evaluation and analysis of soil migration and distribution characteristics of heavy metals in iron tailings. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Kuang, R.; He, Y.; Hu, W.; Huang, B.; Tian, K.; Li, Y.; Zu, Y.; Zhan, F. Source Apportionment of Arsenic in Agricultural Soils from a Typical Mining Area Based on APCS-MLR Model and Geostatistics. Soils 2022, 54, 379–384. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Kuang, H.; Hu, C.; Ge, G. Source Apportionment of Heavy Metal Pollution in Agricultural Soils around the Poyang Lake Region Using UNMIX Model. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, D.; Qin, C.; Nong, Z.; Ling, C.; Zhu, Y.; Chai, X. Pollution characteristics and source identification of farmland soils in Pb-Zn mining areas through an integrated approach. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 2533–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Liu, X.; Xu, J. New Perspectives about Health Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution-Origin and Prospects of Probabilistic Risk Analysis. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2022, 59, 28–37. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Hu, B.; Xu, J.; Liu, X. Potential driving forces and probabilistic health risks of heavy metal accumulation in the soils from an e-waste area, southeast China. Chemosphere 2022, 289, 133182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, H.; Wu, D.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, D. Spatial distribution, sources, and risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in cultivated soils using isotopic tracing techniques and Monte Carlo simulation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 259, 115044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Delgado Martin, J. Bioavailability and health risk of toxic heavy metals (As, Hg, Pb and Cd) in urban soils: A Monte Carlo simulation approach. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, J.; Li, K.; Jiao, L.; Zang, F.; Mao, X.; Tuo, X.; Tai, X. Characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals contamination in sediments from the Lanzhou Yintan wetland park based on Monte Carlo simulation model. Environ. Chem. 2024, 43, 2340–2355. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; He, Y.; Zhao, C.; Kou, Y.; Huang, K. Heavy Metals Pollution Characteristics and Health Risk Assessment of Farmland Soils and Agricultural Products in a Mining Area of Henan Province, China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 3929–3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel, J.V.; Knorr, C.L.; Flores, E.M.M.; Mueller, E.I.; Mesko, M.F.; Primel, E.G.; Duarte, F.A. Feasibility of microwave-induced combustion for trace element determination in Engraulis anchoita by ICP-MS. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 927–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB15618:2018; Soil Environmental Quality Risk Control standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of China: Beijing, China, 2015.
- Gao, T.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zuo, M.; He, Y.; Li, H.; Li, G.; Li, C.; Lis, X.; et al. Characteristics and diversity of microbial communities in lead-zinc tailings under heavy metal stress in north-west China. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 74, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, R.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Jia, L.; Yang, Q.; Zeng, X.; Li, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, R.; et al. Improved Calculations of Heavy Metal Toxicity Coefficients for Evaluating Potential Ecological Risk in Sediments Based on Seven Major Chinese Water Systems. Toxics 2023, 11, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varol, M. Environmental, ecological and health risks of trace metals in sediments of a large reservoir on the Euphrates River (Turkey). Environ. Res. 2020, 187, 109664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Guan, Q.; Tian, J.; Lin, J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, L.; Pan, N. Contamination characteristics, source apportionment, and health risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soil in the Hexi Corridor. Catena 2020, 191, 104573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhao, J.; Chang, S.X.; Collins, C.; Xu, J.; Liu, X. Status assessment and probabilistic health risk modeling of metals accumulation in agriculture soils across China: A synthesis. Environ. Int. 2019, 128, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, S. Health risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the source water and drinking water of China: Quantitative analysis based on published monitoring data. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 410, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Dai, S.; Meng, K.; Wang, Y.; Ren, W.; Zhao, L.; Christie, P.; Teng, Y. Occurrence and risk assessment of potentially toxic elements and typical organic pollutants in contaminated rural soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 630, 618–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Huang, D.; Yang, J.; Wei, X.; Qin, J.; Ou, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zou, Y. Probabilistic risk assessment of Chinese residents’ exposure to fluoride in improved drinking water in endemic fluorosis areas. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 222, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Dai, H.; Skuza, L.; Xu, J.; Shi, J.; Wang, Y.; Shentu, J.; Wei, S. Integrated survey on the heavy metal distribution, sources and risk assessment of soil in a commonly developed industrial area. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 236, 113462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.P.; Lian, B. Characteristics and distribution of soil environmental background values in Gansu Province. Gansu Environ. Res. Monit. 1993, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Rouhani, A.; Gutierrez, M.; Newton, R.A.; Al Souki, K.S. An overview of potentially toxic element pollution in soil around lead-zinc mining areas. Environ. Rev. 2025, 33, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Liu, C.; Zhu, J.; Li, F.; Deng, D.; Wang, Q.; Liu, C. Cadmium availability in rice paddy fields from a mining area: The effects of soil properties highlighting iron fractions and pH value. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 209, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buch, A.C.; Niemeyer, J.C.; Marques, E.D.; Silva-Filho, E.V. Ecological risk assessment of trace metals in soils affected by mine tailings. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, N.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, T. Pollution, cumulative ecological risk and source apportionment of heavy metals in water bodies and river sediments near the Luanchuan molybdenum mining area in the Xiaoqinling Mountains, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 205, 116621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Chu, L.; Sun, J.; Wang, S.; Ge, M.; Deng, L. Health risk assessment of trace metal(loid)s in agricultural soils based on Monte Carlo simulation coupled with positive matrix factorization model in Chongqing, southwest China. J. Mt. Sci. 2024, 21, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; He, M.; Feng, H.; Liu, Q.; Chen, J.; Li, T. Health risk study of cadmium, chromium, lead and arsenic in reservoir water of Changzhou, China. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A-Toxic/Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2023, 58, 680–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omokpariola, D.O.; Omokpariola, P.L. Health and exposure risk assessment of heavy metals in rainwater samples from selected locations in Rivers State, Nigeria. Phys. Sci. Rev. 2021, 8, 1305–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akindele, A.F.I.; Joseph, A. Health risk assessment of lead, cadmium, heavy metals and metalloids in residential paint flakes from indoor wall surfaces. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Le, H.; Kurkin, V.I.; Polekh, N.M.; Lee, C. The ionosphere under extremely prolonged low solar activity. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2011, 116, A04320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Xiang, Q.; Zhu, H.; Wang, S.; Zhu, Q.; Huang, D.; Zhang, Y. Effect of biochar from peanut shell on speciation and availability of lead and zinc in an acidic paddy soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 164, 554–561. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Dang, F.; Li, M.; Zhou, D.; Song, Y.; Wang, J. Environmental and human health risks from metal exposures nearby a Pb-Zn-Ag mine, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
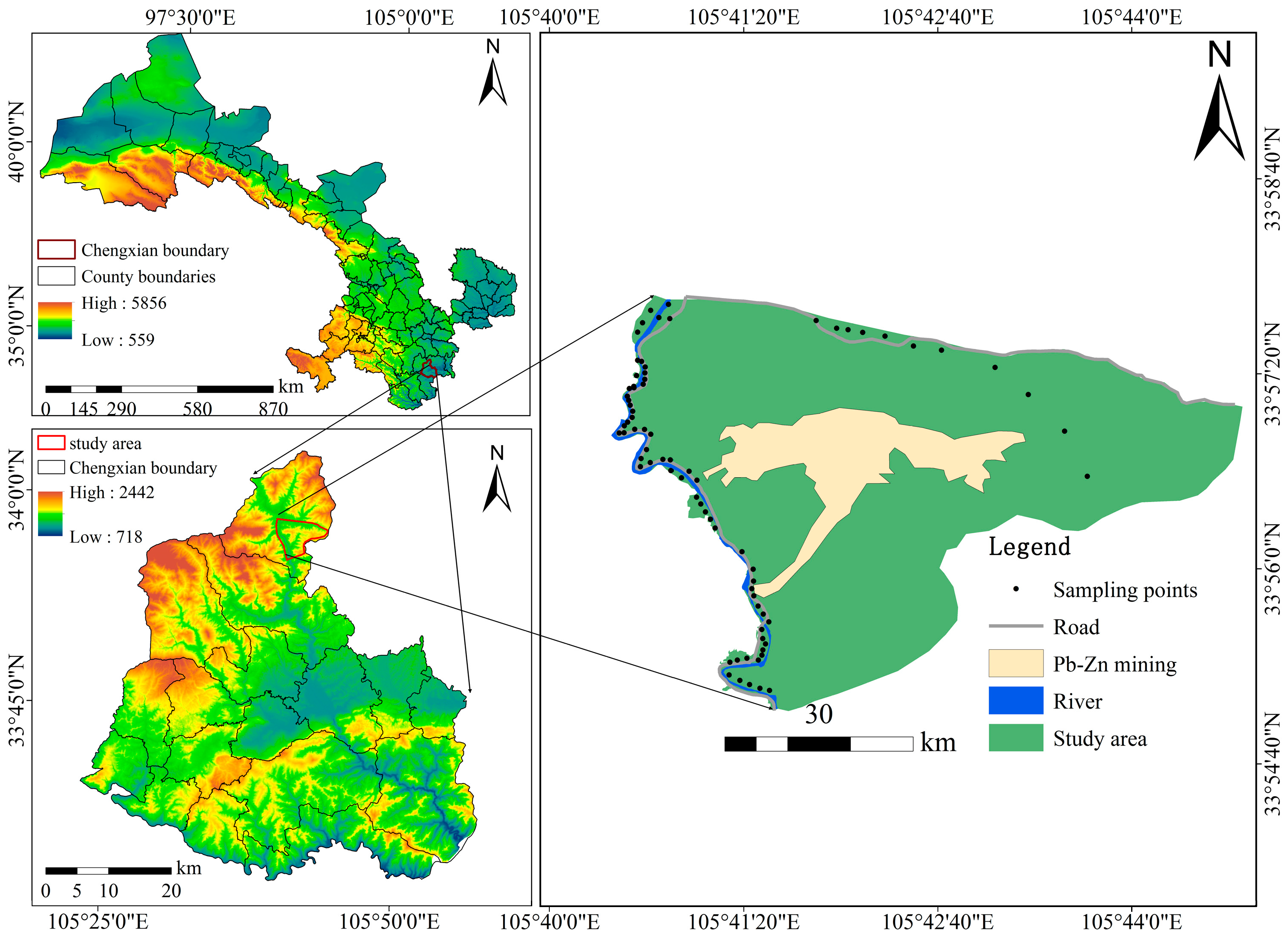
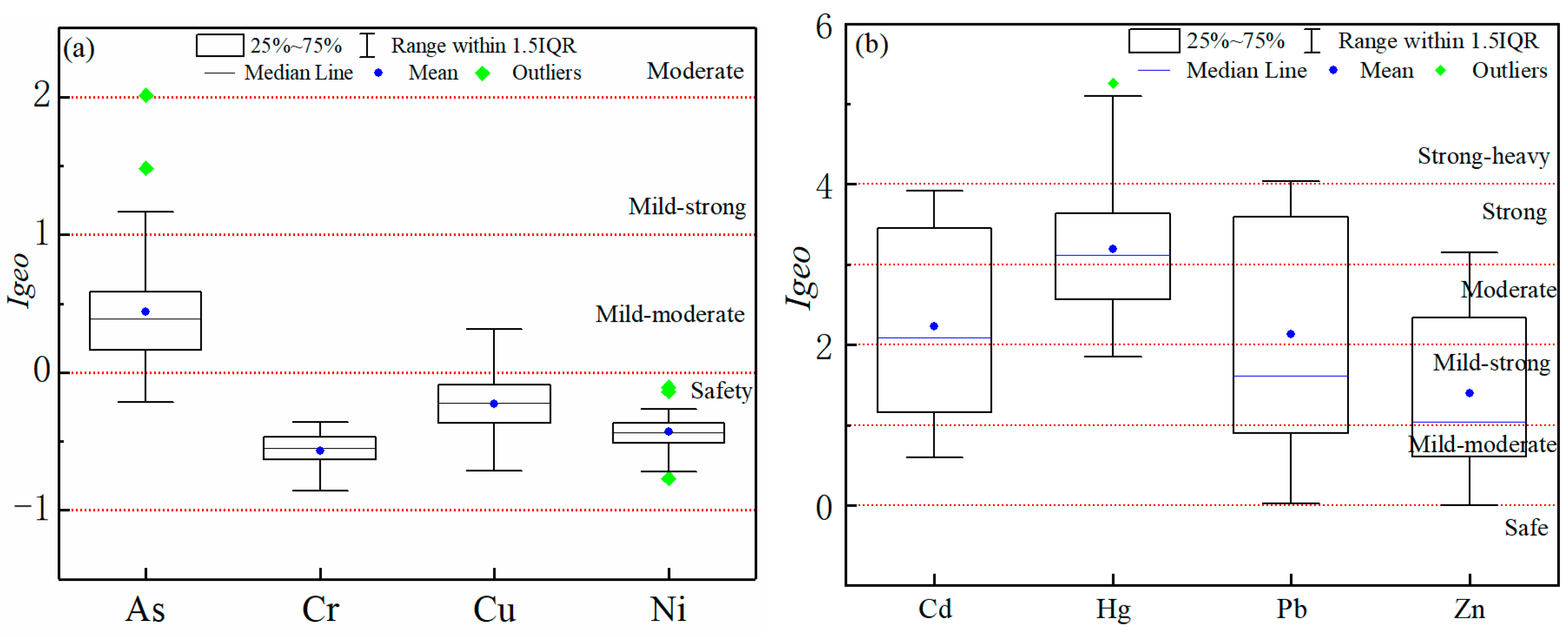
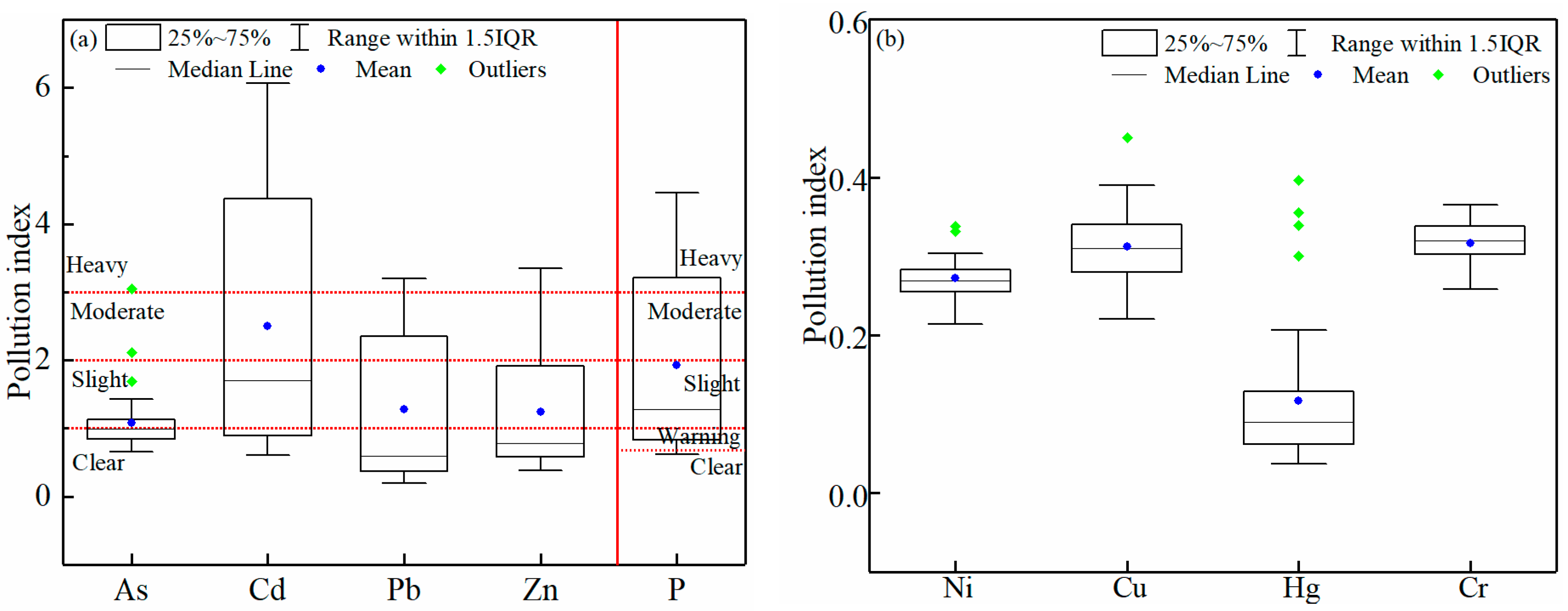


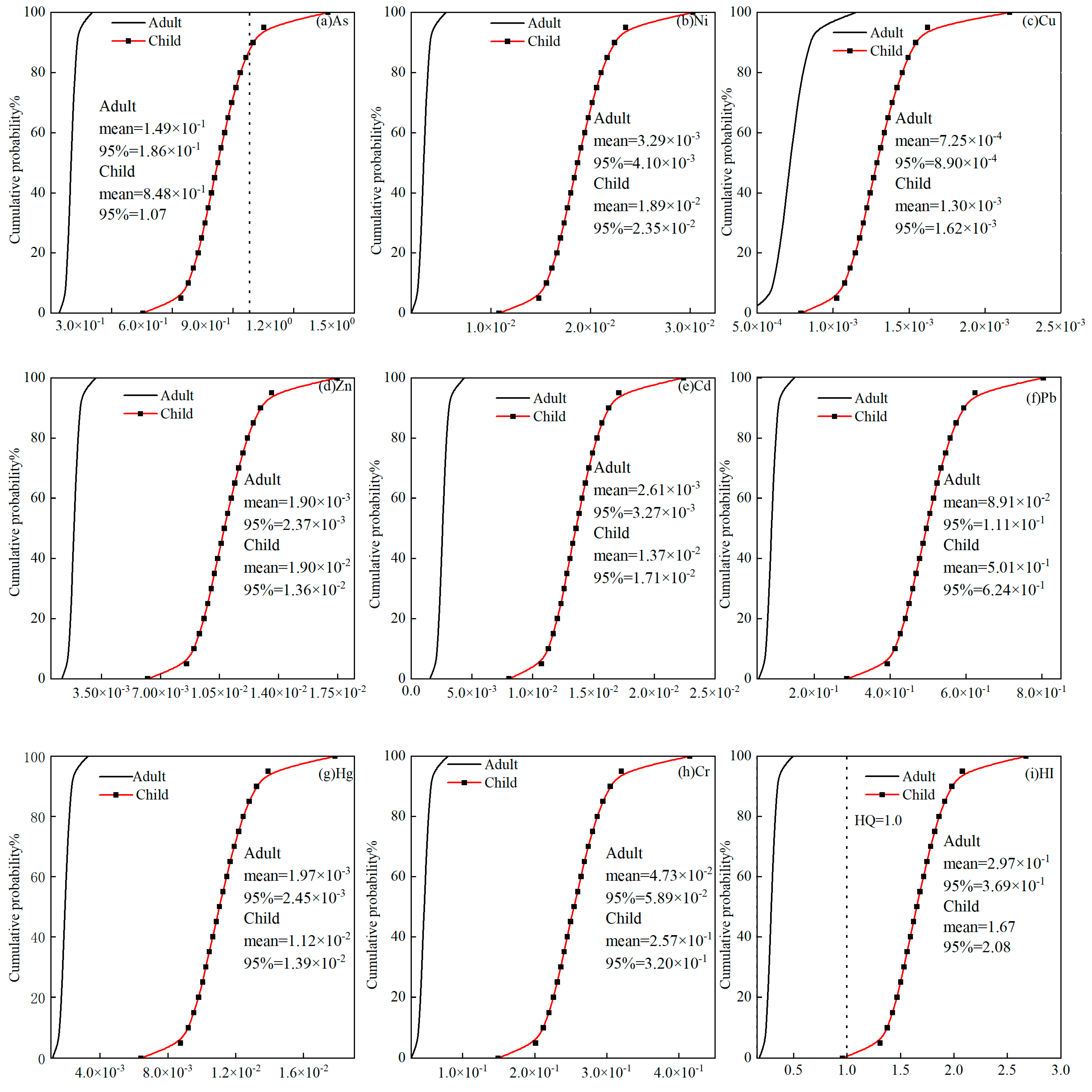
| Igeo | Value range | ||||||
| Contamination degree | Safe | Mild-moderate | Mild-strong | Moderate | Strong | Strong–heavy | |
| Value range | |||||||
| Pollution grade | Clean | Slight | Moderate | Heavy | |||
| Value range | — | ||||||
| Pollution grade | Clean | Warning | Slight | Moderate | Heavy | — | |
| Value range | — | ||||||
| Pollution grade | Slight | Medium | Relatively high | High | Extremely high | — | |
| Value range | — | — | |||||
| Pollution grade | Slight | Medium | Relatively high | High | — | — | |
| Value range | — | ||||||
| Pollution grade | Safe | Warning | Slight | Moderate | Heavy | — |
| Elements | As | Ni | Cu | Zn | Cd | Pb | Hg | Cr | pH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | 76.2 | 49.0 | 45.0 | 920.0 | 2.7 | 464.0 | 1.2 | 82.0 | 8.23 | |
| Min | 16.3 | 31.0 | 22.0 | 104.0 | 0.3 | 28.6 | 0.1 | 58.0 | 6.63 | |
| Mean | 26.92 | 39.46 | 31.18 | 340.23 | 1.13 | 184.61 | 0.34 | 71.15 | 7.46 | |
| Standard deviation | 10.52 | 4.02 | 4.48 | 235.99 | 0.81 | 148.99 | 0.26 | 6.24 | ||
| Cv (%) | 39.1 | 10.2 | 14.4 | 69.36 | 71.7 | 80.7 | 75.5 | 8.8 | ||
| Background value | 12.6 | 35.2 | 24.1 | 69.3 | 0.12 | 18.80 | 0.02 | 70.2 | ||
| Standard | 6.5 < pH ≤ 7.5 | 30 | 100 | 100 | 250 | 0.3 | 120 | 2.4 | 200 | |
| pH > 7.5 | 25 | 190 | 100 | 300 | 0.6 | 170 | 3.4 | 250 | ||
| I/%Excessive Rate I (%) | 100 | 93.4 | 98.3 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 78.3 | ||
| II/%Excessive Rate II (%) | 15.4 | 0 | 0 | 47.5 | 76.3 | 50 | 0 | 0 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Liu, Q.; Bai, R. Soil Heavy Metal Pollution and Health Risk Assessment Based on Monte Carlo Simulation: Case Study of Xicheng Lead-Zinc Mining Area. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3963. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17093963
Wang L, Liu Q, Bai R. Soil Heavy Metal Pollution and Health Risk Assessment Based on Monte Carlo Simulation: Case Study of Xicheng Lead-Zinc Mining Area. Sustainability. 2025; 17(9):3963. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17093963
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lixia, Qiang Liu, and Ronglong Bai. 2025. "Soil Heavy Metal Pollution and Health Risk Assessment Based on Monte Carlo Simulation: Case Study of Xicheng Lead-Zinc Mining Area" Sustainability 17, no. 9: 3963. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17093963
APA StyleWang, L., Liu, Q., & Bai, R. (2025). Soil Heavy Metal Pollution and Health Risk Assessment Based on Monte Carlo Simulation: Case Study of Xicheng Lead-Zinc Mining Area. Sustainability, 17(9), 3963. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17093963





