Runoff Changes and Their Impact on Regional Water Resources in Qinling Mountains from 1970 to 2020
Abstract
1. Introduction
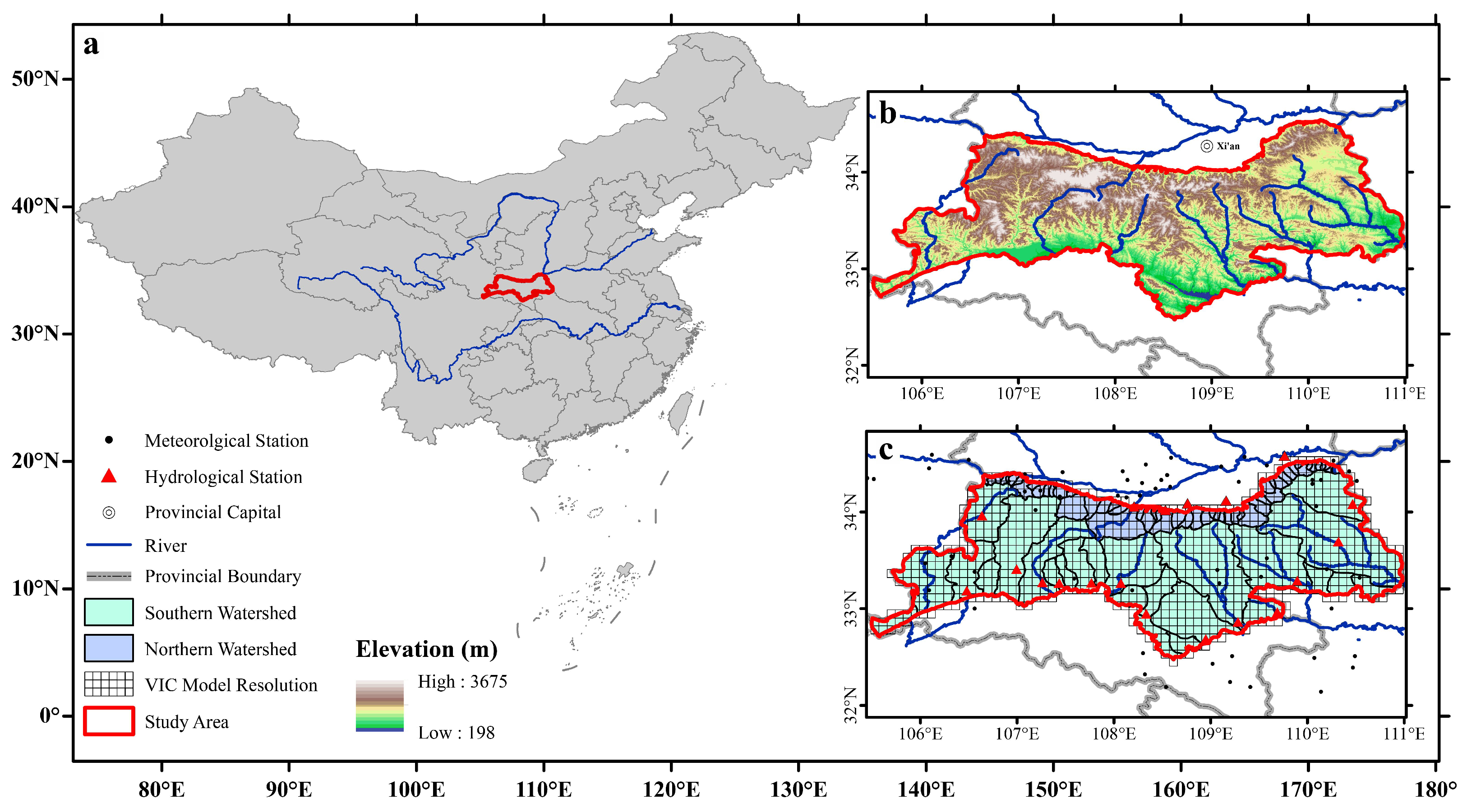
2. Data and Research Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Research Methodology
2.2.1. Spatial Interpolation Using Thin Disk Smooth Spline Function
2.2.2. VIC Hydrological Model
2.2.3. Similarity Transplantation Method of Hydrological Parameters
- (1)
- Precipitation–based hydrological similarity indexwhere is the Precipitation-based hydrological similarity index. and are the values of mean annual precipitation in watersheds A and B, respectively.
- (2)
- Elevation–based hydrological similarity indexwhere is the elevation-based hydrological similarity index. and are the values of average altitude in watersheds A and B, respectively.
- (3)
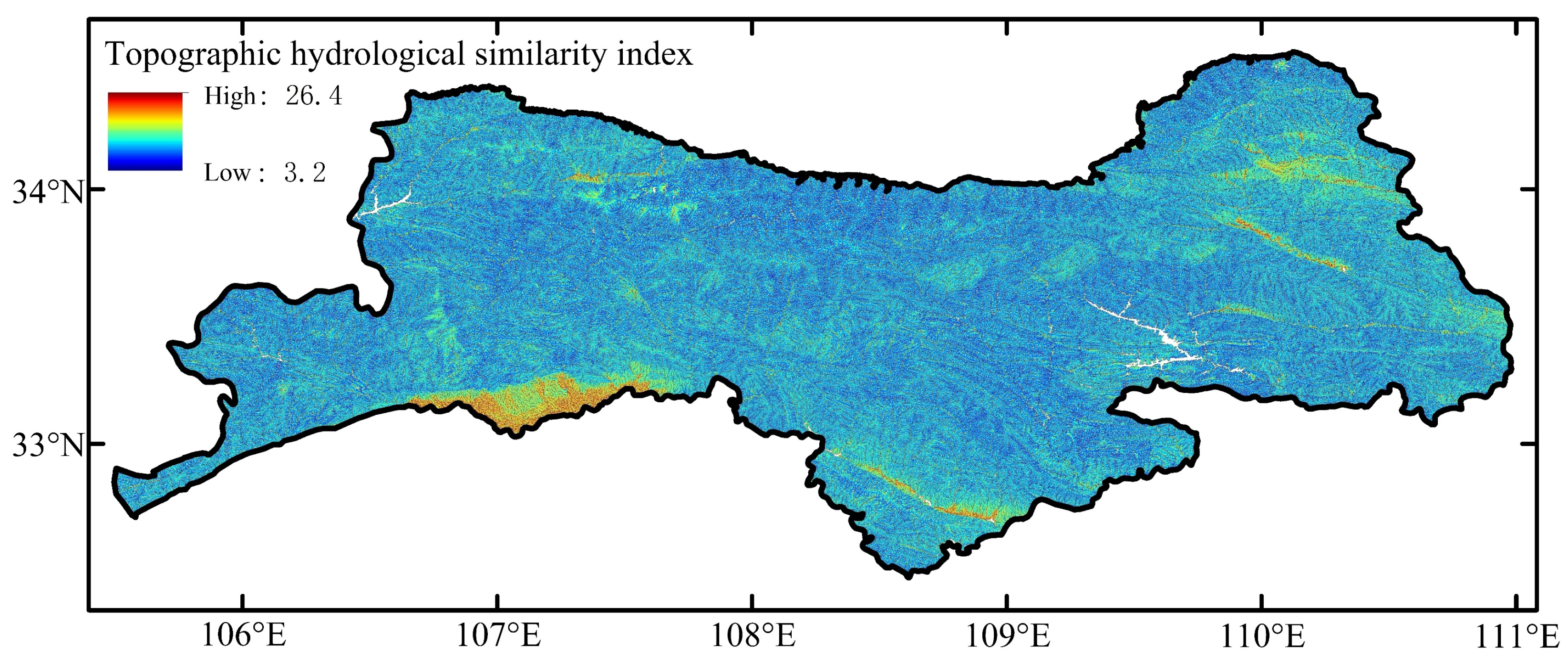
- Topographic hydrological similarity indexDue to the large numerical range of the topographic index within the watershed, the study adopts the segmented area comparison method to calculate the topographic hydrological similarity index.where is the topographic hydrological similarity index. and represent the percentage of the i-th segment area of watershed A and watershed B, respectively. represents the average value of all items for watershed A.
- (4)
- Land type hydrological similarity indexwhere is the Land type hydrological similarity index. , represent the percentage of the i-th land type area of watershed A and watershed B, respectively. represents the average value of all items for watershed A.
- (5)
- Soil texture hydrological similarity indexwhere is the Soil texture hydrological similarity index. , represent the percentage of the i-th soil texture area of watershed A and watershed B, respectively. represents the average value of all items for watershed A.
- (6)
- Weight calculationThe entropy weight method is employed to objectively assign weights to each indicator, and the analytic hierarchy process (AHP) is utilized to calculate the subjective weights of each indicator in the SPSS software (version 19).
- 1)
- Analytic hierarchy process
- 2)
- Entropy weight method
2.2.4. Mann–Kendall Trend Test
3. Results
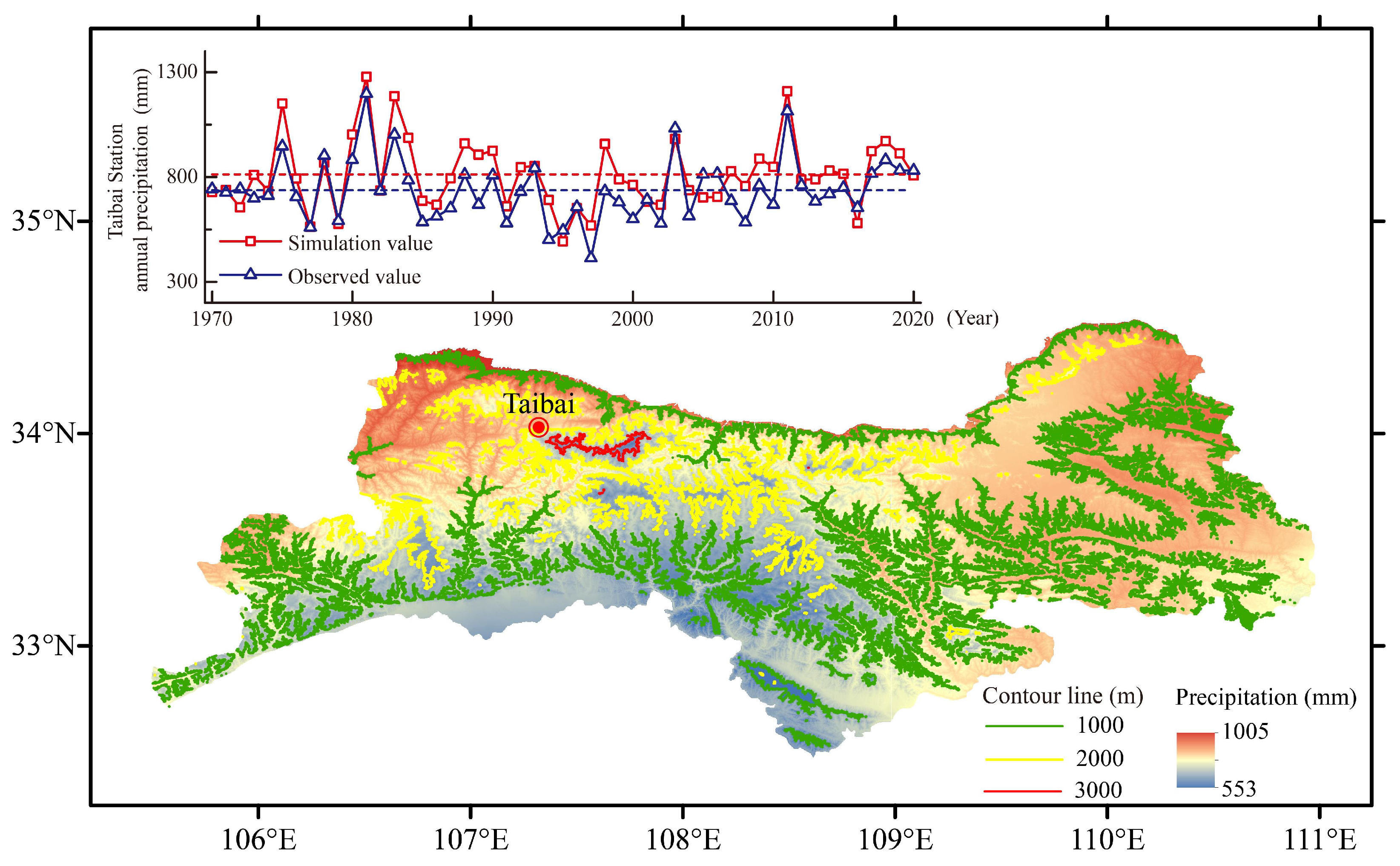
3.1. Interpolation Validation of Meteorological Variables
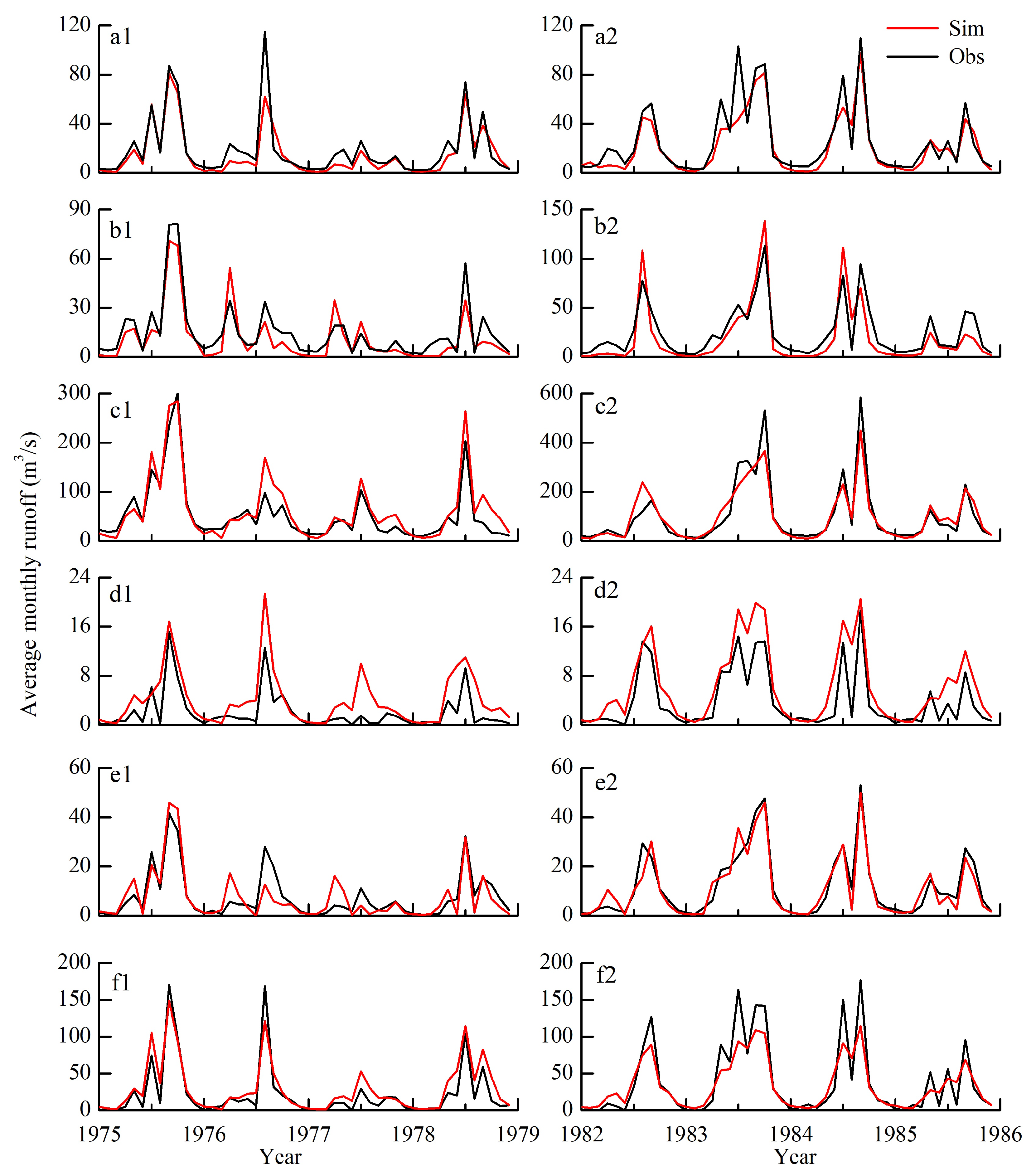
3.2. Evaluation of Runoff Simulation Results
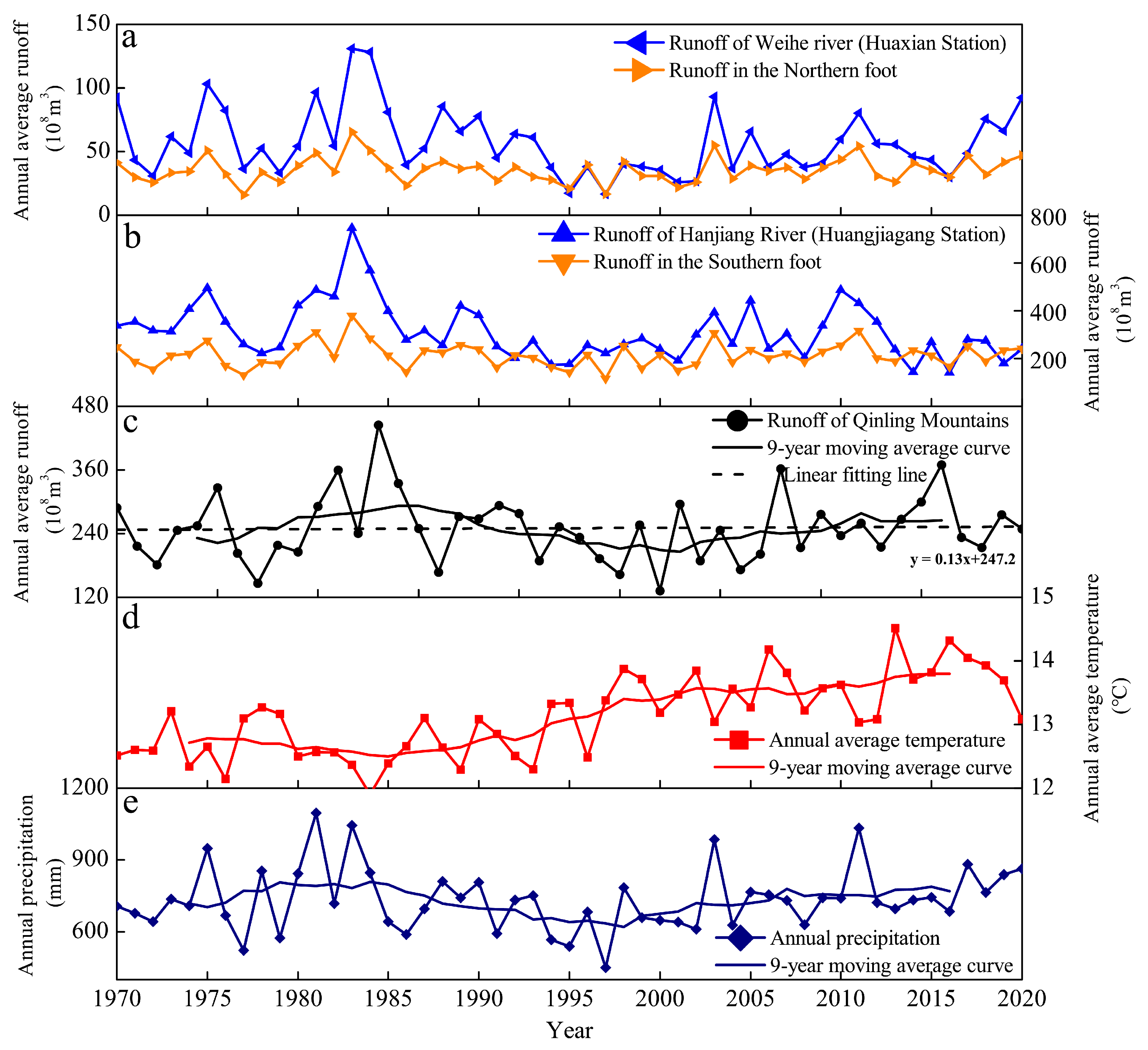
3.3. Runoff Changes in Qinling Mountains from 1970 to 2020
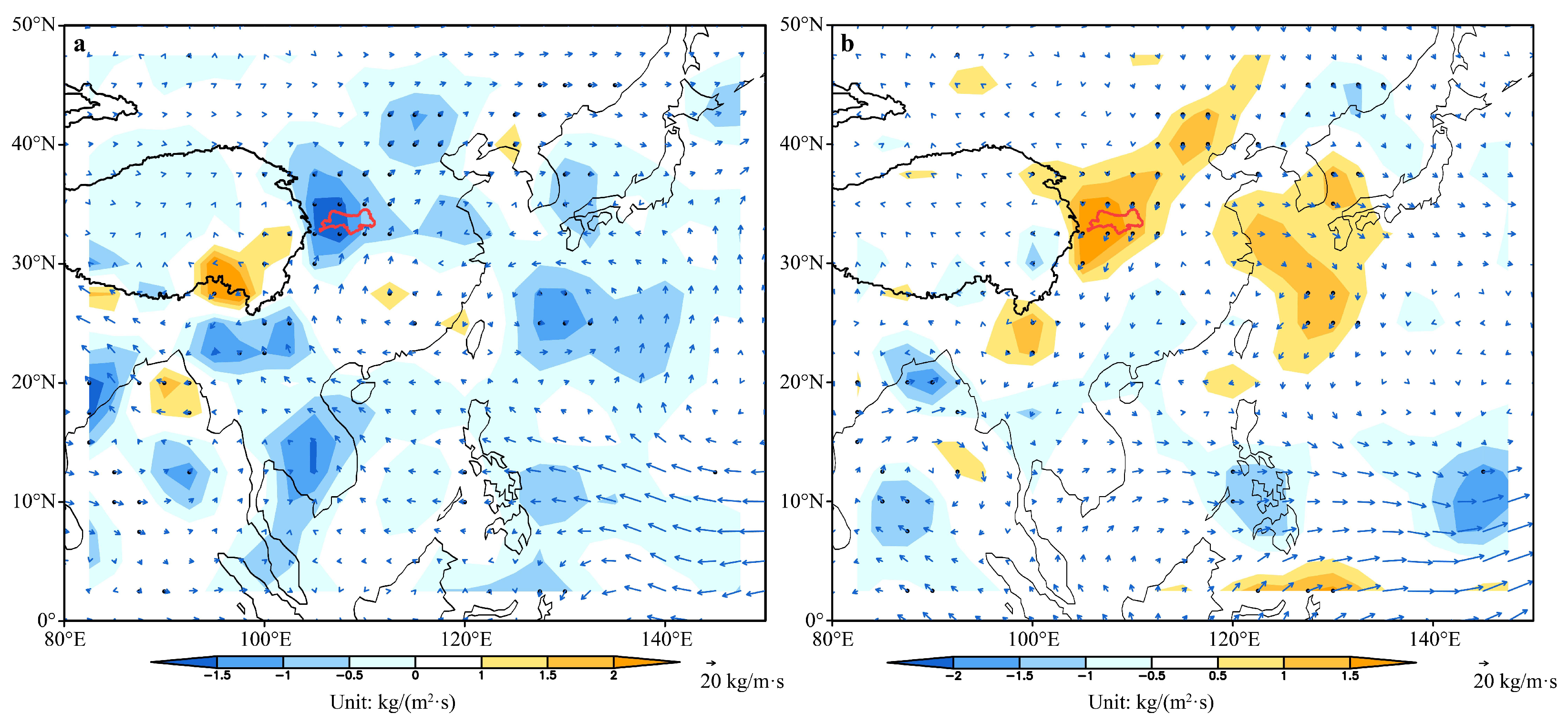
3.4. Relationship Between Runoff Changes and Climate Change in Qinling Mountains
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of Runoff on Regional Water Resources
4.2. Uncertainty Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


| River | Prec (mm) | Elev (m) | Topo | Land-Use (%) | Soil (%) | River | Prec (mm) | Elev (m) | Topo | Land-Use (%) | Soil (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northern foothills | Yao Yu | 591 | 1562 | 6.61 | 32.9 | 37.5 | Gan | 768 | 1633 | 6.29 | 44.5 | 40.4 |
| Qing Jiang | 597 | 1437 | 6.56 | 30.1 | 63.2 | Lao | 768 | 1613 | 6.28 | 31.3 | 65.1 | |
| Qing Shui | 582 | 1401 | 6.73 | 38.8 | 38.3 | Tai Ping | 769 | 1618 | 6.24 | 58.9 | 39.1 | |
| Ma Wei | 591 | 1337 | 6.65 | 56.6 | 51.5 | Gao Guan | 761 | 1621 | 6.33 | 50.5 | 45.5 | |
| Pan Xi | 592 | 1160 | 6.84 | 34.6 | 39.5 | Feng | 761 | 1620 | 6.37 | 34.6 | 36.5 | |
| Fa Yu | 666 | 1199 | 6.8 | 61.9 | 34.6 | Gao | 760 | 1604 | 6.49 | 35.6 | 65.3 | |
| Mai Li | 636 | 1024 | 6.71 | 47.7 | 37.6 | Da Yu | 758 | 1598 | 6.52 | 30.9 | 61.4 | |
| Shi Tou | 643 | 1034 | 6.67 | 54.3 | 36 | Ku Yu | 756 | 1587 | 6.4 | 26.7 | 50.6 | |
| Ba Wang | 630 | 1013 | 6.59 | 39.9 | 41.4 | Chan | 754 | 1633 | 6.57 | 24.9 | 54.2 | |
| Xi Sha | 625 | 1660 | 6.64 | 33.8 | 39.4 | Wang Yu | 750 | 1613 | 6.37 | 27.3 | 55.2 | |
| Tang Yu | 640 | 1358 | 6.69 | 43.1 | 44.4 | Ling | 750 | 1567 | 6.42 | 37.7 | 40.4 | |
| Dong Sha | 629 | 1384 | 6.8 | 39.8 | 52.5 | You | 749 | 1557 | 6.38 | 31.7 | 60.9 | |
| Ni Yu | 738 | 1222 | 6.79 | 55.3 | 25.9 | Chi Shui | 748 | 1542 | 6.62 | 20.8 | 80.1 | |
| Zhu Yu | 719 | 1154 | 6.68 | 41.5 | 24.9 | Shi Ti | 748 | 1583 | 6.56 | 35.5 | 24.1 | |
| Che Yu | 702 | 1220 | 6.51 | 32.9 | 32.9 | Luo Wen | 747 | 1569 | 6.64 | 33.3 | 34.7 | |
| Sha | 694 | 1067 | 6.4 | 30.1 | 42.2 | Fang Shan Yu | 747 | 1569 | 6.74 | 29.2 | 31.6 | |
| Hei | 782 | 1843 | 6.54 | 46.3 | 61.9 | Luo Fu | 746 | 1568 | 6.7 | 22.2 | 34.1 | |
| Jiu Yu | 773 | 1637 | 6.41 | 30.9 | 52.1 | Chang Jian | 745 | 1565 | 6.71 | 25.8 | 32.6 | |
| Tian Yu | 772 | 1438 | 6.4 | 32.9 | 53.6 | Tong | 746 | 1559 | 6.65 | 27.5 | 70 | |
| Geng Yu | 771 | 1344 | 6.28 | 26.7 | 41.7 | total | 710 | 1455 | 6.56 | |||
| Southern foothills | Jia Ling | 713 | 1580 | 6.99 | 34.5 | 18.8 | Chi | 807 | 1500 | 6.54 | 21.3 | 34.5 |
| Heihe | 752 | 1580 | 7.31 | 42.6 | 29.3 | Zi Yang | 812 | 1520 | 6.65 | 30.8 | 38.1 | |
| Yan | 754 | 1612 | 6.84 | 29.6 | 50.2 | Yue | 784 | 1074 | 6.61 | 35.1 | 30.3 | |
| Bao | 755 | 1543 | 6.61 | 23.5 | 25.5 | Xun | 754 | 1208 | 6.61 | 42.6 | 34.3 | |
| Xu Shui | 774 | 1516 | 6.61 | 35.9 | 40.1 | Jin Qian | 721 | 1243 | 6.62 | 31.9 | 45.4 | |
| Yi Shui | 771 | 1570 | 6.82 | 23.7 | 41.2 | Dan | 700 | 969 | 6.73 | 22.8 | 18.9 | |
| Dang Shui | 772 | 1568 | 6.67 | 25.6 | 39.6 | Luo | 684 | 1131 | 6.88 | 24.4 | 37.6 | |
| You Shui | 775 | 1650 | 6.84 | 23.9 | 32.7 | Shu | 751 | 1192 | 7.14 | 16.8 | 16.6 | |
| Jin Shui | 777 | 1740 | 6.9 | 34.4 | 45.2 | You Jiang | 721 | 1235 | 6.62 | 21 | 46.2 | |
| Zi Wu | 810 | 1531 | 6.92 | 33.4 | 44.5 | total | 757 | 1419 | 6.78 | |||
| Total | 726 | 1442 | 6.62 |

References
- Jin, N. Research on the Current Status of Water Resources Development and Utilization in the Northern Foothills of the Qinling Mountains in Shaanxi and a Proposal for Collaborative Allocation. Shaanxi Water Resour. 2024, 10, 47–50. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.W. Analysis on ecosystem protection and restoration at the northern foot of Qinling Mountains. Shaanxi Water Resour. 2019, 2, 103–107. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, H.; Liu, G.; Ma, Q.R.; Cao, L. Present situation of water resources development and utilization and analysis of water saving potential in Guanzhong area of Shaanxi Province. Shaanxi Water Resour. 2019, 6, 75–77. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Z.T. Study on Adaptive Protection Mode and Planning Strategy of Northern Foot of Qinling Mountains (Xi’an Section) from the Perspective of Landscape City. Ph.D. Thesis, Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology, Xi’an, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- He, S.N.; Hao, C.Y. Analysis on spatial-temporal variation characteristics of climate in Qinling-Huaihe demarcation zone since 1961. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.T.; Huang, L.M.; Sheng, B. Catastrophe analysis of annual runoff series in typical basins at the northern foot of Qinling Mountains. J. Water Resour. Water Eng. 2016, 2, 76–79. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Qiu, H.; Song, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Hu, S.; Hu, Y. Quantitative contribution of climate change and human activities to runoff changes in the Bahe River watershed of the Qinling Mountains, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 51, 101729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X.Y.; Wang, N. Comparative study on runoff change law of typical watersheds in north and south of Qinling Mountains. J. Xi’an Univ. Technol. 2019, 4, 452–458. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, C.Y.; He, S.N. The Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Temperature Variability Across Mts. Qinling: A Comparative Study from 1971 to 2022. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.P.; Shen, B.; Lu, J.Q. Effects of climate change and human activities on runoff in the headwater area of Bahe River. J. Water Resour. Water Eng. 2012, 6, 99–101. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.Y.; Bai, J.F.; Zhou, W.B.; Song, Y. Influence of climatic factors on water and sediment change in Bahe River basin. Water Conserv. 2017, 5, 98–105. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, H.Y.; Hou, Q.L.; Ma, X.P.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, B. Hydrological characteristics and its response to precipitation changes in Qianqian River basin of Qinling Mountains in the past 50 years. Geogr. Sci. 2012, 32, 1230–1235. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.; Qiu, H.J.; Yang, D.D.; Cao, M.; Song, J.; Wu, J.; Huang, C.; Gao, Y. Evaluation of the application of climate forecast system reanalysis weather data for hydrologic simulation: A case study in the Bahe River Base of the Qinling Mountains, China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 546–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; He, Y. Impact of Climate Change and Human Activities to Runoff in the Du River Basin of the Qinling-Daba Mountains, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, Q.H. Carrying capacity of tourism water resources in the northern foot of Qinling Mountains in Xi’an. J. Northwest Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2015, 45, 997–1000. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.W.; Duan, K.Q.; Li, S.S.; Shang, W.; Zhang, Z. Vertical variation of precipitation in the central Qinling Mountains. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2022, 7, 1762–1773. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.; Cao, M.M.; Qiu, H.J.; Song, J.; Wu, J.; Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Sun, K. Applicability evaluation of CFSR meteorological data in watershed hydrological simulation—A case study of Bahe River basin. J. Geogr. 2016, 9, 1571–1586. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.P.; Duan, K.Q.; Liu, H.C.; Meng, Y.L.; Chen, R.; Li, D.W.; Li, S.S. Runoff projections of the Qinling Mountains and their impact on water demand of Guanzhong region in Northwest China. J. Mt. Sci. 2022, 19, 2272–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.Z.; Lu, H.Y. Establishment of high-resolution grid data set of temperature and precipitation in Qinling-Dabashan mountains and its indication to regional climate. J. Geogr. 2019, 5, 875–888. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.F.; Yang, X.L.; Cheng, X.R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M. Prediction of main hydrological processes in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River based on CMIP5 and VIC models. J. China Hydrol. 2018, 6, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.L.; Chang, J.X. Application of comprehensive drought index based on VIC model in Yellow River Basin. J. Northwest A&F Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2017, 2, 203–212. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, C.; Zhang, Y.X.; Li, Z.J.; Sun, L. Hydrological simulation and similarity analysis in areas without data. J. Hehai Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2013, 41, 108–113. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.H. Runoff Analysis of the Northern Foot of Qinling Mountains in Xi’an Based on SWAT Model. Master’s Thesis, Chang’an University, Xi’an, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.; Qiu, H.J.; Song, J.X.; Ma, S.; Yang, D.; Pei, Y.; Yang, W.; Cao, M. Influencing mechanisms of climate change on runoff process in the north slope of Qinling Mountains:A case of the Bahe River Basin. Arid Land Geogr. 2017, 40, 976–978. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, W.X. Study on Water Resources and Its Development and Utilization in Qinling Mountains. Master’s Thesis, Northwest University, Xi’an, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, H.Y.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Tian, P. Analysis of runoff change trend and its influencing factors in Weihe River basin. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2008, 1, 76–80. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, A.Q.; Wang, W.K.; Duan, L. Analysis of water use structure change and its driving factors in Guanzhong basin. Resour. Environ. Arid Areas 2011, 9, 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, L.L.; Zhao, X.J.; Zhen, Z.J. Application of drop index method in calculating the relationship between water level and discharge-taking Huangjiagang hydrological station of Hanjiang River as an example. People’s Yangtze River 2013, 23, 70–72. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, M. Study on the Influence of Climate Change on Adjustable Water Quantity and Water Supply Risk in the Middle Route of South-to-North Water Transfer Project. Master’s Thesis, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, V.; Rolf, W. The hydrological significance of mountains: Form regional to global scale. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2004, 8, 1016–1029. [Google Scholar]
- Qiang, Z.; Xu, C.Y.; Hui, T.; Tao, J.; Chen, Y.D. Climate changes and their impacts on water resources in the arid regions: A case study of the Tarim River basin, China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2010, 24, 349–358. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.L.; Chang, J.X. Calibration of parameters for VIC model based on uniform design method. J. Northwest A&F Univ. 2015, 43, 217–224. [Google Scholar]
| Sub–Basin | Hydrological Station | Rate Period | Verification Period | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RE (%) | RE (%) | |||||||
| Southern foothills | Jialing | Fengzhou | 0.73 | 0.91 | 15.79 | 0.69 | 0.93 | 5.10 |
| Qu Shui | Chadian | 0.81 | 0.95 | 24.11 | 0.79 | 0.94 | 17.13 | |
| Bao | Ma Dao | 0.88 | 0.96 | 8.73 | 0.85 | 0.94 | 12.89 | |
| Xu Shui | Sheng Xian Cun | 0.85 | 0.94 | 19.14 | 0.81 | 0.94 | −13.76 | |
| Yi Shui | Chang Tan Cun | 0.73 | 0.87 | 16.53 | 0.65 | 0.84 | −18.95 | |
| You Shui | You Shui | 0.71 | 0.9 | 17.10 | 0.81 | 0.96 | −3.53 | |
| Zi Wu | Liang He Kou | 0.61 | 0.89 | 21.73 | 0.63 | 0.91 | 18.57 | |
| Chi | Ma Chi | 0.83 | 0.92 | 11.32 | 0.72 | 0.9 | −8.1 | |
| Yue | Chang Qiang Pu | 0.81 | 0.93 | 20.59 | 0.83 | 0.95 | 16.48 | |
| Xun | Xiang Jia Ping | 0.82 | 0.94 | 18.41 | 0.87 | 0.94 | −2.10 | |
| Shu | Shu River | 0.71 | 0.85 | −0.52 | 0.88 | 0.95 | −2.67 | |
| Jin Qian | Nan Kuan Ping | 0.63 | 0.94 | 6.21 | 0.61 | 0.84 | −13.21 | |
| Dan | Dan Feng | 0.8 | 0.94 | 21.44 | 0.71 | 0.91 | 18.77 | |
| Luo | Ling Kou | 0.79 | 0.91 | 16.23 | 0.62 | 0.88 | −11.69 | |
| Northern foothills | Hei | Hei Yu Kou | 0.82 | 0.92 | −19.5 | 0.76 | 0.91 | −17.4 |
| Lao | Lao Yu Kou | 0.85 | 0.90 | −14.2 | 0.84 | 0.93 | −11.5 | |
| Ba | Ma Du Wang | 0.78 | 0.93 | −25.1 | 0.74 | 0.91 | −22.2 | |
| Feng | Qin Du Zhen | 0.77 | 0.89 | 2.5 | 0.82 | 0.91 | 3.8 | |
| River | Area (km2) | Runoff (108 m3/Year) | Proportion (%) | Hydrologically Similar Basin | River | Area (km2) | Runoff (108 m3/Year) | Proportion (%) | Hydrologically Similar Basin | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northern foothills | Yao Yu | 473 | 1.64 | 4.61 | Lao | Gan | 77 | 0.2 | 0.56 | Lao |
| Qing Jiang | 79 | 0.25 | 0.7 | Lao | Lao | 303 | 0.92 | 2.58 | - | |
| Qing Shui | 254 | 0.98 | 2.75 | Lao | Tai Ping Yu | 431 | 1.42 | 3.99 | Wang Yu | |
| Ma Wei | 14 | 0.27 | 0.76 | Lao | Gao Guan Yu | 69 | 0.22 | 0.62 | Lao | |
| Pan Xi | 77 | 0.29 | 0.81 | Lao | Feng | 203 | 0.72 | 2.02 | - | |
| Fa Yu | 71 | 0.25 | 0.7 | Lao | Hao | 69 | 0.23 | 0.65 | Lao | |
| Mai Li | 127 | 0.51 | 1.43 | Lao | Da Yu | 152 | 0.5 | 1.4 | Lao | |
| Shi Tou | 66 | 0.26 | 0.73 | Lao | Ku Yu | 273 | 1.02 | 2.86 | Lao | |
| Ba Wang | 63 | 0.25 | 0.7 | Lao | Chan | 572 | 2.21 | 6.21 | Hei | |
| Xi Sha | 720 | 2.8 | 7.86 | Wang Yu | Wang Yu | 1105 | 5.11 | 14.35 | - | |
| Tang Yu | 79 | 0.25 | 0.7 | Lao | Ling | 128 | 0.62 | 1.74 | Lao | |
| Dong Sha | 205 | 0.76 | 2.13 | Lao | You | 127 | 0.55 | 1.54 | Lao | |
| Ni Yu | 148 | 0.49 | 1.38 | Lao | Chi Shui | 77 | 0.24 | 0.67 | Lao | |
| Zhu Yu | 65 | 0.24 | 0.67 | Lao | Shi Ti | 61 | 0.22 | 0.62 | Lao | |
| Che Yu | 60 | 0.23 | 0.65 | Lao | Luo Wen | 469 | 1.7 | 4.77 | Hei | |
| Sha | 60 | 0.26 | 0.73 | Lao | Fang Shan Yu | 469 | 1.7 | 4.77 | Hei | |
| Hei | 1570 | 6.13 | 17.21 | - | Luo Fu | 57 | 0.2 | 0.56 | Lao | |
| Jiu Yu | 65 | 0.21 | 0.59 | Lao | Chang Jian | 84 | 0.2 | 0.56 | Lao | |
| Tian Yu | 203 | 0.68 | 1.91 | Lao | Tong | 91 | 0.21 | 0.59 | Lao | |
| Geng Yu | 617 | 2.16 | 6.07 | Hei | Total | 9448 | 35.6 | 100 | ||
| Southern foothills | Jia Ling | 6868 | 27.89 | 12.98 | - | Chi | 1470 | 7.25 | 3.37 | - |
| Heihe | 2030 | 8.88 | 4.13 | - | Zi Yang | 1542 | 8.25 | 3.84 | Shu | |
| Yan | 771 | 3.4 | 1.58 | You Shui | Yue | 3158 | 13.87 | 6.45 | - | |
| Bao | 3941 | 18.1 | 8.42 | - | Xun | 6448 | 24.24 | 11.28 | - | |
| Xu Shui | 2307 | 12.35 | 5.75 | - | Jin Qian | 4689 | 26.17 | 12.18 | - | |
| Yi Shui | 487 | 2.24 | 1.04 | - | Dan | 7552 | 19.7 | 9.16 | - | |
| Dang Shui | 413 | 1.92 | 0.89 | Yi Shui | Luo | 3072 | 2.3 | 1.07 | - | |
| You Shui | 1261 | 5.76 | 2.68 | - | Shu | 491 | 1.83 | 0.85 | - | |
| Jin Shui | 765 | 3.76 | 1.75 | You Shui | You Jiang | 479 | 8.8 | 4.09 | Shu | |
| Zi Wu | 3639 | 18.21 | 8.47 | - | Total | 51,383 | 214.9 | 100 | ||
| Total | 60,831 | 250.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Wang, T.; Zhu, C.; Xia, Z.; Wu, C.; Duan, K. Runoff Changes and Their Impact on Regional Water Resources in Qinling Mountains from 1970 to 2020. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3948. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17093948
Zhang Z, Wang T, Zhu C, Xia Z, Wu C, Duan K. Runoff Changes and Their Impact on Regional Water Resources in Qinling Mountains from 1970 to 2020. Sustainability. 2025; 17(9):3948. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17093948
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhaopeng, Ting Wang, Chengcheng Zhu, Zhilin Xia, Cai Wu, and Keqin Duan. 2025. "Runoff Changes and Their Impact on Regional Water Resources in Qinling Mountains from 1970 to 2020" Sustainability 17, no. 9: 3948. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17093948
APA StyleZhang, Z., Wang, T., Zhu, C., Xia, Z., Wu, C., & Duan, K. (2025). Runoff Changes and Their Impact on Regional Water Resources in Qinling Mountains from 1970 to 2020. Sustainability, 17(9), 3948. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17093948







