Machine Learning Optimization of Waste Salt Pyrolysis: Predicting Organic Pollutant Removal and Mass Loss
Abstract
1. Introduction
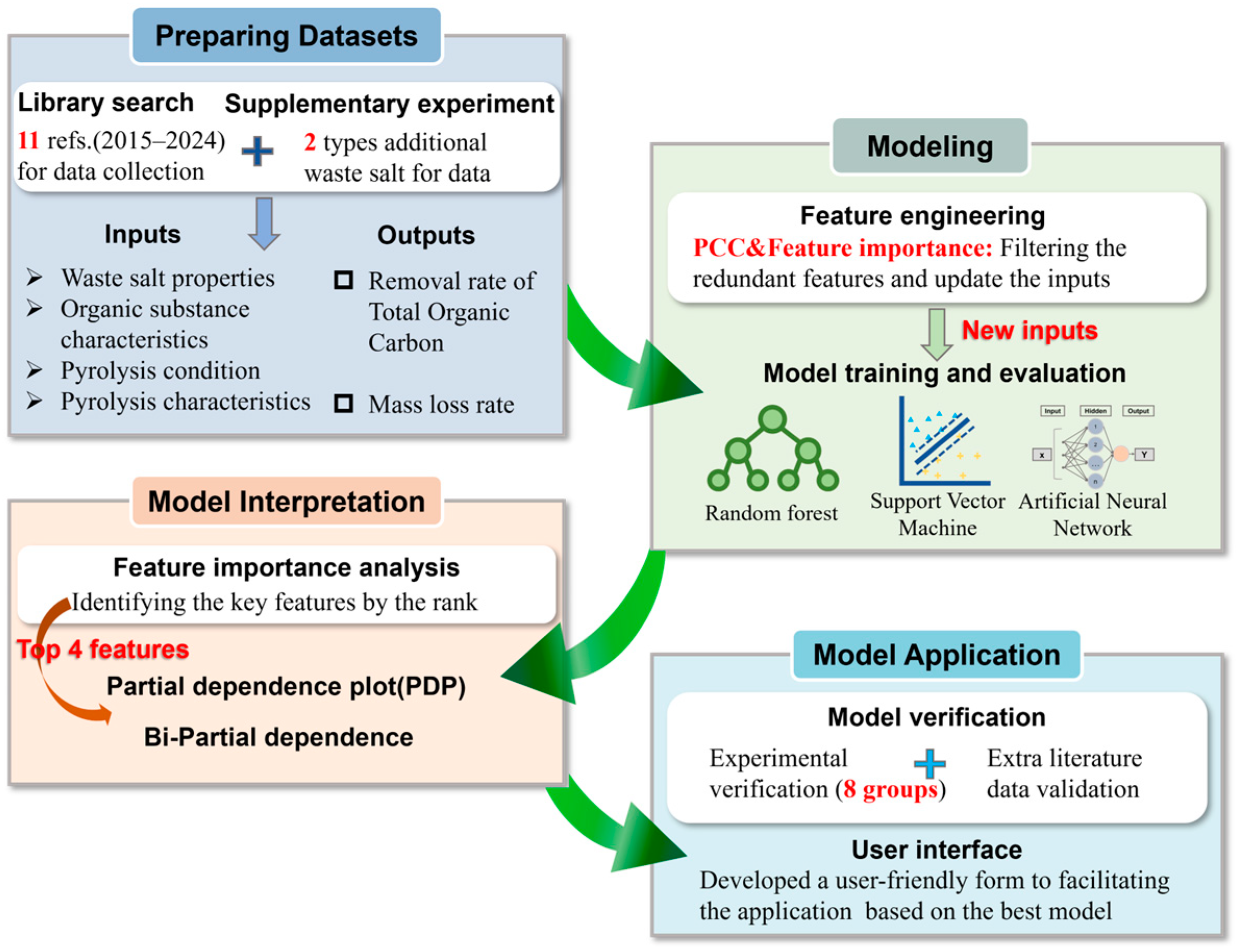
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. ML Model Algorithm
2.3. Model Development and Evaluation
2.4. Model Interpretation
2.5. Pyrolysis Optimization and Experimental Verification
3. Results
3.1. Statistical Analysis of Datasets and Pearson Correlation Coefficients
3.2. Model Evaluation
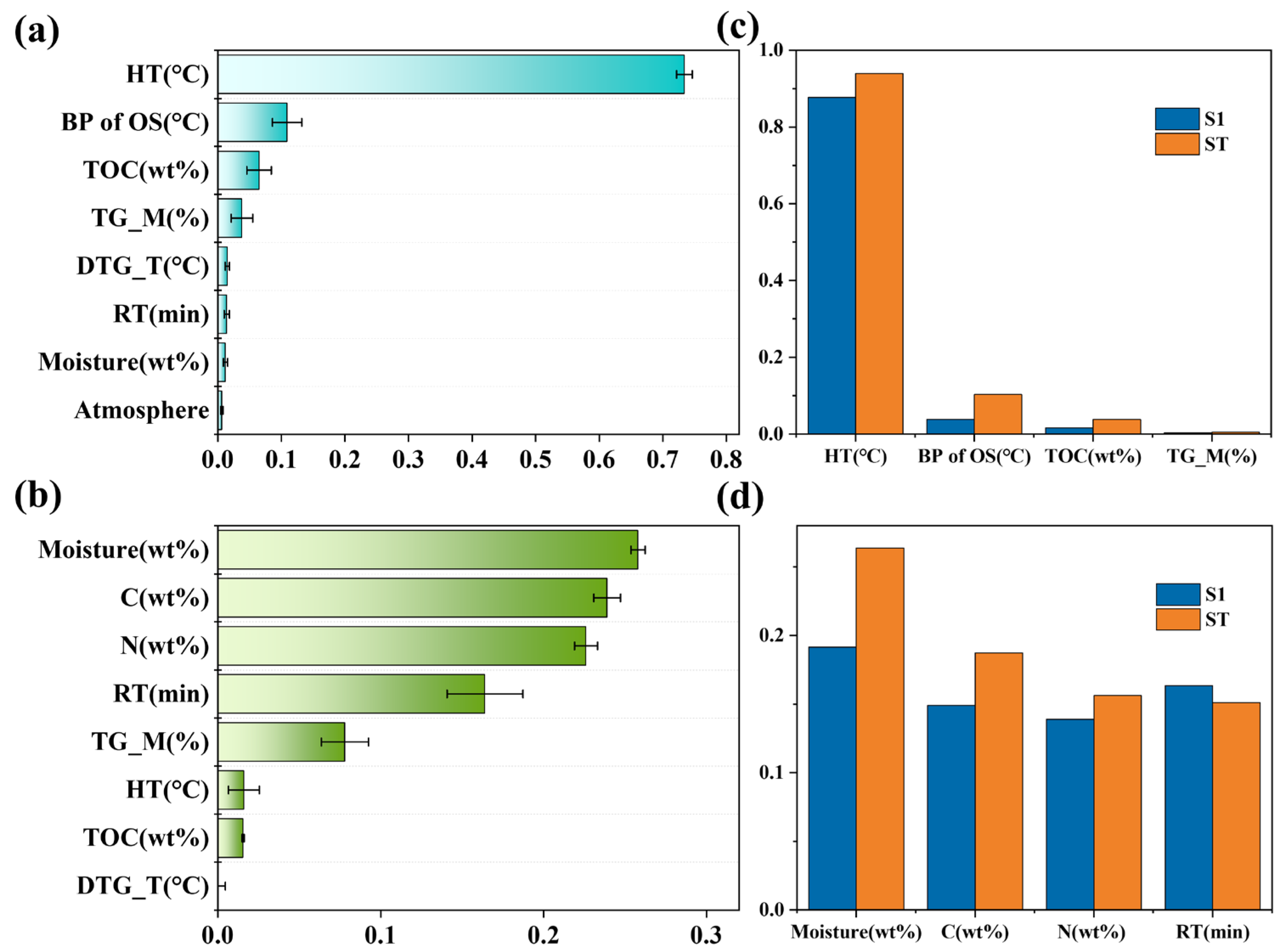
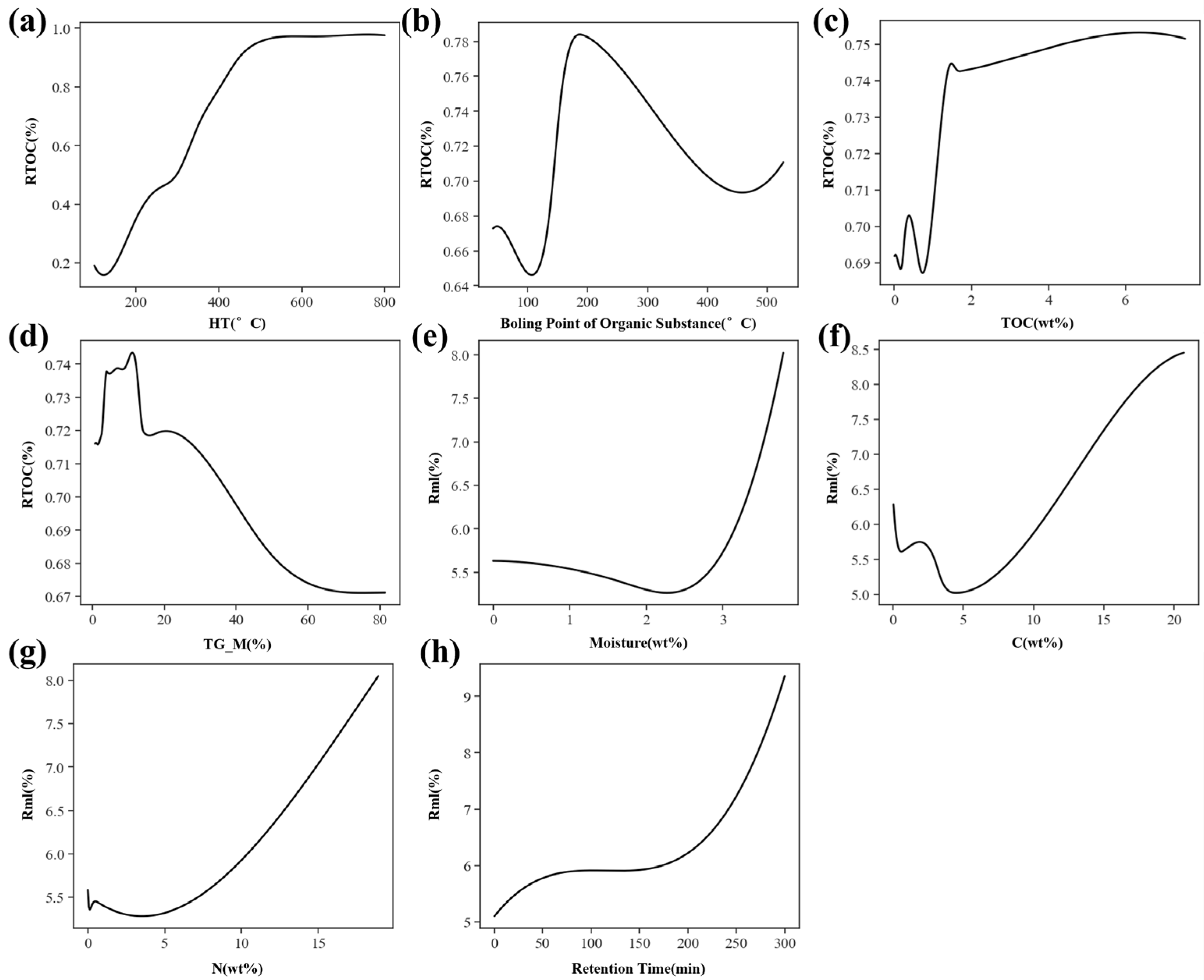
3.3. Model Interpretation
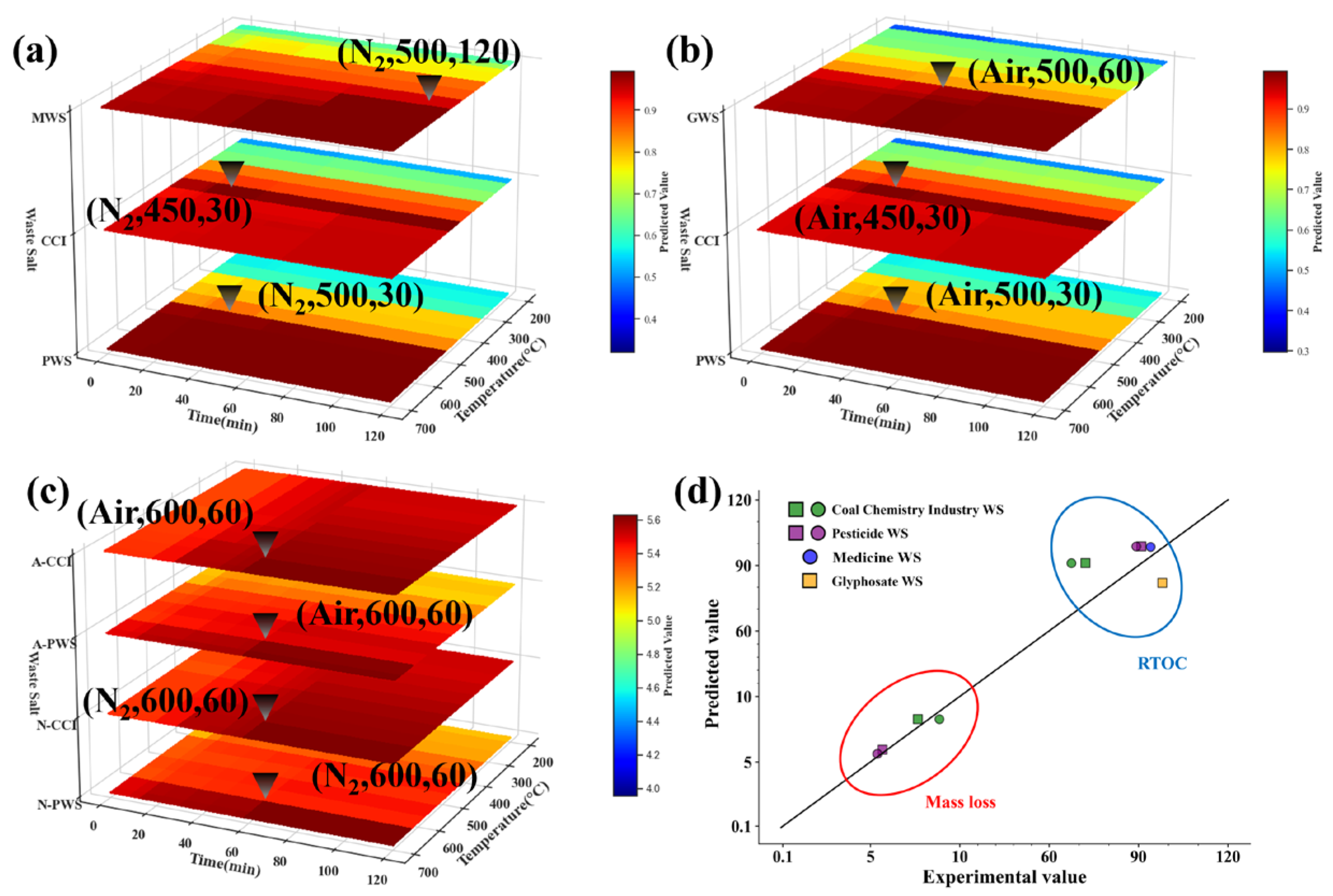
3.4. Model Validation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cui, Z.; Wang, W.; Lin, Y.; Hu, M.; Li, Y.; Pan, B.; Tan, M.; Zhang, Y. Simultaneous ion fractionation and concentration by selectrodialysis for saline wastewater valorization. Desalination 2023, 554, 116489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Guo, X.; Xu, J.; Wu, S. Improved Sedimentation Performance of Low-Rank Coal by Coprocessing with Saline Wastewater. Min. Metall. Explor. 2021, 38, 1267–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Huang, Z.; Lei, G.; Xu, Y.; Huang, A.L.Y.; Huang, Q. Combustion and pyrolysis characteristics of pesticide residue. J. CSEE 2018, 38, 2691–2698. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, L.; Tian, B.; Zhang, L.; Yang, M. Pyrolysis of hydrazine hydrate waste salt: Thermal behaviors and transformation characteristics of organics under aerobic/anaerobic conditions. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 323, 116304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Yuan, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, K.; Tian, S.; Li, M. Research progress of industrial waste salt thermal treatment technologies. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2022, 12, 1668–1680. [Google Scholar]
- Lijia, W. Research on the Valorization and Disposal Technology of Industrial Waste Salt. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang Gongshang University, Hangzhou, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Huo, H.; He, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wei, H. Research progress and inspiration on the generation and treatment technology of chemical waste salt. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2024, 18, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Hong, X.; Fang, G.; Zhang, X. Deep purification of pesticide waste salt containing high-concentration organic pollutants by ethanol solvents washing and heating treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annamalai, S.; Chandrasekaran, K.; Shin, W.S.; Sundaram, M.; Khaleel, T.M. Beyond dumping: New strategies in the separation of preservative salt from tannery waste mixed salt and its reuse for tannery industrial application. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, H.; Chen, X.; Lin, S.; Luo, H.; Cao, Y.; Tang, C.Y.; Liu, G. Resource utilization of coal chemical waste salt by bipolar membrane electrodialysis with thermal pretreatment. Desalination 2024, 580, 117553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gong, Y.; Qin, J.; Cheng, J.; Gong, C.; Jiang, D. Deep removal of organic matter in glyphosate contained industrial waste salt by dielectric barrier discharge plasma. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106295. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, T.; Yang, Q.; Li, H. Synergistic promotion of low-temperature pyrolysis and chloride complexation in waste salt purification process. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2024, 26, 2435–2444. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, P. Study on Heat Treatment Characteristics of Tymiomycin Waste Salt and the Utilization of Generated Carbon. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Weishi, L.; Zechun, H.; Yuqiang, L.; Qifei, H.; Ya, X.; Lu, D.; Jingcai, L. Evaluation of low-medium temperature pretreatment on the removal efficiency of organic toxic pollutants from pesticide waste salts: Characteristics, regularity, and key factors. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 316, 128118. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, L.; Tian, B.; Chen, L.; Yang, M. Purification and recovery of NaCl from epoxy resin waste salt through an integrated process based on aqueous two-phase systems (ATPS). J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113091. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Z.L.; Ma, T.W. High-temperature Treatment of Simulated Sodium Chloride Salt Slag. Environ. Prot. Chem. Ind. 2014, 34, 419–422. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, S.; Wei, X.; Ding, J.; Wang, W.; Lu, J. The removal of organic contaminants from industrial waste salts by pyrolysis and potential use for energy storage. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 425, 138931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L. Study of Pyrolysis Characteristics and Comprehensive Utilization of Organics-Containing Industrial Mixed-Salts. Master’s Thesis, China University of Petroleum, Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L. Study on Heat Treatment of Sodium Chloride Waste Salt by Product from Glyphosate Industry. Master’s Thesis, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, B.; Yang, Y.; Tang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H. Catalytic effect of K and Na with different anions on lignocellulosic biomass pyrolysis. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2024, 18, 141. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Feng, Y.; Huang, Q.; He, Y.; Shi, M. Unraveling the pyrolysis behavior and co-pyrolysis characteristics of EVA and backsheet in spent crystalline silicon photovoltaic modules. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 506, 160164. [Google Scholar]
- Ascher, S.; Watson, I.; You, S. Machine learning methods for modelling the gasification and pyrolysis of biomass and waste. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 155, 111902. [Google Scholar]
- Wolpert, D.H.; Macready, W.G. No free lunch theorems for optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 1997, 1, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.S.-H.; Yao, Y. Machine learning for sustainable development and applications of biomass and biomass-derived carbonaceous materials in water and agricultural systems: A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 190, 106847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Bai, X.; Xu, D.; Li, W. Machine learning prediction of pyrolytic products of lignocellulosic biomass based on physicochemical characteristics and pyrolysis conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 367, 128182. [Google Scholar]
- Potnuri, R.; Rao, C.S.; Surya, D.V.; Kumar, A.; Basak, T. Utilizing support vector regression modeling to predict pyro product yields from microwave-assisted catalytic co-pyrolysis of biomass and waste plastics. Energy Convers. Manag. 2023, 292, 117387. [Google Scholar]
- Cullen, L.; Marinoni, A.; Cullen, J. Machine learning for gap-filling in greenhouse gas emissions databases. J. Ind. Ecol. 2024, 28, 636–647. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Guo, W.; Yang, P.; Zhang, J.; Gao, K.; Shang, J.; Yang, B.; Wu, Z. In-situ infrared and kinetic characteristics analysis on pyrolysis of tar-rich coal and macerals. Fuel 2023, 348, 128601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, L. A Pearson’s correlation coefficient based decision tree and its parallel implementation. Inf. Sci. 2018, 435, 40–58. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Pan, L.; Suvarna, M.; Tong, Y.W.; Wang, X. Fuel properties of hydrochar and pyrochar: Prediction and exploration with machine learning. Appl. Energy 2020, 269, 115166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, P.; Gangil, S. ANN approach for the prediction of pyrolytic behaviour of pigeon pea stalk and insight into thermo-kinetics of pseudo components using RSM. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 449, 141816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Huang, Z.; Jin, M.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Hou, C.; Zhang, X.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, Y. Machine learning prediction of biochar physicochemical properties based on biomass characteristics and pyrolysis conditions. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2024, 181, 106596. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Wang, Z.; Ge, Y.; Liang, R.; Hou, D.; Tao, J.; Yan, B.; Zheng, W.; Velichkova, R.; Chen, G. Characteristics prediction of hydrothermal biochar using data enhanced interpretable machine learning. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 377, 128893. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, G.; Chen, Y. Mechanisms, methods and applications of machine learning in bio-alcohol production and utilization: A review. Chemosphere 2023, 342, 140191. [Google Scholar]
- Genuer, R.; Poggi, J.-M.; Tuleau-Malot, C. Variable selection using random forests. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2010, 31, 2225–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, L.; Yang, L.; Lei, X.; Zhang, W.; Ai, Z.; Yang, Z.; Zhan, H.; Yang, J.; Yuan, X.; Peng, H.; et al. Machine learning predicting and engineering the yield, N content, and specific surface area of biochar derived from pyrolysis of biomass. Biochar 2022, 4, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Zhu, M.; Fan, X.; Song, J.; Peng, P.; Li, K.; Jia, W.; Song, H. Influence of pyrolysis temperature and feedstock on carbon fractions of biochar produced from pyrolysis of rice straw, pine wood, pig manure and sewage sludge. Chemosphere 2019, 218, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Tao, Y.; Ye, H.; Xin, X. Experimental and numerical study on pyrolysis characteristics of organic impurities in waste salt. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 444, 141223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lyu, H.; Cheng, C.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, W. Enhancing pyrolysis process monitoring and prediction for biomass: A machine learning approach. Fuel 2024, 362, 130873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Xu, W.; Wang, Z.; Qin, W.; Lei, J.; Guo, X.; Long, J. Investigation of organic impurity and its occurrence in industrial waste salt produced by physicochemical process. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, S.; Zhou, J.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, X.; Chen, R.; Hu, J.; Guo, Z.; Chen, L.; Chen, W. Compatibility Study between 50% H2O2/H2SO4 Solution and Some Common Organic Solvents. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2024, 28, 2542–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, K.; Cao, X.; Chen, D.; Zhou, J.; Chen, F.; Li, M. Leaching of alkali and alkaline earth metallic species (AAEMs) with phenolic substances in bio-oil and its effect on pyrolysis characteristics of moso bamboo. Fuel Process. Technol. 2020, 200, 106332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Chen, G.; Cheng, Z.; Yan, B.; Ma, W.; Hou, L. The effect of alkali metal chlorides and temperature on acid-hydrolysis residual pyrolysis products. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2019, 137, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Ping, X.; Sun, X.; Han, W. Study on combustion characteristics of waste pharmaceutical Na2SO4 and impurity removal by low-temperature carbonization. Inorg. Chem. Ind. 2021, 53, 76–82. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, X.-J.; Ren, X. Kinetic study of sesame stalk pyrolysis by thermogravimetric analysis. Renew. Energy 2024, 222, 119878. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Cui, H.; Hu, X.; Qu, A. Research on heat treatment of NaCl-KCl waste salt in pesticide industry. Inorg. Chem. Ind. 2023, 55, 106–112. [Google Scholar]
- Mašek, O.; Brownsort, P.; Cross, A.; Sohi, S. Influence of production conditions on the yield and environmental stability of biochar. Fuel 2013, 103, 151–155. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Jiang, G.; An, C.; Fei, Z.; Chi, Y.; Yan, J. Combustion and Pyrolysis Characteristics of Pesticide Residue. Proc. CSEE 2009, 29, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Antoniadis, A.; Lambert-Lacroix, S.; Poggi, J.-M. Random forests for global sensitivity analysis: A selective review. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2021, 206, 107312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, F.G.; Funke, A.; Niebel, A.; Dias, A.P.S. Moisture content as a design and operational parameter for fast pyrolysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2019, 139, 73–86. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Omairey, E.; Cai, J.; Gu, F.; Bridgwater, A.V. Intermediate pyrolysis of organic fraction of municipal solid waste and rheological study of the pyrolysis oil for potential use as bio-bitumen. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 187, 390–399. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, R. Study on Heat Treatment Mechanism of Organic Waste Removal Based on Fluidized Bed. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Satou, M.; Yokoyama, S.; Sanada, Y. Structural analysis and estimation of boiling point of hydrocarbons in a coal-derived liquid by a group contribution method. Fuel 1992, 71, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Song, X.; Lu, G.; Sun, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yu, J. Control of Crystal Morphology and Size of Calcium Sulfate Whiskers in Aqueous HCl Solutions by Additives: Experimental and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Studies. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 4781–4787. [Google Scholar]
- Kwiecińska, B.; Pusz, S.; Valentine, B.J. Application of electron microscopy TEM and SEM for analysis of coals, organic-rich shales and carbonaceous matter. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2019, 211, 103203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Zhuo, J.; Zhang, B.; Yao, Q. Effect of moisture content on the characterization of products from the pyrolysis of sewage sludge. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2013, 104, 632–639. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. Guidelines for Environmental Management of Waste Salt in the Chemical Industry (Draft for Comment). Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/xxgk2018/xxgk/xxgk06/202101/W020210104377240592817.pdf (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Wei, Y.; Shen, C.; Xie, J.; Bu, Q. Study on reaction mechanism of superior bamboo biochar catalyst production by molten alkali carbonates pyrolysis and its application for cellulose hydrolysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 136435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.; Zhuang, X.; Song, Y.; Chang, G.; Wang, Z.; Yin, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, C. Formation and regulatory mechanisms of N-containing gaseous pollutants during stage-pyrolysis of agricultural biowastes. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 117706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Cao, J.-P.; Zhao, X.-Y.; Ren, J.; Wang, J.-X.; Fan, X.; Wei, X.-Y. Nitrogen Evolution during Fast Pyrolysis of Sewage Sludge under Inert and Reductive Atmospheres. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 7191–7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, F.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Guo, M. Thermal and kinetic characteristics of pyrolysis and combustion of three oil shales. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 97, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, H.; Li, A.; Yao, H. Influence of residual moisture on deep dewatered sludge pyrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 1253–1261. [Google Scholar]
- Widyawati, M.; Church, T.L.; Florin, N.H.; Harris, A.T. Hydrogen synthesis from biomass pyrolysis with in situ carbon dioxide capture using calcium oxide. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 4800–4813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Luo, Z.; Yu, C.; Xie, G. Conversion mechanism of fuel-N during pyrolysis of biomass wastes. Fuel 2019, 246, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Lin, S.; Fan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jin, L.; Gao, H. Investigations on the iron-rich textile dyeing sludge pyrolysis characteristics: Thermal decomposition behaviors, products, potential mechanisms. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2023, 169, 105834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glarborg, P.; Jensen, A.D.; Johnsson, J.E. Fuel nitrogen conversion in solid fuel fired systems. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2003, 29, 89–113. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, H.; Fu, L.; Yang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Guo, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y.; et al. Quantitative analysis of pyrolysis characteristics and chemical components of tobacco materials based on machine learning. Front. Chem. 2024, 12, 1353745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, R.; Gao, Q.; Wang, Q.; Xu, G. Machine Learning Optimization of Waste Salt Pyrolysis: Predicting Organic Pollutant Removal and Mass Loss. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3216. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073216
Zhou R, Gao Q, Wang Q, Xu G. Machine Learning Optimization of Waste Salt Pyrolysis: Predicting Organic Pollutant Removal and Mass Loss. Sustainability. 2025; 17(7):3216. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073216
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Run, Qing Gao, Qiuju Wang, and Guoren Xu. 2025. "Machine Learning Optimization of Waste Salt Pyrolysis: Predicting Organic Pollutant Removal and Mass Loss" Sustainability 17, no. 7: 3216. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073216
APA StyleZhou, R., Gao, Q., Wang, Q., & Xu, G. (2025). Machine Learning Optimization of Waste Salt Pyrolysis: Predicting Organic Pollutant Removal and Mass Loss. Sustainability, 17(7), 3216. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073216




