Factors Influencing Transparency in Urban Landscape Water Bodies in Taiyuan City Based on Machine Learning Approaches
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data Acquisition and Analysis Methods
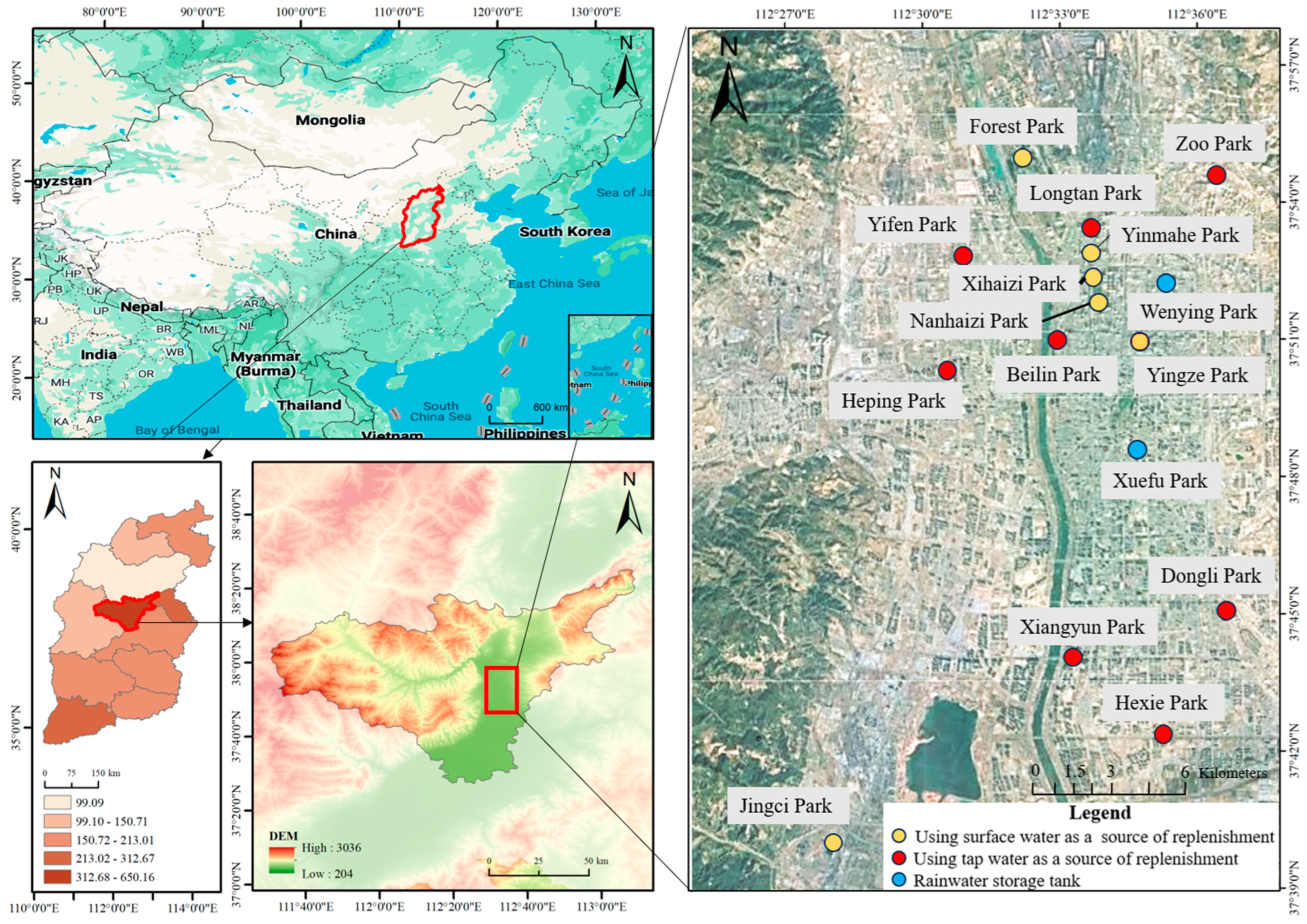
2.1. Study Area and Data Acquisition
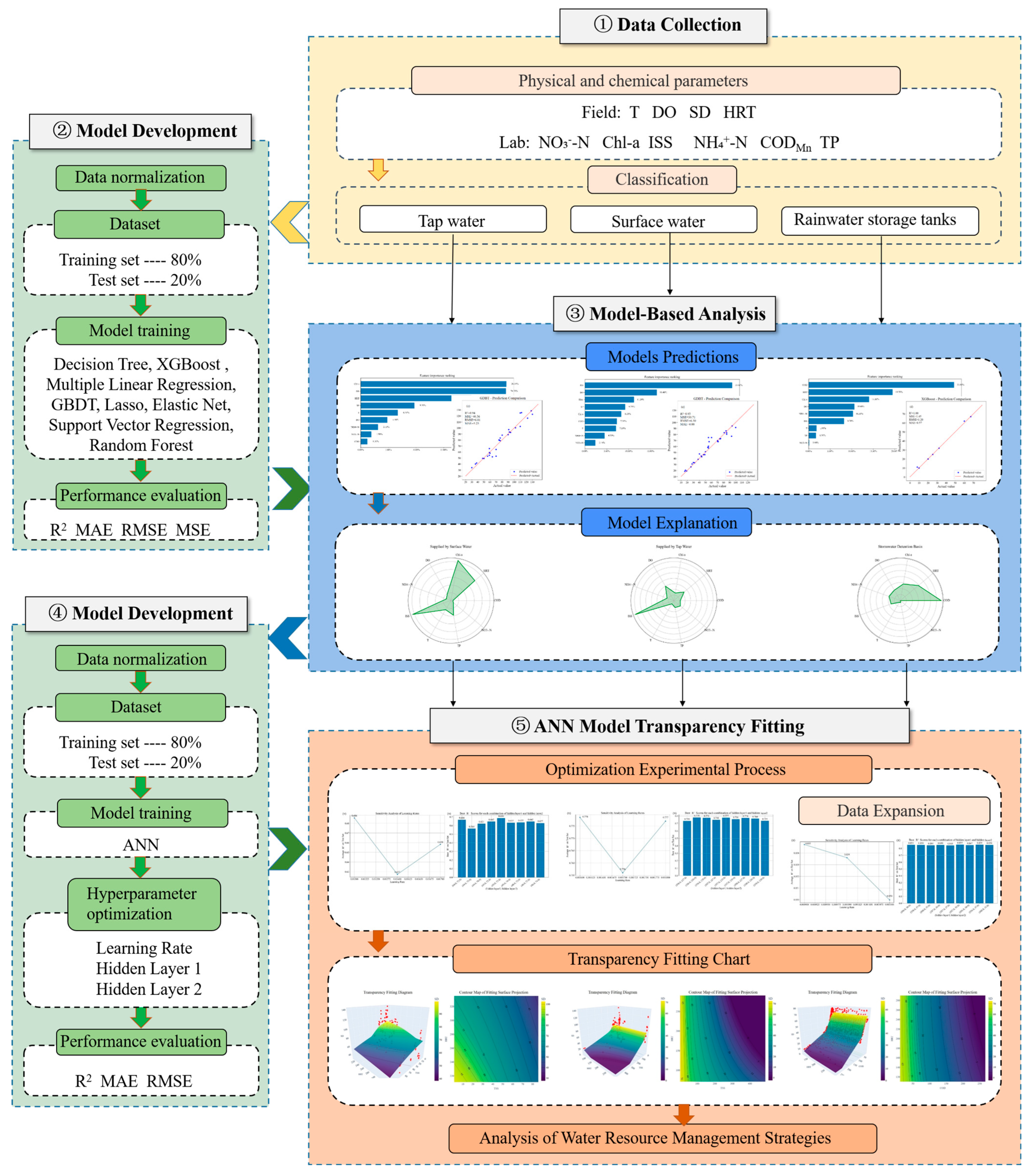
2.2. Analysis Procedure
2.3. Data Selection
2.4. Data Preprocessing
2.5. Machine Learning Models for Importance Analysis of Water Quality Parameters
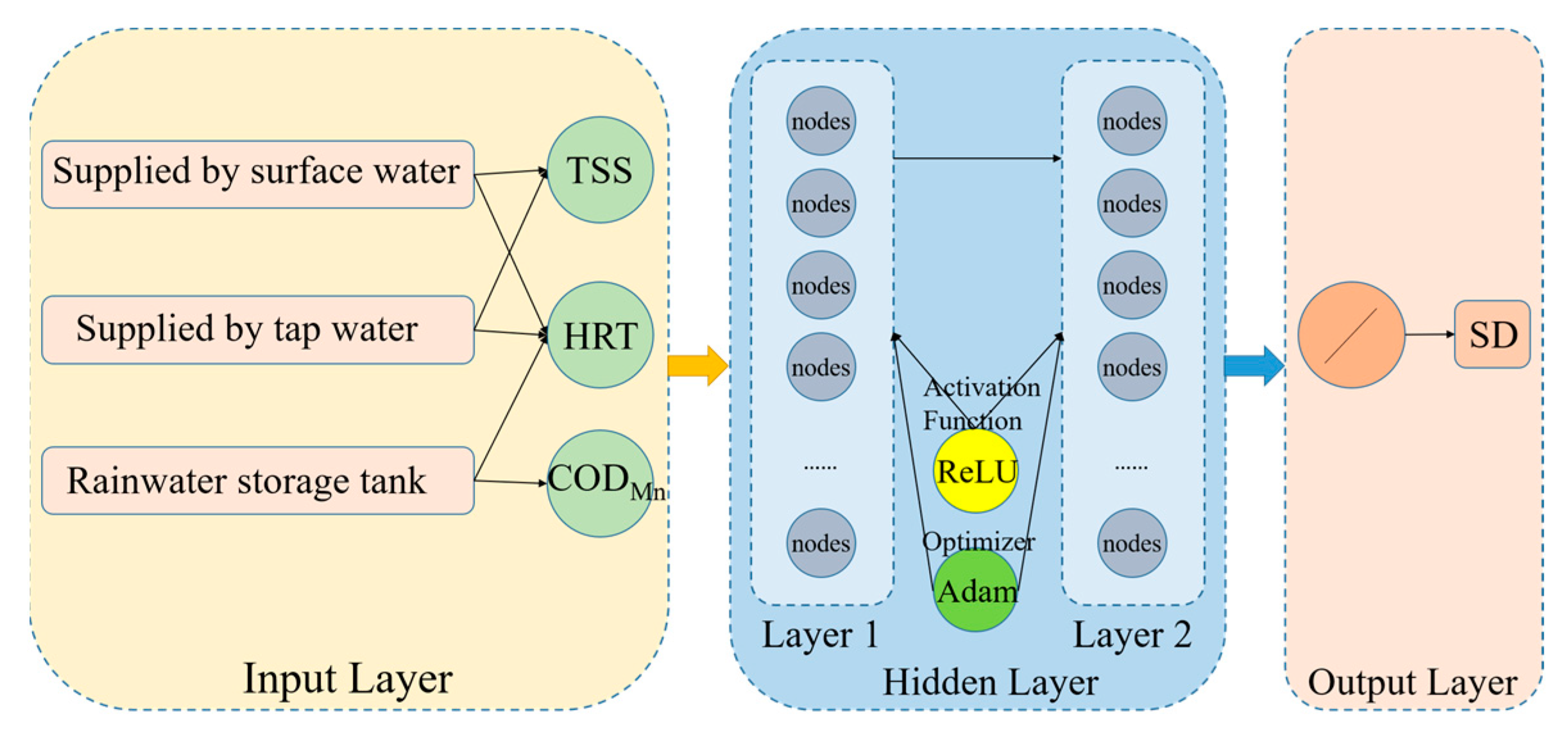
2.6. ANN Model for SD Fitting
2.7. Hyperparameter Optimization
2.8. Evaluation of Data Augmentation Rationality and Model Performance Metrics
3. Results
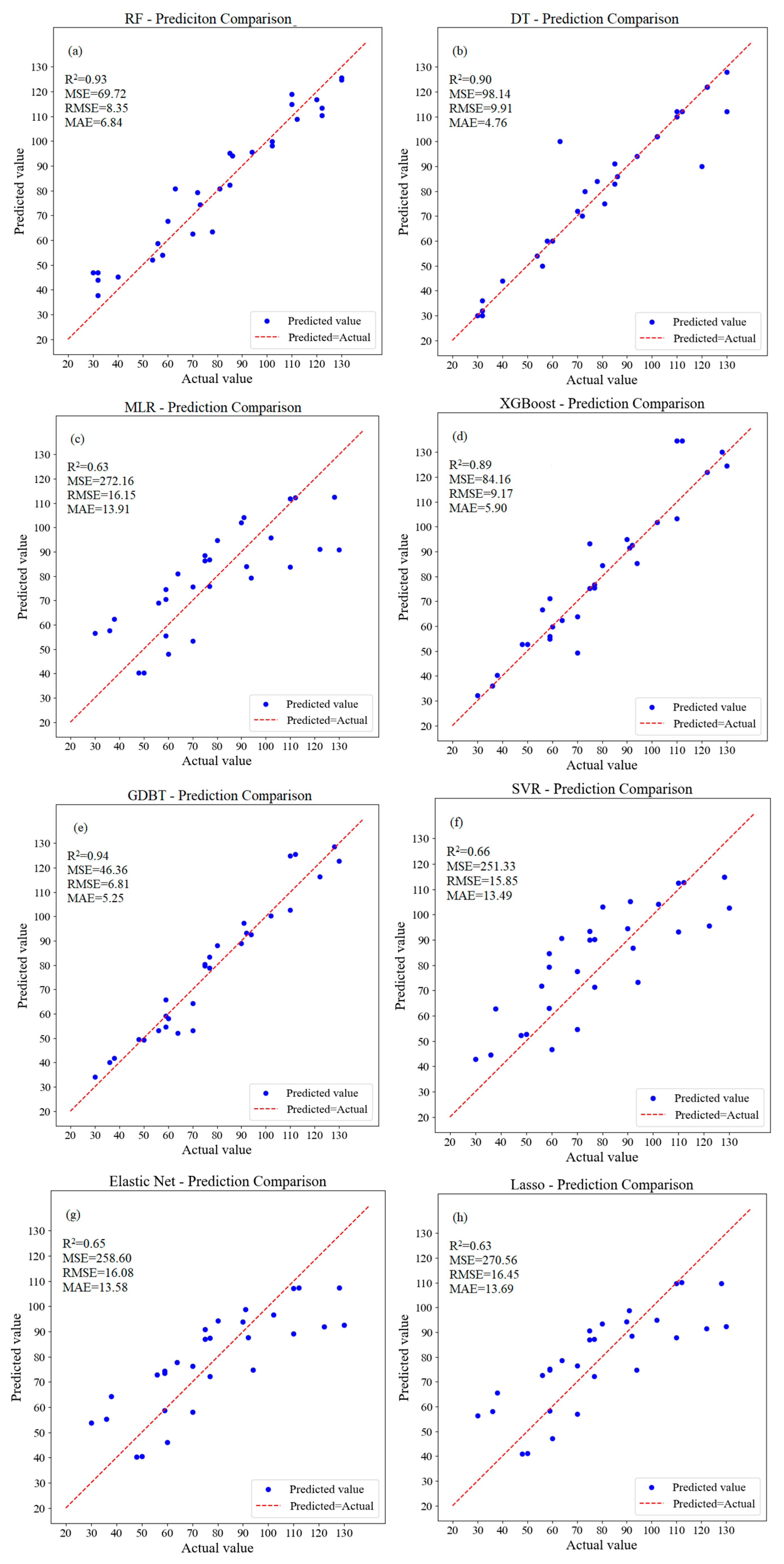
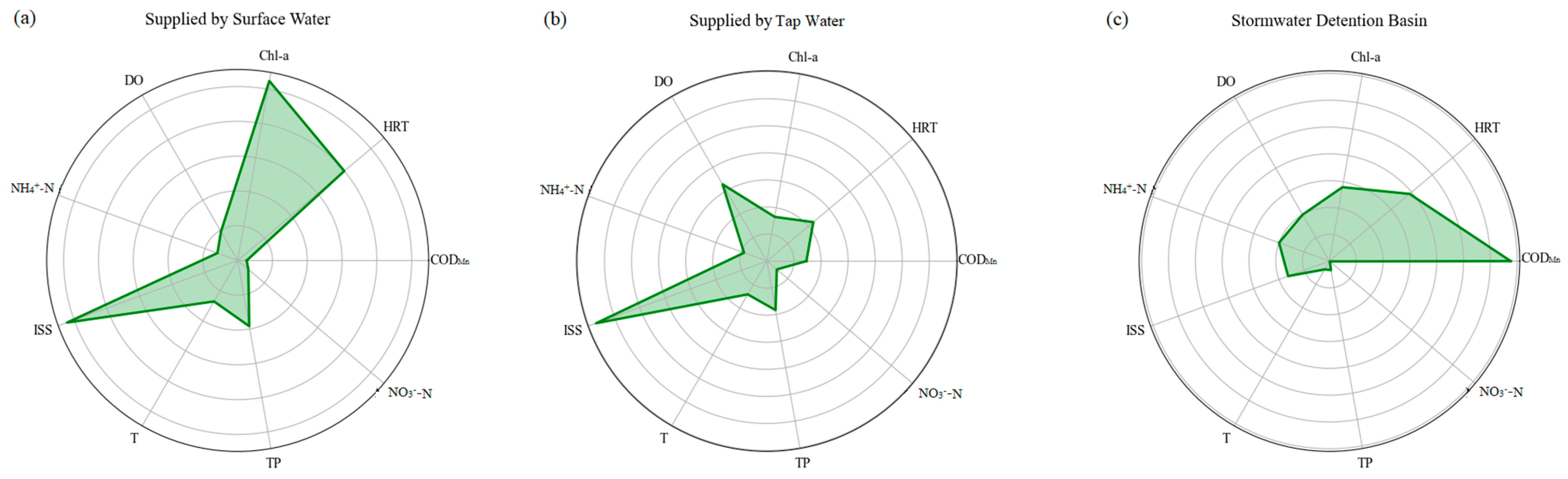
3.1. Machine Learning Analysis of Water Quality Parameters for ULLs with Different Water Supply Sources
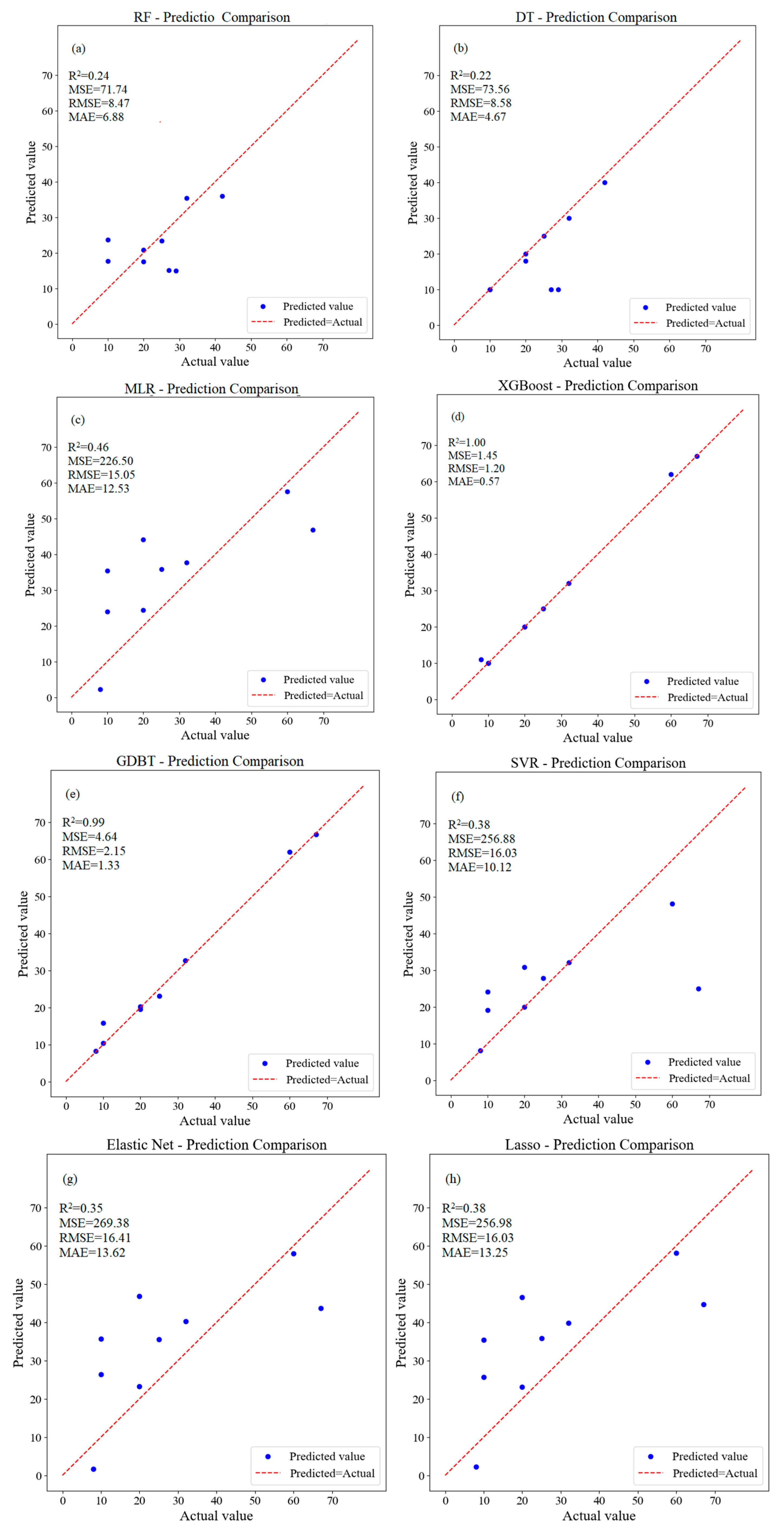
3.1.1. Machine Learning Prediction of Water Quality Parameters for ULLs Supplemented by Surface Water
3.1.2. Machine Learning Prediction of Water Quality Parameters for ULLs Supplemented by Tap Water
3.1.3. Prediction of Water Quality Parameters in Rainwater Storage Ponds Using Machine Learning
3.2. SD Fitting Analysis of Water Quality Parameters Based on ANN
3.2.1. Selection of Input Parameters
3.2.2. Data Augmentation
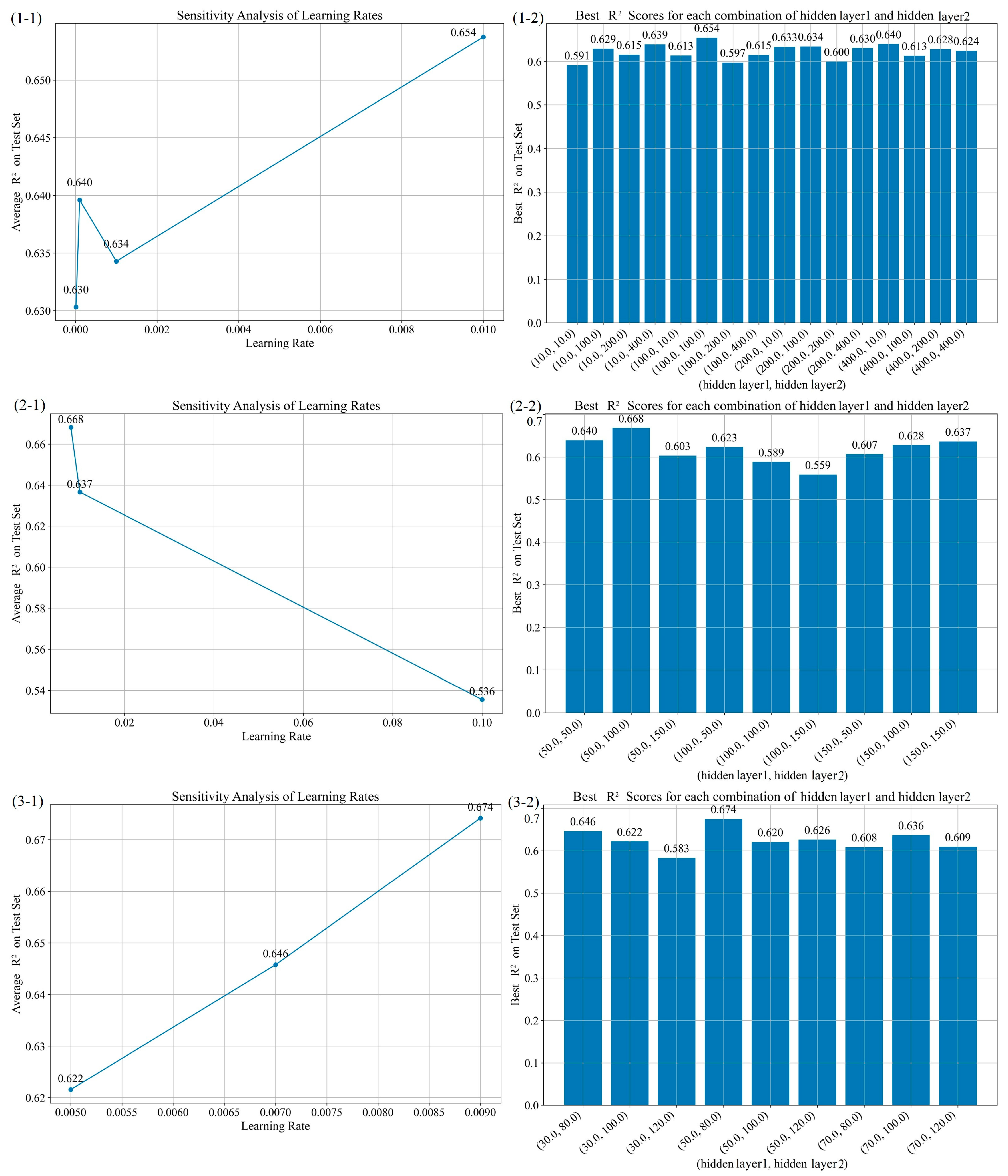
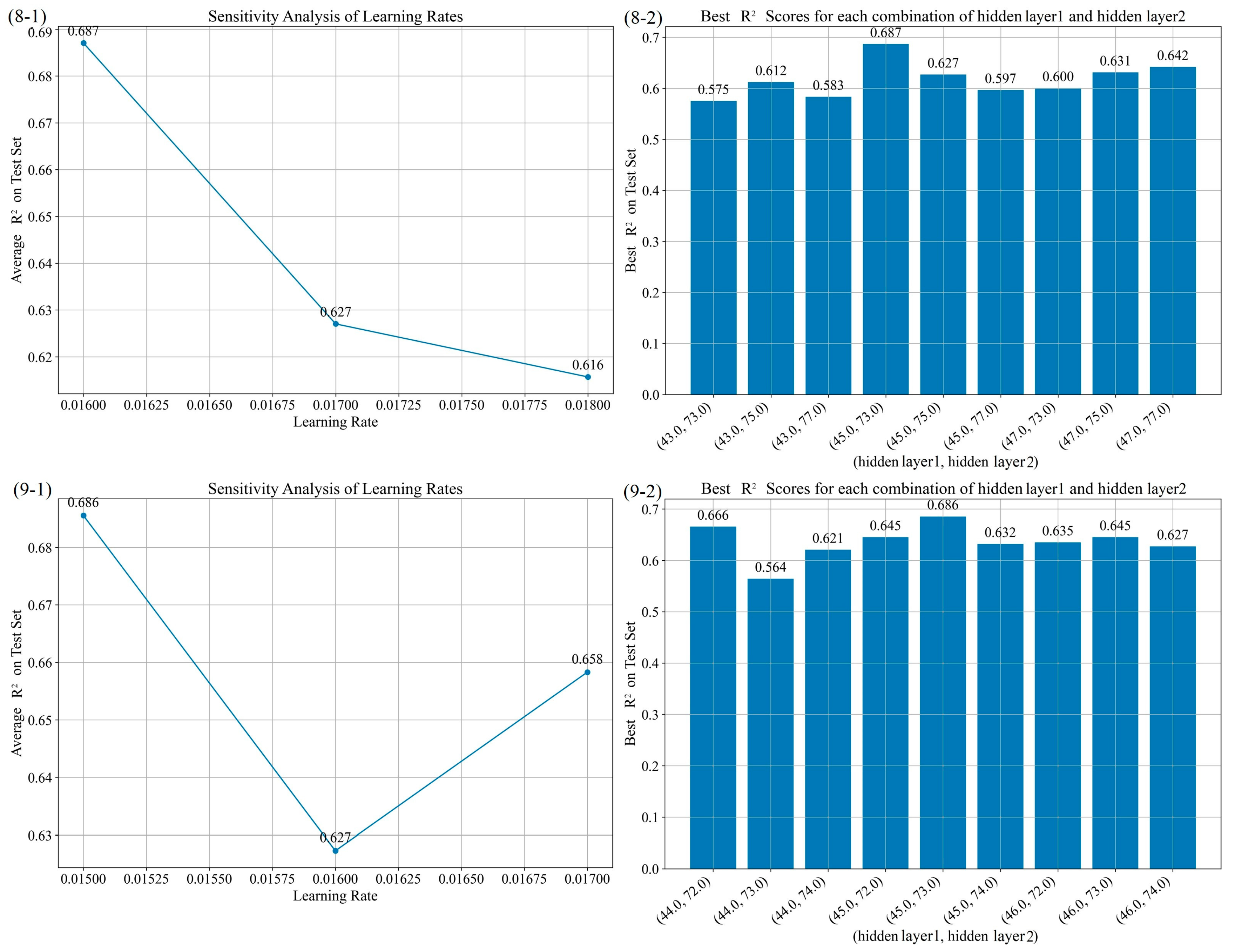
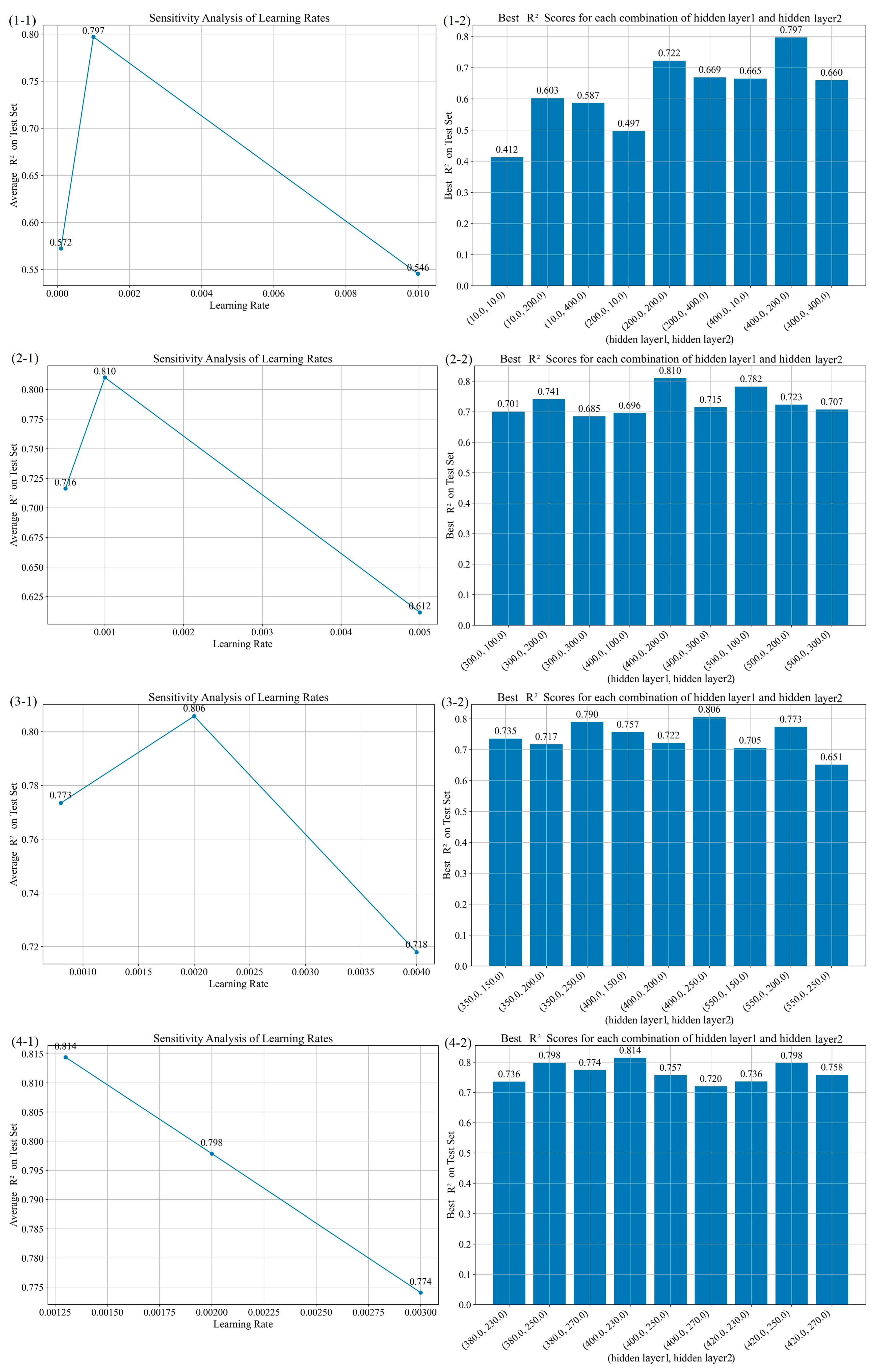
3.2.3. Hyperparameter Optimization Experiment Design
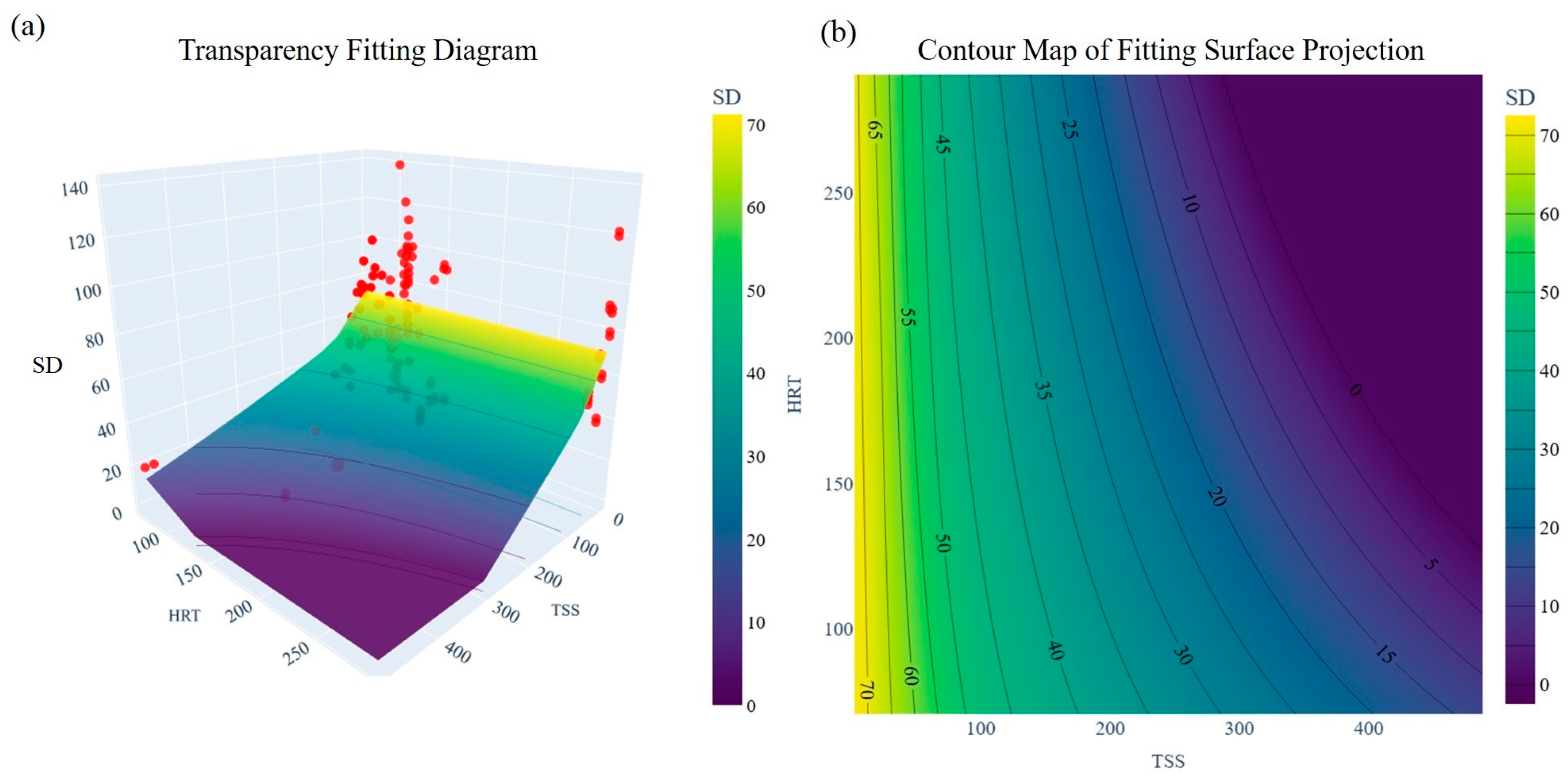
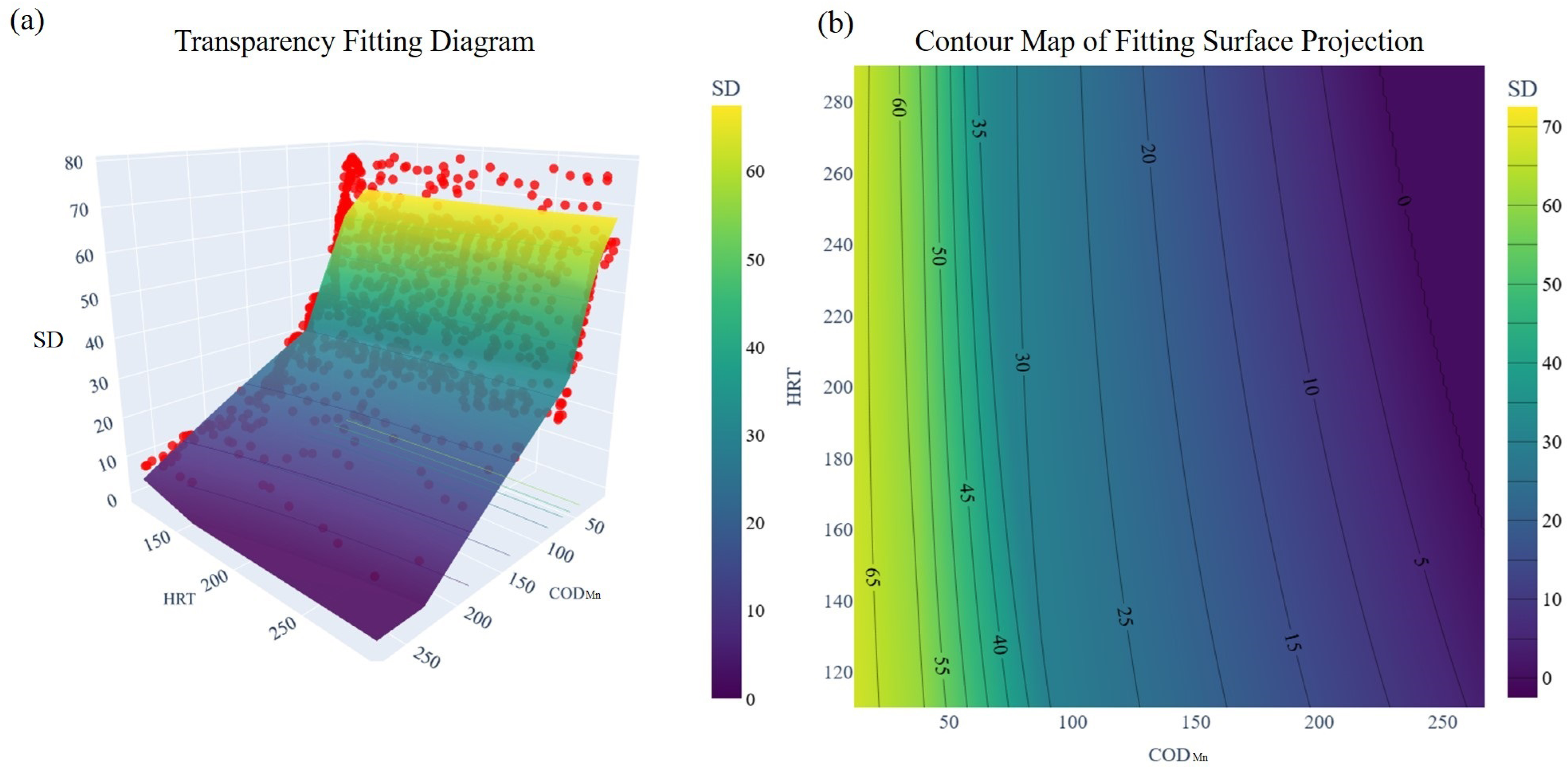
3.2.4. Water SD Fitting with the ANN Model
4. Discussion
4.1. Importance Analysis of Water Quality Parameters Using Machine Learning for Different Water Sources
4.1.1. Importance Analysis of Key Water Quality Factors in ULLs Supplemented by Surface Water
4.1.2. Importance Analysis of Key Water Quality Factors in ULLs Supplemented by Tap Water
4.1.3. Importance Analysis of Key Water Quality Factors in ULLs with Rainwater Storage Functions
4.1.4. Analysis of Water Source Types and Algorithm Selection Reasons
4.2. SD Fitting Analysis of Water Quality Parameters Based on ANN
4.2.1. Fitting Key Water Quality Factors in Surface Water-Supplemented ULLs: Emphasis on TSS and HRT
4.2.2. Key Water Quality Factors in Tap Water-Supplemented ULLs: Focusing on TSS and HRT
4.2.3. Evaluation and Discussion of Key Water Quality Factors for ULLs with Different Water Supply Sources
4.3. ULLs Quality Management Plan
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Misstear, A.A.B.; Sterckx, A.; Vargas, C.R.; Scheihing, K.; Kukuric, N. The United Nations World Water Development Report 2022: Groundwater-Making the Invisible Visible; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Marc Macias-Fauria, P.J.; Zimov, N.; Maihi, Y. Pleistocene Arctic megafaunal evological engineering as a natural climate solution? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2020, 375, 20190122. [Google Scholar]
- Ek, K.; Persson, L. Priorities and Preferences in Water Quality Management—A Case Study of the Alsteran River Basin. Water Resour. Manag. 2020, 34, 155–173. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, N.; Luo, L.; Wang, X.C.; Song, J.; Han, J.; Ao, D. A novel index for assessing the water quality of urban landscape lakes based on water transparency. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 735, 139351. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ao, D. Reclaimed Water Reuse for Replenishing Urban Waters in Water Dificient Cities: Theories and Technologies for Landscape Water Quality Control; Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology: Xi’an, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Xia, X.; Li, X.; Mou, X. Impacts of meteorological variations on urban lake water quality: A sensitivity analysis for 12 urban lakes with different trophic states. Aquat. Sci. 2014, 76, 339–351. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Sun, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. Prelassification improves relationships between water clarity, light attenuation, and suspended particulates in turbid inland waters. Hydrobiologia 2013, 711, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.-H.; Lee, Y.-D. The impact of water quality on the visual and olfactory satisfaction of tourists. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2015, 105, 92–99. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, N.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Luo, L.; Wang, X.C.; Xiong, J.; Han, J. Current status and characteristics of urban landscape lakes in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 135669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.-H. The relationship between visual satisfaction and water clarity and quality management in tourism fishing ports. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2016, 8, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, K.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, W.; Huang, X. Monitoring water transparency, total suspended matter and the beam attenuation coefficient in inland water using innovative ground-based proximal sensing technology. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 306, 114477. [Google Scholar]
- Ao, D.; Luo, L.; Dzakpasu, M.; Chen, R.; Xue, T.; Wang, X.C. Replenishment of landscape water with reclaimed water: Optimization of supply scheme using transparency as an indicator. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 88, 503–511. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Zhou, H.; Liu, Z. Modelling impacts of water diversion on water quality in an urban artificial lake. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 276, 116694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, N. Study on the comrehensive index for water landscape effect assessing of urban water bodies. In Envrionmental Science and Engineering; Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology: Xi’an, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Doron, M.; Babin, M.; Hembise, O.; Mangin, A.; Garnesson, P. Ocean transparency from space: Validation of algorithms estimating Secchi depth using MERIS, MODIS and SeaWiFS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2986–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Duan, H.; Cao, Z.; Xue, K.; Qi, T.; Ma, J.; Liu, D.; Song, K.; Huang, C.; Song, X. Sentinel-3 OLCI observations of water clarity in large lakes in eastern China: Implications for SDG 6.3.2 evaluation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batur, E.; Maktav, D. Assessment of surface water quality by using satellite images fusion based on PCA method in the Lake Gala, Turkey. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 57, 2983–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamloo, A.; Sima, S. Investigating the potential of remote sensing-based machine-learning algorithms to model Secchi-disk depth, total phosphorus, and chlorophyll-a in Lake Urmia. J. Great Lakes Res. 2024, 50, 1023700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Lu, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, B.; Shi, K.; Yang, X. Water clarity mapping of global lakes using a novel hybrid deep-learning-based recurrent model with Landsat OLI images. Water Res. 2022, 215, 118241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiyasha; Tung, T.M.; Yaseen, Z.M. Deep learning for prediction of water quality index classification: Tropical catchment environmental assessment. Nat. Resour. Res. 2021, 30, 4235–4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuck, J.V.R.; Cechinel, M.A.P.; Neves, J.; de Andrade, R.C.; Tristão, R.; Spogis, N.; Riella, H.G.; Soares, C.; Padoin, N. Predicting effluent quality parameters for wastewater treatment plant: A machine learning-based methodology. Chemosphere 2024, 352, 141472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Gu, M.; Gong, C.; Hu, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; He, Z. An advanced remote sensing retrieval method for urban non-optically active water quality parameters: An example from Shanghai. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 880, 163389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Wu, X.; Fan, L.; Xie, Z. Predicting water flux and reverse solute flux in forward osmosis processes using artificial neural networks (ANN) modelling with structural parameters. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 351, 128092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; He, G.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Dong, C.; Feng, J. Prediction of the effects of preparation conditions on pervaporation performances of polydimethylsiloxane(PDMS)/ceramic composite membranes by backpropagation neural network and genetic algorithm. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 89, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.G.; Nash, S.; Olbert, A.I. A review of water quality index models and their use for assessing surface water quality. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107218. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Li, H.; Ye, Z.; Wen, J.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Y. Application of modified water quality index (WQI) in the assessment of coastal water quality in main aquaculture areas of Dalian, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 157, 111285. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miller, T.; Durlik, I.; Adrianna, K.; Kisiel, A.; Cembrowska-Lech, D.; Spychalski, I.; Tuński, T. Predictive modeling of urban lake water quality using machine learning: A 20-year study. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lv, Y.; Dong, J.; Yuan, J.; Hui, X. Sensitivity analysis of urban landscape lake transparency based on machine learning in Taiyuan City. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 12998-91; Water Quality-Guidance on Sampling Techniques. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- GB 3838-2002; Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of China. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater (Version 4); China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Zhang, S.; Chen, X.; Ran, X.; Li, Z.; Cao, W. Prioritizing causation in decision trees: A framework for interpretable modeling. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 133, 108224. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Shen, H.; Huang, T.; Wu, Y.; Guo, B.; Liu, Z.; Luo, H.; Tang, J.; Zhou, H.; Wang, L.; et al. Improved random forest algorithms for increasing the accuracy of forest aboveground biomass estimation using Sentinel-2 imagery. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 159, 111752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, N.B.; Jongkittinarukorn, K.; Bingi, K. XGBoost based enhanced predictive model for handling missing input parameters: A case study on gas turbine. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2024, 10, 100775. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, F.; Song, P.; Baffour, B.A.; Wang, P.; Wang, W.; Li, L. Volcanic lithology identification based on parameter-optimized GBDT algorithm: A case study in the Jilin Oilfield, Songliao Basin, NE China. J. Appl. Geophys. 2021, 194, 104443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lin, C.; Tang, H.; Wen, T.; Tannant, D.D.; Zhang, B. Input-parameter optimization using a SVR based ensemble model to predict landslide displacements in a reservoir area—A comparative study. Appl. Soft Comput. 2024, 150, 111107. [Google Scholar]
- Mignan, A.; Rinaldi, A.P.; Lanza, F.; Wiemer, S. A multi-LASSO model to forecast induced seismicity at enhanced geothermal systems. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2024, 236, 212746. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Geng, T.; Jiang, W.; Fan, S.; Chen, J.; Jia, C.; Ji, S. A new application of Elasticnet regression based near-infrared spectroscopy model: Prediction and analysis of 2,3,5,4′-tetrahydroxy stilbene-2-o-β-D-glucoside and moisture in Polygonum multiflorum. Microchem. J. 2024, 199, 110095. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, X.; He, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, Z. Combining physical laws and ANN for predicting energy consumption of data center cooling systems. Energy Build. 2024, 311, 114170. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, X.; Li, C.-G.; Li, F.-M. Water quality variation of a typical urban landscape river replenished with reclaimed water. Water Cycle 2023, 4, 137–144. [Google Scholar]
- Taheri-Garavand, A.; Beiranvandi, M.; Ahmadi, A.; Nikoloudakis, N. Predictive modeling of Satureja rechingeri essential oil yield and composition under water deficit and soil amendment conditions using artificial neural networks (ANNs). Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 222, 109072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Song, K.; Wen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Shang, Y.; Fang, C.; Du, J. Spatial distribution of diffuse attenuation of photosynthetic active radiation and its main regulating factors in Inland Waters of Northeast China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y. Comparative analysis of machine learning methods for prediction of chlorophyll-a in a river with different hydrology characteristics: A case study in Fuchun River, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 364, 121386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Hou, X.; Zheng, Y. Monitoring and understanding the water transparency changes of fifty large lakes on the Yangtze Plain based on long-term MODIS observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 221, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Huang, L.; Yang, F.; Zhou, Y.; Chang, J. Seasonal and spatial distributions of euphotic zone and long-term variations in water transparency in a clear oligotrophic Lake Fuxian, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 72, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Seo, I.W.; Baek, D. Seasonally varying effects of environmental factors on phytoplankton abundance in the regulated rivers. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannizzaro, J.P.; Carlson, P.R.; Yarbro, L.A.; Hu, C. Optical variability along a river plume gradient: Implications for management and remote sensing. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 131, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, M.; Qian, Z.; Jiang, H.; Huang, B.; Huang, S.; Deng, B.; Peng, Y.; Xie, Y.; Li, F.; Zou, Y.; et al. Assessing the impact of water-sediment factors on water quality to guide river-connected lake water environment improvement. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 168866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Yang, K.; Luo, Y.; Yang, Y. Secchi depth inversion and its temporal and spatial variation analysis—A case study of nine plateau lakes in Yunnan Province of China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 100, 102344. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.-N.; Wu, D.-X.; Huang, C.-Q.; Wu, Q.-Y.; Guan, Y.-T. Impacts of hydraulic retention time and inflow water quality on algal growth in a shallow lake supplied with reclaimed water. Water Cycle 2022, 3, 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Sun, B.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Gao, X.; Han, Z.; Liu, X. Water quality evolution of water-receiving lakes under the impact of multi-source water replenishments. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 53, 101832. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Peng, C.; Li, G.; He, F.; Huang, L.; Sun, X.; Wu, S. Integrated evaluation of the impact of water diversion on water quality index and phytoplankton assemblages of eutrophic lake: A case study of Yilong Lake. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 357, 120707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.-N.; He, J.-T.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Wang, F. Abnormal pH elevation in the Chaobai River, a reclaimed water intake area. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2017, 19, 111–122. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Huang, X.; He, S.; Yu, X.; Sun, M.; Wang, X.; Kong, H. Pilot-scale study on preserving eutrophic landscape pond water with a combined recycling purification system. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 61, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Hou, Z.; Li, Z.; Chu, Z.; Yang, P.; Zheng, B. Succession of phytoplankton functional groups and their driving factors in a subtropical plateau lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Qin, B. Monitoring the river plume induced by heavy rainfall events in large, shallow, Lake Taihu using MODIS 250m imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 173, 109–121. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, C.; Xu, Z.; Yan, X.; Wang, G.; Lin, X.; Zhang, J.; Guo, X. Coupling the measures of pollution source control and water replenishment to improve water quality in the catchment scale of Qianshan River Basin. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 341, 122899. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rao, H.; Shi, X.; Rodrigue, A.K.; Feng, J.; Xia, Y.; Elhoseny, M.; Yuan, X.; Gu, L. Feature selection based on artificial bee colony and gradient boosting decision tree. Appl. Soft Comput. 2019, 74, 634–642. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, L.; Wang, K. Is the relationship between the perceived service quality and passenger loyalty linear or non-linear? A novel model-independent interpretation method is applied. Transp. Policy 2023, 144, 65–79. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Su, L.; Xie, S. Splitting tensile strength of basalt fiber reinforced coral aggregate concrete: Optimized XGBoost models and experimental validation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 416, 135133. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Gitungo, S.W.; Axe, L.; Raczko, R.F.; Dyksen, J.E. Biologically active filters—An advanced water treatment process for contaminants of emerging concern. Water Res. 2017, 114, 31–41. [Google Scholar]
- Parr, L.B.; Perkins, R.G.; Mason, C.F. Reduction in photosynthetic efficiency of Cladophora glomerata, induced by overlying canopies of Lemna spp. Water Res. 2002, 36, 1735–1742. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Dzakpasu, M.; Lian, B.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.C. Development of an indicator for characterizing particle size distribution and quality of stormwater runoff. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 7991–8001. [Google Scholar]
- Dunalska, J.A. Abiotic–biotic method of water treatment in a shore of lake—A new strategy for protection of urban lakes. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2018, 18, 454–458. [Google Scholar]
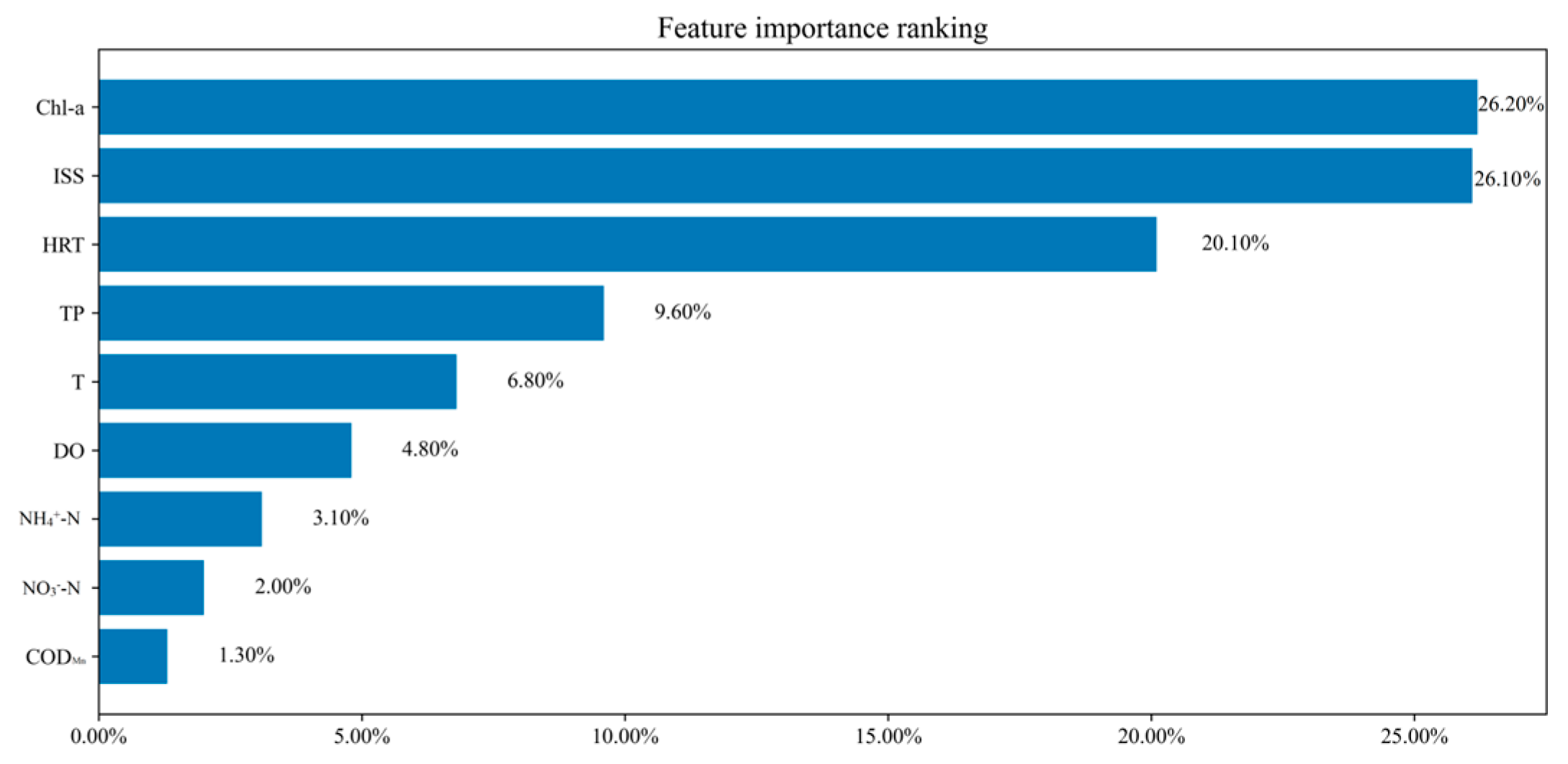

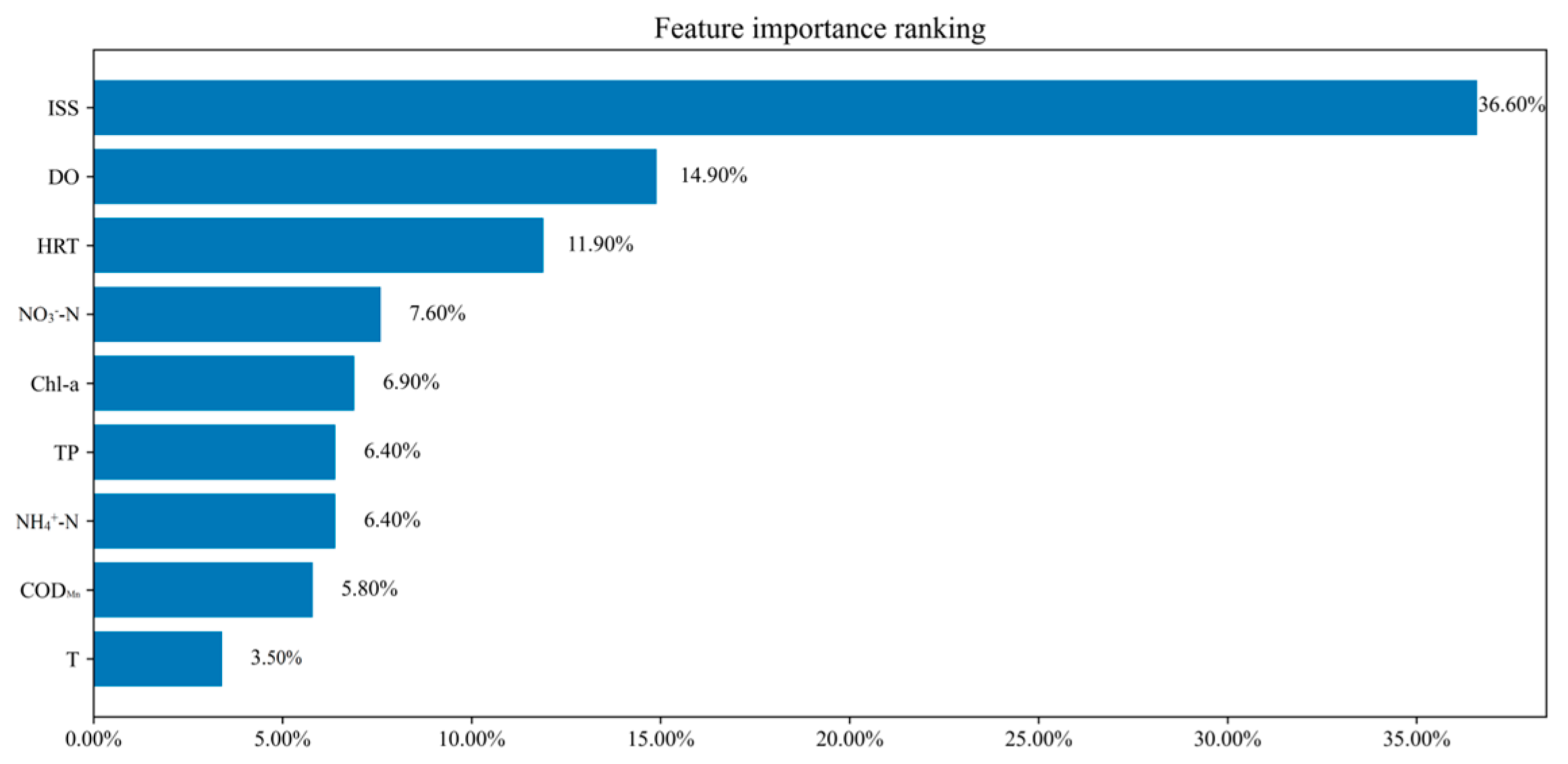
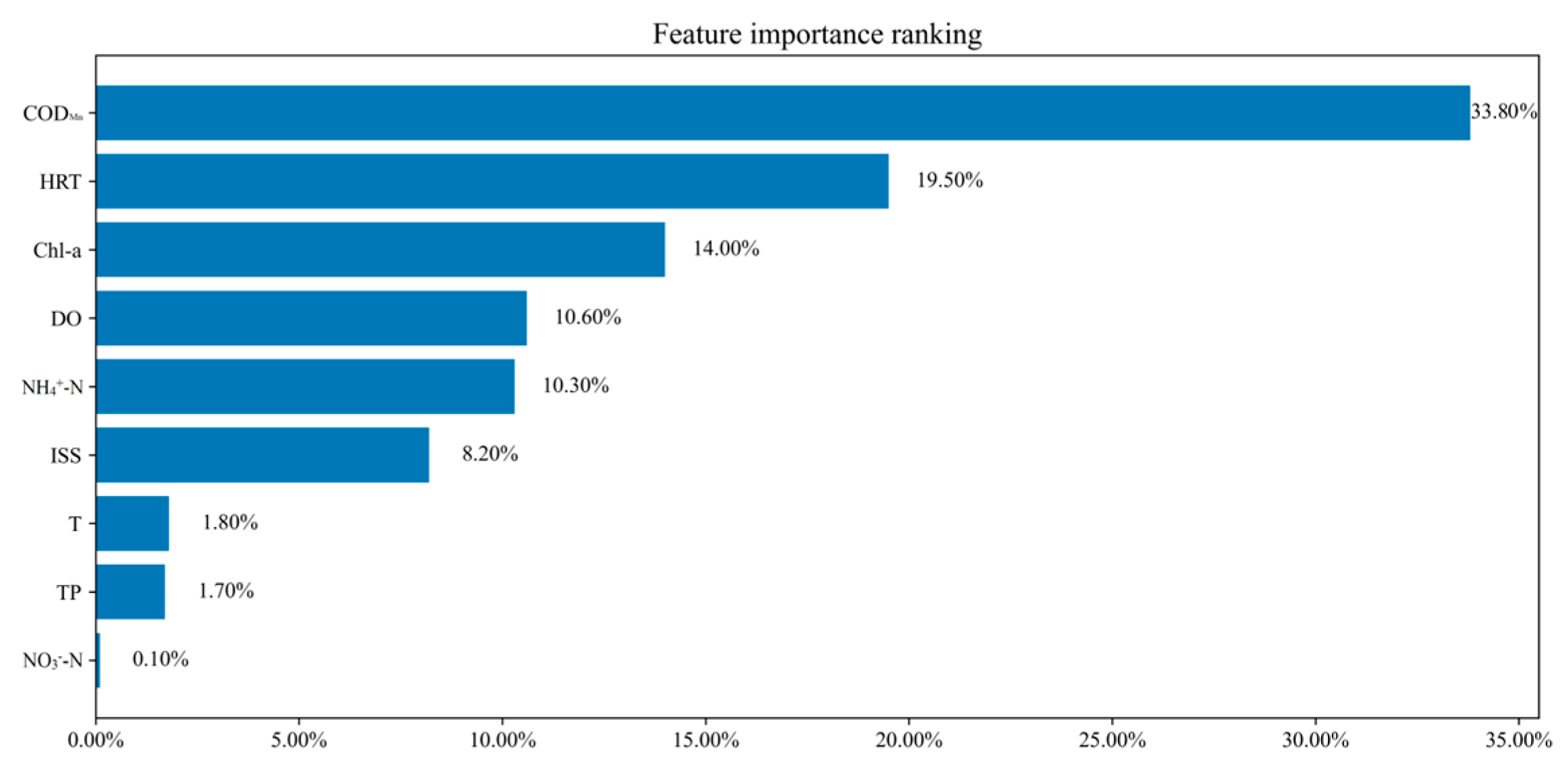


| Xuefu Park | Indicators | SD | CODMn | HRT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original Data | Augmented Data | Original Data | Augmented Data | Original Data | Augmented Data | |||
| Xuefu Park | Residual Analysis | Residual Mean | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Residual Standard Deviation | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| Difference Test | T-statistic | −0.03 | −0.30 | −0.38 | ||||
| p-value | 0.97 | 0.77 | 0.73 | |||||
| Skewness | 1.31 | 1.27 | 1.64 | 1.16 | −2.85 | −3.44 | ||
| Kurtosis | 0.22 | 0.18 | 1.84 | 0.80 | 6.10 | 11.01 | ||
| Wenying Park | Residual Analysis | Residual Mean | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Residual Standard Deviation | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| Difference Test | T-statistic | 0.06 | 0.04 | −0.36 | ||||
| p-value | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.73 | |||||
| Skewness | 0.45 | 0.45 | −0.26 | 0.01 | −2.85 | −3.44 | ||
| Kurtosis | −1.19 | −1.25 | −0.26 | −0.64 | 6.10 | 11.00 | ||
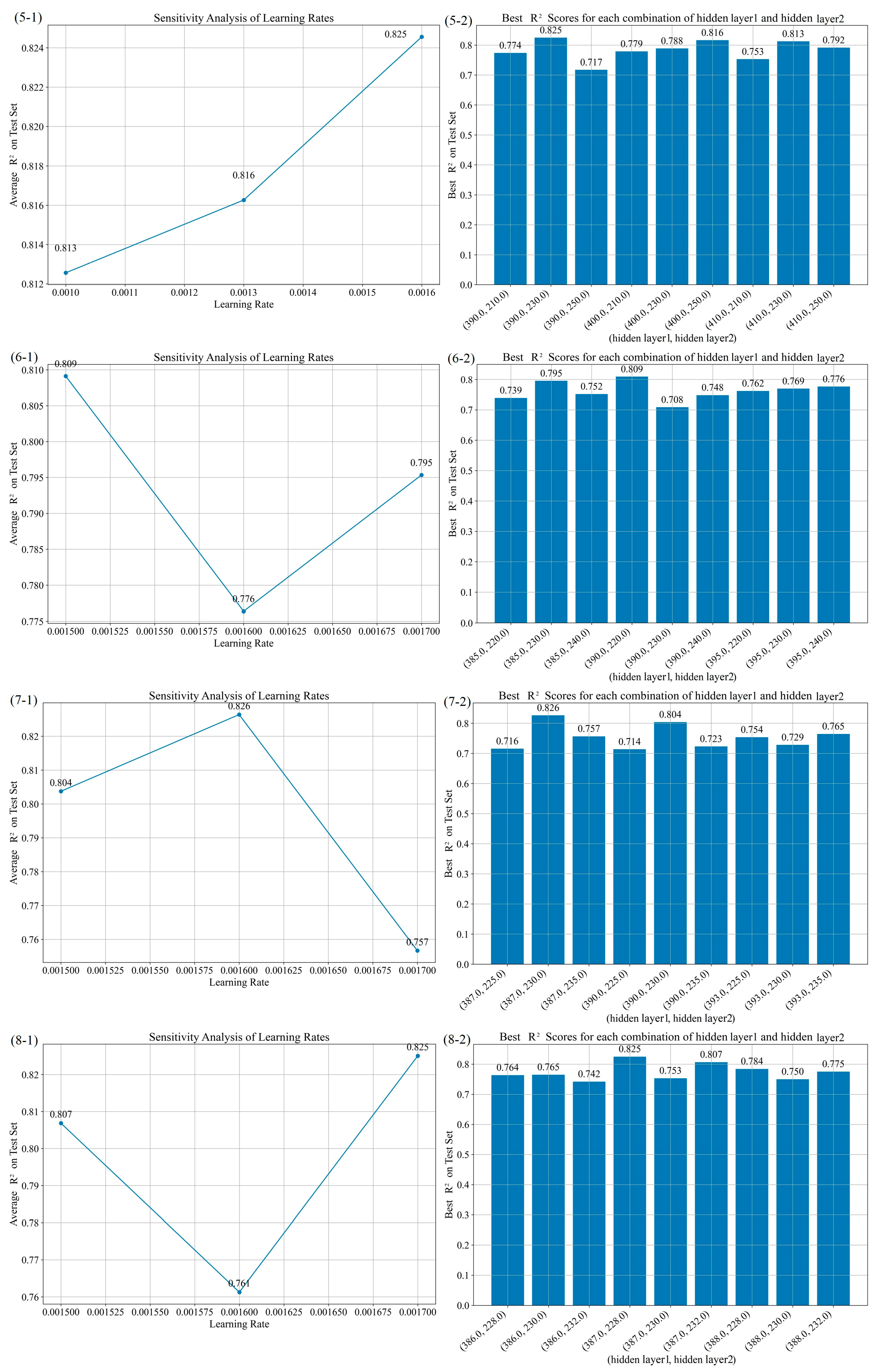
| No. | Experiment Combinations | Optimal Combination | Performance Parameters | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Learning Rate | Hidden Layers 1 | Hidden Layers 2 | Learning Rate | Hidden Layers 1 | Hidden Layers 2 | R2 | RMSE | MAE | |
| 1 | 0.00001, 0.0001, 0.001, 0.01 | 10, 100, 200, 400 | 10, 100, 200, 400 | 0.01 | 100 | 100 | 0.654 | 16.290 | 13.297 |
| 2 | 0.008, 0.01, 0.1 | 50, 100, 150 | 50, 100, 150 | 0.008 | 50 | 100 | 0.668 | 15.947 | 13.205 |
| 3 | 0.005, 0.007, 0.009 | 30, 50, 70 | 80, 100, 120 | 0.009 | 50 | 80 | 0.674 | 15.801 | 12.691 |
| 4 | 0.008, 0.009, 0.01 | 40, 50, 60 | 70, 80, 90 | 0.01 | 60 | 80 | 0.671 | 15.874 | 13.319 |
| 5 | 0.0095, 0.01, 0.015 | 55, 60, 65 | 75, 80, 85 | 0.015 | 55 | 85 | 0.684 | 15.563 | 12.489 |
| 6 | 0.01, 0.015, 0.02 | 50, 55, 60 | 80, 85, 90 | 0.02 | 50 | 80 | 0.686 | 15.511 | 13.031 |
| 7 | 0.017, 0.02, 0.025 | 45, 50, 55 | 75, 80, 85 | 0.017 | 45 | 75 | 0.650 | 16.388 | 13.278 |
| 8 | 0.016, 0.017, 0.018 | 43, 45, 47 | 73, 75, 77 | 0.016 | 45 | 73 | 0.687 | 15.486 | 12.241 |
| 9 | 0.015, 0.016, 0.017 | 44, 45, 46 | 72, 73, 74 | 0.015 | 45 | 73 | 0.686 | 15.523 | 12.939 |
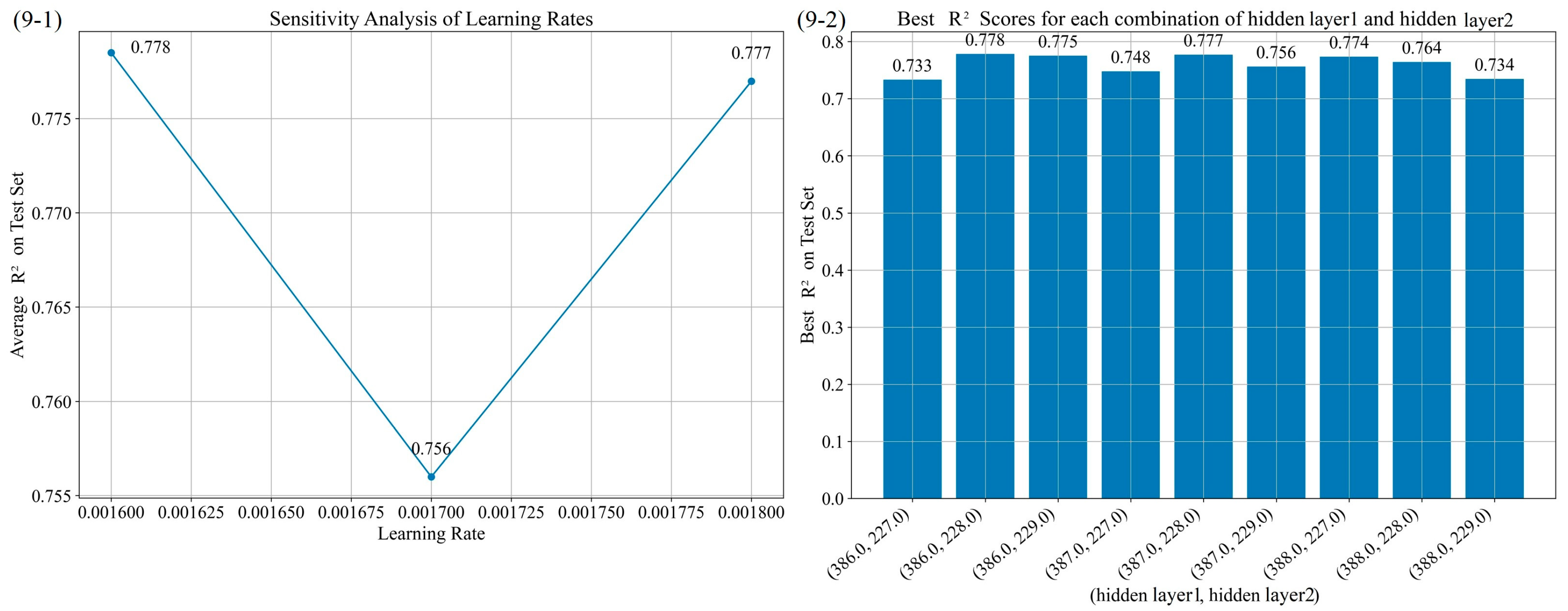
| No. | Experiment Combinations | Optimal Combination | Performance Parameters | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Learning Rate | Hidden Layers 1 | Hidden Layers 2 | Learning Rate | Hidden Layers 1 | Hidden Layers 2 | Learning Rate | Hidden Layers 1 | Learning Rate | |
| 1 | 0.0001, 0.001, 0.01 | 10, 200, 400 | 10, 200, 400 | 0.001 | 400 | 200 | 0.797 | 11.686 | 9.238 |
| 2 | 0.0005, 0.001, 0.005 | 300, 400, 500 | 100, 200, 300 | 0.002 | 400 | 200 | 0.810 | 11.299 | 9.069 |
| 3 | 0.0008, 0.002, 0.004 | 350, 400, 550 | 150, 200, 250 | 0.002 | 400 | 250 | 0.806 | 11.431 | 8.744 |
| 4 | 0.0013, 0.002, 0.003 | 380, 400, 420 | 230, 250, 270 | 0.0013 | 400 | 230 | 0.814 | 11.174 | 8.759 |
| 5 | 0.001, 0.0013, 0.0016 | 390, 400, 410 | 210, 230, 250 | 0.0016 | 390 | 230 | 0.825 | 10.863 | 9.195 |
| 6 | 0.0015, 0.0016, 0.0017 | 385, 390, 395 | 220, 230, 240 | 0.0015 | 390 | 220 | 0.809 | 11.331 | 9.038 |
| 7 | 0.0015, 0.0016, 0.0017 | 387, 390, 393 | 225, 230, 235 | 0.0016 | 387 | 230 | 0.826 | 10.806 | 7.909 |
| 8 | 0.0015, 0.0016, 0.0017 | 386, 387, 388 | 228, 230, 232 | 0.0016 | 387 | 228 | 0.825 | 10.849 | 8.361 |
| 9 | 0.0015, 0.0016, 0.0017 | 386, 387, 388 | 227, 228, 229 | 0.0016 | 386 | 228 | 0.778 | 12.207 | 9.359 |
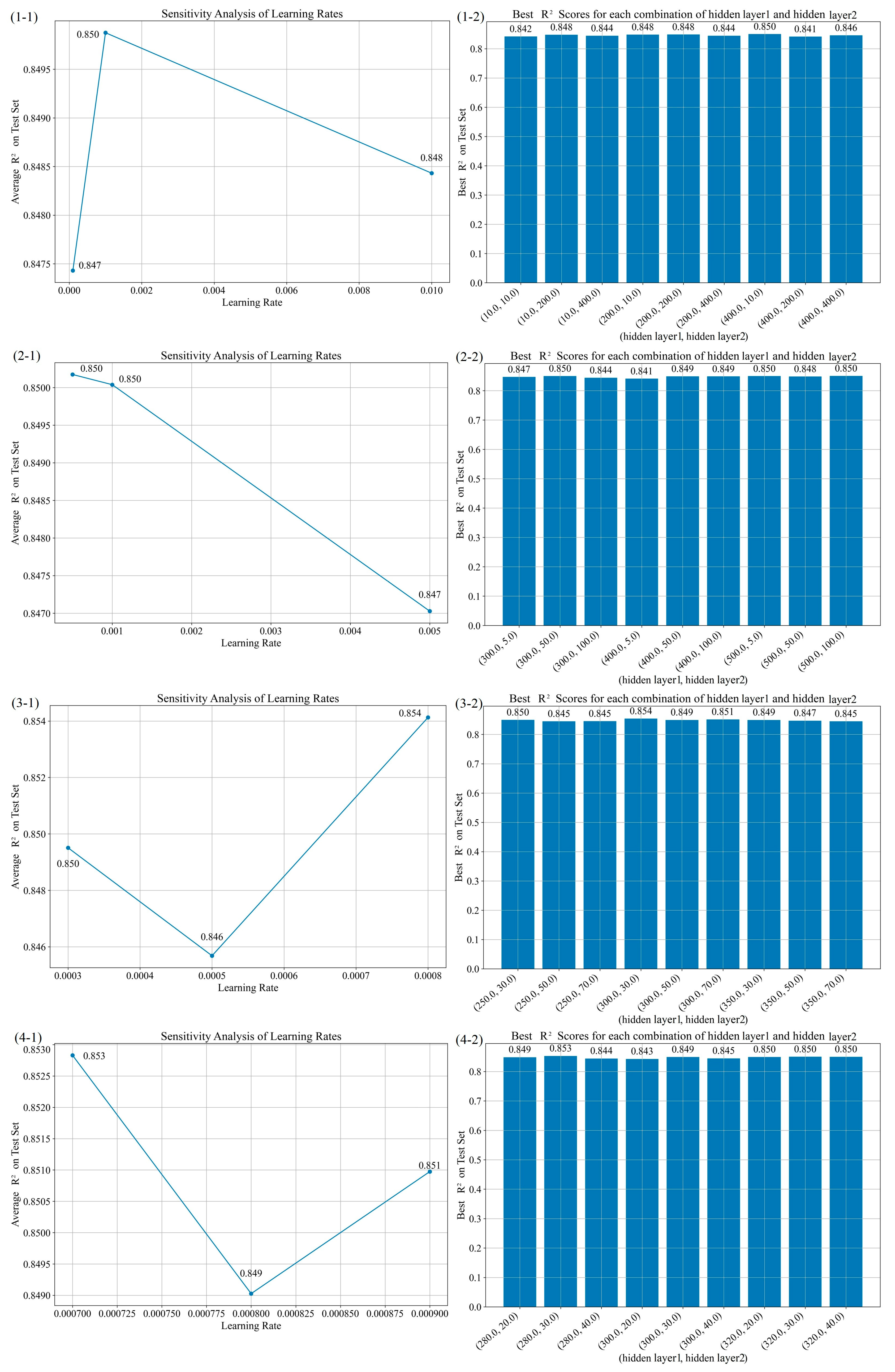
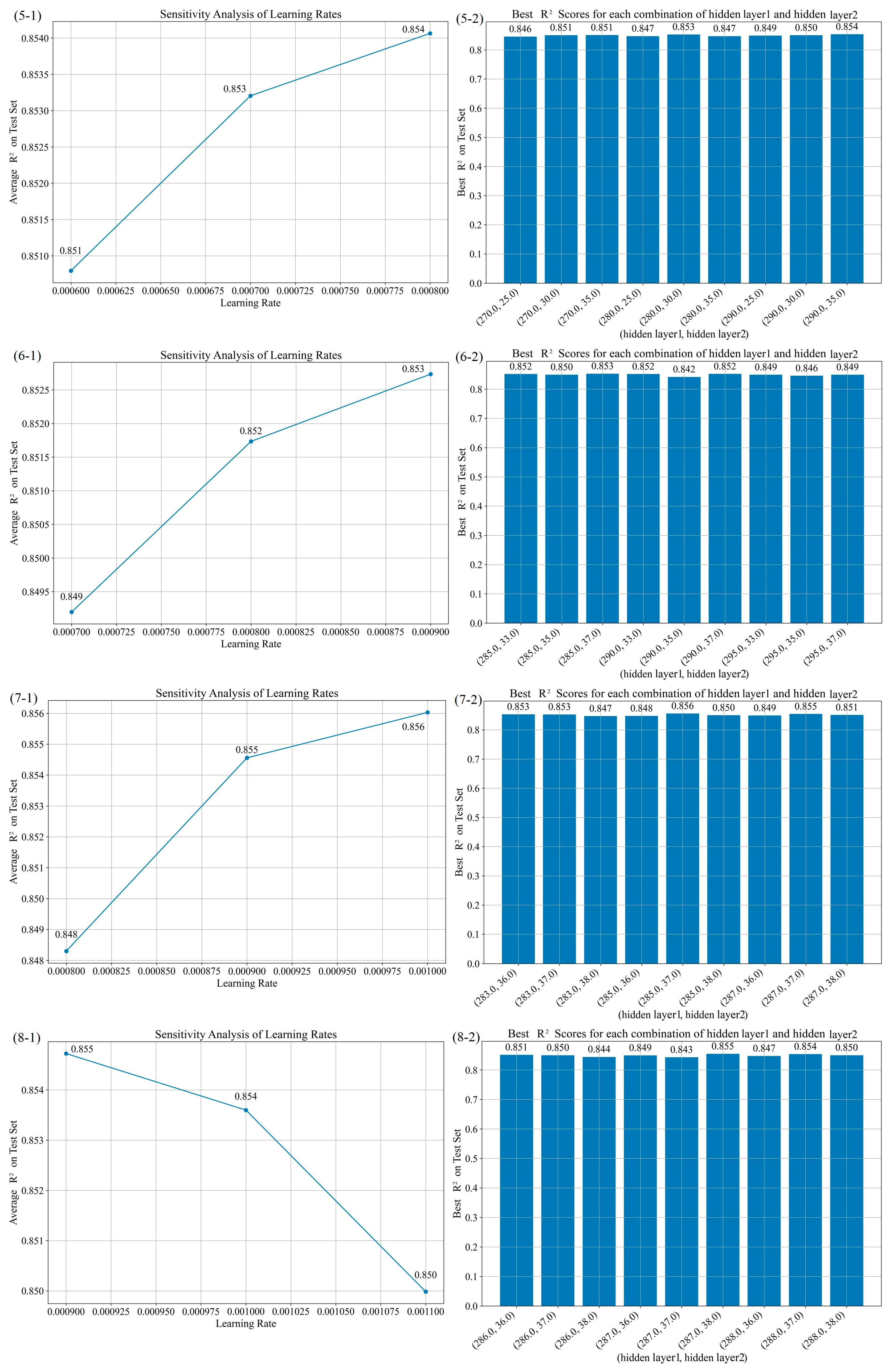
| No. | Experiment Combinations | Optimal Combination | Performance Parameters | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Learning Rate | Hidden Layers 1 | Hidden Layers 2 | Learning Rate | Hidden Layers 1 | Hidden Layers 2 | Learning Rate | Hidden Layers 1 | Hidden Layers 2 | |
| 1 | 0.0001, 0.001, 0.01 | 10, 200, 400 | 10, 200, 400 | 0.001 | 400 | 10 | 0.850 | 6.674 | 3.662 |
| 2 | 0.0005, 0.001, 0.005 | 300, 400, 500 | 5, 50 100 | 0.001 | 300 | 50 | 0.850 | 6.667 | 3.661 |
| 3 | 0.0003, 0.0005, 0.0008 | 250, 300, 350 | 30, 50, 70 | 0.0008 | 300 | 30 | 0.854 | 6.579 | 3.560 |
| 4 | 0.0007, 0.0008, 0.0009 | 280, 300, 320 | 20, 30, 40 | 0.0007 | 280 | 30 | 0.853 | 6.608 | 3.580 |
| 5 | 0.0006, 0.0007, 0.0008 | 270, 280, 290 | 25, 30, 35 | 0.0008 | 290 | 35 | 0.854 | 6.580 | 3.631 |
| 6 | 0.0007, 0.0008, 0.0009 | 285, 290, 295 | 33, 35, 37 | 0.0009 | 285 | 37 | 0.853 | 6.610 | 3.426 |
| 7 | 0.0008, 0.0009, 0.0010 | 283, 285, 287 | 36, 37, 38 | 0.0010 | 285 | 37 | 0.856 | 6.536 | 3.493 |
| 8 | 0.0009, 0.0010, 0.0011 | 286, 287, 288 | 36, 37, 38 | 0.0009 | 287 | 38 | 0.855 | 6.565 | 3.670 |
| Data Collection | Research Area | Monitoring Parameters | Data Points | Optimal Model | Highest Contribution (Only Those Greater Than 20%) | R2 | MES | RMES | MAE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| From October 2013 to September 2015 | Hancheng Lake | SD, ISS, Chl-a, AN, NN, IP | 24 | GBDT | Chla (34.3%), ISS (28.3%), | 0.79 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.03 |
| From January to December 2015 | Xingqing Lake | SD, ISS, Chl-a, AN, NN, IP | 12 | GBDT | ISS (79%) | 0.81 | 0.01 | 0.08 | 0.08 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Y.; Lv, Y.; Dong, J.; Yuan, J.; Hui, X. Factors Influencing Transparency in Urban Landscape Water Bodies in Taiyuan City Based on Machine Learning Approaches. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3126. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073126
Zhou Y, Lv Y, Dong J, Yuan J, Hui X. Factors Influencing Transparency in Urban Landscape Water Bodies in Taiyuan City Based on Machine Learning Approaches. Sustainability. 2025; 17(7):3126. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073126
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Yuan, Yongkang Lv, Jing Dong, Jin Yuan, and Xiaomei Hui. 2025. "Factors Influencing Transparency in Urban Landscape Water Bodies in Taiyuan City Based on Machine Learning Approaches" Sustainability 17, no. 7: 3126. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073126
APA StyleZhou, Y., Lv, Y., Dong, J., Yuan, J., & Hui, X. (2025). Factors Influencing Transparency in Urban Landscape Water Bodies in Taiyuan City Based on Machine Learning Approaches. Sustainability, 17(7), 3126. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073126






