Environmental Regulation and Green Investment Efficiency: Threshold and Spatial Spillover Analysis for China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Analysis and Research Hypothesis
2.1. Environmental Regulation and Corporate Green Investment Efficiency
2.2. Environmental Regulation, Internal Control, and Corporate Green Investment Efficiency
2.3. Spatial Spillover Effects of Environmental Regulation on Corporate Green Investment
3. Data, Methodology, and Models
3.1. SBM–DEA
3.2. Panel Threshold Model
3.3. Spatial Autoregressive Model
3.3.1. The Design of the Spatial Autoregressive Model
3.3.2. Setting the Spatial Weight Matrix
3.4. Variables
3.4.1. Enterprise Green Investment Efficiency (GIE)
3.4.2. Environmental Regulation (EN)
3.4.3. Internal Control (ICQ)
3.4.4. Control Variables
4. Empirical Analysis
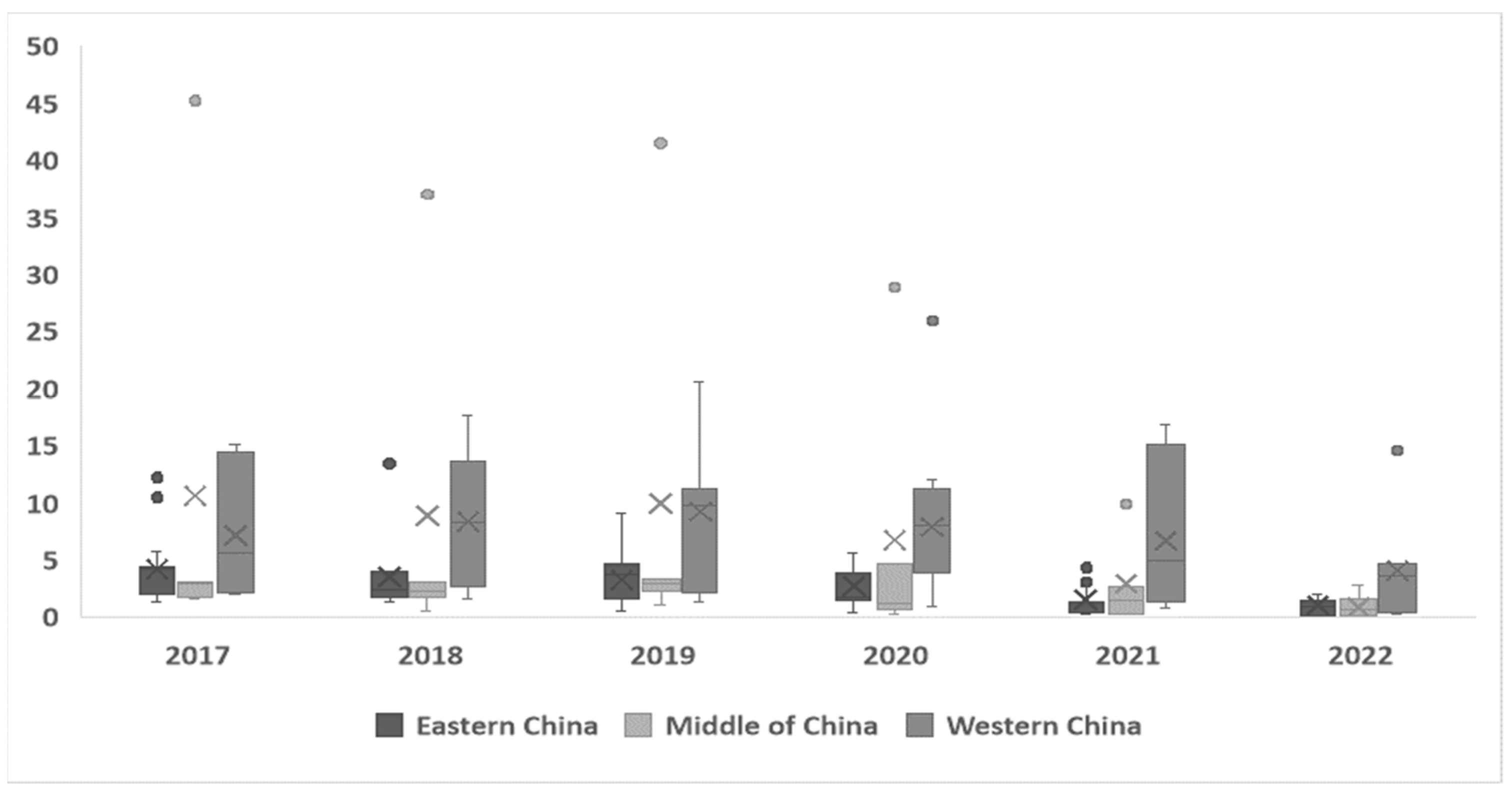
4.1. Results and Discussion of Green Investment Efficiency
4.2. Panel Threshold Model Results and Discussion
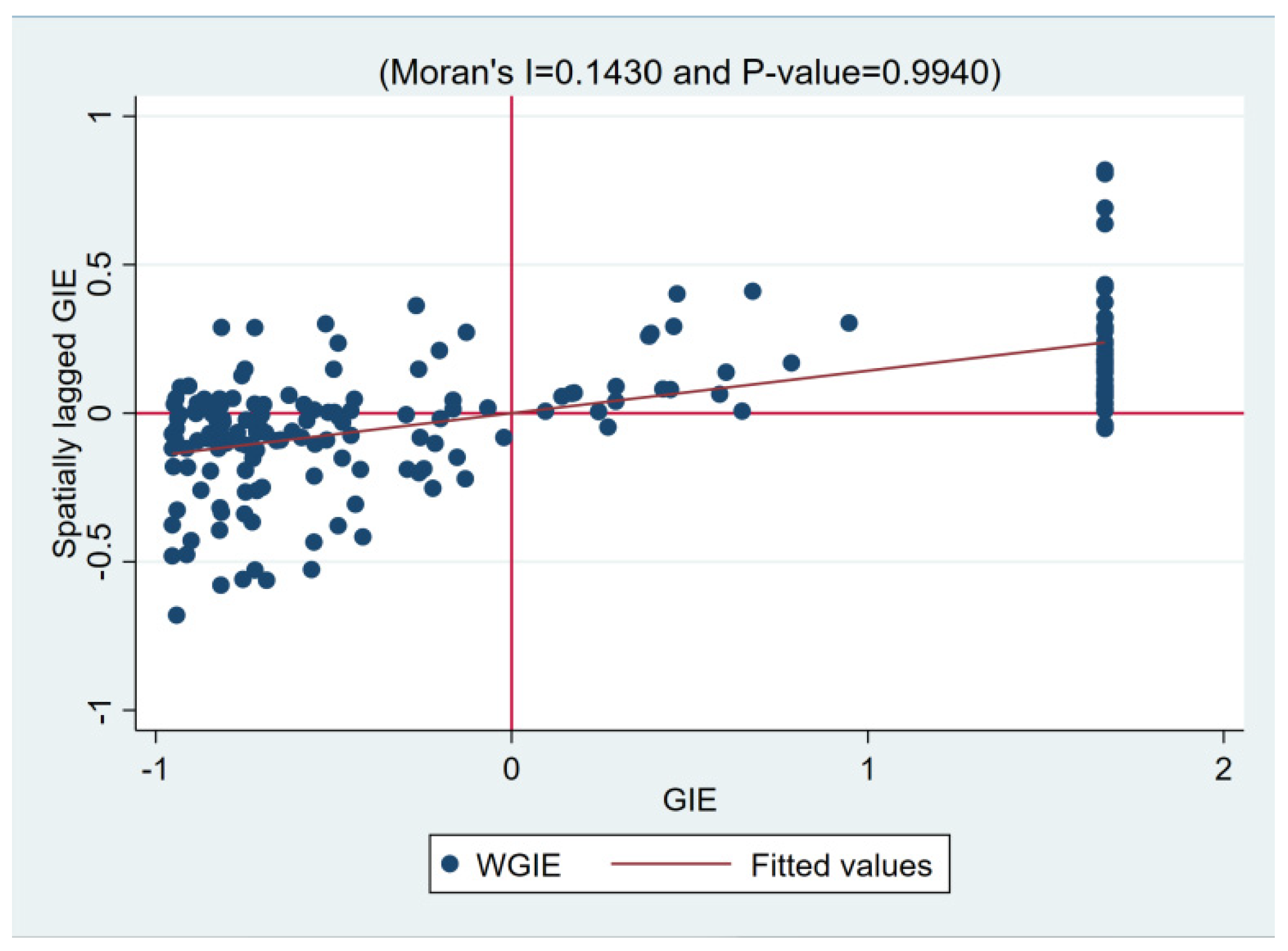
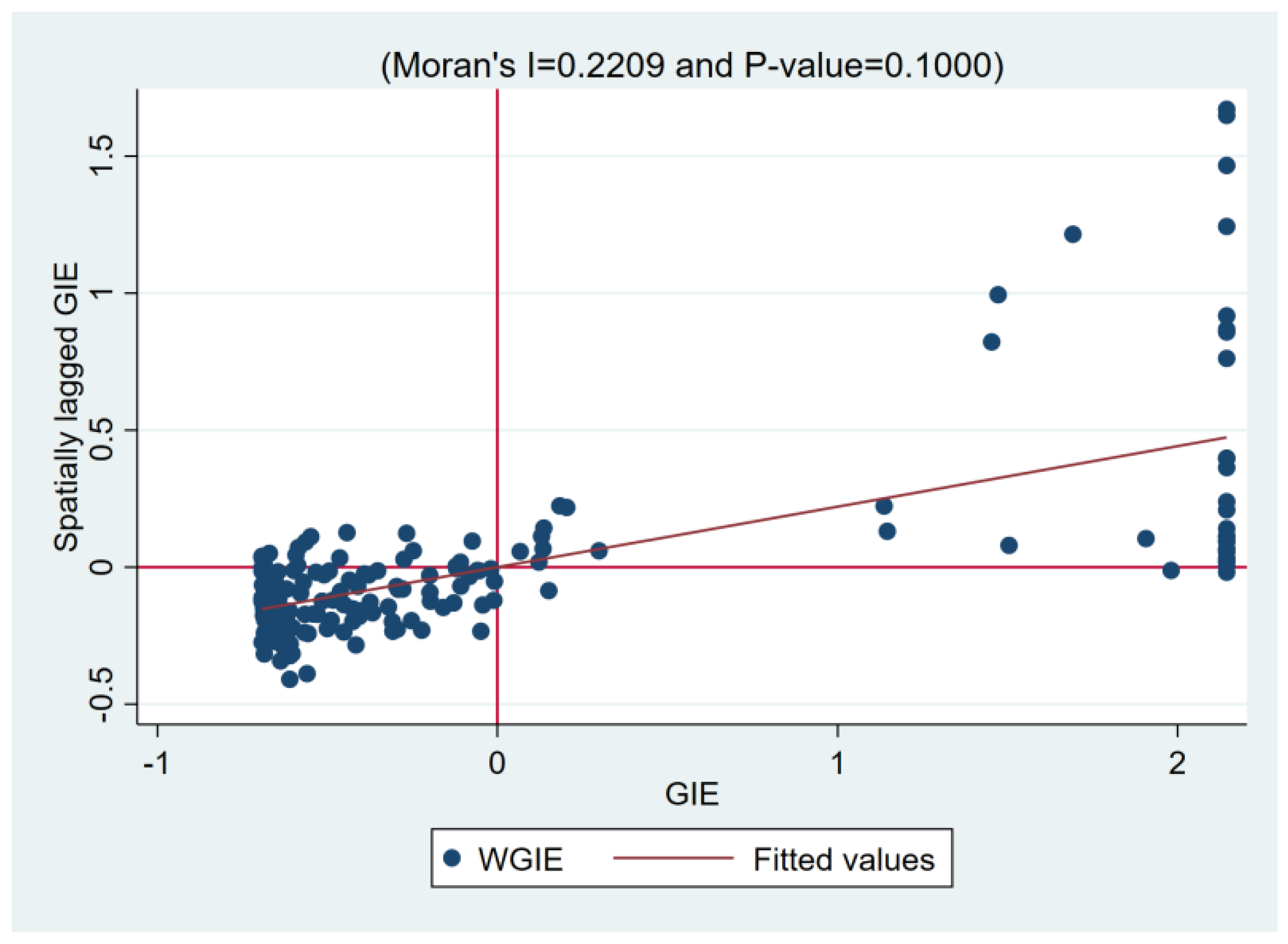
4.3. Analysis of the Spatial Spillover Effect
4.3.1. Baseline Regression
4.3.2. Robustness Test
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, B. Urban spatial structure and total-factor energy efficiency in Chinese provinces. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 126, 107662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Feng, C. The internal-structural effects of different types of environmental regulations on China’s green total-factor productivity. Energy Econ. 2022, 113, 106246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Hao, Y.; Ren, S. How do environmental regulation and environmental decentralization affect green total factor energy efficiency: Evidence from China. Energy Econ. 2020, 91, 104880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, S. The Impact of the ‘Environmental Protection Vertical Reform’ Policy on Urban Economic Green Transformation from the Perspective of Environmental Decentralization. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2024, 34, 47–58. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Wang, Z. The effects of climate policy on corporate technological upgrading in energy intensive industries: Evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 3748–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baixun, W.; Wenjuan, Z. Interplay of renewable energy investment efficiency, shareholder control and green financial development in China. Renew. Energy 2022, 199, 192–203. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Wu, J.; Zhang, B. Environmental Regulation, Emissions and Productivity: Evidence from Chinese Cod-E-mitting Manufacturers. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2018, 92, 54–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.E.; van der Linde, C. Toward a New Conception of the Environment-Competitiveness Relationship. J. Econ. Perspect. 1995, 9, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Zhao, X.; Shang, Y. The impact of low-carbon city construction on ecological efficiency: Empirical evidence from quasi-natural experiments. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 157, 104777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Zhu, J. Impact of energy saving and emission reduction policy on urban sustainable development: Empirical evidence from China. Appl. Energy 2019, 239, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, K.; He, F. Does Public Environmental Attention Improve Green Investment Efficiency?—Based on the Perspective of Environmental Regulation and Environmental Responsibility. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubashkina, Y.; Galeotti, M.; Verdolini, E. Environmental regulation and competitiveness: Empirical evidence on the Porter Hypothesis from European manufacturing sectors. Energy Policy 2015, 83, 288–300. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.; Wang, H.; Kuai, Y. Environmental regulation and green innovation: Evidence from heavily polluting firms in China. Financ. Res. Lett. 2023, 53, 103624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbera, A.J.; McConnell, V.D. The impact of environmental regulations on industry productivity: Direct and indirect effects. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 1990, 18, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, B.; Wang, B.; Du, M.; Zhang, N. Does the SO2 emissions trading scheme encourage green total factor productivity? An empirical assessment on China’s cities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 6375–6388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, L.; Guo, P.; Pan, G.Q. The effect of mandatory environmental regulation on green development efficiency: Evidence from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 9782–9792. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.; Jin, G.; Cheng, Z. The Economic Effects of Environmental Regulation: ‘Emission Reduction’ or ‘Efficiency Enhancement’. Stat. Res. 2019, 36, 88–100. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, R.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, J. Different types of environmental regulations and heterogeneous influence on “green” productivity: Evidence from China. Ecol. Econ. 2017, 132, 104–112. [Google Scholar]
- Song, M.; Zhao, X.; Shang, Y.; Chen, B. Realization of green transition based on the anti-driving mechanism: An analysis of environmental regulation from the perspective of resource dependence in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134317. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, Y. Environmental regulations, energy and environment efficiency of China’s metal industries: A provincial panel data analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 280, 124437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Zheng, Y. The Impact of Environmental Regulation Intensity on Total Factor Energy Efficiency in Chinese Industry: An Empirical Study Based on Panel Data from 30 Provinces from 2003 to 2016. Manag. Rev. 2019, 31, 40–48. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Guo, J. The Impact and Mechanism of Environmental Regulation and Industrial Agglomeration on Energy Efficiency: A Perspective Based on Spatial Effects. J. Nat. Resour. 2022, 37, 3234–3251. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Guo, H.; Zhang, B.; Bu, M. Westward movement of new polluting firms in China: Pollution reduction mandates and location choice. J. Comp. Econ. 2017, 45, 119–138. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, M.; Dhaliwal, D.; Zhang, Y. Does investment efficiency improve after the disclosure of material weaknesses in internal control over financial reporting? J. Account. Econ. 2013, 56, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, K.; Zhao, H.; Wang, L. Director and Officer Liability Insurance and Green Innovation in Manufacturing Enterprises: Based on the Mediating Effect of Internal Control. East China Econ. Manag. 2022, 36, 119–128. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Zhang, J. Can Voluntary Disclosure of Internal Control Audit Fees Enhance the Independence of Internal Control Audits? Audit. Res. 2017, 197, 90–96. [Google Scholar]
- Boulhaga, M.; Bouri, A.; Elamer, A.A.; Ibrahim, B.A. Environmental, social and governance ratings and firm performance: The moderating role of internal control quality. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2023, 30, 134–145. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Q.; Goh, B.W.; Kim, J.B. Internal control and operational efficiency. Contemp. Account. Res. 2018, 35, 1102–1139. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, H. Does internal control affect corporate environmental responsibility? Evidence from China. Int. J. Emerg. Mark. 2024; ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wu, S. Effects of local and civil environmental regulation on green total factor productivity in China: A spatial Durbin econometric analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 153, 342–353. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.L.; Tian, P. How does heterogeneous environmental regulation affect net carbon emissions: Spatial and threshold analysis for China. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 330, 117161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, H.; Chen, Y.; Gong, Q. Polluting thy neighbor: Unintended consequences of China’s pollution reduction mandates. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2016, 76, 86–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland, B.R.; Taylor, M.S. Trade, Growth and the Environment. J. Econ. Lit. 2004, 42, 7–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Yang, Q.; Ni, Q.; Kim, Y. The impact of environmental regulation on employment: An empirical study of China’s Two Control Zone policy. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 26472–26487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, H. Regulatory Officials’ Incentives and Behavioral Preferences: A New Explanation for the Failure of Environmental Regulation Under a Lack of Independence. Manag. World 2016, 2, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Z.; Fu, J. Economic growth, environmental sustainability and China mayors’ promotion. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Du, H.; Zhang, Z.; Mi, Z.; Guan, D.; Zuo, J. Carbon transfer within China: Insights from production fragmentation. Energy Econ. 2020, 86, 104647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Qi, L.; He, J. Analysis of the Spatiotemporal Evolution and Spatial Spillover Effects of Green Investment Efficiency in Chinese Enterprises. Ecol. Econ. 2024, 40, 75–85. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q. Fixed-Effect Panel Threshold Model using Stata. Stata J. Promot. Commun. Stat. Stata 2015, 15, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, L.; Li, J.; Zhong, S. Sulfur dioxide (SO2) emission reduction and its spatial spillover effect in high-tech industries: Based on panel data from 30 provinces in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 31340–31357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.D.; Wu, H.T.; Ren, S.Y.; Ran, Q.Y.; Zhang, J.N. Does the development of the internet contribute to air pollution control in China? Mechanism discussion and empirical test. Struct. Change Econ. Dynam. 2021, 56, 207–224. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.; Sun, S.; Cao, W.; Bu, B.; Xue, R. Make every dollar count: The impact of green credit regulation on corporate green investment efficiency. Energy Econ. 2024, 130, 107307. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, L.; Li, X. The Impact of Green Securities on Corporate Green Investment Efficiency: Evidence from Listed Companies in Six High-Energy-Consumption Industries. Financ. Regul. Res. 2020, 12, 78–97. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Chen, Y. Environmental Regulation, Corporate Bargaining Power, and Green Total Factor Productivity. Financ. Trade Econ. 2019, 40, 144–160. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.; Guo, Y.; Cao, J.; Xu, J. Local Government Financing Platform Debt and Environmental Pollution Control. Manag. World 2022, 38, 96–118. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, S.; Tingting, Y.; Ming, Z. Research on the impact of environmental regulation on enterprise technology innovation-an empirical analysis based on Chinese provincial panel data. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 21835–22184. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, N.; Liu, F.C. Can intensive environmental regulation promote technological innovation? Porter hypothesis reexamined. Chin. Soft Sci. 2012, 4, 49–59. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, G.; Li, L.; Wu, D. Environmental Regulation, Industry Attributes, and Corporate Environmental Investment. Account. Res. 2013, 6, 83–89+96. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Song, X.; Wang, H. Informal Institutions, Hometown Identity, and Corporate Environmental Governance. Manag. World 2017, 3, 76–94+187–188. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Wang, M.; Ma, Y. Debt Contracts and Overinvestment: “Governance Distortion” or “Empire Building”. J. Shanxi Univ. Financ. Econ. 2018, 40, 113–124. [Google Scholar]
- Mahla, D.; Agarwal, S.; Mathur, T. A novel fuzzy non-radial data envelopment analysis: An application in transportation. RAIRO Oper. Res. 2021, 55, 2189–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendell, B.L. Environmental investment decisions of family firms—An analysis of competitor and government influence. Bus. Strat. Environ. 2021, 31, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, D. Green investment efficiency in the Chinese energy sector: Overinvestment or underinvestment? Energy Policy 2022, 160, 112694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Tang, Y.; Liu, Y. How Does Environmental Tax Influence the Scale and Efficiency of Green Investment among China’s Heavily Polluting Enterprises? Sustainability 2023, 15, 15021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.-R.; Wu, T.-F.; Ren, Y.-J.; Liu, X.-Y.; Yuan, X. The impact of environmental regulation on green investment efficiency of thermal power enterprises in China-based on a three-stage exogenous variable model. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidi, K.; Hammami, S. The impact of CO2 emissions and economic growth on energy consumption in 58 countries. Energy Rep. 2015, 1, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, C.; Xie, Z.; Li, Z. Market supervision, innovation offsets and energy efficiency: Evidence from environmental pollution liability insurance in China. Energy Policy 2022, 171, 113267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Li, S. The Emission Trading System and Energy Utilization Efficiency: Measurement and Empirical Analysis of Prefectural-Level Cities and Above. China Ind. Econ. 2020, 9, 5–23. [Google Scholar]
- Umanskaya, V.I.; Barbier, E.B. Can Rich Countries Become Pollution Havens? Rev. Int. Econ. 2008, 16, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, K.; Zhou, L. Local Government Competition, Vertical Environmental Regulation, and Pollution Rebound Effect. Econ. Res. 2020, 55, 35–49. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Bu, H.; Liu, F. Internal Control and Enterprise Green Innovation. Energies 2022, 15, 2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Wei, X.; Wang, W. Does Enterprise Internal Control Improve Environmental Performance—Empirical Evidence from China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Y.; Wang, E.; Qiu, Y.; Möst, D. Impact assessment of population migration on energy consumption and carbon emissions in China: A spatial econometric investigation. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2022, 93, 106744. [Google Scholar]
- Du, L.; Tian, M.; Cheng, J.; Chen, W.; Zhao, Z. Environmental regulation and green energy efficiency: An analysis of spatial Durbin model from 30 provinces in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 67046–67062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, F. Environmental Regulation and Spatial Spillover Effect of Green Technology Innovation: An Empirical Study on the Spatial Durbin Model. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, M. The Spatial Spillover Effects of Environmental Regulation on China’s Industrial Green Growth Performance. Energies 2019, 12, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Sun, S. The Spatial Spillover Effect of Environmental Regulation and Technological Innovation on Industrial Carbon Productivity in China: A Two-Dimensional Structural Heterogeneity Analysis. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 5613525. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Hu, L. Does Environmental Regulation Drive Economic Growth through Technological Innovation: Application of Nonlinear and Spatial Spillover Effect. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Bai, T.; Fan, Y.; Liu, Z. Environmental, social, and governance performance and enterprise sustainable green innovation: Evidence from China. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2024, 31, 3633–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, G.; Jiahui, L. Media attention, green technology innovation and industrial enterprises’ sustainable development: The moderating effect of environmental regulation. Econ. Anal. Policy 2023, 79, 873–889. [Google Scholar]

| Variable Type | Variable | Description of Variables |
|---|---|---|
| Firm level control variable | Size | Natural logarithm of total assets of the enterprise at the end of the year |
| Leverage | Gearing ratio = total liabilities/total assets | |
| GIscale | Ratio of new green investments made by firms in the sample year to total assets at the end of the year | |
| Opportunity | Tobin’s Q = market capitalization/total assets | |
| LSR | Shareholding of the first largest shareholder in the enterprise | |
| BDsize | Total number of directors in the enterprise | |
| Duality | Dummy variable that takes the value of 1 if the chairman and the general manager of the enterprise are the same person, and 0 otherwise | |
| External environment control variable | PGDP | Gross regional product/average total population of the province (autonomous region or municipality directly under the central government) to which the enterprise belongs |
| EQRank | The annual average concentration of PM2.5 in the province (autonomous region or municipality) to which the enterprise belongs | |
| lnIEN | Natural logarithm of the total number of industrial enterprises in the province (autonomous region or municipality directly under the central government) to which the enterprise belongs |
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Std. Dev. | 0.3806 | 0.3478 | 0.2728 | 0.2928 | 0.3491 | 0.3515 |
| Mean | 0.3659 | 0.2871 | 0.2172 | 0.2500 | 0.3320 | 0.2462 |
| Median | 0.1803 | 0.1308 | 0.1090 | 0.1387 | 0.1440 | 0.0833 |
| Green Investment Efficiency Pareto Optimal Number of Firms | 42 | 31 | 11 | 17 | 30 | 26 |
| Optimal Percentage | 23.20% | 17.13% | 6.08% | 9.39% | 16.57% | 14.36% |
| Obs | 181 | 181 | 181 | 181 | 181 | 181 |
| Threshold Variable | Threshold Number | F-Value | p-Value | BS | Critical Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1% | 5% | 10% | |||||
| EN | Single | 91.81 *** | 0.000 | 300 | 13.265 | 9.596 | 8.448 |
| Double | 290.12 *** | 0.000 | 300 | 61.056 | 11.220 | 9.255 | |
| Triple | 23.48 | 0.350 | 300 | 289.876 | 89.238 | 47.311 | |
| EN × ICQ | Single | 14.98 *** | 0.000 | 300 | 5.466 | 3.733 | 2.791 |
| Double | 181.83 *** | 0.000 | 300 | 13.105 | 10.388 | 7.676 | |
| Triple | 9.49 ** | 0.050 | 300 | 14.609 | 9.221 | 6.868 | |
| Regression Coefficient | Regression Coefficient | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| EN (EN ≤ 3.9842) | −0.0218 ** (0.0089) | EN × ICQ (EN × ICQ ≤ −0.397) | −0.00747 *** (0.0028) |
| EN (3.9842 < EN ≤ 4.7055) | 0.1369 *** (0.0085) | EN × ICQ (−0.397 < EN × ICQ ≤ −0.027) | 0.1263 *** (0.00836) |
| EN (EN > 4.7055) | −0.00925 *** (0.00219) | EN × ICQ (−0.027 < EN × ICQ ≤ 0.17) | 0.0362 *** (0.0129) |
| EN × ICQ (EN × ICQ > 0.17) | −0.00863 *** (0.00216) | ||
| Controls | Yes | Controls | Yes |
| _cons | 3.4972 ** (1.1847) | _cons | 4.649 *** (1.2124) |
| Year | Moran’s Index | Z | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 0.143 *** | 4.853 | 0.000 |
| 2018 | 0.151 *** | 5.118 | 0.000 |
| 2019 | 0.251 *** | 8.455 | 0.000 |
| 2020 | 0.194 *** | 6.547 | 0.000 |
| 2021 | 0.162 *** | 5.486 | 0.000 |
| 2022 | 0.221 *** | 7.425 | 0.000 |
| Matrix: The Economic Weight Matrix | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Wald test (lag) | 11.78 | Wald test (error) | 11.23 |
| LR test (lag) | 8.92 | LR test (error) | 2.49 |
| Spatial fixed effect | 42.36 *** | Time fixed effect | 433.59 *** |
| Hausman test | 37.66 *** | ||
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAR | SDM | SEM | FE | |
| EN | −0.00970 *** (0.00234) | −0.00914 *** (0.00338) | −0.00918 *** (0.00221) | −0.00920 *** (0.00248) |
| Size | −0.157 *** (0.0394) | −0.179 *** (0.0488) | −0.151 *** (0.0382) | −0.154 *** (0.0419) |
| Leverage | 0.168 (0.130) | 0.360 ** (0.168) | 0.154 (0.125) | 0.175 (0.138) |
| LSR | −0.00112 (0.00239) | 0.00238 (0.00327) | −0.00128 (0.00230) | −0.000960 (0.00254) |
| Opportunity | 0.00557 (0.0135) | 0.00547 (0.0161) | 0.00558 (0.0131) | 0.00553 (0.0144) |
| BDsize | 0.0105 ** (0.00512) | 0.0102 (0.00666) | 0.0101 ** (0.00493) | 0.0101 * (0.00544) |
| Duality | −0.0303 (0.0267) | −0.0591 (0.0367) | −0.0259 (0.0252) | −0.0298 (0.0284) |
| EQRank | −0.0271 *** (0.00964) | −0.0160 (0.0127) | −0.0264 *** (0.00918) | −0.0253 ** (0.0102) |
| PGDP | 1.76 × 10−6 (1.88 × 10−6) | 1.13 × 10−6 (2.48 × 10−6) | 1.66 × 10−6 (1.80 × 10−6) | 1.62 × 10−6 (1.99 × 10−6) |
| lnIEN | −0.0541 (0.0690) | −0.120 (0.0872) | −0.0460 (0.0669) | −0.0529 (0.0734) |
| GIscale | −0.231 (0.908) | 0.471 (1.079) | −0.271 (0.884) | −0.00920 *** (0.00248) |
| W*EN | −0.000206 (0.0107) | |||
| Spa-rho | −0.232 ** (0.104) | −0.281 *** (0.109) | ||
| lambda | −0.246 ** (0.107) | |||
| sigma2_e | 0.0753 *** (0.00419) | 0.0757 *** (0.00426) | 0.0757 *** (0.00426) | |
| Area/Year fixed effect | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| R-squared | 0.006 | 0.000 | 0.006 | 0.080 |
| Number of IDs | 181 | 181 | 181 | 181 |
| Variable | Direct Effect | Indirect Effect | Total Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| EN | −0.00930 *** (0.00225) | 0.00141 ** (0.000676) | −0.00789 *** (0.00198) |
| Controls | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Observations | 1086 | 1086 | 1086 |
| Model 1 | Model 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Replace Spatial Weight Matrix | Replace Core Explanatory Variable | |
| EN | −0.00723 *** (0.00210) | 0.0277 *** (0.00959) |
| Size | −0.134 *** (0.0355) | −0.157 *** (0.0396) |
| Leverage | 0.259 ** (0.117) | 0.111 (0.129) |
| LSR | −0.000787 (0.00215) | −0.00124 (0.00240) |
| Opportunity | 0.0114 (0.0122) | 0.00742 (0.0135) |
| BDsize | 0.00994 ** (0.00461) | 0.00885 * (0.00514) |
| Duality | −0.0273 (0.0240) | −0.0268 (0.0268) |
| EQRank | −0.0152 * (0.00868) | −0.0293 *** (0.00964) |
| PGDP | 6.27 × 10−7 (1.69 × 10−6) | 2.23 × 10−6 (1.88 × 10−6) |
| lnIEN | −0.0259 (0.0621) | 0.0442 (0.0668) |
| GIscale | −0.639 (0.817) | −0.323 (0.910) |
| Spa-rho | 0.578 *** (0.0499) | −0.221 ** (0.103) |
| sigma2_e | 0.0609 *** (0.00265) | 0.0756 *** (0.00421) |
| Direct (EN) | −0.00754 *** (0.00220) | 0.0267 *** (0.00921) |
| Indirect (EN) | −0.00972 *** (0.00340) | −0.00389 * (0.00226) |
| Total (EN) | −0.0173 *** (0.00531) | 0.0228 *** (0.00796) |
| Area/Year fixed effect | Yes | Yes |
| R-squared | 0.006 | 0.015 |
| Observations | 1086 | 1086 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, L.; Zhang, R. Environmental Regulation and Green Investment Efficiency: Threshold and Spatial Spillover Analysis for China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2934. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17072934
Dai L, Zhang R. Environmental Regulation and Green Investment Efficiency: Threshold and Spatial Spillover Analysis for China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(7):2934. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17072934
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Lixin, and Ruyue Zhang. 2025. "Environmental Regulation and Green Investment Efficiency: Threshold and Spatial Spillover Analysis for China" Sustainability 17, no. 7: 2934. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17072934
APA StyleDai, L., & Zhang, R. (2025). Environmental Regulation and Green Investment Efficiency: Threshold and Spatial Spillover Analysis for China. Sustainability, 17(7), 2934. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17072934






