Spatiotemporal Analysis of Heavy Metal Pollution and Risks in Soils from a Shut-Down Electroplating Plant
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
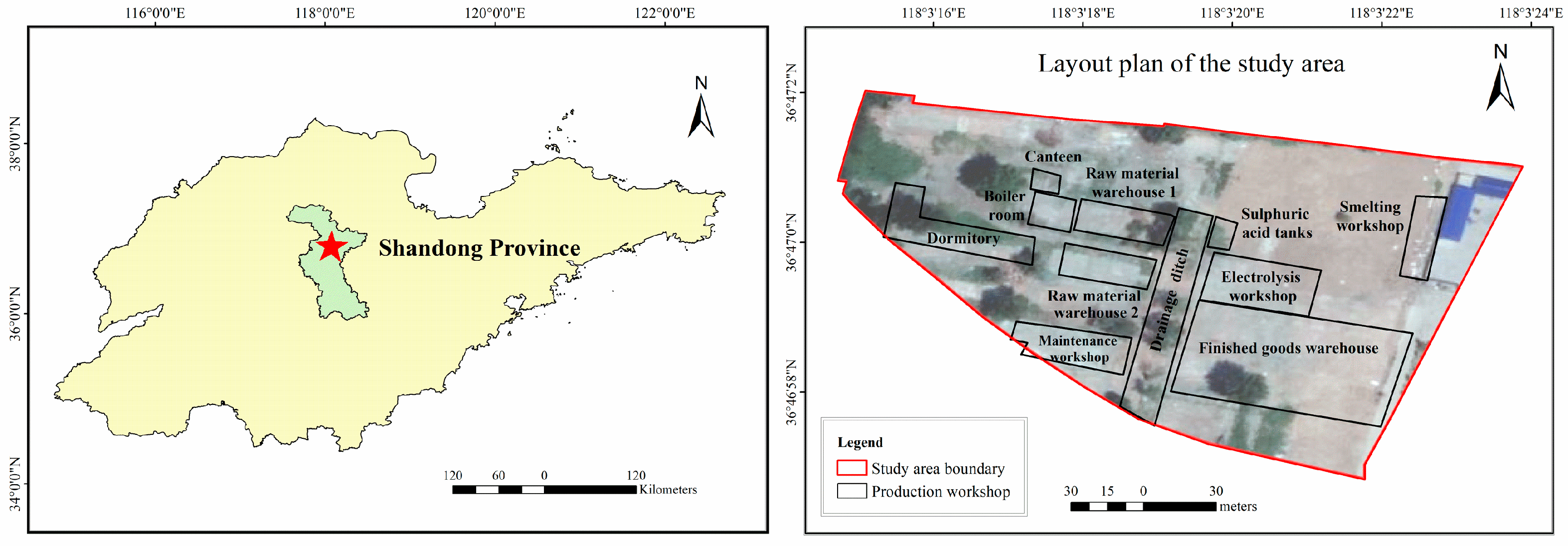
2.1. Study Area
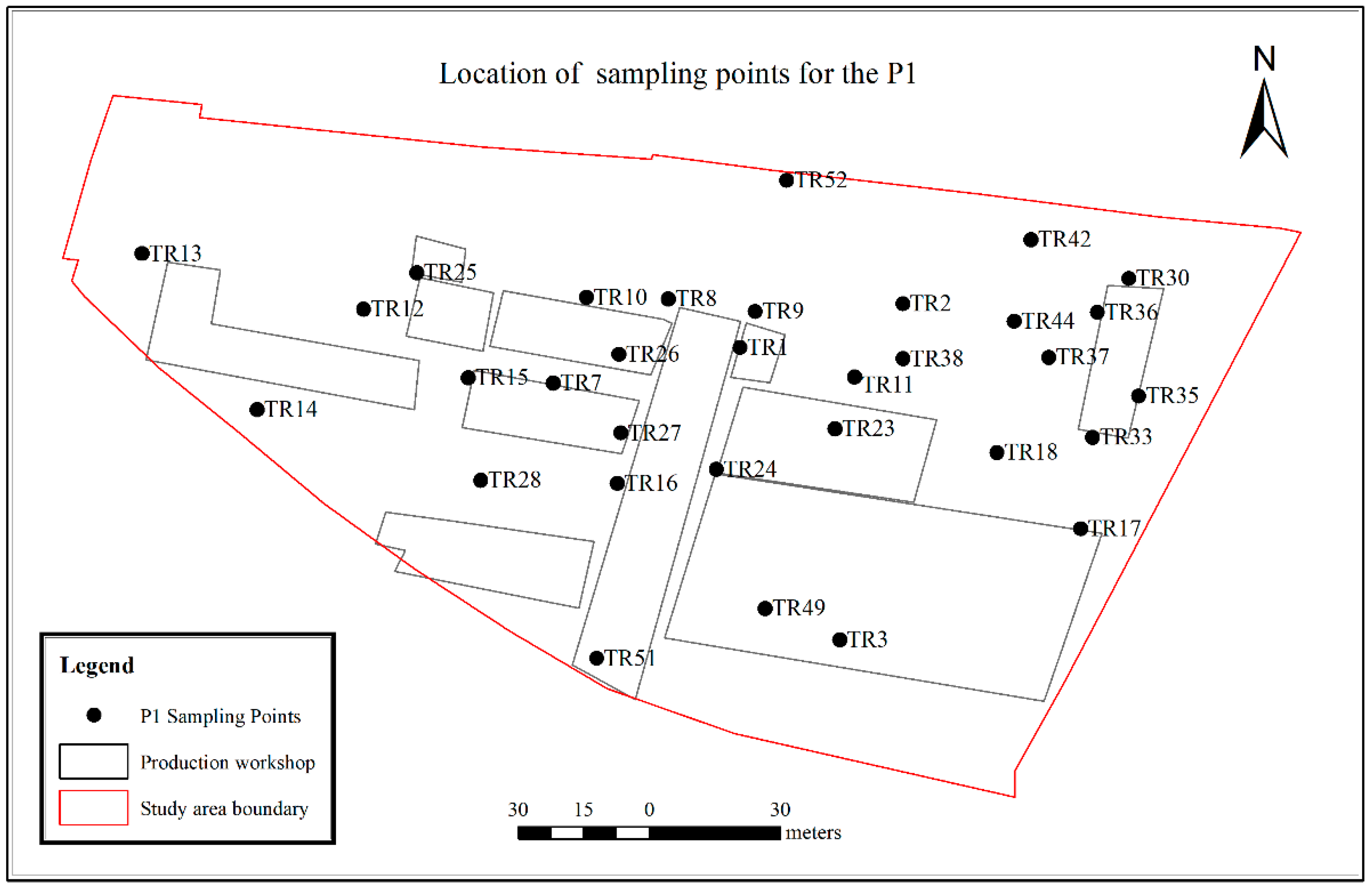
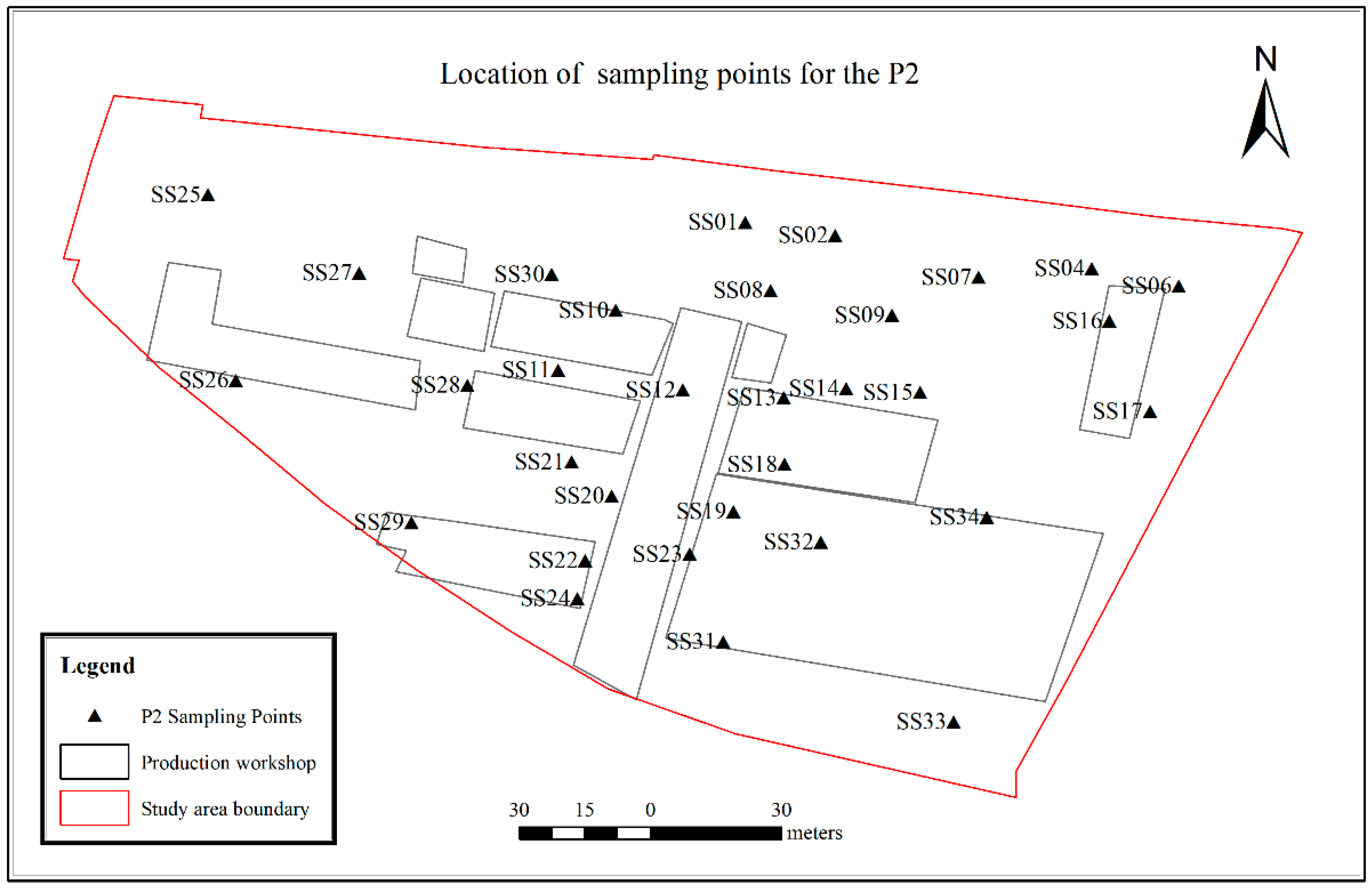
2.2. Sampling and Programs
2.3. Evaluation Methods
2.3.1. Nemerow Pollution Index
2.3.2. Ecological Risk Assessment
2.3.3. Human Health Risk Model
2.4. Hydrus Simulation
- (1)
- Model parameters
- (2)
- Grid division, observation points, and boundary condition
3. Results and Discussion
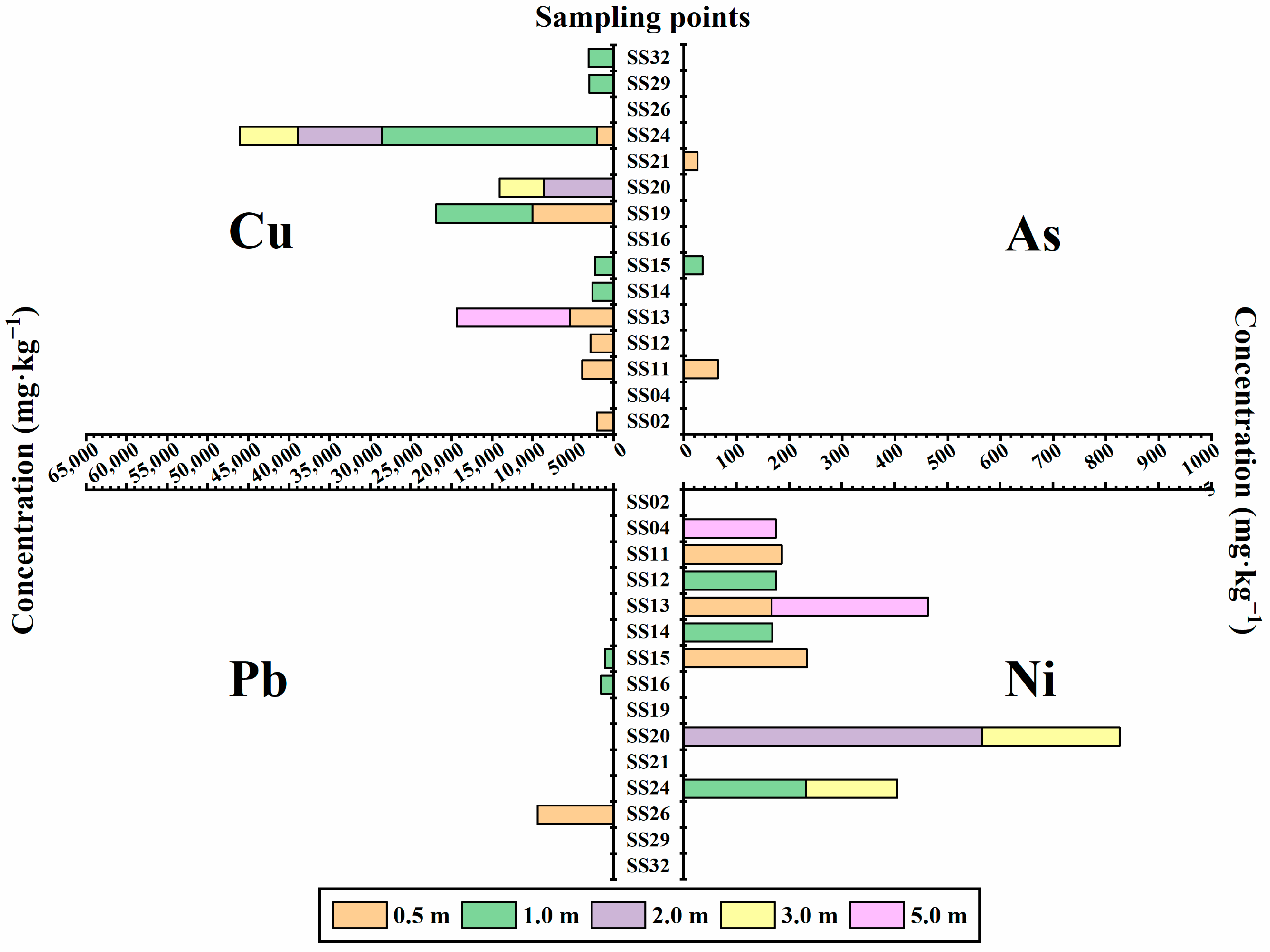
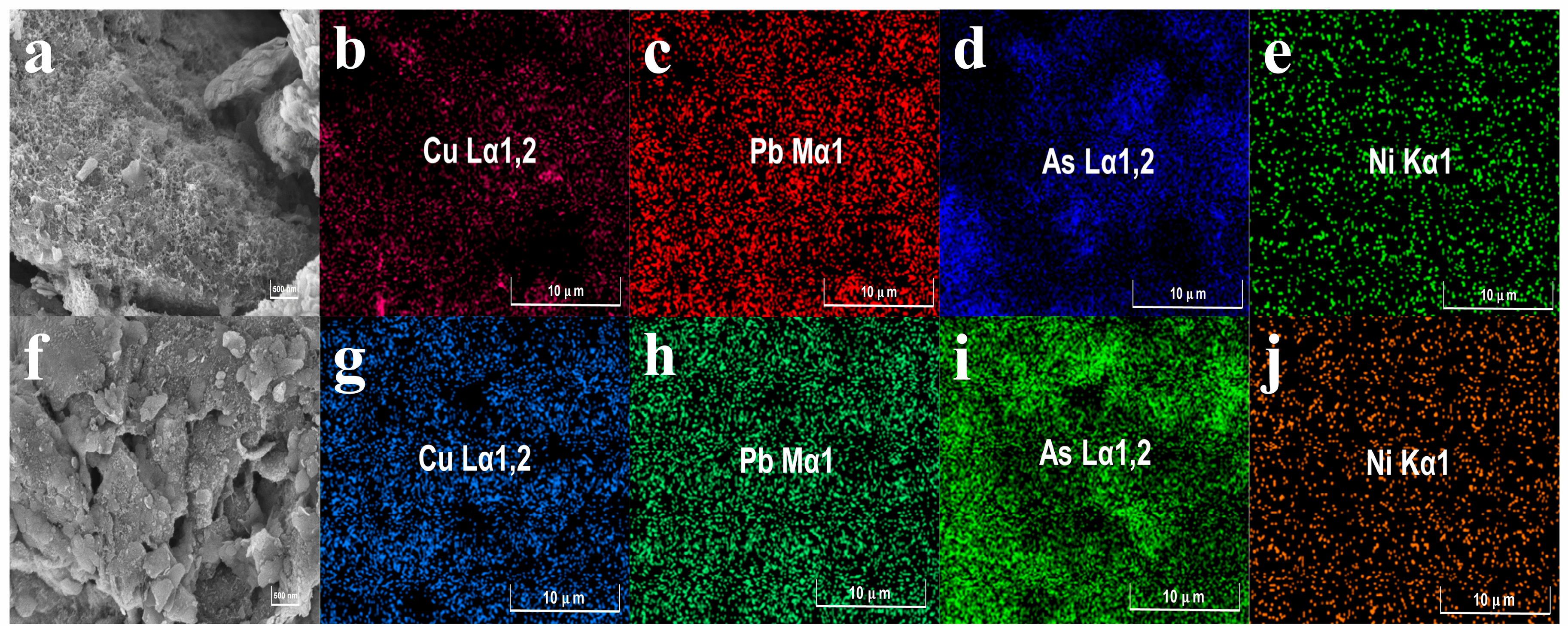
3.1. Heavy Metal Pollution Status in Soil
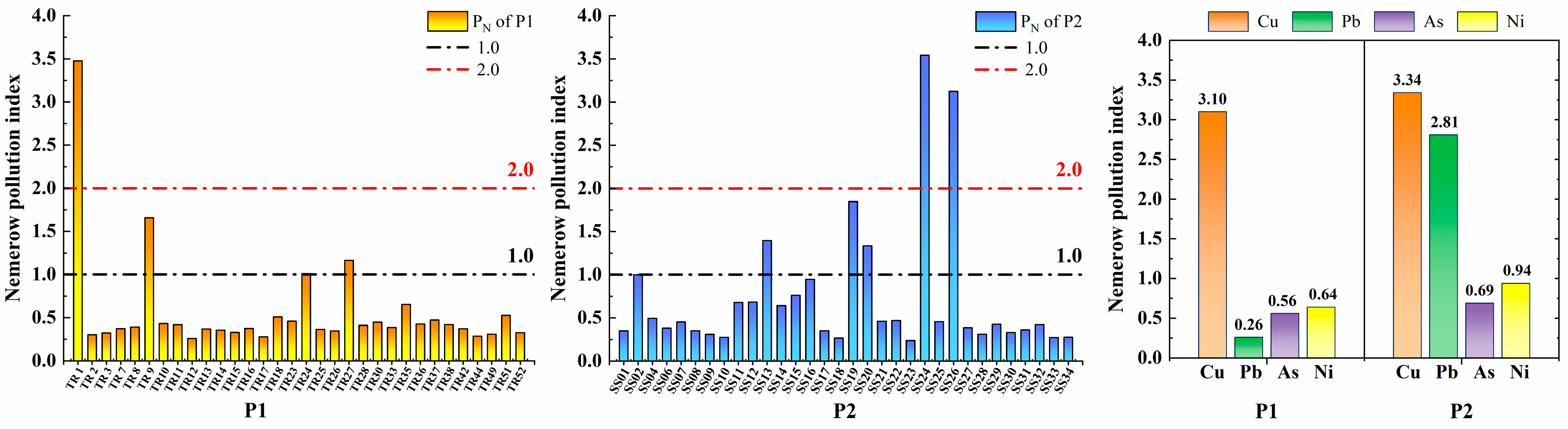
3.2. Soil Environmental Quality Assessment
3.3. Risk Assessment
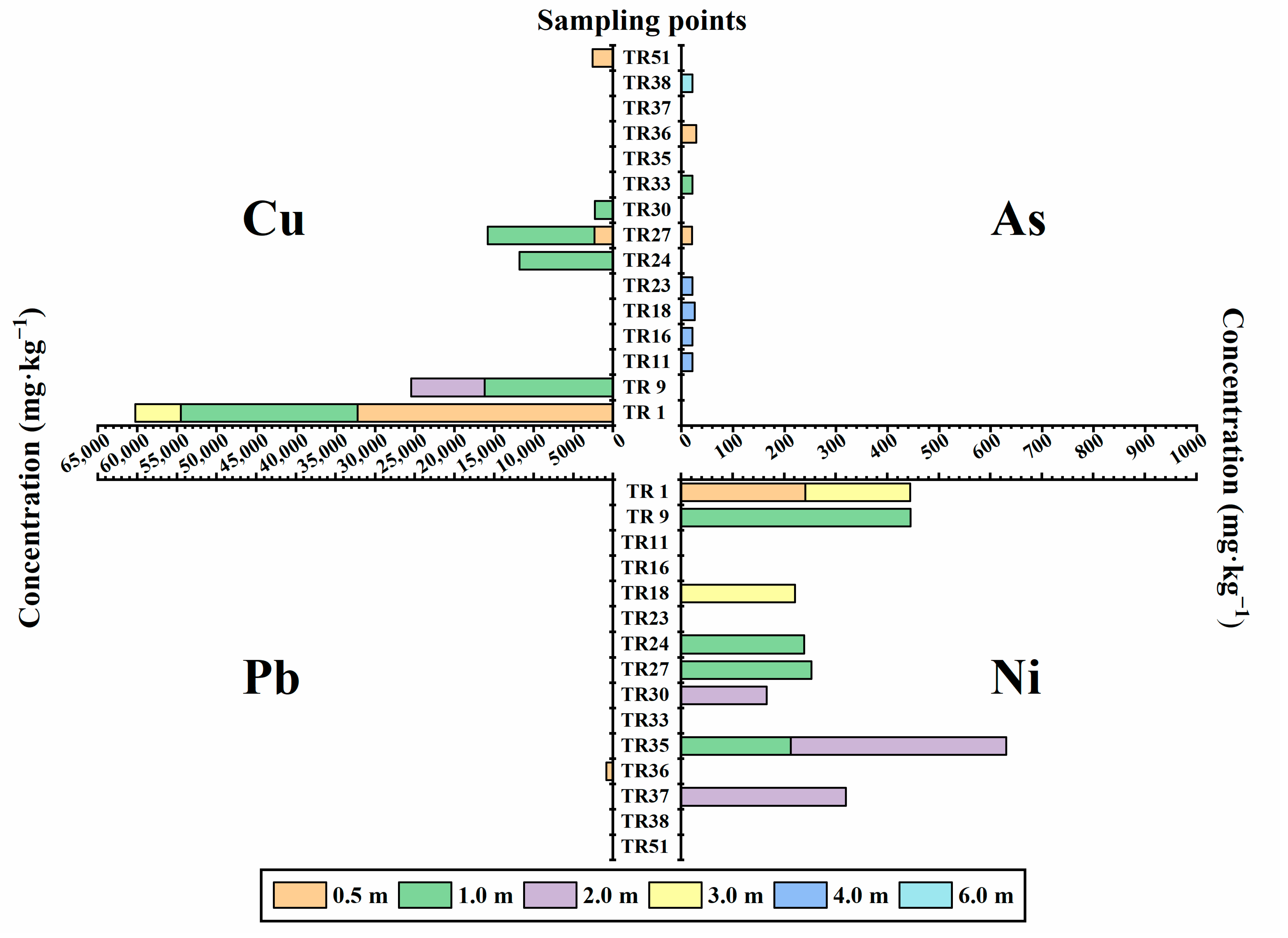
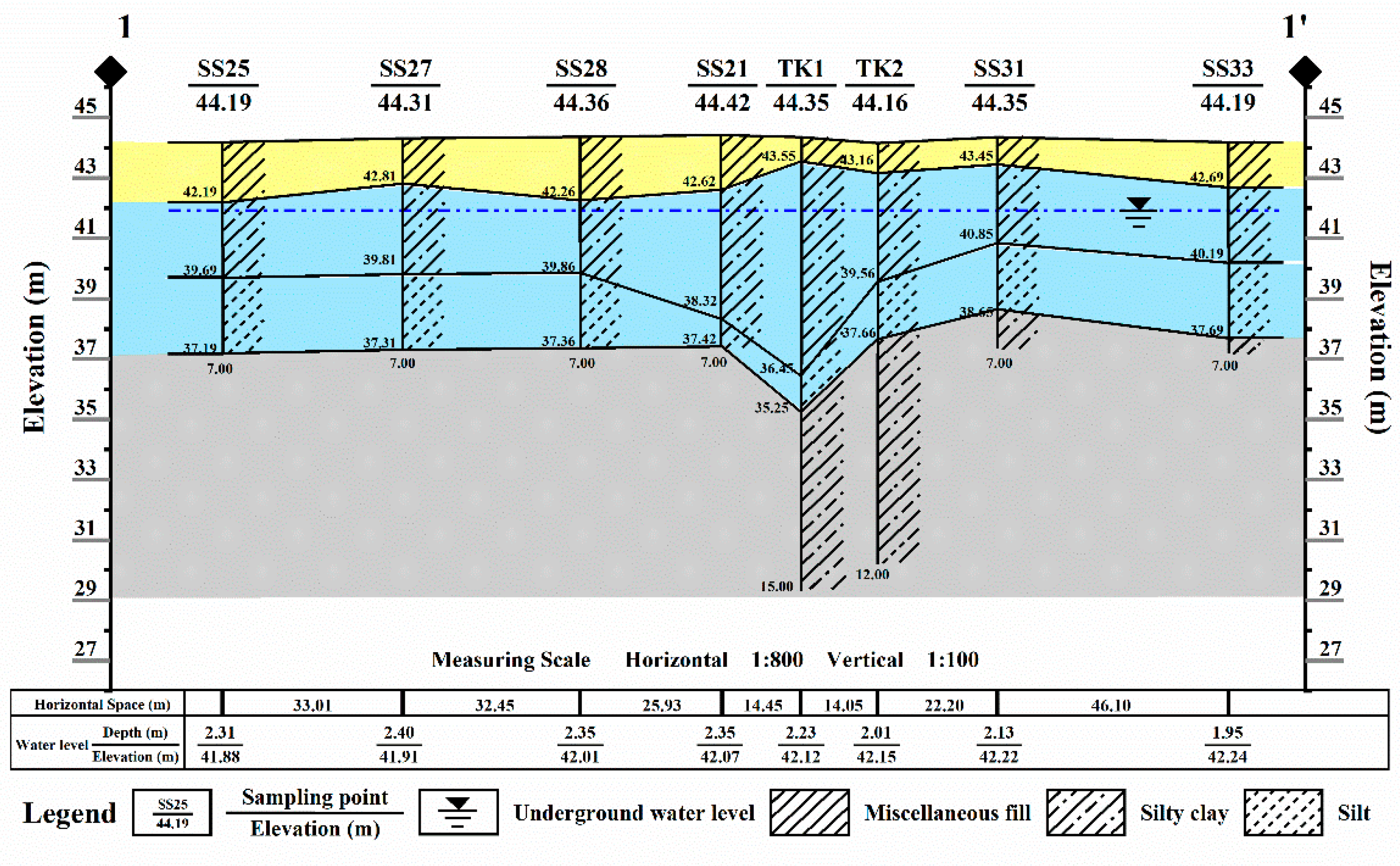
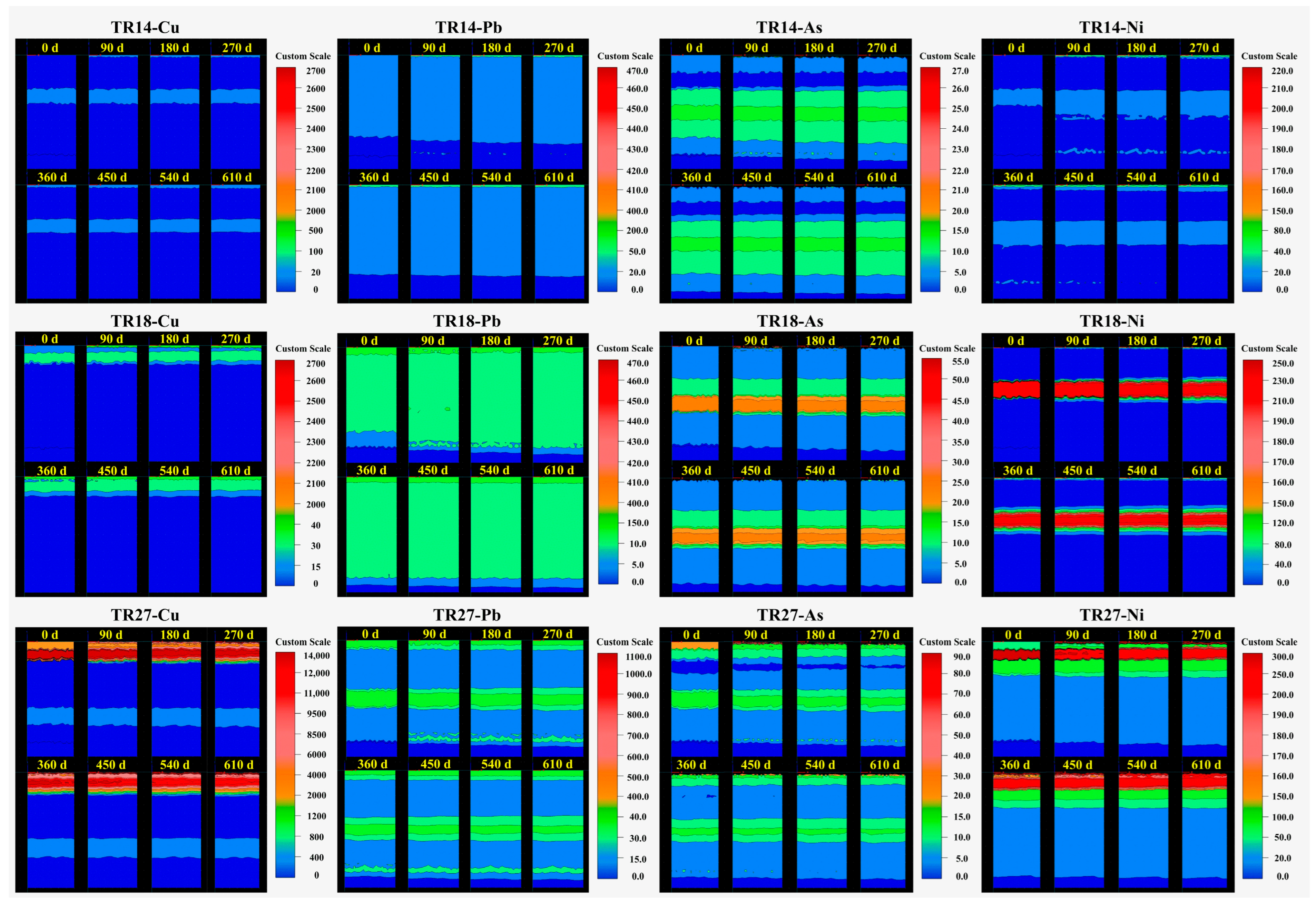
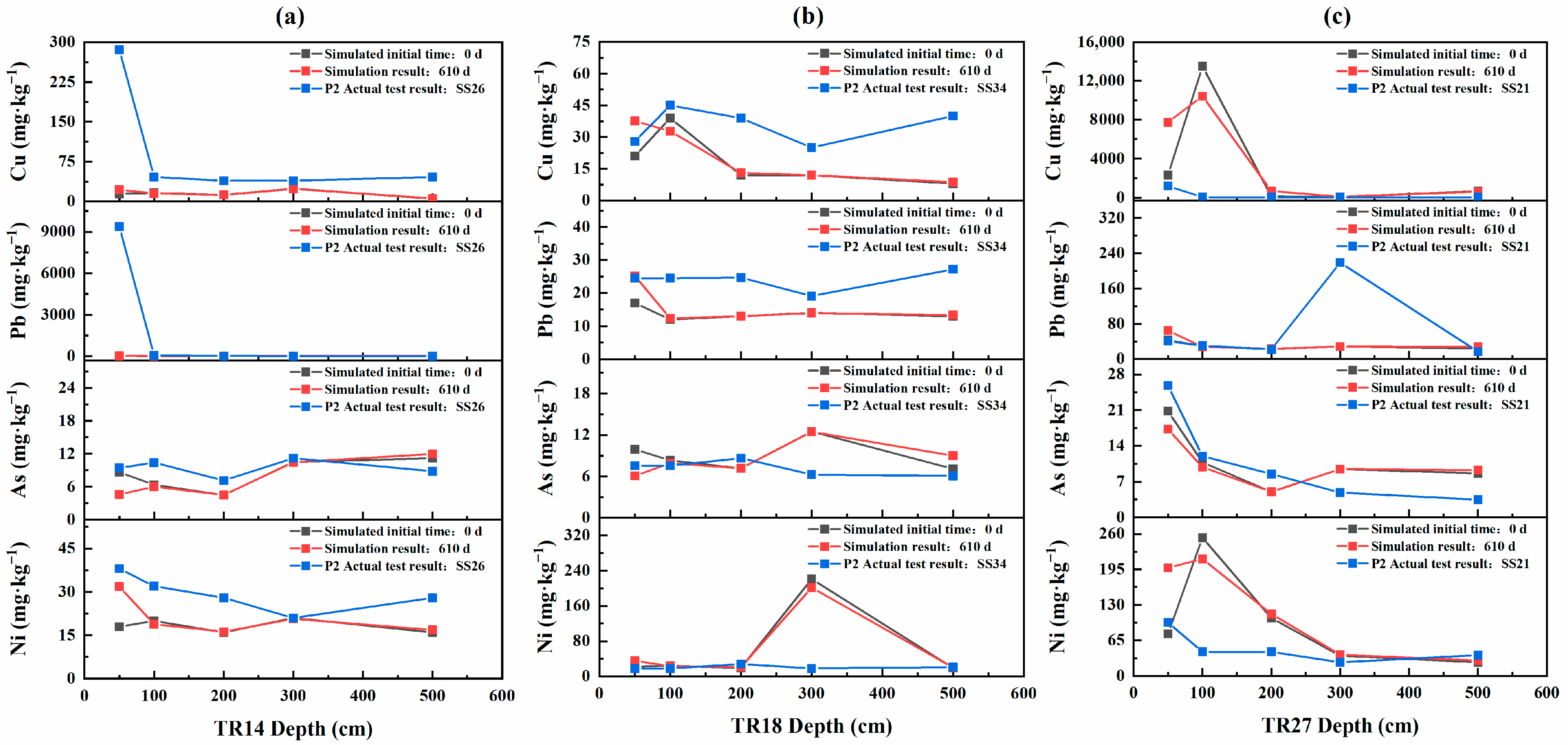
3.4. Migration of Heavy Metals in Soil
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gan, T.; Zhao, H.; Ai, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wen, Y.; Tian, L.; Mipam, T.D. Spatial Distribution and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Alpine Grasslands of the Zoige Basin, China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1093823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Chen, Y.; Yue, X.; Ren, D.; Liu, Y.; Yang, K. Identification and Hazard Analysis of Heavy Metal Sources in Agricultural Soils in Ancient Mining Areas: A Quantitative Method Based on the Receptor Model and Risk Assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 445, 130528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Yu, L.; Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Liu, T. Review of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution in China: Spatial Distribution, Primary Sources, and Remediation Alternatives. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 181, 106261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Chu, C.; Shao, C.; Ju, M.; Dai, E. Study of Integrated Risk Regionalisation Method for Soil Contamination in Industrial and Mining Area. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 83, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theocharopoulos, S.P.; Wagner, G.; Sprengart, J.; Mohr, M.-E.; Desaules, A.; Muntau, H.; Christou, M.; Quevauviller, P. European Soil Sampling Guidelines for Soil Pollution Studies. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 264, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocco, C.; Duro, I.; Di Rosa, S.; Fagnano, M.; Fiorentino, N.; Vetromile, A.; Adamo, P. Composite vs. Discrete Soil Sampling in Assessing Soil Pollution of Agricultural Sites Affected by Solid Waste Disposal. J. Geochem. Explor. 2016, 170, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, P.; Dong, N.; Lei, M.; Yang, S.; Gou, Y. An Effective Method for Determining the Optimal Sampling Scale Based on the Purposes of Soil Pollution Investigations and the Factors Influencing the Pollutants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 418, 126296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Han, Q.; Gui, C.; Cao, J.; Liu, Y.; He, X.; He, Y. Differences in the Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metals between Newly Built and Original Parks in Jiaozuo, Henan Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 676, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB36600-2018; Soil Environmental Quality Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Development Lland. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Chai, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Ma, L.; Cheng, Z.; Su, L. Pollution Characteristics, Spatial Distributions, and Source Apportionment of Heavy Metals in Cultivated Soil in Lanzhou, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; An, M.; Song, Y.; Fu, G.; Ruan, W.; Wu, D.; Li, X.; Yuan, K.; Wan, X.; Chen, Z.; et al. Soil Heavy Metals in Tropical Coastal Interface of Eastern Hainan Island in China: Distribution, Sources and Ecological Risks. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhu, K.; Cai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. Distribution and Ecological Risk Assessment of Arsenic and Some Trace Elements in Soil of Different Land Use Types, Tianba Town, China. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 102041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An Ecological Risk Index for Aquatic Pollution Control.a Sedimentological Approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Feng, X. Potential Ecological Risk and Zoning Control Strategies for Heavy Metals in Soils Surrounding Core Water Sources: A Case Study from Danjiangkou Reservoir, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 252, 114610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Chen, X.; Wei, W.; Li, T.; Yin, F.; Xu, L. Risk Assessment and Source Analysis of Heavy Metal Contamination in the Soil of the Juanshui River Mouth. Environ. Pollut. Bioavailab. 2023, 35, 2212127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Li, K.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xing, H.; Wei, M. Spatial Distribution and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Elements in Rock-Soil in the Mountainous Areas of Southwest China: A Case Study of Xichang. Geol. J. 2023, 58, 3866–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Gong, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.; Fu, Y.; Tang, S.; Ma, S. Spatial Distribution and Ecological Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metals in a Typical Volcanic Area: Influence of Parent Materials. Heliyon 2023, 9, e12993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Chen, M.; Zheng, X.; Chen, W. Determination of Tungsten’s Toxicity Coefficient for Potential Ecological Risk Assessment. Environ. Res. Commun. 2023, 5, 025003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Naushad, M.; Lima, E.C.; Zhang, S.; Shaheen, S.M.; Rinklebe, J. Global Soil Pollution by Toxic Elements: Current Status and Future Perspectives on the Risk Assessment and Remediation Strategies—A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 126039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ 25.3-2019; Technical Guidelines for Risk Assessment of Soil Contamination of Land for Construction. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Mallants, D.; Šimůnek, J.; van Genuchten, M.T.; Jacques, D. Simulating the Fate and Transport of Coal Seam Gas Chemicals in Variably-Saturated Soils Using HYDRUS. Water 2017, 9, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, D.R.; Van Genuchten, M.T.; Biggar, J.W. Water Flow and Solute Transport Processes in the Unsaturated Zone. Water Resour. Res. 1986, 22, 89S–108S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimůnek, J.; van Genuchten, M.T. Modeling Nonequilibrium Flow and Transport Processes Using HYDRUS. Vadose Zone J. 2008, 7, 782–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Šimůnek, J.; Mo, M.; Mccullough-Sanden, B.; Shahrokhnia, H.; Cherchian, S.; Wu, L. Assessing Salinity Leaching Efficiency in Three Soils by the HYDRUS-1D and -2D Simulations. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 194, 104342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, T.; Elkefafy, S.M.; Berndtsson, R.; Elkiki, M.; El-kharbotly, A.A. Heavy Metal Transport in Different Drip-Irrigated Soil Types with Potato Crop. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grecco, K.L.; de Miranda, J.H.; Silveira, L.K.; van Genuchten, M.T. HYDRUS-2D Simulations of Water and Potassium Movement in Drip Irrigated Tropical Soil Container Cultivated with Sugarcane. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 221, 334–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Tu, J.; Jin, Y.; Hua, M.; Wu, X.; Xu, W.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Su, Y.; Cai, L. Contamination Assessment and Source Identification of Heavy Metals in River Sediments in Nantong, Eastern China. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2018, 12, 373–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Tabelin, C.B.; Gao, W.; Tang, L.; Luo, X.; Ke, W.; Jiang, J.; Xue, S. Heterogeneous Distributions of Heavy Metals in the Soil-Groundwater System Empowers the Knowledge of the Pollution Migration at a Smelting Site. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, W.; Shi, W.; Cui, Y.; Chen, L.; Shao, J. Source Apportionment and Migration Characteristics of Heavy Metal(Loid)s in Soil and Groundwater of Contaminated Site. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 338, 122584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Jiang, L.; Wu, P.; Dang, Z.; Zhu, N.; Liu, Z.; Luo, H. Leaching Characteristics of Heavy Metals in Tailings and Their Simultaneous Immobilization with Triethylenetetramine Functioned Montmorillonite (TETA-Mt) against Simulated Acid Rain. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wu, Y.; Shu, J.; Wu, Z. Effect of Particulate Organic Matter Fractions on the Distribution of Heavy Metals with Aided Phytostabilization at a Zinc Smelting Waste Slag Site. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 253, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Y.; Zhang, B.; He, J.; Chen, C.; Liu, H. Dynamics of Vertical Vanadium Migration in Soil and Interactions with Indigenous Microorganisms Adjacent to Tailing Reservoir. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Li, F.; Jin, Z.; Yang, Y. Acidic Leaching of Potentially Toxic Metals Cadmium, Cobalt, Chromium, Copper, Nickel, Lead, and Zinc from Two Zn Smelting Slag Materials Incubated in an Acidic Soil. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 238, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Xing, R.; Zheng, Z.; Qiu, J.; Yang, L. Bacterial Community Structure and Diversity Responses to the Direct Revegetation of an Artisanal Zinc Smelting Slag after 5 Years. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 14773–14788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xing, R.; Yao, C.; Shu, J.; Wu, Z. Effects of Plant Litter Decomposition on Chemical and Microbiological Characteristics of Artisanal Zinc Smelting Slag Using Indigenous Methods. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 190, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majdalani, S.; Michel, E.; Di-Pietro, L.; Angulo-Jaramillo, R. Effects of Wetting and Drying Cycles on in Situ Soil Particle Mobilization. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2008, 59, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.K.; Bulicek, M.C.D.; Metge, D.W.; Harvey, R.W.; Ryan, J.N.; Boehm, A.B. Mobilization of Microspheres from a Fractured Soil during Intermittent Infiltration Events. Vadose Zone J. 2015, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Wu, Y.; Hu, S. Drying–Wetting Cycles Facilitated Mobilization and Transport of Metal-Rich Colloidal Particles from Exposed Mine Tailing into Soil in a Gold Mining Region along the Silk Road. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Y.J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, A.N. Quantitative Contributions of the Major Sources of Heavy Metals in Soils to Ecosystem and Human Health Risks: A Case Study of Yulin, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 164, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Hu, C.; Qin, Z.; Chen, J.; Huo, X.; Tao, Y. Ecological-Health Risks Assessment and Characteristic Pollutants Identification of Heavy Metals in the Soils of a Coking Plant in Production in Guangxi, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zhao, D.; Ren, F.; Huang, L. Spatiotemporal Variation of Soil Heavy Metals in China: The Pollution Status and Risk Assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 871, 161768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, C.; Song, Y.; Liu, F.; Yang, Z.; Kong, M. Characteristics of soil heavy metal pollution and health risk in Xiong’an New District. China Environ. Sci. 2021, 41, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Single Factor Pollution Index () | Pollution Index () | Class Of Pollution Risk |
|---|---|---|
| ≤ 0.7 | ≤ 0.7 | Clean (safe) |
| 0.7 < ≤ 1.0 | 0.7 < ≤ 1.0 | Still clean (warning threshold) |
| 1.0 < ≤ 2.0 | 1.0 < ≤ 2.0 | Low pollution |
| 2.0 < ≤ 3.0 | 2.0 < ≤ 3.0 | Moderate pollution |
| > 3.0 | > 3.0 | Heavy pollution |
| Category | Category | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ≤ 40 | Clean (safe) | ≤ 150 | Slight ecological risk |
| 40 < ≤ 80 | warning threshold | 150 < ≤ 300 | Moderate ecological risk |
| 80 < ≤ 160 | Low pollution | 300 < ≤ 600 | High ecological risk |
| 160 < ≤ 320 | Moderate pollution | > 600 | Very high ecological risk |
| > 320 | Severe pollution |
| Category | Value Range | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|
| Carcinogenic risk | 10−6 < CR < 10−4 | Within the acceptable range |
| CR > 10−4 | Exceeds human tolerance level | |
| Non-carcinogenic risk | HQ < 1 or HI < 1 | No non-carcinogenic risk |
| HQ > 1 or HI > 1 | Non-carcinogenic risk present |
| Water Flow Parameters | ||||||
| Layer | Qr (-) | Qs (-) | Alpha (1/cm) | n (-) | Ks (cm/d) | l (-) |
| Mixed layer of silty clay and miscellaneous fill | 0.07 | 0.36 | 0.005 | 1.09 | 0.48 | 0.5 |
| Silt | 0.034 | 0.46 | 0.016 | 1.37 | 6 | 0.5 |
| Silty clay | 0.07 | 0.36 | 0.005 | 1.09 | 0.48 | 0.5 |
| Air-entry value of −2 cm | ||||||
| Solute Transport Parameters | ||||||
| Layer | Bulk. D. (g/cm3) | Disp. L. (cm) | Disp. T. (cm) | Kd (cm3/g) | μ (-) | β |
| Mixed layer of silty clay and miscellaneous fill | 1.985 | 1.2 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Silty | 1.937 | 3.2 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Silty clay | 2.0 | 1.2 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Diffus. W (cm2/d): Cu: 0.714, Pb: 0.945 [25], As: 0.34 [26], Ni: 0.89; Diffus. G (cm2/d): 0 | ||||||
| Batch | Elements | Max. (mg·kg−1) | Min. (mg·kg−1) | Mean (mg·kg−1) | Median (mg·kg−1) | SD (mg·kg−1) | CV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | Cu | 32,200 | 2.0 | 588.91 | 22 | 3128.42 | 5.31 |
| Pb | 811 | 10.0 | 30.63 | 22 | 57.04 | 1.86 | |
| As | 28.5 | 2.57 | 9.51 | 9.075 | 4.09 | 0.43 | |
| Ni | 445 | 9.0 | 40.31 | 25 | 56.71 | 1.41 | |
| P2 | Cu | 26,500 | 11.0 | 780.25 | 41.5 | 2784.48 | 3.57 |
| Pb | 9380 | 13.0 | 97.60 | 19.65 | 708.71 | 7.26 | |
| As | 64.4 | 2.83 | 9.12 | 8.66 | 5.81 | 0.64 | |
| Ni | 566 | 11.0 | 56.55 | 40.5 | 58.90 | 1.04 |
| Element | Regional Soil Background Value (mg·kg−1) | P1 | P2 | |||||
| Range (mg·kg−1) | Mean (mg·kg−1) | Risk Level | Range (mg·kg−1) | Mean (mg·kg−1) | Risk Level | |||
| Cu | 28.9 | 1.80–1515.27 | 103.79 | Low | 4.05–1627.4 | 142.73 | Low | |
| Pb | 27.9 | 2.41–25.55 | 5.49 | Clean | 2.87–284.8 | 17.04 | Clean | |
| As | 10.0 | 6.68–12.60 | 9.51 | Clean | 5.32–17.27 | 9.10 | Clean | |
| Ni | 32.0 | 2.92–20.18 | 6.30 | Clean | 3.33–29.94 | 8.93 | Clean | |
| / | 16.83–1550.82 | 125.09 | Low | 20.78–1662.76 | 177.80 | Moderate | ||
| Batch | Element | Carcinogenic Risk | Non-Carcinogenic Risk | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRois | CRdcs | CRpis | CRn | HQois | HQdcs | HQpis | HIn | ||
| P1 | Cu | - | - | - | - | 16.08 | 4.580 × 10−2 | 3.902 × 10−2 | 16.17 |
| Pb | - | - | - | - | 4.629 | 8.706 × 10−2 | 4.788 × 10−1 | 5.195 | |
| As | 5.466 × 10−5 | 5.244 × 10−6 | 3.401 × 10−6 | 6.330 × 10−5 | 1.898 | 1.622 × 10−1 | 3.925 × 10−1 | 2.452 | |
| Ni | - | - | 1.739 × 10−6 | 1.739 × 10−6 | 2.407 × 10−1 | 1.714 × 10−2 | 5.537 × 10−1 | 8.115 × 10−1 | |
| P2 | Cu | - | - | - | - | 4.994 | 1.422 × 10−2 | 1.212 × 10−2 | 5.021 |
| Pb | - | - | - | - | 53.54 | 1.007 | 5.538 | 60.08 | |
| As | 1.235 × 10−4 | 1.185 × 10−5 | 7.684 × 10−6 | 1.430 × 10−4 | 4.288 | 3.664 × 10−1 | 8.869 × 10−1 | 5.542 | |
| Ni | - | - | 1.688 × 10−6 | 1.688 × 10−6 | 2.337 × 10−1 | 1.664 × 10−2 | 5.376 × 10−1 | 7.880 × 10−1 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Deng, T.; Xu, R.; Hui, K.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Lu, H. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Heavy Metal Pollution and Risks in Soils from a Shut-Down Electroplating Plant. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2931. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17072931
Wang Y, Deng T, Xu R, Hui K, Zhang J, Li Y, Lu H. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Heavy Metal Pollution and Risks in Soils from a Shut-Down Electroplating Plant. Sustainability. 2025; 17(7):2931. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17072931
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yan, Tianlong Deng, Ruiyang Xu, Kunlong Hui, Jiawen Zhang, Ye Li, and Haojie Lu. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Analysis of Heavy Metal Pollution and Risks in Soils from a Shut-Down Electroplating Plant" Sustainability 17, no. 7: 2931. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17072931
APA StyleWang, Y., Deng, T., Xu, R., Hui, K., Zhang, J., Li, Y., & Lu, H. (2025). Spatiotemporal Analysis of Heavy Metal Pollution and Risks in Soils from a Shut-Down Electroplating Plant. Sustainability, 17(7), 2931. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17072931






