Optimization of Technical Parameters for the Vacuum Preloading-Flocculation-Solidification Combined Method for Sustainable Sludge Utilization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Laboratory Experiments
2.1. Soil Specimens
2.2. Selection of the Admixture Dosage in Experimental Tests
2.3. Procedures for Specimen Preparation and Testing
2.4. Testing Program
3. Results and Discussion
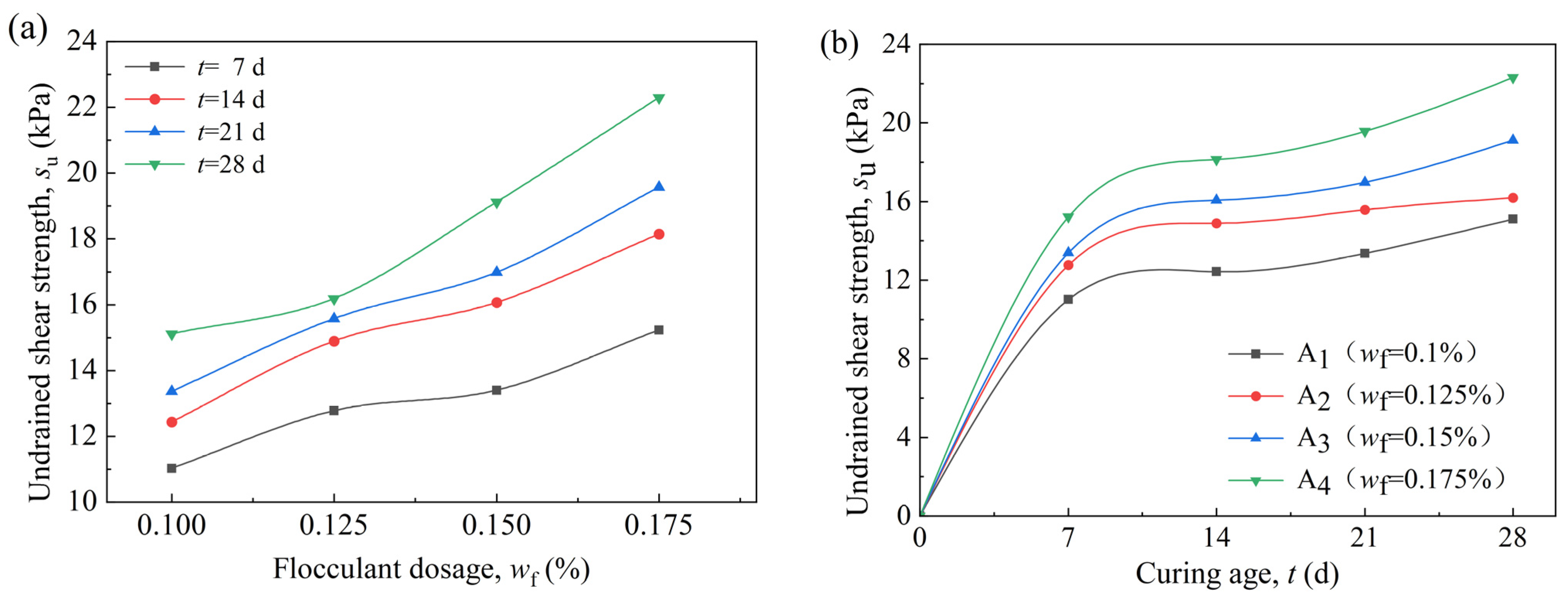
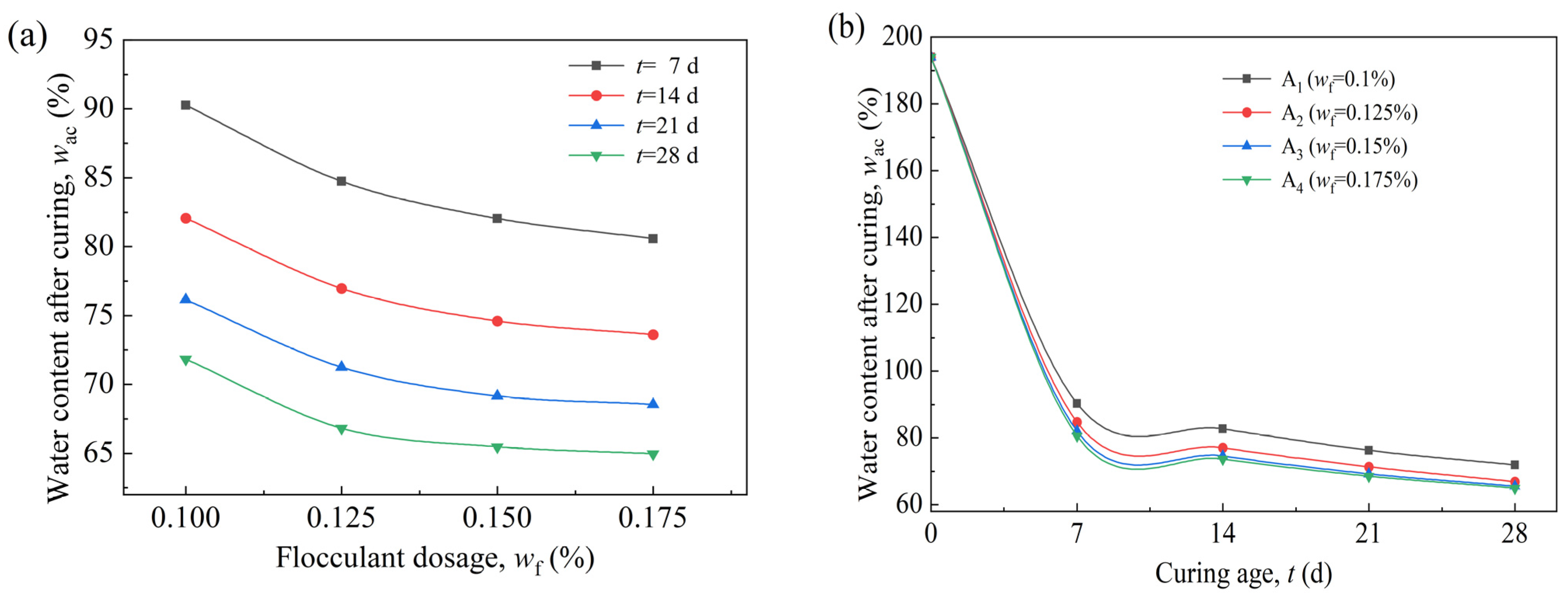
3.1. The Effect of Flocculant Dosage on the VP-FSCM
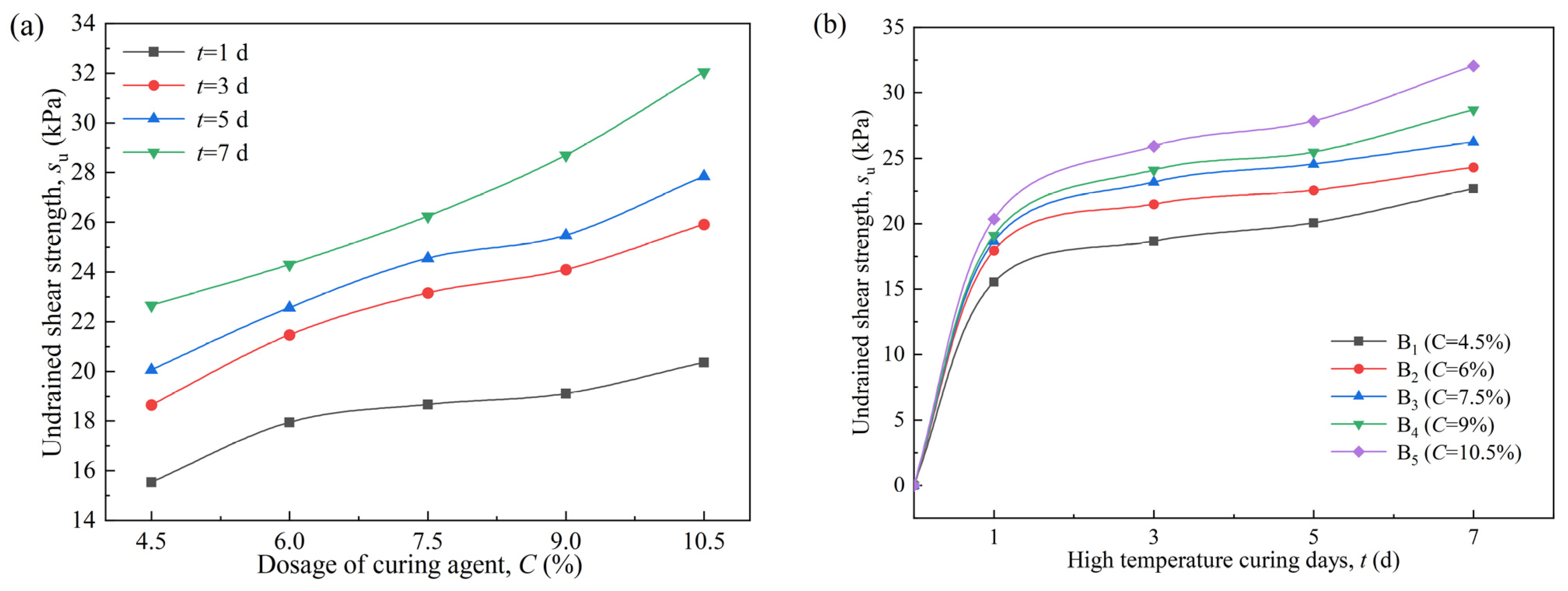
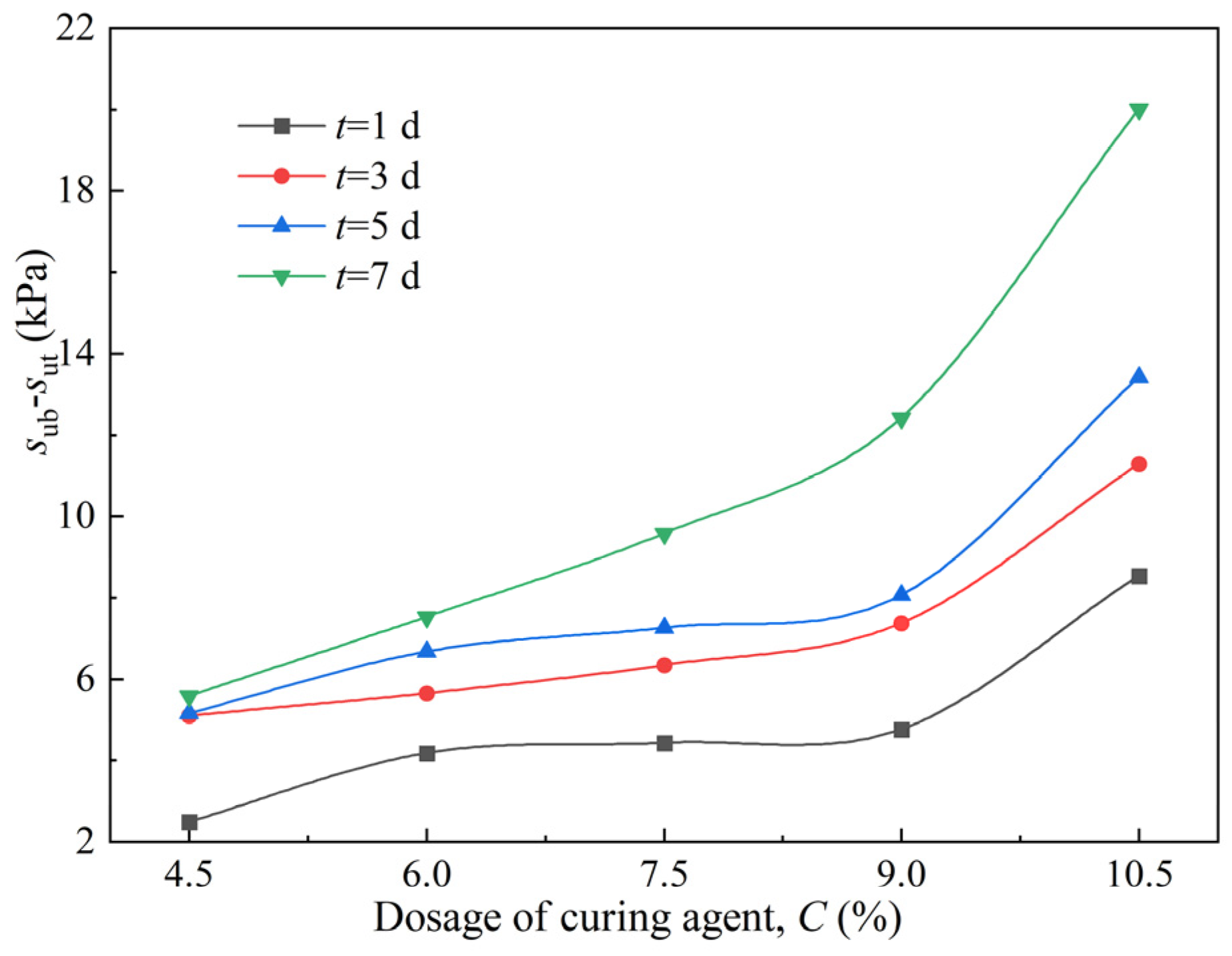
3.2. The Effect of the Curing Agent Dosages on the VP-FSCM
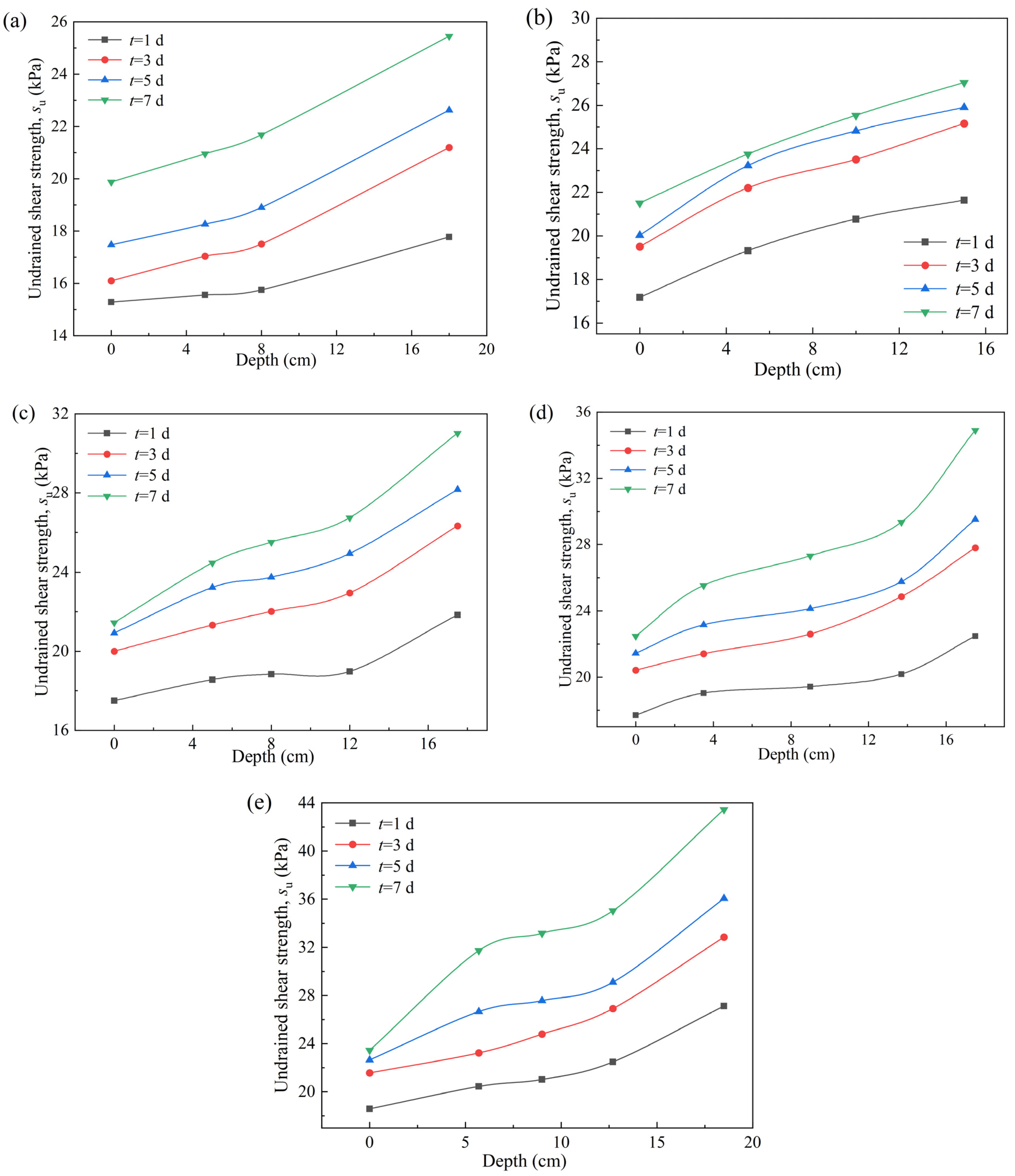
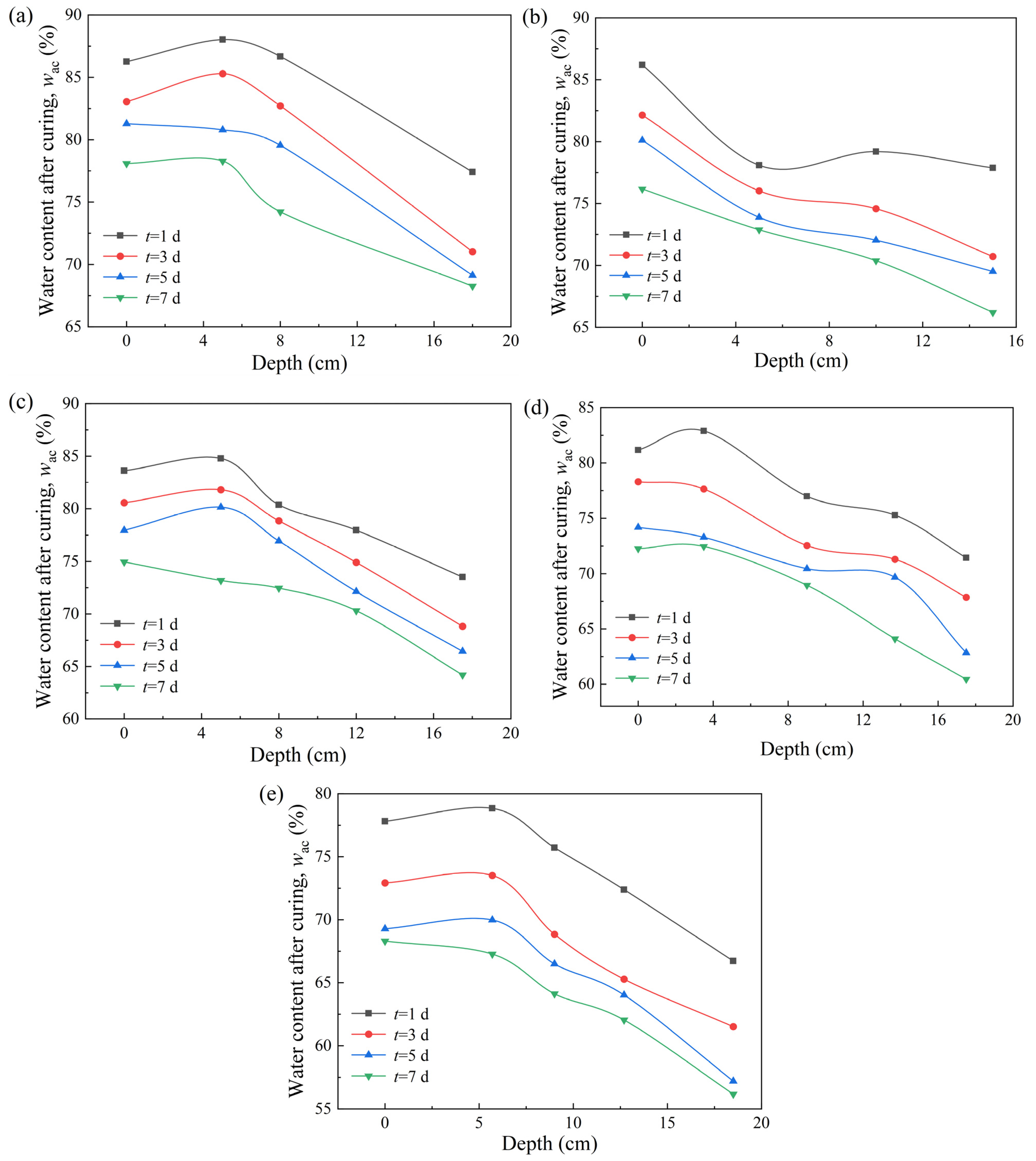
3.3. Characteristics of Strength Spatial Distribution in VP-FSCM
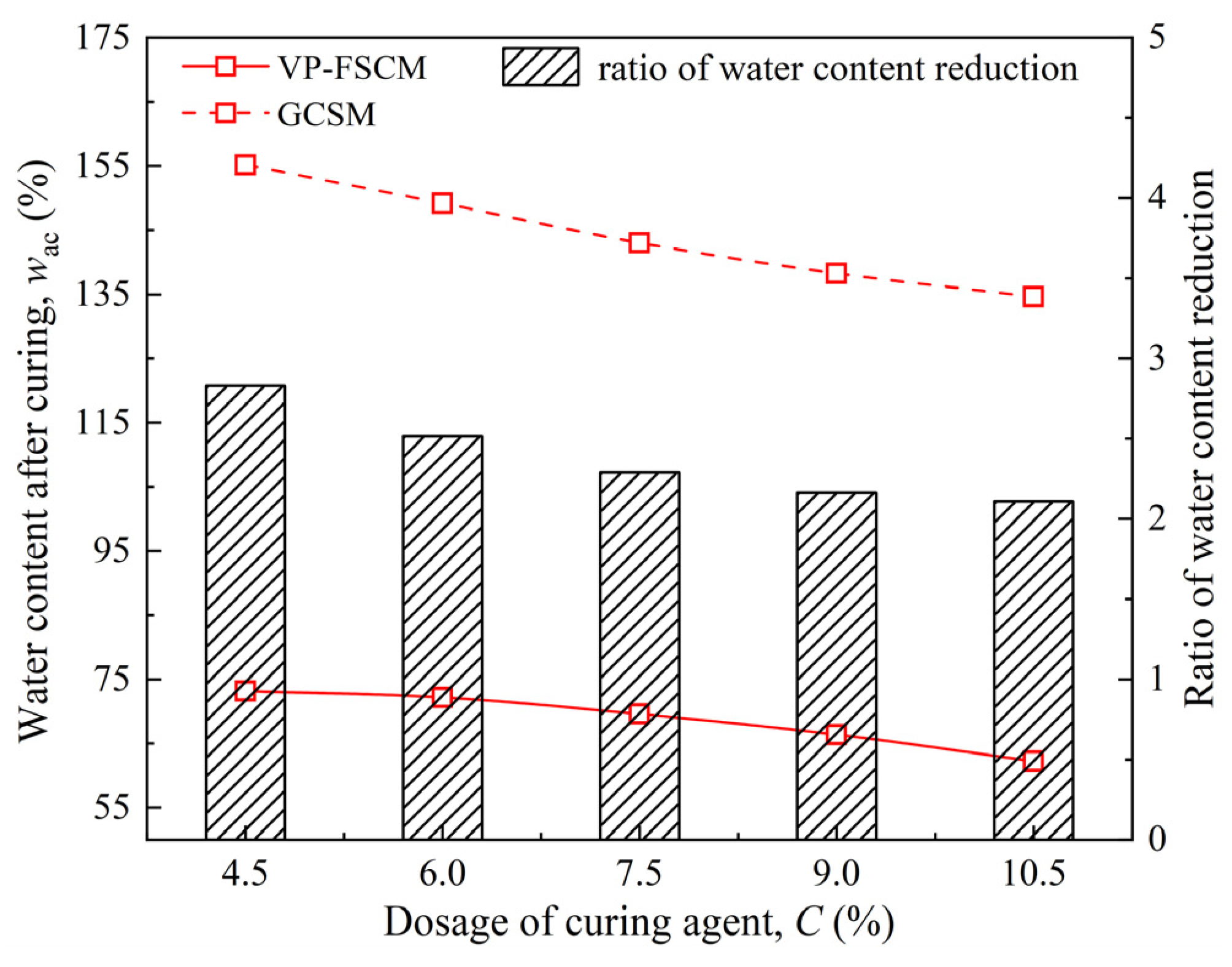
3.4. Comparison of the VP-FSCM and the GCSM
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Notations
| APAM | Anionic polyacrylamide |
| C | Composite the dosage of curing agent (%) |
| ds | Relative density |
| GCSM | GGBS and OPC solidified sludge method |
| GGBS | Ground granulated blast-furnace slag |
| GGBS/OPC | Ratio of ground granulated blast-furnace slag to ordinary Portland cement |
| IP | Plasticity index |
| OPC | Ordinary Portland cement |
| PAM | Polyacrylamide |
| S | Edge deposition (mm) |
| su | Undrained shear strength (kPa) |
| sub | Undrained shear strength of the bottom floor (kPa) |
| sut | Undrained shear strength of the top floor (kPa) |
| t | Curing time (d) |
| V | Water discharge (kg) |
| VP-FSCM | Vacuum preloading-flocculation-solidification combined method |
| wac | Water content after curing (%) |
| wc | Dosage of Ca(OH)2 (%) |
| wei | Equivalent initial water content (%) |
| wf | Flocculant dosage (%) |
| wL | Liquid limit (%) |
| wP | Plastic limit (%) |
References
- Patmont, C.; LaRosa, P.; Narayanan, R.; Forrest, C. Environmental dredging residual generation and management. Integr. Environ. Asses. 2018, 14, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.T.M.; Rabbanifar, S.; Brake, N.A.; Qian, Q.; Kibodeaux, K.; Crochet, H.E.; Oruji, S.; Whitt, R.; Farrow, J.; Belaire, B.; et al. Stabilization of silty clayey dredged material. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 04018199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, N.; Norén, A.; Modin, O.; Fedje, K.K.; Rauch, S.; Strömvall, A.-M.; Andersson-Sköld, Y. Integrated cost and environmental impact assessment of management options for dredged sediment. Waste Manag. 2022, 138, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Cai, Y.; Sun, H.; Geng, X.; Shi, L.; Pan, X. Consolidation considering clogging effect under uneven strain assumption. Int. J. Geomech. 2021, 21, 04020239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Xu, J.; Song, Y.; Gong, W.; Wang, L.; Yu, Z.; Wang, G. Effect of calcination pretreatment on mechanical properties of alkali-activated artificial stone incorporating Yellow River silt. J. Clean Prod. 2022, 364, 132682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Shi, L.; Yin, Y. Enzyme-induced carbonate precipitation (EICP) combined with lignin to solidify silt in the Yellow River flood area. Constr. Build Mater. 2022, 339, 127792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, V.; Castagnoli, A.; Pecorini, I.; Chiarello, F. Identifying technologies in circular economy paradigm through text mining on scientific literature. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0312709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Toma, A.; Bo, Y.; Wang, L.; Wu, H. Reinforcement effect of the stepped-alternating vacuum preloading method on dredged fills. Int. J. Geomech. 2024, 24, 04023272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, P.; Liu, J.; Hu, Y. Experimental investigation of influence of air-boost pressure and duration on air-boost vacuum preloading consolidation. Int. J. Geomech. 2021, 21, 04021088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Huang, J.; Guan, Y.; Chen, H.; Cheng, W. Field test study on vacuum preloading of dredger fill silt. Port. Waterw. Eng. 2010, 04, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, J. Anti-clogging mechanism of freeze-thaw combined with step vacuum preloading in treating landfill sludge. Environ. Res. 2023, 218, 115059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Chu, J.; Guo, W.; Wu, S. Land reclamation using the horizontal drainage enhanced geotextile sheet method. Geotext. Geomembr. 2023, 51, 131–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Xu, G. Synergistic influence of lime and straw on dredged sludge reinforcement under vacuum preloading. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 421, 135642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, S.; Guo, W.; Ren, Y.; Xu, G. Recent developments in the vacuum preloading technique in china. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Q.; Zhou, J.; Li, C.; Zhuang, Y.; Wang, Y. Vacuum preloading combined with electroosmotic dewatering of dredger fill using the vertical-layered power technology of a novel tubular electrokinetic geosynthetics: Test and numerical simulation. Int. J. Geomech. 2022, 22, 05021004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Jiang, M.; Liu, L. Effect of polyacrylamide on improvement of dredger fill with vacuum preloading method. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2019, 31, 04019193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Dong, Z.; Mo, H.; Wu, D. Laboratory tests on new reinforcement technology of newly hydraulic reclamation mud with high clay content. Rock Soil Mech. 2015, 36, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Lu, Y.; Xu, J.; Tran, Q.C.; Vu, Q.V. Experimental investigation on waste slurry improvement using vacuum preloading with calcium oxide. B. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2022, 81, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, M.; Luo, S.; Chang, J.; Zhang, R.; Kuang, X.; Jiang, J. The influences of vacuum-surcharge preloading on pore water pressure and the settlement of a soft foundation. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, M.; Luo, S.; Chang, J.; Zhang, R.; Kuang, X.; Jiang, J. Fluid-Solid coupling numerical analysis of pore water pressure and settlement in vacuum-preloaded soft foundation based on FLAC3D. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.-L.; Pan, F.-R.; Zhang, B.-B.; Wang, X.-Q.; Diao, H.-G. Laboratory test of waste mud treated by the flocculation-vacuum-curing integrated method. Constr. Build Mater. 2022, 328, 127086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wu, W.; Fu, H.; Wang, J.; Hai, J.; Cai, Y.; Hu, X.; Yuan, W.; Lou, X. Application of flocculation combined with vacuum preloading to reduce river-dredged sludge. Mar. Georesour. Geotec. 2019, 38, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Shi, X.-K.; Li, Z.-X.; Zhang, L.; Feng, X.-Y.; Zhou, L.-R. Strength properties of dredged soil at high water content treated with soda residue, carbide slag, and ground granulated blast furnace slag. Constr. Build Mater. 2020, 242, 118126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhou, F.; Zhu, R.; Song, Z.; Hua, S.; Ma, Y. Strength performance of mucky silty clay modified using early-age fly ash-based curing agent. Case Stud. Constr. Mat. 2022, 17, e01595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.-L.; Zhao, L.-Y.; McCabe, B.A.; Chen, Y.-H.; Morrison, L. Dredged marine sediments stabilized/solidified with cement and GGBS: Factors affecting mechanical behaviour and leachability. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 138551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, L.; Chen, B.; Chen, B. Strength evolutions of varying water content-dredged sludge stabilized with alkali-activated ground granulated blast-furnace slag. Constr. Build Mater. 2021, 275, 122111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Xie, Z.; Yao, H.; Fan, M.; Huang, T. Comparative study on the early properties of cement modified with different ionic polyacrylamides. Constr. Build Mater. 2022, 339, 127671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Ruan, Z.; Bürger, R.; Yin, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y. Optimization of flocculation and settling parameters of tailings slurry by response surface methodology. Miner. Eng. 2020, 156, 106488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Hou, Y.; Yang, S.; Chen, X. Study on static and dynamic flocculation settlement characteristics of fine tailings slurry and influence of flocculant on strength of fine tailings backfill. Case Stud. Constr. Mat. 2022, 17, e0525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.-J.; Zheng, Y.-L.; Zheng, J.-J.; Dong, C.-Q.; Lu, Z. Flocculation–solidification combined method for treatment of hydraulically dredged mud at extra high water content. Acta. Geotech. 2019, 15, 1685–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.-J.; Xu, Z.-H.; Zheng, J.-J.; Tu, L.-W.; Huang, Z.-F. Reasonable application range of flocculation–solidification combined method in treatment of hydraulically dredged mud slurry. Mar. Georesour. Geotec. 2021, 40, 370–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zheng, J.; Dong, C.; Lu, Z. Experimental study of flocculation-solidification combined treatment of hydraulically dredged mud at extra high-water content. Rock Soil Mech. 2019, 40, 3107–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 50123-2019,717; Standard for Geotechnical Testing Method. China Renewable Energy Engineering Institute and Nanjing Hydraulic Research Institute: Nanjing, China, 2019.
- GB/T 50145-2007.38; Standard for Engineering Classification of Soil. Nanjing Hydraulic Research Institute: Nanjing, China, 2007.
- Xu, Z.-H.; Zhang, R.-J.; Zheng, J.-J.; Liu, S.-J. Laboratory and field experimental study on efficiency of vacuum preloading–flocculation–solidification combined method for slurry-like mud treatment. Acta Geotech. 2024, 19, 5417–5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, X.; Yang, H.; Duan, K.; Zhang, R.; Wu, L. Study on effect of equivalent initial water content on dredged sludge treated by VP-FSCM. Transp. Geotech. 2023, 42, 101077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Chu, J.; Tan, S.K.; Vu, T.T.; Lam, K.P. Sedimentation behavior of flocculant-treated soil slurry. Mar. Georesour. Geotec. 2016, 35, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedunuri, S.S.S.A.; Sertse, S.G.; Muhammad, S. Microstructural study of Portland cement partially replaced with fly ash, ground granulated blast furnace slag and silica fume as determined by pozzolanic activity. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 238, 117561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X. Mechanical properties and micro-mechanisms of marine soft soil stabilized by different calcium content precursors based geopolymers. Constr. Build Mater. 2021, 305, 124722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.-J.; Zheng, Y.-L.; Dong, C.-Q.; Zheng, J.-J. Strength behavior of dredged mud slurry treated jointly by cement, flocculant and vacuum preloading. Acta. Geotech. 2022, 17, 2581–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhou, W.; Zhu, Z.; Peng, C.; Peng, Y. Study on the preparation of polysilicate ferric flocculant and its treatment of high turbidity tailings water. J. Water Process. Eng. 2021, 44, 102457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.J.; Lu, Y.T.; Tan, T.S.; Phoon, K.K.; Santoso, A.M. Long-Term effect of curing temperature on the strength behavior of cement-stabilized clay. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2014, 140, 01014045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.-J.; Qiao, Y.-Q.; Zheng, J.-J.; Dong, C.-Q. A method for considering curing temperature effect in mix proportion design of mass cement-solidified mud at high water content. Acta. Geotech. 2021, 16, 279–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
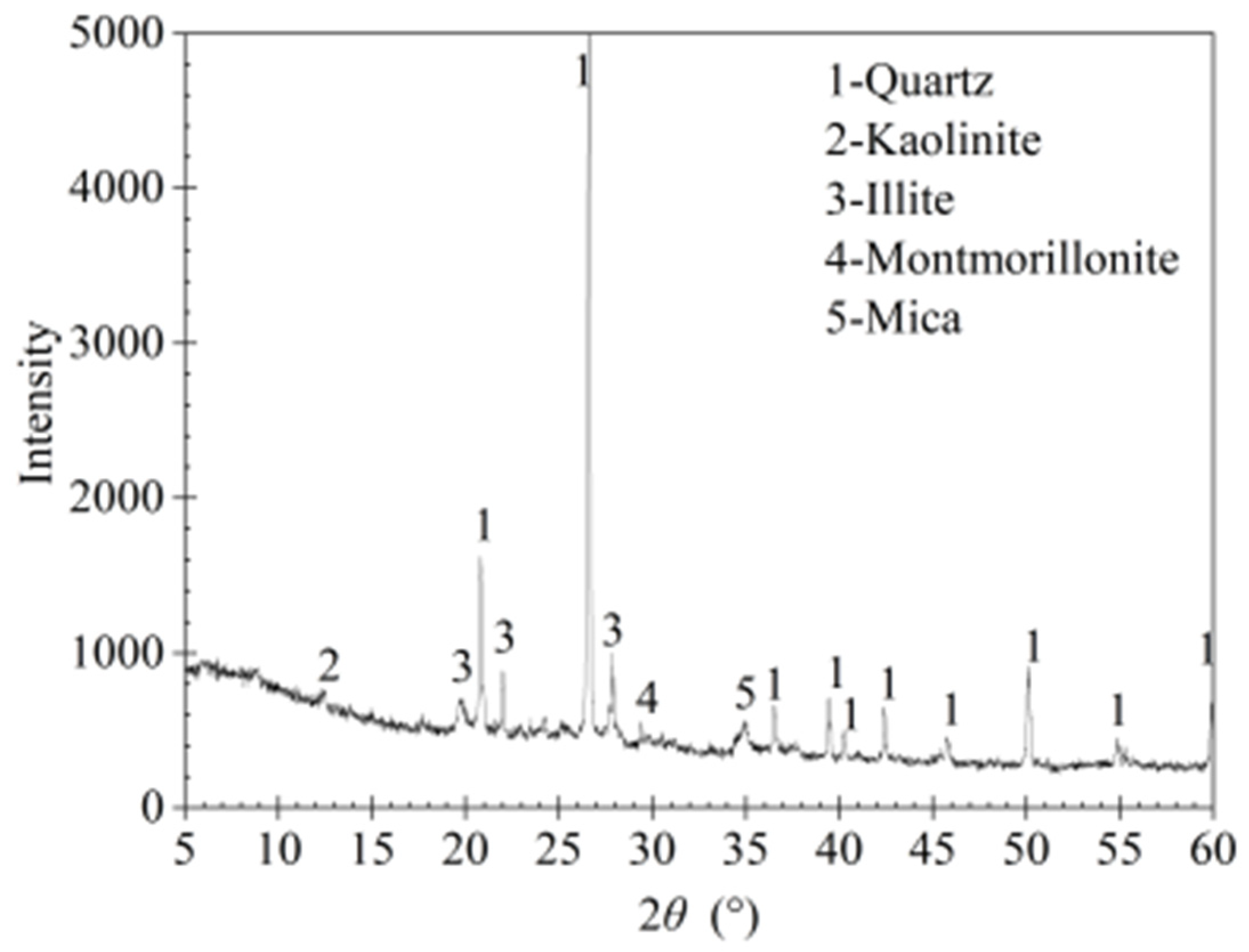

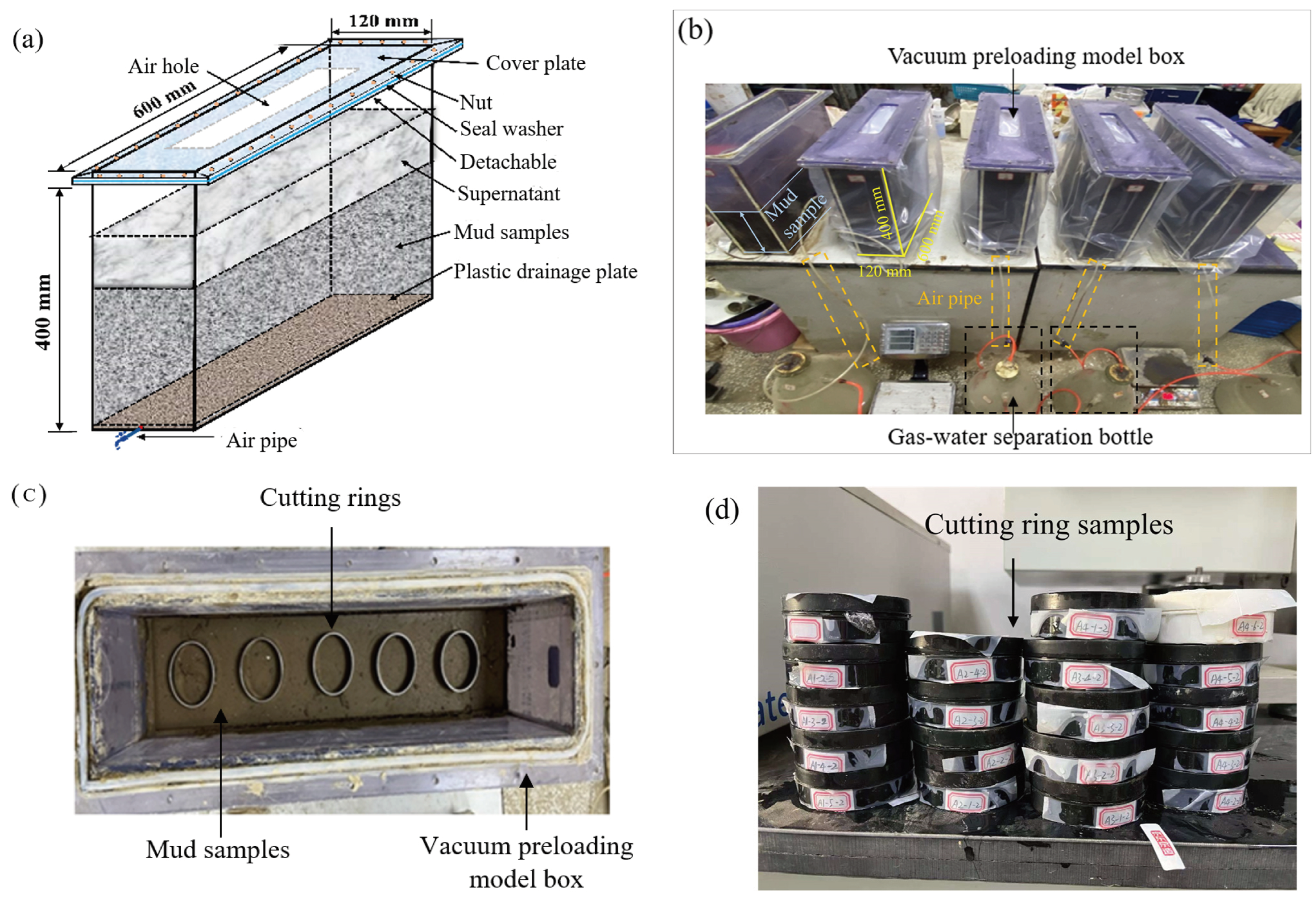





| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Relative density ds | 2.72 |
| Liquid limit wL (%) | 51.4 |
| Plastic limit wP (%) | 32.4 |
| Plasticity index IP | 19.0 |
| Ignition loss (%) | 3.79 |
| Grit fraction (%) (0.075 < diameter < 2 mm) | 4.3 |
| Powder particle fraction (%) (0.005 < diameter < 0.075 mm) | 62.7 |
| Cosmid fraction (%) (diameter < 0.005 mm) | 33.0 |
| Oxide | OPC (%) | GGBS (%) |
|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 22.92 | 30.64 |
| Al2O3 | 6.09 | 15.28 |
| Fe2O3 | 3.64 | 0.33 |
| TiO2 | 0.39 | 0.56 |
| Ca(OH)2 | 59.71 | 36.88 |
| MgO | 0.88 | 5.84 |
| SO3 | 2.82 | 0.04 |
| K2O | 0.76 | 0.2 |
| Na2O | 0.66 | 0.35 |
| Loss on ignition | 2.13 | 0.06 |
| Case No. | Treatment | wei (%) | Dosage of Flocculant | Dosage of Curing Agent | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wc (%) | wf (%) | C (%) | GGBS/OPC | |||
| A1 | VP-FCSM | 200 | 1.5 | 0.1 | 3.0 | 1.0 |
| A2 | 0.125 | |||||
| A3 | 0.15 | |||||
| A4 | 0.175 | |||||
| B1 | VP-FCSM | 200 | 1.5 | 0.125 | 4.5 | 1.0 |
| B2 | 6.0 | |||||
| B3 | 7.5 | |||||
| B4 | 9.0 | |||||
| B5 | 10.5 | |||||
| C1 | GCSM | 200 | 0 | 0 | 4.5 | 1.0 |
| C2 | 6.0 | |||||
| C3 | 7.5 | |||||
| C4 | 9.0 | |||||
| C5 | 10.5 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, C.; Li, H.; Duan, K.; Zhang, R.; Peng, Q.; Liu, L.; Guo, Y.; Sun, K.; Tu, P. Optimization of Technical Parameters for the Vacuum Preloading-Flocculation-Solidification Combined Method for Sustainable Sludge Utilization. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2710. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062710
Han C, Li H, Duan K, Zhang R, Peng Q, Liu L, Guo Y, Sun K, Tu P. Optimization of Technical Parameters for the Vacuum Preloading-Flocculation-Solidification Combined Method for Sustainable Sludge Utilization. Sustainability. 2025; 17(6):2710. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062710
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Chao, Hongwu Li, Kun Duan, Rongjun Zhang, Qian Peng, Liang Liu, Yimu Guo, Ke Sun, and Peng Tu. 2025. "Optimization of Technical Parameters for the Vacuum Preloading-Flocculation-Solidification Combined Method for Sustainable Sludge Utilization" Sustainability 17, no. 6: 2710. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062710
APA StyleHan, C., Li, H., Duan, K., Zhang, R., Peng, Q., Liu, L., Guo, Y., Sun, K., & Tu, P. (2025). Optimization of Technical Parameters for the Vacuum Preloading-Flocculation-Solidification Combined Method for Sustainable Sludge Utilization. Sustainability, 17(6), 2710. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062710





