Abstract
Marine biological shell waste, as a representative renewable resource, can lead to serious environmental problems and resource waste if effective utilization methods are not developed. Therefore, there is an urgent need for innovative solutions to enable the effective recycling and reuse of marine biological shell waste. Although previous studies have explored the applications of marine biological shells in chitin extraction and animal feed production, this study is the first to reveal the possibility of obtaining metal resources from marine biological shells, which is a renewable resource available in large quantities. An analysis of the metal element concentrations in marine biological shells shows that several valuable or important metal elements are present at concentrations that are hundreds of thousands of times higher than in seawater. CaCO3 was identified as the main component for enriching metal elements in marine biological shells. The recovery efficiency of most metal elements from oyster shells could exceed 80%. This study highlights the potential of marine biological shells as a valuable metal resource, offering a sustainable approach to waste management and utilization while alleviating the risk of heavy metal accumulation and environmental pollution associated with traditional composting.
1. Introduction
The ocean is the largest ecosystem on Earth, covering 71% of the planet’s surface area and containing almost 97% of the globe’s water [1]. Due to its huge total amount, seawater is estimated to contain much more metal resources than terrestrial metal ores [2,3]. Attributed to the favorable marine environment, a large number of life forms live in the ocean, including marine shellfish and crustaceans. Due to the reproductive ability of these marine life forms and the replacement behavior of the hard shell of crustaceans [4,5], marine biological shells are a type of renewable resource available in extremely large quantities [6,7]. The total amount of marine biological shell waste generated globally each year is approximately 14 million to 20 million tons, mainly generated by the consumption of seafood that contains shells [8,9]. Due to the lack of techniques for dealing with these marine biological shells, only a small proportion of them are used to extract chitin or produce animal feeds, with the majority of them eventually being disposed of as municipal solid waste and ending up in landfills or the sea [10,11,12]. According to statistics, in 2015, the disposal of marine biological shell waste cost as much as USD 150 per ton, while the commercial value of carapace waste was only about USD 100 to USD 120 per ton [13]. Furthermore, disposed marine biological shells take an extremely long time to degrade in the natural environment, leading to the accumulation of shell waste, which poses hazards to the marine ecosystem and human health [14,15,16,17]. Thus, it is necessary to explore efficient approaches for handling marine biological shell waste in order to realize their high economic value and minimize their environmental hazards.
In fact, marine biological shells have high potential value and merits [18]. They contain approximately 20–40% protein, 20–50% mineral salts (mainly CaCO3), 15–40% chitin, and several other small constituents, such as lipids and pigments [6,19]. Most of the components in marine biological shells have functions in a variety of fields, such as pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, textiles, fertilizers, and animal feeds [20,21,22,23,24]. Due to high operational costs, significant energy consumption, complex recycling processes, an underdeveloped recycling system, and low efficiency, the traditional methods of shell waste utilization have obvious limitations. For example, the extraction of chitin involves multiple steps and requires the use of large amounts of highly corrosive chemicals. Furthermore, the process uses a significant amount of freshwater to repeatedly rinse the treated shells in order to remove residual alkalis and acids [25]. To promote the reutilization of marine biological shells, researchers have explored their potential applications in various fields. One such application involves using them as soil conditioners to enhance the abundance of metal elements in soil [26]. However, as there is still a lack of systematic research on the specific composition and content of the metal elements in marine biological shells, sufficient guidance for the reutilization of marine biological shell waste has not been provided.
Sustainable access to resources is of great importance for the rapid and sustainable development of human society. Due to the continuous improvement of human social productivity and the significant increase in material demands, the reserves of numerous natural resources are rapidly decreasing, and some natural resources may even be almost completely consumed [27,28]. Metal resources are necessary for the production of human life necessities, and they are mainly found in the form of non-renewable minerals that only form over an extremely long time span in the natural environment [29]. Currently, the obtainment of large quantities of critical metal resources mainly depends on the mining, refining, and processing of metal minerals [30]. However, to meet the increasing needs for the production of human life necessities, several natural metal resources, including rare-earth elements, lithium, copper, cobalt, uranium, silver, and gold, are extensively exploited, causing a sharp decrease in their reserves in the natural environment [31,32,33]. In addition, the extraction of one ton of coal generates approximately two tons of mine water, leading to an annual discharge of hundreds of millions of tons of contaminated water [34]. Wastewater contains harmful metal ions and chemicals, leading to substantial energy consumption, water resource depletion, and severe environmental pollution [35]. These challenges highlight the urgent need for alternative and sustainable metal resources. Therefore, exploring new ways of supplying the growing demands for metal resources is an important task.
This is the first study to provide a detailed account of the specific composition and content of metal elements in marine biological shells, highlighting their potential as a new metal resource (Figure 1). The results demonstrate that marine biological shells and coral reefs could enrich certain metal elements from seawater by hundreds of thousands of times. CaCO3 was the main active component for enriching metal elements. In addition, a leaching method was used to dissolve metal elements from oyster shell waste, and finally, metal elements were extracted from the leachate through precipitation. The leaching behavior of various elements in oyster shell waste and the precipitation behavior of metal elements in the leachate were systematically studied. It was expected that metal elements can be efficiently recovered from oyster shell waste and that their resource utilization would be achieved. The findings of this study deepen the understanding of the composition of marine biological shells and coral reefs, and they reveal the potential value of marine biological shells as a metal resource.
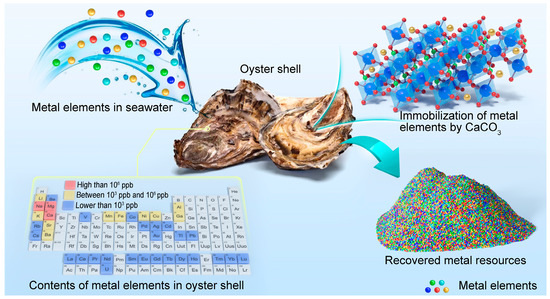
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the enrichment mechanism of metal elements in marine biological shells and the recovery of metal resources.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
To determine the metal element content in crab shells, oyster shells, and coral reefs, samples of these were collected and thoroughly washed with ultrapure water at least three times to remove adsorbed salt. Subsequently, the samples were oven-dried overnight at 40 °C to preserve their integrity without affecting the subsequent metal concentration analysis [36]. After drying, the samples were crushed in a clean grinder and filtered through a 60-mesh screen to collect fine powders for future use. Chemicals, including electronic-grade nitric acid (HNO3, 70% v/v), sodium hydroxide (NaOH, AR, 98% v/v), and hydrochloric acid (HCl, GR, 38% v/v), were sourced from Xilong Scientific in China. A gold standard solution (1000 μg/mL), a mixed standard solution of 16 rare-earth elements (100 μg/mL), a rhodium single-element standard stock solution (10 μg/mL), and an indium single-element standard stock solution (10 μg/mL) were provided by the China National Analysis Center for Nonferrous Metals and Electronic Materials. A mixed standard solution of 27 elements (10 μg/mL, Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2, GR, 30% v/v, Xihua Scientific, China) and chitosanase (≥200 units/g, Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) were also obtained. All chemicals were ready to use without further purification.
2.2. Determination of Metal Element Content
To analyze the metal content in the marine biological shells, 0.10 g of the sample was weighed, and 3 mL of 16 M HNO3 was slowly added. The sample was then placed in a microwave digestion system (Multiwave 7000, Anton Paar, Austria) and heated to 180 °C for 15 min to accelerate digestion. The digested sample was cooled to 55 °C for 30 min after holding at 180 °C for 15 min to ensure thorough decomposition. After digestion, the solution was diluted with ultrapure water. Atomic absorption spectrometry (AAS, EAS002A, Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA), inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES, 5900, Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA), and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS, NexION 5000G, PerkinElmer, MA, USA) offer high sensitivity, high precision, a wide linear range, and excellent resistance to interference, making them suitable for the simultaneous detection of multiple metal elements. During the testing process, instrument performance was optimized using a tuning solution. Quantitative analysis was carried out using a calibration curve, and the appropriate wavelengths were selected to minimize spectral interferences. Instrumental drift and matrix effects were corrected using internal standards. Quality control was ensured by analyzing blank and triplicate samples. The metal content (µg/kg) was calculated using the following formula:
Here, (µg/L) represents the mass concentration of the element in the sample, calculated from the standard curve; represents the dilution factor of the sample; (µg/L) represents the mass concentration of the element in the blank sample; (mL) represents the final volume of the sample after digestion; and (g) represents the mass of the sample.
2.3. Determination of the Main Components for Binding the Metal Elements
To determine the main components binding the metal elements, the major components, including chitin, proteins, and CaCO3, were removed from the oyster shells, crab shells, and coral reefs. To remove chitin, the ground sample was added to a chitosanase solution with a final concentration of 1 mg/ ml, and the reaction was stirred at 37 °C for 3 h [37]. To eliminate the protein, the milled samples were exposed to 1.31 M sodium hydroxide solution for 4 h at 70 °C with moderate stirring [38]. To eliminate CaCO3, the milled samples were subjected to a 1.15 M hydrochloric acid solution and allowed to react for 4 h at 25 °C with moderate shaking [38]. After the removal of individual components, the concentration of the metal elements in the treatment solution were measured using ICP-MS and ICP-OES. During the experimental procedures, corresponding blank samples were set up to minimize the potential errors that could arise during the process.
2.4. Characterization
The microscopic morphology of the samples was observed by using a Verios G4 UC field-emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM) from Thermo Fisher Scientific in MA, USA. An energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) mapping image was obtained using a Talos F200X G2 field-emission transmission electron microscope (FE-TEM) from Thermo Fisher Scientific.
2.5. Recovery of Metal Elements from Marine Biological Shells
To obtain metal resources from the marine biological shells, 1 kg of oyster shells was ground into a powder. An acid leaching experiment was carried out using 16 M HNO3 and 8.82 M H2O2 at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:1.5, followed by precipitation with 5 M NaOH at pH 5 and, finally, filtering and collection after standing for 4 h. After being ashed, the metal content in the ash product was determined using ICP-MS and ICP-OES. The precipitation ratio (P, %), enrichment factor (EF), and recovery rate (R, %) of the metal elements in the ashed product were then calculated using the following formulas:
In the above formulas, (, µg/L) represents the concentration of the element in the leachate, (, µg/L) represents the concentration of the element in the supernatant after precipitation,, µg/kg) represents the element content in the ash product, (, µg/kg) represents the element content in the leachate, (, µg) represents the weight of the metal elements in the ash product, and (, µg) represents the weight of the metal element in the leachate.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
The experimental data were analyzed using Origin 2021 software (OriginLab Corporation, Northampton, MA, USA). Statistical analysis was performed using IBM SPSS Statistics 27 (New York, NY, USA), and one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was conducted to compare the means and differences in the metal element content for the different marine organisms’ shells. Different letters indicate a significant difference, starting from “a”, which was based on a probability level of 0.05.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Metal Element Content and Enrichment Ratios
The content of 39 metal elements in the marine biological samples, including oyster and crab shells, which represent shellfish and crustacean shells, and a coral reef, were determined. The results show that there were significant differences in the metal content among the oyster shells, crab shells, and coral reef (p < 0.05) (Table S1). These 39 elements accounted for 35.17%, 24.06%, and 35.56% of the weight of the oyster shells, crab shells, and coral reef, respectively. Compared with the oyster and crab shells, the coral reef had a higher content of metal elements, which is because coral reefs contain more inorganic components and fewer organic components. Ca was the most abundant element in all three samples, accounting for 96.82%, 89.08%, and 95.55% of the weight of the tested metal elements in the oyster shells, crab shells, and coral reef, respectively. Ca not only provides structural support and physical protection for the exoskeletons but also plays a vital role in the growth and development of these organisms [39,40,41]. Additionally, the marine environment, particularly seawater rich in Ca2+, promotes the deposition of calcium carbonate, further enhancing the formation of the exoskeletons of marine organisms and coral reefs [42,43,44]. Besides Ca, other elements also showed concentrations higher than 1000 ppm, including Na and Mg in the oyster shells; Na, Mg, and Sr in the crab shells; and Na, Mg, and Sr in the coral reef. All the elements with a concentration higher than 1000 ppm accounted for 99.57%, 99.38%, and 99.39% of the weight of the tested metal elements in the oyster shells, crab shells, and coral reef, respectively (Figure 2 and Figures S1–S3, and Tables S2–S4). X-ray energy spectroscopy (EDS) elemental mapping analyses also confirmed the content of these high-concentration metal elements in the oyster shells, crab shells, and coral reef. Sr, K, Al, Fe, Mn, Ba, Ga, Li, and Cu had concentrations between 1 ppm and 999 ppm in the oyster shells, and K, Mn, Al, Fe, Ba, Cu, Ga, Ni, and Li had concentrations between 1 ppm and 999 ppm in the crab shells. However, the coral reef contained Fe, Al, K, Mn, Ba, U, V, Ga, Ni, Rb, and Li with concentrations between 1 ppm and 999 ppm, which were significantly different from those in the oyster and crab shells. This may be because coral reefs form after the death of coral polyps by undergoing the mineralization process, whereas the metal elements in oyster and crab shells are taken up during their growth process [45]. It is worth noting that the Sr content in these three samples exceeded 800 ppm, which is significantly higher than that of seawater (8 ppm) [46] and soil (300 ppm) [47]; this is due to the high chemical similarity between Sr and Ca, as both elements belong to the same family [48]. Sr is a major product of nuclear fission, and the concentration of radioactive Sr elements is continuously increasing in seawater due to the release of nuclear-contaminated water following nuclear plant accidents [49]. A high Sr content in marine biological shells could lead to human health issues, including bone cancer, rickets, and leukemia, through the consumption of marine shellfish and crustaceans [50,51,52]. Therefore, monitoring and managing the levels of radioactive Sr in the marine environment are crucial for ensuring public health and environmental safety. Other elements, including Pb, Co, Ag, Au, Pd, Cs, Be, Cd, Tl, and rare-earth elements (REEs), showed concentrations lower than 1 ppm in all three samples, which might be due to their extremely low concentrations in seawater and the components of marine biological shells having a low binding affinity for them. Regarding high-value or strategic elements, including Au, Ag, Pd, Ga, Li, U, and REEs, they accounted for 0.0020%, 0.0022%, and 0.0021% of the weight of the tested metal elements in the oyster shells, crab shells, and coral reef, respectively, thus proving the merits of marine shells and coral reefs as resources for obtaining high-value or strategic metal elements.
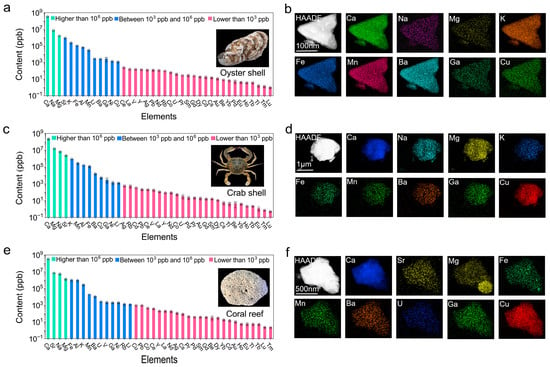
Figure 2.
The content and corresponding EDS analysis of the metal elements in (a,b) oyster shells, (c,d) crab shells, and (e,f) coral reef. The content of the 39 metal elements was determined, and each metal element is presented as individual values ± standard deviation (n = 3). The morphologies of the used oyster shells, crab shells, and coral reef are shown.
The enrichment ratio of the tested metal elements in marine biological shells versus their concentrations in seawater was calculated, and the results show that the three marine biological samples exhibited varying enrichment abilities for most metal elements (Figure S4 and Table S5). In the oyster shells, crab shells, and coral reef, 14, 12, and 18 of the 39 tested metal elements were enriched by more than 10,000 times, respectively, which were mainly for the REEs, Al, Ga, Mn, and Fe, and particularly Pb in the coral reef (Figure 3). It is interesting that most of the REEs were concentrated by more than 10,000 times, which might be due to the fact that REEs are strongly adsorbed onto the surface of Ca/Mg/Sr carbonates and frequently substituted for Ca2+ ions in marine shells or coral reefs [53,54,55,56]. The metal elements with high concentrations in seawater, including Mg, Na, and K, only showed low concentrations. Other high-value metal elements, such as Au and Ag, were also enriched by hundreds of times. The strategic U element, which is fuel for nuclear energy and only has limited reserves in terrestrial uranium ores, was highly concentrated in the coral reef by 839 times, implying that coral reefs might serve as a source of uranium. The different enrichment ratios of the marine biological shells and the coral reef for the different metal elements may be related to differences in their biological structures and living habits. The coral reef had a significantly higher enrichment ability for most metal elements than the oyster and crab shells (p < 0.05) (Table S6), which may be due to the ability of the CaCO3 and proteins in the coral reef to enrich metal elements from seawater. However, this metal enrichment could negatively impact coral health, potentially leading to coral bleaching, and it may further disrupt marine ecosystems through bioaccumulation in the food chain [57].

Figure 3.
The enrichment ratios of the metal elements in (a) oyster shells, (b) crab shells, and (c) coral reef. The enrichment ratios of the tested metal elements are shown in different colors, and the elements that were not tested are shown in gray.
3.2. Functional Components for Enriching Metal Elements
To identify the functional components for enriching metal elements, the components, including CaCO3, protein, and chitin, of the oyster shells, crab shells, and coral reef, were separately removed and the metal element content in these treated samples were determined. After the removal of the different components, changes in the microstructures of the oyster shells, crab shells, and coral reef were observed (Figure 4a–c). Content analysis showed that CaCO3 was the most dominant component and accounted for 79%, 56%, and 88% of the total weight of the oyster shells, crab shells, and coral reef. This was followed by protein, which accounted for 12%, 26%, and 7% of the total weight of the oyster shells, crab shells, and coral reef. Chitin represented the smallest proportion and accounted for 9%, 18%, and 5% of the total weight of the oyster shells, crab shells, and coral reef (Figure 4d–f). The removal of these three components revealed that most of the metal elements were enriched in the CaCO3 sample (Figure 4g–i). However, the elements Cu, Cs, Rb, K, Li, V, and Mn were also mainly distributed in the protein sample, which is because protein contains carboxyl and amino groups that can act as functional groups for binding these metal ions [58]. Er was highly concentrated in chitin, which might be due to the binding ability of the functional groups in the chitin polysaccharide chain. The high metal content in the CaCO3 sample may be attributed to its surface charge properties, microporous structure, and strong adsorption affinity for metal ions. The surface of CaCO3 interacts with metal cations through electrostatic attraction, while its micropores provide a large surface area for adsorption. Additionally, carbonate ions react with metal ions to form insoluble metal carbonates, further enhancing the adsorption capacity [59,60]. Compared to synthetic adsorbents such as zeolite, CaCO3 has natural advantages in terms of its widespread availability and low cost. The natural biomineralization process in CaCO3 offers a sustainable and efficient method for metal ion recovery, making it a promising material for recovering metal elements in marine environments.
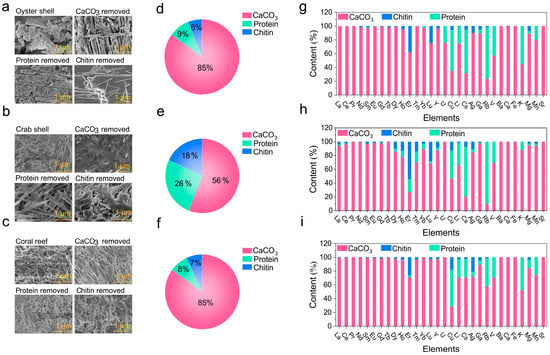
Figure 4.
Main components for enriching metal ions. SEM images of ground (a) oyster shells, (b) crab shells, and (c) coral reef before and after the removal of different components. The ratio of the three components in the (d) oyster shells, (e) crab shells, and (f) coral reef. The distribution of metal elements in the main components of the (g) oyster shells, (h) crab shells, and (i) coral reef.
3.3. Recovery of Metal Elements from Marine Biological Shells
To obtain metal resources from marine biological shells, 1 kg of oyster shells was used as a raw material to extract metal elements from (Figure 5a). Except for Ca, 25 out of 38 metal elements were dissolved in the acid leaching solution, corresponding to a dissolution efficiency of 65.79%. This confirmed the high efficiency of this method in leaching metal elements. Furthermore, the precipitation method was used to extract the metal elements from the acidic leachate by adjusting the pH of the leaching solution to pH 5. The results show that the precipitation rates of the metal content increased with an increase in the precipitation time and gradually stabilized after 4 h (Figure S5). Among them, the precipitation efficiencies of Yb, Tm, Er, Ce, Eu, Sm, Dy, Pr, Gd, Nd, La, Fe, Al, U, and Al exceeded 80%, and the precipitation efficiencies of Be, Ag, and V were higher than 50% (Figure S6). The precipitant was further ashed to obtain an ash product weighing 3.6 g, and then the content of the ash product was determined using ICP-MS and ICP-OES. The results show that the metal element content in the ashed products greatly increased by at least 10 to 200 times compared to those in the initially used oyster shells (Figure 5b). Most of the tested metal elements, including Ce, Fe, Eu, Yb, Er, U, Gd, Pr, and Al, could be recovered from the oyster shells with a recovery rate of more than 80%, and the elements Nd, Dy, La, Sm, and Tm could be recovered with a recovery rate higher than 60% (Figure 5c and Figure S7). These results prove that metal elements can be recovered from marine oyster shells with high efficiency.
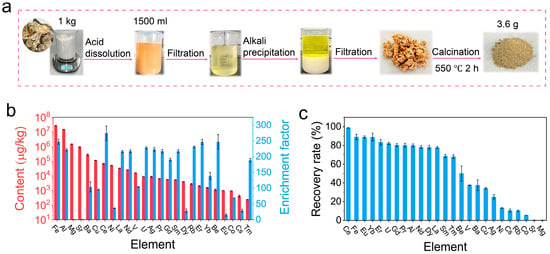
Figure 5.
The extraction of metal elements from oyster shells. (a) The steps for extracting metal elements from oyster shells. (b) The metal content in the ash product and the enrichment factor of the final precipitate. (c) The recovery rate of the metal elements from the oyster shells.
4. Conclusions
As global natural resources become increasingly scarce, especially with the rapid depletion of metal resources, finding sustainable metal resources has become an urgent task for modern society. This study was conducted to investigate and compare the potential of extracting metal resources from marine biological shell waste, and it is the first to reveal the advantages of marine biological shells in metal resource extraction. The findings of this study revealed that several high-value or important metal elements are highly concentrated in marine biological shells, with an enrichment ratio hundreds of thousands of times higher than their concentration in seawater. Based on the large amount of marine biological shells available globally, they may provide a large reserve of several high-value or important metals, including REEs, Li, U, Pd, Au, Ag, and Ga. Although the major components of marine biological shells include CaCO3, chitin, and protein, CaCO3 was found to be the main component for enriching metal elements via the mineralization process. More importantly, by using acid leaching and following the precipitation method, most of the metal elements could be recovered from the oyster shells, with a recovery efficiency higher than 80%. The findings of this study uncover both the value of marine biological shells as new metal resources and their main component for the enrichment of metal elements from seawater, and they can provide instructions for the design of materials to extract metal resources from seawater. Considering that marine biological shells have a regenerable property and are available in large quantities, they have the potential to become sustainable metal resources, thus providing a new solution for the resource utilization of solid waste.
The objective of this study was to explore an approach to increase the value of marine biological shells. The metal-enriching properties of marine biological shells offer new possibilities for developing functional materials, which can be utilized in the synthesis of advanced materials with enhanced adsorption or catalytic properties, thereby expanding their applications in water treatment and chemical synthesis. This resource reutilization reduces the risk of heavy metal accumulation and environmental pollution associated with traditional composting. In addition, treating marine shells as viable metal resources helps transform waste into value, improves resource utilization efficiency, and promotes sustainable development. Although marine biological shells have significant potential as metal resources, the scalability and economic feasibility of this process require further investigation and optimization before it can be applied on a large scale. Furthermore, pilot-scale testing is also required to validate the practical applicability of the process.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/su17062683/s1, Figure S1: Content of metal elements in oyster shells; Figure S2: Content of metal elements in crab shells; Figure S3: Content of metal elements in coral reef; Figure S4: Comparison of the concentration of metal elements in seawater, oyster shells, crab shells, and coral reef; Figure S5: The metal content in the leachate before and after the precipitation process; Figure S6: The precipitation ratio of the metal elements in oyster shells at different time intervals; Figure S7: The weight of the metal elements in 3.6 g of the ash product; Table S1: Analysis of the metal element content in different marine biological shells (ppb); Table S2: Content of metal elements in oyster shells; Table S3: Content of metal elements in crab shells; Table S4: Content of metal elements in coral reef; Table S5: Concentration of metal elements in natural seawater (ppb) [61]; Table S6: Enrichment ratios of metal elements in different marine biological shells compared with their concentrations in natural seawater.
Author Contributions
D.C.: Investigation, Data curation, Visualization, Formal analysis, Writing—original draft. X.C.: Investigation, Validation, Methodology, Formal analysis. X.T.: Methodology, Formal analysis. Q.P.: Conceptualization, Writing—review & editing. J.Z. (Jun Zhang): Methodology, Formal analysis. J.Z. (Jiacheng Zhang): Methodology, Formal analysis. Y.Y.: Supervision, Conceptualization, Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing. N.W.: Supervision, Resources, Writing—review & editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the specific research fund of the Innovation Platform for Academicians of Hainan Province (YSPTZX202214 and YSPTZX202316), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U2167220, 22327807, U23A20104, 22476040, and 32160033), the Hainan Province Science and Technology Special Fund (ZDYF2024SHFZ066), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2023YFC2809000), and the Innovation Fund for Scientific and Technological Personnel of Hainan Province (KJRC2023B01).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Shannon, M.A.; Bohn, P.W.; Elimelech, M.; Georgiadis, J.G.; Mariñas, B.J.; Mayes, A.M. Science and technology for water purification in the coming decades. Nature 2008, 452, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, B.E.; Elimelech, M. Membrane-based processes for sustainable power generation using water. Nature 2012, 488, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, R.; Markham, A.C.; Diaz Diaz, J.E.; Rosa Martinez Garcia, J.; Scarborough, C.; Greenfield, P.; Black, P.; Aguilera, S.E. Revisiting ocean thermal energy conversion. Mar. Policy 2012, 36, 463–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abehsera, S.; Bentov, S.; Li, X.; Weil, S.; Manor, R.; Sagi, S.; Li, S.; Li, F.; Khalaila, I.; Aflalo, E.D.; et al. Genes encoding putative bicarbonate transporters as a missing molecular link between molt and mineralization in crustaceans. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaraj, H.; Natarajan, A. Molecular mechanisms regulating molting in a crustacean. FEBS J. 2006, 273, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotodimas, I.; Ioannou, Z.; Kanlis, G.; Sarris, D.; Athanasekou, C. Sustainable Management of Shrimp Waste to Produce High-Added Value Carbonaceous Adsorbents. Sustainability 2024, 16, 10305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Li, W.; Da, B.; Meng, Y.; Chen, D. Research on properties of waste oyster shell mortar: The effect of calcination temperature of oyster shell powder. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 19, e02639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, J.; Lu, J.; Wang, D. Review of shell waste reutilization to promote sustainable shellfish aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 14, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, K.; Moulay, I.; Lee, D.; Myung, J.; Oh, S.; Kim, S.-H.; Choi, W.Y.; Park, J. Sustainable conversion of oyster shell waste into high-purity calcium carbonate via CO2 mineralization. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 115099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dima, J.B.; Sequeiros, C.; Zaritzky, N.E. Hexavalent chromium removal in contaminated water using reticulated chitosan micro/nanoparticles from seafood processing wastes. Chemosphere 2015, 141, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Shavandi, A.; Carne, A.; Bekhit, A.; Ng, T.; Randy, C.; Bekhit, A. Marine shells: Potential opportunities for extraction of functional and health-promoting materials. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 46, 1047–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Chen, X. Sustainability: Don’t waste seafood waste. Nature 2015, 524, 155–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, Z.; Wang, H.; Hu, S.; Wang, M.; Xu, S.; Zhang, W. Permeability and porosity of light-weight concrete with plastic waste aggregate: Experimental study and machine learning modelling. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnard, M.; Boury, B.; Parrot, I. Key Insights, Tools, and future prospects on oyster shell end-of-life: A critical analysis of sustainable solutions. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddhartha, T.R.; Kooy, E.; Kashif, M.; Che, C.A.; Ghysels, S.; Wu, D.; Ronsse, F.; Heynderickx, P.M. Evaluation of south korean marine waste resources for hydrochar production: Effect of process variables. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 410, 131286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamsomphong, K.; Xu, H.; Yang, P.; Yotpanya, N.; Yokoi, T.; Takahashi, F. Transforming waste into wealth in sustainable shrimp aquaculture: Effective phosphate removal and recovery using shrimp shell-derived adsorbents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 357, 129982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yang, H.; Yan, N. Shell biorefinery: Dream or reality? Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 13402–13421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ma, Z.; Song, L.; Farag, M.A. Maximizing crustaceans (shrimp, crab, and lobster) by-products value for optimum valorization practices: A comparative review of their active ingredients, extraction, bioprocesses and applications. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 57, 59–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamshina, J.L.; Kelly, A.; Oldham, T.; Rogers, R.D. Agricultural uses of chitin polymers. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hülsey, M.J. Shell biorefinery: A comprehensive introduction. Green Energy Environ. 2018, 3, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, G.M.; Mathew, D.C.; Sukumaran, R.K.; Sindhu, R.; Huang, C.-C.; Binod, P.; Sirohi, R.; Kim, S.-H.; Pandey, A. Sustainable and eco-friendly strategies for shrimp shell valorization. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, X. Effects of bean dregs and crab shell powder additives on the composting of green waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 260, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antu, M.A.; Ali, M.S.; Ferdous, M.J.; Ahmed, M.T.; Ali, M.R.; Suraiya, S.; Pangestuti, R.; Haq, M. Recovery and characterization of calcium-rich mineral powders obtained from fish and shrimp waste: A smart valorization of waste to treasure. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, V. In Valorization of Seafood Processing Discards: Bioconversion and Bio-Refinery Approaches. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 611835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ÁLvarez, E.; FernÁNdez-Sanjurjo, M.J.; Seco, N.; NÚÑEz, A. Use of Mussel Shells as a Soil Amendment: Effects on Bulk and Rhizosphere Soil and Pasture Production. Pedosphere 2012, 22, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.; Majumdar, A. Opportunities and challenges for a sustainable energy future. Nature 2012, 488, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampert, A. Over-exploitation of natural resources is followed by inevitable declines in economic growth and discount rate. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jowitt, S.M.; Mudd, G.M.; Thompson, J.F.H. Future availability of non-renewable metal resources and the influence of environmental, social, and governance conflicts on metal production. Commun. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.H.; Giurco, D.; Arndt, N.; Nickless, E.; Brown, G.; Demetriades, A.; Durrheim, R.; Enriquez, M.A.; Kinnaird, J.; Littleboy, A.; et al. Mineral supply for sustainable development requires resource governance. Nature 2017, 543, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diallo, M.S.; Kotte, M.R.; Cho, M. Mining Critical Metals and Elements from Seawater: Opportunities and Challenges. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 9390–9399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Zhao, Y. Mineral resource extraction and environmental sustainability for green recovery. Resour. Policy 2024, 90, 104616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henckens, T. Scarce mineral resources: Extraction, consumption and limits of sustainability. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 169, 105511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Ji, G.; Chen, H.; Yang, S.; Guo, B.; Yang, H.; Huang, Z. Molybdenum sulphide modified chelating resin for toxic metal adsorption from acid mine wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 251, 117407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masindi, V.; Fosso-Kankeu, E.; Mamakoa, E.; Nkambule, T.T.I.; Mamba, B.B.; Naushad, M.; Pandey, S. Emerging remedia-tion potentiality of struvite developed from municipal wastewater for the treatment of acid mine drainage. Environ. Res. 2022, 210, 112944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Feng, L.; Wang, M.; Yuan, Y.; Yu, Q.; Feng, T.; Cao, M.; Wang, N.; Peng, Q. Highly efficient extraction of uranium from seawater by natural marine crab carapace. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 133038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, C.T.; Tran, T.N.; Nguyen, V.B.; Nguyen, A.D.; Wang, S.-L. Reclamation of Marine Chitinous Materials for Chitosanase Production via Microbial Conversion by Paenibacillus macerans. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolaimate, A.; Desbrieres, J.; Rhazi, M.; Alagui, A. Contribution to the preparation of chitins and chitosans with controlled physico-chemical properties. Polymer 2003, 44, 7939–7952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwase, K.; Harunari, Y.; Teramoto, M.; Mori, K. Crystal structure, microstructure, and mechanical properties of heat-treated oyster shells. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2023, 147, 106107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gbenebor, O.; Odili, C.; Lawal, G.; Adeosun, S.; Unilorin, N. Crab (Brachyura) shell Acid and Alkali Treatments- Influence on Thermal and Structural Properties of Isolated Acetamide-Rich Natural Polymer. Niger. J. Technol. Dev. 2023, 20, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, P.; Huang, H.; Lei, L.; Galindo Torres, S.A.; Li, L. Internal hydrodynamics within the skeleton of Acropora pulchra coral. iScience 2025, 28, 111742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, K.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, J.; Pan, H.; Tang, R. Biomineralization strategy: From material manufacturing to biological regulation. Giant 2024, 19, 100317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farfan, G.A.; Apprill, A.; Cohen, A.; DeCarlo, T.M.; Post, J.E.; Waller, R.G.; Hansel, C.M. Crystallographic and chemical signatures in coral skeletal aragonite. Coral Reefs 2022, 41, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, Z.; Zhou, J.; Shi, D.; Zheng, J. Particle size effect on the mechanical behaviour of coral sand—Geogrid interfaces. Geosynth. Int. 2025, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namikawa, Y.; Suzuki, M. Atmospheric CO2 Sequestration in Seawater Enhanced by Molluscan Shell Powders. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 2404–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garai, M.; Yavuz, C.T. Radioactive Strontium Removal from Seawater by a MOF via Two-Step Ion Exchange. Chem 2019, 5, 750–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Dai, X.; Chen, X.; Ali, I.; Chen, H.; Gou, J.; Zhuo, C.; Huang, M.; Zhu, B.; Tang, Y.; et al. Combined forage grass-microbial for remediation of strontium-contaminated soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 450, 131013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostial, K.; Vojvodic, S.; Comar, C.L. Effects of Dietary Levels of Phosphorus and Calcium on the Comparative Behaviour of Strontium and Calcium. Nature 1965, 208, 1110–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Dai, X.; Zhu, L.; Xiao, C.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Alekseev, E.V.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; et al. Distinctive Two-Step Intercalation of Sr2+ into a Coordination Polymer with Record High 90Sr Uptake Capabilities. Chem 2019, 5, 977–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, A.J.; Lytle, D.A.; Harmon, S.; Vu, K.; Chait, H.; Dionysiou, D.D. Removal of strontium from drinking water by conventional treatment and lime softening in bench-scale studies. Water Res. 2016, 103, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-M.; Jeon, H.; Lee, Y.; Choi, M. Sulfur-modified zeolite A as a low-cost strontium remover with improved selectivity for radioactive strontium. Chemosphere 2022, 299, 134309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Chen, X.; Cao, M.; Zhao, S.; Wang, H.; Chen, D.; Ma, Y.; Liu, T.; Wang, N.; Yuan, Y. Decorating Channel Walls in Metal–Organic Frameworks with Crown Ethers for Efficient and Selective Separation of Radioactive Strontium (II). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202312894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parekh, P.P.; Möller, P.; Dulski, P.; Bausch, W.M. Distribution of trace elements between carbonate and non-carbonate phases of limestone. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1977, 34, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terakado, Y.; Masuda, A. The coprecipitation of rare-earth elements with calcite and aragonite. Chem. Geol. 1988, 69, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Mucci, A. Partitioning of rare earth elements (REEs) between calcite and seawater solutions at 25 °C and 1 atm, and high dissolved REE concentrations. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terribili, L.; Rateau, R.; Szucs, A.M.; Maddin, M.; Rodriguez-Blanco, J.D. Impact of Rare Earth Elements on CaCO3 Crystallization: Insights into Kinetics, Mechanisms, and Crystal Morphology. Cryst. Growth Des. 2024, 24, 632–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biscéré, T.; Ferrier-Pagès, C.; Gilbert, A.; Pichler, T.; Houlbrèque, F. Evidence for mitigation of coral bleaching by manganese. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiva, A.; Neder, M.; Kahil, K.; Gavriel, R.; Pinkas, I.; Goobes, G.; Mass, T. Minerals in the pre-settled coral Stylophora pistillata crystallize via protein and ion changes. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, P.U.P.A.; Bergmann, K.D.; Boekelheide, N.; Tambutté, S.; Mass, T.; Marin, F.; Adkins, J.F.; Erez, J.; Gilbert, B.; Knutson, V.; et al. Biomineralization: Integrating mechanism and evolutionary history. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabl9653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.-Q.; Liu, J.-H.; Aymonier, C.; Fermani, S.; Kralj, D.; Falini, G.; Zhou, C.-H. Calcium carbonate: Controlled synthesis, surface functionalization, and nanostructured materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 7883–7943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthoni, J. Oceanic Abundance of Elements. 2006. Available online: www.seafriends.org.nz/oceano/seawater.htm (accessed on 3 February 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).