Analysis of the Quality of Typical Acidic Groundwater of the Guangwang Mining Area and Its Associated Human Health Risks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
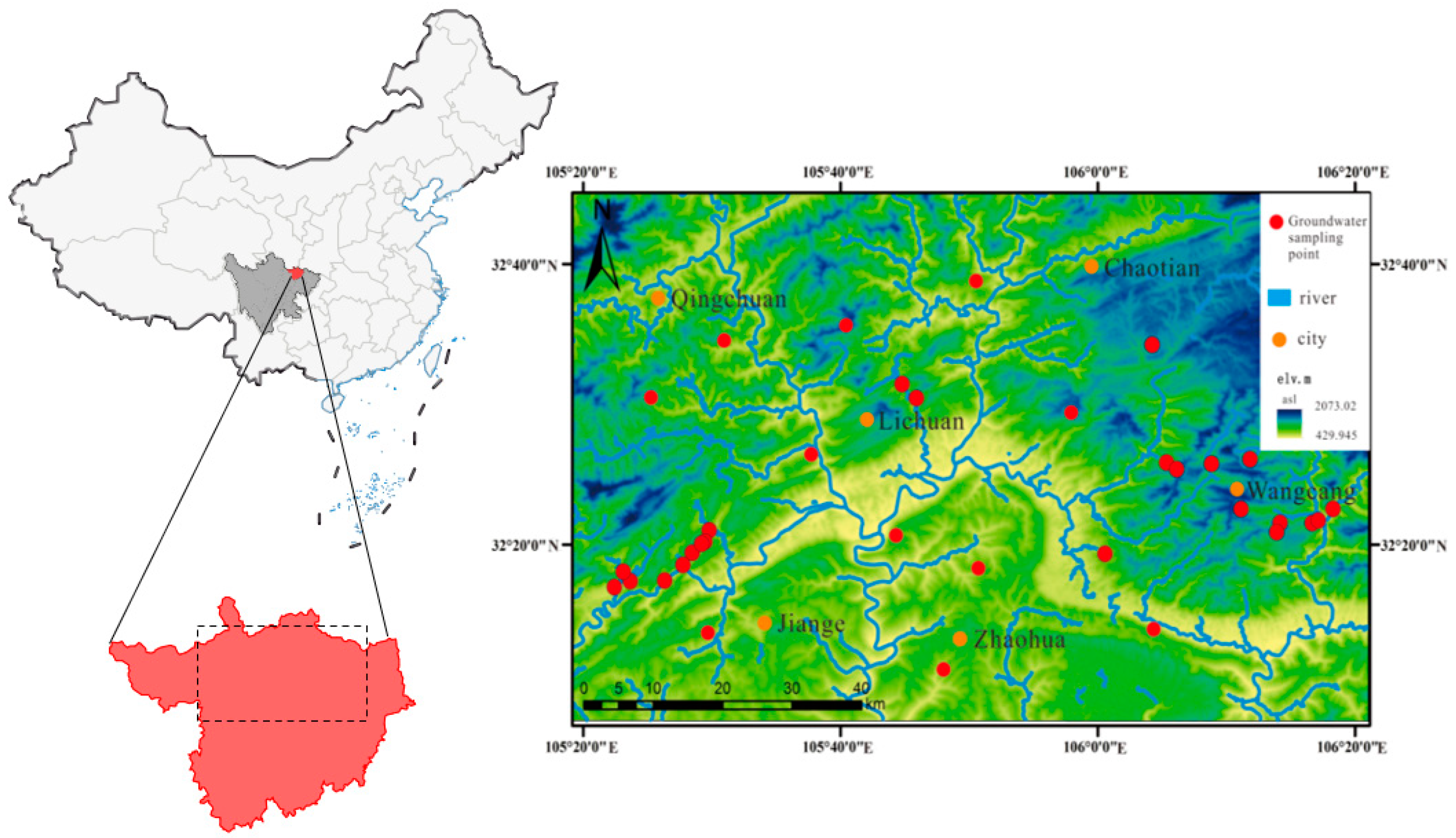
2.1. Area of Study and Sample Positions
2.2. Collection, Preparation, and Analysis of Samples
2.3. Data Analysis
2.4. Entropy-Weighted Water Quality Index (EWQI)
2.5. Appraisal of Human Exposure and the Hazards to Health
2.5.1. Model of Exposure
2.5.2. Characterization of the Hazards
- (1)
- Carcinogenic hazards
- (2)
- Non-carcinogenic hazards
3. Conclusions and Discussion
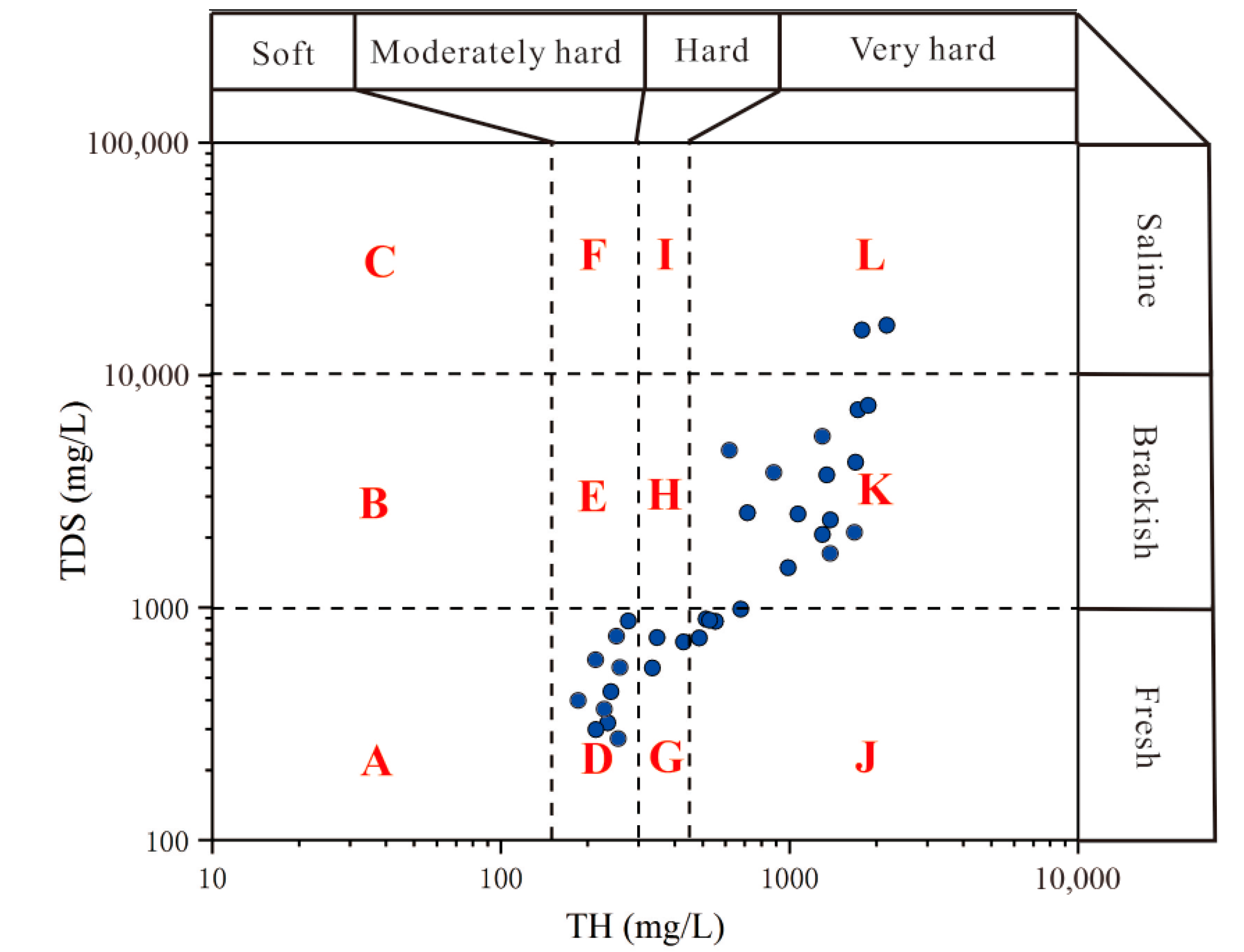
3.1. Hydro-Geochemical Properties of Groundwater
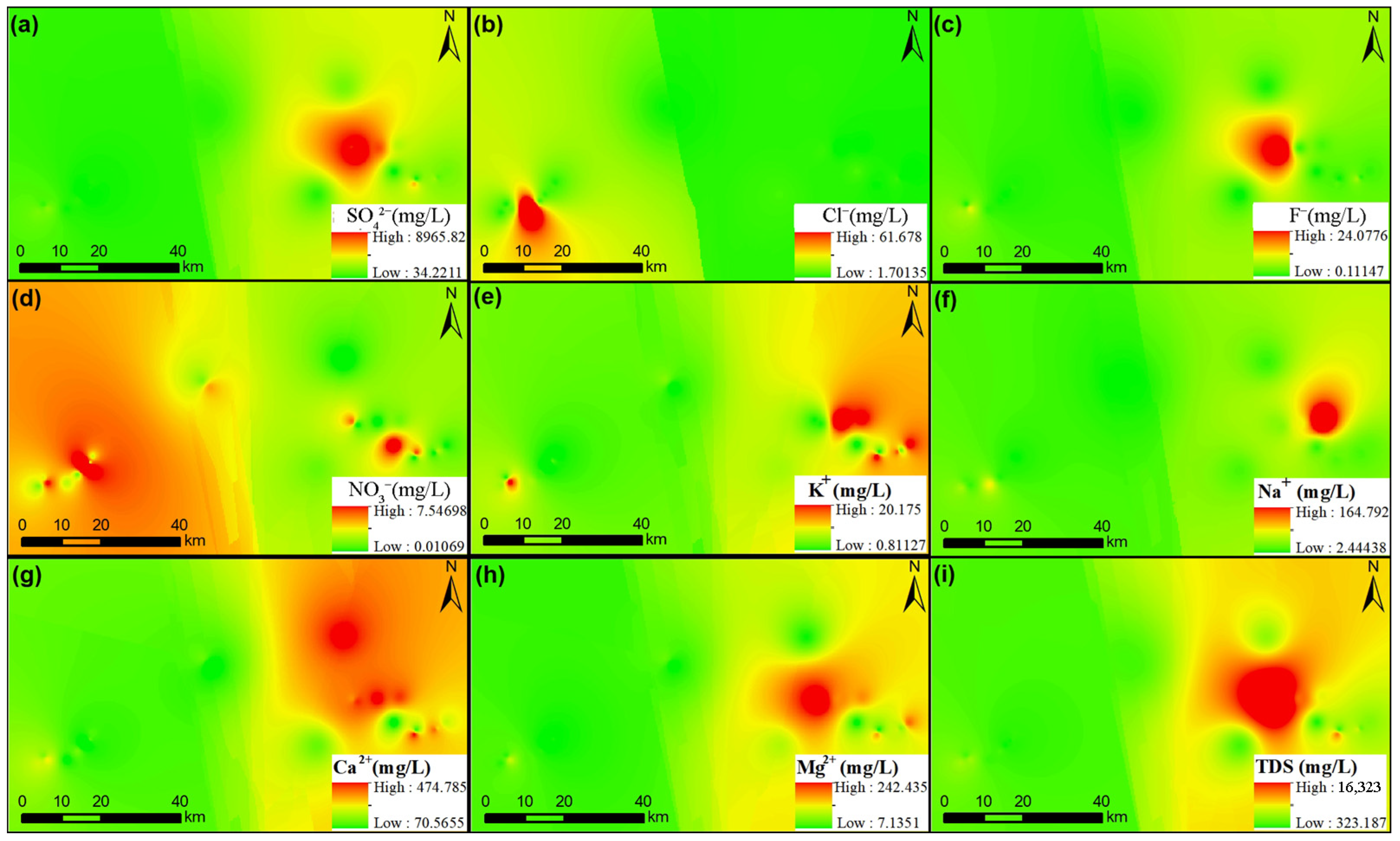
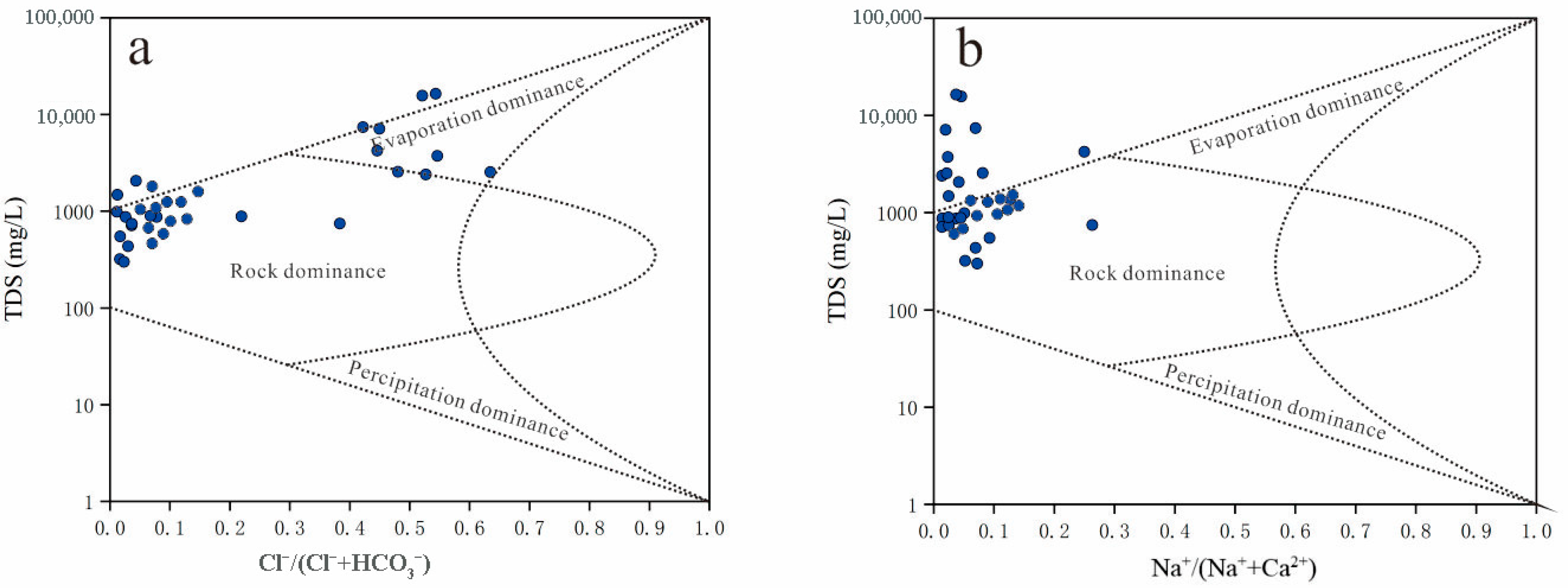
3.2. Factors Regulating Groundwater Chemistry in the Study Region
3.3. Characterization of Groundwater Toxic Metals
Levels of Groundwater Toxic Metals
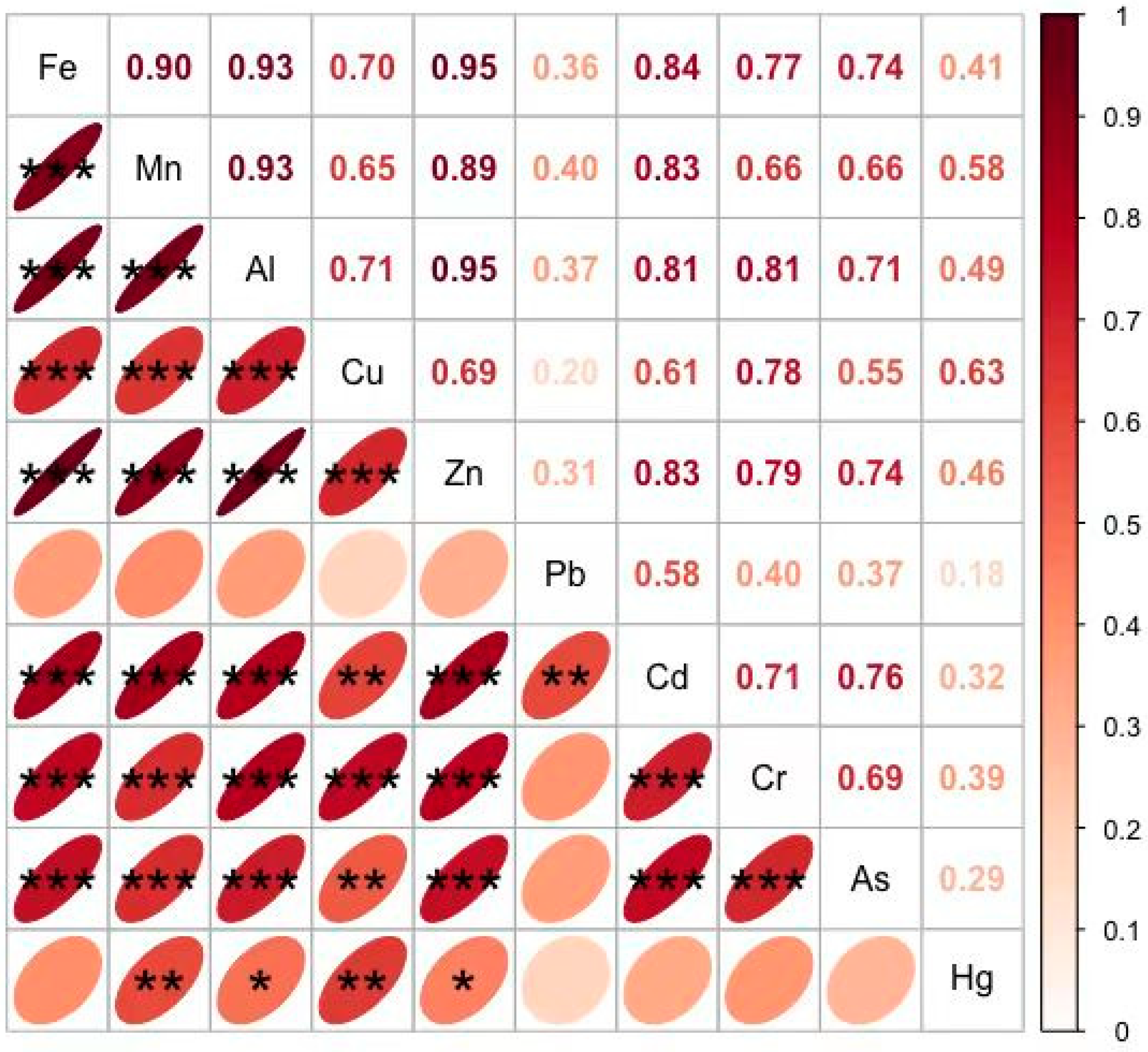
3.4. 2 Relationships Between Metals in the Groundwater Samples
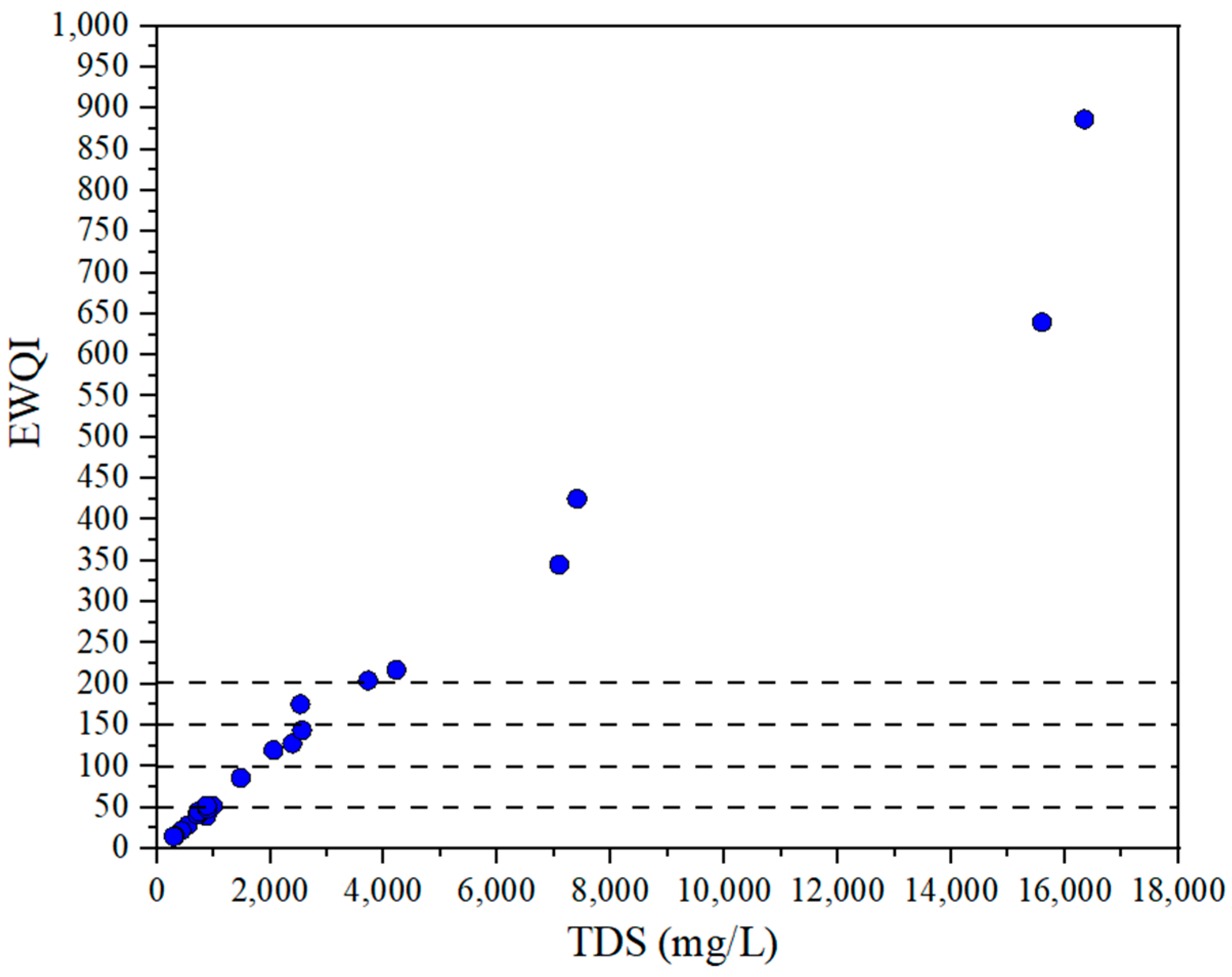
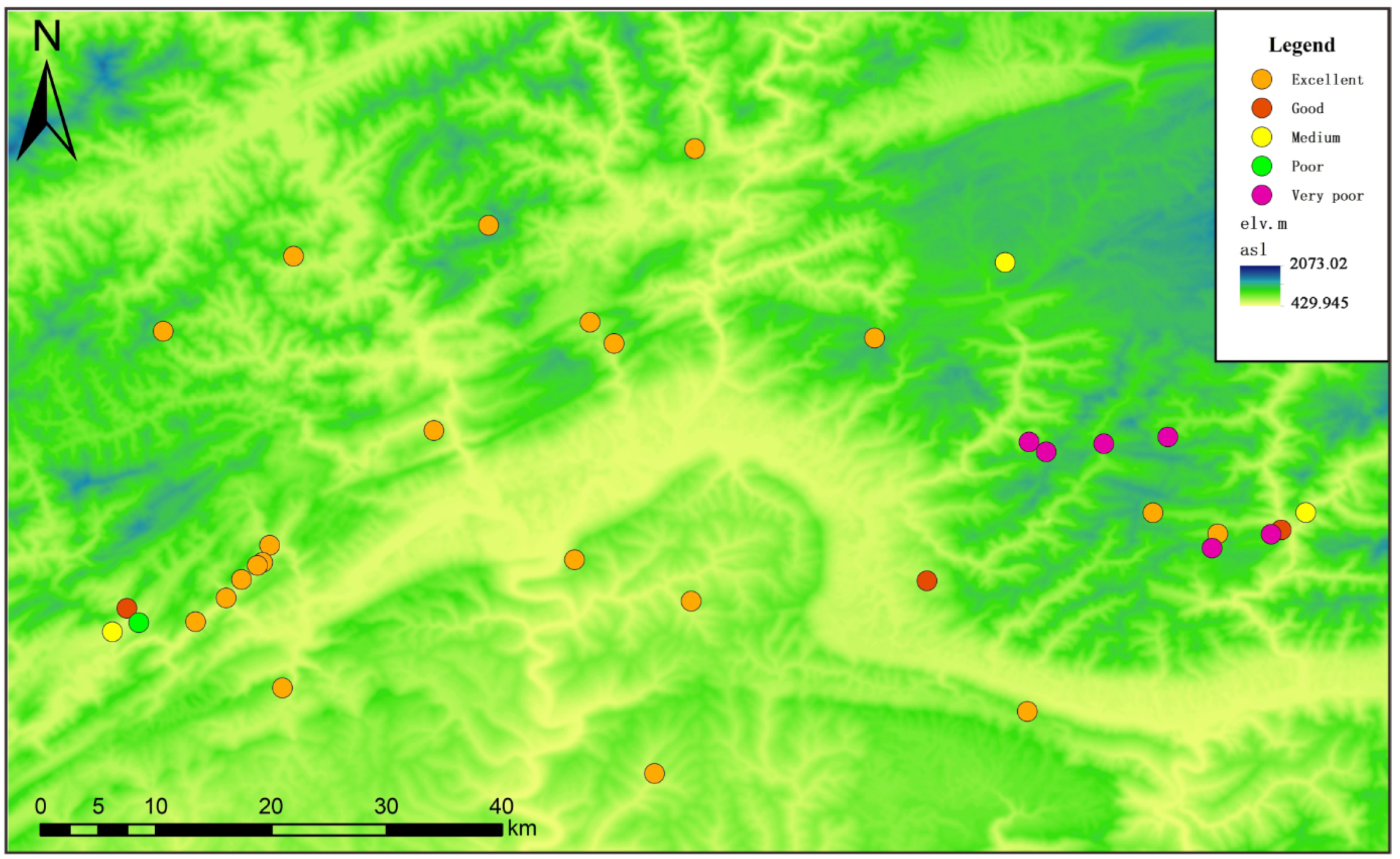
3.5. EWQI Assessment of Groundwater Quality
3.6. Appraisal of the Hazards Posed by the Groundwater Quality to Human Health and Uncertainty Analysis
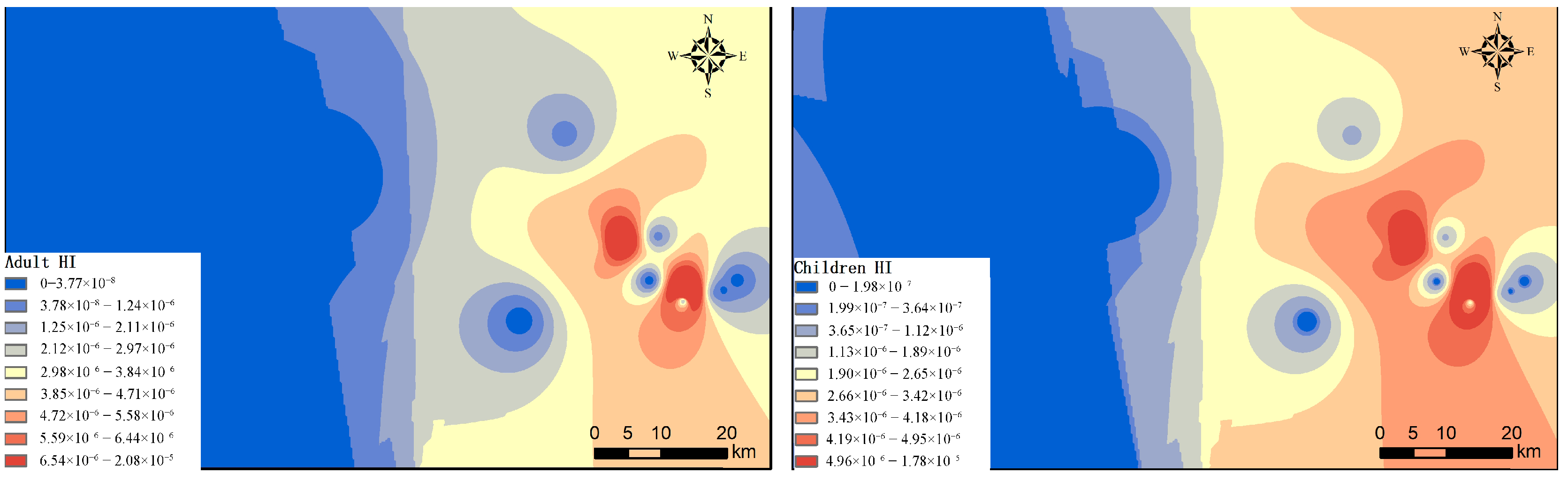
3.6.1. Appraisal of the Health Risk
3.6.2. Sources of Uncertainty
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.H.; Dai, Y.S.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Pei, Q.M. Hydrochemistry, quality and potential health risk appraisal of nitrateenriched groundwater in the Nanchong area, southwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 784, 147186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emenike, P.C.; Nnaji, C.C.; Tenebe, I.T. Assessment of geospatial and hydrochemical interactions of groundwater quality, southwestern Nigeria. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Gao, Z.; Wang, M.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Shi, M.; Zhang, H. Study on the dynamic characteristics of groundwater in the valley plain of Lhasa City. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Peng, Y.; Li, C.; Gao, Z.; Chen, S. Characterization of the hydrochemistry of water resources of the Weibei Plain, Northern China, as well as an assessment of the risk of high groundwater nitrate levels to human health. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, A.; Hassani, H.; Tziritis, E.; Mousavi, S.B.F.; Jabbari, N. Hydrochemical characterization and evaluation of groundwater quality in Dalgan basin, SE Iran. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 10, 100353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Qian, H.; Zheng, L.; Feng, W.; Wang, H.; Gao, Y. Alterations to groundwater chemistry due to modern water transfer for irrigation over decades. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adimalla, N. Application of the Entropy Weighted Water Quality Index (EWQI) and the Pollution Index of Groundwater (PIG) to Assess Groundwater Quality for Drinking Purposes: A Case Study in a Rural Area of Telangana State, India. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 80, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marghade, D.; Malpe, D.B.; Duraisamy, K.; Patil, P.D.; Li, P. Hydrogeochemical evaluation, suitability, and health risk assessment of groundwater in the watershed of Godavari basin, Maharashtra, Central India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 28, 18471–18494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Z.; Lu, G.L.; Yang, C.; Yi, X.Y.; Guo, C.L. Source control and remediation of environmental contamination in metal sulfide mine areas. J. South China Univ. Technol. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2012, 40, 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, S.M.; Zhou, Y.Z.; Gao, Q.Z.; Yang, Z.J.; Zhang, C.B.; Yang, X.Q.; Zhao, Y.Y. Environmental geochemistry of metallic sulfide mines—A review. Earth Environ. 2006, 34, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Nieva, N.E.; Borgnino, L.; García, M.G. Long term metal release and acid generation in abandoned mine wastes containing metal-sulphides. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elijah, M.M.; Wanda, G.C.; Felix, M.T. Hydrogeochemical characterization of water quality evolution within Livingstonia coalfield mining areas in Rumphi district, northern Malawi. Phys. Chem. Earth 2021, 123, 103045. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.L.; Zhao, Q.; Zheng, L.G.; Chen, X.; Li, C.; Ren, M.X. Distribution, source and health risk assessment based on the Monte Carlo method of heavy metals in shallow groundwater in an area affected by mining activities, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 224, 112679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Routha, J.; Dario MSarkar, S.; Wei, L.Z.; Luo, D.G.; Liu, Y. Distribution and mobilization of heavy metals at an acid mine drainage affected region in South China, a post-remediation study. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 138122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour, A.; Gharehchahi, E.; Gharaghani, M.A.; Shahsavani, E.; Golaki, M.; Berndtsson, R.; Khaneghah, A.M.; Hashemi, H.; Abolfathi, S. Assessment of drinking water quality and identifying pollution sources in a chromite mining region. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivares, D.M.M.; Santana, C.S.; Neris, J.B.; Luzardo, F.H.M.; Fausto, A.M.F.; Mol, A.W.; Velasco, F.G. Assessment of potential human health, radiological and ecological risks around mining areas in northeastern Brazil. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.K. Distribution of coal types in the Guangwang coal field. J. Sichuan Geol. 2010, 30, 404–405. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Wu, X.; Qian, C.; Zhu, G. Hydrogeochemistry and groundwater quality assessment of high fluoride levels in the Yanchi endorheic region, northwest China. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 98, 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adimalla, N.; Qian, H.; Li, P.Y. Entropy water quality index and probabilistic health risk assessment from geochemistry of groundwaters in hard rock terrain of Nanganur County, South India. Geochemistry 2019, 80, 125544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, N.S. Hydrogeology: Problems with Solutions; Prentice Hall of India: New Delhi, India, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fryer, M.; Collins, C.D.; Ferrier, H.; Colvile, R.N.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J. Human exposure modelling for chemical risk assessment: A review of current approaches and research and policy implications. Environ. Sci. Policy 2006, 9, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.B.; Li, W.Q.; Guo, J.; Chen, X.P.; Gan, B.; Yang, Y.J.; Yang, Q.; Fan, D.L. Comparison and preference of source analysis models for heavy metal contamination of soil from alum mines in Anhui Province, China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. Trans. CSAE 2024, 40, 321–327. [Google Scholar]
- Giri, S.; Singh, A.K. Risk assessment, statistical source identification and seasonal fluctuation of dissolved metals in the Subarnarekha River, India. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 265, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USEPA. Exposure Factors Handbook; Office of Research and Development: Washington, DC, USA, 1997.
- USEPA. Regional Screening Levels (RSL) Tables; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2011.
- Piper, A.M. A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union. 1944, 25, 914–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Wang, L.; Ma, H.; Yu, K.; Martín, J.D. Hydrochemical characterization and pollution sources identification of groundwater in Salawusu aquifer system of Ordos Basin, China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Jia, Y.; Yang, Y.; Huan, H.; Lian, X.; Xu, X.; Xia, F.; Han, X.; Jiang, Y. Hydrogeochemical and statistical analysis of high fluoride groundwater in northern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 34840–34861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yidana, S.M.; Bawoyobie, P.; Sakyi, P.; Fynn, O.F. Evolutionary analysis of groundwater flow: Application of multivariate statistical analysis to hydrochemical data in the Densu Basin, Ghana. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2018, 138, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality, 4th ed.; WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Saravanan, K.; Srinivasamoorthy, K.; Gopinath, S.; Prakash, R.; Suma, C.S. Investigation of hydrogeochemical processes and groundwater quality in Upper Vellar sub-basin Tamilnadu, India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukate, S.V.; Panaskar, D.B.; Wagh, V.M.; Baker, S.J. Understanding the influence of industrial and agricultural land uses on groundwater quality in semiarid region of Solapur, India. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 22, 3207–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, N.S.; Subrahmanyam, A.; Rao, G.B. Fluoride-bearing groundwater in Gummanampadu Sub-basin, Guntur District, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 70, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, N.S.; Ravindra, B.; Wu, J. Geochemical and health risk evaluation of fluoride rich groundwater in Sattenapalle Region, Guntur district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2020, 26, 2316–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minet, E.; Goodhue, R.; Meier-Augenstein, W.; Kalin, R.; Fenton, O.; Richards, K.; Coxon, C. Combining stable isotopes with contamination indicators: A method for improved investigation of nitrate sources and dynamics in aquifers with mixed nitrogen inputs. Water Res. 2017, 124, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.; Srivastava, P.K.; Pandey, A.C. Fluoride contamination mapping of groundwater in Northern India integrated with geochemical indicators and GIS. Water Supply 2013, 13, 1513–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, N.S.; Sunitha, B.; Adimalla, N.; Chaudhary, M. Quality criteria for groundwater use from a rural part of Wanaparthy District, Telangana State, India, through ionic spatial distribution (ISD), entropy water quality index (EWQI) and principal component analysis (PCA). Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 579–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, R.J. Mechanisms Controlling World Water Chemistry. Science 1970, 170, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.S.U.; Rai, A.K. Groundwater quality assessment in the Lower Ganga Basin using entropy information theory and GIS. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 274, 123077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.W.; Chen, G.Y.; Qiong, D.Z.; Zhou, P.; Wang, J.; Tian, Z. Health risk assessment of residents in Groundwater quality of Lhasa Municipal Landfill. Environ. Chem. 2020, 39, 1513–1522. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.M.; Jiang, Z.C.; Qin, X.Q.; Zhang, L.K. Heavy Metal Distribution and Health Risk Assessment in Groundwater and Surface Water of Karst Lead–Zinc Mine. Water 2024, 16, 2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Rank | EWQI | Water Quality |
|---|---|---|
| I | <50 | Excellent |
| II | 50–100 | Good |
| III | 100–150 | Medium |
| IV | 150–200 | Poor |
| V | >200 | Extremely poor |
| Parameter | Abbreviation | Values | Distribution | Units | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adult | Children | ||||
| Element Concentration | C | Measured | Measured | Log-normal | mg/L |
| Daily Ingestion Rate | IR | 2.2 | 1.32 | Normal | L/d |
| Exposure Skin Area | SA | 17,000 | 13,300 | Fixed value | cm2 |
| Conversion Factor | CF | 0.001 | 0.001 | Fixed value | L/cm3 |
| Skin Permeability Coefficient | PC | 0.0001 (Mn and Pb) 0.001 (Fe, As, Cu and Cd) 0.002 (Cr) 0.0006 (Zn) | Fixed value | cm/h | |
| Exposure Frequency | EF | 350 | 350 | Triangular | d/a |
| Exposure Duration | ED | 70 (Cd, Cr and As) 35 (Fe, Mn, Cu, Zn and Pb) | Fixed value | a | |
| Exposure Time | ET | 0.33 | 0.18 | Fixed value | h/d |
| Body Weight | BW | 60.6 | 42.6 | Normal | kg |
| Average Time | AT | 25,500 (Cd, Cr and As) 12,775 (Fe, Mn, Cu, Zn and Pb) | Fixed value | d | |
| Average Life | L | 70 | 70 | Fixed value | a |
| Non-Carcinogen | RfD (mg kg−1 d−1) | Carcinogen | SF (mg kg−1 d−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ingestion | Dermal | Ingestion | Dermal | ||
| Mn | 1.4 × 10−1 | 8.0 × 10−4 | Cd | 6.1 | 0.38 |
| Zn | 3.0 × 10−1 | 1.0 × 10−1 | Cr | 41 | 0.5 |
| Pb | 1.4 × 10−3 | 4.2 × 10−4 | As | 15 | 3.66 |
| Cu | 5.0 × 10−3 | 1.2 × 10−2 | |||
| Fe Hg | 3.0 × 10−1 1.0 × 10−4 | 4.5 × 10−2 3.0 × 10−4 | |||
| Parameters | Max | Min | Median | Mean | SD | CV (%) | WHO [30] | % of SEL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.06 | 2.49 | 6.28 | 5.48 | 2.12 | 0.39 | 6.5~8.5 | 52.17 |
| TDS | 16,347.00 | 299.00 | 985.00 | 3204.48 | 4485.41 | 1.40 | 1000.00 | 47.83 |
| TH | 2175.00 | 214.00 | 679.00 | 909.13 | 623.28 | 0.69 | 450.00 | 69.57 |
| SO42− | 8980.00 | 34.20 | 484.00 | 1655.15 | 2315.81 | 1.40 | 250.00 | 82.61 |
| Cl− | 61.80 | 1.70 | 2.36 | 5.02 | 12.39 | 2.47 | 250.00 | 0.00 |
| F− | 24.20 | 0.11 | 0.53 | 2.72 | 5.59 | 2.06 | 1.50 | 26.09 |
| NO3− | 7.99 | 0.01 | 1.33 | 1.84 | 2.09 | 1.13 | 45.00 | 0.00 |
| K+ | 20.20 | 0.64 | 3.76 | 6.27 | 5.95 | 0.95 | - | - |
| Na+ | 165.00 | 2.41 | 9.75 | 19.31 | 33.55 | 1.74 | 200.00 | 0.00 |
| Ca2+ | 475.00 | 64.00 | 181.00 | 246.43 | 141.38 | 0.57 | 200.00 | 47.83 |
| Mg2+ | 243.00 | 7.00 | 30.00 | 67.09 | 69.83 | 1.04 | 150.00 | 13.04 |
| Parameters | Max | Min | Median | Mean | SD | CV (%) | WHO [30] | % of SEL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | 2235.00 | 0.01 | 31.40 | 303.24 | 609.12 | 2.01 | 0.30 | 78.26 |
| Mn | 7.80 | 0.01 | 0.61 | 1.72 | 2.52 | 1.47 | 0.50 | 73.91 |
| Al | 545.00 | 0.08 | 1.16 | 66.97 | 147.04 | 2.20 | 0.20 | 78.26 |
| Cu | 3.06 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.29 | 0.87 | 3.04 | 1.00 | 8.70 |
| Zn | 19.00 | 0.01 | 0.32 | 2.98 | 5.52 | 1.85 | 3.00 | 26.09 |
| Pb | 58.30 | 0.12 | 0.70 | 4.50 | 12.74 | 2.83 | 0.01 | 100.00 |
| Cd (μg/L) | 1378.00 | 0.01 | 2.46 | 194.53 | 447.02 | 2.30 | 3.00 | 43.48 |
| Cr | 1.29 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.19 | 0.40 | 2.12 | 0.05 | 26.09 |
| As (μg/L) | 56.20 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 3.67 | 11.69 | 3.19 | 10.00 | 4.35 |
| Hg (μg/L) | 0.36 | 0.01 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.81 | 1.00 | 0.00 |
| Carcinogen | Non-Carcinogen | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element | Cd | Cr | As | Fe | Mn | Cu | Zn | Pb |
| Adults ingestion | 1.36 × 10−2 | 8.74 × 10−2 | 2.06 × 10−5 | 1.16 × 10−5 | 1.41 × 10−7 | 6.54 × 10−7 | 1.13 × 10−7 | 3.68 × 10−5 |
| Children ingestion | 1.16 × 10−2 | 7.46 × 10−2 | 1.75 × 10−5 | 9.87 × 10−6 | 1.20 × 10−7 | 5.59 × 10−7 | 9.68 × 10−8 | 3.14 × 10−5 |
| Adults dermal | 2.16 × 10−6 | 4.46 × 10−4 | 5.24 × 10−8 | 1.97 × 10−7 | 6.27 × 10−8 | 6.95 × 10−10 | 5.21 × 10−10 | 3.13 × 10−8 |
| Children dermal | 2.11 × 10−5 | 2.71 × 10−4 | 3.18 × 10−8 | 1.19 × 10−7 | 3.81 × 10−8 | 4.22 × 10−10 | 3.16 × 10−10 | 1.90 × 10−8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, G.; Gao, M.; Zhu, M.; Ren, S.; Fan, J. Analysis of the Quality of Typical Acidic Groundwater of the Guangwang Mining Area and Its Associated Human Health Risks. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2677. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062677
Liu G, Gao M, Zhu M, Ren S, Fan J. Analysis of the Quality of Typical Acidic Groundwater of the Guangwang Mining Area and Its Associated Human Health Risks. Sustainability. 2025; 17(6):2677. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062677
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Guo, Man Gao, Mingtan Zhu, Shuang Ren, and Jiajun Fan. 2025. "Analysis of the Quality of Typical Acidic Groundwater of the Guangwang Mining Area and Its Associated Human Health Risks" Sustainability 17, no. 6: 2677. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062677
APA StyleLiu, G., Gao, M., Zhu, M., Ren, S., & Fan, J. (2025). Analysis of the Quality of Typical Acidic Groundwater of the Guangwang Mining Area and Its Associated Human Health Risks. Sustainability, 17(6), 2677. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062677





