A Review of the Properties, Transport, and Fate of Organophosphate Esters in Polar Snow and Ice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Persistence Mechanisms of POPs in Snow and Ice
3. OPE Distribution in Snow and Ice
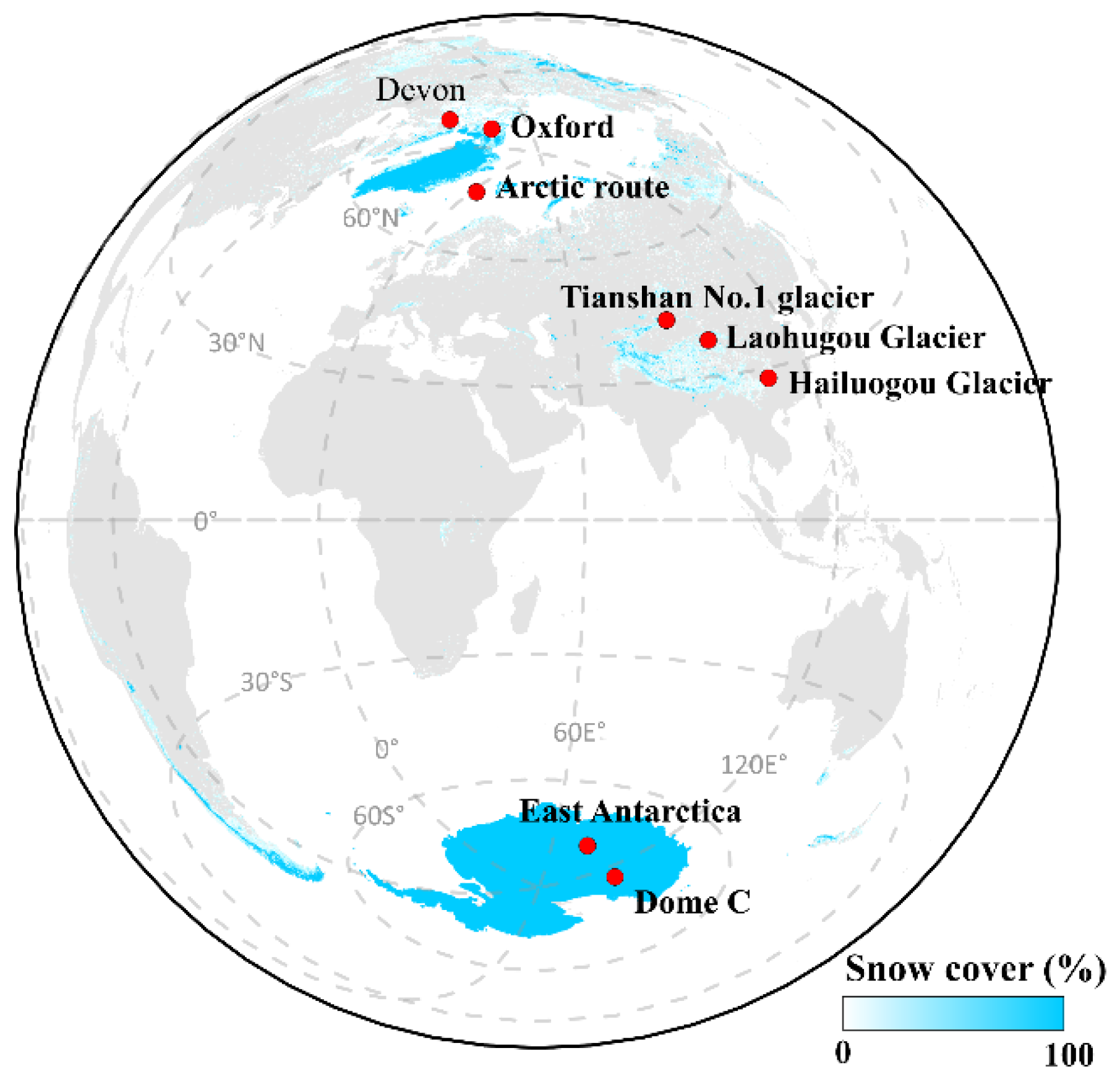
3.1. Arctic
3.2. Antarctica
3.3. Tibetan Plateau
4. Drivers of OPE Distribution in Polar Snow and Ice
4.1. Atmospheric Transport
4.2. Ocean Current Transport
4.3. Local Emissions
5. Research Prospects
- (1)
- Geochemical Cycle of OPEs in Snow and Ice Under Climate Change and Human Activity. Due to the challenges of glacier sampling, research on OPEs in snow and ice primarily focuses on fundamental aspects such as concentration, sources, and distribution characteristics, particularly in high-altitude mountainous regions. However, there is still limited understanding of the environmental behaviors of OPEs in snow and ice, such as atmospheric deposition and post-deposition dynamics. Future research should focus on systematically investigating the storage, spatial distribution, and seasonal deposition patterns of OPEs in ice sheets. Additionally, studies should explore the air-particle distribution characteristics of OPEs during atmospheric transport and assess the process and mechanisms of atmospheric transmission. Snow pit samples could be valuable for understanding photochemical reactions of OPEs in cold and environments and clarifying post-deposition processes. Further, combining increasingly available OPEs data with multi-media fugacity models will help evaluate the environmental behavior of OPEs, including their occurrence, migration, and fate in cold regions.
- (2)
- Impact of OPE Release from Snow and Ice on Downstream Ecosystems. Snow and ice in the cryosphere serve as crucial enrichment zones for OPEs transported from lower latitudes via long-range atmospheric transport. These regions also act as secondary emission sources of OPEs, particularly under the influence of climate warming. However, the full impact of OPEs on the cryosphere ecosystem and human health remains unclear. Further research is needed to investigate the consequences of OPEs on ecosystems exposed to enriched environments, including during the snow and ice melting season. Specific attention should be given to the release of OPEs into meltwater and their subsequent enrichment in downstream rivers and lakes. Quantitative studies are needed to assess the risks posed by OPEs to downstream ecosystems and determine whether the accumulation of OPEs in these ecosystems could elevate toxicological risks.
- (3)
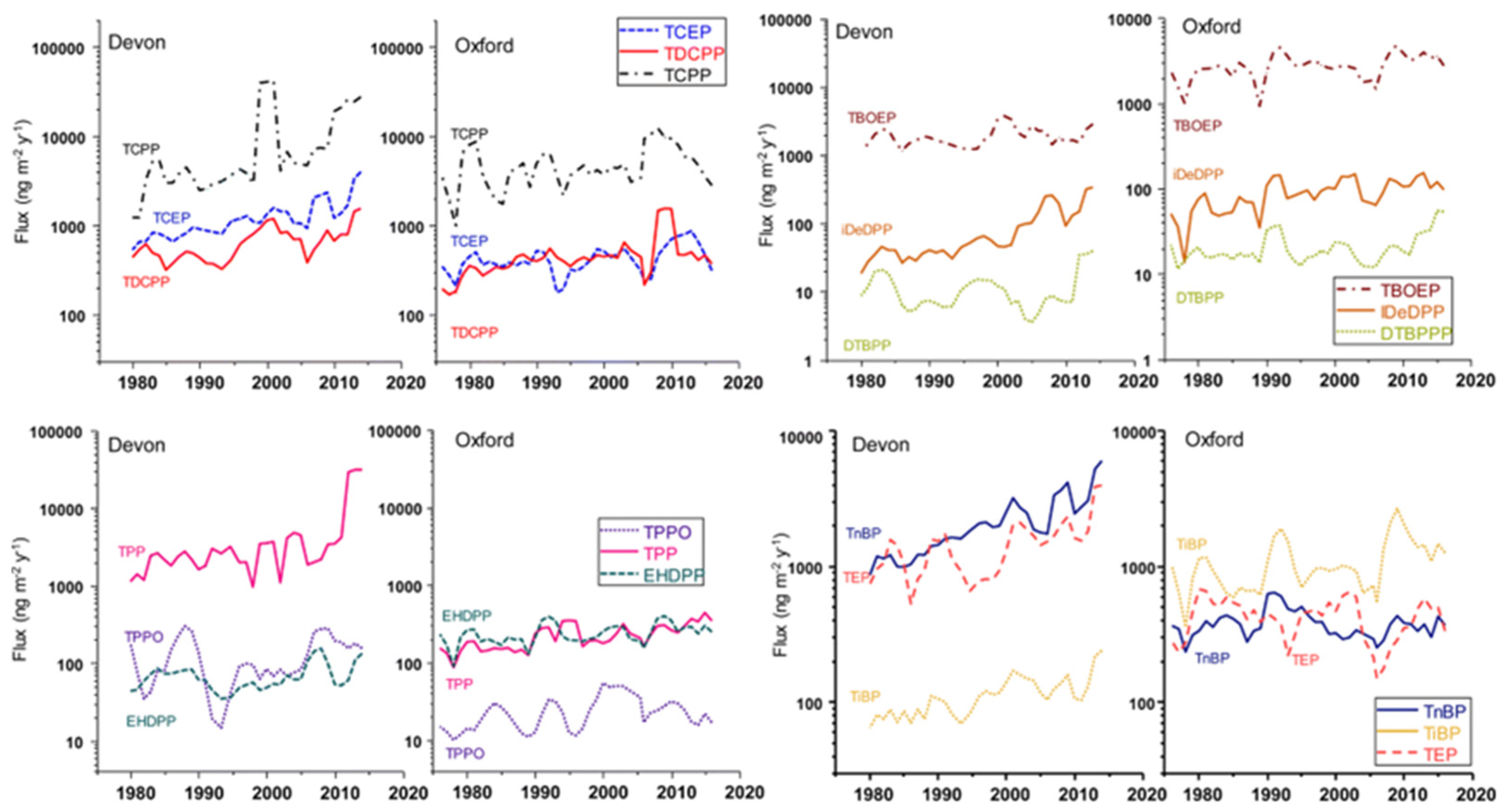
- Using Ice Core Records to Reconstruct Past Human Emissions of OPEs. Ice cores are invaluable for reconstructing historical atmospheric pollution emissions. However, the analysis of OPEs in ice cores is complicated by the need for sample pre-enrichment, which hinders progress. So far, studies on historical changes in OPEs have been limited, with the Devon and Oxford ice cores in the Canadian high Arctic being among the few to have provided data on OPE concentration trends since 1980 [62]. There is a significant gap in research on ice core records of OPEs in Antarctica and in high-altitude mountain glaciers closer to anthropogenic emission sources. Future work should focus on utilizing polar and high-altitude mountain ice cores to reconstruct past OPE deposition trends and clarify the spatiotemporal characteristics of OPEs emitted by human activities. Additionally, improving our understanding of the photochemical behavior of OPEs in snow and ice will enhance the interpretation of ice core data on OPE deposition.
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anisimov, O.A.; Vaughan, D.G.; Callaghan, T.V.; Furgal, C.; Marchant, H.; Prowse, T.D.; Vilhjálmsson, H.; Walsh, J.E. Polar regions (Arctic and Antarctic). Clim. Change 2007, 15, 653–685. [Google Scholar]
- Kallenborn, R.; Hung, H.; Brorström-Lundén, E. Atmospheric long-range transport of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) into polar regions. In Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 67, pp. 411–432. [Google Scholar]
- Wania, F. Assessing the potential of persistent organic chemicals for long-range transport and accumulation in polar regions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 1344–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorkamp, K.; Carlsson, P.; Corsolini, S.; de Wit, C.A.; Dietz, R.; Gribble, M.O.; Houde, M.; Kalia, V.; Letcher, R.J.; Morris, A. Influences of climate change on long-term time series of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in Arctic and Antarctic biota. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2022, 24, 1643–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-F.; Hao, S.; Ma, W.-L.; Yang, P.-F.; Li, W.-L.; Zhang, Z.-F.; Liu, L.-Y.; Macdonald, R.W. Persistent organic pollutants in global surface soils: Distributions and fractionations. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2023, 18, 100311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbante, C.; Spolaor, A.; Cairns, W.R.; Boutron, C. Man’s footprint on the Arctic environment as revealed by analysis of ice and snow. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 168, 218–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Wang, X.; Lin, H.; Ren, J.; Wang, C.; Gong, P. Accumulation of pollutants in proglacial lake sediments: Impacts of glacial meltwater and anthropogenic activities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 7901–7910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Xu, L.; Chen, M.; Gong, P.; Wang, C. Microplastics in a remote lake basin of the Tibetan Plateau: Impacts of atmospheric transport and glacial melting. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 12951–12960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Zhu, T.; Gong, P.; Fu, J.; Cong, Z. Persistent organic pollutants in the polar regions and the Tibetan Plateau: A review of current knowledge and future prospects. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 191–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Wang, X.; Gong, P.; Wang, C. Characterization of Tibetan soil as a source or sink of atmospheric persistent organic pollutants: Seasonal shift and impact of global warming. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 3589–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamon, L.; Von Waldow, H.; MacLeod, M.; Scheringer, M.; Marcomini, A.; Hungerbühler, K. Modeling the global levels and distribution of polychlorinated biphenyls in air under a climate change scenario. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 5818–5824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Jimenez, J.; González-Gaya, B.; Pizarro, M.; Casal, P.; Pizarro-Álvarez, C.; Dachs, J. Organophosphate ester flame retardants and plasticizers in the global oceanic atmosphere. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 12831–12839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, Q.; Yan, X.; Wang, Y.; Liao, C.; Jiang, G. A review of organophosphate flame retardants and plasticizers in the environment: Analysis, occurrence and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 139071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marklund, A.; Andersson, B.; Haglund, P. Screening of organophosphorus compounds and their distribution in various indoor environments. Chemosphere 2003, 53, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, G.-L.; Li, D.-Q.; Zhuo, M.-N.; Liao, Y.-S.; Xie, Z.-Y.; Guo, T.-L.; Li, J.-J.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Liang, Z.-Q. Organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers: Sources, occurrence, toxicity and human exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 196, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; He, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Wu, N.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, Z. Assessing the threats of organophosphate esters (flame retardants and plasticizers) to drinking water safety based on USEPA oral reference dose (RfD) and oral cancer slope factor (SFO). Water Res. 2019, 154, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Jian, K.; Li, J.; Ya, M.; Su, G. Traditional and emerging organophosphate esters (OPEs) in indoor dust of Nanjing, eastern China: Occurrence, human exposure, and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 136494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Wang, P.; Wang, X.; Castro-Jiménez, J.; Kallenborn, R.; Liao, C.; Mi, W.; Lohmann, R.; Vila-Costa, M.; Dachs, J. Organophosphate ester pollution in the oceans. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Song, N.; Guo, R.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Han, Z.; Feng, M.; Li, D.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J. Occurrence and partitioning behavior of organophosphate esters in surface water and sediment of a shallow Chinese freshwater lake (Taihu Lake): Implication for eco-toxicity risk. Chemosphere 2018, 202, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhong, W.; Yang, L. Partition and source identification of organophosphate esters in the water and sediment of Taihu Lake, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 360, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, U.-J.; Kannan, K. Occurrence and distribution of organophosphate flame retardants/plasticizers in surface waters, tap water, and rainwater: Implications for human exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 5625–5633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Chen, Z.-M.; Hou, X.-Y.; Guo, J.-S.; Wang, C.-C.; Gao, J.-M. Occurrence, potential sources and risks of organophosphate esters in the high-elevation region, Tibet, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 151348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Huang, J.; Wang, J.; Lv, M.; Deng, Y.; Su, G. Seasonal Variations of Organophosphate Esters (OPEs) in Atmospheric Deposition, and their Contribution to Soil Loading. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 475, 134845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Gao, Z.; Hu, G.; Su, G. Non-target screening and risk assessment of organophosphate esters (OPEs) in drinking water resource water, surface water, groundwater, and seawater. Environ. Int. 2022, 168, 107443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, L.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, L.; Waniek, J.J.; Pohlmann, T.; Mi, W.; Xu, W. Organophosphate Esters in Air and Seawater of the South China Sea: Spatial Distribution, Transport, and Air–Sea Exchange. Environ. Health 2023, 1, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, R.; Zhang, P.; Zheng, N.; Ji, H.; Shi, R.; Ge, L.; Ma, H. Organophosphate esters in the seawater of the Bohai Sea: Environmental occurrence, sources and ecological risks. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 191, 114883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Xie, Z.; Lohmann, R.; Mi, W.; Gao, G. Organophosphate ester flame retardants and plasticizers in ocean sediments from the North Pacific to the Arctic Ocean. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 3809–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; He, Z.; Yuan, J.; Ma, X.; Du, J.; Yao, Z.; Wang, W. Comprehensive evaluation of organophosphate ester contamination in surface water and sediment of the Bohai Sea, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 163, 112013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Hao, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, R.; Wang, P.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, G. Occurrence and distribution of organophosphate esters in the air and soils of Ny-Ålesund and London Island, Svalbard, Arctic. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Xu, H.; Luo, Y.; Long, T.; Li, J.; Xing, L. Spatial occurrence and composition profile of organophosphate esters (OPEs) in farmland soils from different regions of China: Implications for human exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 276, 116729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, Q.; Cao, S.; Yan, C.; Zhang, L.; Tang, N. Spatial distribution and seasonal variations of atmospheric organophosphate esters (OPEs) in Tianjin, China based on gridded field observations. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Jiménez, J.; Berrojalbiz, N.; Pizarro, M.; Dachs, J. Organophosphate ester (OPE) flame retardants and plasticizers in the open Mediterranean and Black Seas atmosphere. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 3203–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, J.-Y.; Lin, H.; Qin, X.; Ruan, Y.; Leung, K.M.; Zeng, E.Y.; Lam, P.K. Insights into the atmospheric persistence, transformation, and health implications of organophosphate esters in urban ambient air. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 12003–12013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, C.A.; Bossi, R.; Dietz, R.; Dreyer, A.; Faxneld, S.; Garbus, S.E.; Hellström, P.; Koschorreck, J.; Lohmann, N.; Roos, A. Organohalogen compounds of emerging concern in Baltic Sea biota: Levels, biomagnification potential and comparisons with legacy contaminants. Environ. Int. 2020, 144, 106037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Fu, K.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Ye, T.; Gao, K.; Pan, W.; Zhang, A.; Fu, J. Long-range transport, trophic transfer, and ecological risks of organophosphate esters in remote areas. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 10192–10209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-W.; Isobe, T.; Sudaryanto, A.; Malarvannan, G.; Chang, K.-H.; Muto, M.; Prudente, M.; Tanabe, S. Organophosphorus flame retardants in house dust from the Philippines: Occurrence and assessment of human exposure. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 812–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onoja, S.; Nel, H.A.; Abdallah, M.A.-E.; Harrad, S. Microplastics in freshwater sediments: Analytical methods, temporal trends, and risk of associated organophosphate esters as exemplar plastics additives. Environ. Res. 2022, 203, 111830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, L.; Letcher, R.J.; Zhang, Y.; Jian, K.; Zhang, J.; Su, G. A review on organophosphate Ester (OPE) flame retardants and plasticizers in foodstuffs: Levels, distribution, human dietary exposure, and future directions. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, R.W.; Mackay, D.; Li, Y.-F.; Hickie, B. How will global climate change affect risks from long-range transport of persistent organic pollutants? Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2003, 9, 643–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ademollo, N.; Spataro, F.; Rauseo, J.; Pescatore, T.; Fattorini, N.; Valsecchi, S.; Polesello, S.; Patrolecco, L. Occurrence, distribution and pollution pattern of legacy and emerging organic pollutants in surface water of the Kongsfjorden (Svalbard, Norway): Environmental contamination, seasonal trend and climate change. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 163, 111900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghini, F.; Grimalt, J.O.; Sanchez-Hernandez, J.C.; Bargagli, R. Organochlorine pollutants in soils and mosses from Victoria Land (Antarctica). Chemosphere 2005, 58, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonich, S.L.; Hites, R.A. Global distribution of persistent organochlorine compounds. Science 1995, 269, 1851–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wania, F.; Westgate, J.N. On the mechanism of mountain cold-trapping of organic chemicals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 9092–9098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, S.B. Persistent organic pollutants in Antarctica: Current and future research priorities. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Xu, H.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y.; Guo, L.; Wang, X. Persistent organic pollutant cycling in forests. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wania, F.; Mackay, D. Global fractionation and cold condensation of low volatility organochlorine compounds in polar regions. Ambio 1993, 22, 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Grannas, A.M.; Bogdal, C.; Hageman, K.J.; Halsall, C.; Harner, T.; Hung, H.; Kallenborn, R.; Klán, P.; Klánová, J.; Macdonald, R.W. The role of the global cryosphere in the fate of organic contaminants. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 3271–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halsall, C.J. Investigating the occurrence of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in the arctic: Their atmospheric behaviour and interaction with the seasonal snow pack. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 128, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamova, A.; Hermanson, M.H.; Hites, R.A. Organophosphate and halogenated flame retardants in atmospheric particles from a European Arctic site. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 6133–6140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miner, K.; Blais, J.; Bogdal, C.; Villa, S.; Schwikowski, M.; Pavlova, P.; Steinlin, C.; Gerbi, C.; Kreutz, K.J. Legacy organochlorine pollutants in glacial watersheds: A review. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2017, 19, 1474–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, S.H.; Weikusat, I.; Azuma, N. The microstructure of polar ice. Part I: Highlights from ice core research. J. Struct. Geol. 2014, 61, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; De Silva, A.O.; St Pierre, K.A.; Muir, D.C.; Spencer, C.; Lehnherr, I.; MacInnis, J.J. Glacial melt inputs of organophosphate ester flame retardants to the largest high Arctic Lake. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 2734–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdal, C.; Nikolic, D.; Lüthi, M.P.; Schenker, U.; Scheringer, M.; Hungerbühler, K. Release of legacy pollutants from melting glaciers: Model evidence and conceptual understanding. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 4063–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak, F.; Koziol, K.; Polkowska, Z. Chemical hazard in glacial melt? The glacial system as a secondary source of POPs (in the Northern Hemisphere). A systematic review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 145244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinlin, C.; Bogdal, C.; Pavlova, P.A.; Schwikowski, M.; Lüthi, M.P.; Scheringer, M.; Schmid, P.; Hungerbühler, K. Polychlorinated biphenyls in a temperate alpine glacier: 2. Model results of chemical fate processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 14092–14100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Wania, F.; Lei, Y.D.; Teixeira, C.; Muir, D.C.; Bidleman, T.F. Atmospheric distribution and long-range transport behavior of organochlorine pesticides in North America. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrerizo, A.; Muir, D.C.; De Silva, A.O.; Wang, X.; Lamoureux, S.F.; Lafrenière, M.J. Legacy and emerging persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in terrestrial compartments in the high Arctic: Sorption and secondary sources. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 14187–14197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sühring, R.; Diamond, M.L.; Bernstein, S.; Adams, J.K.; Schuster, J.K.; Fernie, K.; Elliott, K.; Stern, G.; Jantunen, L.M. Organophosphate esters in the Canadian arctic ocean. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xiong, S.; Hao, Y.; Yang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Wania, F.; Jiang, G. Organophosphate esters in Arctic air from 2011 to 2019: Concentrations, temporal trends, and potential sources. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 434, 128872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Fu, K.; Hu, B.; Zhou, W.; Fu, Y.; Gu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, A.; Fu, J.; Jiang, G. Source identification of organophosphate esters through the profiles in proglacial and ocean sediments from Ny-Ålesund, the Arctic. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 1919–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xie, Z.; Mi, W.; Lai, S.; Tian, C.; Emeis, K.-C.; Ebinghaus, R. Organophosphate esters in air, snow, and seawater in the North Atlantic and the Arctic. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6887–6896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, A.O.; Young, C.J.; Spencer, C.; Muir, D.C.; Sharp, M.; Lehnherr, I.; Criscitiello, A. Canadian high arctic ice core records of organophosphate flame retardants and plasticizers. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2023, 25, 2001–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Wang, Z.; Magand, O.; Thollot, A.; Ebinghaus, R.; Mi, W.; Dommergue, A. Occurrence of legacy and emerging organic contaminants in snow at Dome C in the Antarctic. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.; Sun, L.; Huang, W.; Ruan, T.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, P.; Ding, R.; Li, M. Detection and distribution of Tris (2-chloroethyl) phosphate on the East Antarctic ice sheet. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 1017–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yin, H.; Wu, D.; Luo, Y.; Deng, X.; Xu, W.; Liu, J. Distribution and Sources of OPEs in Plants and Snow in Hailuogou. Environ. Sci. 2019, 40, 4295–4302. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, X.; Hou, S.; Wu, S.; Liu, K.; Huang, R.; Zhang, W.; Yu, J.; Zhan, Z.; Pang, H. The first detection of organophosphate esters (OPEs) of a high altitude fresh snowfall in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 155615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, F.; Wu, S.-Y.; Mu, J.; Zou, X.; Liu, J.; Zhan, Z. Occurrence, distribution, potential sources, and risks of organophosphate esters in fresh snow on Urumqi Glacier No. 1, eastern Tien Shan, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tin, T.; Fleming, Z.L.; Hughes, K.A.; Ainley, D.; Convey, P.; Moreno, C.; Pfeiffer, S.; Scott, J.; Snape, I. Impacts of local human activities on the Antarctic environment. Antarct. Sci. 2009, 21, 3–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akimoto, H. Global air quality and pollution. Science 2003, 302, 1716–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, P.; Zhao, J.; Fu, M.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Yang, R.; Zhu, Y.; Fu, J.; Zhang, Q. Atmospheric organophosphate esters in the Western Antarctic Peninsula over 2014–2018: Occurrence, temporal trend and source implication. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Xiong, S.; Wang, P.; Yang, R.; Pei, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, G. Novel brominated and organophosphate flame retardants in the atmosphere of Fildes Peninsula, West Antarctica: Continuous observations from 2011 to 2020. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 440, 129776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Fu, K.; Gao, K.; Li, H.; Xue, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Shi, J.; Fu, J.; Zhang, Q. Occurrence and trophic magnification of organophosphate esters in an Antarctic ecosystem: Insights into the shift from legacy to emerging pollutants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 396, 122742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Li, R.; Xu, Y.; Hou, C.; Jia, X.; Li, B.; Gao, H.; Jin, S.; Kong, L.; Na, G. Occurrence and fugacity model simulation of organophosphate esters in atmosphere-soil-vegetation, Fildes peninsula, Antarctica. J. Environ. Sci. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, C.; Rodgers, T.F.; Tan, F. Occurrence and distribution of organophosphate flame retardants in the typical soil profiles of the Tibetan Plateau, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prats, R.M.; Van Drooge, B.L.; Fernández, P.; Grimalt, J.O. Occurrence and temperature dependence of atmospheric gas-phase organophosphate esters in high-mountain areas (Pyrenees). Chemosphere 2022, 292, 133467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prats, R.M.; Van Drooge, B.L.; Fernández, P.; Grimalt, J.O. Passive water sampling and air–water diffusive exchange of long-range transported semi-volatile organic pollutants in high-mountain lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 860, 160509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, R.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Harner, T.; Saini, A.; Liu, H.; Yue, F.; Zeng, L.; Zhu, Y. Oxidation of commercial antioxidants is driving increasing atmospheric abundance of organophosphate esters: Implication for global regulation. One Earth 2023, 6, 1202–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolschke, H.; Sühring, R.; Mi, W.; Möller, A.; Xie, Z.; Ebinghaus, R. Atmospheric occurrence and fate of organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizer at the German coast. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 137, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, W.; Mi, W.; Yan, W.; Guo, T.; Zhou, F.; Miao, L.; Xie, Z. Atmospheric deposition, seasonal variation, and long-range transport of organophosphate esters on Yongxing Island, South China Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wei, G.; Chen, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.-N.; Su, L.; Qin, W. Aqueous OH radical reaction rate constants for organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers: Experimental and modeling studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 2790–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liggio, J.; Harner, T.; Jantunen, L.; Shoeib, M.; Li, S.-M. Heterogeneous OH initiated oxidation: A possible explanation for the persistence of organophosphate flame retardants in air. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Venier, M.; Salamova, A. Spatioseasonal variations and partitioning behavior of organophosphate esters in the Great Lakes atmosphere. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 5400–5408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, G.; Hou, C.; Li, R.; Shi, Y.; Gao, H.; Jin, S.; Gao, Y.; Jiao, L.; Cai, Y. Occurrence, distribution, air-seawater exchange and atmospheric deposition of organophosphate esters (OPEs) from the Northwestern Pacific to the Arctic Ocean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 157, 111243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhring, R.; Diamond, M.L.; Scheringer, M.; Wong, F.; Pucko, M.; Stern, G.; Burt, A.; Hung, H.; Fellin, P.; Li, H. Organophosphate esters in Canadian Arctic air: Occurrence, levels and trends. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 7409–7415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, H.; Halsall, C.; Ball, H.; Bidleman, T.; Dachs, J.; De Silva, A.; Hermanson, M.; Kallenborn, R.; Muir, D.; Sühring, R. Climate change influence on the levels and trends of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) and chemicals of emerging Arctic concern (CEACs) in the Arctic physical environment—A review. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2022, 24, 1577–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, T.F.M.; Truong, J.W.; Jantunen, L.M.; Helm, P.A.; Diamond, M.L. Organophosphate Ester (OPE) Transport, Fate and Emissions in Toronto, Canada, Estimated using an Updated Multimedia Urban Model (MUM). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12465–12474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, Y.; Li, M.; Jiang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, Y.; Xie, J.; He, M. The aomogeneous and heterogeneous oxidation of organophosphate esters (OPEs) in the atmosphere: Take diphenyl phosphate (DPhP) as an example. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 324, 121395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sühring, R.; Serodio, D.; Bonnell, M.; Sundin, N.; Diamond, M.L. Novel flame retardants: Estimating the physical–chemical properties and environmental fate of 94 halogenated and organophosphate PBDE replacements. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 2401–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, D.K.; Galgani, F.; Thompson, R.C.; Barlaz, M. Accumulation and fragmentation of plastic debris in global environments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1985–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compound | Abbr. | Solubility (mg L−1) | Vapor Pressure (Pa) | logKow | logKoa | Residence Time | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gaseous Phase (d) | Particulate Phase (d) | ||||||
| Tris (2-chloroethyl) phosphate | TCEP | 880 | 8.2 | 1.4 | 5.3 | - | - |
| Tris (1-chloro-2propyl) phosphate | TCIPP | 52 | 75 × 10−3 | 2.6 | 8.2 | - | - |
| Tris (1,3-dichloro-2propyl) phosphate | TDCIPP | 1.5 | 3.8 × 10−5 | 3.6 | 11 | 11–14 | 7.9–19 |
| Trimethyl phosphate | TMP | 3.00 × 105 | 55 | −0.65 | 5.9 | - | - |
| Triethyl phosphate | TEP | 1.1 × 104 | 22 | 0.8 | 6.6 | - | - |
| Tripropyl phosphate | TnPrP | 830 | 3.01 | 1.9 | 6.4 | - | - |
| Tri-isopropyl phosphate | TiPrP | 500 | 18 | 2.1 | 6.4 | - | - |
| Tributyl phosphate | TnBP | 280 | 0.15 | 4 | 8.2 | - | - |
| Tri-isobutyl phosphate | TiBP | 16 | 1.7 | 3.6 | 7.5 | - | - |
| Tripentyl phosphate | TPeP | 0.33 | 2.3 × 10−3 | 5.3 | 8.8 | - | - |
| Trihexyl phosphate | THP | 0.01 | 3.3 × 10−4 | 6.8 | 9.9 | - | - |
| Triphenyl phosphate | TPhP | 1.9 | 1.5 × 10−3 | 4.6 | 8.5 | 5.2–6.0 | 3.4–8.5 |
| Tris(2-butoxyethyl) phosphate | TBOEP | 2 | 1.6 × 10−4 | 3.8 | 13 | - | 2.4–5.8 |
| Tris(2-ethylhexyl) phosphate | TEHP | 1.5 × 10−5 | 1.1 × 10−5 | 9.5 | 15 | 3.5–5.6 | 2.7–6.6 |
| 2-ethylhexyl diphenyl phosphate | EHDPP | 0.066 | 4.4 × 10−3 | 5.7 | 8.4 | - | 6.5–16 |
| Tricresyl phosphate | TCrP | 0.21 | 1.6 | 5.1 | 9.6 | - | 2.6–6.5 |
| Di-n-octylphenyl phosphate | DOPP | 4.2 × 10−4 | 9.88 × 10−6 | 8.04 | 12 | - | - |
| Methyl diphenyl phosphate | MDPP | 62 | 1.55 × 10−3 | 2.93 | 8.8 | - | - |
| Region | Antarctica | Arctic | High-Altitude Glaciers | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Location | Dome C | East Antarctic a | Ship Route b | Hailou Gou Glacier | Laohugou Glacier | Tianshan No. 1 Glacier |
| Sample Type | Surface Snow | |||||
| Samples | 7 | 120 | 6 | 5 | 8 | 8 |
| TBEP | - | - | - | 193. 7 | - | - |
| TCEP | 1.13 | 0.70 | 1.29 | 27.80 | 48.46 | 4.39 |
| TCIPP | 8.16 | - | 3.89 | 28.00 | 25.95 | 96.25 |
| TDCIPP | 0.32 | - | 0.01 | 24.20 | 8.55 | 4.55 |
| TEP | 0.96 | - | - | - | 3.49 | 4.61 |
| TnBP | 1.23 | - | 0.63 | 26.70 | 1.80 | 6.60 |
| TiBP | - | - | - | - | - | 3.97 |
| TPeP | 0.19 | - | - | - | - | 2.66 |
| TEHP | 0.18 | - | 0.01 | 11.00 | - | 1.85 |
| TPhP | 0.44 | - | 0.01 | 97.70 | 7.85 | 4.54 |
| TPrP | 0.03 | - | - | - | 3.74 | 1.70 |
| ΣOPEs | 12.61 | 0.70 | 5.84 | 408.40 | 99.84 | 131.25 |
| References | [63] | [64] | [61] | [65] | [66] | [67] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, X. A Review of the Properties, Transport, and Fate of Organophosphate Esters in Polar Snow and Ice. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2493. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062493
Zou X. A Review of the Properties, Transport, and Fate of Organophosphate Esters in Polar Snow and Ice. Sustainability. 2025; 17(6):2493. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062493
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Xiang. 2025. "A Review of the Properties, Transport, and Fate of Organophosphate Esters in Polar Snow and Ice" Sustainability 17, no. 6: 2493. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062493
APA StyleZou, X. (2025). A Review of the Properties, Transport, and Fate of Organophosphate Esters in Polar Snow and Ice. Sustainability, 17(6), 2493. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062493





